China Unicom
China’s state owned telcos slash CAPEX to the lowest in decades!
China’s big three state-owned telecom operators are drastically slashing capital expenditures (CAPEX) before the next wave of heavy spending on 6G mobile network infrastructure beginning in 2030. Over a year ago, the IEEE Techblog reported the planned CAPEX reductions in this post.
- China Telecom expects its capital expenditure to decline by 11% to 83.6 billion yuan in 2025, returning to pre-5G expansion levels.
- China Mobile also plans to cut its capital expenditure by 8% in 2025, bringing spending close to 2012 levels.
- China Unicom, the smallest of the three, recorded the sharpest drop in spending.
Reasons for the Cuts:
- The 5G network infrastructure buildout has largely reached its peak, with China already having 3.5 million 5G base stations.
- The companies are preparing for the next major investment cycle, which is expected to focus on 6G and AI infrastructure.
- The CAPEX cuts are also being driven by government directives to improve market value and increase shareholder dividends.
- The companies are prioritizing investments in AI infrastructure and computational infrastructure.
- China Mobile’s Chairman Yang Jie stated that the next major investment cycle is expected to focus on 6G and is unlikely to begin before 2028.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1. China Mobile, the largest wireless carrier in China with over 1 billion subscribers, slashed its annual capital expenditure by over 9% to 164 billion yuan in 2024. The company plans to cut another 8% this year to 151.2 billion yuan. That amount is approaching the 2012 level of 127.4 billion yuan, and is set to decline further in the years to come.
“The overall investment size in the next two to three years will continue to steadily fall,” Yang Jie, China Mobile’s chairman, told reporters in Hong Kong last Thursday. Asked what would trigger the next capital spending spree, Yang said: “From what I see now, the next investment peak will be on 6G” — but he expects that to kick off around 2028. Until then, the industry veteran expects “the proportion of investment to expand in the areas of computation and AI.”

China Mobile Chairman Yang Jie told reporters in Hong Kong on March 20 that the next telecom investment peak would be for 6G mobile network building. (Photo by Kenji Kawase)
Jefferies telecom analyst Edison Lee, said China Mobile’s capex figures were “lower than expected.” The ratio versus its revenue was 18% last year, marking the first dip below 20%, and he expects this proportion to further sink to 16% this year. “This is negative for equipment vendors such as ZTE,” Lee said, although it provides more room for returns to shareholders.
2. China Telecom (#2 in China) announced on Tuesday that its CAPEX for 2024 came to 93.51 billion yuan ($12.9 billion), 5% lower than the previous year. The forecast for this year is even lower, at 83.6 billion yuan, down 11% and lowering the amount to the level before the peak 5G network investment years of around 2020 to 2023. However, with soaring demand for AI computing, it plans a further hike in digital infrastructure spending. It will boost investment in cloud computing and data centers by 22% to RMB45.5 billion ($6.3 billion), making it the biggest single capex item, accounting for 38% of the total.
The company said it’s focused on four technology directions: network, cloud and cloud-network integration, AI and quantum security. It revealed it had deployed 70,000 5G-A base stations in 121 cities, with 5G RedCap coverage in more than 200 cities, and said it had signed up 2.4 million subs to its pioneering D2D mobile satellite service.
Chairman Ke Ruiwen told Nikkei Asia that “the general trend is heading downward.” He added that “before building the new large-scale network (apparently referring to 6G), the investment trend is going continue falling.” He said the company would continue to pursue its strategy focused on cloud and digital transformation.

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
3. China Unicom, the smallest of the three state owned telcos, also slashed its capital spending by 17% to 61.37 billion yuan in 2024, while planning a further reduction to 55 billion yuan this year. “Our investment emphasis has already shifted away from mobile broadband to computing network capabilities for internet data centers and cloud,” said Tang Yongbo, Unicom’s vice president. He also mentioned the impending heavy investment period when the 6G era arrives.
China Telecom and China Unicom have a “co-build, co-share” partnership for 5G investment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
All three Chinese network operators’ actual capital expenditure in 2024 were lower than the previous guidance they had provided, by an average of 5%. The sum of annual capital expenditure for the three Chinese telcos was 319 billion yuan for 2024, and the combined estimate for 2025 is 289.8 billion yuan. Including China Tower — a tower builder established in 2014 through a merger of the three telecom companies’ related businesses, and publicly listed in 2018 — the total capex last year was 351 billion yuan. This year’s projected amount of 322 billion yuan would be one of the lowest in decades.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/china-telecom-boosts-profit-cuts-capex
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
According to a new research report from Goldman Sachs-China, the three major, state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) are quietly becoming the core beneficiaries of China’s AI boom. One reason is that, thanks to their deployment of China’s most extensive cloud infrastructure, they can serve other cloud companies as well as provide their own cloud services to their end user customers. They also enjoy the cost and scale advantages of owning their own data centers and bandwidth. For some IaaS companies, data center and connectivity together account for as much as 60% of total expense, according to Goldman-China.
Goldman analysts believe that telecom operators’ cloud businesses have obvious cost advantages compared to other cloud companies. Those are the following:
- The big 3 Chinese network operators have built their own Data Centers (DCs) and so do not rely on external DC service providers. They even provide DC services to other cloud companies such as Alibaba, which makes the IDC expenses of their cloud business lower.
- The bandwidth cost of operator cloud business is significantly lower than that of other cloud companies because operators use their own network infrastructure, while other cloud companies need to pay operators for bandwidth and private network fees connecting different data centers.
- For the IaaS cloud business, if external DC and bandwidth are used, data center costs (DC services and bandwidth) will account for a considerable proportion of the total cost of the cloud company. Goldman cites QingCloud Technology as an example, its data center costs (including cabinets, bandwidth, etc.) account for 50%-60% of its total costs.
Looking ahead, the telcos are strongly placed to take advantage of the DeepSeek AI boom, thanks to their early embrace of DeepSeek and the government’s push to promote AI among the state-owned enterprises that account for about 30% of operator revenue, Goldman argues. The report states, “the state-owned enterprise background makes the deployment of AI/Deepseek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises more beneficial to telecom operators.”
In the past two weeks, China’s three major operators have begun to help important customers deploy DeepSeek models. China Mobile supports PetroChina in deploying a full-stack Deepseek model; China Telecom provides the same service to Sinopec; and China Unicom cooperates with the Foshan Municipal Bureau of Industry and Information Technology. More importantly, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC) launched the “AI+” action plan on February 21 to encourage Chinese state-owned enterprises to accelerate the development and commercial application of AI. According to Goldman Sachs research, government-related customers account for about 30% of telecom operators’ cloud revenue. Therefore, the deployment of AI/DeepSeek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises will clearly benefit telecom operators.
Separately, China Mobile announced at Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona that it is leveraging artificial intelligence to transform telecommunications networks and drive unprecedented data growth while positioning itself at the forefront of AI-Native network innovation. China Mobile Executive Vice President Li Huidi outlined the company’s ambitious “AI+NETWORK” strategy in a keynote address titled “AI+NETWORK, Pioneering the Digital-Intelligent Future” during the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit on Sunday.
.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Li Huidi, executive vice president of China Mobile, speaks at the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain, March 2, 2025. (Photo/China Mobile)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://wallstreetcn.com/articles/3741901 (Chinese)
https://www.telecoms.com/partner-content/china-mobile-unveils-ai-network-strategy-at-mwc
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/china-telcos-rush-to-embrace-deepseek
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China adds 20M “5G package” subscribers in July; 1H-2024 earnings gains outpace revenues for all 3 major China telcos
The number of 5G subscribers in China increased by a sizeable 20 million last month, according to new data from the country’s big three state owned network providers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom). Of the three, China Mobile is still the only one to report actual customers using its 5G network; China Telecom and China Unicom are sticking to their 5G package subscribers metric, which essentially means customers signed up to a 5G plan, regardless of whether they use 5G network services (most continue to use 4G).
- China Mobile’s July net adds came in at 13.7 million, pushing its 5G customer base up to a colossal 528 million. China Mobile disclosed that it has 129 million customers using its 5G New Calling over high-definition video service reached 129 million, of which, smart application subscribers numbered 11.82 million.
- China Telecom added 3.1 million 5G package customers for a total of 340 million. They did not talk about 5G in their earnings report (more below).
- China Unicom added 2.9 million 5G package customers for a total of 279 million. China Unicom shared details of its 5G network build-out, pointing out that its 5G mid-band base stations numbered in excess of 1.31 million as of mid-year, while low-band sites reached 780,000.
For each of them, cloud and digital transformation (rather than 5G subs) drove topline growth, profit rose more than revenue and shareholder returns increased.
- China Mobile said net profit had improved 5.3% to RMB80.2 billion ($11.2 billion), outpacing revenue, which rose 3% to RMB546.7 billion ($76.6 billion).
- China Telecom, reported net earnings of 21.8 billion Chinese yuan (US3.1 billion), an 8.2% gain over last year, with revenue up 2.8% and service revenue 4.3% higher.
- China Unicom reported 11.3% higher net income of 13.8 billion ($1.93) on the back of a 2.9% lift in sales to RMB197.3 billion ($27.6 billion).
China Mobile says its digital transformation business grew 11% to RMB147.1 billion ($20.6 billion), accounting for 26% of all revenue. China Telecom reported digital industry sales of RMB73.7 billion ($10.3 billion), a 7% increase, and China Unicom said revenue grew 7% to RMB43.5 billion ($6.1 billion).

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo)
All three state owned telcos experienced double-digit growth in cloud services. China Telecom’s Tianyi Cloud grew revenue by 20% to RMB55 billion ($7.7 billion), while China Mobile Cloud hiked sales by 19% to RMB50 billion ($7 billion) and China Unicom grew 24% to RMB32 billion ($4.5 billion).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Silence is Golden?
There was a distinct lack of 5G commentary in China Telecom’s half year report; it is the last of the three to post numbers and did so alongside the publication of the market’s operational statistics for July. The telco shared its 5G package figures – it added almost 18 million in the first six months of 2024, incidentally – but made no other reference to the technology in a fairly wordy statement about its year-to-date performance. Instead, the operator focused on the progress of its digital transformation strategy, leaning heavily on the promise of artificial intelligence. Specifically, China Telecom is talking up what it terms AI+ – there’s always one – and the Xingchen large language model it launched at the back end of last year.
“The Company strengthened the integration and mutual promotion of capabilities in various fields, continuously enriched the Xingchen large model series product portfolio, empowered the intelligent transformation for thousands of industries, and supported enterprises to achieve costs reduction and efficiency enhancement,” it said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-added-20-million-5g-subs-last-month
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/cloud-digital-transformation-drive-chinese-telcos-h1-growth
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Huawei says it has deployed an “ultra large-scale 5.5G network” (there is no definition, 3GPP approved specs, or ITU-R recommendations/standards for 5.5G) operated by China Unicom in Beijing. The network uses three component carrier (3CC) aggregation to provide 70 percent coverage within Beijing’s 4th urban ring road. Huawei says China Unicom will offer comprehensive 5.5G service (again undefined) across stadiums, metro stations and tunnels, residential areas, scenic spots, business districts, and universities in key areas within the city’s 4th Ring Road and Beijing Municipal Administrative Center.
Editor’s Note: At the 5G Advanced Forum during MWC Shanghai 2023, Huawei’s President of ICT Products & Solutions, Yang Chaobin said, “In 2024, Huawei will launch a complete set of commercial 5.5G network equipment to be prepared for the commercial deployment of 5.5G.” Many believe that 5.5G is another name for 3GPP defined 5G Advanced, which is expected to bring new wireless technology innovations that improve speed, coverage, mobility, power efficiency, and sustainability. 3GPP Release 18 in 2024 is the beginning of 5G Advanced. The second and major release of 5G Advanced, Release 19, will be completed by the end of 2025. This release will focus on enhanced performance and the 5G system’s ability to meet commercial deployment needs.
In the Beijing Action Plan for Promoting 5G-A Technology Evolution and Application Innovation (2024-2026), Beijing Municipal Communications Administration hammered home the importance of Beijing’s role in pioneering 5.5G development. China Unicom Beijing is striving to do its part, with a large-scale 5.5G network demonstration at the beginning of 2024 followed by the ultra-large-scale commercial 5.5G network deployment of recent months, in helping Beijing become a “dual 10 Gbps” city that sets the bar for network construction, device development, and industry enablement. With the first version of 5.5G standards frozen in June 2024 and more than 20 commercial 5.5G devices now on the market, a mature 5.5G industry ecosystem is taking shape.

“Full 5.5G coverage” in Beijing’s core urban areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. Photo: Huawei
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In August 2022, China Unicom Beijing and Huawei commercialized the world’s largest 3.5 GHz 2CC network, which has brought 200 MHz 2CC coverage to more than 85% of Beijing’s urban area while providing comprehensive coverage for Beijing’s core areas and the Beijing Municipal Administrative Center. In 2023, this was further augmented when China Unicom Beijing and Huawei completed a 2.1 GHz band deployment targeting key urban scenarios. These deployments substantially improved the network experience of users in Beijing while laying a solid foundation for the future evolution to 5.5G, and this year’s 5.5G 3CC deployment paves the way for larger-scale 5.5G deployments in the coming years.
The ultra-large commercial 5.5G 3CC network consists of more than 4,000 base stations and covers well-known landmarks in Beijing, such as Wukesong, Capital Indoor Stadium, Workers’ Stadium, Beijing Railway Station, Guijie Street, Panjiayuan, and Beijing University of Technology. Featuring 5.5G capabilities, the network provides powerful support for services such as immersive video, UHD live streaming, and cloud gaming. In addition to consumer scenarios, China Unicom Beijing is proactively pursuing innovations in UHD shallow compression encoding, IoT, and XR split rendering, unlocking the full potential of 5.5G networks to enable various industries.
Yang Lifan, Deputy General Manager of China Unicom Beijing, remarked: “We have the world’s largest 200 MHz 5G network and it makes our 3CC carrier aggregation much easier. 5.5G 3CC coverage will be extended to match that of our current 200 MHz 5G network. With Huawei’s advanced technologies and our smart operations, we will provide users with a much better network experience.”
David Li, President of Huawei Wireless Network 5G<E TDD Product Line, said: “We are honored to mark a groundbreaking milestone in 5.5G network construction with China Unicom Beijing — large-scale commercial 5.5G. We will continue to innovate and provide more efficient, smarter, and greener network solutions, enabling users to enjoy a superior, smooth experience with 5.5G networks.”
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/7/5ga-beijing-3cc#
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
https://blog.huawei.com/en/post/2023/11/14/5-5g-whats-in-a-number
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
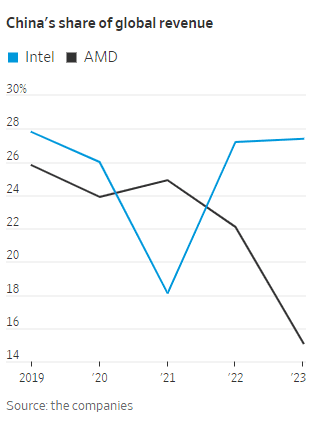
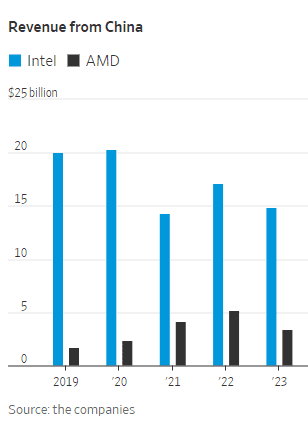
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s largest telecom firms were ordered earlier this year to phase out foreign computer chips from their networks by 2027. That news confirms and expands on reports from recent months. It was reported in the Saturday print edition of the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). The move will hit U.S. semiconductor processor companies Intel and Advanced Micro Devices. Asia Financial reported in late March that these retaliatory bans would cost the U.S. chip firms billions.
The deadline given by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) aims to accelerate efforts by Beijing to halt the use of such core chips in its telecom infrastructure. The regulator ordered state-owned mobile operators to inspect their networks for the prevalence of non-Chinese semiconductors and draft timelines to replace them, the people said.
In the past, efforts to get the industry to wean itself off foreign semiconductors have been hindered by the lack of good domestically made chips. Chinese telecom carriers’ procurements show they are switching more to domestic alternatives, a move made possible in part because local chips’ quality has improved and their performance has become more stable, the people said.
Such an effort will hit Intel and AMD the hardest, they said. The two chip makers have in recent years provided the bulk of the core processors used in networking equipment in China and the world.
China’s MIIT, which oversees the regulation of the wireless, broadcasting and communication industries, didn’t respond to WSJ’s request for comment. China Mobile and China Telecom , the nation’s two biggest telecom carriers by revenue, also didn’t respond.
In March 2023, the Financial Times reported China is seeking to forbid the use of Intel and AMD chips, as well as Microsoft’s operating system, from government computers and servers in favor of local hardware and software. The latest purchasing rules represent China’s most significant step yet to build up domestic substitutes for foreign technology and echo moves in the US as tensions increase between the two countries. Among the 18 approved processors were chips from Huawei and state-backed group Phytium. Both are on Washington’s export blacklist. Chinese processor makers are using a mixture of chip architectures including Intel’s x86, Arm and homegrown ones, while operating systems are derived from open-source Linux software.
Beijing’s desire to wean China off American chips where there are homemade alternatives is the latest installment of a U.S.-China technology war that is splintering the global landscape for network equipment, semiconductors and the internet. American lawmakers have banned Chinese telecom equipment over national-security concerns and have restricted U.S. chip companies including AMD and Nvidia from selling their high-end artificial-intelligence chips to China.
China has also published procurement guidelines discouraging government agencies and state-owned companies from purchasing laptops and desktop computers containing Intel and AMD chips. Requirements released in March give the Chinese entities eight options for central processing units, or CPUs, they can choose from. AMD and Intel were listed as the last two options, behind six homegrown CPUs.
Computers with the Chinese chips installed are preapproved for state buyers. Those powered by Intel and AMD chips require a security evaluation with a government agency, which hasn’t certified any foreign CPUs to date. Making chips for PCs is a significant source of sales for the two companies.
China Mobile and China Telecom are also key customers of both chip makers in China, buying thousands of servers for their data centers in the country’s mushrooming cloud-computing market. These servers are also critical to telecommunications equipment working with base stations and storing mobile subscribers’ data, often viewed as the “brains” of the network. Intel and AMD have the lion’s share of the overall global market for CPUs used in servers, according to data from industry researcher TrendForce. In 2024, Intel will likely hold 71% of the market, while AMD will have 23%, TrendForce estimates. The researcher doesn’t break out China data.
China’s localization policies could diminish Intel and AMD’s sales in the country, one of the most important markets for semiconductor firms. China is Intel’s largest market, accounting for 27% of the company’s revenue last year, Intel said in its latest annual report in January. The U.S. is its second-largest market. Its customers also include global electronics makers that manufacture in China.
In the report, Intel highlighted the geopolitical risk it faced from elevated U.S.-China tensions and China’s localization push. “We could face increased competition as a result of China’s programs to promote a domestic semiconductor industry and supply chains,” the report said.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/china-telecom-intel-amd-chips-99ae99a9 (paywall)
https://www.ft.com/content/7bf0f79b-dea7-49fa-8253-f678d5acd64a
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
China Mobile increased revenue 7.7% to 1.009 trillion Chinese yuan (US$140 billion) in 2023, with earnings up 3.7%. China Mobile’s biggest growth drivers were cloud computing and storage, which grew 66% to RMB83 billion ($11.5 billion), and 5G enterprise, which hiked sales by 30% to RMB47.5 billion ($6.6 billion). It also revealed it had earned RMB5.4 billion ($750 million) in 5G private networking revenue, up 113%. Its “new business” segment, which covers international, investments and applications, expanded 28% to RMB49.3 billion ($6.9 billion).
China Mobile’s capital spending was RMB180.3 billion ($25 billion), a 2.6% decrease from 2022. It gave no guidance for 2024, but CAPEX will surely decrease in 2024 and coming years due to a recent change to retain existing 5G network equipment longer than previously planned.
China Mobile’s Board on Thursday voted to extend the depreciable life of its 5G assets from seven years to ten years, based on the belief that much of its 5G network equipment will continue to be deployed after the arrival of 6G (IMT 2030) at the end of this decade (or later). The state owned telco said it expects “that 5G network investments shall be reused in 6G network infrastructure to the maximum extent, and therefore it is expected that 5G/6G networks will coexist after commercialization of 6G and 5G equipment will have a relatively long life cycle.”
The immediate effect of this decision will be to cut a massive 18 billion yuan ($2.5 billion) out of China Mobile’s depreciation bill this year. It’s the first time any major telco has formally declared that not only is it reluctant to spend on new 6G equipment, but that it also intends to keep its 5G assets as long as possible. That sends a clear warning that in the aftermath of the 5G capex binge, telcos have little appetite for big technology bets without a clear ROI.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Meanwhile, China Unicom boosted net profit by 11.8% and topline revenue by 5.0%. Unicom said it had grown its cloud business by 42% to RMB51 billion ($7.1 billion), while its new computing and digital services business recorded RMB75 billion ($10.4 billion) in sales, up 13%.
“With 5G network coverage nearing completion, the Company’s investment focus is shifting from stable Connectivity and Communications (CC) business to high-growth Computing and Digital Smart Applications (CDSA) business. CAPEX was RMB73.9 billion in 2023. Network investment saw an inflection point.”
In 2023, Connectivity and Communications (CC) business, which encompasses mobile connectivity, broadband connectivity, TV connectivity, leased line connectivity, communications services as well as information services, achieved revenue of RMB244.6 billion. It contributed to three quarters of the service revenue of CC and CDSA combined. The Company’s connectivity scale further expanded, with the total number of CC subscribers exceeding one billion, representing an increase of about 140 million from the end of 2022.
China Unicom capital spending was flat at RMB73.9 billion ($10.3 billion), and it revealed it will slash CAPEX this year by RMB8.9 billion ($1.2 billion) or 12%.

References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/china-mobile-unicom-raise-red-flags-on-network-spend
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0321/2024032100246.pdf
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0319/2024031900241.pdf
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Mobile verifies optimized 5G algorithm based on universal quantum computer
Omdia: China Mobile tops 2023 digital strategy benchmark as telcos develop new services
China Unicom & Huawei deploy 2.1 GHz 8T8R 5G network for high-speed railway in China
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s three state owned telecom operators have announced their subscriber totals for the month of December and for all of 2023. China’ Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) said the big three had a combined net increase of approximately 24.82M 5G package subscribers in China, boosting their combined 5G package subscriber base to nearly 1.373B.
As of the end of December, 5G package subscribers accounted for 80.2% and 78.1% of China Mobile’s and China Telecom’s total mobile subscriber bases, respectively.
C114.net reported that 3.377 million 5G base stations have been built, constituting 28.5 percent of the total mobile base stations. There are 23.02 million ports with gigabit network service capabilities. More than 80% of administrative villages nationwide now have 5G connectivity, telecoms portal.
The foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is constantly being consolidated, with mobile IoT terminal users accounting for 57.5% of the total number of mobile network terminal connections. Technological industry innovation and development, the commercial deployment of 5G customized base stations and 5G lightweight technology, and the launch of the world’s first satellite communication smartphone, 6G, quantum communication, artificial intelligence and other innovative capabilities have significantly improved.
- China Mobile ended last year with 794.5 million subscribers to its 5G package (contract), while its total mobile subscriber base reached 991 million.
- China Telecom had a total of 407.7 million mobile users, of which 318.66 million had signed up to a 5G package (up by 50.7 million during 2023).
- China Unicom’s 5G package subscriber total hit 259.6 million by the end of last year, though disclosure on total mobile subscribers has not been provided. China Unicom also reported that there were 8,563 “virtual 5G industry private network” subscriber for the month of December which was an increase of 554 month-on-month and up 4,758 since the end of 2022.
Mobile Subscriber Stats for China’s Three Main Carriers (Unit: Millions)
| Operator | December 2023 Month-end Total |
% of Combined Installed 5G Sub Base |
December 2023 Net Change |
Net Change Since Prior Year-End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 991.00 | 0.05 | 15.99 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 794.50 | 57.87% | 15.70 | 180.50 |
| China Telecom | 407.77 | 0.54 | 16.59 | |
| 5G Package Subs | 318.66 | 23.21% | 4.03 | 50.70 |
| China Unicom | Not Available | |||
| 5G Package Subs | 259.64 | 18.91% | 5.08 | 46.91 |
China’s fourth 5G telecom network operator, China Broadnet, saw its 5G user base surpass 20 mln on October 19, the company revealed at the 2023 World 5G Convention held in Zhengzhou from December 5-7. Since that time, however, China Broadnet has not publicly released any updated 5G subscriber statistics.
Broadnet officially launched 5G network services just 19 months ago, on June 27, 2022. Because Broadnet is not yet reporting its 5G subscriber totals on a regular, monthly basis, Marbridge is not yet integrating its totals with those of China’s three more established telecom operators above.
Cautionary Note:
The Chinese telecom operators specifically report numbers for 5G packages, rather than citing 5G service users or connections, as while customers may have signed up for a 5G service package offer, that doesn’t necessarily mean they have a 5G-enabled device that enables them to hook up to their network operator’s 5G network, or indeed that their service provider is offering 5G services in their area just yet.

In addition to the growing 5G market in China, the fixed broadband segment is also very large. China Mobile had a total of 298 million wireline broadband customers at the end of December 2023, and throughout the year it added a total of 26 million fixed customers. China Telecom had 190 million fixed broadband subscribers by the year end, having added a total of 9.26 million wireline broadband users in 2023. China Unicom’s operational statistics for the last month of 2023 did not provide a breakdown of broadband customers.
References:
https://en.c114.com.cn/583/a1253372.html
China Unicom & Huawei deploy 2.1 GHz 8T8R 5G network for high-speed railway in China
China Unicom Jilin, the local affiliate of China Unicom in the Jilin province, has completed the deployment of a 2.1 GHz 8T8R 5G network for a segment of the national Harbin-Dalian high-speed railway with 5G network equipment from Huawei.
Tests show that 8T8R AAUs increase the coverage area by 44% compared with 4T4R, and 5G user experience improves by 5.2 times compared with 4G. The train passengers can heartily access the network for entertainment such as HD video, live streaming, and New Calling as well as for work on-the-move such as remote video conferencing.

In 2023, China Unicom embarked on a 5G coverage project along China’s sixteen trunk high-speed railways. Its affiliate in Jilin province contributed to its share of constructing the province’s premium 5G network for high-speed railways within the provincial borders. At first, this network construction project was daunted by four serious challenges. To begin with, the distance between sites is large. What’s worse, the penetration loss was greater with high-speed railways than common railways. Additionally, high-speed mobility increased the Doppler shift, a direct cause of performance deterioration. Lastly, user experience was poor due to short camping time caused by frequent handovers (every 3–4 seconds) on trains running at a high speed of 300 km/hr.
To address these challenges, in this project, China Unicom Jilin deployed the 2.1 GHz 8T8R AAU, and activated the High-speed Railway Excellent Experience feature and Cell Combination feature.
The 2.1 GHz 8T8R AAU solution integrates with technologies like multi-antenna, integrated high-gain array, intelligent beamforming, and precise and fast beam sweeping. Compared with 4T4R, it improves coverage by 7.5 dB, user experience by an impressive 55%, and capacity by 85%. This solution solves the problem of poor coverage caused by large distances and large insertion loss on high-speed railways. It also uses the same antenna as the legacy 4G 1.8 GHz network, simplifying site deployment and reducing tower rental by 10%. This series of solutions with Huawei FDD beamforming technology took home the GSMA GLOMO award for “Best Mobile Technology Breakthrough” and was listed in the “Guangdong Province Energy Saving Technology and Equipment (Product) Recommendation Catalogue”, issued by the Guangdong Energy Bureau in July 2023, for its excellent performance in energy saving.
After the High-Speed Railway Excellent Experience feature is enabled, the 5G base station proactively adjusts the signal frequency to offset the negative impact caused by frequency offset. This solves the Doppler shift problem in high-speed railway continuous coverage scenarios. After Cell Combination feature is enabled, the number of inter-cell handovers can be reduced in a cell combination network, which solves the problems of fast handovers and short camping time on high-speed railways. Test results show that after this feature is enabled, the access success rate increases to 99.4% and the call drop rate decreases by 57%. This overcomes the difficulties of difficult network access in ultra-high-speed scenarios.
This commercial deployment of the 2.1 GHz 8T8R AAU solution will greatly facilitate the operator’s future plans for similar 5G rollouts. China Unicom Jilin will continue to explore 5G network deployments in different scenarios as well as innovative applications of 2.1 GHz 8T8R in order to build differentiated 5G advantages based on service requirements in various 5G scenarios.
China Unicom to deploy Huawei’s 64T64R MetaAAU product-an upgrade of Huawei MetaAAU
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
Huawei’s comeback: 2023 revenue approaches $100B with smart devices gaining ground
ABI Research: Telco transformation measured via patents and 3GPP contributions; 5G accelerating in China
Omdia: China’s 5G network co-sharing + cloud will create growth opportunities for Chinese service providers
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) said that in the first eleven months of 2023, the telecommunication industry’s collective business revenue soared to 1.55 trillion yuan, approximately 218 billion U.S. dollars, marking a 6.9% year-on-year increase.
Emerging sectors such as big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have shown significant growth. China’s three state owned network providers, China Telecom, China Mobile, and China Unicom have leveraged these technologies to catalyze a 20.1 percent surge in revenue from these areas, amounting to 332.6 billion yuan.
Cloud computing and big data have experienced explosive growth. Revenue from cloud computing surging by 39.7 percent and big data by 43.3 percent compared to the previous year. These figures underscore the central role of data-driven technologies in powering China’s telecom industry forward.
Broadband internet services continue to be a strong revenue stream for the three telecom giants, generating 240.4 billion yuan from January to November, which is an 8.5 percent increase year on year. This growth reflects the increasing demand for high-speed internet across China, as the country continues to embrace digital transformation in all sectors.
In conclusion, China’s telecommunication industry’s growth narrative in 2023 is not just a story of numbers but a chronicle of technological evolution and its integration into the fabric of society. With emerging sectors leading the charge, the industry’s upward trajectory seems poised to continue, as these technologies become increasingly embedded in the everyday lives of businesses and consumers alike.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Mordor Intelligence forecasts the China Telecom Market size is expected to grow from USD 478.92 billion in 2023 to USD 547.43 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 2.71% during the forecast period (2023-2028).

References:
https://english.news.cn/20231223/36996f5176e24d48a5677ddc160c99a5/c.html
China’s Telecom Sector Soars with Big Data and Cloud Computing Growth
https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/china-telecom-market