ONF
Intel quietly acquires private 5G software provider Ananki
Intel has acquired private 5G network provider Ananki, several months after the startup spun out of the non-profit Open Networking Foundation (ONF) to commercialize open-source network technologies.
The acquisition was confirmed Monday on LinkedIn by Guru Parulkar, PhD, who was co-founder and CEO of Ananki and executive director of the Open Networking Foundation.
–>His ONF successor was not disclosed, despite my LI comment enquiring about it.
Intel declined to comment on the Ananki acquisition and instead only confirmed a development that Parulkar said was related: that the ONF’s development team has joined Intel’s Networking and Edge Group. Intel’s statement echoed a quote provided by top Intel networking executive and former Stanford Professor Nick McKeown, PhD in a press release published by the non-profit. McKeown was previously a part-time Intel Senior Fellow who joined the company after its 2019 acquisition of Barefoot Networks, which he co-founded.
“The addition of these developers will support [Intel’s Network and Edge Group’s] mission to drive the shift toward software-defined and fully programmable infrastructure – from the cloud, through the Internet and 5G networks, all the way out to the Intelligent Edge. Intel intends to continue to support and contribute to ONF’s open-source efforts,” an Intel spokesperson said. No financial terms were disclosed.
Ananki provides an open-source, software-defined service that aims to make private 5G networks “as easy to consume as Wi-Fi” for enterprises working on so-called Industry 4.0 projects. This involves connecting a variety of things, including cameras, sensors, robots, and autonomous vehicles, over high-speed networks in various settings, from factories to retail stores.
Ananki has a diverse range of products, including a SaaS-based 5G software stack, small cell radios, SIM cards, and a dashboard for monitoring and analyzing network activity. These are provided through a subscription-based service that charges organizations based on how much 5G coverage they need.

Source: Ananki
If Intel continues to offer Ananki’s products as a subscription service, it would fall in line with the semiconductor giant’s plan to buoy hardware sales with a significant increase in software revenue, as The Register has previously reported. Less than two weeks ago, The Register reported that Intel plans to offer the cloud optimization software of Granulate, another startup it plans to acquire, in Xeon CPU sales pitches.
The Ananki transaction is part of a broader effort by the Open Networking Foundation to support the increasing commercialization of its open-source, software-defined networking technologies, which it originally developed with the financial support of its more than 100 members. Those include Intel as well as several other prominent tech companies, such as AMD, AT&T, Broadcom, Cisco, Google, Microsoft, Nvidia, and T-Mobile.
The Open Networking Foundation said this new commercialization shift involves open-sourcing the entirety of its production-ready software, which includes private 5G, SD-RAN, SD-Fabric and SD-Core technologies that serve as the basis of Ananki’s products. The nonprofit has also made its software-defined broadband and P4 programmable network technologies available as open source.
“We have built platforms that naysayers said were doomed to fail, we’ve proven what’s possible, and today a number of our platforms have been deployed in production networks and others are now production ready and expected to be broadly adopted,” said Parulkar, who is now vice president of software within Intel’s Network and Edge Group.
The ONF seems to want to move development from internal open source teams to member organizations. As such, the nonprofit is transitioning a majority of its development team to Intel’s Network and Edge Group, which is also the new home of Ananki.
References:
https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/12/intel_ananki_5g/
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/edge-computing/what-is-the-network-edge.html
https://networkbuilders.intel.com/events2022/big-5g-event
ONF Enters a New Era Focused on Growing Adoption and Community for its Leading Open Source Projects
ONF’s Private 5G Connected Edge Platform Aether™ Released to Open Source
Furthering its mission to seed the industry with innovative open source platforms to advance 5G and software-defined open networking, the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) today announced that its Aether Private 5G + Edge Cloud platform, and related component projects SD-Core™, SD-RAN™ and SD-Fabric™ have now all been released under the permissive Apache 2.0 open source license.
Aether is the first open source 5G Connected Edge platform for enabling enterprise digital transformation. Aether provides 5G mobile connectivity and edge cloud services for distributed enterprise networks. Aether represents a complete, open 5G solution, addressing RAN through Core, democratizing availability of a robust and complete software-defined 5G platform for developers.
In just 2 years, Aether has achieved significant milestones and demonstrated numerous industry firsts:
- Aether was selected for the $30M DARPA Pronto project for building secure 5G
- Aether was deployed in an ongoing field trial with Deutsche Telekom in Berlin
- Aether has been deployed in over 15 locations, operating 7×24 and delivering production-grade uptime
- Aether is the only private 5G solution leveraging the benefits of open RAN for private enterprise use cases
In the process of achieving these remarkable milestones, Aether has matured to the point where it is ready to be released to the community for broad consumption.
Aether is built upon a number of world-class component projects that are each in their own right best-in-class. Today, all the component projects are also being open sourced, including:
SD-Core 4G/5G dual-mode cloud native mobile core
SD-Fabric SDN P4 Programmable Networking Fabric
SD-RAN Open RAN implementation with RIC and xApps
Demonstrating Aether at MWC:
The ONF stand #1F66 at Mobile World Congress (MWC) will showcase an Aether deployment, demonstrated as a cloud managed offering optimized for enterprise private networks. In the demo, devices (UEs), such as mobile phones, cameras, sensors and IoT devices, can be aggregated into device-groups, and each device-group assigned a 5G slice and connected to specific edge applications thereby extending the slicing concept to individual applications and services. Each slice is attached to specific Industry 4.0 application(s), thereby creating distinct slices for different use cases and guaranteeing each slice secure isolation for security along with bandwidth, latency, quality of service (QoS) and resource assurances.
Two Industry 4.0 applications are demonstrated running over the Aether Private 5G using Intel technologies enabling ONF SD-RAN and SD-Core ranging from Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Intel vRAN accelerator ACC100, Intel Tofino Intelligent Fabric Processors, to software offerings such as Intel’s FlexRAN reference architecture, Intel Smart Edge Open, and the Intel Distribution of OpenVINO. The first is a security application built on Intel’s Distribution of OpenVINO toolkit, an intelligent AI/ML edge platform running on Aether 5G and leveraging Aether’s Industry 4.0 APIs to dynamically change the network slice to suit the application’s real time requirements for connectivity. The demo first creates an application slice for video surveillance, grouping together a set of streaming cameras. Next, whenever a human is detected in the field of vision for a camera, the solution automatically increases the 5G bandwidth for the impacted camera and instructs the camera to increase its resolution so a high-def recording can be made. With this approach, 5G wireless capacity is reserved for mission critical applications, and bandwidth is dynamically allocated precisely when and where needed. All of this is performed in real time without human intervention.
Anomaly detection is featured in the second Industry 4.0 application. Based on Intel’s Anomalib, an Aether application slice carries a mission critical video feed of a manufacturing / packaging line which is channeled into an anomaly detection edge-app. The edge app is trained using defect free data and uses probabilistic AI to detect anomalies like spoiled fruit (bananas). Given the time critical nature of detecting faults early, the app is built to work in a real time fashion over Aether to deliver results at line rate for typical industrial and packaging production lines.
Getting Started with Aether:
It is easy to get started using Aether Private 5G. Aether can be deployed by developers on a laptop using Aether-in-a-Box, a simple pre-packaged end-to-end development environment including RAN through mobile core. By making such a complete solution available in a footprint that can run on a laptop, developers can get started with minimal friction. Developers can then organically grow the test deployment at their own pace into a fully disaggregated production-grade deployment, including production-grade RAN radios, disaggregated UPF edge processing and cloud-native mobile core. This makes it easy to get started with Aether, while assuring developers that Aether can scale to meet the needs of even the most demanding commercial applications.
The ONF Community:
Aether has been an amazing collaboration between ONF engineering resources and an active community that includes: Aarna Networks, AirHop, AT&T, Binghamton University, China Mobile, China Unicom, Ciena, Cohere Technologies, Cornell University, Deutsche Telekom, Edgecore Networks, Facebook Connectivity, Foxconn, Google, GSLab, HCL, Intel, NTT Group, Microsoft, Princeton University, Radisys, Sercomm, Stanford University and Tech Mahindra.
About the Open Networking Foundation:
The Open Networking Foundation (ONF) is an operator-led consortium spearheading disruptive network transformation. Now the recognized leader for open source solutions for operators, the ONF first launched in 2011 as the standard bearer for Software-Defined Networking (SDN). Led by its operator partners AT&T, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Google, NTT Group and Türk Telekom, the ONF is driving vast transformation across the operator space. For further information visit http://www.opennetworking.org
References:
To learn more about the project and join our growing community by reviewing the Aether documentation, by visiting the ONF booth at MWC Barcelona (#1F66), or registering here to be sent a pointer to the recorded demo to be released after MWC. Developers can also easily get started by running Aether-in-a-Box on a bare metal machine or VM.
Open Networking Foundation spins off Ananki to deliver open source-based Software Defined Private 5G as per Industry 4.0 requirements
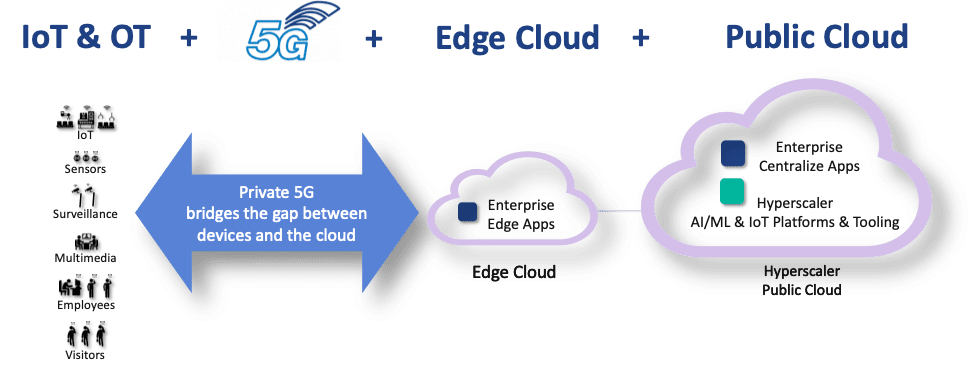
Ananki plans to deliver software defined private 5G that is purpose built for the Industry 4.0 revolution, encompasng M2M mobile networks, IoT, and related communication initiatives.
- Private 5G is the key to empowering the machine-to-application communications necessary to complete this vision, according to the ONF.
- Industry 4.0 is a combination of intelligent devices, edge cloud and cloud-based AI/ML which is intended to enable software-based optimization and innovation.

Ananki’s Software-Defined Private 5G+ was said to deliver:
● Optimized 5G+ Experience – Software-defined, automated, AI powered, application optimized connectivity, with enhanced security enabled by a programmable data plane.
● Cloud First – pre-integrated with hyperscaler cloud and edge, delivering private 5G as a SaaS service, creating a continuously improving experience running on any multi-cloud platform.
● Industry 4.0 Ready – Empowering developers to build transformative IoT, IIoT and OT solutions with rich APIs.
Ananki’s technological foundation leverages ONF’s open source Aether™, SD-RAN™, SD-Fabric™ and SD-Core™ projects, and melds them together into a commercial offering that is delivered as a SaaS, making private 5G as easy to consume as wifi for enterprises. ONF also incorporates developer APIs to accelerate the creation of more powerful digital transformation solutions. This open platform is hardened and optimized for industrial applications, and introduces developer APIs to empower the creation of more powerful digital transformation solutions.

Other Highlights:
— Ananki delivers slice/device level SLA assurance for mission critical applications.
— Proactively identify network bottlenecks before they impact your application performance.
— Define application priority once and let Ananki (Self healing/optimizing/organizing network) deliver optimal application performance.
— CI/CD lets you dynamically upgrade your service to handle evolving application requirements and security threats.
— Telco grade security and resilience to Enterprise operational networks with AI/Ops fault and detection.
Ananki’s Inception:
When ONF’s Aether was selected for the $30M Pronto Project, DARPA encouraged ONF to commercialize the platform in order to advance the impact of the project’s secure 5G research. To date, ONF has operationalized and deployed Aether at 15 locations operating as a cloud managed service.
To accelerate Aether’s adoption, the ONF board voted unanimously to create a new separate venture backed commercial entity to provide an enhanced, hardened solution so vendors and partners can easily incorporate private 5G into the solutions they then build and deliver to enterprises.
Ananki, has been structured as a Public Benefit Corporation to support and promote open source. Furthermore, Ananki shares common executives with the ONF, ensuring that a consistent vision and mission keeps the two entities well aligned.
Quotes:
Andre Fuetsch, ONF Board Chair and AT&T CTO:
“ONF continues to innovate in ways that magnify the power of open systems and open source across our industry. The ONF board recognizes that the lack of support for open source initiatives from commercial companies remains an inhibiting factor for scaled adoption. To meet this challenge, we have agreed to spin out Ananki as an independent company to pursue commercialization of Aether with a view that this will help accelerate the adoption and impact of open source.”
Guru Parulkar, Executive Director ONF and CEO of Ananki:
“Ananki is broadening the impact of the ONF’s work, and will help ONF’s Aether become much more broadly adopted. By providing a commercially supported option for consuming Aether, many more organizations will be able to easily and economically leverage the benefits of Private 5G for building Industry 4.0 solutions. And in turn, Ananki is committed to contributing back to the ONF open source, helping to advance the Aether platform and broaden the ONF community.”
About Ananki:
Ananki delivers a commercially supported Software-Defined Private 5G as-a-service to help facilitate enterprise digital transformation. As a Public Benefit Corporation, Ananki synergistically builds on Open Networking Foundation (ONF) open source software platforms, and in turn contributes focus, funding, developers and contributions to the ONF projects. With Ananki, companies can now choose a commercially supported option when consuming ONF open source.
About the Open Networking Foundation:
The Open Networking Foundation (ONF) is an operator-led consortium spearheading disruptive network transformation. Now the recognized leader for open source solutions for operators, the ONF first launched in 2011 as the standard bearer for Software-Defined Networking (SDN). Led by its operator partners AT&T, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Google, NTT Group and Türk Telekom, the ONF is driving vast transformation across the operator space. For further information visit http://www.opennetworking.org
For more information, please visit ananki.io and/or register to attend a live keynote on September 28th as part of the Private 5G for Industry 4.0 Spotlight event.
References:
Vodafone and NEC Europe trial Open RAN technology with voice call
Vodafone and NEC Europe Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of NEC Corporation, in partnership with Altiostar, have jointly announced the first successful voice call made on an open virtual Radio Access Network (Open RAN) on Vodafone’s network in the Netherlands.
Open RAN technology holds promise and potential for next-generation wireless infrastructure. It’s being driven by innovation and open specifications from various consortiums (O-RAN, TIP Open RAN, and ONF). Today’s announcement demonstrates Vodafone’s strong commitment to sustaining its technological leadership, by bringing in such technological advances.
During the course of this trial, Vodafone and NEC intend to integrate solutions of leading Open RAN technology vendors, such as Altiostar [1.] and various other radio vendors, including NEC’s own 5G radio products, using commercial off the shelf (COTS) hardware from third parties, enabling Vodafone to transform its network to a software-based one suiting multiple deployment scenarios.
Note 1. It’s somewhat surprising that Altiostar was the only OpenRAN software vendor to be mentioned. Altiostar is part-owned by Rakuten and must therefore be near the front of the queue for its OpenRAN vendors. Rakuten has said it would make its Open RAN platform technology available to other operators. If successful, NEC and Altiostar will be involved in more deals as OpenRAN gathers momentum. Separately, there is the Rakuten-NEC 5G Core network (based on 3GPP 5G core “vision” specs) that Rakuten also wants to sell to global network operators.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Image Credit: Rakuten Mobile
“We are proud to embark on this journey together with Vodafone that will transform mobile network economics, while deploying technology with greater flexibility, greater efficiencies, and more agility,” said Yogarajah Gopikrishna, GM at NEC Europe. “By integrating best of breed solutions, NEC, as an experienced Open RAN System Integrator, is committed to bring transformative change to the telecommunications space leveraging our long history and experience in mobile network solutions.”
“We are delighted to work together with NEC towards the first live Open RAN site,” said Ruud Koeyvoets, Vodafone Mobile Networks’ Director. “The introduction of the technology enables us to introduce new suppliers, such as Altiostar, giving us greater flexibility when rolling out our mobile network. We’re proud to be pioneering the development of Open RAN and will be monitoring the performance of this pilot.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Vodafone
VodafoneZiggo is a leading Dutch company that provides fixed, mobile and integrated communication and entertainment services to consumers and businesses. As of June 30, 2020 we have more than 5 million mobile, nearly 4 million TV, nearly 3.4 million fixed broadband internet and 2.4 million fixed telephony subscriptions. VodafoneZiggo is a joint venture by Liberty Global, the largest international TV and broadband internet company, and Vodafone Group, one of the world’s largest telecommunication companies.
About NEC Europe Ltd.
NEC Europe Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of NEC Corporation, a leader in the integration of IT network technologies that benefit businesses and people around the world. NEC Europe Ltd. is building upon its heritage and reputation for innovation and quality by providing its expertise, solutions and services to a broad range of customers, from telecom operators to enterprises and the public sector. For additional information, please visit the NEC Europe Ltd. home page at:
http://uk.nec.com/
References:
https://www.nec.com/en/press/202010/global_20201019_04.html
Why It’s IMPORTANT: Telefonica, Rakuten MOU on Open RAN, 5G Core Network and OSS
Comcast: ONF Trellis software is in production together with L2/L3 white box switches
Jet lagged yet energetic and cheerful, Comcast Senior VP of Next Generation Access Networks Elad Nafshi returned from a motor bike trip in the European alps (via a red eye flight from Frankfurt, Germany to SFO) to deliver an important keynote speech at the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) Connect 2019 conference in Santa Clara, CA this Friday. A graduate of Tel Aviv University, Mr. Nafshi has been with Comcast for over 14 years.
Elad announced that Comcast, the leading ISP in the U.S. by subscribers, has deployed the open source ONF Trellis software and reference hardware design “in multiple markets with real customers.” He noted that “This is not a technical trial or PoC. We have not deployed a new appliance. We deployed an entire ecosystem.”
Trellis is an SDN-based, multi-purpose leaf-spine (AKA spine-leaf) switching fabric designed for access-and-edge networks, NFV, and edge cloud applications. It uses the Open Network Operating System (ONOS) open source SDN controller running in an x86 based compute server and the OpenFlow protocol as a “southbound API” (Control plane to/from Data plane) to interface with multiple interconnected white box/bare metal L2/L3 switches. That configuration is shown in the illustration below.

Comcast, AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, and Infosys collectively authored a reference design for Trellis in April 2019. Reference designs are “blueprints” developed by ONF’s Operator members (AT&T, China Unicom, Comcast, Deutsche Telekom, Google, NTT Group, and Turk Telekom), to address specific use cases for the emerging edge cloud/broadband and mobile access networks.
“In collaboration with the ONF and a team of supply chain vendors, Comcast is deploying the open source Trellis platform as the networking fabric in our next generation access network,” Nafshi said in a press release. “This has been a multiple year journey from design, to extensive field trials and finally to production rollout, and we’re impressed with the results and the advantages that using open source and Trellis are delivering for us as we upgrade our access network,” he added.
While Elad said that Trellis rollouts are accelerating and may “soon come to an area near you,” he declined to answer questions about the locations, size or scale of Comcast’s Trellis deployments. I talked to Elad after his speech and found him to be very engaging and congenial.
………………………………………………………………………………….
Comcast claims an open source- and a white box-based Ethernet backhaul is integral to its next generation network access strategy. By using Trellis, Nafshi said Comcast improved network scalability as well as space and power facility efficiencies in its cable head-ends.
Trellis plays a key role in Comcast’s next generation Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) [1] strategy, which uses an Ethernet-based converged interconnect network (CIN). Comcast is using Trellis within this CIN.
Note 1. Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) enables the evolution of cable networks by decentralizing and virtualizing headend and network functions. DAA extends the digital portion of the head-end or hub domain out to the fiber optic node and places the digital to RF interface at the optical-coax boundary in the node. Replacing the analog optics from the head-end converts the fiber link to a digital fiber Ethernet link, increasing the available bandwidth improving fiber efficiencies (wavelengths and distance), and directional alignment with NFV/SDN/FTTx systems of the future.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
“This has been a multiple year journey from design, to extensive field trails and finally to production rollout, and we’re impressed with the results and the advantages that using open source and Trellis are delivering for us as we upgrade our access network,” Elad said.
While Comcast’s conventional network currently relies on embedded routing and switching protocols running on individual vendor specific switches, Trellis software runs in a cloud-native SDN fashion on a cluster of standard compute server nodes each of which implements a centralized control plane via the ONOS SDN controller. This new SDN based architecture makes network design, deployment, debug and upgrades much simpler, while minimizing network complexity and cost.
“This is real, true production at scale,” said ONF VP of Marketing Timon Sloane. “The design has been vetted and tested and hardened over multiple years. It’s in multiple markets, with tens of thousands of subscribers.”
“The open source ecosystem created by ONF has collectively established a new ‘Distributed DevOps’ model through the process of trialing, hardening and deploying Trellis with Comcast. This has established a new formula for open source whereby an operator, ONF and a consortium of commercial entities come together to collectively build and stand behind a deployment,” said Saurav Das, Vice President of Engineering for the ONF.
Earlier at this week’s ONF Connect 2019 event, Arthur D. Little, AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, and Telefónica released a study that found virtualized, cloud-based architectures can save network operators 40% in capex and 25% in opex.
References:
https://www.opennetworking.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/ONF-Reference-Design-Trellis-032919.pdf
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/operators/comcast-puts-open-source-networking-software-into-production