UScellular Launches 5G Mid-Band Network in parts of 10 states
UScellular today announced the launch of its 5G mid-band network, with customers in parts of 10 states who now have access to the benefits of the company’s faster and stronger network. UScellular’s 5G mid-band technology combined with a mid-band enabled device can provide up to 10x faster speeds than its 4G LTE network and low-band 5G. This technology has more capacity, enhances the mobile experience, and has business and fixed wireless applications.
By the end of June, UScellular’s 5G mid-band network will be available mainly in parts of Illinois, Iowa and Wisconsin, including sections of Rockford, Ill., Des Moines, Iowa and Milwaukee. Communities in Maine, Missouri, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Oregon, Virginia and Washington are also included in the initial rollout. By the end of the year, the company plans to cover more than 1 million households in its operating footprint with its 5G mid-band network. The company is using 5G network equipment from Nokia and Ericsson.
“We view mid-band as the sweet spot of 5G because it provides broad coverage, low latency and fast speeds – enabling more people to connect to what matters most at home or on-the-go,” said Mike Irizarry, executive vice president and chief technology officer for UScellular. “As we approach serving 100,000 High-Speed Internet customers later this summer, mid-band will play an important role in furthering the reach and enhancement of that product. We’ve made it a priority to expand the technology to more communities in the coming years.”
Broader 5G coverage (see map) with mid-band technology provides customers and businesses with even faster data connection speeds for a better experience. UScellular will continue to expand its device portfolio, including adding more options for its High-Speed Internet product and additional IoT devices, to further enhance its mobile and fixed connectivity offerings.
UScellular now offers customers low-band, mid-band and high-band mmWave 5G speeds and services. The company expects nearly 3 million households in its operating footprint will have access to 5G mid-band connectivity by the end of 2024.
UScellular’s 5G mid-band network is using 3.45 GHz spectrum that was purchased through Auction 110 granted in 2022. The company is partnering with Nokia and Ericsson for its mid-band buildout. The company was among the top five bidders in the FCC’s 3.45 GHz Auction 110, where it spent over $579 million. It also acquired C-band spectrum for about $1.46 billion in 2021; that spectrum starts to become available later this year.

UScellular did not need to coordinate with the Department of Defense (DoD) for the 3.45 GHz sites that are part of this launch, but DoD coordination is needed for some sites that are to be deployed in the future, according to a company spokesperson.
Speaking at the Wireless Infrastructure Association’s Connect(X) conference in New Orleans last month, Irizarry said the company expects a “rapid acceleration” of its mid-band spectrum 5G deployment to occur in 2024.
About UScellular:
UScellular is the fourth-largest full-service wireless carrier in the United States, providing national network coverage and industry-leading innovations designed to help customers stay connected to the things that matter most. The Chicago-based carrier provides a strong, reliable network supported by the latest technology and offers a wide range of communication services that enhance consumers’ lives, increase the competitiveness of local businesses and improve the efficiency of government operations.
Through its After School Access Project, the company has pledged to provide hotspots and service to help up to 50,000 youth connect to reliable internet. Additionally, UScellular has price protected all of its plans, promising not to increase prices through at least the end of 2024.
To learn more about UScellular, visit one of its retail stores or www.uscellular.com.
References:
https://www.uscellular.com/coverage-map
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/uscellular-lights-345-ghz-parts-10-states
US Cellular touts 5G millimeter wave and cell tower agreement with Dish Network
IDC IoT investment forecast: 10.4% CAG over 2023-2027
Worldwide spending on the Internet of Things (IoT) is forecast to grow 10.6% this year to a value of $805.7 billion, according to the latest forecast from IDC. Investments in the IoT ecosystem are expected to surpass $1 trillion in 2026 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4% over the 2023-2027 forecast period.
“The last few years have shown that connecting with a digital infrastructure is no longer a luxury, but a necessity,” said Carlos M. González, research manager for the Internet of Things at IDC. “For organizations to excel in data-driven operations, investing in IoT projects is essential. Connecting devices to data networks to gather insight, expand operations, and increase performance are the hallmarks of executing an IoT ecosystem.”
Discrete and Process Manufacturing are the industries that will see the largest investment in IoT solutions in 2023 and throughout the forecast period, accounting for more than one third of all IoT spending worldwide. Professional Services, Utilities, and Retail are the next largest industries in terms of overall IoT spending with roughly 25% of the worldwide total. State/Local Government and Telecommunications will deliver the fastest spending growth over the five-year forecast with CAGRs of 12.0% and 11.7% respectively.
IoT investment is a key building block to supporting an increasingly digital and distributed organizational footprint. Most of these investments are seeking solutions that can help organizations achieve a specific business goal or customer challenge, such as cost savings or supply chain efficiency. As such, use cases are the focus of most IoT investment plans.
The two IoT use cases that will receive the most investment in 2023 are both closely tied to the manufacturing industries: Manufacturing Operations ($73.0 billion) and Production Asset Management ($68.2 billion). The next largest use cases – Inventory Intelligence ($37.6 billion), Smart Grid (Electricity) ($36.9 billion), and Supply Chain Resilience ($31.6 billion) – will benefit from strong investments from the Retail and Utilities industries. The use cases that will experience the fastest spending growth represent the diverse application of IoT technologies – Electric Vehicle Charging (30.9% CAGR), Next Generation Loss Prevention (14.5% CAGR), Agriculture Field Monitoring (13.9% CAGR), and Connected Vending and Lockers (13.8% CAGR).
“Updates to the IoT use case taxonomy in this release of the IoT Spending Guide reflect the evolving Digital Transformation investment objectives of enterprises. Thematically, greater investment in goods production and supply chains resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic and global reactions that caused massive business and societal disruptions are evident in the new use cases. These production and supply chain related use cases can be seen in the Discrete Manufacturing, Process Manufacturing, Retail, and Transportation industries,” said Marcus Torchia, research vice president with IDC’s Data & Analytics Group. “Meanwhile, digital business investments are ramping up in other industries such as the Resource Industries. For example, IoT is helping to improve upstream supply chain processes in Agriculture, such as growing, harvesting, and delivering higher quality produce to market.”
This release of the IoT Spending Guide also includes a Video Analytics overlay forecast that is intended to provide high-level insight into a broadly adopted use case (i.e., found in most or all enterprise industries). Video analytics refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and other advanced algorithms to recognize, detect and analyze live or stored video feeds in a variety of uses, including business analytics, security surveillance, and other rapidly evolving adaptations of this technology. These uses are found in numerous settings (e.g., business analytics in manufacturing and retail, in government for crowd management and traffic congestion management, and broadly for security surveillance). Video analytics requires IP networked capable cameras to support the advanced software whether embedded in hardware or provided by third party vendors.
IDC expects spending on Video Analytics solutions across all industries to be more than $23.5 billion this year. Future releases of the IoT Spending Guide will include additional broadly adopted use cases, such as smart buildings.
From a technology perspective, IoT services will be the largest area of spending in 2023 and through the end of the forecast, accounting for nearly 40% of all IoT spending worldwide. Hardware spending is the second largest technology category, dominated by module/sensor purchases. Software will be the fastest growing technology category with a five-year CAGR of 11.0% and a focus on application and analytics software purchases.
Western Europe, the United States, and China will account for more than half of all IoT spending throughout the forecast. Although Western Europe and the United States currently have similar levels of spending, Western Europe will expand its lead with an 11.0% CAGR over the 2023-2027 forecast, compared to an 8.0% CAGR for the United States. China’s IoT spending is forecast to surpass the United States by the end of the forecast due to its 13.2% CAGR.
The Worldwide Internet of Things Spending Guide (V1 2023) forecasts IoT spending for 18 technology categories and 70 named use cases (87 including sub-use cases) across 19 industries in nine regions and 53 countries. The spending guide also includes an IoT connectivity forecast for cellular, Low-Power Wide Area Networks, and other connectivity (e.g. wired, satellite). This provides tech buyers and providers with a tool to understand how the plethora of IoT use cases call for multiple connectivity types, driven by different expectations in terms of latency, bandwidth, and data frequency.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Rational Stats says the global IoT platforms market was estimated at a market value of $15.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of over 15.2% over the forecast period of 2023-2028.
The main drivers of this expansion are the increased availability of inexpensive sensors and the rising need for connected devices across a range of sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. IoT platforms must be scalable to handle the rising number of connected devices and the growing volume of generated data.
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS50936423#
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=US49578922
https://www.openpr.com/news/3094459/global-iot-platforms-market-analysis-and-forecast-2023-2028
European Internet Exchange operators to use new 100G LR-1 (single laser/PAM4) transceivers
With the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and better performance, the world’s leading Internet Exchange (IX) operators DE-CIX, LINX, AMS-IX & BCIX, will be introducing a new generation of optical transceivers, the 100G LR-1 (referred to as LR), to their platforms, starting in Frankfurt, London, Amsterdam, and Berlin.
While the existing 100G LR-4 uses four lasers, each carrying a signal of 25 Gbps, the new 100G LR technology uses only a single laser and uses pulse amplitude modulation (PAM4) to transmit data at 100 Gbps. The reduction in transceiver design complexity of the increasingly deployed 100G LR technology will result in power savings as well as better transceiver pricing. These advances not only provide advantages in the short to mid-term but will also unlock new transceiver form factors that open up the potential for even greater performance and efficiency improvements in the future. The 100G LR technology is already available with a wide range of compatible routers from all major vendors and is compatible with current fiber technology. In order to satisfy today’s customer demand for 100G LR, DE-CIX, LINX, AMS-IX, and BCIX will provide support in the upcoming months.
“With the new 100G LR technology, we are paving the way for the next generation of transceiver technology that will dominate the market for years to come. The future design of our DE-CIX interconnection platform will not only bring better programmability and higher scalability, commercial flexibility, and wider geographical reach, it will also make interconnection even easier for our customers through simplified technical processes,” says Dr. Thomas King, Chief Technology Officer at DE-CIX.
Richard Petrie, CTO at LINX stated, “For LINX, we will be enabling our London locations first after approving the solution in our lab. We will roll out as demand grows and as we see that LINX members need support in the shift to the improved optics. This will realise both benefits in cost and power for us and the LINX member base.”
Ruben van den Brink, CTO at AMS-IX says, “Offering 100G LR makes perfect sense, both for AMS-IX and for its customers. The lab tests proved that the new optics can be used for all the switches that are currently deployed in our Amsterdam PoPs. I appreciate the fact that we were able to collaborate with our partners in pushing this new standard. When Internet Exchanges join efforts, customers benefit, so I hope many more exchanges will start offering 100G LR soon.”
“After testing 100G LR and other 100G single-lambda standards in our lab, we have already introduced this new technology into our production network. By doing so we have built a very cost-efficient interconnection between data centers on the same campus. Offering the same benefits to our peers is just the next logical step,” says André Grüneberg, CTO at BCIX.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About DE-CIX:
DE-CIX (German Commercial Internet Exchange) is the world’s leading operator of Internet Exchanges (IXs). DE-CIX offers its interconnection services in more than 50 metro-markets in Europe, Africa, North America, the Middle East, and Asia. Accessible from data centers in over 600 cities world-wide, DE-CIX interconnects thousands of network operators (carriers), Internet service providers (ISPs), content providers and enterprise networks from more than 100 countries, and offers peering, cloud, and interconnection services. DE-CIX in Frankfurt, Germany, is one of the largest Internet Exchanges in the world, with a data volume of almost 34 Exabytes per year (as of 2022) and close to 1100 connected networks. More than 200 colleagues from over 30 different nations form the foundation of the DE-CIX success story in Germany and around the world. Since the beginning of the commercial Internet, DE-CIX has had a decisive influence – in a range of leading global bodies, such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) – on co-defining guiding principles for the Internet of the present and the future. As the operator of critical IT infrastructure, DE-CIX bears a great responsibility for the seamless, fast, and secure data exchange between people, enterprises, and organizations at its locations around the globe. Further information at www.de-cix.net.
About the London Internet Exchange (LINX):
With over 900 ASNs connecting from over 80 different countries worldwide, members of The London Internet Exchange (LINX) have access to direct routes from a large number of diverse international peering partners. LINX is much more than just the UK’s leading peering community. LINX can also connect you to cloud services, help you create closed user groups and private VLANs, and gain access to colocated infrastructure. With direct routes between your infrastructure and your most important customers and services, you can manage all your connectivity instances with confidence. Discover the flexibility and transparency of a member-owned organisation, and the reliability of trusting your traffic to critical national infrastructure. For additional information about LINX, please visit linx.net
About AMS-IX:
AMS-IX (Amsterdam Internet Exchange) is a neutral member-based association that operates multiple interconnection platforms around the world. Our leading platform in Amsterdam has been playing a crucial role at the core of the internet for almost 30 years and is one of the largest hubs for internet traffic in the world with over 11 Terabits per second (Tbps) of peak traffic. Connecting to AMS-IX ensures customers such as internet service providers, telecom companies and cloud providers that their global IP traffic is routed in an efficient, fast, secure, stable and cost-effective way. This allows them to offer low latency and engaging online experiences for end-users. AMS-IX interconnects more than 1000 IP-networks in the world. AMS-IX also manages the world’s first mobile peering points: the Global Roaming Exchange (GRX), the Mobile Data Exchange (MDX) and the Internetwork Packet Exchange (I-IPX) interconnection points.
About BCIX:
BCIX is the leading Internet Exchange Point in Berlin, Germany. We operate a distributed infrastructure between 11 data centers across the city of Berlin, providing peering and interconnection services to our partners. We serve nearly 150 connected networks with a peak bandwidth of 900 Gigabits per second (Gbps). As a community we form a nexus for Berlin’s rapidly growing and highly creative Internet scene, organized in a neutral, not-for-profit association. Our friends and associates from businesses and academic institutions support us in serving the internet at large. We are pleased to meet each other regularly at our roundtables.
References:
https://www.de-cix.net/en/about-de-cix/media/press-releases/next-generation-ix
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Introduction:
Despite mounting pressure on venture capital in a difficult economic environment, money is still flowing into generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) startups. Indeed, AI startups have emerged as a bright spot for VC investments this year amid a wider slowdown in funding caused by rising interest rates, a slowing economy and high inflation.
VCs have already poured $10.7 billion into Generative AI [1.] start-ups within the first three months of this year, a thirteen-fold increase from a year earlier, according to PitchBook, which tracks start-ups.
Note 1. Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, synthetic data, images, and audio. The recent buzz around Generative AI has been driven by the simplicity of new user interfaces for creating high-quality content in a matter of seconds.
….………………………………………………………………………………….
Tech giants have poured effort and billions of dollars into what they say is a transformative technology, even amid rising concerns about A.I.’s role in spreading misinformation, killing jobs and one day matching human intelligence. What they don’t publicize is that the results (especially from ChatGPT) may be incorrect or inconclusive.
We take a close look at Generative AI Unicorns with an emphasis on OpenAI (the creator of ChatGPT) and the competition it will face from Google DeepMind.
Generative AI Unicorns and OpenAI:
AI startups make up half of all new unicorns (startups valued at more than $1B) in 2023, says CBInsights.
At Generative AI firms, startups are reaching $1 billion valuations at lightning speed. There are currently 13 Generative AI unicorns (see chart below), according to CBInsights which said they attained their unicorn status nearly twice as fast as the average $1 billion startup.
Across the 13 Generative AI unicorns, the average time to reach unicorn status was 3.6 years but for the unicorn club as a whole the average is 7 years — almost twice as long.
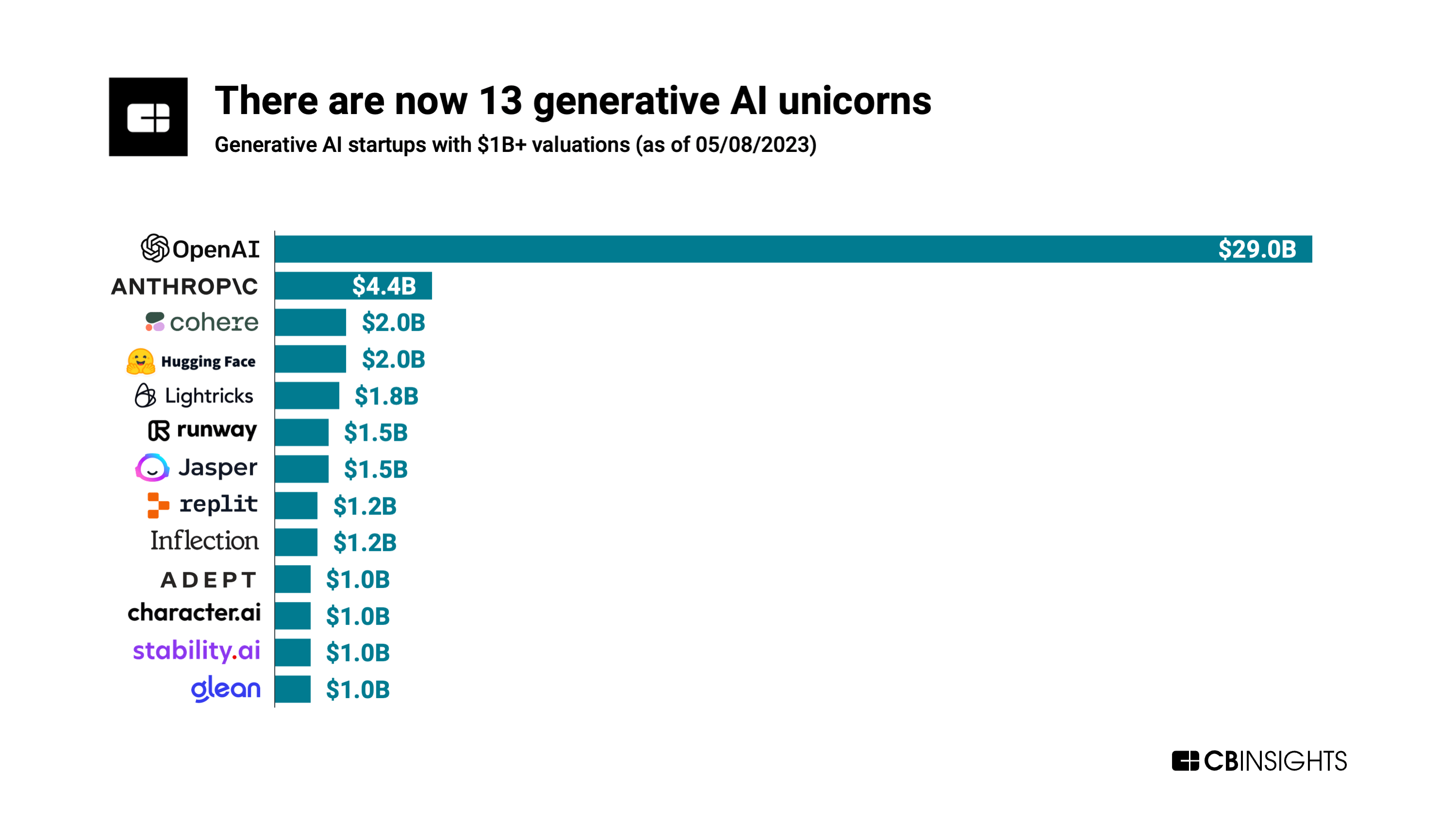
OpenAI, the poster child for Generative AI with its Chat GPT app, tops the list with a valuation of almost $30 billion. Microsoft is the largest investor as it provided OpenAI with a $1 billion investment in 2019 and a $10 billion investment in 2023. Bloomberg reported that the company recently closed an investment fund, exceeding expectations with a value that surpasses $175 million.
However, OpenAI may have a formidable competitor in Google DeepMind (more details in DeepMind section below).
….……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Anthropic is #2 with a valuation of $4.4B. It’s an AI safety and research company based in San Francisco, CA. The company says they “develop large-scale AI systems so that we can study their safety properties at the technological frontier, where new problems are most likely to arise. We use these insights to create safer, steerable, and more reliable models, and to generate systems that we deploy externally, like Claude (to be used with Slack).”
In Q1-2023, Generative AI companies accounted for three of the entrants to the unicorn club with Anthropic, Adept, and Character.AI all gaining valuations of $1B or above.
New Generative AI Unicorns in May:
Ten companies joined the Crunchbase Unicorn Board in May 2023 — double the count for April 2023. Among them were several AI startups:
- Toronto-basedCohere, a generative AI large language model developer for enterprises, raised $270 million in its Series C funding. The funding was led by Inovia Capital valuing the 4-year-old company at $2.2 billion.
- Generative video AI company Runway, based out of New York, raised a $100 million Series D led by Google. The funding valued the 5-year-old company at $1.5 billion.
- Synthesia, a UK-based artificial intelligence (AI) startup, has raised about $90 million at a valuation of $1 billion from a funding round led by venture capital firms Accel and Nvidia-owned NVentures. “While we weren’t actively looking for new investment, Accel and NVIDIA share our vision for transforming traditional video production into a digital workflow,” said Victor Riparbelli, co-founder and CEO of Synthesia.
….…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Google DeepMind:
Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai said in a blog post, “we’ve been an AI-first company since 2016, because we see AI as the most significant way to deliver on our mission.”
In April, Alphabet Inc. created “Google DeepMind,” in order to bring together two leading research groups in the AI field: the Brain team from Google Research, and DeepMind (the AI startup Google acquired in 2014). Their collective accomplishments in AI over the last decade span AlphaGo, Transformers, word2vec, WaveNet, AlphaFold, sequence to sequence models, distillation, deep reinforcement learning, and distributed systems and software frameworks like TensorFlow and JAX for expressing, training and deploying large scale Machine Learning (ML) models.
By launching DeepMind as Google’s Generative AI solution, there could be a new battle front opening in quantum computing, machine learning perception, gaming and mobile systems, NLP and human-computer interaction and visualization.
A recent DeepMind paper says the Alphabet unit has extended AI capabilities with faster sorting algorithms to create ordered lists. Their paper says it shows “how artificial intelligence can go beyond the current state of the art,” because ultimately AlphaDev’s sorts use fewer lines of code for sorting sequences with between three elements and eight elements — for every number of elements except four. And these shorter algorithms “do indeed lead to lower latency,” the paper points out, “as the algorithm length and latency are correlated.”
Their researchers created a program based on DeepMind’s AlphaZero program, which beat the world’s best players in chess and Go. That program trained solely by playing games against itself, getting better and better using a kind of massively automated trial-and-error that eventually determines the most optimal approach.
DeepMind’s researchers modified into a new coding-oriented program called AlphaDev, calling this an important next step. “With AlphaDev, we show how this model can transfer from games to scientific challenges, and from simulations to real-world applications,” they wrote on the DeepMind blog. The newly-discovered sorting algorithms “contain new sequences of instructions that save a single instruction each time they’re applied. AlphaDev skips over a step to connect items in a way that looks like a mistake, but is actually a shortcut.”
….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
While many luminaries, such as Henry Kissinger, Eric Schmidt and Daniel Huttenlocher, have lauded Generative AI as the greatest invention since the printing press, the technology has yet to prove itself worthy of the enormous praise. Their central thesis, that a computer program could “transform the human cognitive process” in a way tantamount to the Enlightenment, is a huge stretch.
Gary Marcus, a well-known professor and frequent critic of A.I. technology, said that OpenAI hasn’t been transparent about the data its uses to develop its systems. He expressed doubt in CEO Sam Altman’s prediction that new jobs will replace those killed off by A.I.
“We have unprecedented opportunities here but we are also facing a perfect storm of corporate irresponsibility, widespread deployment, lack of adequate regulation and inherent unreliability,” Dr. Marcus said.
The promise and potential of Generative AI will not be realized for many years. Think of it as a “research work in progress” with many twists and turns along the way.
….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/generative-ai-unicorns-valuations-revenues-headcount/
https://pitchbook.com/news/articles/Amazon-Bedrock-generative-ai-q1-2023-vc-deals
Curmudgeon/Sperandeo: Impact of Generative AI on Jobs and Workers
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
ITU-R report: Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages
At its June 2023 meeting (#44), ITU-R WP 5D has completed its work towards the development of a new report: ITU-R M.[IMT.APPLICATIONS] on Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages. WP5D agreed to elevate this PDNR to a Draft New Report (DNR).
Backgrounder:
Enterprises can generally expect reliable and secure network services with IMT (4G LTE and 5G) for fixed and mobile broadband applications across a wide coverage area. While there are subtle differences across different industrial sectors, IMT applications typically involve the following: video surveillance, remote control, autonomous vehicles and robots, automation, and immersive experiences.
The emergence of IMT-2020 “5G RAN” technologies provides manufacturers with the much-needed reliable connectivity solutions, enabling critical communications for wireless control of machines and manufacturing robots, and IoT sensor solutions, which will unlock the full potential of Industry 4.0.
Apart from manufacturing, many other industries are also looking at IMT-2020 technologies as the backbone for their equivalent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The opportunity to address industrial connectivity needs of a range of industries includes diverse segments with diverse needs, such as those in the mining, port, energy and utilities, automotive and transport, public safety, media and entertainment, healthcare, agriculture and education industries, among others.
Some recent trials of IMT-2020 technologies in port operations demonstrated the “3GPP 5G” capabilities for critical communications enablers such as ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to support traffic control, AR/VR headsets and IoT sensors mounted on mobile barges and provided countless possibilities to improve efficiency and sustainability in the complex and changing industrial environments, e.g., ports and mining. Some ports are increasing/accelerating their adoption of digital processes, automation and other technologies to enhance efficiency and resiliency to crises such as a global COVID-19 pandemic.
Similarly, in mining exploration sites, the drilling productivity could be substantially increased through automation of its drills and other technologies. Additional savings from improved efficiency and sustainability could also lead to lower capital expenditures for mines (CapEx) as well as a better safety and working environments for their personnel.
An example of an application in health care that need critical communications supported by the capabilities of IMT-2020 is remote robotic surgery. A latency of one millisecond is critical in providing haptic feedback to a surgeon that is connected through a mobile connection to a surgical robot. A high data rate is needed to transfer high-definition image streams. As an ongoing surgery cannot be interrupted an ultra-reliable communication is needed to keep connection down-time and packet loss very low.
Integration of IMT-2020 networks with industrial communication networks:
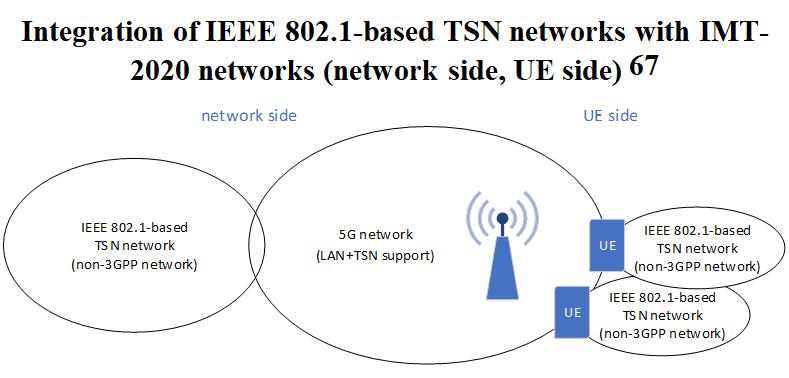
‘Industrial 5G’ networks need to be integrated in existing industrial communication networks. In order to support this, a ‘5G LAN’ interface is necessary, that supports Virtual LANs and Ethernet. Furthermore, support of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and integration of IMT-2020 in industrial TSN networks is of importance. Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is an important functionality of IEEE 802.1-based industrial communication networks in order to provide deterministic, reliable, real-time communication, and the integration of IMT-2020 networks and IEEE 802.1-based TSN networks is very beneficial.
The integration between the IEEE 802.1-based networks and the IMT-2020 networks can be through the ‘5G LAN’ service of the IMT-2020 network on the network side and/or on the UE side (see below Figure).
The integration on the UE side is used, for instance, in use cases where machinery, AGVs, or robots with their own internal network (wired, TSN) are connected to the backhaul part of the industrial communication network through an IMT-2020 link in order to enable mobility or tether less movements.
IEEE 802.1AS-based time synchronization is an important functionality in such industrial TSN communication networks. The accuracy of the time synchronization between the time transmitter (sync master) and any time receiver (sync device) needs to be in the range of 1 µs. The clock synchronization accuracy of the IMT-2020 system needs to be smaller than this value, since IMT-2020 network is only a part in this integrated industrial network.
Depending on the actual physical process, the actual cyber-physical control application, the design of the machinery, AGVs, and robots, and the design of the integrated industrial communication network, different mappings of TSN/time synchronization functionalities to IMT-2020 network elements are possible.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other important outputs from the June 2023 ITU-R WP 5D meeting:
- A related Draft New Report in the works: ITU-R M.[IMT.MULTIMEDIA] – Capabilities of the terrestrial component of IMT-2020 for multimedia communications.
- SWG IMT 2030 has submitted one draft new Recommendation ITU-R M. [IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND] – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond together with the relevant Liaison Statements.
- The long delayed revision of ITU-R M.1036 Frequency Arrangements for Terrestrial IMT was agreed upon and will be forwarded to ITU-R SG 5 for approval.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2020/Pages/default.aspx
Nikkei Asia: Huawei demands royalties from Japanese companies
Huawei Technologies is seeking patent licensing fees from roughly 30 small to midsize Japanese companies for the use of patented technology, Nikkei Asia has learned. That indicates the sanctions-hit Chinese telecommunication giant’s growing reliance on such revenue. A source at Huawei’s Japan unit revealed that “talks are currently underway with about 30 Japanese telecom-related companies.”
The telecom equipment and phone maker is believed to be stepping up royalty collection in Southeast Asia as well. It is highly unusual for a major manufacturer to directly negotiate with smaller clients regarding patent fees. Huawei is facing an increasingly tough business environment as U.S. sanctions stemming from data security concerns have made it difficult to sell products overseas.
Huawei is seeking fees from manufacturers and others that use components called wireless communication modules. Sources at several Japanese companies said businesses as small as just a few employees to startups with over 100 workers have received requests from Huawei.
Requested payment levels range from a fixed fee of 50 yen (35 cents) or less per unit to 0.1% or less of the price of the system.
“The level is on par with international standards,” said Toshifumi Futamata, a visiting researcher at the University of Tokyo.
Huawei holds a high share of so-called standard-essential patents that are crucial to using such wireless communications standards as 4G or Wi-Fi. Equipment made by other companies compatible with those IEEE 802.11/ITU-R standards also use Huawei’s patented technology. This means if Huawei demands it, many companies using related internet-connected devices will have to pay patent royalties.
Even Japanese companies that do not use Huawei products could incur unexpected expenses. Furthermore, many small and medium-sized companies are unfamiliar with patent negotiations, raising concerns about signing contracts with unfavorable terms.
“Depending on the content of the contracts, it could lead to data leaks for Japanese companies,” Futamata warned. “They need to enlist lawyers and other experts for help to avoid signing disadvantageous contracts.”
Contracts that include authorization to access the communication module’s software pose risk of data leaks, Futamata added.
Negotiations over telecommunications technology patents are generally conducted between major equipment manufacturers. Such negotiations are time-consuming and selling their own products is far more profitable.
But Huawei’s profit has plunged as U.S. sanctions have cut its access to American technology and goods. Without access to Google’s Android, for example, it has struggled to sell devices overseas. Growing U.S.-China tensions have prompted Japanese companies to avoid adopting Huawei products.
As patent royalties are not subject to trade restrictions, this could be a source of stable income for Huawei. The company established an intellectual property strategy hub in Japan to oversee its IP business in the Asia-Pacific region, including Singapore, South Korea, India and Australia.
Japanese automaker Suzuki Motor agreed with Huawei by the end of 2022 to license standard essential patents related to 4G communications technology used for connected cars. More Japanese companies could face payments demands from Huawei. Wireless communication modules using Huawei’s patented technology are indispensable for connected Internet of Things (IoT) networks, according to Tokyo-based research company Seed Planning. The technology is being adopted in autonomous driving, automated factories, medicine, power and logistics.
References:
Huawei forecast to increase mobile phone shipments despite Android ban
UAE’s Du demonstrates 5G VoNR with Huawei and Nokia
Huawei says 5.5G is necessary with fully converged cloud native core network
Huawei’s blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G and the “intelligent world”
Huawei reinvents itself via 5G-enabled digitalized services to modernize the backbone of China’s industrial sectors
Vertical Systems Group’s 2022 U.S. Wavelength Services Leaderboard
Lumen, Zayo, Verizon and AT&T topped Vertical Systems Group’s Wavelength Services Leaderboard [1.] for 2022 as they did the previous year. Those companies each have 4% or more of the U.S. market for retail and wholesale wavelength services — which involve the allocation of capacity on an optical network, essentially creating dedicated highways for data.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note 1. A Wavelength Service is a large bandwidth connection providing high-speed Internet or data service delivered over lit fiber-optic lines using Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM) to create wavelengths or optical channels.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Vertical Systems Group found that expansion of the U.S. base of wavelength circuits is being driven by double-digit growth for 100+ Gbps connections and expects that to continue through 2027.
High bandwidth requirements are driving the growth of wavelength services in the U.S., according to Vertical Systems Group Principal Rick Malone. Telecom carriers use wavelength services to extend their core backbone networks, connect mobile towers and strengthen the resiliency of their network infrastructures, while hyperscale network operators employ wavelengths for data center interconnectivity, cloud computing, business continuity and backup/disaster recovery.
“Enterprises are purchasing wavelength services for their backbone networks, driven by IT cloud transformations, and for specific applications requiring predictable latency and low jitter,” Malone stated. U.S. network providers have upgraded their fiber footprints to support wave services above 10 Gbps, with general availability of 100 Gbps circuits nationwide.
“At the same time, fiber footprints have been expanded to include buildings that previously may have had only a single fiber provider,” he told Fierce Telecom. “And with multiple wavelength providers in a building, customers are negotiating more favorable pricing terms.”
Market Players include all other wavelength providers with U.S. circuit share below the one percent (1%) threshold. For year-end 2022, Market Players include the following wavelength providers (in alphabetical order): 11:11 Systems, Armstrong Business Solutions, Astound Business Solutions, Breezeline Business, Brightspeed Business, Cogent, Colt, Consolidated Communications, C Spire, Comcast Business, DQE Communications, Epsilon, Everstream, Exa Infrastructure (formerly GTT), ExteNet Systems, Fatbeam, FiberLight, First Digital, FirstLight, Frontier, Great Plains Communications, Horizon, Lightpath, Logix Fiber Networks, LS Networks, Midco, Ritter Communications, Segra, Shentel Business, Silver Star Telecom, Sparklight Business, Spectrum Enterprise, Syringa, T-Mobile, TDS Telecom, Unite Private Networks, Uniti, U.S. Signal, WOW!Business, Ziply Fiber and others.
Billable installations of 400+ Gbps services are emerging as wavelength providers expand availability and roll out new services to support higher speeds across a wider footprint. Many are actively planning for 400 and 800 Gbps service deployment in response to “early adopter requirements,” according to Malone.
Zayo recently debuted a new Waves on Demand product for customers looking to rapidly light up added bandwidth, for example. Waves on Demand will initially focus on providing 100G services across eight routes, though a 400G route between Newark, NJ and New York is available.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/broadband/lumen-and-zayo-hold-strong-us-wavelength-service-leaders
Lumen Technologies tops Vertical Systems Group’s 2021 U.S. Wavelength Services Leaderboard
China Mobile to deploy 400G QPSK by the end of 2023
China Mobile is preparing to deploy 400G optical links and expects to call its first tenders by the end this year. At the 2023 China Optical Network Symposium on Thursday, Li Han, director of the Basic Network Technology Research Institute of China Mobile Research Institute , gave a speech and revealed that China Mobile has confirmed the availability of 400G technology and will start the centralized procurement of 400G products at the end of this year to promote 400G to enter the commercial stage. “It’s time for 400G, and the industry is looking forward to it.”
 China Mobile completed the world’s first 400G QPSK pilot with vendor partner ZTE in March, achieving high-speed transmission over 5,616 kilometers of ultra-long-distance land real-time live network transmission. The verified computing power network 400G all-optical network technology is the core technology of the next-generation intergenerational evolution of the backbone transport network.
China Mobile completed the world’s first 400G QPSK pilot with vendor partner ZTE in March, achieving high-speed transmission over 5,616 kilometers of ultra-long-distance land real-time live network transmission. The verified computing power network 400G all-optical network technology is the core technology of the next-generation intergenerational evolution of the backbone transport network.
Li Han believes that 400G is an intergenerational technology of optical communication and a disruptive technology. The reason is that 400G optical communication has entered the broadband era, and the C6T+L6T band is disruptive to the entire system including core optical devices. Specific to the application scenario, the backbone network considers the long distance and adopts the QPSK method, and the metropolitan area network considers the cost, and mainly deploys 16QAM-PCS or 16QAM. In different scenarios, different techniques are used.
China Mobile’s 400G research and development has gone through 5 years. From 2018 to 2021, it will mainly study 16QAM-PCS or 16QAM; in 2022, with the development of 130G baud rate optical modules, the industry chain will turn to QPSK driven by the three major manufacturers. This is of decisive significance to the development trend of 400G.
Li Han finally emphasized that 400G still needs to continue to improve technology, such as EDFA, which needs to substantially integrate C-band and L- band . In terms of optical fiber , research on anti-resonant hollow-core optical fiber should be promoted.
In a white paper, China Mobile said Jiuzhou would encompass 400G optical connectivity and a distributed cloud architecture, with edge computing and three levels of latency, from 1 millisecond in the city to 20 milliseconds in the countryside. The paper said the 400G OTN would initially be deployed at major computing hub nodes, then in the backbone.
A major driver of China Mobile’s optical plans is a government scheme to build out China’s national “computing power network” – a chain of data centers and high-speed fiber links that will support the new computer-intensive era of AI, deep learning, 5G Advanced and the industrial Internet.
One key part of this is the East-West plan, in which data from the industrialized eastern seaboard is being hauled to lower cost, renewables-powered data centers in the less developed west over high-speed links. So far China Mobile has deployed more than 40 super-large data centers with more than 1.3 million racks and over 1,000 edge nodes.
Li said the telco’s 400G R&D had initially focused mainly on 16QAM-PCS and 16QAM, but last year had turned to QPSK, driven by breakthroughs from three domestic vendors.
Zhang Bin, vice president of FiberHome’s network business unit, said he believes 400G OTN will dominate optical fiber for the next ten years. But he said Chinese manufacturers would need to invest more in R&D to keep pace with the large-scale rapid rollout
References:
https://www.c114.com.cn/news/22/c22780.html
Omdia: China Mobile tops 2023 digital strategy benchmark as telcos develop new services
China Mobile explores buyout of Hong Kong telecom firm HKBN
China Mobile Partners With ZTE for World’s First 5G Non Terrestrial Network Field Trial
China Mobile and ZTE complete commercial trial of optical network co-routing detection
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
StrandConsult Analysis: European Commission second 5G Cybersecurity Toolbox report
by John Strand, StandConsult (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
European Commissioner Thierry Breton presented the European Commission’s plan for banning High-Risk Suppliers like Huawei and ZTE from European telecommunications networks. Here is the first portion:
The security of 5G networks is essential. They are critical infrastructures in their own right and for other sectors that depend on them, such as energy, transport, health and finance.
This is why, in January 2020, the EU unanimously adopted a toolbox on the security of 5G networks. The “5G cybersecurity toolbox” defined the risks and the measures to be taken by Member States and telecoms operators to address them.
In particular, it recommended that the use of equipment in the core and access (RAN) parts of the networks should be restricted or prohibited for entities considered to be “high-risk suppliers”, notably because they are subject to highly intrusive third-country laws on national intelligence and data security.
3 years on, almost all Member States have transposed the toolkit’s recommendations into their national law. In other words, they can now decide to restrict or exclude suppliers on the basis of security risk analysis. But to date, only 10 of them have used these prerogatives to restrict or exclude high-risk vendors.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The Commission also released a status report on “Member States’ Progress in implementing the EU Toolbox on 5G Cybersecurity.”
Breton’s message is that the member must move more quickly to implement the 5G toolbox.
Here are Breton’s key points with Strand Consult’s assessment (SC):
- All EU member states are committed to implementing the EU´s 5G Toolbox. To date, 24 Member States have adopted or are preparing legislative measures giving national authorities the powers to perform an assessment of suppliers and issue restrictions.
- SC: This means that all EU countries support the 5G Toolbox, the implement of which will work to remove Huawei and ZTE from European networks.
- 10 Member States have imposed such restrictions, and an additional 3 Member States have relevant national legislation underway.
- SC: This is a significant improvement compared to a few months ago when Strand Consult’s released its report The Market for 5G RAN in Europe: Share of Chinese and Non-Chinese Vendors in 31 European Countries. Given the Commission’s communication we the remaining more operators in 14 countries to move more expeditiously to remove Huawei and ZTE equipment.
- The Commission considers that decisions adopted by Member States to restrict or exclude Huawei and ZTE from 5G networks are justified and compliant with the 5G Toolbox.
- SC: This statement is very important to support the member states where Huawei and China attempt to thwart the implementation of the toolbox. China has made unseemly threats in certain members states. Now these states have meaningful European Commission support. For example, in December 2019, Wu Ken, the Chinese ambassador to Germany, was quoted as threatening the German auto manufacturing industry that access to the Chinese market could be restricted should Chinese Huawei be excluded from participating in contracts to build Germany’s 5G networks. The statement dampened Germany’s enthusiasm for opening its EU toolbox and examining its requirements.
- The Commission will take measures to avoid conducting its official communications via mobile networks built with Huawei and ZTE equipment.
- SC: If an EU mobile operator uses Huawei or ZTE equipment in its 5G network, the European Commission will not do business with that operator. In practice EU operators which use Huawei and ZTE will be labeled as “non-trusted operators.” This will likely accelerate the exodus of corporate customers from European operators which don’t want to conduct their business on Chinese networks. Strand Consult described this in its 2019 research note The pressure to restrict Huawei from telecom networks is driven not by governments, but the many companies which have experienced hacking, IP theft, or espionage. This is a needed and important step from the Commission.
- The Commission also intends to reflect this decision in all relevant EU funding programs and instruments.
- SC: The EU will further restrict grants, subsidies, and financing to European entities which use Huawei and ZTE equipment. This will have consequences for rural EU operators which receive EU money and recipients of European Investment Bank (EIB) loans.
Strand Consult is not surprised by today’s announcements. They are consistent with the security analyses and recommendations Strand Consult has published for years.
Some EU countries and operators will find it difficult to implement the EU’s new security and procurement policy. However Strand Consult believes that it is good business for an operator communication that it takes security seriously and backs it up with a clean network free of Huawei and ZTE equipment.
Strand Consult predicts that Huawei will make the road ahead difficult and will attempt to sabotage the European Commission’s efforts. Nations and operators should prepare for pushback by reading Strand Consult’s reports on Huawei’s tactics. Moreover, non-Chinese employees will likely find that working for Huawei has reputational risks.
How foreign network equipment is treated in China.
The foundation of any economy, be it the EU, the US or China, is national security. Some may find the EU approach tough, but it pales in comparison the blockade that China has imposed on foreign technology providers for years.
China restricts these technologies for ideological and economic reasons. Most people take for granted that the websites and media they access everyday are not available in China. These foreign technologies and their operators have been denied access to the world’s single largest online market, hundreds of millions of internet users, and a multi-trillion-dollar opportunity. Moreover, the Chinese people are denied to freedom to engage on an open internet.
Building upon censorship frameworks in traditional media which had been in place for decades in China, its State Council adopted rules and regulations to control internet traffic beginning in 1996.
The media focuses mainly on US and EU network security and associated vendor policies. However few if any investigate the rules in China.
A detailed review is available from White & Chase, February 2022. In general, China’s rules are significantly more rigid than those of the US and EU. These rules do not entail the same process and transparency which are standard and expected in the West.
The New Measures list the following main factors for assessing national security risk during cybersecurity review.
- The risk of any critical information infrastructure being illegally controlled, tampered with or sabotaged after any product or service is used.
- The risk of an interruption in the supply of any product or service endangering the continuity of any critical information infrastructure.
- The security, openness, transparency, diversity of sources and reliability of any supply channel of any product or service, and the risk of its supply being interrupted due to political, diplomatic, trade or other factors.
- The compliance of the provider of any product or service with the laws, administrative regulations, and departmental rules of China.
- The risk of any core data, important data or a large amount of personal information being stolen, leaked, destroyed, illegally used, or illegally transferred abroad.
- The risk of any critical information infrastructure, core data, important data, or a large amount of personal information being affected, controlled, or maliciously used by foreign governments, as well as any network information security risk.
- Any other factor that may endanger the security of any critical information infrastructure, network security or data security.
The effect of these rules is to limit foreign providers from the market from the start and to favor Chinese providers.
While the media sensationalizes cases like Huawei and TikTok, these pale in comparison to the systematic restriction undertaken by China against foreign technology for the last 20 years. Moreover, Chinese technology companies enjoy more freedom abroad than foreign technologies do in China.
Conclusions:
Technological and informational control and restriction are widely practiced across China. This fulfills many political, social, cultural, economic, and religious objectives for the PRC,and is practiced by the government, corporations, and individual themselves. It has increased under General Secretary Xi. This Censorship is coupled with pervasive surveillance of people. Meanwhile PRC has attempted to export this “new world media order.”
Strand Consult addresses Chinas restrictions in its 2020 report You Are Not Welcome: An Analysis of Thousands Foreign Technology Companies Blocked by China Since 1996. It describes how and why China has systematically restricted thousands of foreign internet technologies like online news and media outlets, social media platforms, virtual private networks, content delivery networks, mobile applications, telecommunications equipment, cloud services, and other technologies.
With its new 2023 report The Market for 5G RAN in Europe: Share of Chinese and Non-Chinese Vendors in 31 European Countries, Strand Consult brings valuable evidence of the location, amount, and share of Chinese and non-Chinese equipment in European telecom networks. This report, the second of its kind, describes the respective amounts of 5G equipment from Huawei, ZTE, and non-Chinese vendors in European mobile networks and the share of such in equipment in the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN).
References:
https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/statement_23_3312
StrandConsult: 2022 Year in Review & 2023 Outlook for Telecom Industry
IEEE ComSoc/SCU SoE March 22, 2022 event: OpenRAN and Private 5G – New Opportunities and Challenges. Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i7QUyhjxpzE
Strand Consult: Open RAN hype vs reality leaves many questions unanswered
O-RAN Alliance tries to allay concerns; Strand Consult disagrees!
Dish says its 5G network now covers 70% of the U.S. population
Dish Network says its 5G network is available to more than 240 million people and covers 70% of the U.S. population. That 70% threshold is what regulators demanded for it to keep valuable spectrum licenses. Dish says it has satisfied all June 14th deadlines set by the FCC, including having launched over 15,000 5G sites. Dish will continue to face 5G buildout deadlines set by federal regulators, including one in 2025 that Dish will likely need to invest billions in a rural buildout to meet. Investors have punished the stock, sending shares to near their lowest level since around 1999 amid worries that the company is struggling to stand up its wireless network without a partner.
Dish is also the first wireless service provider to launch 5G voice service – called voice over new radio (VoNR) – in the U.S. Since going live in Las Vegas last year, Dish steadily increased VoNR functionality to additional markets. Our VoNR service now covers more than 70 million people across the U.S. through both Boost Mobile and Boost Infinite. Dish plans to continue rolling out VoNR service as the network is further optimized for this next-generation voice technology.

Image Credit: Dish Networks
“As a leader in Open RAN technology, Dish is playing a major role in the transformation of America’s wireless infrastructure and the way the world communicates,” said John Swieringa, president and chief operating officer, Dish Wireless. “We have made significant progress on our network buildout, and can now focus on monetizing the network through retail and enterprise growth. With more markets across the country offering the Dish 5G network for voice, text and data services, our business can start realizing the benefits of owner economics.”
The company “can now focus on monetizing the network through retail and enterprise growth,” COO John Swieringa said in a news release, a nod to shareholder impatience with a costly project. Dish now has a month to prove it to the Federal Communications Commission with detailed documentation. Dish will file its FCC buildout report no later than July 14, 2023.
LightShed Partners analyst Walt Piecyk notes that confirmation that regulators are satisfied might soothe investors, but he doesn’t expect the FCC to comment “for the foreseeable future, if ever,” a silence that poses an “incremental hurdle for Dish to raise needed capital.”
References:
For a complete list of DISH’s wireless partners, please visit DISHWireless.com/home