AMD
Reuters: US Department of Energy forms $1 billion AI supercomputer partnership with AMD
The U.S. Department of Energy has formed a $1 billion partnership with Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) to construct two supercomputers that will tackle large scientific problems ranging from nuclear power to cancer treatments to national security, U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright and AMD CEO Lisa Su told Reuters.
The U.S. is building the two machines to ensure the country has enough supercomputers to run increasingly complex experiments that require harnessing enormous amounts of data-crunching capability. The machines can accelerate the process of making scientific discoveries in areas the U.S. is focused on.

U.S. Energy Secretary Wright said the systems would “supercharge” advances in nuclear power, fusion energy, technologies for defense and national security, and the development of drugs. Scientists and companies are trying to replicate nuclear fusion, the reaction that fuels the sun, by jamming light atoms in a plasma gas under intense heat and pressure to release massive amounts of energy. “We’ve made great progress, but plasmas are unstable, and we need to recreate the center of the sun on Earth,” Wright told Reuters.
The second, more advanced computer called Discovery will be based around AMD’s MI430 series of AI chips that are tuned for high-performance computing.
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s largest telecom firms were ordered earlier this year to phase out foreign computer chips from their networks by 2027. That news confirms and expands on reports from recent months. It was reported in the Saturday print edition of the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). The move will hit U.S. semiconductor processor companies Intel and Advanced Micro Devices. Asia Financial reported in late March that these retaliatory bans would cost the U.S. chip firms billions.
The deadline given by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) aims to accelerate efforts by Beijing to halt the use of such core chips in its telecom infrastructure. The regulator ordered state-owned mobile operators to inspect their networks for the prevalence of non-Chinese semiconductors and draft timelines to replace them, the people said.
In the past, efforts to get the industry to wean itself off foreign semiconductors have been hindered by the lack of good domestically made chips. Chinese telecom carriers’ procurements show they are switching more to domestic alternatives, a move made possible in part because local chips’ quality has improved and their performance has become more stable, the people said.
Such an effort will hit Intel and AMD the hardest, they said. The two chip makers have in recent years provided the bulk of the core processors used in networking equipment in China and the world.
China’s MIIT, which oversees the regulation of the wireless, broadcasting and communication industries, didn’t respond to WSJ’s request for comment. China Mobile and China Telecom , the nation’s two biggest telecom carriers by revenue, also didn’t respond.
In March 2023, the Financial Times reported China is seeking to forbid the use of Intel and AMD chips, as well as Microsoft’s operating system, from government computers and servers in favor of local hardware and software. The latest purchasing rules represent China’s most significant step yet to build up domestic substitutes for foreign technology and echo moves in the US as tensions increase between the two countries. Among the 18 approved processors were chips from Huawei and state-backed group Phytium. Both are on Washington’s export blacklist. Chinese processor makers are using a mixture of chip architectures including Intel’s x86, Arm and homegrown ones, while operating systems are derived from open-source Linux software.
Beijing’s desire to wean China off American chips where there are homemade alternatives is the latest installment of a U.S.-China technology war that is splintering the global landscape for network equipment, semiconductors and the internet. American lawmakers have banned Chinese telecom equipment over national-security concerns and have restricted U.S. chip companies including AMD and Nvidia from selling their high-end artificial-intelligence chips to China.
China has also published procurement guidelines discouraging government agencies and state-owned companies from purchasing laptops and desktop computers containing Intel and AMD chips. Requirements released in March give the Chinese entities eight options for central processing units, or CPUs, they can choose from. AMD and Intel were listed as the last two options, behind six homegrown CPUs.
Computers with the Chinese chips installed are preapproved for state buyers. Those powered by Intel and AMD chips require a security evaluation with a government agency, which hasn’t certified any foreign CPUs to date. Making chips for PCs is a significant source of sales for the two companies.
China Mobile and China Telecom are also key customers of both chip makers in China, buying thousands of servers for their data centers in the country’s mushrooming cloud-computing market. These servers are also critical to telecommunications equipment working with base stations and storing mobile subscribers’ data, often viewed as the “brains” of the network. Intel and AMD have the lion’s share of the overall global market for CPUs used in servers, according to data from industry researcher TrendForce. In 2024, Intel will likely hold 71% of the market, while AMD will have 23%, TrendForce estimates. The researcher doesn’t break out China data.
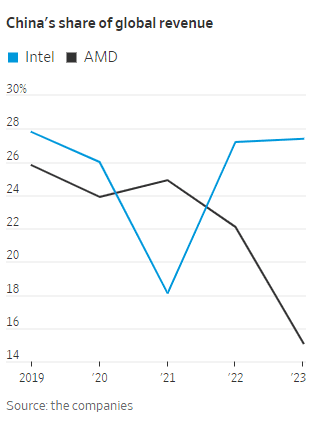
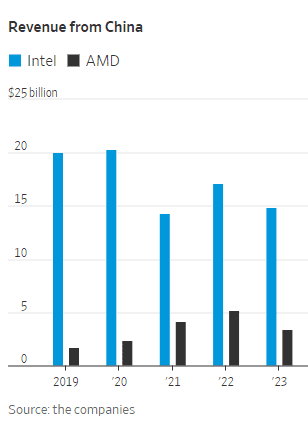
China’s localization policies could diminish Intel and AMD’s sales in the country, one of the most important markets for semiconductor firms. China is Intel’s largest market, accounting for 27% of the company’s revenue last year, Intel said in its latest annual report in January. The U.S. is its second-largest market. Its customers also include global electronics makers that manufacture in China.
In the report, Intel highlighted the geopolitical risk it faced from elevated U.S.-China tensions and China’s localization push. “We could face increased competition as a result of China’s programs to promote a domestic semiconductor industry and supply chains,” the report said.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/china-telecom-intel-amd-chips-99ae99a9 (paywall)
https://www.ft.com/content/7bf0f79b-dea7-49fa-8253-f678d5acd64a
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY