EdgeQ
IEEE ComSocSV/SCU SoE New Event (free): Inside a Telecom Chip Start-up and its 4G+5G Base Station SoC
Date & Time: May 30th, 2:30pm to 5pm
Venue: Santa Clara University – SCDI 1308
Register at: https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/421628
Agenda/Timeline:
⦁ 2:30pm-3pm Registration & Networking
⦁ 3pm Opening Remarks
⦁ 3:05pm-4pm Presentation
⦁ 4pm-4:30pm Panel Discussion/Conversation
⦁ 4:30pm-4:50pm Audience Q & A
⦁ 4:50pm-4:55pm Closing Remarks & Acknowledgements
Abstract:
As 5G evolves for both public and private networks, edge demands will impact the fluidity and constructs of 5G infrastructure. Mobile network operators (public 5G) and enterprises (private 5G) are confronted with a daunting fundamental challenge:
How to deploy a wireless infrastructure that can effortlessly scale across all future upgrades (e.g. 5G Advanced) and demands, without incurring the traditional capital and operating expense of a system redesign and rip-and-replace costs?
This talk will cover the starting point of all wireless infrastructure – the 4G+5G baseband System on a Chip (SoC). We will discuss: how a”soft modem” can scale with evolving infrastructural demands across small cells and macro cells, new application use cases, emerging megatrends (such as 5G non-terrestrial networks), market fundamentals impacting 5G deployments, and personal insights into the starting and evolution of a 5G semiconductor startup company in the era of AI.
Five years in the making, EdgeQ emerged in 2018 as one of the very few semiconductor startups [1.] focusing on 5G wireless infrastructure. Led by executives from Qualcomm, Intel, and Broadcom, EdgeQ is pioneering converged connectivity and AI that is fully software-customizable and programmable. The company has raised multiple financing rounds, backed by world-renowned investors across all major continents. See below for awards EdgeQ has received.
Note 1. There’s been a significant decline in funding for semiconductor startups over the past 10 years due to a maturing industry, high capital requirements, and fewer exits. In 2021, chip startups globally raised $8.3 billion in 263 deals, but in 2023, U.S. startups have only raised $262 million in 17 deals. There have been EVEN FEWER semiconductor startups focusing on wireless telecommunications as EdgeQ has done.
Speakers and Panelists:
- Adil Kidwai, Head of Product Management, EdgeQ
- Edward Wu, Head of Marketing & Market Development, EdgeQ
Moderator: Alan J Weissberger, IEEE Techblog Content Manager, SCU SoE Scholar in Residence, IEEE GCN North American Correspondent
………………………………………………………………………………….
EdgeQ Awards:
2023 GLOMO Award Winner

CTO Choice Award for Outstanding Mobile Technology
Best Digital Technology Breakthrough for Companies with Under $10M Annual Global Revenue
2022 Mobile Breakthrough Award Winner Small Cell Technology Innovation of the Year

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Addendum:
Video recording is at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-v42TnNjIfM
“Qualcomm will be a tough competitor if they seriously enter into the wireless infrastructure market. They make good modems,” Adil said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.edgeq.io/edgeq-debuts-worlds-first/
https://www.edgeq.io/static/Tech_Pcie_Explosion-f48f32134ee6e58752aab6683a63abf4.mp4
EdgeQ’s breakthrough demos and partnerships showcased at MWC 2024 & MWC 2023
EdgeQ Inc, an innovative 4G/5G System on a Chip (SoC) semiconductor startup, had several defining showcases at MWC 2024 as well partnership announcements which included:
1. A partnership with DenseAir and Radisys to deliver industry’s first cloud-native, neutral host solution for mobile networks. It’s the world’s first O-RAN split 6 solution where multiple operators and multiple data streams are all supported off a common platform – single box, single silicon.
- EdgeQ fundamentally enabled DenseAir to deliver a solution that converged 4G+5G on a single silicon, while providing elastic scaling up to 4 component carriers and 256 users, with software-defined O-RAN split 6.
2. EdgeQ and BlinQ showcased a single integrated 5G+WiFi platform (PCW-400i), running simultaneously 5G at 3.3-4.2GHz frequency band spectrum and Wi-Fi 2.4GHz and 6GHz spectrum. This fully integrated small cell solution by BlinQ operates in bands n48, n77 and n78 along with the three bands from the Wi-Fi 7 standard. Using EdgeQ’s SoC, BlinQ enables novel deployment schemes like completely 5G cable-less backhaul, while enabling PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt is the latest and most powerful Power over Ethernet standard. It provides up to 100 watts of power per port. at affordable unit economics).
- “Not only does the PCW-400i provide incredible capacity, it also incorporates BLiNQ’s enterprise-level management suite and zero-touch provisioning, making it easy to install and operate in any size organization,” says Pete Vavra, VP of Sales at BLiNQ. “The product was designed with scalability and ease of deployment in mind without taking the focus away from performance,” Vara added.
- “Our collaboration with BLiNQ is about massively converging two major wireless protocols into a single platform that give customers flexibility and freedom of choice. This is a phenomenal achievement delivering state-of-the art 5GNR and Wi-Fi 7 in a sleek, compact form factor that can elastically scale with connection density and capacity demands while maintaining breakthrough unit economics at unprecedented low power,” says Ziyao Xu, Director of Product Management at EdgeQ. “This will compel the market with novel use cases for enterprise, private networks, and home,” Xu added.
3. EdgeQ’s silicon was featured by both ARM and Analog Devices. Two landmark capabilities were revealed:
- Multi-Operator, Multi-Carrier 4cc Aggregation Running on a Single SoC Converging 4G+5G+AI.
- Industry First 5G PHY + 5G L2/L3 + Embedded User Plane Function (UPF) running on EdgeQ’s SoC:
-
Local Processing of UPF reduces the WAN tax, allowing for a lighter, less burdened core network. Having an embedded UPF can save cost, reduce latency, and maintains the pilot data from needing to leave the premise.
-
At the same time, there is enough headroom in EdgeQ’s processor architecture to run other edge applications (DPDK, virtualization, containers, etc…etc…).
-
4. Actiontec and EdgeQ announced the commercial release of ASC-308: Revolutionizing Network Flexibility, Performance and Future-Proofing 4G & 5G Small Cell.
- Enabled by EdgeQ SoC, Actiontec’s ASC-508 offers a programmable architecture, 4G & 5G multi-technology support, and ease of deployment to empower operators to build future-proof networks. The ASC-508 boasts a programmable and modular architecture, allowing operators to adapt easily the platform to their band support, specific use cases, and evolving network requirements.
- Support for various O-RAN compliant Split options, including All-in-One Split 0, Split 2, and Split 6, ensures future-proof adaptability. This is all due to the programmable nature of EdgeQ’s “Base Station-on-a-Chip.”
–>Significantly, EdgeQ’s SoC product entered production last year and has generated meaningful revenue with customers worldwide.
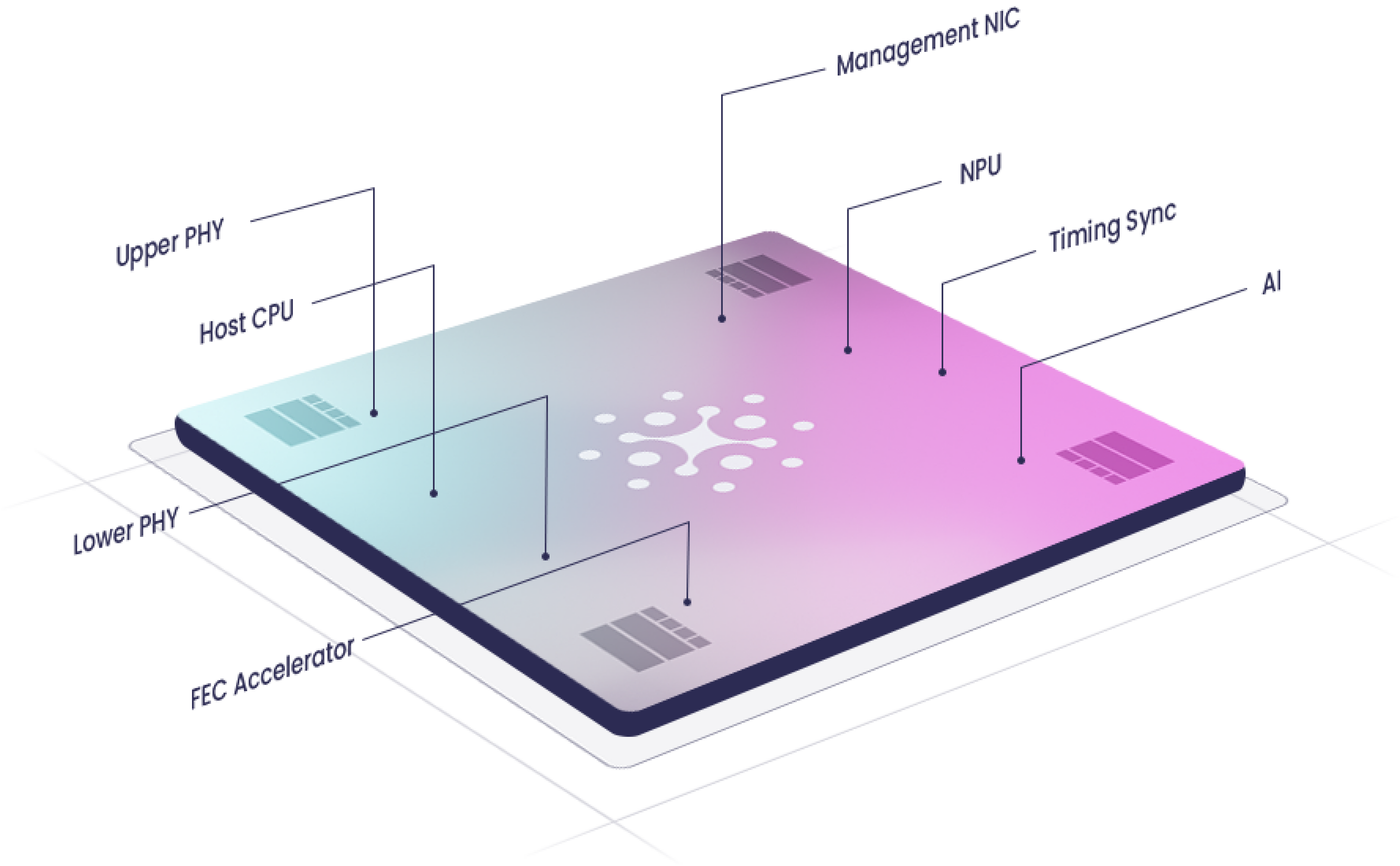
Image Credit: EdgeQ Inc.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
At MWC 2023, EdgeQ collaborated with Vodafone, a leading telecommunications mobile operator in Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN), and Dell Technologies to debut a state-of-the-art O-RAN-based, massive MIMO solution at last year’s Mobile World Congress (MWC 2023) in Barcelona, Spain. As a result, the company received the prestigious “CTO Choice Award for Outstanding Mobile Technology” and “Best Digital Technology Breakthrough.”
The collaboration and design between the three companies is a massive MIMO 5G network that leverages in line acceleration technologies to deliver high user capacity, high network bandwidth at relatively low power for the new O-RAN based deployments.
Hosted at the Vodafone stand, the live system comprised of a Dell PowerEdge XR11 server and an EdgeQ M-Series L1 accelerator will demonstrate impressive throughput of 5Gbps, with the accelerator drawing less than 50 watts. The collaboration and design between the three companies demonstrate the principles of a 5G O-RAN infrastructure solution on a standard server, an inline acceleration, a Radio Unit (RU) system, and third party L2/L3 software stack from collaborating companies.
“Vodafone is committed to driving 5G O-RAN deployments at scale. Our showcase with EdgeQ and Dell Technologies validates how open innovation can drive better performance and cost efficiencies. Technologies such as EdgeQ’s high capacity in-line L1 acceleration should enable Vodafone to scale our macro cell infrastructure to new levels of performance and efficiency without compromise,” said Paco Martin, Head of OpenRAN Product Team, Network Architecture, Vodafone.
EdgeQ’s multi-node 4G/5G Base Station-on-a-Chip solution [1.] converges connectivity, compute, and networking in a disruptively innovative software-defined platform. The highly scalable, flexibly adaptive EdgeQ platform solution uniquely features a production-grade L1 stack that is open and customizable. The scalable architecture maximizes throughput performance, compute processing, across a large range of concurrent users and multiple carriers, all within a compact power and cost envelope.
“EdgeQ was founded on the belief of reconstituting the network in simple and intuitive terms. Together with Vodafone and Dell Technologies, we have shown the first instantiation of a new market paradigm that scales openly and flexibly, without the cost burden and power penalties of traditional platform approaches,” said Vinay Ravuri, CEO and Founder at EdgeQ.
Note 1. In December 2023, EdgeQ announced a converged 4G, 5G, and AI base station SoC at 1/2 cost, 1/3 the power, and 1/10 the space of previous designs. EdgeQ’s 4G/5G base station SoC features:
- 3 to 4 Multi-carrier operation on a 4T4R small cells for enterprise private networks.
- Asymmetric carrier aggregation across multiple bandwidths – ex: 100+20, 20+10, …….
- Asymmetric carrier aggregation between licensed bands and PAL/GAA spectrum assets.
EdgeQ is the only company providing an integrated 4G+5G solution, complete with a multi-mode L1 (Physical Layer), an interoperable L2/L3 software stack, all on a single chip. Telcos and private network customers can leverage a single converged solution, upgrade over-the-air at compelling unit economics of 1/2 the cost and 1/3 the power of previous base station designs.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On March 22, 2022, EdgeQ’s Product Development Manager Adil Kidwai participated in an IEEE ComSocSCV virtual panel session, organized by this author, where he discussed the benefits of his company’s 4G/5G SoC solution for O-RAN and private 5G networks. That virtual panel session was summarized in the November 2022 IEEE Global Communications Newsletter which was published in the November 2022 IEEE Communications magazine. You can watch a video of that very informative session here.
About EdgeQ:
EdgeQ is a leading innovator in 5G systems-on-a-chip. The company is headquartered in Santa Clara, CA, with offices in San Diego, CA and Bangalore, India. Led by executives from Qualcomm, Intel, and Broadcom, EdgeQ is pioneering converged connectivity and AI that is fully software-customizable and programmable.
The company is backed by world-renowned investors. To learn more about EdgeQ, visit www.edgeq.io. Media Contact: [email protected] 804-612-5393
References:
https://www.edgeq.io/edgeq-wins-multiple
https://www.edgeq.io/edgeq-debuts-worlds-first
EdgeQ Samples World’s 1st Software-Defined 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip
Intel FlexRAN™ gets boost from AT&T; faces competition from Marvel, Qualcomm, and EdgeQ for Open RAN silicon
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9946966
SoC start-up EdgeQ comes out of stealth mode with 5G/AI silicon for 5G private networks/IIoT
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6736761
Intel FlexRAN™ gets boost from AT&T; faces competition from Marvel, Qualcomm, and EdgeQ for Open RAN silicon
Dell’Oro Group estimates the RAN market is currently generating between $40 billion and $45 billion in annual revenues. The market research firm forecasts that Open RAN will account for 15% of sales in 2026. Research & Markets is more optimistic. They say the Open RAN Market will hit $32 billion in revenues by 2030 with a growth rate of 42% for the forecast period between 2022 and 2030.
As the undisputed leader of microprocessors for compute servers, it’s no surprise that most of the new Open RAN and virtual RAN (vRAN) deployments use Intel Xeon processors and FlexRAN™ software stack inside the baseband processing modules. FlexRAN™ is a vRAN reference architecture for virtualized cloud-enabled radio access networks.
The hardware for FlexRAN™ includes: Intel® Xeon® CPUs 3rd generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor (formerly code named Ice Lake scalable processor), Intel® Forward Error Correction Device (Intel® FEC Device), Mount Bryce (FEC accelerator), Network Interface Cards – Intel® Ethernet Controller E810 (code name Columbiaville). Intel says there are now over 100 FlexRAN™ licensees worldwide as per these charts:
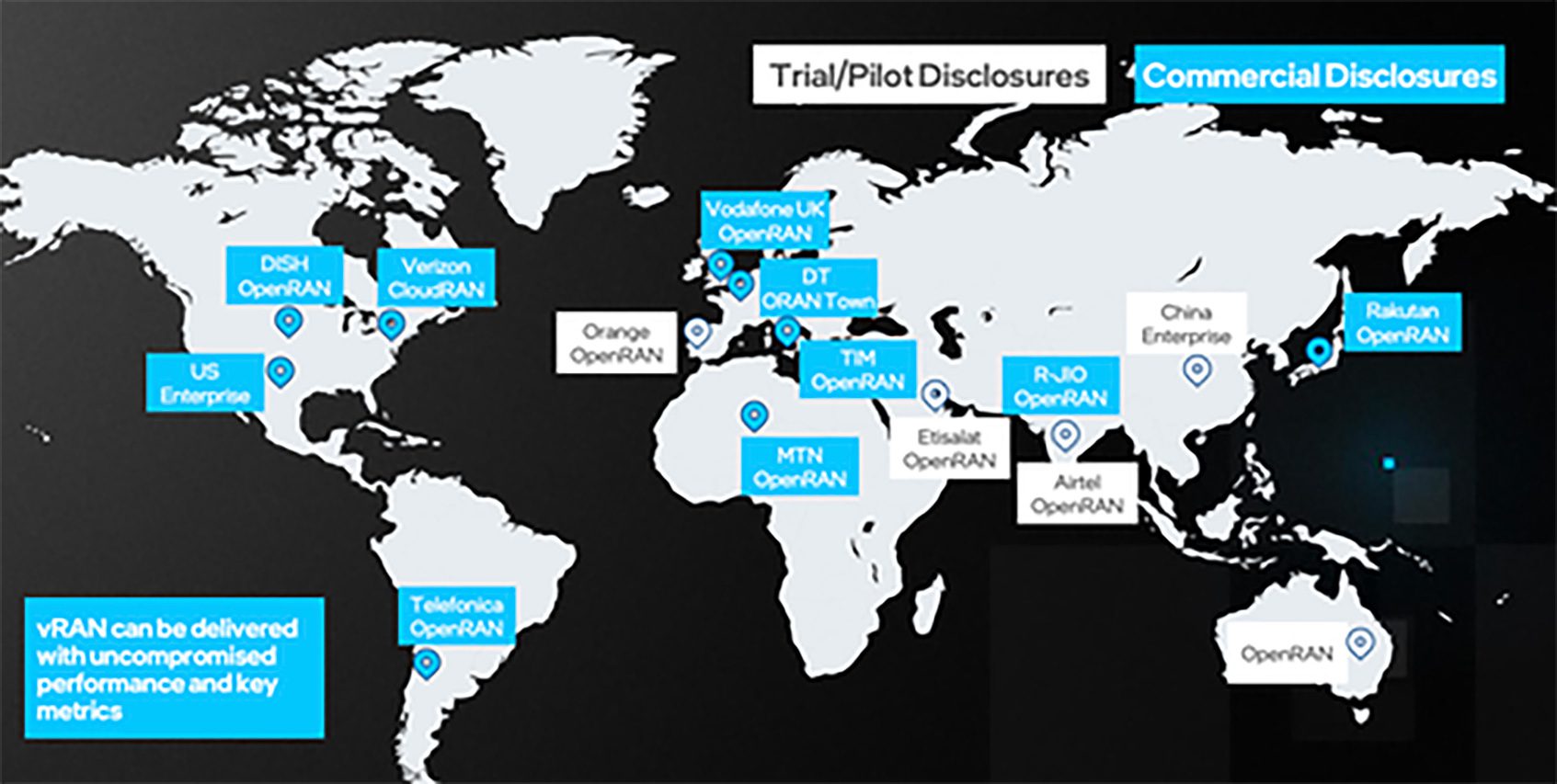

Source: Intel
A short video on the FlexRAN™ reference architecture is here.
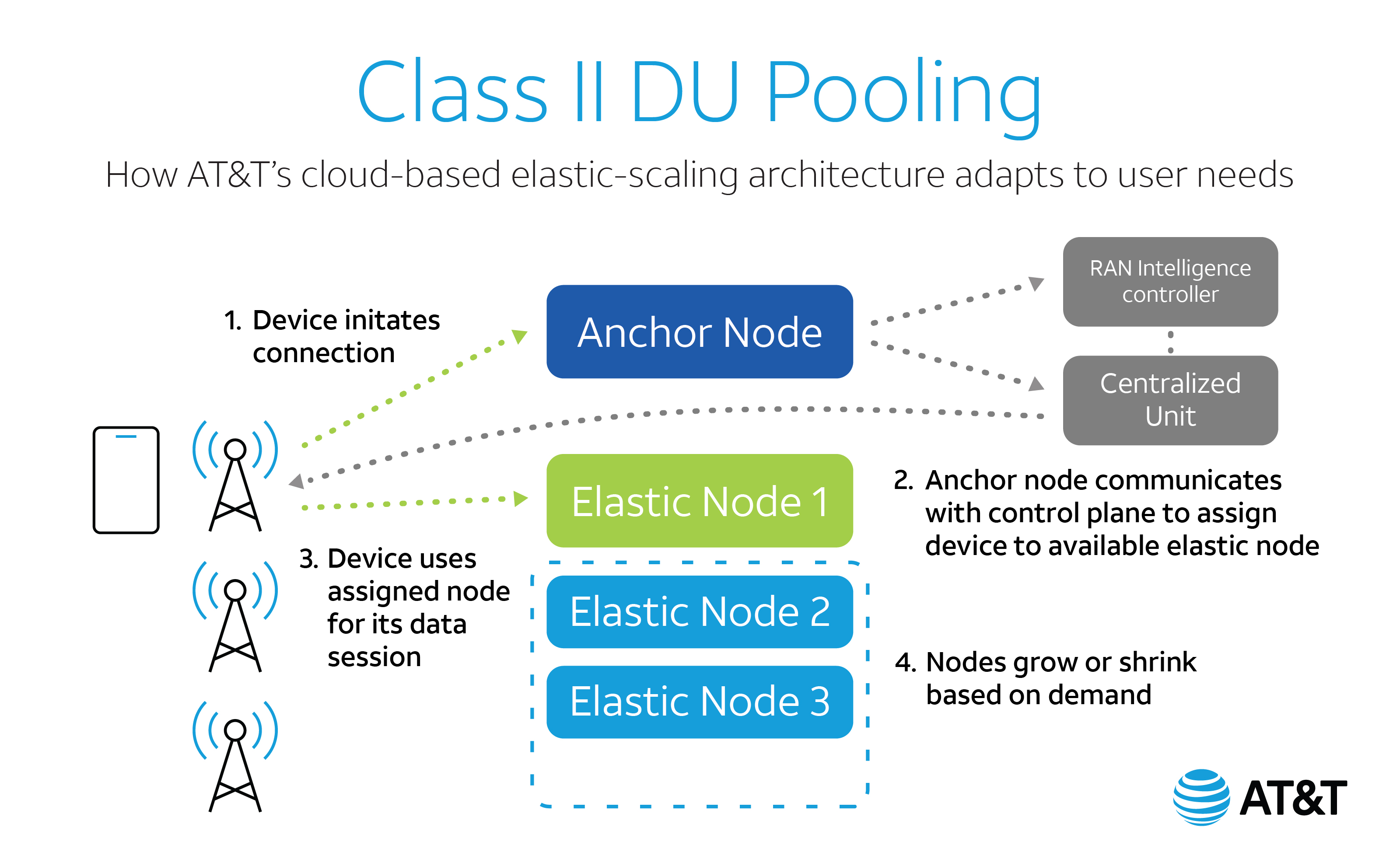
FlexRAN™ got a big boost this week from AT&T. In a February 24, 2022 blog post titled “Cloudifying 5G with an Elastic RAN,” Gordon Mansfield, AT&T VP Mobility Access & Architecture said that “AT&T and Intel had co-developed an industry-leading advanced RAN pooling technology freeing 5G radios from the limitations of dedicated base stations, while enabling more efficient, resilient, and green 5G networks. DU-pooling will eventually be usable by the entire 5G operator community to drive the telecom industry’s goals of green and efficient wireless networks forward.”
DU pooling technology was made possible by combining AT&T’s deep knowledge of Open RAN technologies as one of the co-founders of the O-RAN Alliance with Intel’s expertise in general purpose processors and software-based RAN through its FlexRAN™ software stack running on Intel 3rd generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors. The open standards for communications between radios and DUs that were published by O-RAN enabled its development, and the result is a technology demonstrator implemented on FlexRAN™ software.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Intel is now facing new Open RAN competition from several semiconductor companies.
Marvell has just unveiled a new accelerator card that will slot into a Dell compute server (which uses x86 processors). Based on a system called “inline” acceleration, it is designed to do baseband PHY layer processing and do it more efficiently than x86 processors. A Marvell representative claims it will boost open RAN performance and support a move “away from Intel.” Heavy Reading’s Simon Stanley (see below) was impressed. “This is a significant investment by Dell in open RAN and vRAN and a great boost for Marvell and the inline approach,” he said.
Qualcomm, which licenses RISC processors designed by UK-based ARM, has teamed up with Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) on the X100 5G RAN accelerator card. Like Marvel’s offering, it also uses inline acceleration and works – by “offloading server CPUs [central processing units] from compute-intensive 5G baseband processing.”
There is also EdgeQ which is sampling a “Base Station on a Chip” which is targeted at Open RAN and private 5G markets. Three years in the making, EdgeQ has been collaborating with market-leading wireless infrastructure customers to architect a highly optimized 5G baseband, networking, compute and AI inference system-on-a-chip. By coupling a highly integrated silicon with a production-ready 5G PHY software, EdgeQ uniquely enables a frictionless operating model where customers can deploy all key functionalities and critical algorithms of the radio access network such as beamforming, channel estimation, massive MIMO and interference cancellation out of the box.
For customers looking to engineer value-adds into their 5G RAN designs, the EdgeQ PHY layer is completely programmable and extensible. Customers can leverage an extendable nFAPI interface to add their custom extensions for 5G services to target the broad variety of 5G applications spanning Industry 4.0 to campus networks and fixed wireless to telco-grade macro cells. As an industry first, the EdgeQ 5G platform holistically addresses the pain point of deploying 5G PHY and MAC software layers, but with an open framework that enables a rich ecosystem of L2/L3 software partners.
The anticipated product launches will be welcomed by network operators backing Open RAN. Several of them have held off making investments in the technology, partly out of concern about energy efficiency and performance in busy urban areas. Scott Petty, Vodafone’s chief digital officer, has complained that Open RAN vendors will not look competitive equipped with only x86 processors. “Now they need to deliver, but it will require some dedicated silicon. It won’t be Intel chips,” he told Light Reading in late 2021.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Inline vs Lookaside Acceleration:
While Marvell and Qualcomm are promoting the “inline” acceleration concept, Intel is using an alternative form of acceleration called “lookaside,” which continues to rely heavily on the x86 processor, offloading some but not all PHY layer functions. This week, Intel announced its own product refresh based on Sapphire Rapids, the codename for its next-generation server processors.
Simon Stanley, an analyst at large for Heavy Reading (owned by Informa), said there are two key innovations. The first involves making signal-processing tweaks to the Sapphire Rapids core to speed up the performance of FlexRAN™, Intel’s baseband software stack. Speaking on a video call with reporters, Dan Rodriguez, the general manager of Intel’s network platforms group, claimed a two-fold capacity gain from the changes. “In the virtual RAN and open RAN world, the control, packet and signal processing are all done on Xeon and that is what FlexRAN enables,” he said.
The other innovation is the promise of integrated acceleration in future Sapphire Rapids processors. Sachin Katti, who works as chief technology officer for Intel’s network and edge group, said this would combine the benefits of inline acceleration with the flexibility of x86. That is preferable, he insisted, to any solution “that shoves an entire PHY layer into an inflexible hardware accelerator,” a clear knock at inline rivals such as Marvell and Qualcomm. Despite Katti’s reference to inline acceleration, Stanley does not think it is Intel’s focus. “None of this rules out an inline acceleration solution, but it does not seem to be part of the core approach,” he told Light Reading. “The key strategy is to add maximum value to Xeon Scalable processors and enable external acceleration where needed to achieve performance goals.”
Both inline and lookaside involve trade-offs. Inline’s backers have promised PHY layer software alternatives, but Intel has a major head start with FlexRAN™, which it began developing in 2010. That means lookaside may be a lot more straightforward. “The processor is in control of everything that goes on,” said Stanley during a previous conversation with Light Reading. “It is essentially the same software and makes life very easy.”
Larger network operators seemed more enthusiastic about inline during a Heavy Reading survey last year. By cutting out the processor, it would reduce latency, a measure of the delay that occurs when signals are sent over the network. That could also weaken Intel, reducing power needs and allowing companies to use less costly CPUs. “If you use inline, you probably need a less powerful processor and less expensive server platform, which is not necessarily something Intel wants to promote,” Stanley said last year.
References:
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/communications/virtualizing-radio-access-network.html
EdgeQ Samples World’s 1st Software-Defined 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip
SoC start-up EdgeQ comes out of stealth mode with 5G/AI silicon for 5G private networks/IIoT
System on a Chip (SoC) start-up EdgeQ (Cupertino, CA) announced its launch from stealth with $51 million in total funding, including $38.5 million in a Series A round. Backed by investors Threshold Ventures (formerly DFJ), Fusion Fund, Yahoo! co-founder Jerry Yang (AME Cloud Ventures) and an unannounced strategic customer, EdgeQ will address the 5G infrastructure market with products aimed at delivering 5G connectivity with AI computing.
The company counts experience in cellular modem development from Qualcomm, Intel and Broadcom on its team. It sees a limited number of players in the market, focused especially on smartphones, leaving room for new providers targeting edge devices and infrastructure.
EdgeQ said it will deliver a converged 5G and AI silicon platform that is open and software programmable for both devices and edge infrastructure. By introducing open programmability to the baseband, EdgeQ wants to provides a new software-driven development model for OEMs and operators, supporting existing cellular protocols such as 4G and 5G as well as the next generation of networks.
EdgeQ’s AI-5G SoC is aimed at emerging 5G private networks that are viewed as the backbone of industrial Internet of Things and other data-driven enterprise deployments. Along with manufacturing, the AI chip maker said Tuesday (Nov. 17) it is targeting the automotive, construction, energy and telecommunications sectors.
“We are rapidly evolving from a smartphone economy to a constellation of intelligent edge devices,” said Vinay Ravuri, CEO and founder of EdgeQ. “This will cause massive disruption to the current paradigm, where existing fixed-function approaches are inadequate to meet the scale, speed, and breadth of new end connections.”
“We provide an open platform converging 5G plus AI, which abstracts much of the complexities for our customers working on 5G deployment—from supporting multiple chipsets, different software stacks, board design, cost, power, and latencies in transferring data in between, not to mention, potential security hazards. Though we are not ready to disclose the hardware details, our 5G chip architecture uniquely lends itself to AI in a way without needing an extra AI accelerator hardware, saving both power and cost to the end customer.”
The combination of 5G connectivity, AI hardware and a “software-friendly” design is intended to enable an “open and programmable platform that is adaptable, configurable and economical for 5G-based applications,” added Ravuri, a former Qualcomm vice president for product management.
Ravuri said Qualcomm’s 5G SoC design (targeted at 5G endpoints) was closed while EdgeQ’s was open. “Their chip technology does not support 5G connectivity and AI computing, making it inadequate for enterprise-grade 5G infrastructure, which needs robust computing capabilities in addition to 5G,” he said. “We can bring the best of breed here—the cellular, but also offer to the market what they’re really looking for, which is an open ecosystem where they are able to innovate and add/develop features on this chipset that they can’t do otherwise. That is what we see as a big departure from the existing Qualcomm offerings.”
The software-defined SoC is aimed at replacing existing wireless and legacy networks with edge components that can be used to divide and partition 5G spectrum for emerging private wireless networks. The networking equivalent of private clouds, those high-bandwidth connections are being promoted as “industrial-strength” platforms that could be used to link sensors, massive amounts of raw data and AI-enabled manufacturing platforms in real time.
Yang and other early investors assert that EdgeQ’s programmable silicon moves beyond custom AI chip designs with limited use cases. “This technology will disrupt the market for silicon and democratize access to 5G for the first time,” said Yang.
Industry analysts note that AI and 5G technologies are advancing in tandem as new automation and edge use cases emerge. Among the operational efficiencies provided by AI-powered 5G networks is “predictive remediation,” in which potential outages can be identified before networks crash. “We are getting there with the help of AI,” said Will Townsend, an analyst with Moor Insights & Strategy.
Other analysts have predicted emerging AI systems on a chip. The adoption of 5G “may someday lead to convergence of the radio spectra for these disparate radio channels and convergence of network interfaces down to single chips that are agile at maintaining seamless connections across multiple radio access technologies,” James Kobielus, research director at Futurum Research, wrote last year.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/5g-and-ai-soc-vendor-edgeq-out-starter-blocks-51m-funding


