MTN Consulting
MTN Consulting’s Network Operator Forecast Through 2027: “Telecom is essentially a zero-growth industry”
MTN Consulting’s Mid Year Update:
There are three different types of network operators: telecom operators (telcos), webscale network operators (webscalers), and carrier-neutral operators (CNNOs). In 2022, these three groups accounted for $4.1 trillion (T) in revenues, $559 billion (B) in capex, and 8.87 million employees. The report provides 2011-22 actuals and projections through 2027, and includes projections from past forecasts for reference.
Review of the 3 Market Segments:
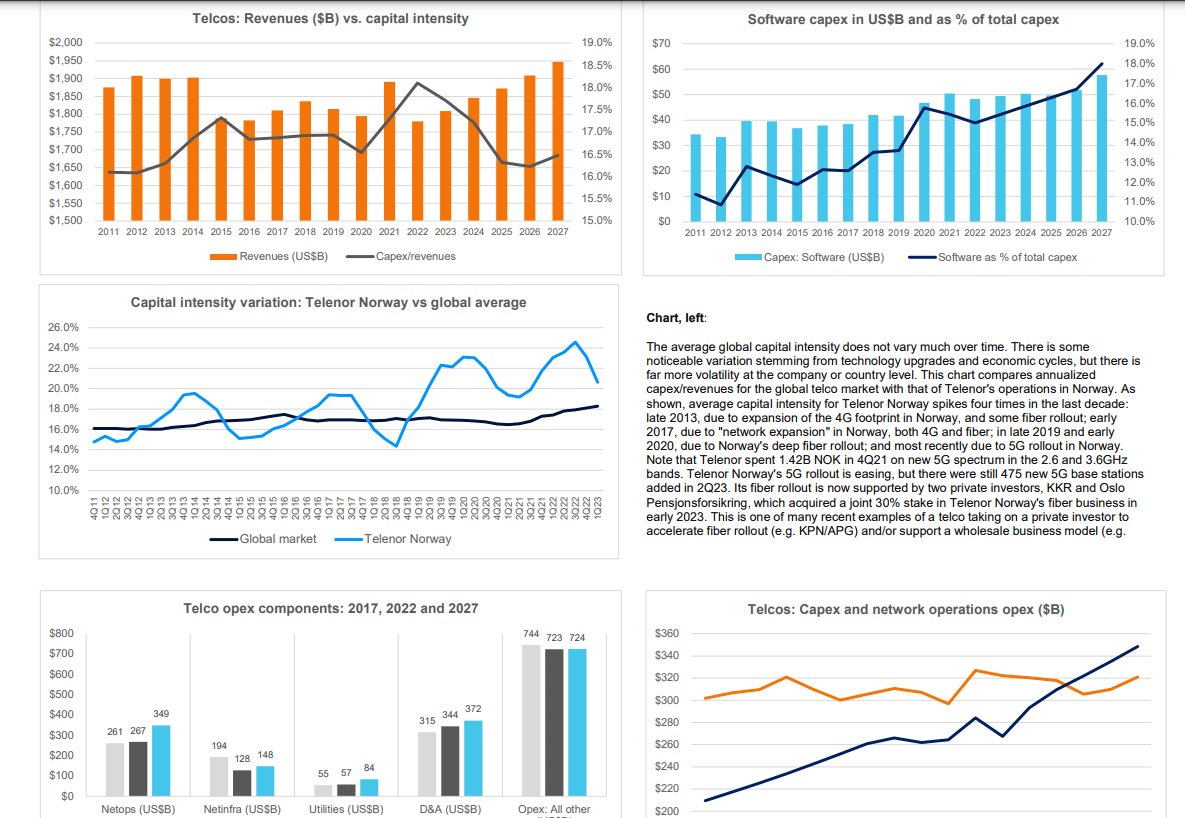
1. Telco: Telecom is essentially a zero-growth industry. Specific countries and companies do grow from time to time, in part from market share shifts, the different timing of growth cycles, or M&A. But global telco revenues have hovered in a narrow range ($1.7-$1.9 trillion) since 2011, and this will likely remain true through 2027. In 2022, revenues were $1.78T, and will grow an average annual rate of 1.8% to reach $1.95T by 2027.
Capex continues to vary with technology upgrade cycles (e.g. 5G) and government actions (e.g. newly issued spectrum, or rural fiber subsidies). In 2022, capex totaled $322B, or 18.1% of revenues; that’s an all-time high capital intensity, for coverage timeframe (2011-present). Capex will decline slightly through 2025, though, and then rise modestly again to reach $321B in 2027, which would be a 16.5% capital intensity. US capex surged in 2022, but will drop dramatically in 2023; we already expected this, though, so the current forecast is not significantly different. Software capex is growing more slowly than expected, and now likely to remain under 20% of total capex for the forecast period.
Headcount in telecom is declining faster than expected, and now likely to fall below 4.2 million in 2027, from just under 4.6 million in 2022. Labor costs per head will revert to a growth trajectory in 2023, as telcos develop a more IT/software-centric workforce.
2. Webscalers: growth from webscale has lifted the overall network operator market over the last decade. Webscalers surged during COVID, by all measures – revenues, capex, employment. Demand for data center chips and related gear also surged. Now, parts of the sector are cutting back slightly.
In 2022, revenues were $2.23 trillion, up just 4% YoY, far less than the average growth of 12% per year from 2011-22. We expect revenues to grow at a ~6% CAGR through 2027. Webscale capex was $203B in 2022, a healthy increase from 2021; due in part to generative AI interest, capex will grow again in 2023 and 2024, dip for a couple years of capacity absorption, and then end 2027 at around $231B. A larger portion of this capex will be for Network/IT/software investments: around 46%, from 44% in 2022. R&D spending by webscalers will remain high but fall from the record-breaking level of 2022 (12.0% of revenues), to about 10% in 2027. As topline growth gets harder for webscalers, they will become more cost conscious and short-term oriented.
3. CNNOs: the carrier-neutral sector remains tiny, with just $95B in 2022 revenues, but will grow to about $132B by 2027. Webscalers and telcos alike will both rely more on CNNOs over time for expansion of their data center, tower and fiber footprints.
Telcos will continue to spin out portions of their infrastructure to third-parties – both traditional CNNOs, and joint ventures like Gigapower, the AT&T-Blackrock partnership. Total CNNO capex for 2022 was $34B, and will grow to about $45B by 2027; a large chunk of the CNNO sector’s expansion will be inorganic, though, via acquisition of existing assets from other sectors. By 2027, the CNNO sector will have under its management approximately 3.7 million cell towers (2022: 3.3M), 1,607 data centers (2022: 1,224), and 1.1M route miles of fiber (2022: 960K).
Source: MTN Consulting
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Market drivers, constraints and risk factors:
This forecast represents only a modest revision from the edition published in December 2022. Most of the realities facing the operator market today were anticipated by our last forecast. For instance, we already expected that service revenues were not growing for telcos, and that 5G device sales distorted the market; an MTN Consulting report published in 2Q23 confirmed this fact, and supports a more cautious outlook for telco spending. We also thought that open RAN was overhyped, and was not likely to change the capex calculus for most established mobile operators. The 2023 dip in US telco capex was baked into our old forecast. The one big sector-specific change from the last forecast to this one is, the recent spike in interest in generative AI. This is a plus for the webscale market’s capex outlook, even if new revenue models are unclear and government regulations will slow adoption.
What about the macroeconomic climate? Wars, economic growth, inflation, interest rates, climate change, etc. Russia’s war on Ukraine remains ongoing, but hasn’t expanded to new countries. China has not invaded Taiwan as of yet, although this is a serious risk over the 5-year forecast horizon. Global economic growth is weaker than historic averages – about 3% this year and next, per the IMF – but inflation is easing, and the IMF’s GDP growth outlook improved slightly from April to July 2023. Interest rates continue to rise; the US federal funds rate has risen from 3.83% to 5.08% between 12/22 and 7/23, and further increases seem likely. Rising interest rates were already assumed to modestly depress 2023-24 capex, though.
Climate change is the one macro area that is quite a bit different than 8 months ago. The news gets worse each week. Government action continues to be gradual and consensus is hard to achieve. Increasingly the pressure will be on private companies to make voluntary, verifiable changes in how they operate. This doesn’t impact the forecast directly, but will impact how operators spend their tech budgets, as we have discussed in separate reports. Energy, sustainability and climate change will continue to be key themes in MTN Consulting research.
References:
MTN Consulting: Top Telco Network Infrastructure (equipment) vendors + revenue growth changes favor cloud service providers
MTN Consulting reports [1.] that the top three Telco Network Infrastructure (NI) equipment vendors continue to be Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia. They account for 37.4% of the total market in annualized 1Q23, or 34.8% in 1Q23 alone. While the trio has captured >40% share of the market for most of 2016-22, Huawei’s share has fallen recently, and all three giants have been pressured by vendors in the cloud and IT services space (e.g. Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet, Dell, VMWare…).
Note 1. This MTN Consulting study tracks 134 Telco NI vendors, providing revenue and market share estimates for the 1Q13-1Q23 period. Of these 134 vendors, 110 are actively selling to telcos; most others have been acquired by other companies in the database. For instance, ADVA is now part of Adtran, but both companies remain in the database because of historic sales.
Focusing on the top three, Huawei has dropped in the last three periods (due to global sanctions), but remains dominant due to China.
Ericsson’s share decline was a function of lower RAN spending among its largest customers as the 5G rollout pace ebbs. The Swedish vendor hopes to offset this decline soon with new revenues from its blockbuster acquisition of network API platform vendor, Vonage. It expects the first revenues from the acquisition later this year and a ramp up further in the next two years.
Nokia, including (Alcatel-Lucent) ALU for pre-acquisition years, has also dipped as 5G RAN rollouts slowed. But it gained market share slightly in 1Q23 on account of 45% growth in its optical networks business along with some benefits from catch-up sales related to the supply chain challenges it witnessed in 2022.
China Comservice and ZTE have been trading the 4 and 5 spots off and on since early 2019. Notably, though, China Comservice is majority owned by Chinese telcos, and is not truly independent. Intel is in the 6th position due to data center, virtualization, edge compute and other telco projects, some done directly and some on an OEM basis.
CommScope remained at seventh position while NEC managed to surpass Cisco in the latest annualized 1Q23 period, as Cisco (9th position) witnessed a stark drop in its Telco NI revenues in 1Q23. Cisco’s decline is worrying, as its largest market (the U.S.) has a growing focus on 5G core, which Cisco has flagged in the past as key to the company growing telco revenues. Amdocs is ranked 10th due to its strength in network software.
Biggest Telco NI revenue changes on a YoY basis:
Three out of the top five vendors, in terms of YoY revenue growth, are the same for both single quarter and annualized 1Q23: Alphabet, Microsoft, and Lenovo. Two of these are cloud vendors (Alphabet and Microsoft) who are steadily improving their penetration of the telco vertical market with a range of solutions – digital transformation, service design, 5G core, workload offshift, etc. Lenovo is gaining traction with its disaggregated, virtual radio access network (vRAN), and multi-access edge computing (MEC) solutions. Clearfield is a small fiber company focused on the booming US market.
Other companies to show improvement in both periods include Tejas Networks which bagged a mega deal for a BSNL-MTNL 4G network; Rakuten Group (Symphony) benefiting from key deployments of its cloud-based Open RAN solutions; Harmonic which has benefited from strong cable access spending and a growing customer list; YOFC (a Chinese fiber company), and two large US-based engineering services-focused companies (DyCom and MasTec) benefiting from a fiber boom.
Declines in the 1Q23 annualized period include Cisco which continues to be worrisome on account of lower customer spending, though it noted improvement in supply chain constraints in the latest quarter. Extreme Networks, Casa, and Airspan all dipped, but noted that the supply chain challenges of previous quarters are improving. Cisco, the largest among the annualized decliners, remains optimistic about prospects as telcos move to 5G SA cores.
Supply chain issues improving:
For the past two years, vendors in the Telco NI market have been plagued with supply chain constraints. The situation is now easing though, if a review of vendor earnings from 1Q23 is anything to go by. Most significant vendors confirm the assessment of three months ago: shortages in specific component areas continue to be an issue but are improving with time, with normalcy likely in 2H23.
Nokia notes that “Going forward, growth rates are expected to slow in the coming quarters as Q1 benefited from some catch-up, as supply chains normalize”. Ericsson echoed this, saying that “…the big effect really comes from the ongoing inventory adjustments, and that comes because they build up large inventories when supply chain was tight and those inventory levels are now normalizing. We expect these adjustments to be completed during Q2, but some could slip into Q3 clearly”.
Juniper has a slightly more cautious view – “While supply has improved for the majority of our products, we continue to experience supply constraints for certain components, and supply chain costs remain elevated”.
Casa, Calix, and Ciena are also witnessing good improvements in supply chain and are expecting further improvements over the course of 2023. F5 Networks is benefiting from its strategy of redesigning the “hardest-to-get components” and “opening up new supply” sources.
Spending outlook:
Most large vendors appear to be cautiously optimistic about the spending outlook in Telco NI. While supply chain issues are expected to clear up by 2Q or 3Q 2023, MTN Consulting expects the market will start to flatten in the next few quarters. Per our latest official forecast, we expect telco capex – the main driver of Telco NI market – to reach $330B in 2023, and a small decline to $325B in 2024. However, it’s likely that both figures may be $5B or more too high. Ericsson, a key telco vendor, has signaled a cautious telco capex spend outlook in its latest earnings call: “In the second quarter, we expect operators to remain cautious with CapEx similar to Q1 and continue with the inventory adjustment that we have described”.
Lower expectations have been apparent on many 4Q22 earnings calls. DT, for instance, expects US capex will see a “strong decrease” in 2023, and thereafter stability. Verizon’s capex is set to fall nearly 20% YoY in 2023. Charter Communications cut its capex outlook for 2023 by about $500M, hitting both the low & high range. Orange expects a “strong decrease” (same wording) in total “ecapex” this year as its FTTH deployment peak has passed and it aims to increase its dividend. Canada’s BCE says that 2022 was the peak year in its accelerated capex program, and capex will begin to fall this year until capital intensity is back down to pre-COVID levels. Vodafone expects group capex in its current fiscal year to be flat to slightly down, as it pursues a “disciplined approach to capital allocation.” Telefonica says its declining capital intensity is proof that the investment peak is behind it. The MTN Group says capital intensity will decline from 18% to 15% over the next few years.
There are several factors to help explain lower expectations: some are company-specific, e.g. BCE is naturally reaching a latter phase in its buildout. There are also general factors, such as: rising interest rates; higher operating costs due to inflation, especially in energy; 5G’s failure to lift service revenues, leaving telcos highly dependent on volatile device revenues for any topline growth; and, cloud providers’ continually more aggressive pitches of new solutions to telcos. Cloud-based offerings can shift some capex to opex.
Amid all the cautious optimism, India as a market has emerged as a bright spot for the vendors. In 1Q23, Ericsson saw strong growth for its Networks business in India where it continues to rapidly roll out 5G. “It will make India a leading 5G nation and the leading nation for digitalization. And what we see is that the subscribers on 5G are using even more data than on 4G…” said Ericsson in its earnings call.
Ciena attributed its 60% YoY revenue growth in the Asia Pacific region to India, “which was up 88% year-over-year in Q2 to about $70 million, reflecting consistent strong demand from service providers in that market. India is going through a big cycle of 5G rollout and extension. And I think that’s going to happen over the next 1 to 3 years”.
Nokia also witnessed double-digit growth in both its Network Infrastructure and Mobile Networks divisions, reflecting the rapid 5G deployments in India: “…Q1 largely played out as we expected, with 5G deployments in India heavily influencing our Q1 top line.”
Telco Revenues Continue to Decline:
In 4Q22, global telco revenues plunged the most in more than a decade to post $429.6B, or -9.3% YoY – the fifth consecutive slump in a row. This impacted annual revenues and its growth rate for the year 2022 – they were $1,779.9B, down 5.9% YoY over the previous year. The sluggish top-line turned telcos cautious around spending on capex, the main driver for the Telco NI market, which declined for the second straight quarter to post $87.9B in 4Q22, down 5.1% YoY. This decline also knocked down annualized capex to $322.1B in 4Q22, from the peak of $330.0B in 2Q22.
On the brighter side, capex has held out better than revenues, pushing annualized capital intensity to a new all-time high of 18.1% in 4Q22. This was driven by a few countries who are in the midst of deploying 5G networks, notably India; while many more continue to scale up 5G to reach mass market coverage, and deploy fiber to support fixed broadband and to connect all the new radio infra (including small cells) needed for 5G.
Cloud vendors are also making critical inroads into the telco sector, aided by a growing number of stand-alone 5G core networks.
References:
MTN Consulting on Telco Network Infrastructure: Cisco, Samsung, and ZTE benefit (but only slightly)
MTN Consulting: Network Infrastructure market grew 5.1% YoY; Telco revenues surge 12.2% YoY
MTN Consulting: Satellite network operators to focus on Direct-to-device (D2D), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud-based services
Satellite network operators are being forced to expand their addressable markets in the near term, due to several factors: rising competition, with the emergence of players such as SpaceX along with several upstarts including AST SpaceMobile and Lynk. A difficult funding climate resulting from a grim economic outlook and rising interest rates is a challenge. There are also market concentration risks arising from the current focus on satellite broadband internet.
To address these challenges, satellite network operators are raising stakes in new pursuits and developing new offerings. MTN Consulting expects three new potential addressable markets to provide transformational opportunities for satellite operators in the next 2-4 years. These include Direct-to-device (D2D), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud-based services.
Looking at these market opportunities, a thought may arise whether satellite operators are trying to disrupt the traditional telecom market. But the reality is that telcos will continue to be the primary service provider for wireless access. Telcos are also going to benefit from partnerships with satellite operators as they will aid in providing an enhanced experience for telco customers, reinforced by ubiquitous coverage. For satellite operators though, navigating the regulatory hurdles and ensuring constant capital flow are key concerns; several players from the current herd will vanish in the next 3-5 years.
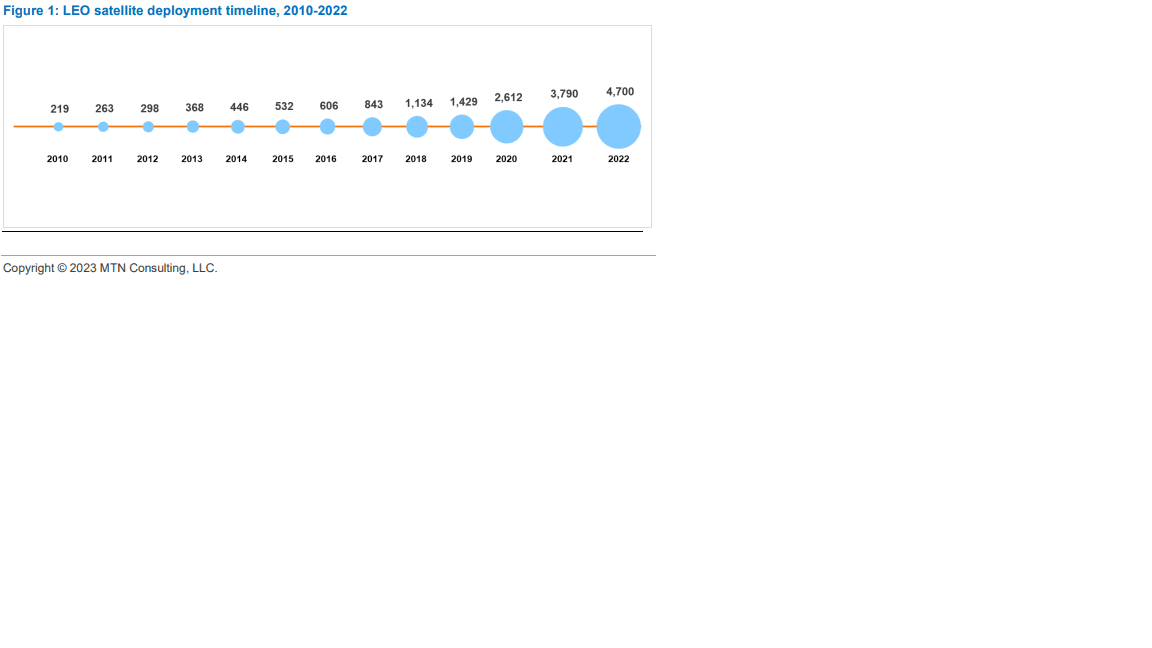
The battle for space based Internet gained momentum in the year 2022 as several satellite operators, notwithstanding their size and years of operations, shifted gears with the launch of commercial broadband internet through low earth orbit (LEO) satellites. The space rush, aided by the advancement in satellite development and large-scale manufacturing, witnessed the sudden surge in large fleets of LEO satellites being deployed in recent years, as shown in Figure 1. As of May 2022, about 4,700 active LEO satellites are girdling the planet; that’s 16x the number of active LEO satellites deployed a decade ago.
Separately, MTN found that a number of large telcos have high debt, low margins, and/or weak top line growth, and may have to curtail spending in 2023-2024 in order to cope with this reality. In particular:
- Total telco debt in 4Q22 was $1.14 trillion, 17% due in next year
- Software capex as a % of revenues was 1.9% in 2022, up a bit from 1.8% in 2021.
- Spending on acquisitions amounted to 0.5% of revenues in 2022, the lowest figure since 2012.
- At the industry level, the ratio of net debt to EBITDA in 2022 was 1.9, a bit up from 2021 but down from 2020.
- A number of large telcos face short-term debt levels over 30% of total debt
- Average margins for the industry in 2022 disappointed: free cash flow margin for the telco industry in 2022 was 11.4%, down from 12.6% in 2021; EBITDA margin was 33.7% (2021: 34.0%), and EBIT margin was 14.4% (2021: 14.9%).
References:
Satellite players bet on direct-to-device (D2D), IoT, and cloud for next big liftoff
MTN Consulting: Network operator capex forecast at $520B in 2025
Executive Summary:
Telco, webscale and carrier-neutral capex will total $520 billion by 2025 according to a report from MTN Consulting.. That’s compared with $420 billion in 2019.
- Telecom operators (telco) will account for 53% of industry Capex by 2025 vs 9% in 2019;
- Webscale operators will grow from 25% to 39%;
- Carrier-neutral [1.] providers will add 8% of total Capex in 2025 from 6% in 2019.
Note 1. A Carrier-neutral data center is a data center (or carrier hotel) which allows interconnection between multiple telecommunication carriers and/or colocation providers. It is not owned and operated by a single ISP, but instead offers a wide variety of connection options to its colocation customers.
Adequate power density, efficient use of server space, physical and digital security, and cooling system are some of the key attributes organizations look for in a colocation center. Some facilities distinguish themselves from others by offering additional benefits like smart monitoring, scalability, and additional on-site security.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The number of telco employees will decrease from 5.1 million in 2019 to 4.5 million in 2025 as telcos deploy automation more widely and spin off parts of their network to the carrier-neutral sector.
By 2025, the webscale sector will dominate with revenues of approximately $2.51 trillion, followed by $1.88 trillion for the telco sector and $108 billion for carrier-neutral operators (CNNOs).
KEY FINDINGS from the report:
Revenue growth for telco, webscale and carrier-neutral sector will average 1, 10, and 7% through 2025
Telecom network operator (TNO, or telco) revenues are on track for a significant decline in 2020, with the industry hit by COVID-19 even as webscale operators (WNOs) experienced yet another growth surge as much of the world was forced to work and study from home. For 2020, telco, webscale, and carrier-neutral revenues are likely to reach $1.75 trillion (T), $1.63T, and $71 billion (B), amounting to YoY growth of -3.7%, +12.2%, and 5.0%, respectively. Telcos will recover and webscale will slow down, but this range of growth rates will persist for several years. By 2025, the webscale sector will dominate with revenues of approximately $2.51 trillion, followed by $1.88 trillion for the telco sector and $108 billion for carrier-neutral operators (CNNOs).
Network operator capex will grow to $520B by 2025
In 2019, telco, webscale and carrier-neutral capex totaled $420 billion, a total which is set to grow to $520 billion by 2025. The composition will change starkly though: telcos will account for 53% of industry capex by 2025, from 9% in 2019; webscale operators will grow from 25% to 39% in the same timeframe; and, carrier-neutral providers will add 8% of total capex in 2025 from their 2019 level of 6%.
By 2025, the webscale sector will employ more than the telecom industry
As telcos deploy automation more widely and cast off parts of their network to the carrier-neutral sector, their employee base should decline from 5.1 million in 2019 to 4.5 million in 2025. The cost of the average telco employee will rise significantly in the same timeframe, as they will require many of the same software and IT skills currently prevalent in the webscale workforce. For their part, webscale operators have already grown from 1.3 million staff in 2011 to 2.8 million in 2019, but continued rapid growth in the sector (especially its ecommerce arms) will spur further growth in employment to reach roughly 4.8 million by 2025. The carrier-neutral sector’s headcount will grow far more modestly, rising from 90 million in 2019 to about 119 million in 2025. Managing physical assets like towers tends to involve a far lighter human touch than managing network equipment and software.

Example of a Carrier Neutral Colo Data Center
RECOMMENDATIONS:
Telcos: embrace collaboration with the webscale sector
Telcos remain constrained at the top line and will remain in the “running to stand still” mode that has characterized their last decade. They will continue to shift towards more software-centric operations and automation of networks and customer touch points. What will become far more important is for telcos to actively collaborate with webscale operators and the carrier-neutral sector in order to operate profitable businesses. The webscale sector is now targeting the telecom sector actively as a vertical market. Successful telcos will embrace the new webscale offerings to lower their network costs, digitally transform their internal operations, and develop new services more rapidly. Using the carrier-neutral sector to minimize the money and time spent on building and operating physical assets not viewed as strategic will be another key to success through 2025.
Vendors: to survive you must improve your partnership and integration capabilities
Collaboration across the telco/webscale/carrier-neutral segments has implications for how vendors serve their customers. Some of the biggest telcos will source much of their physical infrastructure from carrier-neutral providers and lean heavily on webscale partners to manage their clouds and support new enterprise and 5G services. Yet telcos spend next to nothing on R&D, especially when compared to the 10% or more of revenues spent on R&D by their vendors and the webscale sector. Vendors who develop customized offerings for telcos in partnership with either their internal cloud divisions (e.g. Oracle, HPE, IBM) or AWS/GCP/Azure/Alibaba will have a leg up. This is not just good for growing telco business, but also for helping webscale operators pursue 5G-based opportunities. One of the earliest examples of a traditional telco vendor aligning with a cloud player for the telco market is NEC’s 2019 development of a mobile core solution for the cloud that can be operated on the AWS network; there will be many more such partnerships going forward.
All sectors: M&A is often not the answer, despite what the bankers urge
M&A will be an important part of the network infrastructure sector’s evolution over the next 5 years. However, the difficulty of successfully executing and integrating a large transaction is almost always underappreciated. There is incredible pressure from bankers to choose M&A, and the best ones are persuasive in arguing that M&A is the best way to improve your competitiveness, enter a new market, or lower your cost base. Many chief executives love to make the big announcements and take credit for bringing the parties together. But making the deal actually work in practice falls to staff way down the chain of command, and to customers’ willingness to cope with the inevitable hiccups and delays brought about by the transaction. And the bankers are long gone by then, busy spending their bonuses and working on their next deal pitch. Be extremely skeptical about M&A. Few big tech companies have a history of doing it well.
Webscale: stop abusing privacy rights and trampling on rules and norms of fair competition
The big tech companies that make up the webscale sector tracked by MTN Consulting have been rightly abused in the press recently for their disregard for consumer privacy rights, and overly aggressive, anti-competitive practices. After years of avoiding increased regulatory oversight through aggressive lobbying and careful brand management, the chickens are coming home to roost in 2021. Public concerns about abuses of privacy, facilitation of fake news, and monopolistic or (at the least) oligopolistic behavior will make it nearly impossible for these companies to stem the increased oversight likely to come soon from policymakers.
Australia’s pending law, the “News Media and Digital Platforms Bargaining Code,” could foreshadow things to come for the webscale sector, as do recent antitrust lawsuits against Facebook and Alphabet. Given that webscale companies are supposed to be fast moving and innovative, they should get out ahead of these problems. They need to implement wholesale, transparent changes to how they treat consumer privacy and commit to (and actually follow) a code of conduct that is conducive to innovation and competition. The billionaires leading the companies may even consider encouraging fairer tax codes so that some of their excessive wealth can be spread across the countries that actually fostered their growth.
ABOUT THIS REPORT:
This report presents MTN Consulting’s first annual forecast of network operator capex. The scope includes telecommunications, webscale and carrier-neutral network operators. The forecast presents revenue, capex and employee figures for each market, both historical and projected, and discusses the likely evolution of the three sectors through 2025. In the discussion of the individual sectors, some additional data series are projected and analyzed; for example, network operations opex in the telco sector. The forecast report presents a baseline, most likely case of industry growth, taking into account the significant upheaval in communication markets experienced during 2020. Based on our analysis, we project that total network operator capex will grow from $420 billion in 2020 to $520 billion in 2025, driven by substantial gains in the webscale and (much less so) carrier-neutral segments. The primary audience for the report is technology vendors, with telcos and webscale/cloud operators a secondary audience.
References:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
January 8, 2021 Update:
Analysys Mason: Cloud technology will pervade the 5G mobile network, from the core to the RAN and edge
“Communications Service Providers (CSPs) spending on multi-cloud network infrastructure software, hardware and professional services will grow from USD4.3 billion in 2019 to USD32 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 40%.”
5G and edge computing are spurring CSPs to build multi-cloud, cloud-native mobile network infrastructure
Many CSPs acknowledge the need to use cloud-native technology to transform their networks into multi-cloud platforms in order to maximise the benefits of rolling out 5G. Traditional network function virtualisation (NFV) has only partly enabled the software-isation and disaggregation of the network, and as such, limited progress has been made on cloudifying the network to date. Indeed, Analysys Mason estimates that network virtualisation reached only 6% of its total addressable market for mobile networks in 2019.
The telecoms industry is now entering a new phase of network cloudification because 5G calls for ‘true’ clouds that are defined by cloud-native technologies. This will require radical changes to the way in which networks are designed, deployed and operated, and we expect that investments will shift to support this new paradigm. The digital infrastructure used for 5G will be increasingly built as horizontal, open network platforms comprising multiple cloud domains such as mobile core cloud, vRAN cloud and network and enterprise edge clouds. As a result, we have split the spending on network cloud into spending on multiple cloud domains (Figure 1) for the first time in our new network cloud infrastructure report. We forecast that CSP spending on multi-cloud network infrastructure software, hardware and professional services will grow from USD4.3 billion in 2019 to USD32 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 40%.
https://www.analysysmason.com/research/content/comments/network-cloud-forecast-comment-rma16/