Month: November 2020
Ericsson Mobility Report: 5G forecast increased due to China uptake (?)
According to the latest Ericsson Mobility Report, there are signs of an acceleration in 5G deployments. Ericsson estimates that by the end of this year, more than 1 billion people – or 15 percent of the world’s population – will live in an area with 5G coverage. This is expected to reach 60 percent in 2026, when there will be an estimated 3.5 billion 5G users in the world.
Ericsson raised its year-end 2020 estimate for global 5G subscriptions to 220 million, due mainly to faster take-up in China [1.]. More than one in ten Chinese mobile subscribers are expected to use 5G by year-end, and they will account for almost 80 percent of all 5G users in the world (175 mln). The growth in China is driven by a national strategic focus, intense competition between service providers, as well as increasingly affordable 5G smartphones from several vendors, Ericsson said.
Note 1. We have argued for quite some time that China government numbers on 5G (and everything else) can’t be trusted.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
North America is the second-largest market for 5G, says Ericsson, with an estimated 4 percent of subscribers using 5G by the end of 2020. Commercialization there is now moving at a rapid pace and by 2026, Ericsson forecasts that 80 percent of North American mobile subscriptions will be 5G, the highest level of any region in the world.
Europe is seeing a slower roll-out of 5G, due in part to delays in spectrum auctions earlier this year. Ericsson predicts the region will end 2020 with about 1 percent of mobile users on 5G subscriptions.
The report further looks at some of the emerging 5G applications, such as cloud gaming and mission critical IoT, which covers real time-sensitive services (e.g. ultra low latency). However, that won’t happen unless URLCC is completed specified/performance texted in 3GPP Release 16 and then implemented.
The Ericsson report has this to say about cellular networks and public safety:
“2020 has also proven to be an exceptional year for cellular networks used for public safety applications. Together with AT&T, we have looked into how FirstNet – the nationwide network deployed to serve first responders in the US – stood up to the test of this year’s emergencies related to the pandemic, one of the most active hurricane seasons on record, and severe wildfires. As society rapidly changes, it is clear that cellular networks are a critical infrastructure that will continue to support many aspects of our everyday life.”
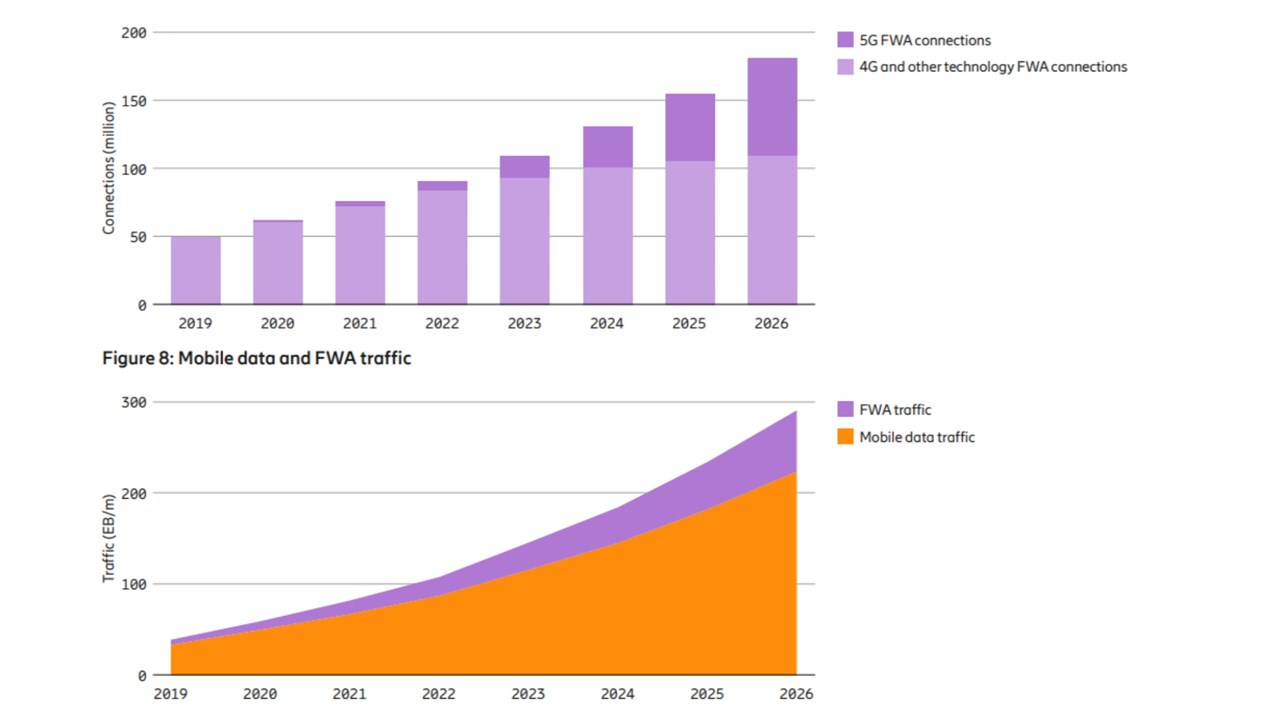
Ericsson also found that almost two-thirds of 5G operators are offering some form of fixed-wireless access (FWA) service. The company forecasts FWA connections to grow more than threefold and reach more than 180 million by the end of 2026, accounting for about a quarter of total mobile network data traffic.
Editor’s Note:
A very interesting point is that 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), which is not even an IMT 2020 Use Case, is being deployed and gaining market traction (along with 4G FWA). The report states that FWA connections will more than threefold by the end of 2026, reaching over 180 million. That service is forecast to account for ~25 percent of total mobile network data traffic globally.
Check out the following two FWA related graphs from the report:
Some of the topics covered in the report include:
- Time-critical communications with 5G
- Mobile cloud gaming – an evolving business opportunity
- Service provider strategies ( three alternative paths to success)
- But the big numbers are still important, So what’s happening with global mobile network growth, 5G in particular?
- 5G’s population coverage is projected to hit 15 per cent this year – over 1 billion people (that’s covered, not all connected)
- 5G’s subscription total will be 3.5 billion in 2026 with 220 million 5G subs expected by the end of this year
- There are around 7.9 billion mobile subscriptions now but this will increase to 8.8 billion by the end of 2026, and 91 percent of those will be for mobile broadband.
- Smartphones account for about 75 per cent of all mobile phone subscriptions
- Cellular IoT has not followed through on all those early, but wildly optimistic projections for cellular IoT. In 2026, NB-IoT and Cat-M technologies are expected to make up just 45 percent of all cellular IoT connections.
- North East Asia leads in cellular IoT connections (China, South Korea and at the end of 2020 is expected to account for 64 per cent of all cellular IoT connections, a figure set to increase to 69 percent by 2026.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/mobility-report/reports/november-2020
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/5g/ericsson-mobility-report-5g-is-here-and-happening-40337/
KPN collaborating on quantum network for Nederlands metro areas
Netherlands telco KPN is partnering QuTech, SURF and OPNT on a project to develop a first-of-its-kind quantum network in the Randstad metropolitan area (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague and Utrecht). The Fast Mode reports that the project will focus on connecting different quantum processors, a significant distance apart, to create ‘the first fully functional quantum network using high speed fibre connections’. A quantum network is a radically new internet technology, with the potential for creating pioneering applications. Such a network connects quantum processors to each other via optical channels, enabling the exchange of quantum bits (qubits) – which have a number of features very different from the bits in commonplace networks. For example, quantum communication is potentially immune to eavesdropping practices. Quantum networks are expected to evolve over time towards a global quantum network allowing secure communication, position verification, clock synchronisation, computation using external quantum computers, and more.
- QuTech is a leading R&D institute for advanced research in the field of quantum computing and quantum internet.
- SURF is the collaborative organisation for ICT in Dutch education and research.
- OPNT is a Dutch enterprise which has its roots in the science department of VU University Amsterdam.
The project will focus on connecting different quantum processors, a significant distance apart, over a Dutch network. The aim is to build the very first fully functional quantum network using high-speed fibre connections.
A quantum network is a radically new internet technology, with the potential for creating pioneering applications. Such a network connects quantum processors to each other via optical channels, and this enables the exchange of so-called quantum bits (qubits). Qubits have a number of features that make them very different from the bits we currently know and use in classical networks. For example, quantum communication is potentially immune to eavesdropping practices. Quantum communication networks are expected to evolve over time towards a global quantum network, and this would allow secure communication; position verification; clock synchronisation; computation using external quantum computers; and more. Among other things, the project is intended to lead to new techniques, insights and standards that will bring a quantum network closer.
Different parties in the collaboration each contribute their own areas of expertise. Ultimately, the mix of skills will help to create a programmable quantum network that connects quantum processors in different cities. Erwin van Zwet, Internet Division Engineering Lead at QuTech, underlined the project’s importance: “Working with these partners, we expect to have taken significant steps towards a quantum network by the end of the TKI project.”
Although the technology is still at an early stage, all four parties see the benefit of joining forces now. Wojciech Kozlowski, a postdoc at QuTech and responsible for one of the work packages in the TKI project: “Every day we are working on finding answers to the question of how network operators, such as KPN or SURF, can deploy a quantum network, and what sort of services they can offer their users. Although we are still in an early stage of development, we are already building the quantum internet ecosystem of the future by working with key partners. This ecosystem will prove crucial as our quantum network evolves into a fully-fledged quantum internet.”
References:
https://www.commsupdate.com/articles/2020/11/27/kpn-collaborating-on-quantum-network-development/
https://www.overons.kpn/en/news/2020/qutech-kpn-surf-and-opnt-join-forces-to-build-a-quantum-network
IMT 2020.SPECS approved by ITU-R but may not meet 5G performance requirements; no 5G frequencies (revision of M.1036); 5G non-radio aspects not included
ITU-R Approves IMT 2020.SPECS:
At it’s November 23rd meeting, ITU-R SG 5 approved WP5D’s draft recommendation IMT 2020.SPECS which is the first official 5G RAN standard. The document contains the description and implementation details for three new technologies that conform with the International Mobile Telecommunications 2020 (IMT-2020) vision, but this author (and others) do not believe they meet the ITU M.2410 Performance Requirements for the URLLC (ultra reliable, ultra low latency communications) 5G use case. That is because 3GPP’s 5G NR enhancements for URLLC in the RAN had not been completed or performance tested when 3GPP Release 16 was frozen in early July 2020 (see detailed description below) and is therefore NOT included in the IMT 2020.SPECS detailed implementation for 5G NR.
The three Radio Interface (RIT)/Set of Radio Interface (SRIT) Technologies are: 3GPP 5G-SRIT and 3GPP 5G-RIT submitted by 3GPP (contains both Release 15 and 16 functionality), and 5Gi submitted by Telecommunications Standards Development Society India (TSDSI). The 3GPP submissions include support by China and South Korea, which had submitted their own RIT’s that were determined to be “technically identical” with 3GPP’s 5G NR submission so they were effectively combined into one RIT.
TSDSI’s RIT is based on the 3GPP 5G NR RIT with additional functionality to support “Low Mobility Large Cell” (LMLC). The TSDSI-RIT incorporates India specific technology enhancements that can enable longer coverage for meeting the LMLC requirements. The TSDSI-RIT, which is mainly to address the LMLC requirements, exploits a new transmit waveform that increases cell range developed by research institutions in India (IIT Hyderabad, CEWiT and IIT Madras) and supported by several Indian companies. It enables low cost rural coverage. It has additional features which enable higher spectrum efficiency and improved latency. TSDSI-RIT is a key enabler for 5G based rural broadband usage scenario in India and similarly placed geographies.
Author’s NOTEs:
1. It is critically important to understand that IMT 2020.SPECs only apply to the 5G RAN and NOT the 5G core network or any other non-radio aspects of 5G. Also, that the frequencies to be used for 5G RAN are specified in a YET TO BE COMPLETED revision to ITU M.1036 recommendation which should include WRC 19 frequency arrangements (especially for mmWave spectrum).
–>That means there are no official guidelines on what frequencies might be used with any of the IMT 2020 RITs specified.
2. Here’s a description of the ITU-R recommendations that were used for evaluation of IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT submissions to ITU-R WP5D:
- ITU-R M.2410 describes key requirements related to the minimum technical performance of IMT-2020 candidate radio interface technologies.
- ITU-R M.2411 deals with the requirements, evaluation criteria, and submission templates, providing service, spectrum, and technical performance requirements.
- ITU-R M.2412 provides guidelines for the procedure, the methodology, and the criteria (technical, spectrum, and service) to be used in the IMT 2020 evaluation process.
With these documents, the evaluation procedure is designed in such a way that the overall performance of the candidate RITs/SRITs is fairly and equally assessed on a technical basis, ensuring that the overall IMT-2020 objectives are met.
Reference:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2020/Pages/submission-eval.aspx
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
During the multi-year development and evaluation process by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R), these technologies were deemed to be sufficiently detailed to enable worldwide compatibility of operation and equipment, including roaming.
The outcome of this first release of IMT-2020 supporting 5G is a set of terrestrial radio interface specifications which are incorporated into a global standard in the ITU-R Recommendation titled ‘Detailed specifications of the radio interfaces of IMT-2020.’ This is in final approval to the 193 Member States of ITU.
“IMT-2020 specifications for the fifth generation of mobile communications (5G) will be the backbone of tomorrow’s digital economy, transforming lives and leading industry and society into the automated and intelligent world,” said Houlin Zhao, ITU Secretary-General. “5G will enable much faster data speeds, reliable connectivity and low latency to international mobile telecommunications (IMT) — all needed for our new global communications ecosystem of connected devices sending vast amounts of data via ultrafast broadband.”
Mario Maniewicz, Director of the ITU Radiocommunication Bureau, said: “The successful completion of the evaluation process and the release of this global standard is a significant milestone for the global telecommunication industry and its users. 5G technologies will further enrich the worldwide communications ecosystem, expand the range of innovative applications and support the burgeoning Internet of Things, including machine-to-machine communication.”
The evaluation of the candidate technologies was not carried out by ITU-R alone. It was a highly collaborative process with substantial input from and coordination with ITU Member States, equipment manufacturers, network operators, and involved national, regional, and international standards development organizations, partnerships, the academic community and fora, since ITU-R provides a unique global framework to discuss the capabilities of new radio technologies.
In early 2012, ITU initiated the development of “IMT for 2020 and beyond”, setting the stage for 5G research activities and in 2015 established the vision and requirements for the globalization of 5G. Under ITU’s ongoing IMT programme, ITU membership is continuing its long-standing contribution to mobile communications, facilitating its mission to be “committed to connecting the world.“
Note 1. For the URLLC use case, M.2410 specifies a minimum of 1 msec in the data plane and 10 ms in the control plane for latency (1 way in the RAN). Actual latency (1-way) is the sum of latency in the RAN, core network, and edge network (if any).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3GPP Release 16 5G NR-URLLC in the RAN spec status as of as of October 11, 2020:
- RP-191584 5G NR Physical Layer Enhancements for Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) was 53% complete
- RP-190726 Performance part: Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) was 0% complete
“In Release 15 the basic support for URLLC was introduced with TTI structures for low latency as well as methods for improved reliability. Use cases with tighter requirements, e.g. higher reliability up to 1E-6 and short latency in the order of 0.5 to 1ms, have been identified as important areas for NR. This work item [1] was approved based on the outcome of the study items as shown in TR 38.824 [2] and TR 38.825 [3].
This work item specifies PDCCH enhancements, UCI enhancements, PUSCH enhancements, enhanced inter UE TX prioritization/multiplexing and enhanced UL configured grant transmission.”
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Information/WORK_PLAN/
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3493
(Sept 15, 2020 version of Release 16 Description; Summary of Rel-16 Work Items)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The Role of ITU-R:
International Telecommunications Union (ITU), formerly CCITT, is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs), fostering innovation among 193 member states. For more than 150 years, ITU has been coordinating the radio spectrum, establishing standards that foster connectivity globally across multiple technology systems. And for the past 30 years, the ITU Radiocommunication sector (ITU-R) has been coordinating efforts with governments and industries to develop unified global broadband multimedia international mobile telecommunications systems, also known as IMT.
ITU-R plays an important role in achieving the objective of global harmonization and wide industry support for each generation of mobile communication technologies. 2G in the 1990s was the first generation of digital mobile communication system. These technologies provided dramatically enhanced capabilities relative to previous analog technologies, beginning the ongoing prevalence of mobile communication in our daily life. Despite the success of 2G during that era, the fragmented technology standards were incompatible for purposes of global roaming and economies of scale.
Global operation and economies of scale are key requirements for the success of mobile telecommunication systems. In order to achieve this goal, ITU-R established the concept of IMT, which includes a harmonized timeframe for future development, taking into account technical, operational, and spectrum-related aspects. Since then, ITU-R has been striving for harmonized global standards all through the process of IMT-2000 and IMT-Advanced.
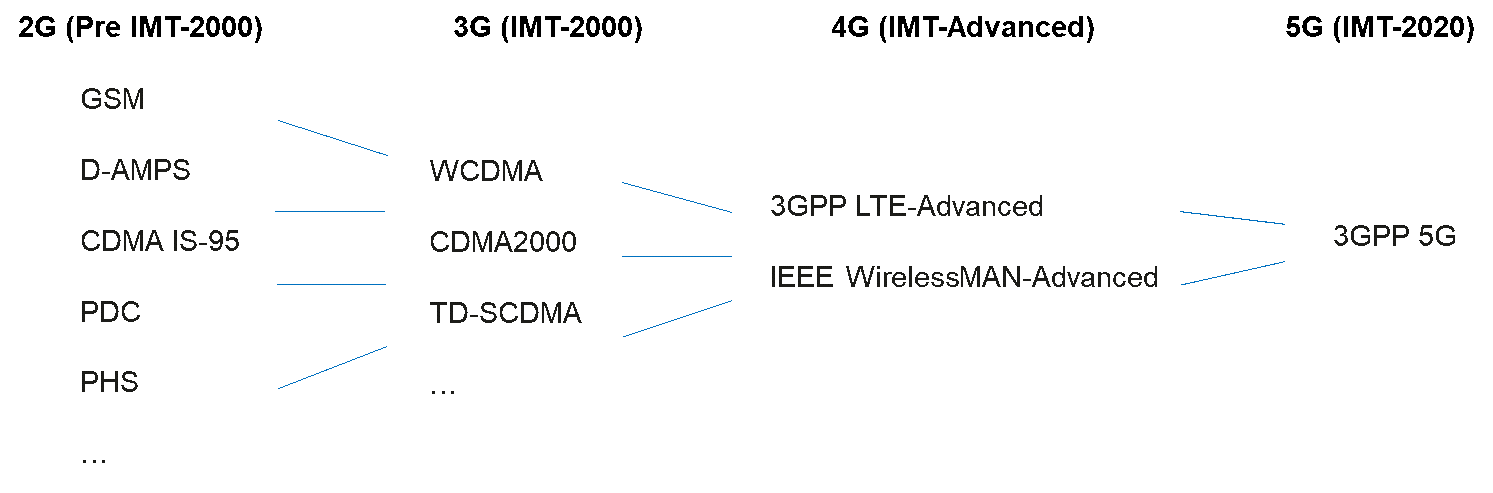
ITU-R Progress from 2G to 5G Credit Dell’Oro Group
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/pr26-2020-evaluation-global-affirmation-imt-2020-5g.aspx
https://www.itu.int/pub/R-REP-M.2410
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status, and 3GPP’s RIT submissions
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=349
8https://www.itu.int/md/R15-IMT.2020-C-0021/en
Only domestic network equipment may be used for 5G in Russia; Revision of ITU-R M.1036 urgently needed
Russian state radio frequencies commission (SRFC) has decided that only equipment of domestic origin may be use for the development of 5G in the country, reports Comnews Russia citing Oleg Ivanov, deputy minister in the Ministry of Digitization. Comnews.ru stated:
When deploying 5G in Russia, only domestic network equipment should be used. Most likely, during the construction of Internet of Things networks, base stations with the status of domestic equipment will be needed. This follows from the results of yesterday’s meeting of the SCRF.
“Naturally, domestic equipment will be used. This is a common decision across the entire 5G spectrum. will use exclusively domestic equipment. There is such a solution. ” He added that according to the principle of technical neutrality, operators will be able to build a 5G network in all frequency bands in which they already have the right to build LTE networks.
“In connection with the general trend for domestic equipment, they were given sufficient time to resolve this issue. We will insist [on the exclusive use of domestic IoT base stations], and then the decision is up to the management,” added Oleg Ivanov.
A list of frequencies for 5G services for Russia has been approved. The frequency ranges are: 694-790 МHz, 2,300-2,400 МHz, 2,570-2,620 МHz, 4,400-4,990 МHz and 24.25-27.5 GHz. The 3,400-3,800 MHz band is absent from the list.
Rostec has been identified as the basic contractor to ensure the production of domestic equipment for 5G networks. The NIIR representative at the meeting said that tests of the Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) technology, which will enable the deployment of 5G on the operators’ existing frequencies for 2G, 3G and 4G, are planned to be carried out on the commercial network in December 2020 and completed by March 2021, submitting the results to the SCRF no later than June 2021. He noted that the testing uses equipment from Nokia, Huawei and Ericsson.
Last week, a roadmap for the development of 5G in Russia was approved, according to which the delivery of domestic 5G equipment will begin in 2024 (see ComNews news of November 20, 2020). The press service of PJSC MegaFon explained: “The clarification of the SCRF has been made in accordance with the provisions of the roadmap. Taking into account the decisions made, we forecast a delay in the introduction of 5G technology in Russia for five to six years. According to our data, at the moment, services based on 5G are presented over than 100 operators in the world. ”
PJSC “MTS” is ready to purchase competitive Russian equipment with the required characteristics, quality and prices. “The main thing is that this does not lead to a lag in the deployment of 5G in Russia. The company regularly comes up with initiatives in this direction. In particular, in December 2019, MTS signed an agreement with the Element group of companies and Skoltech on the development and production of 5G in Russia -equipment based on international open radio access standards of the Open RAN project, and in October this year, within the framework of this project, a 5G pilot zone was opened in Skolkovo. We are also working on other projects to test domestic equipment, “the press service said. MTS to the ComNews correspondent.
Igor Guryanov, General Director of Spectrum Management LLC, believes that even if we assume the readiness of the entire line of domestically produced radio access equipment on the SA architecture in 2023, all existing networks in Russia are now working with the NSA architecture, and for the transition to a new architecture on new equipment, time. “Therefore, taking into account the announced plans for the readiness of domestic equipment, full-scale 5G networks are unlikely to appear before 2025. Some dedicated 5G networks without the baggage of already operating LTE networks and without the need to work in many bands at once may appear earlier,” Igor Guryanov comments. a solution for 5G networks is possible if you make efforts in terms of time and funding comparable to those of the largest manufacturers of telecommunications equipment. For this reason, if domestic equipment appears, then most likely it will be in the form of integration and refinement of open marketable components of the 5G solution, for example, within the Open RAN concept and similar concepts for the core and transport component of the network. And if the state insists on the “domesticity” of the equipment, then it would be correct not only to write down the requirements for import substitution, but also to define the requirements for open interfaces and criteria for classifying equipment as domestic when it is assembled from software and hardware components of foreign origin. “However, I am sure Igor Guryanov, even this path has a lot of problems associated with the complexity of the implementation of a commercial competitive product in the market of 5G network infrastructure. ” If the Open RAN concept and related processes stall in the USA, Europe and the developed countries of Asia, Russia will not be able to take advantage of open developments in this area for the so-called domestic equipment. In any case, even in advanced countries and operators, it will take at least several years to solve many problems related to the integration of open solutions, “concluded Igor Guryanov.
Vitaly Solonin, head of the Wireless Technologies Department at J’son & Partners Consulting, agrees: the requirement to build 5G networks in Russia exclusively on domestic equipment will delay the launch of such networks in the country for at least several more years. “The first contracts with operators for the supply of Russian base stations are planned to be concluded in 2023, but this is hard to believe, primarily due to the unavailability of domestic chipsets for 5G. 5G networks are the basis for the digitalization of many industries, transport, healthcare, education. Dozens of projects have been launched in the world, and maybe hundreds already, demonstrating the potential of 5G and the economic effect of this technology. ”According to J’son & Partners Consulting forecasts, by 2030.
……………………………………………….,…………………………………………………………………………..,………………………………………………………………
New Russian Private 5G Network:
Separately, Russian communications service provider Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) is ready to deploy an Ericsson-powered 5G-ready dedicated network for gold and silver producer Polymetal at the Nezhdaninskoye gold deposit in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). The network will be introduced at the end of 2020 and will be built on Ericsson Dedicated Networks solution. The network will provide critical communications infrastructure and the Internet of Things (IoT).
After successfully implementing a number of pilot projects with leading Russian enterprises and deploying Private LTE and 5G-ready networks for various industrial needs, MTS will build the first commercial Private LTE network in Russia for remote monitoring and managing critical processes in difficult geographic and weather conditions. Together with Polymetal, one of the world’s largest producers of gold and silver, MTS will deploy Russia’s first 5G-ready Private network at the Nezhdaninskoye gold deposit.
……………………………………………….,…………………………………………………………………………..,………………………………………………………………
ITU recommendation M.1036 revision not completed:
In a contribution approved by ITU-R WP 5D to the November 23, 2020 ITU-R SG5 meeting, the Russian Federation stated that the development of a draft revision of Recommendation ITU-R M.1036 (Frequency arrangements to be used for the terrestrial component of IMT), taking into account the WRC-19 decisions, is urgently needed. The last few 5D meetings failed to consider proposals on amending this Recommendation. The Russian Federation, along with this author, believe that the revision of ITU-R M.1036 is an urgent, critical issue that requires an additional 5D meeting to address.
It’s somewhat of a contradiction that ITU-R WP5D approved IMT 2020.specs (3GPP NR + TSDSI 5Gi for India) at its Nov 2020 meeting, but the Frequency WG was not in session so no action could be taken to revise M.1036. Hence, there are NO assigned frequencies/ arrangements for terrestrial 5G!
References:
https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-M.1036/en
How fast is 5G really? OpenSignal and Reviews.org provide answers
Most IEEE Techblog readers know that 5G speeds are dependent on the spectrum used, with mmWave providing by far the fastest bit rates.
- Millimeter wave spectrum, championed by Verizon, is available in very large block widths, and can therefore deliver very high speeds. But coverage (propagation) is very poor.
- Low frequency spectrum offers very good coverage, but poor speeds.
- The sweet spot for 5G is therefore mid-band spectrum*, which offers the most compelling blend of coverage and capacity/speed.
* According to telecom research analyst Craig Moffett, not all mid-band spectrum is the same. The propagation differences between T-Mobile’s 2.5 GHz spectrum and the 3.7 to 4.2 GHz C-Band spectrum that will be auctioned off in a matter of weeks (and which is likely to be the cornerstone of Verizon’s future mid-band deployments) are dramatic. For a given cell site, the area covered in open space by T-Mobile’s 2.5 GHz will likely be 10x greater than that covered by a cell site in the C-Band.
OpenSignal examined 5G download speeds in five U.S. cities and found that Verizon is crushing it compared to the other big wireless carriers, so far. But some, including T-Mobile’s President of Technology Neville Ray, have questioned the wisdom of leading a 5G strategy with mmWave deployments. Verizon’s early lead with the high-band spectrum could begin to vanish as the other two carriers’ 5G deployments mature.
In each of the five cities, the average 5G download speed was over three times faster using Verizon than on either AT&T or T-Mobile. But OpenSignal notes that most of these measurements were taken before Verizon’s launch of its Nationwide 5G, which includes the use of lower frequency bands. As Verizon adds more lower frequency spectrum into the mix, its lead on speed will likely decline.
OpenSignal’s lead analyst Ian Fogg said the variation in mmWave download speeds depends on how each carrier has deployed. Verizon has deployed very densely in some urban areas while the other two carriers have deployed less densely. One of the big downsides to mmWave is its limited propagation. Fogg said, “If you’re on the edge of the range of the signal, you may get more error correction,” among other factors that will slow the speed.

OpenSignal also reported on mmWave upload speeds, which are drastically lower than mmWave download speeds.
Since cellular networks are asymmetric, upload speeds are always much slower. “If you are sending information from a large antenna on a cell site, it’s easy to transmit down to a small phone,” said Fogg. “But when the phone is transmitting back, you have a small battery device that’s transmitting in the other direction.”
But since upload is used for such things as sharing photos and videos, consumers are going to want faster and faster upload speeds. Fogg noted that the cameras of smartphones get improved in each new generation, becoming more capable of high-resolution images that result in larger file sizes.
Aside from 5G being used to improve mobile broadband, the technology also promises to earn its return on investment for business use cases. One of those use cases will be fixed wireless access (FWA) deployments. In that case, the upload constraints could be mitigated by the types of devices deployed. Fogg noted that for FWA “you don’t have a battery constraint in the same way.” He said, “You’ll probably have a smaller antenna than you would on a cell tower. There’s still an asymmetry dynamic, but not quite the same.”
There are three notable 5G developments:
- Verizon nationwide 5G. After October 13, Verizon started its nationwide 5G rollout using dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) to allow Verizon to offer 5G on lower frequency spectrum bands that are also available for use simultaneously for Verizon’s 4G users. The use of lower frequency bands will change the nature of Verizon’s 5G service compared with the exclusively mmWave service used beforehand, likely increasing 5G Availability but lowering average 5G Download Speeds.
- T-Mobile’s mid-band 5G extension. Similar to Verizon, T-Mobile is also altering the mix of 5G spectrum it uses for its 5G service. In the last quarter of 2020, T-Mobile is aiming to greatly expand the reach of its 2.5GHz mid-band 5G service to many more cities which should enable faster speeds. The company claims its mid-band coverage will increase from 30 million to 100 million people by the end of 2020. It is also looking to extend the reach of its standalone 5G technology which should help T-Mobile to improve its 5G Availability as well.
- The arrival of the 5G iPhone. All iPhone 12 models support both 5G and mmWave 5G in the U.S. and their arrival should accelerate 5G adoption. The first units arrived in customers’ hands on October 23. Apple’s smartphones are a key part of the U.S. wireless market. AT&T in particular was the first carrier to market the iPhone and it continues to have a strong iPhone share. This launch means all major smartphone makers offer 5G models. It also means that the U.S. wireless customers who prefer Apple — approximately half of U.S. mobile users — now have a 5G option that the carriers can market.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
To help consumers understand the difference between current 4G internet speeds and 5G internet speeds, Reviews.org crunched the numbers to put these speeds into perspective:
What this illustrates is that the jump from 4G to 5G is not a minor boost, according to Joe Hanlan of Reviews.org. A decade ago it seemed impossible to imagine watching TV and movies on our phones, and now it is something that lots of people do every day. New 5G networks will open up our gadgets to a range of new possibilities, and while it is hard to imagine exactly the kinds of things we’ll be doing in a decade from now, our 5G future makes it possible.
To compare flight durations to mobile network speeds, REVIEWS.org sourced average download speeds from 4G and 5G networks from Opensignal. The research firm then converted the difference in speeds between networks to a non-stop flight from Perth to London (17:20 duration).
References:
https://www.opensignal.com/2020/11/24/understanding-5g-availability-in-us-cities
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/verizon-s-5g-mmwave-crushing-it-but-for-how-long
5G speeds: here’s how much faster new internet speeds will be
Millimeter Wave Market Projected to reach 7.38B by 2027; 37% CAGR
The global telecom millimeter wave technology market size is projected to reach USD 7.38 billion by 2027, registering a CAGR of 37.01%.
Millimeter Waves (MMW) can transmit a large amount of data efficiently, operating in the electromagnetic spectrum of 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Millimeter waves are also known as Extremely High-Frequency (EHF) waves owing to its operational frequency spectrum. The property of transmitting a large amount of data has made the technology popular across the telecommunication application.
The MMW technology industry is prominently dependent on the applications in various verticals where it is used extensively. Major application areas include telecommunication, military and defense, security services, and medical and healthcare. Evolution of 5G technology is likely to occur over the coming years on account of recent developments and continuous research and progress in the telecom industry.
Millimeter waves are anticipated to play a vital role in the development of 5G technology on account of the technology’s demand for higher-bandwidth. The 5G technology is predicted to emerge in the coming years and the market is likely to witness its adoption significantly. Eventually, the demand for MMW technology is expected to boost, in turn, propelling the overall MMW technology market, particularly across the telecom industry.
Increased government funding and initiatives coupled with intensive R&D carried out from the military and private sectors are leading towards the improvement of the MMW technology. In addition, the E-band frequency segment having extensive application in the telecommunication sector is estimated to generate the highest revenue. The E-band frequency segment is projected to keep on dominating in the telecom industry owing to the growing telecom applications. Therefore, the overall telecom millimeter wave technology market is poised to witness significant growth worldwide over the forecast period at a notable pace.
Telecom Millimeter Wave Technology Market Report Highlights:
- North America accounted for the largest market share in the telecom MMW technology market owing to the technology’s early and greater adoption rate
- U.S. being the highest revenue generating country in 2019 in North America, the regional market is predicted to exhibit steady growth over the forecast period
- E-band frequency segment is anticipated to grow rapidly over the estimated duration owing to its extensive adoption in the telecom applications
- The telecom industry in the Asia Pacific is poised to expand substantially over the coming years, and the E-band frequency segment is likely to witness lucrative opportunity in the regional telecom industry
- Besides, growing urbanization in the Asia Pacific region and competition amongst the telecom service providers to offer superior quality of internet and other related services in order to enlarge customer base is another factor expected to drive the telecom MMW technology market
- Online streaming of high-quality videos, online gaming, and other entertainment stuff which demand high bandwidth and consume heavy data are again likely to fuel the overall demand for MMW technology in the telecom sector globally.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) communication systems have attracted significant interest regarding meeting the capacity requirements of the future 5G network. The mmWave systems have frequency ranges in between 30 and 300 GHz where a total of around 250 GHz bandwidths are available. Although the available bandwidth of mmWave frequencies is promising, the propagation characteristics are significantly different from microwave frequency bands in terms of path loss, diffraction and blockage, rain attenuation, atmospheric absorption, and foliage loss behaviors. In general, the overall loss of mmWave systems is significantly larger than that of microwave systems for a point-to-point link.
Fortunately, the small wavelengths of mmWave frequencies enable large numbers of antenna elements to be deployed in the same form factor thereby providing high spatial processing gains that can theoretically compensate for at least the isotropic path loss. Nevertheless, as mmWave systems are equipped with several antennas, a number of computation and implementation challenges arise to maintain the anticipated performance gain of mmWave systems. Toward this end, this chapter discusses key enabling techniques of the mmWave based 5G network from the link level perspective. The link level performance of the mmWave wireless system depends on a number of factors, including the transmission scheme (i.e., whether we employ beamforming, multiplexing, or both), the approach to identifying the channel, how to design the transmitted signal waveform structure and access strategies.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/millimeter-wave
G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance/WEF: 36 cities to develop policy roadmap
The World Economic Forum (WEF), the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation, has selected 36 cities across 22 countries to create a new worldwide policy roadmap for smart cities developed by the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance.
Established in June 2019, the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance unites municipal, regional and national governments, private-sector partners and cities’ residents around a shared set of principles for the responsible and ethical use of smart city technologies. The Alliance establishes and advances global policy norms to help accelerate best practices, mitigate potential risks, and foster greater openness and public trust. The WEF serves as secretariat for the Alliance.
The selected 36 cities will adopt policies for privacy protection, accountability for cyber security, improved broadband coverage, increased openness of city data, and improved accessibility for elderly/disabled people to digital city services. These 26 cities include Belfast, Leeds and London in the UK; Barcelona and Bilbao in Spain; Toronto in Canada; Moscow, Russia; Melbourne and Newcastle in Australia; Milan, Italy; Apeldoorn in the Netherlands; and Bengaluru, Faridabad and Hyderabad in India.
“This roadmap is not about theoretical ideas and pipe dreams, it is built on practical, real-world policies from leading cities around the globe,” said Jeff Merritt, Head of the Internet of Things and Urban Transformation, World Economic Forum. “City governments are on the frontline of a global crisis and need to be able to act quickly and decisively to curtail this pandemic and set course for their economic recovery. Technology is an essential tool in this fight but governments cannot risk falling into the usual traps related to privacy, security and vendor lock-in. That’s where the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance can help.”
“This initiative originated in Japan last year from our Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a fact I’m very proud of,” said Koichi Akaishi, Vice Minister for Science, Technology and Innovation for the Cabinet Office of the Government of Japan. “I hope to see more cities participating in the Alliance following the model set by these first pioneer cities.”

Leaders of organizations participating in this program had the following comments:
Miguel Eiras Antunes, Global Smart Cities Leader, Deloitte Global, said “The transformation from a traditional city to a ‘smart city’ does not just happen overnight. Success depends on the quality of the decisions that are made and the way those decisions are executed. Deloitte is committed to working closely together with the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance to co-design policy frameworks that will empower governments to accelerate smart cities initiatives for sustainable developments.”
“Being a pioneer city in the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance is an excellent opportunity for us to promote the innovative work that is taking place in Leeds right now, but also facilitates the opening of doors where we can learn from other leading cities around the world and implement best practice in our city,” said Stephen Blackburn, Head of Smart Cities, Leeds.
London’s Chief Digital Officer, Theo Blackwell, said “We need to work together to realize the potential of data to solve city challenges by putting it in the hands of those who can make a difference. But we also need to do it in a way that is safe, ethical and responsible. London is proud to join this global initiative as a pioneer city to promote the adoption of ethical smart city policies.”
Will Cavendish, Digital Services Leader at Arup said “COVID-19 has driven a step-change in the use of digital services in cities, and many of these changes will only accelerate beyond the pandemic. The policies developed by the G20 Smart Cities Alliance will be fundamental in ensuring that the enabling digital connectivity and data infrastructures, along with the rapidly-emerging technology-enabled services, are deployed in an inclusive, transparent and mutually beneficial manner.”
“Technology and knowledge are two strategic assets to build inclusive, data-driven, and sustainable smart cities capable of tackling new and emerging challenges,” said Roberta Cocco, Deputy Mayor for Digital Transformation and Services to Citizens, Milan. “That is why Milan is joining the G20 Global Smart City Alliance, as this initiative will allow us to share best practices with innovative cities around the world. Today more than ever, in fact, we need to collaborate with each other to identify the most effective tools to face global threats like COVID-19. It is only by joining our forces that we can beat this common enemy that is threatening the health, the economy, and the future of our citizens.”
Dr. Julia Glidden, Corporate Vice President, Worldwide Public Sector, Microsoft Corporation, said “Accessibility and privacy policies are critical to making cities more inclusive and transparent. Microsoft congratulates the Forum and G20 for creating model policies that aid cities in serving all citizens.”
“We will adopt a transparent and participatory philosophy of local governance in the city of Istanbul,” said Ekrem İmamoğlu, Mayor of Istanbul. “Our aim is to empathize with all segments of society, and value the participation of everyone, ensuring that the majority of the people are represented – not the few.”
Gilvan Maximo, Secretary of Science, Technology and Innovation, Brazil, said “The G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance will provide us with a global partnership to accelerate the adoption of technologies in a responsible manner and for the benefit of the citizen, debating complex issues and seeking joint solutions. Therefore, Brasilia is eager to participate in this joint work.”
“This opportunity to collaborate as a G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance pioneer city on a new roadmap for safely adopting new technology is very welcome indeed as we work to develop a Belfast Smart District and to weave digital innovation into every part of our economy,” said Alderman Frank McCoubrey, Lord Mayor of Belfast. “We’ll be exploiting new technologies and data to tackle city challenges in areas such as health and mobility to improve our citizens’ quality of life – and we must ensure this is done ethically and in a way that prioritizes transparency, privacy, equity and inclusion. Being part of the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance means that each of the partner cities will benefit from expert, tailored insights and policy tools and this collaborative approach will allow us all to make progress in how we govern technology more swiftly and effectively, for the benefit of all our citizens.”
Dr. Frank Mentrup, Mayor of Karlsruhe, said “The G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance offers a unique opportunity to develop common ethical standards, foster digital sovereignty and therefore create and build a new resilient ‘trust infrastructure for cities and citizens’, as trust is going to become one of the most important and most vulnerable resources of our future.”
We believe that technology is a key enabler that can transform our cities in to smart cities leading to delivery of improved services to citizens and businesses”, said K.T. Rama Rao, Minister of Municipal Administration and Urban Development, Industries and Information Technology, Electronics and Communication, Government of Telangana, India. “We are keen to collaborate with G20 cities in formulating policy frameworks to improve quality of life of our citizens using emerging technologies.”
“Transforming our cities into smart cities is a great tool to improve people’s life quality,” said Horacio Rodriguez Larreta, Mayor of Buenos Aires. “That is why we are committed to continue incorporating technology, developing innovative public policies, and to work together with the G20 cities to build a modern and efficient state that makes life easier for everyone who lives, works, studies or visits us in Buenos Aires.”
“The pandemic presents an opportunity to reshape our future, with renewed digital rights and tools that should allow access for all and people-centred government. Local and regional governments will need to lead this shift to ensure the application of technology promotes human rights through equitable public service provision; putting our communities and planet first,” said Emilia Saiz, Secretary General of the United Cities and Local Governments. “The G20 Smart Cities Alliance is an important mechanism to help facilitate this transformation, bringing together a critical network of partners to collectively address and mitigate future crises”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://globalsmartcitiesalliance.org/
Highlights of AT&T CFO and CTO remarks at Morgan Stanley Investor Conference
Network quality driven by significant investments in 5G and fiber:
AT&T believes that its recent and anticipated network investments will bolster its network foundation to compete as the need for high-quality connectivity only continues to increase. At a Morgan Stanley European Investor Conference, AT&T CFO John Stephens indicated that AT&T’s integrated fiber strategy is expected to improve the company’s connectivity offering for both consumer and enterprise markets and enhance its 5G network quality in a cost-efficient manner.
COVID-19 Impact:
AT&T CTO Andre Fuetsch said: “Obviously what happened was everyone basically started working, started schooling from home, and all of a sudden we had to readjust our lives to work from home, learn from home, and all of a sudden we had to adapt very quickly to that. Within our homes, we had to have these different personas that we normally don’t do — whether it’s doing your day job, performing that duty, helping your children get online so they can do their schooling, and then all the other things in life. That was a blurring, in a way, of these sort of enterprise and consumer segments coming together.”
“All of this technology is great, but at the end of it, we are humans and anything we can do to help facilitate [and] build better, stronger human connections” will benefit society at large, Fuetsch added. “This year we’re really getting pushed and challenged to do that. I really think this type of technology is just going to make things better.”
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Improves Operations:
Some of these technologies, like Artificial Intelligence (AI), are already helping AT&T improve its operations, especially among its field technicians, he said, noting that AT&T’s entire routing and scheduling program relies heavily on AI.
“Any given day we have 35,000 network technicians driving around in trucks installing, and repairing, and maintaining our network. It’s essentially a very complex logistics algorithm and, as you can imagine with a company of our scale, just a single percentage improvement in efficiencies can lead to big, big dollars,” Fuetsch said.
AT&T is also trialing the use of drones with computer vision analytics to help improve inspections of its roughly 70,000 cell sites. When those drones take flight, they are scanning towers, looking for excessive heat dissipation, corrosion, loose cables, and bird nests, among other signs that indicate a required repair.
“All of this is getting fed back into a neural network, which is basically AI based,” and that program identifies the repair checklist, the technician and skill sets required, and the parts needed to remedy the problem, Fuetsch said.
AT&T’s experiences here and elsewhere gives him confidence that “the camera is still and will be the killer app” for the foreseeable future. However, the use of cameras is undergoing dramatic changes, he said.
“We carry about 400 petabytes a day across our network. About 50% of that traffic we carry is video traffic. Most of that is going out in a sort of downstream way. The future is going to be about upstream,” Fuetsch said.
Use of Video Cameras:
Fuetsch envisions new applications that “can help better manage our lives through a simple video camera” with the aid of video analytics and sensing. These advancements are occurring not just despite the scourge of COVID-19, but rather because of it in some ways as well, he said.
“This pandemic has really created some new norms here. I think the good news for operators is connectivity is so important and so relevant for everything we do. As we go into 2021, certainly with hopefully a light at the end of the tunnel here in terms of the pandemic with the latest news we’re hearing about vaccines, I’m actually very optimistic.”
“As we go into 2021, certainly with hopefully a light at the end of the tunnel here in terms of the pandemic with the latest news we’re hearing about vaccines, I’m actually very optimistic,” Fuetsch added.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2020/john_stephens_update.html
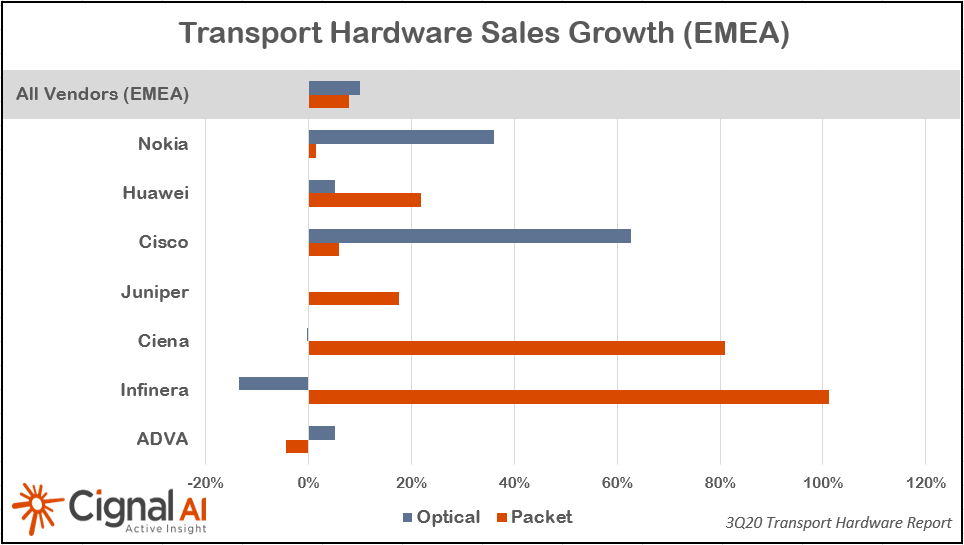
Dell’Oro and Cignal AI: Optical Transport Equipment Market Grows in 3Q 2020
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, the optical transport equipment revenue increased 9 percent year-over-year in 3Q 2020 reaching $3.8 billion. The market growth was largely attributed to higher demand in Asia Pacific.
“Sales slowed in North America following a strong first half of the year,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “Whether it was due to network demand caused by people working and studying from home or new projects at the beginning of the year, the demand for optical equipment in the region rose 11 percent in the first half of 2020. But I think there was enough concern surrounding the longevity of the pandemic that service providers grew cautious and refrained from overextending their capital. As a result, optical revenue in North America declined 7 percent in the third quarter,” continued Yu.
Growth in Asia Pacific more than offset the lower revenue in North America and Latin America. Optical revenue grew 22 percent year-over-year in Asia Pacific, driven largely by higher deployments in China and Japan. Also, with lockdown restrictions easing, some regions such as Middle East and Africa (MEA), significantly rebounded in the quarter following a sharp decline in 1H 2020. Sales in China, Japan, and MEA each grew over 25 percent.
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments (by speed including 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps, and 800 Gbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), optical switch, optical packet platforms, data center interconnect (metro and long haul), and disaggregated WDM. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit https://www.delloro.com
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
|
|||
 |
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
About the Transport Hardware Report
About Cignal AI
|
Dell’Oro: RAN growth accelerates due to “torrid pace” of 5G NR in 3Q2020
Dell’Oro has upgraded its near-term outlook for the RAN market to reflect stronger-than-expected activity in China, Europe and North America. The market researcher now expects the market to approach USD 70-80 billion over the combined 2020 and 2021 period.
The improved outlook in Dell’Oro’s Q3 RAN market report indicates continued positive momentum. The upswing begun in the second half of 2018 extended into the third quarter, with surging demand for 5G propelling the RAN market to robust year-over-year growth, the researcher said. It estimates that the overall 2G to 5G RAN market advanced 10-20 percent year-on-year in the third quarter, meaning annual growth in eight out of the last nine quarters.
“While we correctly identified that the RAN market would appear disconnected from the underlying economy throughout this year, we also underestimated the pace and the magnitude of these 5G rollouts,” said Stefan Pongratz, analyst with the Dell’Oro Group. “This shift from 4G to 5G, including low-band-and mid-band 5G NR, continued to accelerate at a torrid pace in the quarter, underpinned by stronger-than-expected 5G activity in multiple regions.”
Additional highlights from the 3Q20 RAN report:
- RAN revenue shares were impacted to some degree by the state of the 5G rollouts in China and North America, resulting in share gains for both Huawei and ZTE over the 1Q20-3Q20 period.
- The near-term outlook remains favorable for both macro and small cells, with combined 2020 and 2021 2G-4G and 5G base station shipments projected to eclipse 10 M units.
- We have adjusted the near-term RAN market outlook upward, to reflect stronger than expected activity in China, Europe, and North America, with total RAN projected to approach $70 B to $80 B for the combined 2020 and 2021 period.
Editor’s Note: The RAN market today is almost entirely provided by a handful of vendors making cellular base stations and small cells. Those are: Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung, ZTE, and Fujitsu. In the future, there is a movement to both Open RAN and Cloud RAN which would disrupt the current deployments with disaggregated hardware and open software. We are very skeptical of those two over hyped industry initiatives.

Radio Access Network illustration from Resource Gate
Dell’Oro Group’s RAN Quarterly Report offers a complete overview of the RAN industry, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, transceivers or RF carrier shipments, macro cell and small cell BTS shipments for 5G NR Millimeter Wave, 5G NR Sub 6 GHz, LTE, and WCDMA/GSM. The report tracks the RAN market by region and includes market data for Massive MIMO. The report also includes a four-quarter outlook. To purchase this report, please contact us by email at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit https://www.delloro.com
References:
Surging Demand for 5G Accelerates RAN Growth, According to Dell’Oro Group