5G
New ITU-T Standards for IMT 2020 (5G) + 3GPP Core Network Systems Architecture
New ITU-T standards related to “5G”:
ITU-T has reached first-stage approval (‘consent’ level) of three new international standards defining the requirements for IMT-2020 (“5G”) network systems as they relate to network operation, softwarization and fixed-mobile convergence.
The standards were developed by ITU-T’s standardization expert group for future networks, ITU-T Study Group 13.
Note: The first-stage approvals come in parallel with ITU-T Study Group 13’s establishment of a new ITU Focus Group to study machine learning in 5G systems.
End-to-end flexibility will be one of the defining features of 5G networks. This flexibility will result in large part from the introduction of network softwarization, the ability to create highly specialized network slices using advanced Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and cloud computing capabilities.
The three new ITU-T standards are the following:
- ITU Y.3101 “Requirements of the IMT-2020 network” describes the features of 5G networks necessary to ensure efficient 5G deployment and high network flexibility.
- ITU Y.3150 “High-level technical characteristics of network softwarization for IMT-2020” describes the value of slicing in both horizontal and vertical, application-specific environments.
- ITU Y.3130 “Requirements of IMT-2020 fixed-mobile convergence” calls for unified user identity, unified charging, service continuity, guaranteed support for high quality of service, control plane convergence and smart management of user data.
ITU’s work on “International Mobile Telecommunications for 2020 and beyond (IMT-2020)” defines the framework and overall objectives of the 5G standardization process as well as the roadmap to guide this process to its conclusion by 2020.
ITU’s Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is coordinating the international standardization and identification of spectrum for 5G mobile development. ITU’s Telecommunications Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is playing a similar convening role for the technologies and architectures of the wireline elements of 5G systems.
ITU standardization work on the wireline elements of 5G systems continues to accelerate.
ITU-T Study Group 15 (Transport, access and home networks) is developing a technical report on 5G requirements associated with backbone optical transport networks. ITU-T Study Group 11 (Protocols and test specifications) is studying the 5G control plane, relevant protocols and related testing methodologies. ITU-T Study Group 5 (Environment and circular economy) has assigned priority to its emerging study of the environmental requirements of 5G systems.
ITU-T Study Group 13 (Future networks), ITU’s lead group for 5G wireline studies, continues to support the shift to software-driven network management and orchestration. The group is progressing draft 5G standards addressing subjects including network architectures, network capability exposure, network slicing, network orchestration, network management-control, and frameworks to ensure high quality of service.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
The “5G” wireline standards developed by ITU-T Study Group 13 and approved in 2017 include:
- ITU Y.3071 “Data Aware Networking (Information Centric Networking) – Requirements and Capabilities” will support ultra-low latency 5G communications by enabling proactive in-network data caching and limiting redundant traffic in core networks.
- ITU Y.3100 “Terms and definitions for IMT-2020 network” provides a foundational set of terminology to be applied universally across 5G-related standardization work.
- ITU Y.3111 “IMT-2020 network management and orchestration framework” establishes a framework and related principles for the design of 5G networks.
- ITU Y.3310 “IMT-2020 network management and orchestration requirements” describes the capabilities required to support emerging 5G services and applications.
- Supplement 44 to the ITU Y.3100 series “Standardization and open source activities related to network softwarization of IMT-2020”summarizes open-source and standardization initiatives relevant to ITU’s development of standards for network softwarization.
Reference:
http://news.itu.int/5g-update-new-itu-standards-network-softwarization-fixed-mobile-convergence/
…………………………………………………………….
“5G” Core Network functions & Services Based Architecture:
The primary focus of ITU-R WP5D IMT 2020 standardization efforts are on the radio aspects (as per its charter). That includes the Radio Access Network (RAN)/Radio Interface Technology (RIT), spectral efficiency, latency, frequencies, etc.
To actually deliver services over a 5G RAN, a system architecture and core network are required. The core network provides functions such as authentication, session management, mobility management, forwarding of user data, and (possibly) virtualization of network functions.
3GPP Technical Specification (TS) 23.501 — “System Architecture for the 5G System” — is more commonly referred to as the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) for the 5G Core network. It uses service-based interfaces between control-plane functions, while user-plane functions connect over point-to-point links. This is shown in the figure below. The service-based interfaces will use HTTP 2.0 over TCP in the initial release, with QUIC transport being considered for later 3GPP releases.
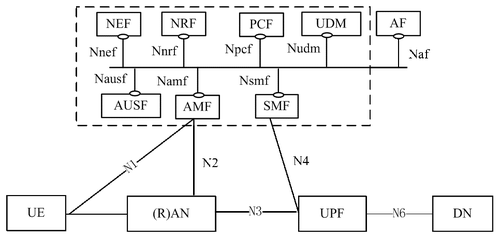
There are many aspects to this, but the white paper highlights:
- How the idea of “network function services” (3GPP terminology) aligns with the micro-services based view of network service composition
- How operators may take advantage of decoupled control- and user-plane to scale performance
- How the design might enable operators to deploy 5GC functions at edge locations, such as central offices, stadiums or enterprise campuses
The first 5G core standards (really specifications because 3GPP is not a formal standards body) are scheduled to be included in 3GPP Release 15, which “freezes” in June next year and will be formally approved three months later. This will be a critical release for the industry that will set the development path of the 5G system architecture for years to come.
Download white paper: Service-Based Architecture for 5G Core Networks
Editor’s Note:
From http://www.3gpp.org/specifications:
“The 3GPP Technical Specifications and Technical Reports have, in themselves, no legal standing. They only become “official” (standards) when transposed into corresponding publications of the Partner Organizations (or the national / regional standards body acting as publisher for the Partner).”
References:
http://www.lightreading.com/mobile/5g/5g-core-and-the-service-based-architecture/a/d-id/738456?
https://img.lightreading.com/downloads/Service-Based-Architecture-for-5G-Core-Networks.pdf
Preview of Fog World Congress: October 30th to November 1st, Santa Clara, CA
The Fog World Congress (FWC), to be held October 30th to November 1st in Santa Clara, CA, provides an innovative forum for industry and academia in the field of fog computing and networking to define terms, discuss critical issues, formulate strategies and organize collaborative efforts to address the challenges. Also, to share and showcase research results and industry developments.
FWC is co-sponsored by IEEE ComSoc and the OpenFog Consortium. It is is the first conference that brings industry and research together to explore the technologies, challenges, industry deployments and opportunities in fog computing and networking.
Don’t miss the fog tutorial sessions which aim to clarify misconceptions and bring the communities up to speed on the latest research, technical developments and industry implementations of fog. FWC Research sessions will cover a comprehensive range of topics. There will also be sessions designed to debate controversial issues such as why and where fog will be necessary, what will happen in a future world without fog, how could fog disrupt the industry.
Here are a few features sessions:
- Fog Computing & Networking: The Multi-Billion Dollar opportunity before us
- Driving through the Fog: Transforming Transportation through Autonomous vehicles
- From vision to practice: Implementing Fog in Real World environments
- Fog & Edge: A panel discussion
- Fog over Denver: Building fog-centricity in a Smart City from the ground up
- Fog Tank: Venture Capitalists take on the Fog startups
- 50 Fog Design & Implementation Tips in 50 Minutes
- Fog at Sea: Marine Use Cases For Fog Technology
- NFV and 5G in a Fog computing environment
- Security Issues, Approaches and Practices in the IoT-Fog Computing Era: A panel discussion
View the 5 track conference program here.
Finally, register here.
For general information about the conference, including registration, please email: [email protected]
About the Open Fog Consortium:
The OpenFog Consortium bridges the continuum between Cloud and Things in order to solve the bandwidth, latency and communications challenges associated with IoT, 5G and artificial intelligence. Its work is centered around creating an open fog computing architecture for efficient and reliable networks and intelligent endpoints combined with identifiable, secure, and privacy-friendly information flows between clouds, endpoints, and services based on open standard technologies. While not a standards organization, OpenFog drives requirements for fog computing and networking to IEEE. The global nonprofit was founded in November 2015 and today represents the leading researchers and innovators in fog computing.
For more information, visit www.openfogconsortium.org; Twitter @openfog; and LinkedIn /company/openfog-consortium.
Reference:
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2017/07/20/att-latency-sensitive-next-gen-apps-need-edge-computing/
Ericsson Survey: Network Operators Focus on New Markets for 5G Revenue
Survey Highlights:
Most network operators say they’re ready for “5G” even if they don’t know what it will actually deliver (the RAN and other key functions haven’t even been discussed by ITU-R WP5D for IMT 2020, let alone agreed upon), Ericsson found in a survey of wireless network operators around the world (see References and hyper-links below). Many expect the enterprise market and Internet of Things (IoT) applications to drive revenue growth from 5G technology.
More than three-quarters of the respondents said they were in the midst of 5G trials. That corresponds with research from the Global Mobile Suppliers Association research which found 81 5G trials underway in 42 countries.
23% of survey respondents plan to migrate 4G subscribers to 5G with enhanced services and revenues (but when?). Yet nearly two thirds (64%) of operators said they can’t pay for 5G by simply raising rates on consumers, because consumers are “tapped out.” Eighteen percent of respondents said they expect to monetize 5G by “expanding to new markets—enterprise/ industry segments.”
“In 2016, 90% pointed to consumers as the central segment in their planning and only 34% focused on specialized industries,” the Ericsson researchers wrote in this year’s report. An increased emphasis on the enterprise market is a key shift since a previous Ericsson 5G operator survey was conducted in 2016.
“This year, operators are seeing that the consumer market is saturated, so planning for 5G is more evenly split across specialized industry segments (58%), business users (56%) and consumers (52%),” the Ericsson researchers added.
Specific industry segments on which operators expect to focus 5G monetization efforts include media/entertainment (cited by 69% of respondents), automotive (59%), public transport (31%), healthcare (29%) and energy/ utilities (29%).
Providing industry-specific services to these industry segments will be important in 5G monetization, according to 68% of respondents. The single most important use case in the media/entertainment segment is high-quality streaming, respondents said. Other top use cases by segment included:
- Automotive: autonomous vehicle control
- Public transport: Smart GPS
- Healthcare: Remote robotic surgery
- Energy & utilities: Control of edge-of-grid generation
More than three quarters (77%) of respondents said third-party collaboration is an essential element in 5G monetization and 68% said they need to find new revenue-sharing models.
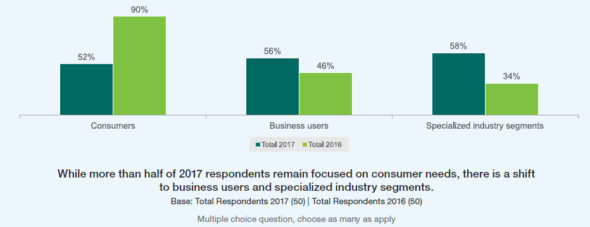
Chart courtesy of Ericsson’s 5G Readiness Survey
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Survey Questions and Methodology:
Some of the questions asked in the survey:
-Exactly how have preparations for 5G evolved over the past year?
-Where do telcos stand now in their 5G activities and developments?
-What actions are service providers taking now in anticipation of 5G?
-What priorities drive their initiative?
-How ready are they to take leadership positions in the 5G future?
The survey’s objective was to obtain a snapshot of the state of the industry in relation to next-generation mobile technology. Last year, we struggled to find 50 executives globally who were far enough along in 5G to answer the survey questions.
This year, Ericsson says they “easily identified 50 executives, both business and technical leaders, from 37 operators around the world. As leaders of their organizations’ 5G efforts, they are at the center of the 5G evolution. That increase clearly signifies the growing recognition among industry leaders of 5G’s importance.”s
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/assets/local/narratives/networks/documents/5g-readiness-survey-2017.pdf
5G Monetization Survey: Operators Look to IoT for Revenue Growth
Global Data: 5G subs to outnumber 3G subs in South Korea by 2020
Is it possible for South Korea to have more 5G then 3G subscribers BEFORE the official “5G” = ITU-R WP5D – IMT 2020 standards are completed?
Indeed, South Korean mobile network operators plan to take an early lead in the deployment of 5G (perhaps because of the February 2018 Winter Olympics in Pyeongchang). That would help them overcome stagnating traditional wireless service revenues, according to market research firm GlobalData.
The South Korean market’s 5G subscriber base is forecast to outnumber the 3G base by 2020, two years after the world’s first commercial 5G deployment during next year’s Pyeongchang Winter Olympics, GlobalData said in its report.
That will occur at a time when mobile voice service revenues are expected to decline at an average rate of 7% per year through to 2021, GlobalData telecom market analyst Malcolm Rogers stated.
“Operators around the globe faced with the same challenge, evolve to something more than a pipe provider or offer services that come with more utility. However, the Korean operators have been among the most proactive in growing business outside the core of communication,” he said.
“Whereas operators in some markets have been slow to react to the digital disruption caused by OTTs and internet giants like Google and Amazon, the players in South Korea have been investing in new digital business for years.”
The main South Korea wireless network operators – SK Telecom, KT and LG U+ – are focusing on a range of non-core segments including industrial IoT, payment platforms, media and commerce, Rogers added.
From the report description (see Reference below):
SK Telecom and LG U+ now offer cellular based wireless payment platforms that allow small retailers, traders and vendors to conduct business from anywhere. All three major telecom providers have also invested in B2C and B2B e-commerce operations, venturing into an entirely new industry. 5G networks will enable operators to provide new services for industry, government and consumers. Korea Telecom (KT) has already completed trial to offer 5G enabled entertainment services such as high definition virtual reality and 8K mobile video while SKT and KT are developing driverless car solutions and security platforms based on 5G technologies.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
South Korea plans to complete the deployment of a commercial 5G mobile network in the second half of 2019, Heo Won-seok, director of ICT and Broadcasting Technology Policy at South Korea’s Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, said during a keynote presentation at the Global 5G Event, May 25, 2017 in Tokyo, Japan.
KT recently launched an AI-based home assistant service while both SK Teleom and LG U+ are offering cellular based wireless payment platforms. All three carriers are investing in business-to-consumer and business-to-business e-commerce offerings, which is an entirely new industry for those network operators.
Against this backdrop, 5G networks are expected to allow the network operators to introduce new services targeting industry, government and consumer markets, according to GlobalData.
For example, KT is already exploring offering 5G-enabled entertainment services including 8k mobile video streaming, while SK Telecom and KT are developing driverless car solutions and security platforms based on 5G technologies.
References:
https://www.globaldata.com/south-korean-telcos-bank-5g-digital-traditional-business-stagnate/
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/5g-subs-overtake-3g-korea-2020
https://phys.org/news/2017-02-south-korea-olympics-5g-year.html
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20170525/5g/south-korea-launch-first-commercial-5g-network-2019
Telecom Italia “5G” trial to blanket San Marino in 2018
According to the Financial Times (on line subscription required):
Telecom Italia plans to test its home grown “5G” technology in the micro-state of San Marino next year, making it the first country in the world to boast a nationwide 5G network. The state of San Marino, which has little more than 30,000 citizens, extends to only 61 sq km, making it the smallest republic in the world.
Telecom Italia Mobile (TIM) has signed a memorandum of understanding with the government of the tiny country to upgrade the existing 4G-LTE network in advance of a trial of “5G” services in 2018. It will double the number of mobile sites and will install a network of small cells in downtown San Marino, a Unesco heritage site, this year that will provide the backbone of the future commercial network. Investment in 5G network trials are taking place around the world with carriers in South Korea, China and the US among the most active in testing 5G technology. Giovanni Ferigo, head of technology for Telecom Italia Mobile, said San Marino’s 5G network would be the first in Europe “for sure.”
It was not revealed who created the specs for the Italian telco’s “5G” network or where Telecom Italia will procure the end point devices/handsets. One would assume that Ericsson is supplying TIM with the “5G” base stations, based on a MOU signed between the two companies in March of this year. TIM wrote in a press release on March 2, 2017:
TIM and Ericsson are committing to share skills, projects, laboratories and resources for designing, testing and building the technological components of the new 5G network needed to create a complete and open ecosystem around next-generation digital services.
In particular, the agreement will directly involve the research and innovation structures of the two companies, focusing on the design and testing of access infrastructure, the respective antenna systems and network virtualisation solutions, particularly through joint participation in Italian and European research projects and integration of service platforms for testing in the field of innovative Use Cases.
The 5G system will provide peak speeds of up to dozens of Gbps for UltraHD services and cloud computing solutions, a decrease in communication latency, reducing it to a few milliseconds, reliability for mission-critical services and service density with the ability to connect up to a hundred thousand terminals per cell. These characteristics mean that 5G will become the reference mobile network for next-generation digital services (such as virtual reality) and for the industrial Internet (robotics, manufacturing, health, environment, self-driving logistics).
The agreement is part of the “5G for Italy” initiative launched in 2016 by TIM and Ericsson for the establishment of an ecosystem of experimental industrial partners, confirming the commitment of the two companies to innovating technologies and networks in support of the socio-economic growth of the country.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Telecom Italia is also testing “5G” in Milano and Torino, but has more freedom in San Marino to experiment because of fewer restrictions on the use of airwaves than in Italy.
“We need to experiment as soon as possible,” Mr Ferigo said. The work done in San Marino would play a critical role in the future of 5G technology in Italy but was also crucial to the wider European sector as standards for the new network are refined.
“For 5G, our intention is a European leadership in standardization,” he said. The European Commission published a 5G action plan last year when it estimated that sectors such as healthcare, transport, cars and utilities would see economic benefits of €113bn by 2025 from the technology. However, the European Commission does not generate any telecom standards. For Europe, that’s ETSI which contributes to 3GPP and its members contribute to ITU-R WP 5D which is standardizing true 5G (as we’ve noted in numerous blog posts/articles).
Earlier this year, Telecom Italia Mobile (TIM) said LTE customers are expected to account for around 90% of its mobile broadband customers by 2019; That’s due to almost blanket LTE coverage of Italy with network speeds up to 75 Mbps and peaks of 500 Mbps in the main cities via the use of LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation.
The above referenced FT “5G” article states:
Some countries have committed to the first 5G launches in 2019 but the wider telecoms industry is still struggling to define exactly what 5G technology is and some have argued that it is not yet clear how they can justify spending billions on the new network.
Mr Ferigo said the San Marino launch would be “very important” in defining the use case for 5G that would transform all sectors from healthcare to robotics to public transport. Telecom Italia has started working with companies including Maserati and Ducati on the use of better wireless technology but also the makers of parmesan cheese who want to better monitor the cows in their fields. Small territories have been used in the past for telecoms testing. The first 3G trial in the UK took place on the Isle of Man, while the remote Isle of Bute in Scotland was used to test “white space” technology.
Copyright The Financial Times Limited 2017. All rights reserved.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
http://www.telecomitalia.com/tit/en/archivio/media/note-stampa/market/2017/PN-TIM-Turin-5G-Day.html
https://www.ericsson.com/assets/local/publications/white-papers/wp-5g.pdf
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news-and-events/press-center/media-kits/5g


