Dell’Oro: Total RAN market to grow 10-15% in 2021; Microwave Transmission equipment grows 11% YoY
Dell’Oro Group has once again upgraded its forecast for the total RAN market, now projecting it to grow 10-15% this year. As expected, Huawei and ZTE are gaining market share in China, while Ericsson and Nokia are gaining everywhere else. Ericsson and Samsung increased their RAN revenue outside of China.
“The underlying long-term growth drivers have not changed and continue reflect the shift from 4G to 5G, new FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) and enterprise capex, and the transitions towards active antenna systems,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst with the Dell’Oro Group. “At the same time, a string of indicators suggest this output acceleration is still largely driven by the shift from 4G to 5G, which continued at a torrid pace in the quarter (but only for the RAN; not for the 5G SA core network), even as LTE surprised on the upside,” continued Pongratz.
“With the improved outcome in Latin America, we estimate that four out of the six regions we track increased at a double-digit rate in the second quarter,” Stefan said via email. He was kind enough to send me these charts:
Additional highlights from Dell’Oro’s 2Q 2021 RAN report:
- RAN rankings did not change – Huawei and ZTE were the No.1 and No.2 suppliers in China while Ericsson and Nokia maintained their No.1 and No.2 positions outside of China.
- Revenue shares changed slightly – preliminary estimates suggest Ericsson and Samsung recorded revenue share gains outside of China, while Huawei and ZTE improved their positions in China.
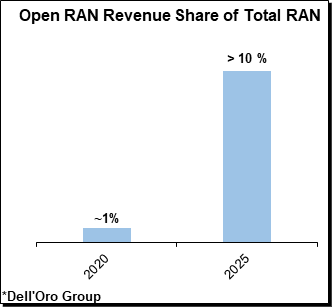
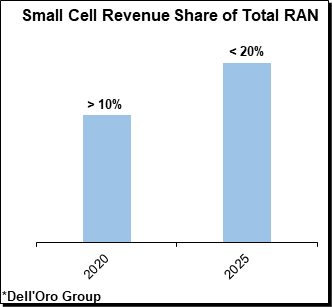
- The combined share of the smaller RAN suppliers, excluding the top five vendors, improved by ~1% between 2020 and the first half of 2021, in part as a result of the ongoing Open RAN greenfield deployments in Japan and the U.S. “It’s all relative and it will take some time before open RAN moves the needle,” Pongrantz said.
- The RAN market remains on track for a fourth consecutive year of growth. The short-term outlook has been revised upward – total RAN is now projected to advance 10 to 15% in 2021.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Dell’Oro Group’s RAN Quarterly Report offers a complete overview of the RAN industry, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, transceiver, macro cell, small cell BTS shipments, and Open RAN for 5G NR Millimeter Wave, 5G NR Sub 6 GHz, and LTE. The report tracks the RAN market by region and includes market data for Massive MIMO. The report also includes a four-quarter outlook.
- Segments: LTE, Sub 6 GHz 5G NR, Millimeter Wave 5G NR, Massive MIMO, Macro Cell, Small Cell, Open RAN
- Regions: North America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, Asia Pacific, China and CALA (Caribbean and Latin America)
To purchase this report, please contact: [email protected]
References:
2021 Outlook Upgraded for RAN Market, According to Dell’Oro Group
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Dell’Oro Group says that the demand for Microwave Transmission equipment grew 11% year-over-year in the first half of 2021, driven by LTE and 5G. In that period, microwave revenue from mobile backhaul application grew 16 percent.
“The Microwave Transmission market is recovering from the decline caused by the spread of COVID-19 as evidenced by the strong growth in the first half of 2021,” stated Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “Almost all of the vendors in this industry are benefiting from the improving mobile backhaul market, especially the top vendors. Since demand is rising, each vendor’s performance this year will come down to how well they navigate the supply issues created by the pandemic and semiconductor shortages,” added Yu.
Highlights from the 2Q 2021 Quarterly Report:
- All regions contributed to the positive market growth this quarter with the exception of Latin America. Latin America declined year-over-year for a ninth consecutive quarter, shrinking to its lowest quarterly revenue level that we have on record.
- The top three vendors in the quarter continued to be Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia. In 2Q 2021, Huawei regained most of the market share lost in the previous quarter and returned to holding a 10 percentage point lead over Ericsson.
- E/V Band revenue growth remained positive for another consecutive quarter and held its double-digit year-over-year growth rate.
The Dell’Oro Group Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, ports/radio transceivers shipped, and average selling prices by capacities (low, high and E/V Band). The report tracks point-to-point TDM, Packet, and Hybrid Microwave as well as full indoor and full outdoor unit configurations.
The following markets are covered in the report:
- TDM, Packet, and Hybrid Microwave
- Microwave Transmission by Application: Mobile Backhaul and Verticals
- Split mount units, Full indoor units, and full outdoor units
- E/V Band systems
To purchase this report, please contact [email protected]
References:
5G and LTE Drive Mobile Backhaul Microwave Market 16 Percent in 1H 2021, According to Dell’Oro Group
Dell’Oro: 5G SA indecisions slowing 5G Core network growth
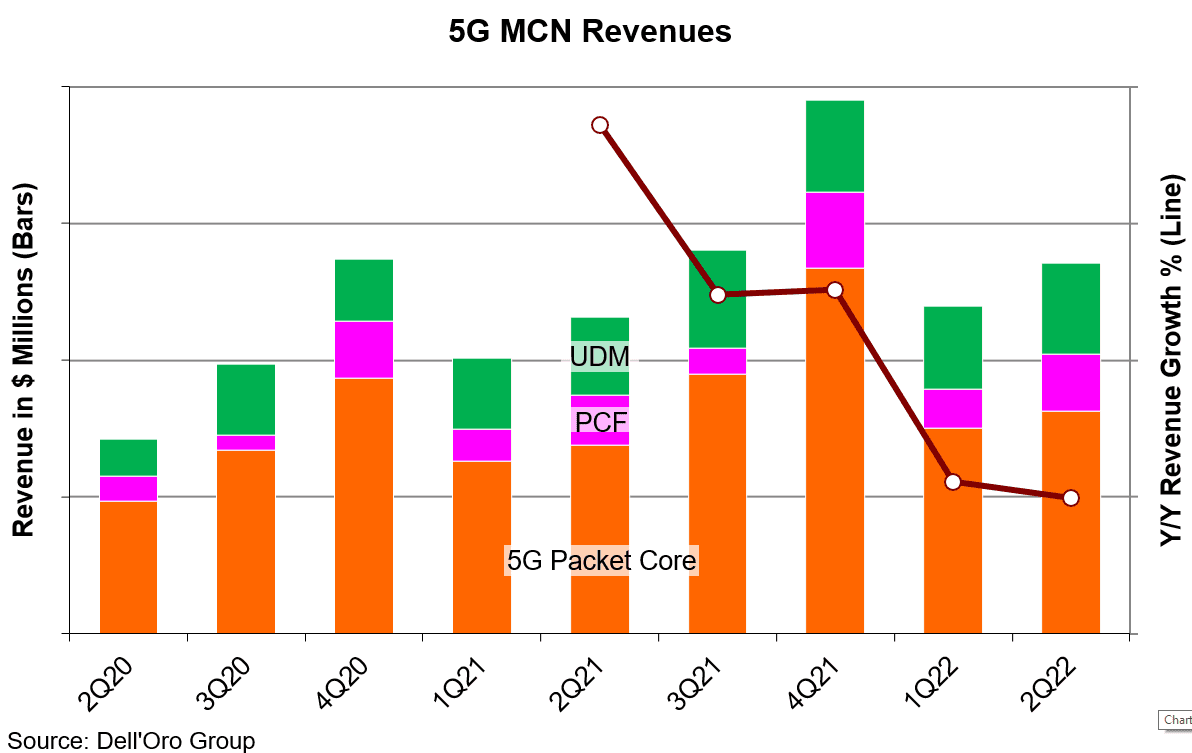
Revenues for the Mobile Core Network (MCN) [1.] market slowed to 6% year-over-year growth in 2Q 2021 after four quarters of double-digit growth, according to a new report by Dell’Oro Group.
Communication Service Providers (CSPs) indecisions about moving forward with 5G Standalone (5G SA/core network are slowing 5G Core market growth (except in China). It is now expected to decelerate over the next four quarters dropping to 17% year-over-year in 2Q 2022.
Note 1. The Mobile Core Network is in a transitional stage from 4G to 5G and a new type of core network called the 5G Core Service Based Architecture (SBA). The 5G Core SBA is designed to be a universal core that can be the core for mobile and fixed wireless networks, wireline networks, and Wi-Fi networks. This includes the ability to be the core for 2G/3G/4G, so only one core is necessary for the long term. In addition, the IMS Core will migrate into the 5G Core SBA.
With Network Function Virtualization (NFV) the 5G Core SBA is best served with Cloud-native Network Functions that disaggregates the hardware from the software and operates in a stateless function with the data separated from the control function among other things.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“We attribute the slowdown to the slow uptake of 5G Standalone (SA) networks. CSPs need to make decisions about which direction to take for 5G SA deployments. CSPs have several options to mull over, with new choices that were not available during the switch from 3G to 4G,” stated David Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “One decision CSPs need to make is about the selection of Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI). NFVI can be procured from a 5G core vendor, a third-party, the public cloud, or another platform like the Rakuten Communications Platform.”
Additional highlights from the 2Q 2021 Mobile Core Network Report:
• The Asia Pacific region accounted for 70% of the revenues for 5G Core as the Chinese SPs continue to build and Japanese SPs begin their buildouts.
• Top vendor ranking remains unchanged based on the four trailing quarters ending in 2Q 2021: Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Mavenir.
• 4G MCN (EPC) revenues are now in continual decline, but still represented 70% of the mix between 4G and 5G.
About the Report:
The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions.
To purchase this report, please contact at [email protected].
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Closing Comments:
The slowdown in 5G SA/core network growth should come as no surprise to IEEE Techblog readers. We’ve pounded the table for a very long time, stating that in the absence of an ITU standard or 3GPP IMPLEMENTATION spec, the 5G SA/core network growth would be slow with many different versions implemented by CSPs. That will inhibit interoperability and portability of 5G endpoints which have 5G SA software.
Equally important is that ALL 5G services and features (e.g. network slicing, automation, MEC, etc) require a 5G Core network while almost all 5G deployments today are 5G NSA which has a 4G core (EPC) network.
References:
CSPs’ Indecisions Slow 5G Core Growth Except for China, According to Dell’Oro Group
Why It’s Important: Rakuten Mobile, Intel and NEC collaborate on containerized 5G SA core network
RootMetrics touts 5G performance in Korea while users complain; No 5G SA in Korea!
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
Dell’Oro: MEC Investments to grow at 140% CAGR from 2020 to 2025
Telcos Loss: Private 5G & MEC/5G SA Core Network – Cloud Giants Take Market Share
T-Mobile Announces “World’s 1st Nationwide Standalone 5G Network” (without a standard)
Evaluating Gaps and Solutions to build Open 5G Core/SA networks
Ericsson Consumer Lab: Pandemic-driven online adoption habits to be future norm
- Ericsson released its largest consumer study to date, representing the opinions of 2.3 billion consumers across 31 markets
- On average, consumers will add 2.5 new services to their online activities by 2025
- Consumers’ time spent online is set to increase by ten hours per week on average by 2025
Called The Future Urban Reality, the Ericsson ConsumerLab report is Ericsson’s largest consumer study to date. It reveals key insights about what consumers believe will happen beyond the pandemic to the year 2025.
Representing the equivalent opinions of 2.3 billion consumers across 31 markets worldwide, the report predicts that consumers will not only continue to manage routine activities – such as remote work, e-learning, e-health and online grocery shopping – online but will also add an average of 2.5 new services. The report predicts that consumers will instead prioritize their leisure time to travel more, practice mindful living and spend time with friends and family.
As a result of increased online activities, consumers are predicted to spend, on average, an extra ten hours per week online when they enter the next normal. This move is also expected to close the gap between moderate and advanced online users, with the more moderate online users having introduced more online services in their daily life over the course of the pandemic.
Zeynep Ahmet, Senior Researcher, ConsumerLab, Ericsson Research, says: “Throughout the pandemic, information and communication technologies (ICT) have become the key means for consumers to manage many aspects in their everyday lives. Our latest findings suggest that this will continue well into the ‘next normal’ and beyond. This trend can support consumers to prioritize more of the important things in life, whether that is spending more time with loved ones or leading a healthier lifestyle. As an enabler of new online habits, it is clear that both mobile networks and digital inclusion efforts will play a crucial role in building tomorrow’s resilient, inclusive and equal societies.”
Key findings from the report:
- Anything routine will happen online by 2025: one in two consumers expect to use e-learning for upskilling. More than half of consumers globally believe all their entertainment activities will be online. More than one-third of consumers will order their groceries mainly online going forward.
- 64 percent of consumers expect heightened stress-levels within society: more than three-in-five consumers believe that it will be necessary to juggle multiple jobs to maintain a decent income. At the same time, seven-in-ten consumers expect to lead healthier lives.
- Convenience will come at the cost of privacy: while 75 percent of consumers predict that life will be steered by convenience in 2025, seven-in-ten also expect to pay more attention to their online security and privacy.
- Local shopping will lead the way: driven partly by environmental concerns, half of consumers globally expect to shop for more locally made products and produce as a new future norm.
- Half of consumers express a concern for climate change, yet 67 percent are looking to increase their leisure travel going forward: while most consumers believe that more sustainable travel options should be made accessible, only one in three indicate that they will refrain from flying when traveling for leisure in the future.
- Time spent online will increase by an average of 10 hours per week by 2025: the dependence on online platforms is expected to continue beyond the pandemic, with consumers predicting that they will add 2.5 more services on average to their daily online activities by 2025. This reiterates the importance of digital inclusion in ensuring an equal and resilient ‘next normal.’
China telcos add 43.71 5G subscribers in July, while capital spending declines
5G Subscriber Adds:
China’s network operators recorded a net addition of 43.71 million 5G subscribers in July, according to the carriers’ latest available reports.
- China Mobile, the world’s largest operator in terms of subscribers, added 28.91 million 5G subscribers in July. It had 279.60 million 5G subscribers at the end of July, compared to 84.05 million 5G customers in July 2020. The telco’s overall mobile subscriber base at the end of July reached 947.46 million, up compared to 945.50 million in June 2020.
- China Unicom said it added a total of 7.74 million 5G subscribers during July. During the first seven months of the year, Unicom added a total of 50.24 million 5G subscribers. The telco ended July with 121.07 million 5G subscribers. China Unicom reported an overall mobile base of with 311.61 million subscribers at the end of last month, up from 310.45 million in June.
- China Telecom added 7.06 million 5G subscribers in July to take its total 5G subscribers base to 138.21 million. The telco added 51.71 million 5G customers in the January-July period. China Telecom’s overall mobile base amounted to 364.62 million subscribers at the end of the July, after adding 2.13 million customers during the month.
China Telco CAPEX Crash:
However, total capital spending by the three state owned China telecom operators declined by 35% in the first half, with the number of new 5G base stations down 34% compared with last year. Spending on 5G by the two biggest telcos, China Mobile and China Telecom, slid 19%. China Unicom, has not disclosed its 5G spending but said it had reached only a fifth of its full-year capex target.
China Unicom revealed it had spent only RMB14 billion ($2.2 billion) of its 2021 capex budget of RMB70 billion ($10.8 billion), down 45% from 2020. It has a year-end target for 5G of RMB35 billion ($5.4 billion), the same as 2020.
China Mobile’s 5G investment of RMB50.2 billion ($7.8 billion) was 9% lower than last year, and only 46% of its full-year target of RMB110 billion ($17 billion).
China Tower reported a 28% fall in capex to 10.4 billion yuan ($1.6 billion).
China Telecom’s 5G spend plunged 45% to RMB11.1 billion ($1.71 billion), just over a quarter of its full-year forecast of RMB39.7 billion ($6.1 billion). Total capex declined 37% for the half. From the Chinese website Yicai.com:
From the data point of view, China Telecom’s capital expenditure in the first half of this year was less than one-third of the annual capital expenditure, and the investment progress was lagging behind. Liu Guiqing said that 5G was the largest investment in the first half of the year, including investment in 3.5GHz and 2.1GHz equipment. “On the whole, the investment in 3.5GHz equipment is relatively normal; for 2.1GHz investment, we make corresponding adaptations according to the current situation of the entire industry chain and the terminal ecology. At present, the purchase of 2.1GHz equipment has been completed, 3.5GHz telecom equipment is being negotiated, and there will be results soon.” He said that 87 billion yuan of investment can be completed this year, of which 5G investment is 39.7 billion yuan.

The China telcos maintain the same capex guidance for the full year of around 185 billion yuan ($28.6 billion), slightly up from last year’s 182 billion yuan ($28.1 billion). Yet for China Telecom and China Unicom, those capex numbers look quite challenging.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5G Base Station Builds:
China’s three major mobile carriers have already activated 961,000 5G base stations and connected 365 million 5G-compatible devices by end-June, Chinese press reported, citing comments by press secretary for the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) Tian Yulong.
Unicom said it had built just 80,000 new base stations in the first half and was aiming to deploy another 240,000 in the latter half of this year.
Meanwhile, China Broadcast Network and China Mobile have recently completed a tender to deploy 400,000 5G base stations this year, as part of the companies’ efforts to launch a shared 5G network. The contracts had been won by Huawei, ZTE, Datang, Nokia and Ericsson.
China Mobile has attributed its lower 5G investment to issues around its partnership with China Broadcast Network in building a new 5G network in the 700MHz band. The main tender was set in July. China’s 5G rollout is a high priority infrastructure project closely supervised by the national government. The two carriers expect this shared 5G network to reach nationwide coverage within the next two years.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5G Subscriber Forecast & 5G SA Core Network:
China is forecast to reach 739 million 5G subscribers by 2025, according to a recent study by ABI Research. That would represent nearly 40% of the total global 5G subscriber market.
Earlier this year, Liu Liehong, vice minister of industry and information technology, had said that 5G Standalone (5G SA) networks covered all prefecture-level cities across China.
We wonder if all China’s telcos have implemented the same specification for 5G SA/core network and whether it is “cloud native” or not? Also, whether they use NFV (virtual machines) or containers?
Note there is no standard or implementation specification(s) that would ensure vendor interoperability on 5G SA networks from different telcos.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20210824/5g/chinese-carriers-add-43-million-5g-subscribers-july
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/chip-shortage-taking-its-toll-on-china-5g-rollout/d/d-id/771681?
https://www.yicai.com/news/101136803.html
China Telcos Lose Subscribers; 5G “Co-build and Co-share” agreement to accelerate
Facebook tests voice and video calls in its main app

Zayo to deploy 400G b/s network across North America and Western Europe
Zayo Group Holdings today announced the planned deployment of 31 high capacity, 400G b/s enabled long haul routes across North America and Western Europe.
The availability of 400G b/s client-side wavelength capabilities will enable Zayo to deliver multi-terabit capacity across its underlying global network, enabling higher transmission rates, reduced cost per bit, increased data transfer speeds and significantly greater bandwidth capacity — key features that support enterprises on their digital transformation journeys. Up to 800G transmission will be available in select areas as Zayo deploys significant speed enhancements in anticipation of future network needs.
This optimized wavelength network is designed to provide a direct route for multi-cloud and multi-market connectivity, ideal for content providers, hyper-scalers, carriers and data centers. The upgrade will also enable reduced physical space requirements as well as reduced operation and maintenance costs resulting from a 40% reduction in power consumption.
The race to 400Gb/s has accelerated in recent years, with an increasing number of users, applications and devices driving exponential demand for increased bandwidth. Exceeding the current standard of 100G, Zayo’s new routes will provide a fourfold increase in maximum data transfer speed, supporting 5G technologies including Internet of Things, cloud-based computing, edge computing, virtual reality, high-definition video streaming and artificial intelligence.
“400G is rapidly becoming the prevailing requirement for networks and Zayo is breaking new ground with its 800G capabilities,” said Brian Lillie, Zayo Chief Product and Technology Officer. “This deployment underscores Zayo’s commitment to maintaining the leading edge of communications infrastructure and providing state-of-the art network solutions critical to our customers’ digital transformation journeys.”
C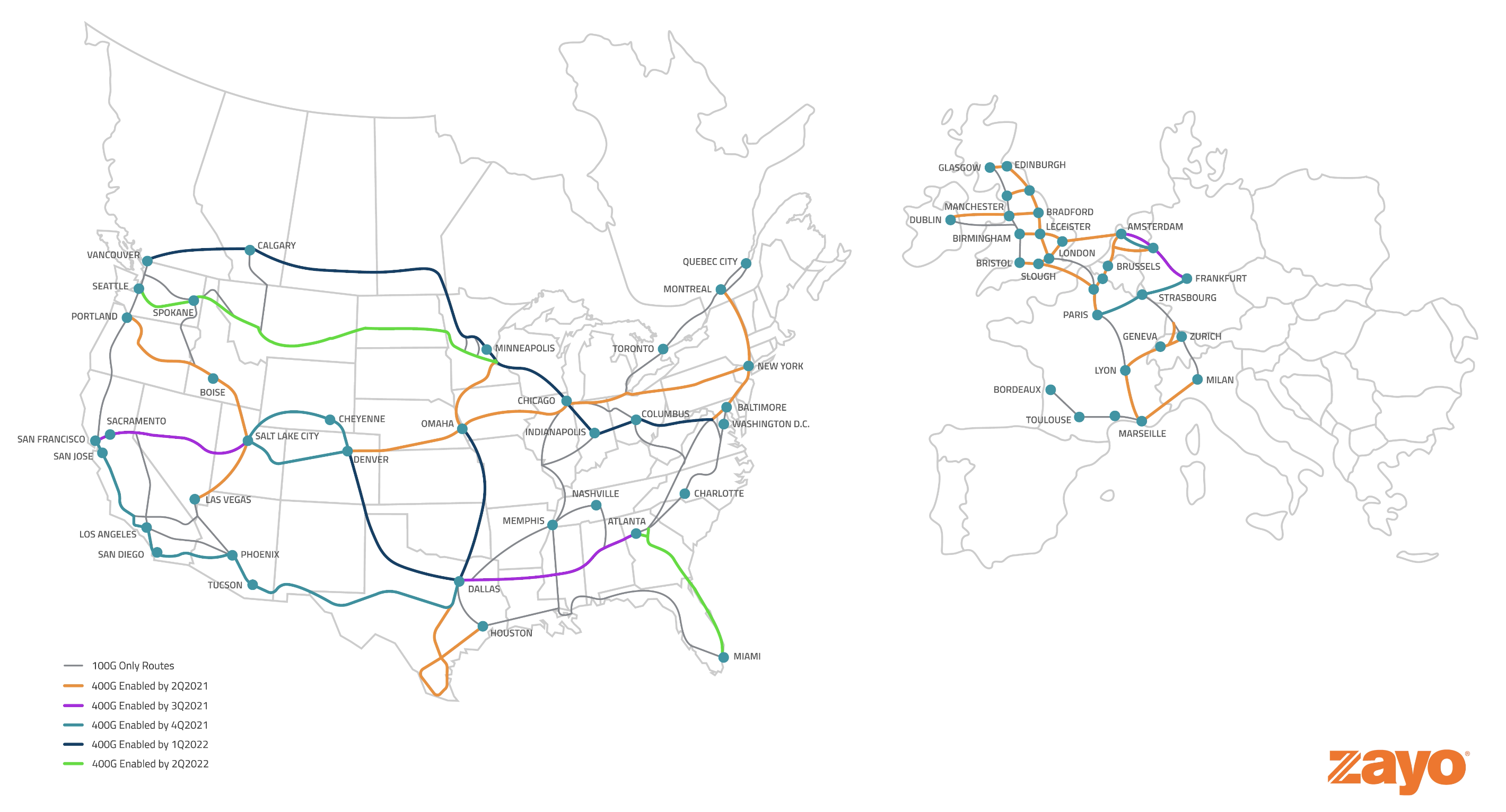 Chart courtesy of Avery Anderson of Zayo Group
Chart courtesy of Avery Anderson of Zayo Group
About Zayo Group:
Zayo’s 126,000-mile network in North America and Europe includes extensive metro connectivity to thousands of buildings and data centers. Zayo’s communications infrastructure solutions include dark fiber, private data networks, wavelengths, Ethernet, dedicated internet access and data center connectivity solutions.
Zayo owns and operates a Tier 1 IP backbone and through its CloudLink service, Zayo provides low-latency private connectivity that attaches enterprises to their public cloud environments. Zayo serves wireless and wireline carriers, media, tech, content, finance, healthcare and other large enterprises. For more information, visit https://zayo.com
References:
IDC: Global Managed Edge Services Market forecast ~$2.8B in 2025
According to IDC, Managed Edge Services [1.] will deliver worldwide revenues of about $445.3 million this year – a 43.5% increase over 2020. In addition, the IT market research firm forecasts that managed services revenues will hit nearly $2.8 billion in 2025. Over the 2021-2025 forecast period, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for managed edge services is expected to be 55.1%.
Note 1. Managed Edge Services seems to be a misnomer or at least a redundant term. That’s because all Multi-Access Edge Compute (MEC) services will be managed by a service provider (telco, cloud, or CDN) or network equipment vendor/managed services provider for on-premises edge computing.
“Managed edge services represent an emerging market opportunity that promises to provide a wide variety of low-latency services with the potential to enhance customer experience, drive operational efficiencies, and improve performance. It is a highly contested marketplace among key providers including communications SPs, hyper-scalers, CDN providers, and managed SPs with strategic partnerships and alliances forming to establish early commercial success and leadership,” said Ghassan Abdo, research VP, Worldwide Telecommunications at IDC.
“At the same time, service providers are keenly aware of the potential impact of the edge on their current market position and are watching closely for unforeseen competition from adjacent markets and new disruptors. Technology vendors including network equipment providers (NEPs) and software, datacenter, and networking vendors are vying to shape this market and play a significant role in delivering innovative edge services. Technical challenges abound including interoperability, open interfaces, and varying standards. The potential, however, is there to positively transform industries and user experiences,” he added.
IDC has identified three primary deployment models for managed edge services.
- On-premises deployment: This represents managed edge use cases where the edge compute infrastructure is deployed at the enterprises’ premises, also referred to as private deployment. This deployment model is intended to address the need for extra low latency and is applicable to industrial use cases, healthcare, and AR/VR applications.
- Service provider edge deployment: This represents managed edge services provided by edge compute deployed at the provider edge, both fixed and mobile. IDC expects this deployment model to spur development of a wide range of vertical use cases.
- CDN edge deployment: This represents managed edge services provided by edge compute deployed at the CDN POPs or edge locations. These use cases will enhance content delivery with personalized, high-fidelity, and interactive rich media customer experience.
IDC projects the on-premises edge to be the fastest growing segment with a five-year CAGR of 74.5%. The service provider edge will be the second-fastest growing segment with a CAGR of 59.2%, which will enable it to become the largest market segment by 2022. The CDN edge segment is expected to have a five-year CAGR of 41.9%.
The IDC report, Worldwide Managed Edge Services Forecast, 2021–2025 (IDC report #US47308121), provides a worldwide forecast for managed edge services covering 2021–2025. The forecast quantifies the revenue opportunities for service providers (SPs) that offer managed edge services on a monthly recurring revenue contractual arrangement. Service providers, in this context, comprise communications SPs, content delivery network (CDN) providers, public cloud providers or hyper-scalers, and managed service providers. This is the first forecast provided by IDC on this new and developing market.
For more information, contact:
Michael Shirer [email protected] or 508-935-4200
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

June was a busy month for managed edged compute deals:
- Vodafone outsourced its European MEC infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS);
- Ericsson and Google agreed to collaborate on edge compute solutions for mutual benefit; and
- AT&T sold its Network Cloud technology to Microsoft which will also provide Azure (public cloud) based 5G SA/core network for AT&T.
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS48179321
https://telecoms.com/511025/managed-edge-services-revenue-expected-to-hit-2-8-billion-by-2025/
Dell’Oro: MEC Investments to grow at 140% CAGR from 2020 to 2025
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) Market, Applications and ETSI MEC Standard-Part I
Juniper Research: 5G smartphone trends
A new study by Juniper Research has found that 5G‑compatible smartphones will account for over 50% of smartphone sales revenue by 2025; rising to $337 billion from $108 billion in 2021. It urged mobile handset vendors to ensure hardware maximizes the benefits of future mobile cloud computing solutions. Mobile cloud computing enables service providers to offload intensive tasks to the cloud; freeing on-device resources for essential device processes.
The new research, 5G Smartphones: Trends, Regional Analysis & Market Forecasts 2021-2026, predicts that successful handset vendors will include radios that are able to process large bandwidths and ultra-low latency to ensure that handset users are able to use cloud computing services efficiently, whilst remaining price competitive.
Android OS Handsets to Dominate in Emerging Regions
The report anticipates that increasing the availability of lower-tier 5G smartphones is crucial to propagate 5G handset adoption in emerging markets. It predicts that by 2025, global Android smartphone prices will be 65% lower than global iOS smartphone prices. It also highlights that this lower average cost of Android devices will lead to Android dominating 5G handset markets in regions such as Latin America.
Conversely, the research expects that the enduring popularity of iOS devices in developed markets will make 40% of global 5G smartphone revenue attributable to North America and Europe by 2025.
Development of 5G Handsets:
It is likely that the smartphone market will not see meaningful growth until another significant upgrade becomes available to the majority of consumers, not just those capable of purchasing high-end premium handsets. In addition to developments such as foldable handsets and biometrics, smartphone manufacturers are anticipating that the widespread introduction of 5G handsets will serve to reinvigorate the market, in the same way that the introduction of 4G in 2010 boosted the sales of OEMs, such as HTC and Samsung.
‘Right-to-Repair’ Laws to Impact Shipments
The report warns that long-term 5G smartphone shipment revenue will be limited by impending ‘right-to-repair’ legislation in North America and Europe, as more handset users choose to repair older models rather than upgrading to newer generation devices.
Research author Adam Wears explained:
‘The effect of these laws will not be felt initially, as consumers adopt 5G smartphones to leverage the high speeds and reduced latency of 5G networks. Hardware vendors must use this opportunity to build out new device capabilities to encourage consumers to continue regularly upgrading and avoid churn to competitors.’
References:
https://www.juniperresearch.com/document-library/white-papers/how-to-monetise-future-5g-services
https://www.juniperresearch.com/researchstore/devices-technology/5g-smartphones-research-report
Triangle Communications replaces Huawei gear with Mavenir 4G/5G Open RAN radios and software
Montana service provider Triangle Communications is swapping out Huawei gear from its network and implementing 4G/5G open RAN products from upstart tech vendor Mavenir.
Late October is the target timeline as to when the FCC’s rip and replace reimbursement program opens. However, Triangle Communications is already at work to overhaul equipment for its fixed wireless access service. Texas-based Mavenir was chosen for Triangle’s entire network replacement and will act as systems integrator for the project, which qualifies for the FCC funding.
“This is a complete network swap out, so everything in the entire network from core to RAN [radio access network] and replacing it all with virtualized solutions,” Mavenir’s Sr VP John Baker said in an interview with Fierce Wireless.
Mavenir is providing a containerized evolved packet core (vEPC) IMS, open virtualized RAN (Open vRAN) compliant with O-RAN Alliance specifications for open interfaces, and the Mavenir Webscale platform that will enable Triangle to run applications on private, public or hybrid clouds.
It’s deploying the O-RAN Alliance 7.2 open interfaces for the 4G-LTE radios. All of the equipment will also be 5G ready. Triangle is using band 12/700 MHz spectrum.
Once Triangle gets equipment that’s virtualized up and running, Mavenir said the operator’s ability to respond to changes and the market should be significantly faster. It’s notable that the Triangle is planning to deploy open RAN architecture and technology.
In filings with the FCC, Triangle said that it doesn’t see any disadvantages in taking an open RAN approach. According to an April filing (PDF), the service provider’s own research “found ORAN equipment to be competitively priced and fully functional compared to legacy vendors’ equipment options which lock you into always using their equipment.”
“This will be the first network that will be deployed using Mavenir designed radios,” Baker said, and the first of several Mavenir-branded commissioned radios the software vendor plans to introduce over the next couple of quarters. Mavenir has done radios before, but it’s the first the vendor commissioned, designed, manufactured, and deployed in the U.S. market and for U.S. frequency bands.
As an open RAN vendor, and vocal champion, Mavenir has been clear on its stance of the need for U.S.-based radio suppliers in a market currently dominated by Ericsson and Nokia as RAN vendors.
Triangle and Mavenir did not disclose the value of their new deal, but the companies said Triangle’s core network swap-out is underway and that work on the radio access network (RAN) would stretch into next year.
Perhaps the most noteworthy element in Mavenir’s deal with Triangle is that it encompasses both the company’s hardware and software. Mavenir entered the RAN hardware business (mostly radios which are outsourced to Asian suppliers) in order to complement its existing software offerings.
Mavenir last year described its new open RAN hardware strategy as an attempt to “break the incumbent’s monopoly in the global market.” But the company’s efforts also highlight the complexity of the open RAN market considering open RAN technologies are intended to allow operators to mix and match equipment from a variety of vendors rather than buying everything from one source.
This could be the first of many U.S. ongoing “rip and replace” program as the FCC’s program to eliminate Huawei equipment gathers steam.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
Triangle Communications Serving Area in Montana:
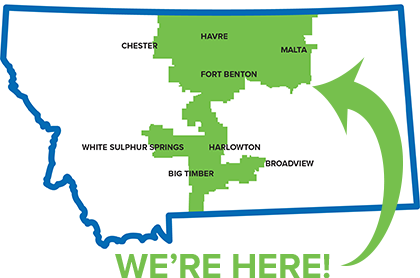
Triangle Telephone Cooperative (TTC) is a company owned by its members. The cooperative was incorporated on March 24, 1953 in Havre, Montana by rural residents of Central Montana. In 1994, TTC purchased 13 exchanges from US West (now CenturyLink/Lumen Technologies) and formed a subsidiary named Central Montana Communication (CMC). Triangle Communications is the name TTC and its subsidiaries have chosen to do business as since 2008.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.fiercewireless.com/tech/mavenir-swaps-out-triangle-s-huawei-gear-for-open-ran
https://itstriangle.com/about-us
Kagan: U.S. Broadband Market Continues to Grow
The U.S. is still experiencing robust growth in fixed broadband connections, driven predominately by the cable market, according to a new report published this week. Meanwhile, download speeds are increasing faster than expected due to cable companies and new telco FTTH deployments.
U.S. broadband gains illustrated durable demand for wireline connections in the second quarter, allaying fears of a 2021 hangover, according to Kagan, a media research group within S&P Global Market Intelligence. While the 945,000 new broadband subs in second quarter 2021 fall short of the year-ago boom, that increase far exceeds the second-quarter 2019 figure that cable operators have been pointing to as a more likely template for current-year success.
The combined residential cable, telco and satellite broadband subscribers topped 109.2 million at the end of the second quarter, up 4.3% annually with nearly 4.5 million net adds year over year, according to Kagan’s full industry estimates.
The U.S. broadband market soared in the first half of 2020 as Covid-19 drove working from home to new levels and customers felt the need for more reliable – and faster – Internet connections. Kagan last year noted that the number of residential wireline subscribers with a broadband service of 100 Mbps or more increased by 5.5% in the first six months of 2020, compared with end-2019.

Additional takeaways from Kagan’s Q2 2021 report:
- Cable subscriber growth in the first half was down from the outsized gains of the pandemic-boosted demand for connectivity. But with 1.9 million residential and commercial net adds year-to-date, cable accounted for 96% of broadband customer gains across the U.S. cable, telco and satellite segments in the first six months of 2021.
- The surging enthusiasm for FTTH upgrades is boosting telco wireline broadband net adds, albeit at relative magnitudes. While the segment’s residential net adds in the second quarter pale in comparison to cable’s growth, it represents a dramatic improvement over the second quarter track record since 2016.
- Combined, the established satellite broadband providers lost 24,000 U.S. subscribers while Starlink begins to establish early momentum.
Kagan declined to share figures for growth in net broadband additions for Q2 last year, simply stating that the 2021 numbers “fall short of the year-ago boom.” However, Q2 this year was far ahead of the same period in 2019, which it – and the industry itself – would serve as a more accurate benchmark for future growth. In the second quarter of 2019, wireline broadband net adds came in at 339,000.
The overall residential broadband market in the US reached 109.2 million subscribers at the end of June, an increase of 4.3% year-on-year; net adds over the 12 months hit nearly 4.5 million. Again, Kagan did not provide comparative figures. As per the above chart, residential broadband penetration is now above 83%, rising to 84.5% if satellite broadband is included.
The cable companies are still leading the U.S. broadband market. 1.9 million net additions in the first half of the year across the residential and commercial sectors give cablecos/MSOs a 96% share, leaving the telco and satellite providers sharing the remaining 4%, or just under 80,000 customers.
With the satellite broadband companies together losing 24,000 customers over that period, that means the telcos probably signed up at least 100,000 new customers in the first half of 2021.
The Need for Speed:
As of June 30, Kagan estimates that 78.4% of residential wireline subscribers took download speeds of 100Mbps and above. With speed and bandwidth at the forefront of consumers’ minds, the 1Gbps tier logged the largest increase.
Subscribers taking 1 Gig or higher rose to an estimated 7.8% of the residential broadband universe in the second quarter of 2020, up from 4.3% at year-end 2019.
The under 25 Mbps tier fell to 2.7% of wireline broadband households or 2.8 million subscribers for whom slower speeds likely impeded in-home online activities, including entertainment, during the pandemic. The telco sector, still somewhat held back by legacy copper systems, accounted for the vast majority of the lower end speed category, with an estimated 87.2% of all wireline broadband subscribers in the below 25 Mbps category.
References:
https://telecoms.com/511015/no-covid-hangover-in-us-broadband-market-yet/