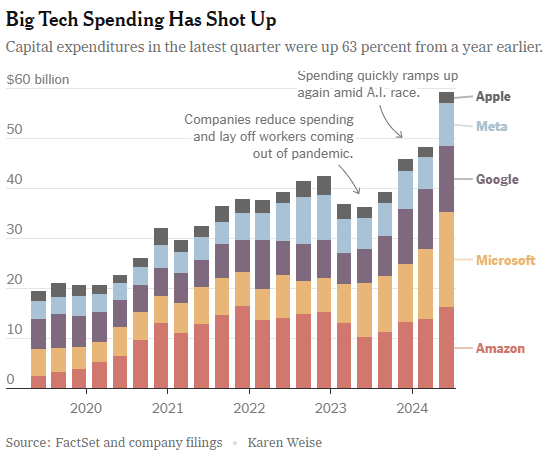
Amazon
AI wave stimulates big tech spending and strong profits, but for how long?
Big tech companies have made it clear over the last week that they have no intention of slowing down their stunning levels of spending on artificial intelligence (AI), even though investors are getting worried that a big payoff is further down the line than most believe.
In the last quarter, Apple, Amazon, Meta, Microsoft and Google’s parent company Alphabet spent a combined $59 billion on capital expenses, 63% more than a year earlier and 161 percent more than four years ago. A large part of that was funneled into building data centers and packing them with new computer systems to build artificial intelligence. Only Apple has not dramatically increased spending, because it does not build the most advanced AI systems and is not a cloud service provider like the others.
At the beginning of this year, Meta said it would spend more than $30 billion in 2024 on new tech infrastructure. In April, he raised that to $35 billion. On Wednesday, he increased it to at least $37 billion. CEO Mark Zuckerberg said Meta would spend even more next year. He said he’d rather build too fast “rather than too late,” and allow his competitors to get a big lead in the A.I. race. Meta gives away the advanced A.I. systems it develops, but Mr. Zuckerberg still said it was worth it. “Part of what’s important about A.I. is that it can be used to improve all of our products in almost every way,” he said.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
This new wave of Generative A.I. is incredibly expensive. The systems work with vast amounts of data and require sophisticated computer chips and new data centers to develop the technology and serve it to customers. The companies are seeing some sales from their A.I. work, but it is barely moving the needle financially.
In recent months, several high-profile tech industry watchers, including Goldman Sachs’s head of equity research and a partner at the venture firm Sequoia Capital, have questioned when or if A.I. will ever produce enough benefit to bring in the sales needed to cover its staggering costs. It is not clear that AI will come close to having the same impact as the internet or mobile phones, Goldman’s Jim Covello wrote in a June report.
“What $1 trillion problem will AI solve?” he wrote. “Replacing low wage jobs with tremendously costly technology is basically the polar opposite of the prior technology transitions I’ve witnessed in my 30 years of closely following the tech industry.” “The reality right now is that while we’re investing a significant amount in the AI.space and in infrastructure, we would like to have more capacity than we already have today,” said Andy Jassy, Amazon’s chief executive. “I mean, we have a lot of demand right now.”
That means buying land, building data centers and all the computers, chips and gear that go into them. Amazon executives put a positive spin on all that spending. “We use that to drive revenue and free cash flow for the next decade and beyond,” said Brian Olsavsky, the company’s finance chief.
There are plenty of signs the boom will persist. In mid-July, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, which makes most of the in-demand chips designed by Nvidia (the ONLY tech company that is now making money from AI – much more below) that are used in AI systems, said those chips would be in scarce supply until the end of 2025.
Mr. Zuckerberg said AI’s potential is super exciting. “It’s why there are all the jokes about how all the tech C.E.O.s get on these earnings calls and just talk about A.I. the whole time.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
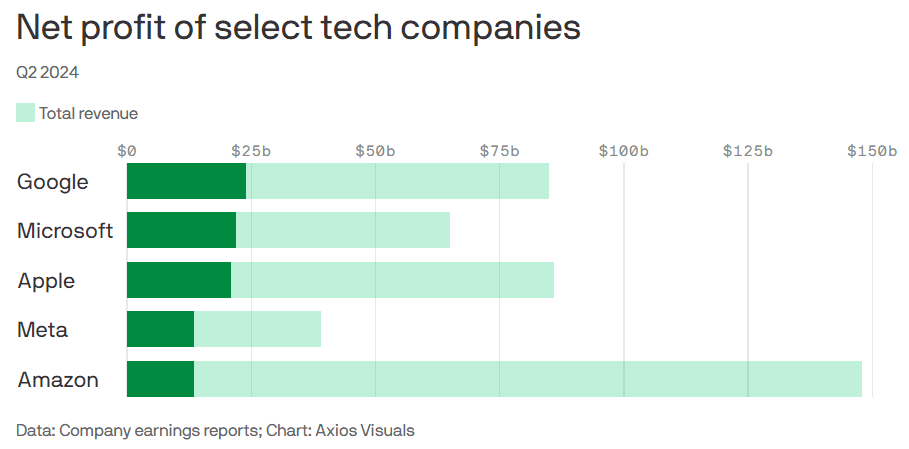
Big tech profits and revenue continue to grow, but will massive spending produce a good ROI?
Last week’s Q2-2024 results:
- Google parent Alphabet reported $24 billion net profit on $85 billion revenue.
- Microsoft reported $22 billion net profit on $65 billion revenue.
- Meta reported $13.5 billion net profit on $39 billion revenue.
- Apple reported $21 billion net profit on $86 billion revenue.
- Amazon reported $13.5 billion net profit on $148 billion revenue.
This chart sums it all up:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/08/02/technology/tech-companies-ai-spending.html
https://www.axios.com/2024/08/02/google-microsoft-meta-ai-earnings
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/grace-hopper-superchip/
AI Frenzy Backgrounder; Review of AI Products and Services from Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Google and Meta; Conclusions
IHS Markit: Microsoft #1 for total cloud services revenue; AWS remains leader for IaaS; Multi-clouds continue to form
Following is information and insight from the IHS Markit Cloud & Colocation Services for IT Infrastructure and Applications Market Tracker.
Highlights:
· The global off-premises cloud service market is forecast to grow at a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16 percent, reaching $410 billion in 2023.
· We expect cloud as a service (CaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) to be tied for the largest 2018 to 2023 CAGR of 22 percent. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and software as a service (SaaS) will have the second and third largest CAGRs of 14 percent and 13 percent, respectively.
IHS Markit analysis:
Microsoft in 2018 became the market share leader for total off-premises cloud service revenue with 13.8 percent share, bumping Amazon to the #2 spot with 13.2 percent; IBM was #3 with 8.8 percent revenue share. Microsoft’s success can be attributed to its comprehensive portfolio and the growth it is experiencing from its more advanced PaaS and CaaS offerings.
Although Amazon relinquished its lead in total off-premises cloud service revenue, it remains the top IaaS provider. In this very segmented market with a small number of large, well-established providers competing for market share:
• Amazon was #1 in IaaS in 2018 with 45 percent of IaaS revenue.
• Microsoft was #1 for CaaS with 22 percent of CaaS revenue and #1 in PaaS with 27 percent of PaaS revenue.
• IBM was #1 for SaaS with 17 percent of SaaS revenue.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Multi-clouds [1] remain a very popular trend in the market; many enterprises are already using various services from different providers and this is continuing as more cloud service providers (CSPs) offer services that interoperate with services from their partners and their competitors,” said Devan Adams, principal analyst, IHS Markit. Expectations of increased multi-cloud adoption were displayed in our recent Cloud Service Strategies & Leadership North American Enterprise Survey – 2018, where respondents stated that in 2018 they were using 10 different CSPs for SaaS (growing to 14 by 2020) and 10 for IT infrastructure (growing to 13 by 2020).
Note 1. Multi-cloud (also multicloud or multi cloud) is the use of multiple cloud computing and storage services in a single network architecture. This refers to the distribution of cloud assets, software, applications, and more across several cloud environments.
There have recently been numerous multi-cloud related announcements highlighting its increased availability, including:
· Microsoft: Entered into a partnership with Adobe and SAP to create the Open Data Initiative, designed to provide customers with a complete view of their data across different platforms. The initiative allows customers to use several applications and platforms from the three companies including Adobe Experience Cloud and Experience Platform, Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Azure, and SAP C/4HANA and S/4HANA.
· IBM: Launched Multicloud Manager, designed to help companies manage, move, and integrate apps across several cloud environments. Multicloud Manager is run from IBM’s Cloud Private and enables customers to extend workloads from public to private clouds.
· Cisco: Introduced CloudCenter Suite, a set of software modules created to help businesses design and deploy applications on different cloud provider infrastructures. It is a Kubernetes-based multi-cloud management tool that provides workflow automation, application lifecycle management, cost optimization, governance and policy management across cloud provider data centers.
IHS Markit Cloud & Colocation Intelligence Service:
The bi-annual IHS Markit Cloud & Colocation Services Market Tracker covers worldwide and regional market size, share, five-year forecast analysis, and trends for IaaS, CaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and colocation. This tracker is a component of the IHS Markit Cloud & Colocation Intelligence Service which also includes the Cloud & Colocation Data Center Building Tracker and Cloud and Colocation Data Center CapEx Market Tracker. Cloud service providers tracked within this service include Amazon, Alibaba, Baidu, IBM, Microsoft, Salesforce, Google, Oracle, SAP, China Telecom, Deutsche Telekom Tencent, China Unicom and others. Colocation providers tracked include Equinix, Digital Realty, China Telecom, CyrusOne, NTT, Interion, China Unicom, Coresite, QTS, Switch, 21Vianet, Internap and others.