Year: 2020
Spain waits for 700MHz 5G auction as coronavirus impacts supply chains
Spain’s telecom market is one of the largest in Europe, supported by a population of more than 46 million. Mobile penetration is on a par with the European average and there remains room for further growth, particularly in the mobile broadband segment which has been supported by continuing investment in infrastructure among operators. With LTE almost universally available in Spain, the focus among operators has shifted to services based on 5G. Vodafone Spain was the first operator to launch a 5G network, in June 2019.
The other wireless network operators planned to wait until after the auction of spectrum in the 700MHz band. Last month, the Spanish government confirmed that it will delay a planned auction of 5G spectrum due to the outbreak of the novel coronavirus in the country. The government expected to award frequencies in the 700 MHz band, which had been previously used by Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT) services. A new date for the spectrum auction will be announced once the measures adopted by the government to contain the pandemic come to an end.
[Note that there have also been 5G spectrum auctions delayed in a number of European countries including Portugal, Austria, France, and the Czech Republic.]
In July 2018, the Spanish government raised a total of EUR 438 million through the sale of 5G frequencies by auctioning spectrum in the 3.6 GHz to 3.8 GHz range, which will be key for the launch of commercial 5G services in the country. The government had set a reserve price of EUR 100 million for the 5G spectrum.
Spanish carriers Movistar, Orange, Vodafone all acquired 5G spectrum after 34 rounds of bidding. These carriers submitted bids for a total of 200 megahertz of spectrum, which was sold under 20-year licenses for lots of five megahertz at a minimum price of EUR 2.5 million each.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/66738669/acastro_180430_1777_5G_0001.0.0.jpg)
The fixed-line broadband sector has also been backed by investment in fiber infrastructure, enabling providers to develop improved bundled services and to compete more effectively. The regulator has fostered competition by providing access to Telefonica’s DSL and FTTP networks, while network sharing agreements have meant that Orange Spain, Vodafone Spain and MsMvil have become significant operators. By the beginning of 2020 fibre accounted for about 67% of all fixed broadband connections. Telefonica alone expected to provide complete FTTP coverage by 2024.
The outbreak of the Coronavirus in 2020 is having a significant impact on production and supply chains globally. During the coming year the global telecoms sector to various degrees is likely to experience a downturn in mobile device production, while it may also be difficult for network operators to manage workflows when maintaining and upgrading existing infrastructure. Overall progress towards 5G may also be postponed or slowed down in some countries.
On the consumer side, spending on telecoms services and devices is under pressure from the financial effect of large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes. However, the crucial nature of telecom services, both for general communication as well as a tool for home-working, will offset such pressures. In many markets the net effect should be a steady though reduced increased in subscriber growth.
Although it is challenging to predict and interpret the long-term impacts of the COVID-19 crisis as it develops, these have been acknowledged in the industry forecasts. As government agencies and regulators react to the pandemic crisis, they will try to ensure that citizens can continue to make optimum use of telecom services. This can be reflected in subsidy schemes and the promotion of telehealth and tele-education, among other solutions.
Ultimately, however, the full impact of the pandemic is still unknown. It’s unclear when European spectrum auctions may finally go ahead, or when governments may lift the restrictions that are making work to deploy physical infrastructure challenging. And amidst the economic uncertainty caused by the crisis and people sequestered at home, it’s no wonder nobody can fully commit to rollout schedules made before the crisis hit.
Deloitte revises Tech, Media and Telecom (TMT) predictions for 2020
Deloitte just revised their predictions on the five topics most relevant for telecom due to the COVID-19 pandemic:
Our original prediction for 2020 smartphone sales was $484 billion, up 5.8% from 2019. There are a wide range of forecasts coming out after a weak Q1 and an anticipated collapse in Q2, but a 10% global decline for the full year now looks probable.
We had predicted that the smartphone multiplier (the revenues of things that accompany smartphones, such as apps, ads and accessories) would be $459 billion in 2020, and we now expect that to be $393 billion. Longer term, and post-pandemic, we would expect the market for both smartphones and the things that accompany them to return to growth, with the multiplier growing even faster than smartphone sales themselves.
Not all smartphones have dedicated artificial intelligence (AI) chips (neural processing units, or NPUs, worth an estimated $3 per phone)…but we predicted about a third of phones would have NPUs in 2020, accounting for an estimated 500 million chips out of a total 750 million edge AI processors. We have cut that by 100 million units, to only 650 million, but that will still be more than double the number of phones with edge AI chips that sold in 2017. The presence or absence of an edge AI chip has significant implications on data transmitted, as well as on privacy and security, so this drop will matter.
Longer term, our 2024 call for 1.6 billion edge AI chips still looks likely, and could even be low as new edge AI chips – that are even smaller and cheaper than smartphone NPUs, which in turn are smaller and cheaper than the chips used in data centres for AI training and inference – are hitting the market now. These will not be in phones, but will be in millions (billions, over time) of sensors, Internet of Things machinery, and smart city/smart home solutions.
Although 2020 deployments/launches of public 5G networks have been mixed because of the pandemic (faster in some countries, but delays in others), our prediction for private 5G trials and pilots looks like it will be exceeded. We’re taking our prediction for private 5G tests from “over 100” for the year to “under 1000” based on many trials of private 5G solution just in Q1 of 2020 that we are aware of. It is difficult to say if the more rapid pace of private 5G trials is connected with the pandemic. Testing a new technology while a factory is otherwise idle might make sense, and we have seen some private 5G trials in medical and logistics/distribution verticals, which could well have been accelerated by COVID-19 stresses.
We are moving our prediction for the number of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) data satellites in orbit by the end of 2020 from “more than 700” to “more than 1,000.” OneWeb went bankrupt, but before it did it launched 68 satellites in Q1-2020, and Starlink has placed 300 satellites in orbit as of April, with another 60 per month expected for the balance of the year. Partial service is expected late this year. Hence, we expect more LEO satellites by the end of this year.
Once again, it is hard to know how directly the pandemic is influencing the more rapid deployment of LEO sats. But as hundreds of millions of people work and learn from home, as governments try to fill coverage gaps for rural broadband, and as carriers look for more backhaul for the increased traffic due to people staying (and streaming) at home…demand for data from orbit looks stronger than it did when we wrote the original prediction.
All that streaming video is running relatively well over global telecoms networks so far but will likely need help from Content Delivery Networks (CDNs.) We originally called this market to be up 25% to $14 billion, and it now looks like 30-40% is possible for the year, or up to $15.5 billion.
Many clients have asked what we think the impact of COVID-19 will be for telemedicine and telework and the rollout of 5G due to health concerns. No comment as of now…but tune in December 8, 2020 for our 2021 TMT Predictions report, where all three topics will be addressed!

References:
Open RAN Policy Coalition: U.S. attempt to exclude Chinese 5G network equipment vendors?
Believe it or not, there is now a third Open RAN consortium, joining the ORAN Alliance and TIP OpenRAN. Even more astonishing is that none of the three consortiums have any liaison or co-operation with ITU-R or ITU-T which are standardizing 5G as IMT 2020 radio and non-radio aspects, respectively. Nor do these consortiums liaise with 3GPP which is the REAL mover and shaker developing 5G specs that are implementable.
Thirty-one global technology companies have launched the Open RAN Policy Coalition to promote policies that will advance the adoption of open and interoperable solutions in the Radio Access Network (RAN) as a means to create innovation, spur competition and expand the supply chain for advanced wireless technologies including 5G.
Open RAN Policy Coalition founding members include Airspan, Altiostar, AT&T, AWS, Cisco, CommScope, Dell, DISH Network, Facebook, Fujitsu, Google, IBM, Intel, Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Microsoft, NEC Corporation, NewEdge Signal Solutions, NTT, Oracle, Parallel Wireless, Qualcomm, Rakuten Mobile, Samsung Electronics America, Telefónica, US Ignite, Verizon, VMWare, Vodafone, World Wide Technology, and XCOM-Labs.
“Open RAN networks are a significant departure from the traditional industry model and legislators need to know the advantages and how government actions can help accelerating the development and deployment of open and interoperable solutions,” said Thierry Maupilé, Altiostar’s executive vice president, in a statement.
“As evidenced by the current global pandemic, vendor choice and flexibility in next-generation network deployments are necessary from a security and performance standpoint,” said Diane Rinaldo [1.], Executive Director, Open RAN Policy Coalition. “By promoting policies that standardize and develop open interfaces, we can ensure interoperability and security across different players and potentially lower the barrier to entry for new innovators.” Yet that is exactly what the O-RAN Alliance and TIP OpenRAN project were set up to do.
Note 1. Ms. Rinaldo was until recently the deputy assistant secretary for communications and information at the US Department of Commerce (DoC).
In past generations of mobile networks, the networks were deployed using fully integrated cell sites, where the radios, hardware and software were provided by a single manufacturer as a closed proprietary solution. Today, the industry is working towards standards and technical specifications that define open interfaces between the radios, hardware and software so that networks can be deployed using more than one vendor.
Multi-vendor deployments enable a more competitive marketplace and give network operators greater ability to manage their networks and flexibility to draw on the innovations of multiple suppliers to upgrade their infrastructure with the latest technology.
Using multiple interoperable suppliers also allows operators to potentially move more quickly to replace or address vulnerable network equipment when reacting to threats, and shift network capacity on demand.
The coalition believes that the U.S. Federal Government has an important role to play in facilitating and fostering an open, diverse and secure supply chain for advanced wireless technologies, including 5G, such as by funding research and development, and testing open and interoperable networks and solutions, and incentivizing supply chain diversity.
Isn’t that a clear indication the coalition has and will continue to exclude Chinese vendors like Huawei and ZTE?
The launch of the new group, interestingly, comes several weeks after a bipartisan group of US senators proposed investing more than $1 billion in open RAN technologies. Under their plans, the funds would come from spectrum auction proceeds and be managed by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rakuten leads the way forward for Open RANs:
Rakuten Mobile has deployed a version of Open RAN in Japan. The greenfield virtualized, open RAN build was made available for commercial LTE services in April with plans to move to 5G on the virtualized infrastructure. A number of Rakuten Mobile’s vendors, including NEC, are members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition. Further, Rakuten Mobile has expressed interest in providing its network model to other operators interested in following a similar virtualized OPEN RAN 5G network.
However, analysts have remained skeptical that Rakuten can challenge Japan’s old guard with a cloud-only mobile network. In a research note published in March, shortly before Rakuten’s launch, Atul Goyal, an analyst with Jefferies, flagged “numerous connectivity issues” when Rakuten introduced its beta service in late 2019. “A poor-quality, low-price network is likely to fail in Japan,” he wrote. Its failure would be a huge setback for open RAN.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Parallel Wireless is on board:
Parallel Wireless CEO Steve Papa told RCR Wireless that the open RAN business model matches the generational shifts in cellular. “The economics of a coverage technology and architecture don’t scale well as a capacity architecture. The entire business models of the incumbent vendors don’t work and don’t map to what the people deploying the equipment require given the economic realities.”
Papa continued to say that open RAN “is exposing this to more innovators to participate, which is good. But more importantly, the U.S. government is waking up to its role in supporting the semiconductor market.” He noted the Made in China 2025 focus on developing semiconductor expertise and other moves he characterized as “a state actor tipping to playing field…Our commercial market in communications infrastructure equipment is being distorted by a state actor. We can let that happen or we can counter it in a similar way.”
“We see this coalition as an important addition to the standards work that O-RAN Alliance is doing and also global deployments driven by TIP,” said Steve Papa, the CEO of Parallel Wireless, in comments emailed to Light Reading.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20200505/policy/open-ran-policy-coalition-launches
TIP OpenRAN and O-RAN Alliance liaison and collaboration for Open Radio Access Networks
Vodacom launches 5G in South Africa-mobile and fixed wireless services
by Paula Gilbert, Editor, Connecting Africa
Vodacom has officially launched 5G in three cities in South Africa, as promised earlier this year.

Johannesburg-headquartered Vodacom said in an emailed statement on May 4th that it had switched on its live 5G mobile network in Johannesburg, Pretoria and Cape Town – with further rollouts planned for other parts of the country.
The network is intended to support both mobile and fixed wireless services and is currently available on 20 live 5G sites, 18 of which are in Gauteng and two in the Western Cape.
“Vodacom’s 5G launch in South Africa comes at an important time as it will help us improve our network efficiency during the COVID-19 national state of disaster,” said Vodacom Group’s CEO, Shameel Joosub.
Vodacom was recently assigned temporary spectrum by the Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) for the duration of South Africa’s national state of disaster, including 50MHz in the 3.5GHz band, which has been used to fast-track its 5G launch.
Joosub said the temporary spectrum has already mitigated the network congestion Vodacom experienced during the five-week lockdown period in the country.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From Vodacom’s press release:
Vodacom is currently offering the following 5G enabled devices, which customers can use to experience the 5G network within the coverage area of the 20 live sites (listed under Notes to Editors):
- Smartphones : LG V50 5G smartphone
- Fixed Wireless Access Routers: Huawei 5G CPE PRO
Customers can check if they are in a 5G coverage area on the Vodacom website (https://www.vodacom.co.za/vodacom/services/internet/5g ). They can then either sign up for a new 5G device deal or upgrade online. The new 5G device will be delivered to the customer’s home during the national lockdown period.
5G improves significantly on 4G in three key areas:
1. Faster speeds:
In comparison to 4G, peak speeds on 5G will increase significantly. 5G will enable fibre-like speeds using the mobile network. This will be extremely useful to download media content like 4K and even 8K movies in seconds. The higher speeds from 5G will also enable entirely new applications in future like augmented and Virtual Reality (VR) which will be helpful to realise new applications such as e-education and also new forms of entertainment like watching a sports game or music concert live in VR from home.
2. Lower latency & better reliability:
Latency is the time it takes for devices to send and receive signals between each other. Latency is very important for applications which require near real time responses, for example, between the user device and a cloud server used in gaming. In comparison to 4G where latencies are typically between 20-30 milliseconds, 5G can support latencies as low as 1 millisecond.
The lower latency from 5G will also enable entirely new applications in future such as remote robotic surgery, where decisions must be made by the remote surgeon and sent back to the surgery robot in near real time.
3. More capacity:
5G networks can also provide much more capacity for data. 5G uses spectrum in a much more efficient manner than 4G technology and is able to fit more data into the same amount of spectrum.
5G devices can connect many more “things” to the network at the same time, enabling the realization of new applications such as smart homes and smart cities. 5G is also more efficient than 4G in terms of the energy required per bit of data which is transmitted or received.
Vodacom was the first network operator to launch a 5G commercial service in Africa in Lesotho in 2018 and was also first to bring 2G, 3G and 4G services to South Africa. The widespread rollout of 5G will support the Government’s 4IR objectives in future, and will facilitate the creation of an entirely new technologically enabled world. 5G supports entirely new applications which will enable a much smarter and more convenient way of both living, working and playing and which current 3G and 4G networks might not be able to support.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.vodacom.com/news-article.php?articleID=7485
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom Cooperate on 5G/ICT to combat COVID-19 Pandemic
SK Telecom held a video conference with Deutsche Telekom to deepen the two companies’ cooperation in information and communication technologies (ICT) to alleviate challenges caused by the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
Several executives of the two companies gathered for a video conference on Wednesday and discussed their cooperation on 5G network, mobile edge computing and artificial intelligence technology. SK Telecom said it would also share its experience of COVID-19 countermeasures, including remote work solutions and online recruitment procedures.
The South Korean telecom firm added that it was going to dispatch a group of engineers to Germany to share their know-how in managing 5G network infrastructure, as well as measures to handle heavy traffic loads on communications networks. The two companies also discussed measures to improve cloud-delivered solutions to prepare for the post-coronavirus world.
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom have been working closely since 2016 to lead innovations in ICT. SK Telecom has been sharing its diverse fixed and wireless technologies with Deutsche Telekom.
Especially, with the outbreak of the novel coronavirus throughout the globe, network infrastructure and online solutions are becoming ever more important to seamlessly support people’s new way of living. In response to this, executives from SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom discussed detailed plans to utilize their innovative ICT, including 5G, artificial intelligence (AI) and mobile edge computing (MEC), to help improve the current situation and thoroughly prepare for the post-coronavirus era.
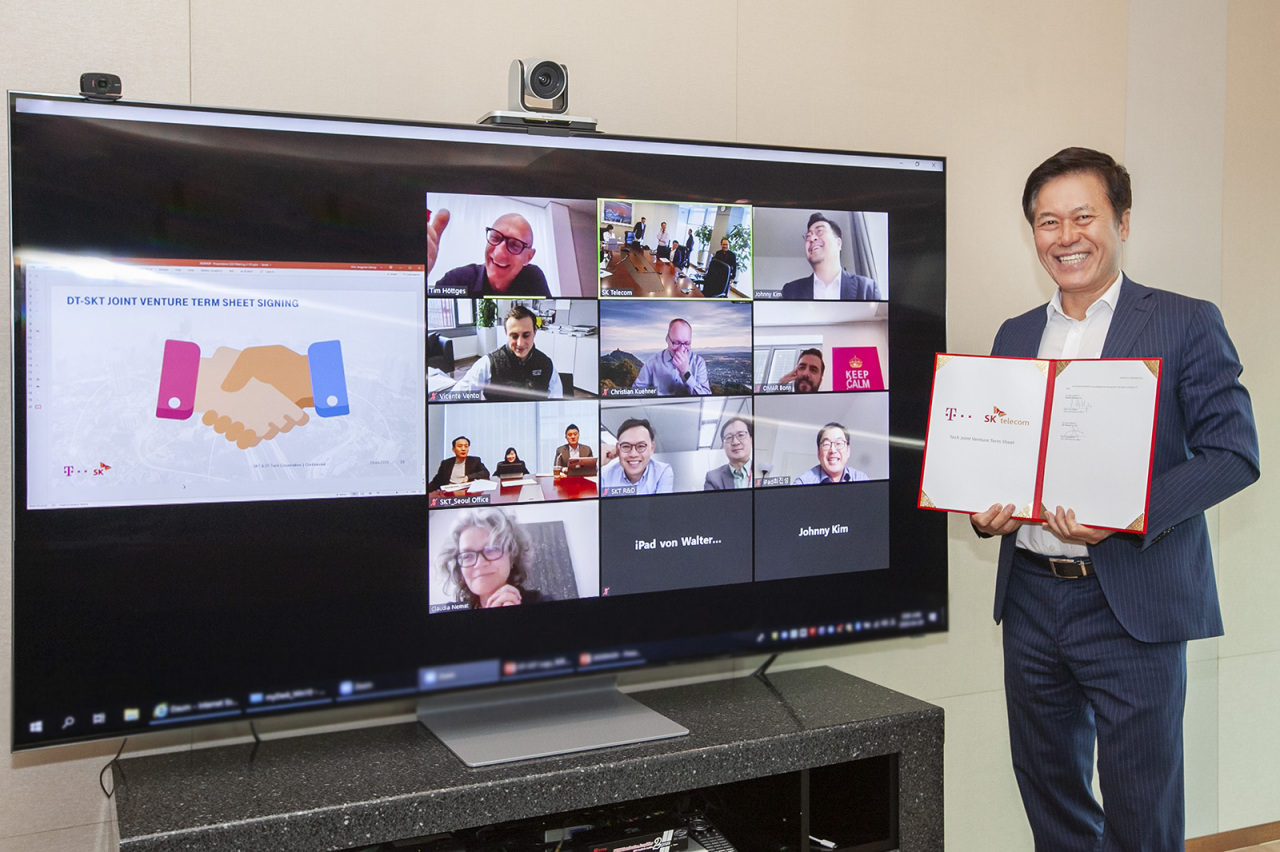

SK Telecom CEO Park Jung-ho poses for pictures after the video conference with Deutsche Telekom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
On April 29, 2020, the two companies signed a term sheet for a technology joint venture that will launch within this year. Through this joint venture, SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom will collaborate to expand the global 5G ecosystem by accelerating 5G deployment in Europe. SK Telecom has already provided its 5G repeaters to Deutsche Telekom to support its customer trial for 5G indoor coverage in Germany and plans to promote the adoption of its 5G repeaters in Europe. The two companies will also develop diverse MEC use cases and AI-powered solutions including immersive video calling and smart meeting solutions.
Moreover, SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom agreed to exchange their technological expertise through Network Engineer Exchange Program once the situation improves. Through the program, SK Telecom’s network engineers will be dispatched to Germany to share their knowhow in 5G network commercialization and operation, as well as their experience in handling data traffic surges caused by a dramatic increase in the number of people working or learning from home.
The two companies also decided to increase Deutsche Telekom Capital Partners’ investment in Korean 5G startups as well as global ventures with competitive online solutions such as video conferencing platforms and cloud call centers.
“The current global crisis can be effectively addressed if we, ICT companies, join forces with our technology and expertise,” said Park Jung-ho, President and CEO of SK Telecom. “SK Telecom will continue to work closely with Deutsche Telekom to flawlessly support our customers in this new normal era brought by the coronavirus.”
About SK Telecom
SK Telecom is Korea’s leading ICT company, driving innovations in the areas of mobile communications, media, security, commerce and mobility. Armed with cutting-edge ICT including AI and 5G, the company is ushering in a new level of convergence to deliver unprecedented value to customers. As the global 5G pioneer, SK Telecom is committed to realizing the full potential of 5G through ground-breaking services that can improve people’s lives, transform businesses, and lead to a better society.
SK Telecom boasts unrivaled leadership in the Korean mobile market with over 30 million subscribers, which account for nearly 50 percent of the market. The company now has 47 ICT subsidiaries and annual revenues approaching KRW 17.8 trillion.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit the Linkedin page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-telecom.
Media Contact
Irene Kim
SK Telecom Co., Ltd.
+ 82 2 6100 3867
Reference:
http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20200503000101
Empowering Low-Power Wide-Area Networks to Meet the IoT Challenge
by Swarun Kumar, PhD, Assistant Professor – Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University (CMU)
Introduction:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding to connect everyday objects in homes, office buildings, retail stores and factories, impacting sectors as diverse as manufacturing, agriculture and public governance.
While conversations around “5-G and beyond” traditionally focus on faster wireless networks, it is inevitable that the majority of devices connected to future cellular networks will be IoT endpoint. This is primarily due to their sheer scale of deployment. Indeed, massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC) that seeks to connect billions of low-power IoT devices to the cellular network is a pivotal thrust of the 5G vision. It is one of three 5G use cases for IMT 2020, the soon to be completed ITU st of standards for 5G radio (ITU-R) and non radio aspects (ITU-T).
Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LP-WANs) are a leading approach to achieve this objective [1]. LP-WANs allow extremely low power devices connected by 10-year AA batteries to transmit at low speeds (few kbps) to cellular base stations as far as 10 kilometers away. 3GPP’s Narrow Band IoT (NB-IoT) is a leading LP-WAN technology being rapidly deployed for cellular networks. It has been accepted by ITU-R WP5D as part of the IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT submissions from 3GPP, China, Korea, and TSDSI (India). Other other LP-WAN technologies in the unlicensed bands such as LoRa and SIGFOX have also attained strong market traction.
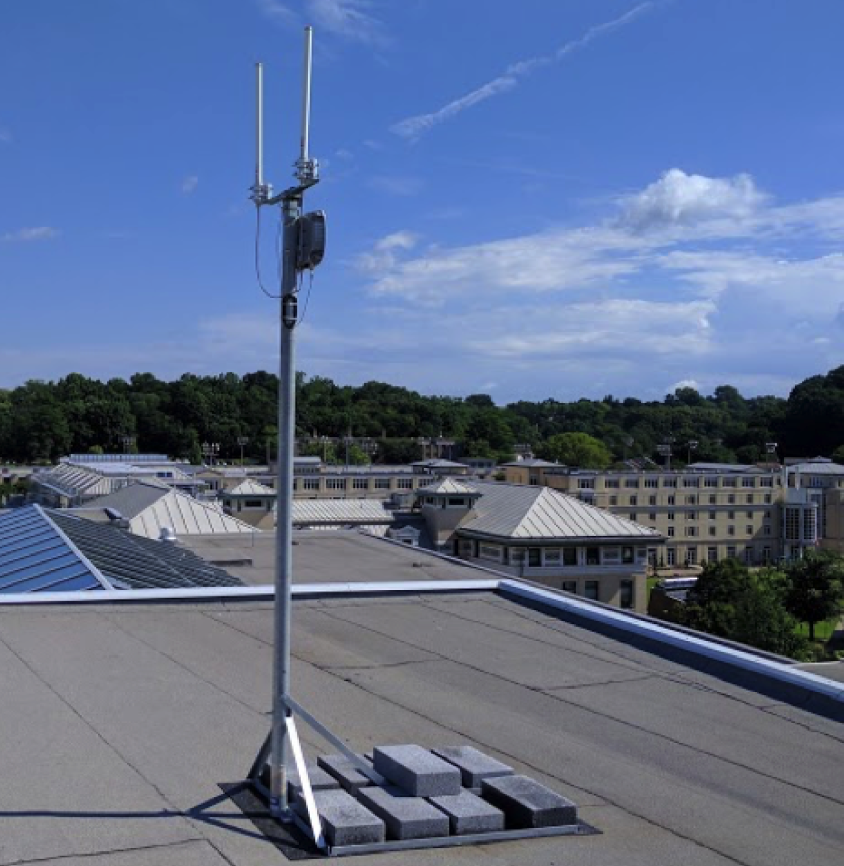

WiTech Lab Project: Pushing the Limits of LP-WANS. Photo credit: Carnegie Mellon University
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
LP-WAN Performance Analysis:
In reality, there remains a large gap between the promised performance of LP-WANs in theory and their performance on the field, particularly in city environments. At Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), we have built a wide-area LP-WAN testbed in our campus and surrounding neighborhoods, spanning much of the City of Pittsburgh [2].
Our findings show that the range of LP-WANs is significantly impacted by large buildings and obstructions, to often less than a kilometer, providing performance significantly below the 10 kilometer performance advertised in more suburban and rural spaces. More problematic is that LP-WAN performance is further degraded by severe collisions between radios deployed at large scale as they are too energy-starved to coordinate prior to transmission. Further, even minor changes to configuration such as choice of transmit frequency can severely degrade device battery-life if not carefully explored and chosen. That in and of itself is a battery-intensive task.
Across all these diverse challenges a common thread emerges – devices in LP-WANs are too simple and energy-starved to make complex Physical layer decisions that impact their performance, scalability and battery life. That includes capabilities that have been taken for granted in the traditional mobile phone context.
Our work at the Emerging Wireless Technologies Lab (WiTech) lab at CMU has sought to build next-generation LP-WANs that obtain substantial improvements in range, scale and battery life. Our strategy has been to push complex Physical layer functionalities from the end-user devices to the base station infrastructure and the cloud.
We maintain that redirection of Physical layer functions benefits LP-WANs in three pivotal ways:
- First, it frees low-power clients from the burden of signal processing, simplifying their design and reaping associated battery benefits.
- Second, it allows advanced signal processing and machine learning to be implemented at the much more capable cloud in ways previously never possible at the clients, directly improving end-to-end system performance metrics such as range, scale and battery life.
- Third, it creates the opportunity for programmability – allowing for new optimizations and new services such as location-tracking, sensing, data analytics and beyond to be implemented as software updates in the cloud rather than requiring the deployment of new hardware.
Our results on a 10 square kilometer testbed in the City of Pittsburgh [2] have demonstrated several benefits of our methodology over the years to tackle diverse and fundamental problems in LP-WANs, which have greatly improving scale (by 6x [4]), range (by 3x [1]) and battery life (by 3x [5]) when compared to the state-of-the-art.
Our research work has resulted in several publications [2,3,4,5] at top research venues, including two best paper award winners [2,3].
Expanding the Range Limits of LP-WANs:
Our approach is best understood by focussing our attention on a specific problem – how do we expand the range of LP-WANs particularly in urban settings where their range is extremely limited by buildings that heavily attenuate wireless signals?
The fundamental problem is that the LP-WAN signals from clients deep inside buildings are too weak to decode at any base station, even if within close proximity. Our solution relies on the multiplicity of LP-WAN gateways, specifically with the rapid deployment of femtocells in the cellular context, on street lamps and traffic lights and beyond.
We seek to transfer received signals across base stations to the cloud. Those signals may be individually weak, yet can collectively be coherently combined at the cloud to result in a much stronger signal that can be decoded.
This principle closely mirrors the CloudRAN model which seeks to offload computation at the base stations to the cloud. Yet, a key problem remains in the low-power IoT context – how do base stations know which signals to ship to the cloud if an LP-WAN signal is too weak and noisy to be detected at any base station?
Simply transmitting all received signals to the cloud will be expensive in terms of backhaul bandwidth and immensely wasteful. Our scheme is to build a mechanism to make more intelligent predictions about the presence of weak LP-WAN signals buried underneath the noise at the base stations. We do this by looking for unique and telltale patterns in the noise that correspond to the signal structure of LP-WAN packets. Different from prior work that only looks for these patterns in the preamble (i.e. the beginning) of LP-WAN transmissions, our solution scans the entire packet resulting in greater accuracy.
We further improve our methodology by letting base stations collaboratively share news about packet detection. For instance, if a weak signal from a transmitter is detected by the base station, it alerts its neighbors to transmit signals received at about the same time to the cloud.
Our experiments revealed significant improvements in the range of LP-WANs by a factor of 3x through a wide-area demonstration at Pittsburgh. [That work received the best paper award at ACM/IEEE IPSN 2018 [2] – a major international conference.]
Scaling LP-WAN Deployments:
Beyond physical range, LP-WANs also need to perform at massive scale. ITU has set lofty goals for mMTM communications of as many as a million devices per square kilometer. At these massive scales, LP-WAN devices are likely to interfere with each other rampantly, causing massive data loss.
In part, this is because inexpensive and battery-hungry devices traditionally do not take the classic “listen before you transmit” approach to take turns and therefore lack a mechanism to realize that they are producing interference.
Our solution to address this challenge of rampant interference in LP-WANs at scale turns the low cost of LP-WAN hardware to our advantage. Specifically, we observe that the transmissions from cheap LP-WAN devices often have unique imperfections, such as shifts in frequency or time, depending on hardware manufacturing defects. These defects can then be used as filters to separate signals from multiple devices that interfere with each other.
Given the traditionally narrow bandwidth of LP-WANs, this approach allows us to massively scale up the number of devices that can concurrently transmit. Our paper in SIGCOMM 2017 reports an overall 6-fold improvement in the scale of LP-WAN networks compared to the state-of-the-art.
Maximizing the Battery Life of LP-WAN Devices:
Perhaps the most important requirement of LP-WANs is the need to maximize battery-life. A key selling point of LP-WAN is the ten-year battery life that allows for most consumers of IoT devices to simply not worry about maintenance or recharging of batteries through the lifetime of the device.
Our research has shown that this battery-life cannot be taken for granted, even if the devices are installed statically at a fixed location for the duration of its life. For instance, our work in NSDI 2020 [5] has shown that carefully selecting the frequency of operation of a device can substantially improve the battery life of a device, by 230%, rather than choosing a default frequency.
We presented a method and mechanism to intelligently configure LP-WAN devices using intelligence at the cloud, without requiring any advanced computation at the devices themselves, barring the occasional transmission of a beacon packet. Our award-winning paper at IPSN 2020 [3] also showed how teams of individually wimpy LP-WAN devices can collectively convey useful information without draining the battery of each device significantly.
More importantly, such information can be conveyed very quickly within the duration of one LP-WAN packet to then be processed by machine learning algorithms running on cloud resident compute servers. We showed how such a system could have wide-ranging applications from diagnosis of faults in sensor networks to rapid and large-scale spatial tracking of wildfires.
The Future of IoT is in the services it enables:
While much of our research to date has focussed on delivering the energy consumption and communication performance that LP-WANs promise, we believe that LP-WANs can play a pivotal role in shaping the applications that IoT will enable in the future.
Imagine, a postage-stamp sized device that can be used to track the physical location of packages deployed anywhere in the world. Consider how swarms of IoT devices deployed in the city can collectively measure and model vibrations from earthquakes.
Future Work of CMU WiTech lab:
Funded by the prestigious CAREER award from the National Science Foundation, we at the CMU WiTech lab are currently working on intelligently processing LP-WAN signals in the cloud to take a step toward these applications and beyond. We are further devising mechanisms to improve the security and privacy of user data in a world where IoT devices are everywhere around you.
More broadly, we believe that next-generation cellular networks, beyond serving as communication pipes, have the potential to actively shape the applications of the future in the emerging IoT era.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
[1] LPWAN to Application standardization within the IETF, Alan J Weissberger, 2019,
https://techblog.comsoc.org/category/lpwans/
[2] Charm: Exploiting Geographical Diversity Through Coherent Combining in Low-Power
Wide-Area Networks , Adwait Dongare, Revathy Narayanan, Akshay Gadre, Artur Balanuta,
Anh Luong, Swarun Kumar, Bob Iannucci, Anthony Rowe, IPSN 2018 (Best Paper Award)
[3] Quick (and Dirty) Aggregate Queries on Low-Power WANs, Akshay Gadre, Fan Yi, Anthony
Rowe, Bob Iannucci and Swarun Kumar, IPSN 2020 (Best Paper Award)
[4] Empowering Low-Power Wide Area Networks in Urban Settings , Rashad Eletreby, Diana
Zhang, Swarun Kumar, and Osman Yagan, SIGCOMM 2017
[5] Frequency Configuration for Low-Power Wide-Area Networks in a Heartbeat, Akshay Gadre,
Revathy Narayanan, Anh Luong, Swarun Kumar, Anthony Rowe and Bob Iannucci, NSDI 2020
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Swarun Kumar:
Swarun Kumar, PhD is an Assistant Professor at Carnegie Mellon University’s ECE department. His research builds next-generation wireless network protocols and services. Swarun leads the Emerging Wireless Technologies (WiTech) lab at CMU. He is a recipient of the NSF CAREER and Google Faculty Research awards.
Dr. Kumar received the George Sprowls Award for best Ph.D thesis in Computer Science at MIT and the President of India gold medal at IIT Madras.

Photo of Swarun Kumar, PhD and Assistant Professor at CMU
China Mobile and Huawei deploy 5G base station at 6,500m on Mt Everest!
China Mobile and Huawei have together built the highest elevation 5G (or any other) base station on this planet– at 6500 meters (21,300 feet) at Mount Everest where there are no roads or trails. [Note that the summit is 8,848 meters, but will be measured again this year].
The base station along with two others at lower elevations, will enable China Mobile to run its 5G wireless network on the world’s highest mountain. It will surely be a great aid to climbers which had to previously use satellite phones for ultra high altitude communications with their high camps.
Zhou Min, general manager of Tibet branch of China Mobile, said the facility will ensure reliable telecommunication for the activities of mountain climbing, scientific research, environmental monitoring and high-definition live streaming. The building of 5G infrastructure is in tandem with the measuring of the height of the peak, which officially started on Thursday.
“It comes on the 60th anniversary of the first successful ascent of Mount Everest from the northern slope and the 45th anniversary of China’s first official accurate measurement of Mount Everest,” declared the press release. “Significantly, the 5G network on Mount Everest will provide communication services for the 2020 Mount Everest re-measurement.”
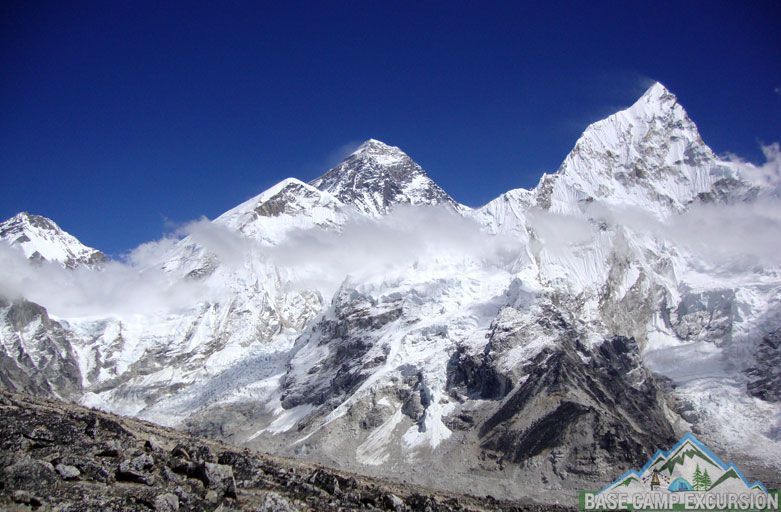

The base station launch marks the 60th anniversary of the first successful ascension of Mount Everest from the northern slope. Base stations are now at the Mount Everest Base Camp at 5,300 metres, the Transition Camp at 5,800 metres, and the Forward Camp at 6,500 meters.
A China Mobile technician told state media that the new 5G network is fast enough for climbers and scientists to have 4K and VR live streaming on the mountain.
Huawei’s 5G AAU and SPN technologies were applied at the base stations, managed and maintained by a dozen network specialists stationed there 24/7 at altitudes of 5,300 meters and above.
Huawei claims that its 5G AAU is highly integrated into a compact size, making it easy for deployment and installation and it fits particularly well for infrastructure in extreme environments such as Mount Everest. In this project, a network in the “stand-alone plus non-stand alone” (SA+NSA) mode connects five 5G base stations.Meanwhile, the 5G connectivity is achieved by Huawei’s Massive MIMO technology.
Huawei’s Massive MIMO comes with three-dimensional narrow beams. At an altitude of 5,300 meters, the 5G download speed exceeded 1.66 Gbps, where the upload speed tops 215 Mbps, claims Huawei. Some of the other technologies being employed by the Chinese telecom equipment giant are Intelligent OptiX Network and HoloSens intelligent video surveillance system. The 5G base station at Everest base camp includes a Gigabit ONT, Huawei’s 10G PON OLT and 200G ultra-high-speed transmission platform, and the HoloSens intelligent video surveillance system.


Pictures of 5G Base station at 6500 meters Photo credits: Huawei
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The press release concluded as follows:
Huawei strongly believes that technology means to make the world better. The beauty of Mount Everest can be displayed via 5G high-definition video and VR experience, which also provides further insights for mountaineers, scientists and other specialists into the nature. The ground-breaking establishment on Mount Everest once again proves that 5G technology connect mankind and the Earth harmoniously.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/press-events/news/2020/4/china-mobile-huawei-deliver-world-highest-5g
https://www.bloombergquint.com/technology/5g-signal-now-available-on-mount-everest-peak
Omdia: Global smartphone shipments plunge in Q1-2020; Mobile communications revenue to drop 4.1% in 2020
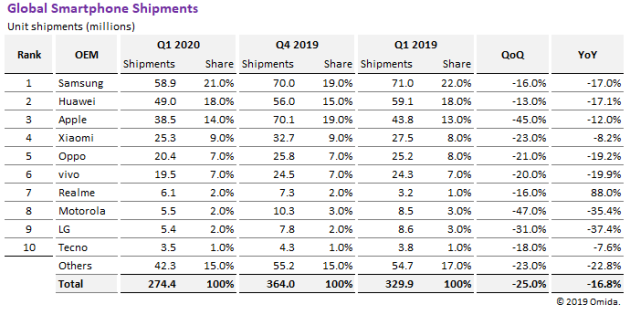
Omdia reported today that global smartphone shipments dropped by 16.8 percent in the first quarter of 2020 as vendors struggled to manage coronavirus-driven production shutdowns, product-launch delays and depressed consumer demand.
Shipments in the first quarter fell to 274.4 million units, down from 329.9 million during the same period in 2019, according to the Omdia Smartphone Intelligence Service. This plunge impacted all the major smartphone brands, with nine of the top-10 OEMs suffering shipment declines compared to the first quarter of 2019.
Editor’s Opinion: The decline will be much greater in Q2-2020 due to all the lockdowns all over the world. Who needs a smartphone when you’re confined to your residence? I hardly use mine at all as I prefer a laptop or tablet when at home.
“Early in the first quarter, the smartphone market was sent reeling by the shutdown of production at facilities in China, which halted the manufacturing of phones and their key components,” said Jusy Hong, smartphone research and analysis director at Omdia. “While concerns about this situation have been alleviated, the smartphone brands also faced new challenges, including disrupted launch schedules for new phones. Even more troubling for smartphone makers is a major decline in global demand due to government lockdown mandates.”
Despite expected rebounds in some countries, the rest of the year is expected to be challenging for smartphone OEMs. Omdia forecasts global smartphone shipments will decline to 1.20 billion units this year, down 13.1 percent from 1.39 billion in 2019.
OEMs feel the pain in the first quarter
Almost across the board, smartphone OEMs faced significant declines in unit shipments compared to the first quarter of 2019.
Samsung retained the top position, with 58.9 million units shipped during the first quarter—a 17 percent decline compared to the first quarter of 2019. Second-ranked Huawei saw its shipments decline by more than 17 percent, to 49 million units, down from 59.1 million in the first quarter of 2019.
Apple, in third place, saw shipments decline to 38.5 million units, down from 43.8 million a year earlier. The 12.0 percent decline comes during the first quarter, historically the weakest period of the year for Apple.
Rounding out the Top 5 are Xiaomi and OPPO. Out of the Top 10, Xiaomi experienced the second least severe decline in the quarter, of 8.2 percent. Only Tecno, in 10th place, attained a lower decrease better with a 7.6 percent year-over-year decline. Xiaomi shipped 25.3 million units in the first quarter, compared to 27.5 million units in 2019. OPPO, on the other hand, suffered a 19.2 percent decline, with shipments falling to 20.4 million units, down from 25.2 million a year earlier.
Realme bucks the downturn
The rest of the Top 10 is made up of vivo, Realme, Motorola, LG, and Tecno. The bright spot here is Realme, which achieved year-over-year growth based on its continued success in India. seventh-ranked Realme was the only top-10 OEM to attain growth during the quarter, with shipments totaling 6.1 million units, up 88 percent from 3.2 million during the first quarter of 2019.
For the others in this group, the first quarter brought significant challenges. Looking at vivo, company shipments declined 19.9 percent, falling from 24.3 million units last year to 19.5 million this year. Motorola, in eighth place, saw shipments decline 35.4 percent to 5.5 million units. While Motorola finally launched its updated RAZR, featuring a foldable display, the publicity surrounding that high-profile device was not enough to support the overall performance of Motorola’s product portfolio.
With or without the impact of the pandemic, LG continues to struggle with its mobile handset division. Shipments declined to 5.4 million units, down from 8.6 million units a year ago—a drop of 37.4 percent. Rounding out the top 10 is Tecno, which saw units decline by a relatively modest 7.6 percent, declining from 3.8 million units last year to 3.5 million units in the first quarter.
First-half struggles
“The smartphone market will face major struggles in the first half of 2020 as different countries experience the initial shock and recovery periods at different times. That’s why OEMs are more afraid of second-quarter sales results,” Hong said. “However, Omdia does expect the smartphone market to start to recover in some countries and regions in the second half of the year.”
Early in the first quarter, the most severe impact on the smartphone market was the shutdown of production and supply chain facilities in China. However, fears over a prolonged closure of essential production, supply chain and logistics operations in China have been alleviated, as signs point to economic activity ramping up quickly in the country.
Smartphone makers in the first quarter also had their product-launch plans disrupted by the cancellation of the Mobile World Congress event in Barcelona, Spain, where many companies had planned to roll out new products.
“Because of the cancellation of the Mobile World Congress, and uncertainty in the supply chain, original product schedules had to be re-evaluated,” said Gerrit Schneemann, senior analyst, smartphones, at Omdia. “However, OEMs seem to have found their footing on how to address new device launches going forward.”
Demand disaster
The impact of the outbreak on the smartphone business has now shifted almost completely to the demand side of the equation.
“Although handsets can be produced at nearly normal levels, the markets for these handsets are mostly in some state of shutdown,” Hong said. “Some countries have made more progress in dealing with the outbreak, while others are still in the midst of fighting the pandemic, and still others won’t feel the full effects of the pandemic until later in the year.”
In Europe, where some countries have been under strict lockdown rules for some time, initial efforts have been made to ease restrictions. Similarly, South Korea has taken steps to open up. In other countries, like in some parts of the United States, only the last few weeks of the quarter were impacted by broad stay-at-home orders, while consumer behavior had remained unrestricted until then.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Earlier today, Omdia issued this press release:
Coronavirus crisis deals a $51 billion blow to the global mobile communications industry outlook Mobile revenue to drop 4.1 percent worldwide; regional impact to vary
LONDON (April 30, 2020) — Mobile services represent critical infrastructure that’s allowing people to stay connected during the coronavirus crisis. However, that doesn’t mean these services are immune to the pandemic’s economic shock, with 2020 market revenue now expected to come in about $51 billion short of the previous forecast, according to Omdia.
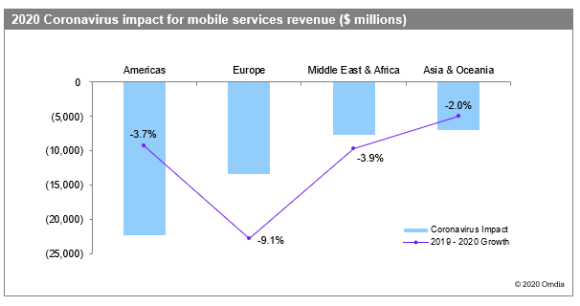
Worldwide mobile communications services market revenue will total $749.7 billion this year, down from the prior forecast of $800.3 billion. This compares to $781.5 billion in 2019. Annual revenue will fall by 4.1 percent this year, with the decline amounting to $31.8 billion.
“Mobile phone companies around the world are experiencing usage spikes as more countries encourage or enforce social distancing and work-from-home rules to slow the spread of the COVID-19,” said Mike Roberts, research director at Omdia. “However, the spikes aren’t enough to overcome the impact of the pandemic on consumer behavior. These rules are having a dramatic impact on various regions of the world, halting new subscriptions and upgrades in the United States, while slashing revenue for operators in Europe.”
Consumer uptake of 5G will be slower than previously forecasted, due to the economic situation as well as the possibility of delays in 5G network deployment and in the availability of 5G devices. Omdia will release more details on 5G shortly.
In the Americas, mobile service revenue is set to decline by 3.7 percent to $237 billion in 2020. Most of that loss will come in the United States as both net additions and upgrades to higher data plans slow or stop altogether.
Europe will suffer the largest impact of the crisis, with mobile service revenue falling 9.1 percent to $131 billion, representing a downgrade of 9.3 percent compared to Omdia’s previous forecast. This decline will be driven by significant reductions in mobile prepaid revenue and a dramatic drop in inbound roaming revenue.
Vodafone UK, for example, said mobile Internet traffic has increased by 30 percent and mobile voice traffic by 42 percent due to the crisis. At the same time, mobile service providers are seeing new business grind to a halt as retail stores close and consumers stop buying new phones as job losses mount. One example of this widespread trend is AT&T, which is closing 40 percent of its retail stores in the United States.
The Middle East and Africa will see a 3.9 percent decline in mobile service revenues to $84 billion, representing a downgrade of 8.4 percent from Omdia’s previous forecast. Major factors for the decline include the impact of low oil prices on Gulf economies and the fragility of economies and health care systems in parts of Africa.
While the impact of the coronavirus on the mobile market is significant in every region, it pales in comparison to the impact the crisis is having on sectors such as travel, tourism, hospitality and retail, which have suffered partial or complete shutdowns. The International Monetary Fund now expects the global economy to contract by 3 percent in 2020, according to its latest World Economic Outlook, which was released earlier this month.
“The massive contraction will clearly impact every segment of the economy, including mobile, but how long it will last in each country and region is virtually impossible to predict,” Roberts said. “One bright spot is that in China, the first country hit by the pandemic, there are signs that the mobile market and broader economy is starting to come back to life.”
Given the high level of economic and commercial uncertainty created by the COVID-19 pandemic, Omdia will be producing a full revision of its global mobile forecasts next quarter.
About Omdia
Omdia is a global technology research powerhouse, established following the merger of the research division of Informa Tech (Ovum, Heavy Reading and Tractica) and the acquired IHS Markit technology research portfolio*.
We combine the expertise of over 400 analysts across the entire technology spectrum, analyzing 150 markets publishing 3,000 research solutions, reaching over 14,000 subscribers, and covering thousands of technology, media & telecommunications companies.
Samsung and Huawei dominate global 5G smartphones; Samsung expects sales to be down significantly due to COVID-19
Strategy Analytics reports that Samsung has become the leader of the 5G smartphone market, shipping 8.3 million handsets across the world during the first quarter of 2020 for a 34.4 percent market share. The South Korean conglomerate took advantage of its strong global distribution networks and operator partnerships and the popularity of its S20 5G and S20 Ultra 5G devices to top the ranking. Strategy Analytics stated that the biggest markets for 5G smartphones were China, South Korea, the U.S. and Europe.

Huawei was the #2 global smart phone vendor with a 33.2 percent market share after shipping 8.0 million 5G smartphones, nearly all in China. Note that Apple isn’t listed because the Cupertino, CA company has yet to announce a 5G smartphone.
The top 5 was rounded out by three other Chinese vendors – Vivo, Xiaomi and Oppo – with 12.0 percent, 10.4 percent and 5.0 percent of the global market, respectively.
Table 1: Global 5G Smartphone Vendor Shipments and Marketshare in Q1 2020

The Strategy Analytics report stated that worldwide shipments of 5G smartphones in the first quarter of 2020 came to 24.1 million, easily topping shipments of 18.7 million in 2019 as a whole. That’s despite the firm’s earlier forecast that global smartphone shipments would be down 25% in 2020.
Chinese smartphone vendors captured 61 percent of top 5 vendor 5G smartphone shipment volumes in Q1 2020, with the majority of those volumes going to the China 5G market. This reflects the speed with which Chinese operators have rolled out 5G networks, as well as the underlying demand for 5G smartphones, despite the Covid-19 pandemic that shut down large parts of China during the Q1 2020 period. As China continues to ramp up economic activity, Strategy Analytics expects 5G shipments to this market to continue to expand dramatically in 2020.
Samsung Electronics disagrees with that forecast as they warned in today’s earnings report that 5G infrastructure investments may face reductions or delays – both internationally and domestically – during the second quarter of 2020.
Sales and profits of set products business, including smartphones and TVs, are expected to decline significantly as COVID-19 affects demand and leads to store and plant closures globally.
In the second half, uncertainties driven by COVID-19 will persist as the duration and impact of the pandemic remain unknown. The Company plans to focus on optimizing resource allocation in the short term, while continuing to strengthen its technology leadership and develop innovative set products.
The Mobile Communications Business aims to strengthen its product lineup by introducing new premium models and expanding offerings of 5G models for the mass market. The Networks Business will focus on developing technologies and enhancing global competitiveness to reinforce the 5G business.
For the Consumer Electronics Division, under the risk of current economic uncertainties, the Company will closely monitor the market situation and will continue to focus on minimizing negative impacts by investing in efficient marketing and promotions tailored to each region and by optimizing its logistics.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
A shrinking smartphone market and store closures will lead to an “inevitable” drop in earnings for the current quarter, Jong min Lee, Samsung’s vice president of mobile, said along with other important items on Samsung Electronics earnings call.
In the first quarter, overall market demand drastically decreased quarter-on-quarter as a result of supply chain issues in China caused by the COVID-19 break — outbreak only in this quarter and travel restrictions in the last few weeks of the quarter following the global spread of the pandemic. As the impact of COVID-19, including those on logistics, began to take effect in March, our smartphone shipments also decreased quarter-on-quarter. However, we maintained sound profitability quarter-on-quarter by efficiently deploying marketing investment by improving overall product mix while increasing the sales portion of our premium and 5G model.
Now let me move on to the outlook for the second quarter. With the global spread of COVID-19, demand is expected to drop sharply in most regions due to the economic downturn caused by lockdown across the globe and a corresponding decline in consumer sentiment. As the market shrinks and effects of store closures continue to have direct impact, a drop in sales of our major products and overall performance seems inevitable. Although market uncertainty is higher than ever, we will focus on improving cost effectiveness and strengthening online and B2B channels. In case there are additional disruptions at our production sites, we will respond by effectively utilizing our diversified manufacturing capabilities around the globe. However, we are committed to protecting the health and safety of our employees as well as preventing community spread. We have been thoroughly implementing disinfections and prevention measures in our offices and production facilities in all regions.
For the network business, it is possible that investments in 5G networks will be reduced or delayed domestically and internationally as more effects of COVID-19 unfold.
Finally, I will share our outlook for the second half. In the midst of uncertainties such as the possibility of the prolonged pandemic and the timing of market recovery, we expect the competition to intensify further as companies try to recover from weakness in the first half. For the mobile business, while continuing to offer differentiation in the premium segment with new foldable and Note model launches, we plan to widen the range of choices for our customers and enhance competitiveness within each price range by introducing 5G models to our mass market lineup.
In addition, we will also improve operational efficiency across all areas, including R&D, production, supply, channel and marketing. For the network business, despite uncertainties around the 5G invest plan, we will continue to strengthen our technological competitiveness while improving our 5G business compatibilities globally for the mid- to long term. Thank you.
References:
Strategy Analytics: Global Smart Phone Market to Decline 25% in 2020
https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-electronics-announces-first-quarter-2020-results
Highlights of Cisco Roundtable: Expanding the Internet for the Future: Supporting First Responders and Society at Large
The agenda at Cisco’s April 28th roundtable “Expanding the Internet for the Future, Today: Supporting First Responders and Society at Large,” was focused on how the coronavirus is impacting our use of the internet from expanded online learning for students and adults alike to increased telehealth platforms (more on this subject below).
The discussion featured guest panelists including representatives from AT&T, Comcast, Cox Communications, Facebook, Verizon, and the University Texas-Gavelston Medical Branch. The panelists first took turns giving their individual perspectives on the current state of the internet before shifting focus on innovating to meet the demands of the future.
The conference opened with host Jonathan Davidson, senior vice president and general manager, Mass Scale Infrastructure Group at Cisco sharing some choice illustrative Cisco Webex data. So far this month, Cisco has hosted more than 20 billion virtual meeting minutes. For perspective, that is up from a mere 14 billion last month. These March 2020 totals doubled the meeting minutes from February. Around the globe, traffic appears to be leveling off or decreasing from recent highs.
Speakers included AT&T’s FirstNet SVP Jason Porter (a long time colleague and September 2020 IEEE ComSocSCV workshop speaker) and Andrés Irlando, president of Verizon’s “public sector” that sells services to public-safety officials.
Almost all roundtable participants said they have been working overtime during the past few weeks to make sure doctors, nurses and other medical professionals and first responders remain connected as they fight COVID-19. “This was like a fire, flood and tornado in every single city at the same time,” said AT&T’s Porter commented on the demand for FirstNet services. Jason and other speakers said their networks have managed to meet that demand, and that traffic growth is beginning to plateau.
However, “this gives us a peak at what the future looks like,” argued Verizon’s Irlando, explaining that traffic likely will start to decline as most Americans return to work, but some things won’t return to the way things were.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Cisco has a website to help healthcare providers transition to virtual healthcare. There you will find resources for scheduling, conducting, and joining virtual consultations between Doctors and patients.
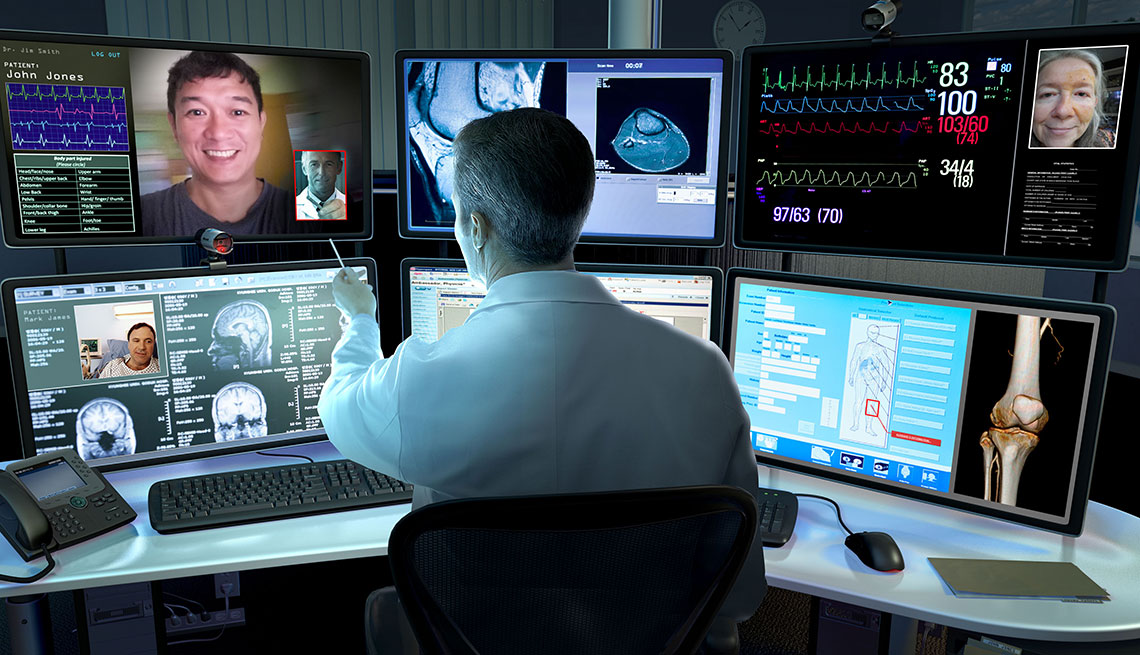

Telehealth and complex video session between Doctor and Patient
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
During the second half of the roundtable, panelists each shared the vision on ways to revolutionize the current model to provide access for people around the globe. Ideas ranged from the importance of government subsidies when it comes to building this infrastructure in some areas, to reverse auctioning portions of spectrum to cover more isolated communities. Facebook Vice President of Connectivity Dan Rabinovitsj floated the idea of allowing spectrum sharing in more remote areas without facing fines as well as the idea of utilizing the recently opened 6 GHz band for internet access around the globe. As individuals posed questions, Cisco executive Stephen Liu touched on the idea of a flexible consumption system to revolutionize the traditional service model.
“This allows Service Provider customers to procure equipment fully loaded with all the bandwidth they need, but only pay for what they use based on licensing. That way, if surges occur such as what happened with COVID-19, the capacity can be added immediately and paid for at a later time. The licenses can be pooled as well so that capacity could be moved from lower traffic areas into high traffic areas,” Liu said.
A huge problem for telehealth is insurance coverage. Light Readings Mike Dano wrote in a blog post:
One of the biggest obstacles was how healthcare insurance, including Medicare and Medicaid, account for telehealth services. Prior to the pandemic, healthcare pricing generally discouraged the use of videoconferencing and phone calls for doctor’s visits, but new rules implemented due to COVID-19 now incentivize the practice, King explained.
In the telecom sector, the FCC is working to promote telehealth offerings. Earlier this month, the agency voted to adopt a $200 million telehealth program as part of Congress’ CARES Act.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Currently, billions of people remain without internet access despite efforts to close the digital divide. Today, Cisco published the “Cisco Inclusive Future Report 2020” estimating that bringing those currently with internet access online would increase the worldwide economy by nearly $7 trillion and “would lift 500 million people out of poverty.” More than one-third (35%) of people in developing countries lack access to the internet compared to 80% of individuals in more “advanced economies.” The report also discusses the problems inherent with so-called digital literacy meaning a person’s basic understanding of using the internet, one of the principal roadblocks preventing “digital inclusion.” Internationally, nearly one-quarter of adults lack such digital literacy.
As the coronavirus continues to take its toll on populations and economies around the globe, the inadequacies of our digital infrastructure have been thrust into the spotlight. Current barriers to internet access has innumerable disadvantages for humans and economies around the globe. As has been illustrated during this pandemic-induced grand digital experiment, a well-equipped digital infrastructure has far-reaching social and economic implications for humans around the globe.

References:
https://www.webex.com/webexremotehealth.html



