Month: March 2021
Huawei and China Mobile test 5G indoor Massive MIMO
The pilot was conducted using LampSite, Huawei’s 5G digital indoor network product, based on the 2.6 GHz inter-frequency networking (80 MHz + 80 MHz). Distributed Massive MIMO was enabled in multiple 5G indoor cells to provide the large capacity needed to support 5GtoB (5G to Business) services and meet their high requirements for uplink experience. The peak uplink experience was quadrupled compared with traditional 4T4R cells.
Indoor distributed Massive MIMO introduces Massive MIMO for macro base stations to indoor networks. It is an innovative approach by Huawei to continuously increase the capacity of indoor 5G networks. The technology supports up to 64T64R channels and pools beamforming, MU-MIMO, and other technologies to ensure high capacity in the uplink and consistent user-perceived data speeds. Such a high level of performance makes it perfectly for smart production in which service terminals are frequently relocated for flexible production. Adding another competitive edge to empower 5G to transform industries.
The pilot is of great significance to indoor 5G, providing carriers with a new option to ensure premium uplink experience for emerging industrial services, such as video transfer and AGV operations, and expand 5G to factories, ports, power grids, airports, transportation, security, and many other industrial markets.
 Huawei will continue to work with China Mobile Guangdong in innovating 5G to improve 5G performance, build competitive 5G networks, and lead the development of 5G to Business customers.
Huawei will continue to work with China Mobile Guangdong in innovating 5G to improve 5G performance, build competitive 5G networks, and lead the development of 5G to Business customers.
India 4G Spectrum Auction Raises 778 billion Rupees
After much delay, India’s 4G spectrum auction has ended in just two days, raising Indian Rupee (INR) 778 billion (US $10.6 billion) for the government. The auction was held on March 1st and 2nd by India’s Department of Telecommunications. The airwaves acquired will help India’s telecom network operators add 4G capacity and get ready for 5G.
India auctioned spectrum in the 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz and 2500 MHz frequency bands. However, the 700MHz spectrum remained unsold because of the high reserve price.
India telecom network operators Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, and Vodafone Idea won spectrum in the government’s latest auction.
India’s largest telco, Reliance Jio announced it has acquired the right to use spectrum in all 22 circles across India in the auction. The upstart network operator secured spectrum in the 800 MHz, 1800 MHz and 2300 MHz frequency bands, which increases Jio’s spectrum footprint by 55 percent to 1,717 MHz.
Jio will pay INR 571.23 billion for the right to use this spectrum for a period of 20 years. Payments can be made over a period of 18 years (2-year moratorium plus 16-year repayment period), with interest at 7.3 percent per year.
Reliance Jio now claims to have the highest amount of sub-GHz spectrum with 2×10 MHz contiguous spectrum in most circles. It also has at least 2×10 MHz in the 1800 MHz band and 40 MHz in the 2300 MHz band in each of the 22 circles. The operator also reports it has achieved complete spectrum derisking, with average life of owned spectrum of 15.5 years. Reliance Jio will acquire the spectrum with an effective cost of INR 608 million per MHz. Jio also says the acquired spectrum can be used for provision of 5G services.
“The acquired spectrum can be utilized for transition to 5G services at the appropriate time, where Jio has developed its own 5G stack,” says the Jio press release.
India’s second-largest network service provider, Bharti Airtel acquired 355.45 MHz of spectrum across sub-GHz, mid-band and 2300 MHz bands for a total price of INR 186.99 billion. Airtel will use this spectrum to upgrade its deep indoor and in-building coverage in urban towns. In addition, this spectrum will also help improve its coverage in villages by offering the superior Airtel experience to an additional 90 million customers in India. Airtel also plans to use this spectrum to deliver 5G services in future.
An Airtel statement mentioned that the “the reserve pricing of these bands [700MHz and 3.5GHz] must be addressed on priority in future. This will help the nation to benefit from the digital dividend that will inevitably arise out of this.”
“Airtel has now secured pan-India footprint of sub GHz spectrum that will help improve its deep indoor and in building coverage in every urban town,” as per the company’s statement.
Vodafone Idea entered this spectrum auction “holding the largest quantum of spectrum with a very small fraction, which was administratively allocated and used for GSM services, coming up for renewal”.
As a result, Vodafone Idea acquired spectrum in only five circles for INR 19.93 billion. The operator said it has used this opportunity to optimize spectrum holdings post-merger to create further efficiencies in a few circles. Vodafone Idea expects the spectrum it has acquired in five circles to help it enhance its 4G coverage and capacity.

India’s just completed spectrum auction does not contain any airwaves for 5G
……………………………………………………………………………………………
Reliance Jio’s decision to be the biggest spenders at the auction comes shortly after its holding company, Jio Platforms, reported ₹22,858 crore in revenue during the quarter to December, which was a 30% improvement from the year prior.
Last year, Jio Platforms sold a third of itself to others for ₹152,056 crore. Buyers included Google, Facebook, Silver Lake, Vista Equity Partners, General Atlantic, KKR, Mubadala, ADIA, TPG, L Catterton, PIF, Intel Capital, and Qualcomm Ventures.
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/india-completes-spectrum-auction-raises-inr-778-billion–1374417
Internet 2’s Next Generation Infrastructure team deploys 800Gbps optical link
On February 26, 2021, Internet2 deployed its first 800 Gbps single-carrier optical circuit between Phoenix and Tucson, AZ as part of its Next Generation Infrastructure (NGI) program.
This milestone marks the first 800G native link to be deployed by a U.S. research and education network. The optical circuit leverages a 102 Ghz carrier generated by a single Ciena Waveserver 5 transponder at each endpoint.
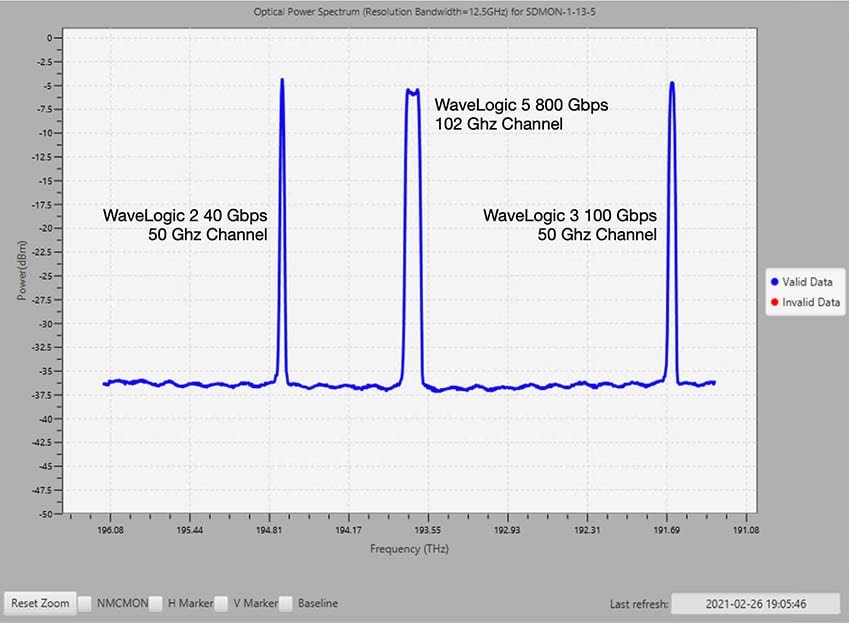
On February 25, 2021, the Internet2 project team completed the upgrade of all Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers (ROADMs) to flex spectrum on all east-west long-haul routes nationwide. Additionally, the majority of the optical fiber was upgraded from LEAF to SMF28 to better match the coherent transmission technologies being used to convey the new 800 Gbps optical link.
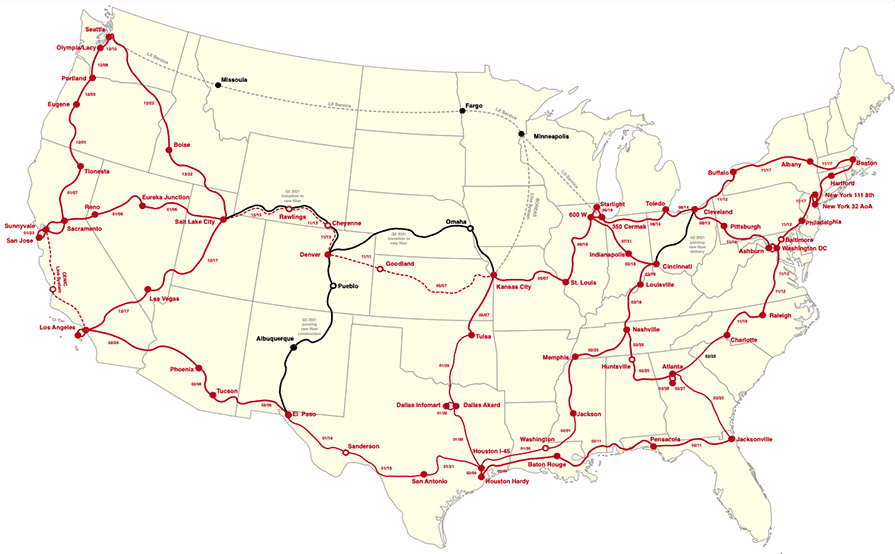
Internet2 plans to rapidly expand its 400G and 800G transmission capabilities along these newly flex-grid enabled routes; more link capacity will come online as our phase 2 hardware deployment team (GDT) continues to move across the country. The Internet2 team is deploying the Cisco 8200 and Ciena Waveserver 5 platform. Completion is targeted for the end of this month (March 2021).
The successful deployment of this initial 800 Gbps optical link is the culmination of thousands of hours of effort from both the Internet2 community and teams in many organizations, including Internet2, GlobalNOC at Indiana University, Ciena, Lumen, and GDT.
Just two weeks ago, Telefonica said it had trialed an 800 Gbps optical link, using Huawei and Nokia network equipment. However, there are no 800 Gps links in any commercial production network, as far as we can determine.
References:
North Carolina School District deploys WiFi 6 from Cambium Networks; WiFi 6 vs 6E Explained
Cambium Networks a leading global provider of wireless networking solutions, today announced its multi-year agreement with the school district of Burke County, N.C., with the addition of Wi-Fi 6 access points to provide multi-gigabit speeds in classrooms.
Using E-Rate funding for education, Burke County will upgrade its network to the latest Wi-Fi 6 technology to improve learning for students. The project, which began in late 2020, is delivering 1,500 multi-gigabit high-density access points to the district’s 27 schools and 12,000 students. This will allow students to simultaneously use Zoom and view streaming videos in the classroom using the latest XV3-8 access points, as well as XMS cloud management that seamlessly integrates with Google G-Suite and other embedded education systems.
“When the technology works, the students win, and so does our community. That is especially important as we navigate the pandemic and students return in March,” said Dr. Melanie Honeycutt, CIO of the Burke County School District. “Cambium is our solution for great performance at an affordable price for high density classrooms, and just in time as COVID accelerated our 1:1 laptop program and the increased use of streaming video.”
Cambium’s Wi-Fi 6 and XMS end-to-end cloud-management solutions provide multi-gigabit Wi-Fi access at a proven low total cost of ownership. With easy integration to existing systems, planning, provisioning, installation and centralized cloud management, Cambium’s solutions can be rapidly deployed to deliver end-to-end multi-gigabit wireless speeds.
“We love to work with visionary and discerning customers,” said Atul Bhatnagar, president and CEO, Cambium Networks. “Dr. Honeycutt and Burke County understand that this is the time to address the digital divide. They have done so in a way that gives students what they require for excellence in education.”
……………………………………………………………………………………..
What is WiFi 6 and 6E?
The IEEE 802.11ax standard was dubbed Wi-Fi 6 by the WiFi Alliance. At the time of publication, it was limited by U.S. law to a wireless spectrum that only covered the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
In a 2.4GHz band, there are three non-overlapping channels—and that bandwidth is shared by all users. If too many end point WiFi devices compete for bandwidth on the same wireless channel, then some of those signals will be dropped.
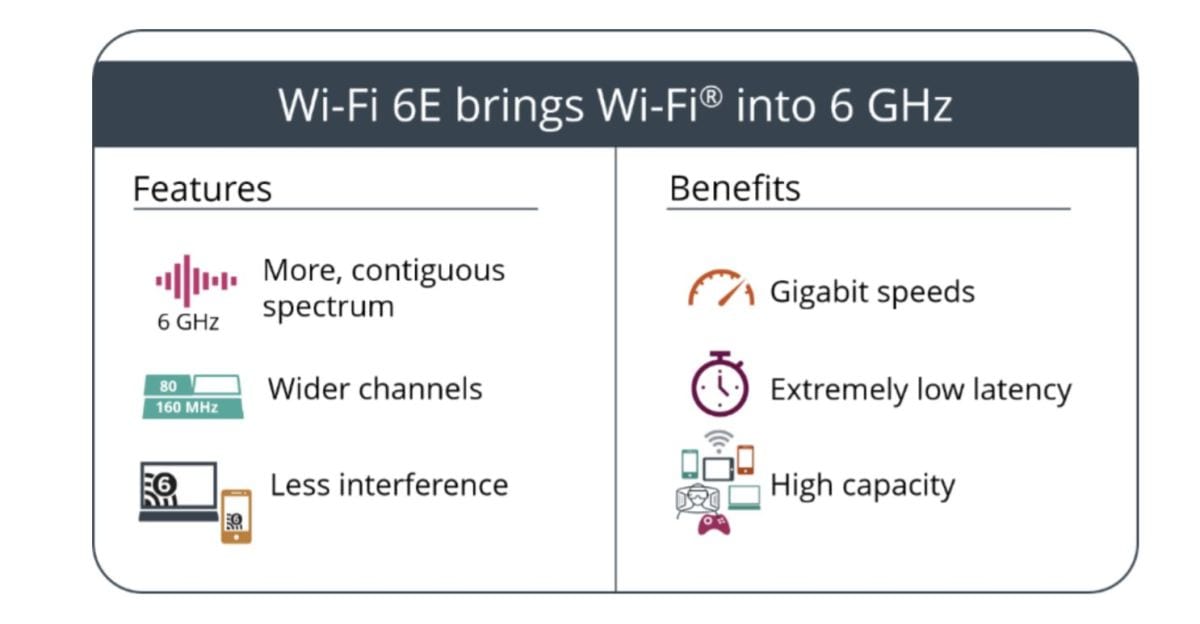
In April of 2020, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) voted unanimously to open up the 6GHz band for unlicensed use. With that policy change, significantly more airwaves are open that WiFi routers can use. The WiFi Alliance named versions of IEEE 802.11ax that operate at or above 6GHZ as WiFi 6E.
Images Courtesy of WiFi Alliance
…………………………………………………………………………………….
The opening of the 6GHz band is essentially quadruples the amount of airwaves (14 additional 80MHz channels, and seven additional 160MHz channels) available for WiFi routers and smart WiFi devices. That means less signal interference.
Wi-Fi Alliance® is introducing new terminology to distinguish forthcoming Wi-Fi 6 devices that are capable of 6 GHz operation, an important portion of unlicensed spectrum that may soon be made available by regulators around the world. Wi-Fi 6E brings a common industry name for Wi-Fi® users to identify devices that will offer the features and capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 – including higher performance, lower latency, and faster data rates – extended into the 6 GHz band. Wi-Fi 6E devices are expected to become available quickly following 6 GHz regulatory approvals, utilizing this additional spectrum capacity to deliver continuous Wi-Fi innovation and valuable contributions to consumers, businesses and economies.
So, what’s the difference?
Early-adopter devices using Wi-Fi 6 (such as the first batch of Wi-Fi 6 routers) are limited to the 2.4GHz and 5GHz spectrum, while Wi-Fi 6E-compliant devices will have access to all those much richer 6GHz airwaves.
References:
https://www.wi-fi.org/news-events/newsroom/wi-fi-certified-6-delivers-new-wi-fi-era
https://www.wi-fi.org/news-events/newsroom/wi-fi-alliance-brings-wi-fi-6-into-6-ghz
IBM’s Cloud Satellite service in Generally Available Orbit
IBM’s Cloud Satellite service is now in generally available (GA) orbit. The service extends the IBM Cloud control plane to run virtually anywhere, whether that be on commodity hardware, some edge device, or inside another public cloud.
IBM manages Cloud Satellite deployments, which is different than from most other software-defined hybrid cloud platforms. It provides an administrative control plane and as-a-service operation of IBM cloud services using a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster.
IBM explained that the GA push now makes the platform available to all customers. It allows users to run their IBM Cloud service on-premises or in edge locations managed through a single pane of glass in the public cloud.
The first two services for IBM Cloud Satellite will be Cloud Pak for Data and OpenShift as a Service.
IBM’s not alone in looking to data as one of the first services to be offered on hybrid. Amazon Outposts offers RDS for MySQL and PostgreSQL; Azure Arc data services include SQL Managed Instance and PostgreSQL Hyperscale; while Google recently added BigQuery Omni to its Anthos software-defined hybrid cloud as part of a multi-cloud and edge play.
The rationale as to why data services are so elemental to hybrid cloud is that, for many organizations or use cases, data needs to stay local for reasons ranging from latency issues to data residency requirements. OpenShift as a service will provide a route for customers seeking to build their own private cloud K8s environments. IBM is announcing that this will also be early on the list.
As part of this collaboration, customers will be able to:
- Deploy applications across more than 180,000 connected enterprise locations on the Lumen network to provide a low latency experience
- Create cloud-enabled solutions at the edge that leverage application management and orchestration via IBM Cloud Satellite
- Build open, interoperable platforms that give customers greater deployment flexibility and more seamless access to cloud native services like AI, IoT and edge computing

IBM said it has more than 65 “ecosystem partners” building services to run in the Cloud Satellite environment. Partner include Cisco, Dell Technologies, and Intel. They intend to develop cloud services which can run across the multi-cloud and premises platform services include storage, networking, and server options.
“IBM is working with clients to leverage advanced technologies like edge computing and [artificial intelligence], enabling them to digitally transform with hybrid cloud while keeping data security at the forefront,” said Howard Boville, Head of IBM Hybrid Cloud Platform, in a statement. He added that “clients can securely gain the benefits of cloud services anywhere, from the core of the data center to the farthest reaches of the network.”
IBM highlighted three partners, among them Lumen Technologies and Portworx, that are both heavily leveraging 5G to deliver PaaS services for edge computing, and F5, which is developing vertical solutions for banking institutions.
IBM noted that Lumen Technologies (formerly CenturyLink) was using the hybrid cloud platform to deliver its Edge Compute service. That capability relies on Red Hat’s OpenShift that runs within Cloud Satellite to host the applications running close to Lumen’s edge locations. Lumen touts that it has approximately 450,000 route fiber miles in its network spread across more than 60 countries.
Lumen struck a similar deal earlier this year with VMware that will see both vendors “fast-track the design, development, and delivery of edge computing and more secure, work-from-anywhere solutions.”
Does anyone remember IBM’s Satellite Business Systems (SBS) of the late 1970s? It was a pioneer in delivering data services to businesses as a precursor of the Internet.
References:
https://www.ibm.com/cloud/satellite
https://developer.ibm.com/blogs/distributed-cloud-development-ibm-cloud-satellite/
https://www.zdnet.com/article/ibm-cloud-satellite-goes-ga/
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/ibm-cloud-satellite-boosted-to-ga-orbit/2021/03/
IBM Cloud Satellite: Build faster. Securely. Anywhere. Now generally available. To get started, visit: https://www.ibm.com/cloud/satellite.
For more information on how IBM is working with its ecosystem of partners, visit: www.ibm.com/cloud/blog/ibm-partner-ecosystem-and-cloud-satellite
For more information on IBM Cloud Pak for Data as a Service, visit:
https://www.ibm.com/blogs/journey-to-ai/ibm-cloud-pak-for-data-with-ibm-cloud-satellite
For more information on how IBM is helping developers build on IBM Cloud Satellite, visit:
https://developer.ibm.com/blogs/distributed-cloud-development-ibm-cloud-satellite
For more information on how IBM Cloud Satellite is supported by IBM Storage, visit: www.ibm.com/blogs/systems/improve-it-infrastructure-with-ibm-hybrid-cloud-storage-for-ibm-cloud-satellite
For more information on IBM Global Technology Services capabilities for IBM Cloud Satellite, visit: ibm.biz/PC_IaaS
To learn more about how Lumen has integrated Cloud Satellite across 180K global edge locations, visit: https://blog.lumen.com/speeding-innovation-at-the-edge-with-lumen-technologies-and-ibm-cloud-satellite
About IBM:
For further information visit: www.ibm.com/cloud/