Year: 2024
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
T-Mobile US, in a partnership with Ericsson and Qualcomm Technologies, has successfully tested the aggregation of six component carriers in sub-6 GHz spectrum in its live production 5G network.
The test involved aggregating two channels of 2.5 GHz, two channels of PCS spectrum and two channels of AWS spectrum, according to T-Mobile US, which produced an “effective 245 MHz of aggregated 5G channels.”
T-Mo said that they were able to “achieve download speeds of 3.6 Gbps in sub-6 GHz spectrum. That’s fast enough to download a two-hour HD movie in less than 7 seconds!”
5G carrier aggregation allows T-Mobile to combine multiple 5G channels (or carriers) to deliver greater speed and performance. In this test, the Un-carrier merged six 5G channels of mid-band spectrum – two channels of 2.5 GHz Ultra Capacity 5G, two channels of PCS spectrum and two channels of AWS spectrum – creating an effective 245 MHz of aggregated 5G channels.
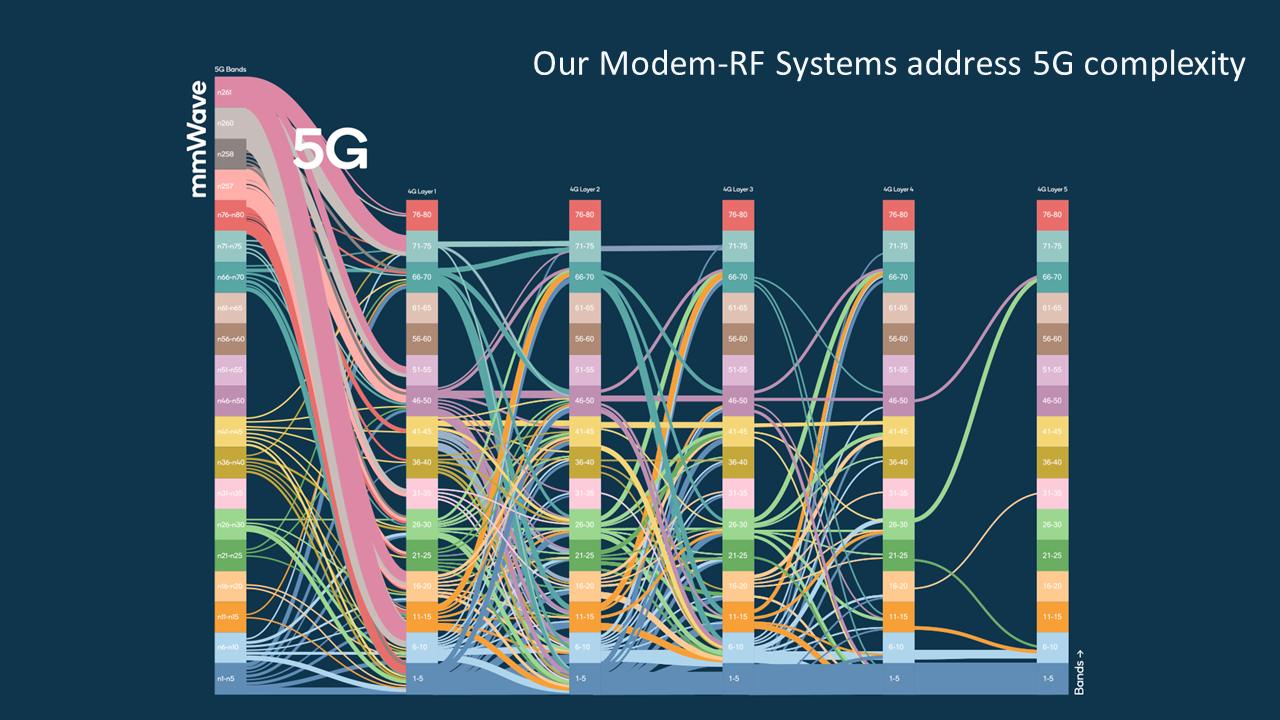
Image Courtesy of Qualcomm Technologies
“We are pushing the boundaries of wireless technology to offer our customers the best experience possible,” said Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “With the first and largest 5G standalone network in the country, T-Mobile is the only mobile provider serving 10s of millions of customers to unleash new capabilities like 5G carrier aggregation nationwide, and I am so incredibly proud of our team for leading the way.”
T-Mobile US announced in May of 2023 that it was rolling out four component-carrier aggregation across its 5G Standalone network, which it said at the time can achieve peak speeds of 3.3 Gbps. In that case, T-Mobile US relies on two 2.5 GHz channels, one 1.9 GHz channel and one 600 MHz channel. The first device able to access 4CA capabilities was the Samsung Galaxy S23.
The carrier also touted its testing of five-component-carrier aggregation in sub-6 GHz spectrum at last year’s Mobile World Congress Barcelona. In that trial, working with Nokia and Qualcomm, T-Mo aggregated two FDD and three TDD carriers and achieved peak downlink throughput speeds that exceeded 4.2 Gbps.
T-Mobile claims to be the leader in 5G, delivering the country’s largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network. The Un-carrier’s 5G network covers more than 330 million people across two million square miles — more coverage area than AT&T and Verizon combined. 300 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G with over 2x more square miles of coverage than similar offerings from the Un-carrier’s closest competitors.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/ran/carrier-aggregation
Ookla: T-Mobile and Verizon lead in U.S. 5G FWA
T-Mobile combines Millimeter Wave spectrum with its 5G Standalone (SA) core network
Verizon, T-Mobile and AT&T brag about C-band 5G coverage and FWA
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
T-Mobile US at “a pivotal crossroads” CEO says; 5,000 employees laid off
Ookla Q2-2023 Mobile Network Operator Speed Tests: T-Mobile is #1 in U.S. in all categories!
T-Mobile and Google Cloud collaborate on 5G and edge compute
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
T-Mobile US today said that SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket on Tuesday with the first set of Starlink satellites that can beam phone signals from space directly to smartphones. The U.S wireless carrier will use Elon Musk-owned SpaceX’s Starlink satellites to provide mobile users with network access in parts of the United States, the companies had announced in August 2022. The direct-to-cell service at first will begin with text messaging followed by voice and data capabilities in the coming years, T-Mobile said. Satellite service will not be immediately available to T-Mobile customers; the company said that field testing would begin “soon.”
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/73PVHSXKT5LIHDTFDWHUSDQTL4.jpg)
SpaceX plans to “rapidly” scale up the project, according to Sara Spangelo, senior director of satellite engineering at SpaceX. “The launch of these first direct-to-cell satellites is an exciting milestone for SpaceX to demonstrate our technology,” she said.
Mike Katz, president of marketing, strategy and products at T-Mobile, said the service was designed to help ensure users remained connected “even in the most remote locations”. He said he hoped dead zones would become “a thing of the past”.
Other wireless providers across the world, including Japan’s KDDI, Australia’s Optus, New Zealand’s One NZ, Canada’s Rogers will collaborate with SpaceX to launch direct-to-cell technology.
References:
https://www.theguardian.com/science/2024/jan/03/spacex-elon-musk-phone-starlink-satellites
Starlink Direct to Cell service (via Entel) is coming to Chile and Peru be end of 2024
Starlink’s Direct to Cell service for existing LTE phones “wherever you can see the sky”
Could Transpositional Modulation be used to solve the “spectrum crunch” problem
Transpositional Modulation (TM) permits a single carrier wave to simultaneously transmit two or more signals, unlike other modulation methods. It does this without destroying the integrity of the individual bit streams.
TM Technologies (TMT) is a wireless technology company offering dramatic data throughput increases for existing wireless and wired networks, using TM.
TMT’s In Band Full Duplex (IBFD) is a MIMO-compatible antenna and software technology providing signal interference cancellation via its Adaptive-Array Antenna which allows simultaneous transmit and Receive = Doubling Data Rates. TM-IBFD development has shown a combined 120 db noise reduction in two-way communications, which provides up to a 100% gain in wireless data transport efficiency.
TMT believes that the use of its patented methods can prevent or delay the onset of a wireless “bandwidth crunch” and focuses on developing products for a range of applications. These products will use core technology to provide solutions and create value for customers, the economy, and the global wireless infrastructure. The company says that the TM-IBFD is backwards compatible and complimentary with existing beam forming or beam shaping installations.
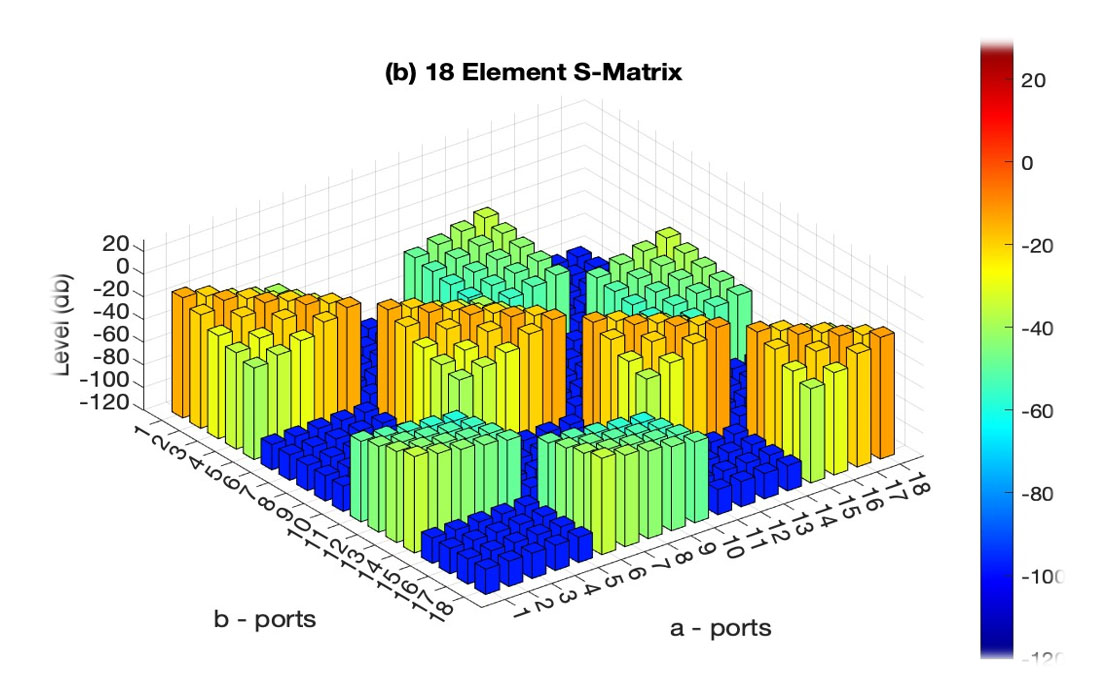
Image Courtesy of TM Technologies (TMT)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Using the latest Xilinx RFSoC devices, TMT has produced a Software Defined Radio (SDR) format with OFDM as primary modulation with multiple TM channel overlays. This is applicable to nearly any access or backhaul radio device with adequate head-space and operating within the 3GPP Rel 16 specifications.
Industry analyst Jeff Kagan wrote: “Spectrum shortage remains a problem that is not going to solve itself. That’s why new solutions like this are necessary….In the case of solving this spectrum crisis, there are two different groups to focus on. One, is the wireless carriers. Two, are wireless network builders. Either, the customer, which is the wireless network needs to demand this from their network builders. Or the network builders need to embrace this as a competitive advantage and as a solution to their customers.”

Jeff Kagan
References:
Kagan: Could TM Technologies help solve wireless spectrum shortage?
IEEE 5G/6G Innovation Testbed for developers, researchers and entrepreneurs
Courtesy of IEEE member David Witkowski (see his bio below the article):
David’s career began in the US Coast Guard where he led deployment and maintenance programs for mission-critical telecom, continuity of government, and data networking systems. After earning his B.Sc. in Electrical Engineering from University of California @ Davis, he held managerial and leadership roles for high technology companies ranging from Fortune 500 multi-nationals to early-stage startups.
David serves as Executive Director of the Civic Technology Program at Joint Venture Silicon Valley, Senior Advisor for Broadband at Monterey Bay Economic Partnership, and is a Fellow of the Radio Club of America and a Senior Member of the IEEE. He previously served as as Co-Chair of the GCTC Wireless SuperCluster at NIST, on the Board of Expert Advisors for the California Emerging Technology Fund.
David’s IEEE activities include:
-
Co-Chair of the Deployment Working Group at IEEE Future Networks (FNTC)
-
Life Member of the IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques Society (MTT-S)
-
Member of the IEEE International Committee on Electromagnetic Safety (ICES)
-
Member of the IEEE Committee on Man and Radiation (COMAR)


