fiber optics
PON’s Vulnerability to Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
by Shrihari Pandit
Introduction:
The dominant architecture used in fiber optic deployment -Passive Optical Networks (PONs) may be vulnerable to attack. It is important to bring attention to this under-appreciated weakness and discuss what steps are possible to protect fiber infrastructure.
As various PON technologies are long standing and widely deployed, this is a matter of no small concern. PONs are widely deployed by Verizon FiOS, AT&T U-verse and many others.
The PON architecture is a hodgepodge of old and new technologies, hardware and strategy, limited budget and often is not overseen by a single team.
In this article we describe how fiber optic infrastructure based on PONs may be open to potential denial of service (DoS) attacks via optical signal injections. Security experts warn that this is a growing issue, which could take down entire sectors of PON segments.
Considering the ever increasing state-sponsored and non-state-actor cyber attacks, these types of vulnerabilities that allow for massive disruption for large groups of people are very attractive targets.
PON Overview:
The cost advantages of PON architecture make it the overwhelming choice for FTTH deployments. PON allows wireline network providers to deliver service to businesses and homes without having to install costly active electronics on roads, curb-side or even within buildings themselves.
Active electronics, on the other hand, add cost and create operational complexity as deployments scale. The conveniences and differentiators of PONs are precisely what opens up the floodgates to serious vulnerabilities.
PONs are fundamentally susceptible due to the architecture from the passive optical splitter (POS) to the optical network unit (ONU) within the overall network infrastructure. The POS component of the network functions like a bridge, allowing any and all communications to transverse without the ability to filter, limit or restrict flow.
The fiber optic market currently boasts 585.9 million subscribers worldwide, with that number set to grow to 897.8 million subscribers by 2021.
The industry has moved to upgrade 1st generation GPONs and EPONs to next-generation PONs, like NG-PON2 (the favorite), XG-PON1 and XGS-PON. For example, Verizon uses the Calix AXOS E9-2 Intelligent Edge System for large-scale NG-PON2 deployments that began in the first quarter of 2018.
However, with subscriber density significantly increasing per PON segment, the risks increase as more subscribers are affected by a cyber attack on a single fiber.
Sidebar: NG-PON2
NG-PON2 combines multiple signals onto a single optical fiber by using the different wavelengths of laser light (wave division multiplexing), and then splits transmission into time slots (time division multiplexing), in order to further increase capacity. NG-PON2 is illustrated in the figure below.

Legend:
OLT =Optical Line Termination ONT =Optical Network Termination
NGPON2 has three key advantages for operators:
1. Cost
Firstly, it can co-exist with existing GPON and NGPON1 systems and is able to use existing PON-capable outside plant. Since the cost of PON FTTH roll out is 70 per cent accounted for by the optical distribution network (ODN), this is significant. Operators have a clear upgrade path from where they are now, until well into the future.
2. Speed
Initially NGPON2 will provide a minimum of 40 Gb/s downstream capacity, produced by four 10 Gb/s signals on different wavelengths in the O-band multiplexed together in the central office with a 10 Gb/s total upstream capacity. This capability can be doubled to provide 80 Gb/s downstream and 20 Gb/s upstream in the “extended” NGPON2.
3. Symmetrical upstream/downstream capacity
Both the basic and extended implementations are designed to appeal to domestic consumers where gigabit downstream speeds may be needed but more modest upstream needs prevail. For business users with data mirroring and similar requirements, a symmetric implementation will be provided giving 40/40 and 80/80 Gb/s capacity respectively.
………………………………………………………………………………………
The Essence of a PON Cyber Attack:
Given the flashpoints around the globe, it doesn’t take much imagination to envision how state and non-state actors might want to cause such a chaotic and widespread disruption.
If a “cyber criminal” gains access to the underlying fiber, they could inject a wideband optical signal to disrupt communications for all subscribers attached to the PON segment.
Alternatively, at your home the adversary could manipulate the ONU’s optical subsystem to transmit abnormal PON signals and impact service to all subs on that segment. Communications including internet, voice and even analog TV signals that operate on nearby wavelengths would be susceptible to these serious DoS attacks.
Possible Solutions, Preventive Methods and Procedures:
So, what can be done with current equipment without a massive and costly fiber optic network overhaul? The unfortunate answer is that an overarching vulnerability will always exist as long as the passive components are in place. A reactionary process is the best and only option.
The current primary solution for operators is to reduce the number of subscribers per PON segment as a way to manage risks. If an attack was detected, the network operator would be able to localize the source and identify and disconnect the bad actor from the network. But it’s easier said than done.
This sort of manual process is not ideal. Extensive PON outages means spending the time and money to send personnel to optical line terminals to check each individual port until the attacker is found. The installation of active electronics on each PON segment or near PON subscribers is unrealistic and impractical. That undertaking would actually be more costly in terms of time, money and location.
The best ongoing solution is that operators should consider installing passive tap points per PON segment. Each can be independently routed back and managed at a provider’s operations center and allow operators to effectively analyze segments and detect unusual optical light levels that may signal an attack.
At that point the operator could physically dispatch techs on-site to continue the localization and resolution process while ensuring other non-threatening users remain unaffected. This solution is to effectively take a reactionary restriction and make it as automatic and proactive as currently possible.
Conclusions:
P2MP (point to multi-point) architecture has become the most popular solution for FTTH and FTTP. Yet there needs to be a severe increase in awareness to potential PON vulnerability into the next generation.
If we can catalyze the telecom industry to develop methods and measures to protect infrastructure, such crippling network security issues will be stopped before widespread exploits occur.
The industry needs to address these concerns sooner rather than later or else be left without effective countermeasures against these very real threats.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-a-denial-of-service-attack-dos
https://s2.ist.psu.edu/paper/ddos-chap-gu-june-07.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G93I_v2pa24
……………………………………………………………………………….
About Shrihari Pandit:
Shrihari Pandit is the President and CEO of Stealth Communications, the NYC-based ISP he co-founded in 1995. Stealth, having built its own fiber-optic network throughout the city, provides high-bandwidth connectivity services to a broad roster of customers in business, education and government.
Prior to Stealth, Mr. Pandit was a network-security consultant to various software and telecom companies, including MCI, Sprint and Sun Microsystems. He also served as an independent consultant to several U.S. agencies, including NASA and the National Infrastructure Protection Center (NIPC), now part of the Department of Homeland Security.
Telefonica in 800 Gbps trial and network slicing pilot test

With this initiative the intention is also to begin building services for customers to be marketed via Telefónica’s 5G network. The project will thus enable Telefónica to obtain key results that will serve to drive the ecosystem and promote the interoperability and standardisation of this technology with a view to its marketing towards the end customer. Some of the sectors that can benefit the most from Network Slicing are the State Security Corps and Forces, media and communication, cars, industry and hotels.
Fiber optic coverage in Brazil to reach 5.5K municipalities by 2024; telcos want fiber over underground sewage ducts and systems
By 2024, optical fiber should reach 5,500 Brazilian municipalities that do not now have fiber coverage. This is one of the new objectives of Brazil’s General Plan for Universalization Goals. On Thursday, Brazil’s Communications Ministry approved the issuance of debentures for investments in the telecommunications infrastructure, taking the total initiatives to stimulate the development of the sector to seven. The document was published in the Federal Official Gazette and gathers the obligations that fixed-line operators must fulfill in the next five years.
According to the plan, fiber optic connections should have a minimum capacity of 10 GB per second from the beginning to the end of the stretch that serves the municipality, and cover at least 10% of its territory by December 31, 2021. If the new target is met, the estimate is that internet coverage by fiber optics will reach around 5.500 cities by 2024. This would be equivalent to 99% of Brazilian municipalities.
Anatel (the National Telecommunications Agency in Brazil) has a period of 3 months to draw up the list of cities that will be covered. In Brazil, fiber connections already account for almost a third of total fixed broadband connections, according to data from regulator Anatel. All major carriers are expanding their FTTH network.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Brazilian telecom operators want to be allowed to pass critical telecom transport networks, namely fiber optics, over underground sewage ducts and systems. The topic was discussed during a 5G event held by the Lide group on Thursday, where sector executives called for the issue to be included in the new rules for the sanitation sector. With the aim of making the sector more attractive to private investors, last year saw a new sanitation framework approved by congress and signed into law by President Jair Bolsonaro.
“It’s hard to pass fiber on the surface and sewer systems can be a lever for telecom infrastructure,” said Leonardo Capdeville, chief technology officer at TIM Brasil. “The systems can even be used to pass fiber up to homes and buildings. We could take advantage of the sanitation framework,” he said.
It is a “win-win” relationship, according to the CTO. On the one hand, it generates additional revenue for the sanitation company, while at the same time allowing it to benefit from connectivity that can help improve operating control and management, by preventing leaks in a timely manner for example.
Operators have sought to find alternatives to the obstacles they claim to face in the form of bureaucracy, excessive costs and licenses for rolling out fiber along highways, and also high fees charged by power utilities for the use of lampposts.
Echoing Capdeville, TIM’s regulatory affairs director, Mario Girasole, defended advances in fiber backhaul (transport networks) by joint construction and deployment with power distributors, road concessionaires and sanitation companies. The idea of using sewage systems and other forms of infrastructure sharing was also defended by the CEO of local telco Oi, Rodrigo Abreu, and Ericsson’s Eduardo Ricotta.
“Optical fiber needs a very large investment and we see this [sharing] trend as a way of no return,” said Ricotta, who is head of the Southern Cone at the Swedish telecom infra provider. In São Paulo, state utility Sabesp is currently discussing ways to deploy 5G transport infra via sewage systems, according to Adriano Stringhini, the company’s corporate management officer.
References:
LG U+ first to deploy 600G backbone network in Korea with Ciena’s ROADM equipment
South Korea network operator LG U+ today announced it is the first carrier in South Korea to deploy 600Gb/sec on a single wavelength for long haul, using Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 technology. LG U+ made this upgrade to support remote experiences.
The company will establish a ROADM (Re-configurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) backbone network to strengthen the competitiveness of business. LG U+’s newly constructed and dedicated nationwide ROADM backbone network will satisfy the needs of customers and preemptively respond to increased traffic following the introduction of the remote era. For this network transformation, LG U+ has selected Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme and WaveLogic Ai coherent optical solutions.
Sung-cheol Koo who’s in charge of LG U+’s wired business said, “Amid the expansion of cloud services such as telecommuting, video conferencing and remote classes, we are building a new backbone network that can accommodate the needs of various corporate customers. With a flexible and stable transmission network, we expect that companies can provide a higher level of service.”
LG U+ also applied the Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) technology, which measures the loss of optical lines, disconnection points, and distances across the entire section of the new backbone network. By intuitively monitoring the condition of the line in real time, it is possible to shorten the response time in case of a failure.
With rapidly increasing traffic, Ciena will enable LG U+ to transmit single-carrier 600G wavelengths over the new flexible grid backbone that has six times the network capacity compared to the existing network. The new backbone network will provide enhanced availability through low-latency, multiple route diversity and direct connections between large cities without the need for regeneration.
LG U+ is in the process of implementing a major capacity upgrade, including multi-terabits of additional capacity, to accommodate large-capacity customers and enable stable traffic management. By applying OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) technology to all sections of the backbone network, real-time and intuitive line condition monitoring is possible to shorten troubleshooting time and enable smooth network management and operations.
 In addition, Ciena’s 6500 ROADM equipment can reliably configure DR (Disaster Recovery) line services to public government, financial institutions and compute centers of large enterprises through third party interworking certification. LG U+ can also provide a dedicated line service with enhanced security through optical transport encryption.
In addition, Ciena’s 6500 ROADM equipment can reliably configure DR (Disaster Recovery) line services to public government, financial institutions and compute centers of large enterprises through third party interworking certification. LG U+ can also provide a dedicated line service with enhanced security through optical transport encryption.
LGU+ will be using Ciena’s Manage, Control and Plan (MCP) SDN controller to be able to automate service delivery via next-generation OPEN APIs to improve customer experience and increase operational efficiencies.
References:
https://www.ciena.com/about/newsroom/press-releases/lg-u-builds-new-nationwide-backbone-network.html
Telecompaper: FTTH spurs growth in Netherlands broadband market
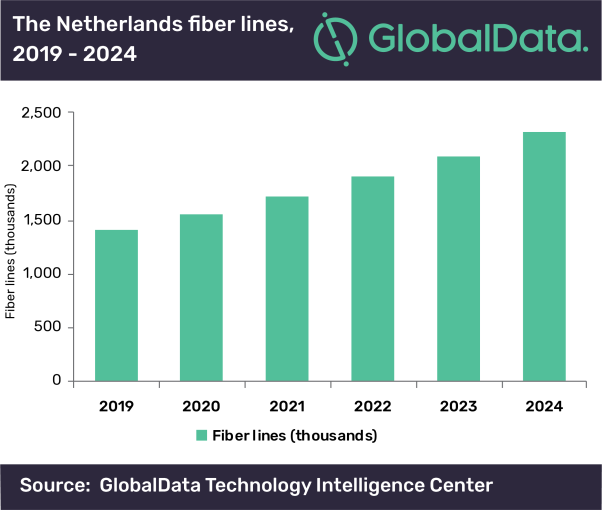
FTTH accounted for all of the new growth on the Netherlands broadband market in Q3 2020, the latest research by Telecompaper shows. Cable operators lost broadband subscribers for the first time on record, suggesting the fiber market is really taking off.
The mass market (consumer + SOHO) added 32,000 fixed broadband subscribers in the third quarter, the same number as in Q2 and slightly less than the year-earlier period, according to Telecompaper’s quarterly Dutch Broadband report.
FTTH growth accelerated to 68,000 new connections, while cable lost 8,000 customers and DSL shed 28,000 lines. The decrease in cable customers was driven by market leader Ziggo, which lost 7,000 broadband subscribers in the period. This is the first time it has lost customers since launching cable broadband. Nevertheless, Ziggo remains market leader, with over 43 percent of Dutch broadband subscribers.
KPN was the biggest gainer on the market, adding 37,000 broadband customers in Q3. KPN’s growth is driven by the takeover of customers from its discontinued Telfort brand and an accelerating FTTH roll-out in the past year. The KPN brand added over 40,000 FTTH subscribers in the quarter, more than four times the rate of growth in Q3 2019. This increased its share of the total FTTH market to 53.5 percent of connections.
T-Mobile Netherlands also continued to grow, adding 31,000 broadband subscribers. This makes it the third-largest broadband brand with a 5.3 percent market share. In the FTTH segment, T-Mobile is number two with just over 13 percent of connections, followed closely by Caiway with 12 percent.
“The figures suggest KPN’s strategy to speed up its FTTH roll-out is starting to pay off and stem the loss of broadband subscribers,” said Kamiel Albrecht, Telecompaper’s senior research analyst for the Dutch fixed market. “Ziggo is not sitting still and should soon complete its nationwide roll-out of gigabit service, putting the companies on more equal footing. More intensive marketing of the top speeds can be expected in 2021, as the importance of broadband remains top of the mind during the pandemic.”
The above figures are based on Telecompaper’s continuous analysis of the Dutch broadband market. For a comprehensive overview of market data and trends, including a five-year forecast, the Q3 2020 edition of the Dutch Broadband report is now available for purchase on the Telecompaper website.
From Global Data:
Reference:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/fibre-dominates-dutch-broadband-growth-in-q3-2020–1364963
FTTH accelerating in Europe: penetration forecast to reach 65% in 2026
The number of FTTH/B subscribers in Europe is expected to more than double in the next six years, to 208 million in 2026 compared to an estimated 86 million this year. According to the forecasts by iDate presented at the annual (this time virtual) FTTH Council Europe conference, the number of homes passed by fiber will grow over the same period to 317 million from 195 million. That translates into approximately two-thirds fiber network penetration rate, compared to less than half currently.

Roland Montagne of Idate DigiWorld presenting during the second day of the conference.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The forecasts cover 39 countries across Europe. Idate also looked at the 27 EU members plus the UK and found similar growth rates. The number of FTTH/B subscribers in these countries is expected to roughly triple by 2026, to 148 million from 49 million this year, driven by accelerating roll-out in key markets such as Germany, the UK and Italy. Homes passed in the 28 countries are estimated at 202 million in 2026, versus 105 million this year. Some markets are expected to experience an outstanding growth in the number of homes passed in 2026 compared with 2019, including Germany (+730 per cent), United Kingdom (+548 per cent) and Italy (+218 per cent).
While the Covid pandemic has underlined the need for fast broadband at home, other trends were already underway to support fibre take-up, the researchers said. These include the upcoming switch-off of copper networks, more network-sharing and co-investment agreements, strong commitments from public authorities to FTTH, and the need for fiber backhaul on 5G mobile networks.
In the country rankings, it is predicted that Russia will continue leading in terms of FTTH/B homes passed. However, it is also anticipated that Germany will bag the second spot in the 2026 ranking.
In terms of subscribers, the forecast predicts a further increase to around 148 million in 2026 for EU27+UK and approximately 208 million for EU38+UK. The FTTH/B take-up rate is likely to reach 73 per cent in 2026, demonstrating an upward trend compared with a recorded 23.4 per cent in 2012.
The FTTH Council Europe published a separate study by Wik following up on its research last year into the progress with copper shutdowns. While the situation is fragmented in Europe, progress in some countries shows turning off copper and switching to fibre can have significant benefits for the economy and the environment, as well as improving reliability and customer satisfaction.
Consumer awareness about the copper shutdown has been a positive factor in some countries in stimulating fiber take-up. The latest forecasts on fibre take-up are also based in part on the increased perception of broadband’s importance since the coronavirus pandemic. Nevertheless, additional measures by policy-makers aimed at increasing take-up are still crucial for Europe to benefit from the potential of full fiber, the Council said.
FTTH/B deployments are intensifying across Europe, so it is worth noting that a new digital divide for teleworking performance was revealed by the Covid-19 crisis. Beyond its impact on public policies, it is clear that Covid-19 has changed public perception of the importance of broadband and willingness to accept premium for fiber. This new trend is one of the key drivers for the very high estimates for FTTH/B take up. However, additional measures by policy-makers aimed at increasing take-up are still crucial for the future of full fiber.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.fibre-systems.com/news/fibre-forecasts-revealed-ftth-conference
India’s Telco and Infrastructure Groups: Fiber Optic Network Growth Essential
Growth in fiber optic network deployments are essential to further improve the quality of telecom services and support the surging mobile Internet demand as well as have potential to bring substantial social and economic benefits to consumers, businesses and state governments, India’s telco and infrastructure groups said. The Delhi-based telecom body represents Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea.
“Growth of fibre is the foremost priority for the ongoing exponential increase in data demand and improved quality of services,” the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) director-general SP Kochhar told ETTelecom.
Currently, India has an optical fiber-based network spanning across 28 lakh (100,000) kilometres as against the target set up by the National Broadband Mission to deploy as much as 50 lakh kilometres of optical fiber by 2024.
Kochhar’s views were seconded by the Towers and Infrastructure Providers Association (Taipa) that lobbies for companies such as Bharti Infratel, American Tower Corporation (ATC) India, Ascend Telecom Infrastructure, Indus Towers and Sterlite Technologies.
“The fiberisation of existing telecom infrastructure has the potential to bring substantial social and economic benefits to governments, citizens and businesses through an increase in productivity, competitiveness, improvements in service delivery, and optimal use of scarce resources like spectrum,” Tilak Raj Dua, director-general at Taipa said.
Editor’s Note:
The National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) is a project initiated in 2011 and funded by Universal Service Obligation Fund to provide broadband connectivity to over 200,000 gram panchayats of India at an initial cost of ₹200 billion (US$2.8 billion). This is to be achieved utilizing the existing optical fiber and extending it to the Gram Panchayats and Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), is a special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), PSU set up under companies act by Govt of India under Rule 1956 has been registered on Feb 25, 2012 for management and Operation of NOFN. More info at: http://www.bbnl.nic.in/index1.aspx?lsid=13&lev=1&lid=13&langid=1

Indian Railways Fiber Optic Network Map
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The pan India average of fiber to the tower ratio presently stands at 32% as against the target of 70% by 2024, envisaged by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), according to Taipa statistics.
Following the progression in the fourth-generation (4G) network deployments over the last couple of years, and the upcoming fifth-generation (5G) cellular technology, experts caution that low fiberization would eventually impact the service delivery, and a uniform policy across the country is much needed.
“In the last four years we have not had an increase in backhaul spectrum, hence, we are dealing with constrained factors and have to manage the quality of services based on existing capacity, for everybody’s good,” Kochhar said.
Coai said that the increased fiberization would meet the present requirement of bandwidth and future technologies such as 5G, and other emerging technologies,” Kochhar said and added that the early allocation of E and V bands to meet the backhaul requirements is also being considered by the government.
Dua further said that in order to address the increased data consumption in rural and urban areas and remote working following the Covid-19 outbreak, the role of fiberisation to propel digitalisation has increased multifold.
India, according to Crisil needs a tectonic shift in the fiberization landscape, and investment in fiberised backhaul infrastructure providing unlimited capacity and higher data speeds has to gain further traction if 5G has to become a reality.
Sandeep Aggarwal, co-chairman of the Telecom Equipment and Services Export Promotion Council (Tepc) believes that it is imperative to have a robust fibre infrastructure in the country to complement the next-generation or 4G and 5G technologies in line with the National Digital Communications Policy (NDCP) unveiled in 2018.
Former telecom secretary Shyamal Ghosh-headed Tepc represents Aksh Optifibre, Birla Cables, Paramount Wires & Cables, Himachal Futuristic Communications, Finolex Cables and Polycab Wires.
“With nearly 3 million kilometres of optic fibre cable (OFC) presently deployed, India will need to further enhance the footprint with an average of 2-kilometre of fibre per person,” Aggarwal said and added that more than 1 million kilometres of cable TV (CATV) fibre has been laid over the last one year in the country.
Private and public sector entities such as Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea, Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) and RailTel majorly contribute to the current fibre footprint in the country in addition to Centre’s ambitious BharatNet program that further aims to deploy nearly 8 lakh kilometres of fibre network separately.
There is a need to adopt new business models such as hiving off fibre assets via the Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) model that will help in reducing capital expense requirements and allowing telecom operators to focus on topline growth opportunities, according to Aggarwal.
Billionaire Mukesh Ambani-owned Reliance Jio and Sunil Mittal-driven Bharti Airtel have already sold-off their fiber verticals to become financially-nimble pure-play telecom services companies.
Taipa’s Dua feels that the upcoming cities would be built on the basis of readily available optical fiber cables, and next-generation telecom infrastructure and technologies like 5G.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
ICRA: Indian Telecom Industry Must Migrate from Copper to Dense Fiber Optic Networks
Swisscom achieves 50 Gbps on a fixed PON connection – a world first!
Swisscom has achieved transmission speeds of 50 Gbps in a real PON (Passive Optical Network) environment test – a world first, according to the company. Swisscom has upgraded existing OLT (Optical Line Termination) hardware with a 50 Gbps PON Line Card prototype to reach a download speed of 50 Gbps and an upload speed of 25 Gbps on a fixed network.
The PON technology can be ready to market and deployed in around two years, according to Swisscom. It can be an option for business customers initially. Progressive network virtualization will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements.
The 10 Gbps service is expected to be sufficient for the residential mass market for several years yet, the company said. The 50 Gbps option allows for flexible deployment using existing fibre-optic infrastructure.
Markus Reber, Head of Swisscom Networks, said: “There is no question that the bandwidth need will continue to increase over the coming years. That’s why, here at Swisscom, we are already considering how our technology needs to develop to ensure that Switzerland continues to be ready to take advantage of the latest digital services with the best possible experience in the future. The results of testing based on PON technology and architecture clearly demonstrate that we have some powerful options available.”
“In my opinion, PON with 50 Gbit/s will be an option for the business customer market initially. Progressive network virtualisation will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements, for instance. In contrast, the 10 Gbit/s already available in the residential mass market should be more than enough for several years to come. However, the 50 Gbit/s option offers even more opportunities, as it allows the existing fibre optic infrastructure to be deployed in a more versatile way. As an example, the technology will soon facilitate access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, as the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households. With a transmission speed of 50 Gbit/s, there is ample bandwidth available.”
The technology also will support fiber optic access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, since the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households.
Swisscom says that “over the coming years, the development of digital applications will result in a similar growth in bandwidth need as seen in recent years, when it increased more than tenfold within a decade. Swisscom is therefore investing in network expansion on an ongoing basis, deploying the latest innovative technologies to do so and safeguarding Switzerland’s high degree of digital competitiveness.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In April 2020, market research powerhouse Omdia (owned by Informa) forecast that In the 2018-2025 timeframe, the PON market will see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% to be worth $8.4 billion by 2025. “This market remains in an upswing as operators continue to expand and upgrade their fiber-based access networks for both residential and non-residential subscribers and applications,” states the Omdia team in their report (published prior to the global impact of COVID-19, it should be noted).
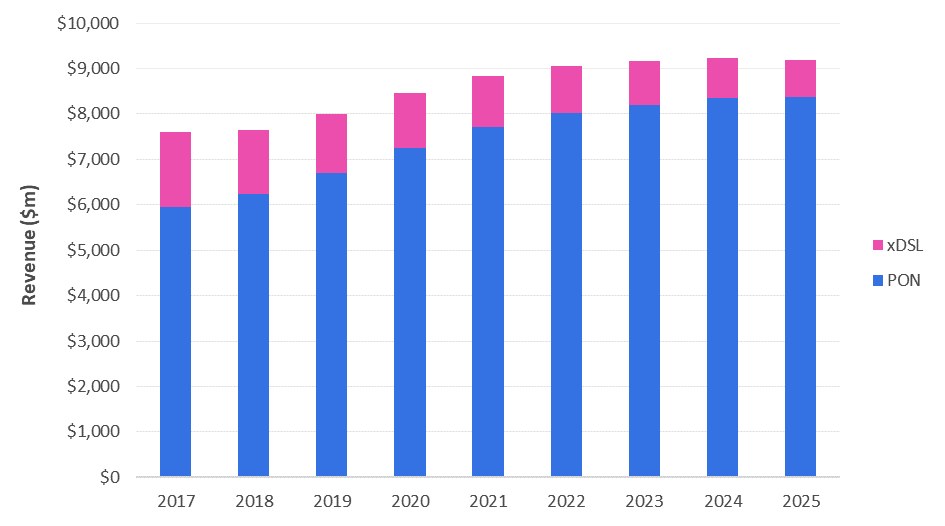
Omdia: PON and xDSL/Gfast equipment market by major segment, 2017–2025
Growth in the PON market will be driven by increasing demand for next-generation PON equipment, including 10G GPON, 10G EPON, NG-PON2 and 25G/50G PON, according to Omdia: By 2021, most GPON OLT (optical line terminal) shipments are expected to be 10G.
Omdia expects demand for NG-PON2 equipment (which is expensive because it includes tunable lasers) is expected to be limited, with significant deployments anticipated only by one major operator, Verizon.
In Western Europe, PON investments are only just starting: That market is set for a CAGR of 16.5% to be worth $1.6 billion in 2025.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.swisscom.ch/en/about/news/2020/10/08-weltpremiere.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/swisscom-reaches-50-gbps-in-real-network-environment–1357116
http://www.broadbandworldnews.com/document.asp?doc_id=758638
Deutsche Telekom in 10-year contract with Telefonica Germany for FTTH access

Telia International Carrier Business (#1 Internet Backbone Network) Sold for $1.3B to Swedish Pension Funds
Telia Company today announced that it reached an agreement with Polhem Infra for the sale of its international carrier business. At the same time, Telia Company entered a long-term strategic partnership with Telia Carrier, securing continuous world-leading network solutions to Telia’s customers. The acquisition is Polhem Infra’s first investment in this field. The company is jointly owned by the Swedish pension funds First AP Fund, Third AP Fund and Fourth AP Fund.
Allison Kirkby, president and CEO of Telia, confirmed that the majority of the proceeds from the sale of Telia Carrier to the Polhem Infra unit “will be used to strengthen our balance sheet and thereby provide a solid financial base for Telia Company and our shareholders. Telia can now fully concentrate on our Nordic and Baltic footprint.”
Telia Carrier holds the #1 position in the global ranking of companies with Internet backbone networks. Content, services and operator customers of Telia Carrier account for 65% of global Internet routes. Its network spans across Europe, North America, and Asia, connecting customers in more than 120 countries, with the Scandinavian footprint being particularly strong through the so-called Scandinavian Ring – the part of Telia Carrier’s network that connects major Baltic and Nordic cities.


The change of ownership will enable Telia Carrier, with its 530 employees, “to drive a level of investment in network development, services and customer care programs that brings benefits to content providers, operators and enterprises beyond that of any competitor.”
Kirkby has been CEO since early May, but has already been making her mark. As well as streamlining the Nordic telco’s operators, she has also assembled a new-look management team.
Jefferies said the sale of Telia Carrier appeared supportive and highlighted the use of near 30% of proceeds to top up the dividend. “This is a welcome first move of the new, highly respected CEO,” the investment bank said in a note to clients. Jefferies said the sale of Telia Carrier appeared supportive and highlighted the use of almost 30% of the proceeds to top up the dividend.
Nick Del Deo of Moffett-Nathanson wrote about Telia Carrier vs Cogent Communications (U.S.) in a note to clients:
While Telia Carrier doesn’t break out its business mix, a substantial share of its revenue comes from transit, likely in the same range as Cogent’s, or about one third of the total. It’s one of the four largest transit providers globally, along with CenturyLink, Cogent, and NTT. A broad suite of other services – DIA, wavelengths, wholesale voice, etc. – round out its product portfolio. Like Cogent, its internet backbone spans the globe, with its presence concentrated in Europe and North America. The comparisons may not be perfect, but Telia Carrier claims to have 67K km route miles of fiber vs. Cogent’s 93K km of intercity fiber, and 300 PoPs globally vs. the ~1K carrier-neutral data centers to which Cogent connects. Their route maps look quite similar, but Cogent extends into more small markets than Telia Carrier and has more of a presence in Latin America and Asia-Pacific.
Telia Carrier’s Global Fiber Optic Network:

Image Credit: Telia Carrier
References:


