fiber optics
UK’s CityFibre launches 5.5Gbit/s wholesale broadband service- 3 times faster than BT Openreach
CityFibre, the UK’s largest independent full fiber optic platform, has unveiled a new 5.5Gbit/s wholesale broadband internet service based on 10Gbit/s XGS-PON technology that has already been rolled out across 85% of the company’s network. CityFibre claims its new product is more than three times faster than the highest rate available service from its much larger rival, Openreach (the network access arm of BT). and available at a much lower wholesale cost, CityFibre’s 5.5Gb symmetrical product will enable partners to offer a range of Multi-Gig speed tiers to customers, improving margins whilst providing a valuable customer retention tool for the long term.
Highlights:
- CityFibre’s new 5500/5500Mbps service offers >3x faster downloads, >45x faster uploads than BT Openreach’s fastest full fibre service which is 1800/120Mbps and is delivered over its GPON network.
- CityFibre’s upgraded XGS-PON network provides numerous benefits over GPON technology, including network cost savings, reduced power consumption, improved performance, and enhanced efficiency.
- CityFibre’s launch of its new Multi-Gig products enables the UK to keep pace with countries including France, the Netherlands, New Zealand and the United States of America where consumers are already making the most of affordable Multi-Gig services.

Photo Credit: CityFibre
Greg Mesch, CEO of CityFibre, said: “The UK’s full fibre future is here, thanks to CityFibre’s powerful, 10Gb XGS-PON network. Our ISP partners are already connecting customers with speeds over 2Gb and exceeding expectations when it comes to quality and reliability, but our next generation of full fibre will set a new standard for what’s possible.
“CityFibre started out to challenge the incumbents and bring choice and competition to the UK market. This is another huge step-forward, giving ISPs more power and flexibility than ever before and bringing affordable Multi-Gig speeds and an unrivalled experience to millions of UK consumers.”
Even faster multi-gig services will be launched in 2026 the company promises.
CityFibre’s network now passes more than 4.3 million premises, which the company says means it is more than halfway along its journey towards its “rollout milestone” of 8 million premises. Actual service take-up, however, has reached just 518,000, an increase of around 181,000 customers on its previous total. During the year covered by the earnings statement, CityFibre announced a partnership with Sky that will see the UK’s second-largest broadband provider launch services on CityFibre’s network later this year.
References:
https://cityfibre.com/news/cityfibre-unveils-new-5-5gb-wholesale-product-its-fastest-ever
Nokia and CityFibre sign 10 year agreement to build 10Gb/second UK broadband network
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications fiber growth accelerates in Q1 2025
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
Google Fiber planning 20 Gig symmetrical service via Nokia’s 25G-PON system
STELLAR Broadband offers 10 Gigabit Symmetrical Fiber Internet Access in Hudsonville, Michigan
Frontier Communications fiber growth accelerates in Q1 2025
Frontier Communications reported record fiber subscriber net adds in Q1-2025. However, the “fiber first” carrier had a loss of $0.26 per share, compared to break-even earnings per share a year ago. The telco posted revenues of $1.51 billion for the quarter ended March 2025, compared to year-ago revenues of $1.46 billion.
“We had the strongest start to a year yet, led by continued strength in our fiber business,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier. “Consumers, business owners and technology companies are increasingly relying on fiber to power networks and connect to the digital economy – and that trend is shining through in our results. The team delivered 19% growth in fiber broadband customers and 24% growth in fiber broadband revenues this quarter, which taken together drove record first-quarter growth in both revenue and Adjusted EBITDA.”
Jeffery continued, “We also hit a milestone in the first quarter, growing our fiber network to reach more than 8 million passings. We started this turnaround journey with a goal of 10 million fiber passings and four years later, I’m proud to say that we’re nearly there. As we scale our network, we’re expanding access for millions of Americans and building a legacy that will continue to endure long after our planned combination with Verizon.”
First-Quarter 2025 Highlights
- Added 321,000 fiber passings to reach 8.1 million total locations passed with fiber
- Added 107,000 fiber broadband customers, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 19.3% year-over-year
- Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $68.21 increased 4.7% year-over-year
- Revenue of $1.51 billion increased 3.4% year-over-year as growth in fiber-based products was partly offset by declines in copper-based products
- Operating income of $76 million and net loss of $64 million
- Adjusted EBITDA of $583 million increased 6.6% year-over-year driven by revenue growth and lower content expense, partially offset by higher customer acquisition costs1
- Cash capital expenditures of $757 million plus $16 million of vendor financing payments resulted in total cash capital investment of $773 million2
- Generated net cash from operations of $519 million
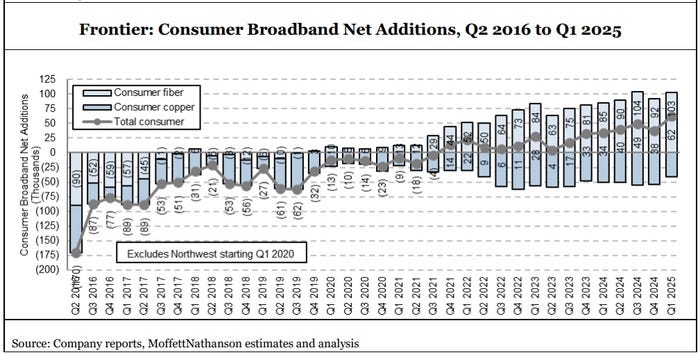
Frontier added 103,000 residential fiber broadband customers in Q1 2025, beating the 95,000 expected by MoffettNathanson (see graph below). Frontier’s residential fiber additions in the quarter were just shy of the record 104,000 it added in Q3-2024. The fiber facilities based carrier gained a record 59,000 net broadband customers in the period, which included losses of legacy copper subscribers.
Frontier built another 321,000 fiber passings in Q1-2025, pushing its total past the 8 million mark. Alongside subscriber growth, Frontier’s consumer fiber broadband average revenue per unit (ARPU) also climbed – to $68.21, up 4.7% versus the year-ago period.
Frontier said the “vast majority” of new fiber subs are now taking multi-gigabit speeds. A specific number wasn’t shared, but back in Q2 2024 more than 60% of new Frontier fiber customers took speeds of 1 Gbit/s or more.
CEO Jeffery said Frontier is sticking with its plan to build fiber to 1.3 million locations in 2025. The current pace puts Frontier on a path to reach its 10 million fiber passing goal around the third quarter of 2026, New Street Research analyst Jonathan Chaplin said in a research note.
Jeffery said Frontier’s “fiber build machine” is capable of going faster, but he stressed that the current pace gives the company the time it needs to also sell, service and support fiber broadband as it builds. “The whole company needs to be in balance. We want more customers and higher ARPU, and we’ve demonstrated that it’s doable,” Jeffery said.
He attributed ARPU growth to multiple factors, including customers taking higher-level speed tiers and subscribing to additional, premium services. Frontier estimates that more than 50% of new customers take some type of add-on, including whole-home Wi-Fi and YouTube TV.
Jeffery said Frontier is seeing good adoption of “Unbreakable Wi-Fi,” a $25 per month add-on that flips to 4G cellular backup (with 130 gigabytes of data per billing cycle) when the primary fiber connection is down. Those customers can also opt for a battery backup that provides up to four hours of backup power.
Frontier’s Q1 results come as it moves ahead with its proposed acquisition by Verizon which is currently expected to close by the first quarter of 2026. Jeffery would only say that the deal process is going smoothly at the state and federal levels.
“My job is now very much to deliver this asset in the best possible shape it can be to its future owner, Verizon,” he said. “I’m delighted to say that that’s really been evident in our first quarter results.”
References:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250429128668/en/Frontier-Reports-First-Quarter-2025-Results
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Frontier Communications recovering from unknown cyberattack!
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
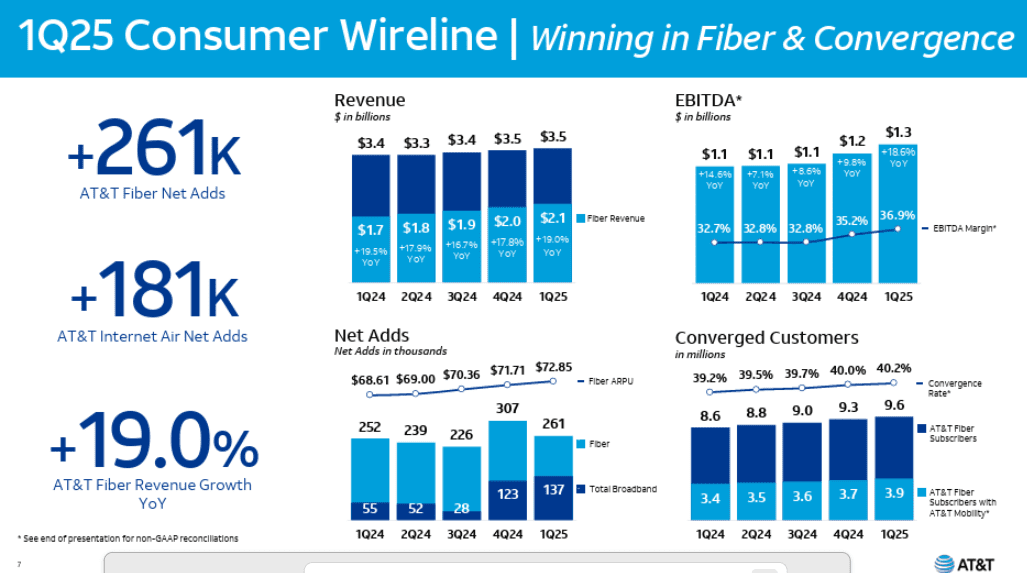
In the 1st quarter of 2025, AT&T’s fiber business showed strong performance, with fiber revenue growing by 19% year-over-year and 261,000 net fiber subscribers added. This growth helped drive overall wireline revenue and operating income, with fiber revenue contributing significantly to the 9.6% broadband revenue increase. AT&T’s fiber strategy is a key part of its broader plan for growth, including 5G wireless, and is expected to continue contributing to strong financial results. At the end of the 1Q2025, AT&T said that 29.5 million locations were passed with its fiber network. The company expects to surpass 30 million by midyear, months ahead of its original target. Consumer fiber broadband revenue was $2.1 billion in the quarter, up 19% year-over-year, as more customers upgraded to faster service tiers. Executives noted that more than 40% of AT&T Fiber households now also subscribe to AT&T wireless, part of a deliberate strategy to drive “converged” customer relationships.
AT&T continues to lead the Fiber-to-the-Home market, and has reportedly been in talks to acquire Lumen Technologies’ consumer fiber business in a deal valued at more than $5.5 billion, according to Bloomberg and Reuters
CFO Pascal Duroche on the 1Q2025 earnings call:
“We delivered 261,000 AT&T Fiber net adds, up from 252,000 in the first quarter of last year. This was driven by growth in our consumer locations served with fiber, which reached 23,800,000 at the end of 1Q and growing contribution of net adds in regions served with Giga Power Fiber. We love the return profile of fiber and the lift it provides our mobility business only makes investing in fiber more attractive. AT and T Internet Air net adds were 181,000 in the quarter, which is a significant improvement from a year ago, driven by broader availability across our distribution channels. Our combined success with these two services helped us deliver 137,000 total broadband net adds in the quarter.
This marks our seventh straight quarter of overall broadband subscriber growth and second consecutive quarter with more than 100,000 broadband net adds. We grew Consumer Wireline revenue by 5.1% versus the prior year. This was driven by fiber revenue growth of 19%, reflecting subscriber gains and solid fiber ARPU growth of 6.2%. Consumer wireline EBITDA grew 18.6% for the quarter. Our first quarter results benefited from vendor settlements that positively impacted our total wireline operating expenses by approximately $100,000,000 Roughly $55,000,000 of the impact was in Consumer Wireline with the rest in Business Wireline.”
AT&T is investing heavily in its fiber network which is reflected in the increase in its capital expenditures (CAPEX) which are expected to remain in the $22 billion range annually from 2025 through 2027.

AT&T logo on a building in Pasadena, California, U.S., January 24, 2018. REUTERS/Mario Anzuoni/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Where we have fiber, we win,” said CEO John Stankey. “This dynamic continues to drive growth, shown by our increasing rate of convergence, customer penetration and significant wireless share gains within our fiber footprint.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/1q-earnings.html
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
Corning to Build New Fiber Optic Plant in Phoenix, AZ for AT&T Fiber Network Expansion
AT&T CEO John Stankey: 30M or more locations could be passed by AT&T fiber (he said that in Sept. 2021)
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
Evercore: T-Mobile’s fiber business to boost revenue and achieve 40% penetration rate after 2 years
T-Mobile’s fiber business could serve about 5 million U.S. customers and generate up to $5 billion in revenue during the next five years, according to financial analysts at Evercore. That call is the investment advisor firm’s first take at evaluating the maturation of T-Mobile’s fiber plans. It’s based on the assumption that T-Mobile will close its deal to acquire fiber operator Metronet, following the recent closure of another deal with EQT for fiber operator Lumos. Evercore’s projections do not assume that T-Mobile will make a play for another fiber operator like Lumen Technologies.
“Looking to 2030, we expect 14 million [fiber] passings … and 4.8 million subscribers,” the analysts wrote in a note to investors this week. “Assuming a $75 ARPU [average revenue per user] growing 4% year over year implies ~$5 billion of revenue in 2030. “While it hasn’t shared subscriber targets, [T-Mobile] management has expressed confidence that it would see higher long-term market penetration than typical [fiber] overbuilders (e.g., ~35%) benefitting from its national brand and advertising, digital and retail distribution, ability to take advantage of the waiting list it has for FWA [fixed wireless access] in markets where demand outstrips supply,” the Evercore analysts added.
Evercore assumes that T-Mobile Fiber (see plans below) will be able to capture 10% market share within six months of launch and 20% within a year. After two years, the analysts predict T-Mobile Fiber will command 40% penetration (meaning, 40% of the customers reached by its fiber connections will subscribe to those connections).
T-Mobile Fiber Plans:
- Fiber 500 (500 Mbps): Superfast performance for gaming, streaming, and more.
- Fiber 1 Gig (1000 Mbps): Blistering speeds for every device and user in your home.
- Fiber 2 Gig (2000 Mbps): Our fastest speeds and largest capacity for more devices and users.
 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….“For now, until there’s greater color from management, we’ve assumed T-Mobile will see 25% EBITDA [earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization] margins on its Fiber revenue. This could be conservative over time,” the Evercore analysts wrote. They predicted overall EBITDA from T-Mobile Fiber of around $340 million in 2026, growing to $1.24 billion in 2030. And that, they said, would equate to free cash flow of $270 million in 2026, growing to $1 billion by 2030.
“Pricing will evolve as T-Mobile acquires and operates Metronet and Lumos’ subscribers along with the competitive dynamics across the broadband market. T-Mobile has a clear history of being a disruptor, so it could be more aggressive on pricing than we expect, resulting in downside to our ARPU and revenue estimates,” the Evercore analysts warned. They noted that T-Mobile Fiber in some Colorado markets today costs $55 per month for 500 Mbit/s connections. That’s similar to local incumbents Lumen Technologies ($50 for 500 Mbit/s) and Comcast ($55 per month for 600 Mbit/s).

Convergence of mobile and fiber access will provide a tailwind for T-Mobile, potentially driving increased postpaid phone share and revenue. “Despite management’s tone around the benefits of convergence, we believe there will clearly be an opportunity to drive higher postpaid phone share across the growing number of households that ultimately end up taking T-Mobile fiber,” according to the Evercore analysts. They predicted that T-Mobile’s fiber operations would eventually help improve the operator’s postpaid smartphone net customer additions by up to 650,000 per year, and that it will drive the operator’s annual wireless service revenues up by $200 million to $350 million.
An important insight into T-Mobile’s convergence strategy emerged in the wake of its acquisition of Lumos. “New and existing customers will enjoy VIP treatment through Magenta Status, which includes exclusive benefits like discounts on food, gas, entertainment and top brands, plus freebies every Tuesday in the T-Life app. All with T-Mobile’s standard ‘no exploding bills’ pricing structure,” T-Mobile said of its new Lumos customers.
“One app. All the things,” T-Mobile proclaims of the T-Life app it launched roughly a year ago. The app is available to all T-Mobile smartphone customers – and now its new fiber customers.
“Get the latest exclusive perks from T-Mobile Tuesdays, and take advantage of all your Magenta Status benefits,” T-Mobile said of its T-Life app. “You can also pay your bill, add a line to your account, and track orders straight from the app. And you can manage your account, configure your T-Mobile Home Internet gateway, and more. If you need help with anything, customer care is available at the tap of a button.”
The analysts expect T-Mobile’s fixed wireless access business to continue gaining traction, potentially reaching 7% of the total broadband subscriber base by 2025.
Separately, Verizon is now Evercore’s top pick among wireless network operators and is its top value idea.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://fiber.t-mobile.com/
https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/t-mobile-fiber-could-see-5m-customers-and-5b-in-revenue-by-2030
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T claims it achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network (spanning Newark, New Jersey to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania). That is four times faster than its current top speed of 400Gb/s per wavelength!
The 1.6Tb/s wavelength carried two IEEE 802.3df-2024 standard-based 800 Gigabit Ethernet end-to-end circuits, an industry first. It is a full, uninterrupted data path utilizing a single light frequency across the entire fiber length between two endpoints. The single-carrier 1.6 Tb/s wavelength was transported alongside existing live customer traffic on 100Gb/s and 400Gb/s wavelengths.
Open-sourced white box switches were the network equipment used during the trial. The white boxes are designed using the Broadcom Jericho3 packet processor chip and can provide up to 18 x 800G network interface ports all within a 2RU platform. The (Israel based) DriveNets Network Cloud software-based solution is hardware-agnostic and runs open APIs on the white boxes to perform data and control plane functions, including routing at 800G. The use of white boxes and the disaggregation of the hardware and software control costs and facilitate faster innovation.
The two 800GbE signals from the white box were multiplexed to 1.6 Tb/s in Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 Extreme coherent optical transponder, which is the first coherent optical solution to use a 200Gbaud design and 3nm coherent DSP ASIC and to reach speeds up to 1.6 Tb/s on a single carrier. The WL6e technology reduces the space and power per transmitted bit by 50% compared to current 800G transponders. This trial is the first to demonstrate WL6e at 1.6Tb/s with standards compliant 800GbE clients.
In the Newark and Philadelphia offices, 800G DR8 pluggable transceivers from Coherent were installed in the white box router and WL6e transponder to create the cross-office connectivity between the packet and optical technologies. And 800GbE client signals, provided by Keysight’s AresOne-M 800GE testset, fed the white box through additional pairs of 800G DR8 pluggable client optics, allowing verification of end-to-end performance of the two 800GbE services from Newark to Philadelphia.
Quotes:
“Traffic on AT&T’s network continues to increase as consumers are using more connected devices,” said Mike Satterlee, vice president, Network Infrastructure and Services, AT&T. “We anticipate network traffic growth to double by 2028 and the technologies demonstrated in this trial will play a key role in AT&T’s continued efforts to keep up with increasing customer demand to send data, watch videos, and use streaming services.”
“This groundbreaking achievement with AT&T adds to a growing list of Ciena industry-firsts that push the boundaries of optical network speed and capacity,” said Dino DiPerna, senior vice president, Global Research and Development, Ciena. “Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 coherent optics will support AT&T’s next gen converged optical network and efforts to build a cloud-based and AI-ready network with greater scale, flexibility and efficiency.”

Verizon’s 1.6Tb/s on Metro Fiber Network:
AT&T’s announcement comes just a few months after arch-rival Verizon announced a 1.6 Tb/s milestone of its own. Verizon also, working with Ciena, achieved that peak speed on a single wavelength, but on its metro fiber (not long distance) network. Verizon is mainly looking to advance through M&A. Its proposed acquisition of Frontier Communications is still pending, with some Frontier shareholders insisting that the US$20 billion price tag undervalues the operator.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T has spent the past six months demonstrating that it aims to build its way to fiber domination. It rolled out fiber to around 600,000 premises in the 4th quarter of last year, taking its total fiber footprint to 28.9 million locations; it is shooting for 50 million by the end of 2029.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/data-transport.html
https://www.business.att.com/products/wavelength-services.html
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/at-t-touts-1-6-tbps-fibre-speed-milestone-as-us-battle-continues
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
Nokia, Windstream Wholesale and Colt complete world’s first ultra-fast 800GbE optical and IP service trial
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
Bell Canada buying Ziply Fiber for C$7 billion; will become 3rd largest fiber ISP in U.S.
Bell Canada buying Ziply Fiber for C$7 billion; will become 3rd largest fiber ISP in U.S.
Bell Canada (owned by BCE) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Ziply Fiber in a deal with a transaction value of around C$7 billion (C$3.65 billion in cash plus the assumption of debt). The acquisition is expected to close in the second half of 2025, subject to certain customary closing conditions and the receipt of certain regulatory approvals. Following the deal closure, Ziply Fiber, a fiber Internet provider in the Pacific Northwest of the U.S, will operate as a separate business unit and will continue to be headquartered in Kirkland, Washington.
BCE said the acquisition enhances Bell’s growth profile and strategic position by giving it a foothold in the large, underpenetrated U.S. fiber market. The deal will increase its scale, diversify its operating footprint and unlock significant growth opportunities. This deal would make Bell Canada the third largest fiber internet services provider in North America, after AT&T and Verizon. It follows Verizon’s recent announcement that it’s acquiring Frontier Communications for $20 billion.
Currently, AT&T passes 28 million locations with fiber, and Verizon passes 17.8 million.

AT&T says it will pass 30 million locations by the end of 2025 and may ultimately choose to pass 45 million locations.
Verizon says it will pass 30 milli
on locations after the Frontier buyout closes.
When the Ziply buy-out is finalized, Bell Canada will have about 9 million fiber locations, combining its 7.7 million locations in Canada with Ziply’s 1.3 million in the U.S. Bell Canada said it has a goal of passing 12 million fiber locations in North America by 2028.
Lumen’s original target for its residential Quantum Fiber expansion was 12 million locations, but the company cut its target to between 8 million and 10 million. Lumen expects to exceed 500,000 new passings in 2024.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Ziply was founded in May 2020 when it purchased network assets from Frontier in the states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana. The company was founded by CEO Harold Zeitz and Steve Weed, who’s the executive chairman. Ziply’s current owners are Wave Division Capital and Searchlight Capital, which are selling to Bell Canada.
Zeitz told Fierce Network about two-thirds of Ziply’s broadband footprint is currently fiber, and it’s working to overbuild its remaining copper plant with fiber. “In addition to building in the ILEC footprint, we’re also building outside that footprint in adjacent markets,” said Zeitz. By “adjacent markets” he was referring to the many towns “adjacent” to Ziply markets where Lumen Technologies is the main broadband provider. Ziply has a goal to build fiber in about 80% of its footprint, but it may expand that. And under Bell’s ownership it plans to build 20% faster.
“We just want to deliver a refreshingly great experience to all the towns in our four-state area,” Zeitz said. “We think there’s tremendous opportunity organically. There are 50-60 million households that don’t have fiber. I think over time we’ll see more acquisitions,” he added.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analysts at AlixPartners said there are more than 400 small fiber providers in the U.S. that could be acquired by investors or larger fiber optic telcos. The firm conducted a survey in August of 60 executives at different fiber companies and 1,000 U.S. residents. According to the survey, 93% of respondents said consolidation is happening or will happen soon. “It’s clear based on the results that this is a buyer’s market—but sellers can use this knowledge to their advantage as well, the firm noted.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/bces-bell-canada-buy-ziply-fiber-around-c-7-bln-cash-debt-deal
Nokia, Windstream Wholesale and Colt complete world’s first ultra-fast 800GbE optical and IP service trial
Nokia, Windstream, and Colt Technology Services have completed an 800 Gigabit Ethernet (800 GbE) trial spanning 8,500km between London and Chicago over a subsea and terrestrial route. The trial showcased innovative power-saving networking technologies from the three global tech businesses to test the boundaries of next-generation wavelength, capacity, speed and latency between two of the world’s largest financial trading hubs.
Colt’s five transatlantic subsea cables and part of its extensive terrestrial fiber optic network were connected with Windstream Wholesale’s domestic U.S. low latency, optical fiber Intelligent Converged Optical Network (ICON) monitoring speed and performance. Colt and Windstream Wholesale have partnered to demonstrate the world’s first transoceanic 800 gigabit ethernet (GbE) end-to-end service transport from router to router over 1Tbps optical transport. The trial was successfully delivered using Nokia’s sixth-generation Photonic Service Engine (PSE-6s) coherent optics and 7750 Service Router (SR) high-performance routing platforms boosting internet service speeds and supporting ultra-high wavelength capacity, while maintaining power efficiency.
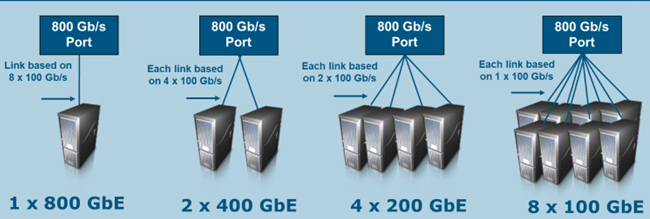
The companies say that 800G marks a breakthrough in service bandwidth, doubling capacity to support advanced network applications like AI data center networking, content delivery networks, and financial data hub connections.
| Ethernet Rate | AUI | BP | Cu Cable | MMF 50m | MMF 100m | SMF 500m | SMF 2km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Gb/s | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4 pairs |
| 800 Gb/s | 8 lanes | 8 lanes | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs |
Quotes:
Buddy Bayer, Chief Operating Officer of Colt Technology Services, said: “Pushing the boundaries of technology innovation is a fundamental part of our customer commitment: it means we stay a step ahead of the market, so we’re ready when our customers ask, “What’s next for us?” This trial has seen us build a powerful industry collaboration to explore the ‘what’s next?’. It’s tested the limits of infrastructure performance and capability across thousands of miles of land and sea with incredible networking technologies, and it’s demonstrated the power and potential of what can be achieved, without skipping a beat.”
Joe Scattareggia, President of Windstream Wholesale, said: “Our latest innovation represents a true game-changer for global connectivity. By partnering with two extraordinary leaders in the industry, we’re enabling unprecedented bandwidth capabilities that are essential for driving AI-powered applications worldwide for our customers. As an optical technology leader, Windstream Wholesale and our partners are establishing 800GbE as the next evolutionary advancement increase for wave services. This collaboration has pushed the boundaries of what’s possible, creating a network solution like no other. Together, we’re not just meeting the demands of the future—we’re shaping it.”
Federico Guillén, President of Network Infrastructure at Nokia, said: “Such an ambitious project — to link two of the world’s most important financial hubs — sets the bar very high for network capacity, speed, security and reliability. This demonstration would simply not have been possible without the commitment of Nokia and our partners to the highest standards of innovation in networking technology. Together, we are redefining the art of the possible for IP and optical networks enabling cross-continental subsea and terrestrial communications.”
Following the successful completion of the trial, the organizations are currently exploring options to bring 800GbE connectivity services to market for global business customers.
Resources and additional information:
Webpage: Nokia PSE-6s
Webpage: Nokia Optical Networks
About Nokia:
As a B2B technology innovation leader, we are pioneering networks that sense, think and act by leveraging our work across mobile, fixed and cloud networks. In addition, we create value with intellectual property and long-term research, led by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs.
With truly open architectures that seamlessly integrate into any ecosystem, our high-performance networks create new opportunities for monetization and scale. Service providers, enterprises and partners worldwide trust Nokia to deliver secure, reliable and sustainable networks today – and work with us to create the digital services and applications of the future.
About Colt Technology Services:
Colt Technology Services (Colt) is a global digital infrastructure company which creates extraordinary connections to help businesses succeed. Powered by amazing people and like-minded partners, Colt is driven by its purpose: to put the power of the digital universe in the hands of its customers, wherever, whenever and however they choose.
Since 1992, Colt has set itself apart through its deep commitment to its customers, growing from its heritage in the City of London to a global business spanning 40+ countries, with over 6,000 employees and more than 80 offices around the world. Colt’s customers benefit from expansive digital infrastructure connecting 32,000 buildings across 230 cities, more than 50 Metropolitan Area Networks and 250+ Points of Presence across Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Africa and North America’s largest business hubs.
Privately owned, Colt is one of the most financially sound companies in the sector. Obsessed with delivering industry-leading customer experience, Colt is guided by its dedication to customer innovation, by its values and its responsibility to its customers, partners, people and the planet.
For more information, please visit www.colt.net
About Windstream Wholesale:
Windstream Wholesale is an innovative optical technology leader that delivers fast, flexible, and customized wavelength and dark fiber solutions to carriers, content providers, and hyperscalers in the U.S. and Canada. Windstream Wholesale is one of three brands managed by Windstream. The company’s quality-first approach connects customers to new opportunities and possibilities by delivering a full suite of advanced communications services. Windstream also offers fiber-based broadband to residential and small business customers in 18 states as well as managed cloud communications and security services to mid-to-large enterprises and government entities across the U.S. Windstream is a privately held company headquartered in Little Rock, Ark. Additional information about Windstream Wholesale is available at windstreamwholesale.com. Follow us on X (Twitter) @Windstream and LinkedIn at @Windstream.
To view the Windstream Wholesale network map, visit https://www.windstreamwholesale.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Windstream-Wholesale-National-Network.pdf
References:
https://standards.ieee.org/beyond-standards/ethernets-next-bar/
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
Ethernet Alliance multi-vendor interoperability demo (10GbE to 800GbE) at OFC 2023
Cisco 800G line card for Cisco 8000 Series Routers powered by Silicon One ASIC
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Wall Street Journal reported today that Verizon is on the verge of buying Frontier Communications for as much as $7 billion in a deal that would bolster the company’s fiber network to compete with rivals notably AT&T. With a market value of over $7 billion, Dallas, TX based Frontier provides broadband (mostly fiber optic) connections to about three million locations across 25 states. Frontier is in the midst of upgrading its legacy copper landline network to cutting-edge fiber. Rising interest rates sparked fears among investors, however, that the business would run out of cash and not be able to raise more before completing those upgrades. Frontier has a 25-state footprint and serves largely rural areas. It reported sales of $5.8 billion in 2023, with about 52% of total revenue from activities related to its fiber-optic products and bills itself as “largest pure-play fiber internet company in the US.”
An all-cash deal between the two companies could be announced as soon as Thursday, a person familiar with the negotiations told Bloomberg.
Fiber M&A has heated up as telecom companies and financial firms pour capital into neighborhoods that lack high-speed broadband or offer only one internet provider, usually from a cable-TV company. New fiber-optic construction is expensive and time-consuming, making existing broadband providers attractive takeover targets.
Verizon, with a market valuation of around $175 billion, will be under pressure from shareholders to justify any big purchase after the company paid more than $45 billion to secure C-band 5G wireless spectrum licenses and spent billions more to use them. Executives have said they are focused on trimming the telecom giant’s leverage to put it on a firmer financial footing.
Verizon, the top cellphone carrier by subscribers, has faced increased pressure from competitors and from cable-TV companies that offer discounted wireless service backed by Verizon’s own cellular network. Faced with slowing wireless revenue growth and an expensive dividend, Verizon has invested in expanding its home-internet footprint. It has both 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and its Fios-branded fiber to the premises network.
T-Mobile is the only major U.S. cellphone carrier that lacks a large landline business. Since its 2020 takeover of rival carrier Sprint, the company has focused on 5G dominance and succeeded in growing its cellphone business faster than rivals. That network has also linked millions of customers to its fixed 5G broadband service, which offers cablelike service over the air. T-Mobile’s strategy has shifted in recent months, however, as the company dabbles in partnerships and wholesale leasing agreements with companies that build fiber lines to homes and businesses. The wireless “un-carrier” in July agreed to spend about $4.9 billion through a joint venture with private-equity giant KKR to buy Metronet, a Midwestern broadband provider.
Photo Credit: Jeenah Moon/Bloomberg News
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
A deal for Frontier would be a round trip of sorts for some of the network infrastructure that Frontier bought from Verizon in 2016 for $10.54 billion in cash. Frontier later filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in April 2020 as it burned through cash and was burdened by a heavy debt load. It emerged as a leaner business in 2021 with about $11 billion less debt and focused on building a next-generation fiber optic network.
Frontier’s biggest investors today include private-equity firms Ares Management and Cerberus Capital Management. The company drew the attention of activist Jana Partners last year, which built a stake in the business. Jana delivered a letter to Frontier’s board late last year asking the company to take steps immediately to help reverse its sinking share price, including a possible outright sale.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T has focused on expanding its fiber network since spinning off its WarnerMedia assets in 2022 to Warner Brothers Discovery. AT&T has 27.8 million fiber homes/businesses passed, growing at ~2.4 million per year, plus more locations passed via its Gigapower joint venture. AT&T’s fiber internet business is expected to contribute to an increase in consumer broadband and wireline revenue. AT&T expects broadband revenue to increase by at least 7% in 2024, which is more than double the rate of growth for wireless service revenue. In contrast, Verizon only has about 18 million fiber locations, growing at about 500,000 per year.
Other recent deals in the fiber transport market sector include the $3.1 billion acquisition, including debt, of fiber provider Consolidated Communications in late 2023 by Searchlight Capital Partners and British Columbia Investment Management.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
It’s All About Convergence (fiber based home internet combined with mobile service):
Speaking at a Bank of America investors conference today, Verizon’s CEO for the Consumer Group Sowmyanarayan Sampath said when Verizon bundles Fios with wireless, it sees a 50% reduction in mobile churn and a 40% reduction in broadband churn. He said they don’t see the same benefits with FWA. Sampath was scheduled to speak at the Mobile Future Forward conference tomorrow, but he canceled at the last minute, which may be a sign that this deal for Frontier is imminent.
The analysts at New Street Research led by Jonathan Chaplin said Verizon’s rationale for the purchase is “convergence baby.” They wrote, wrote, “Verizon seemed complacent. No longer.” Indeed, Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg was challenged on the company’s second quarter 2024 earnings call by analysts who questioned whether Verizon had a big enough fiber footprint to compete in the future. The New Street analysts said Sampath’s comments today “marked a shift in rhetoric from: ‘convergence is important, but we can do it with FWA.”
The analysts at New Street wrote today, “We have been arguing for a couple of years that all the fiber assets would eventually be rolled up into the three big national carriers (AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile). We always knew that if one carrier started the process, others would have to follow swiftly because there are three wireless carriers and only one fiber asset in every market with a fiber asset.”
Other potential fiber companies that the big three national carriers might be eyeing include Google Fiber, Windstream, Stealth Communications and TDS Telecom.
After its annual summer conference in August in Boulder, Colorado, the analysts at TD Cowen, led by Michael Elias, said there was a lot of conversation about the wireline-wireless “convergence” frenzy. “We believe convergence is a race to the bottom, but if one player is going in with a slight advantage (AT&T), the others must reluctantly follow,” wrote TD Cowen. In the mid-term they speculated that T-Mobile might look at fiber roll-ups with Ziply or Lumen (formerly or other regional players.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/deals/verizon-nearing-deal-for-frontier-communications-9e402bb4
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/verizon-rumored-buy-frontier-its-convergence-game
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/verizon-talks-buy-frontier-communications-180419091.html
https://videos.frontier.com/detail/videos/internet/video/6322692427112/why-fiber
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Verizon Q2-2024: strong wireless service revenue and broadband subscriber growth, but consumer FWA lags
Summary of Verizon Consumer, FWA & Business Segment 1Q-2024 results
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia have agreed to work on artificial intelligence (AI) assisted “fiber sensing,” a wired network technology that employs AI to monitor the environment around optical cables. The two companies signed a memorandum of understanding (see photo below) last Wednesday, with a plan to “accumulate empirical data based on machine learning” from SKT’s commercial network. SKT, South Korea’s largest mobile network carrier, said on Monday that it will utilize Nokia’s product to detect earthquakes, climate changes and other unexpected situations that might arise from nearby construction areas in order to stabilize network conditions. The objective is nationwide deployment in South Korea by the end of this year.
In a joint statement, the companies explained when data runs through an optical cable, the phase of the light can change due to various factors like temperature fluctuations or physical strain on the cable. The changes can be detected and analyzed to provide precise measurements of the environmental conditions affecting the fiber. Using AI-based technology, SKT and Nokia aim to stabilize fiber optic networks in advance by tracking the impact of weather conditions and construction on optical cables. The statement added “fiber sensing” has no distance limitations, unlike some existing wired network monitoring technologies, making it possible to quickly apply the new technology to major backbone networks.
SKT-Nokia monitors wired network status with AI:
– Tracking the impact of weather, earthquakes, construction, etc. on optical cables with ‘fiber sensing’ technology
– Immediately applicable to existing networks and no distance restrictions, making it easy to apply to backbone networks
– Both companies’ capabilities will be combined to quickly internalize new AI-based wired network technology
A signing ceremony for the memorandum of understanding took place at SK Telecom’s headquarters Wednesday in central Seoul. SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, attended the event.

SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, right, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, pose for a photo after a signing ceremony at SK Telecom’s headquarters in central Seoul on Wednesday, August 7th. Photo Credit: SK TELECOM
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In July, SKT and Singtel announced that they have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to collaborate on building next-generation telecommunications networks that will drive innovation, improve network performance and security and deliver enhanced customer experiences over the next two years. The partners will explore the use of artificial intelligence (AI), orchestration tools, and deepen the domain knowledge of network virtualization and other technologies – central to laying the necessary building blocks for progressing to 6G.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7228552138988134402/
AT&T’s leads the pack of U.S. fiber optic network service providers
AT&T and Verizon are spending billions of dollars to grow their existing fiber-optic networks and add to the millions of broadband clients they already serve, mostly in regions covered by their historical landline-telephone infrastructure. Meanwhile, T-Mobile has five partnerships with fiber-optic internet providers that could serve millions of customers in the coming years. There are other fiber based internet providers that mostly serve business customers. Those include Comcast Business, Frontier Communications, Lumen, and Google Fiber (which also serves residential customers).
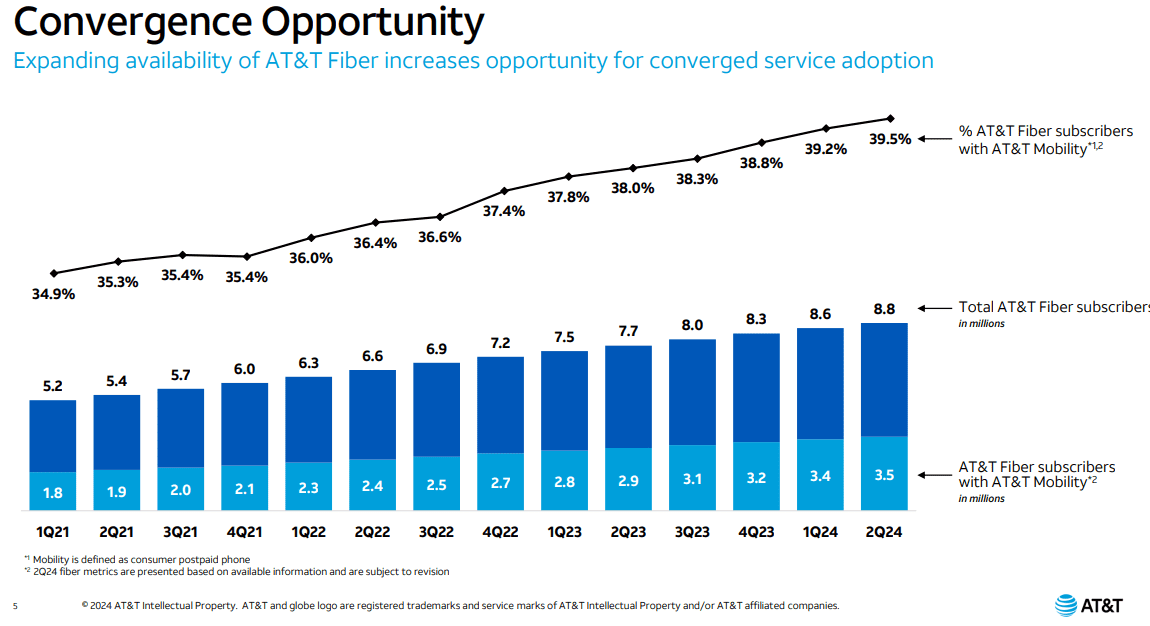
AT&T’s fiber business has remained incredibly strong, with fiber revenues growing almost 18% YoY. That led to strong top line EBITDA and EBITDA margin growth in 2Q-2024. There were 239,000 AT&T Fiber net adds in the quarter. AT&T has posted 200,000+ net fiber adds for 18 consecutive quarters – quite an enviable record. The company has managed to grow to 8.8 million total fiber subscribers, as average fiber revenue has gone up to almost $2 billion quarterly.
According to Seeking Alpha (subscription required), AT&T is substantially more reliable than Comcast, offers symmetric up and down bandwidth, and has no data caps. That makes it a much more pleasing experience. The company has worked to chase synergies with its AT&T mobility business, with not only fiber subscriptions growing, but the % of customers with AT&T mobility has grown as well. That ratio is now almost 40%.
“For the past four years, we’ve delivered consistent, positive results that have repositioned AT&T. Our solid performance this quarter demonstrates the durable benefits of our investment-led strategy,” said John Stankey, AT&T CEO. “AT&T is leading the way in converged connectivity as customers increasingly seek one provider who can seamlessly connect them in their home, at work and on the go. This is proving to be a winning strategy. Today, nearly four of every 10 AT&T Fiber households also choose AT&T wireless service. As the nation’s largest consumer fiber builder, we see this as an opportunity to continue to grow subscribers and revenues, while deepening customer relationships.”
Fiber investment drives valuable convergence opportunities:
• Wireless penetration of fiber subscribers has increased more than 400 bps since 2Q21
• Expansion of fiber footprint enables increased opportunities to sell into high quality cohort
• Converged customers are valuable and durable, with longer customer lives
“Our combined customers are happier customers,” AT&T CEO John Stankey said on a call with analysts. “Why a race to convergence? Because that’s a good way to make money, and it’s a good way to keep customers in the fold.”
AT&T CEO John Stankey meeting with fiber-optic workers at an Evansville, Ind., job site in 2022. Photo: Scotty Perry/Bloomberg News
References:
https://www.labs.att.com/story/2024/q2-earnings.html
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4708956-att-earnings-highlights-continued-recovery-potential
https://www.wsj.com/business/telecom/t-mobile-fiber-optic-internet-connection-380957ef