Starlink
Amazon launches first Project Kuiper satellites in direct competition with SpaceX/Starlink
Amazon has finally joined the race to build massive constellations of satellites that can blanket the globe in internet connectivity — a move that puts the tech company in direct competition with SpaceX and its Starlink satellite Internet system. The first two prototype satellites for Amazon’s Project Kuiper space network, launched aboard a United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 2:06 p.m. ET Friday. The Protoflight launch is the first mission in a broader commercial partnership between ULA and Amazon to launch the majority of the Project Kuiper constellation.
“This is Amazon’s first time putting satellites into space, and we’re going to learn an incredible amount regardless of how the mission unfolds,” Rajeev Badyal, a vice president of technology for Project Kuiper at Amazon, said in a statement from the company before the launch. “We’ve done extensive testing here in our lab and have a high degree of confidence in our satellite design, but there’s no substitute for on-orbit testing,” he added.
“This initial launch is the first step in support of deployment of Amazon’s initiative to provide fast, affordable broadband service to unserved and underserved communities around the world,” said Gary Wentz, ULA vice president of Government and Commercial Programs. “We have worked diligently in partnership with the Project Kuiper team to launch this important mission that will help connect the world. We look forward to continuing and building on the partnership for future missions.”
United Launch Alliance cut off the livestream of the launch after the first stage of its rocket — the portion that provides the initial boost at liftoff — finished firing its engines off. The company did confirm “mission success,” and said in a news release that it “precisely” delivered the satellites. Amazon could not immediately confirm contact with the satellites.

A ULA Atlas V rocket carrying the Protoflight mission for Amazon’s Project Kuiper lifts off from Space Launch Complex-41 at 2:06 p.m. EDT on October 6.
Photo by United Launch Alliance
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
If successful, the mission could queue up Amazon to begin adding hundreds more of the satellites into orbit, eventually building a network of more than 3,200 satellites that will work in tandem to beam internet connectivity to the ground.
But why wasn’t a Blue Origin (owned by Jeff Bezos) rocket used to launch the Project Kuiper satellites? It’s because Blue Origin has yet to launch anything into orbit. Although its suborbital space tourist rocket New Shepard has made many flights, the New Glenn rocket that it has been developing for more than a decade to take payloads like Kuiper satellites to orbit is at least three years behind schedule. Its debut flight is penciled in for next year. In April last year, Amazon announced a gigantic purchase of up to 83 launches, the largest commercial purchase of rocket launches ever. That includes 27 from Blue Origin and the rest from two other companies, Arianespace of France and United Launch Alliance of the United States. The contracts with the other companies also rely on new rockets that have not yet flown: the Ariane 6 from Arianespace and the Vulcan from United Launch Alliance.
The leading satellite Internet company is Starlink, the SpaceX subsidiary that has been growing rapidly since 2019. SpaceX has more than 4,500 active Starlink satellites in orbit and offers commercial and residential service to most of the Americas, Europe and Australia.
The space industry is in the midst of a revolution. Until relatively recently, most space-based telecommunications services were provided by large, expensive satellites in geosynchronous orbit, which lies thousands of miles away from Earth. The drawback with this space-based internet strategy was that the extreme distance of the satellites created frustrating lag times. Now, companies including SpaceX, OneWeb and Amazon are looking to bring things closer to home.
Even before those companies began to build their services, the satellite industry dreamed of delivering high-speed, space-based internet directly to consumers. There were several such efforts in the 1990s that either ended in bankruptcy or forced corporate owners to shift plans when expenses outweighed the payoffs.
Such widespread high-speed internet access could be revolutionary. As of 2021, nearly 3 billion people across the globe still lacked basic internet access, according to statistics from the United Nations. That’s because more common forms of internet service, such as underground fiber optic cables, had not yet reached certain areas of the world.
SpaceX is well ahead of the competition in terms of growing its service, and its efforts so far have occasionally thrust the company into geopolitical controversy. The company notably faced significant blowback in late 2022 and early 2023 for preventing Ukrainian troops on the front lines of the war with Russia from accessing Starlink services, which had been crucial to Ukraine’s military operations. (The company later reversed course, and SpaceX founder Elon Musk discussed the Ukraine controversy in a recent book.) It’s possible Amazon’s Project Kuiper constellation could become part of that conversation — facing similar geopolitical pressures — if the network proves successful.
“I’m also curious if Amazon plans dual-use capabilities where government/defense will be a major client. This may result in the targeting of Kuiper like that of Starlink in Ukraine,” said Gregory Falco, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Cornell University, in a statement.
Despite the promises of a global internet access revolution, the massive satellite megaconstellations needed to beam internet across the globe are controversial. Already, there are thousands of pieces of space junk in low-Earth orbit. And the more objects there are in space, the more likely it is that disastrous collisions could occur, further exacerbating the issue.
The Federal Communications Commission, which authorizes space-based telecom services, recently began enhancing its space debris mitigation policies. The satellite industry has largely pledged to abide by recommended best practices, including pledging to deorbit satellites as missions conclude.
In a May blog post, Amazon previously laid out its plans for sustainability, which include ensuring its satellites are capable of maneuvering while in orbit. Amazon also pledged to safely deorbit the first two test satellites at the end of their mission.
Separately, astronomers have also continuously raised concerns about the impact all these satellites in low-Earth orbit have on the night sky, warning that these manmade objects can intrude upon and distort telescope observations and complicate ongoing research.
Amazon addressed those concerns in a statement to CNN, saying one of the two prototype satellites it launched Friday will test antireflective technology aiming to mitigate telescope interference. The company has also been consulting with astronomers from organizations such as the National Science Foundation, according to Amazon spokesperson Brecke Boyd. However, SpaceX has made similar commitments.
It remains to be seen how well Project Kuiper will compete with SpaceX’s Starlink. And while Starlink already has more than 1 million customers, documents recently obtained by the Wall Street Journal showed that the SpaceX megaconstellation hasn’t been as successful as once projected.
As far as consumer price points go: People can purchase a Starlink user terminal for a home for about $600 plus the cost of monthly service.
Amazon has said it hopes to produce Project Kuiper terminals for as low as about $400 per device, though the company has not yet begun demonstrating or selling the terminals. The company has not revealed a price for monthly Kuiper services.
SpaceX has had the clear advantage of using its own Falcon 9 rockets to launch batches of Starlink satellites to orbit.
Amazon does not have its own rockets. And while the Jeff Bezos-founded rocket company Blue Origin is working on a rocket capable of reaching orbit, the project is years behind schedule.
For now, Kuiper satellites are launching on rockets built by United Launch Alliance, a close partner of Blue Origin. In addition to ULA and Blue Origin, Amazon has a Project Kuiper launch contract with European launch provider Arianespace.
On August 28, The Cleveland Bakers and Teamsters Pension Fund, which owns a stake in Amazon, filed a lawsuit against the company over the launch contracts. The lawsuit alleges Amazon executives “consciously and intentionally breached their most basic fiduciary responsibilities” in part by forgoing the option of launching Project Kuiper satellites on rockets built by SpaceX, which the suit claims is “one of the most cost-effective launch providers.”
“The claims in this lawsuit are completely without merit, and we look forward to showing that through the legal process,” said an Amazon spokesperson.
If all goes to plan, Amazon said it intends to launch its first production satellites early next year and begin offering beta testing to initial customers by the end of 2024, according to a news release.
References:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/10/06/science/amazon-project-kuiper-launch.html
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
Japan network operator KDDI announced today that it has signed an agreement with SpaceX to introduce satellite-to-cellular service in Japan. Leveraging SpaceX’s Starlink low earth orbit (LEO) satellites and KDDI’s extensive national wireless spectrum, this partnership aims to enhance cellular connectivity in areas, including remote islands and mountains that have been traditionally hard to reach using conventional 4G and 5G networks.
The partnership is slated to introduce SMS text services as the initial step, starting as early as 2024. At a later date, voice and data services will follow suit. The company also announced the service will work with almost all existing smartphones on the KDDI network.
The service is planned to be provided based on the establishment of radio-related laws and regulations in Japan.

Source: SpaceX
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
SpaceX first announced plans to provide cellular connectivity with T-Mobile in the US last year. At the time Elon Musk invited other companies to join them, and while there were no immediate takers, KDDI is now the third company to sign a deal.
Earlier this year New Zealand’s telecommunications company, One NZ (formerly known as Vodafone), announced it has signed an agreement with SpaceX to offer mobile coverage across the country, eliminating cellular dead zones.
KDDI and SpaceX also invite carries worldwide to join the ecosystem of mobile network operators bringing next generation satellite enabled connectivity to their customers.
■About KDDI:
KDDI’s au network enables our customer’s daily lives and helps them share unforgettable moments. We are proud of providing 99.9% “population coverage” to the people of Japan. Unfortunately, only a small portion of the Japanese land mass is habitable and often it is difficult to use traditional technologies to provide coverage from coast to coast. Our extensive network continues to grow in coverage as we deploy more fiber and satellite backhauled base stations. In addition to our continued efforts, we will provide “connecting the unconnected” experience, by enabling smartphones to connect to satellites.
■About Starlink by SpaceX:
Starlink delivers high-speed, low-latency internet to users all over the world. As the world’s first and largest satellite constellation using a low Earth orbit, Starlink delivers broadband internet capable of supporting streaming, online gaming, video calls and more. Starlink is engineered and operated by SpaceX. As the world’s leading provider of launch services, SpaceX is leveraging its deep experience with both spacecraft and on-orbit operations to deploy the world’s most advanced broadband internet system, as well as a Direct to Cell constellation of satellites to provide connectivity directly to unmodified LTE cell phones.
References:
https://news.kddi.com/kddi/corporate/english/newsrelease/2023/08/30/6937.html
KDDI teams up with SpaceX to bring Starlink-powered cellular service to Japan
Telstra partners with Starlink for home phone service and LEO satellite broadband services
Telstra, Australia’s #1 telco, will partner with SpaceX’s Starlink to provide phone and broadband services to rural Australia using Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites. Telstra said it planned to offer the new services before year’s end according to a blog post. It also promises higher download speeds compared to copper-based ADSL internet access.
Starlink, operated by Elon Musk’s SpaceX (private company). has built a fast-growing network of more than 3,500 satellites in Low-Earth Orbit that can provide connectivity in remote areas.
“Telstra will be able to provide home phone service and Starlink broadband services to Aussies as a bundle offer, as well as local tech support and the option of professional installation,” the telco said in the same blogpost. “This agreement also provides connectivity options for our business customers, with a higher bandwidth business option available in areas without fixed and mobile connectivity. The business offer will be available to purchase from Telstra both locally and in select countries overseas.”
Using LEO satellites will bring new capabilities to commercial satellite services in Australia, including faster communications. Signal distances travelled are shorter, as LEO satellites are vastly closer to earth compared to geostationary satellites at around 35,000 km above earth. It requires less power for an earthbound device to transmit to a satellite and there’s a reduced latency (delay) in transmission time.

Telstra said in its blog post:
One of the benefits of LEO satellites are that they are much closer than geostationary satellites to Earth with multiple satellites that are a part of a “constellation”, allowing them to send and receive signals much faster. As well as offering great data throughput, the proximity of these satellites reduces latency making them a great and more consistent option for services that need low latency, like voice and video calls.
The latency, download speeds and general experience in most circumstances will be far superior to copper-based ADSL and be better suited for most modern connectivity needs. Our team has been testing out in the field Starlink’s service and how we can best offer it to customers, including evolving our own modem specifically to support Starlink connectivity and Aussie households. We’re extremely excited to show you what this looks like later in the year.
Partnerships between telcos and LEO satellite providers will allow consumers to make satellite-connected calls using their regular smartphone from almost anywhere on the planet, whether there is a local cellular network or not. In Australia, mobile calls and even video calls will be possible on regular smartphones operating in remote and rural regions of Australia.
At Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona in March 2023, Telstra told ChannelNews it was working on adding LEO satellite audio and video calls to its network. Taiwanese chip designer MediaTek demonstrated the chips that phones would use for LEO satellite communications at the same conference.
UK phone maker Bullitt Group announced it was working with Motorola to bring satellite texting to regular phones in Australia this year, with video calling via LEO satellites to come within another two years. Their texting service has already rolled out in Europe and the US.
Telstra’s move is in line with emerging partnerships between telcos and satellite providers in the US, with T-Mobile forging a deal with Starlink and AT&T with AST SpaceMobile. T-Mobile and Starlink began testing their service in March.
Optus is yet to announce any service involving LEO satellite services locally, although it has been conducting tests. In November last year, Optus demonstrated satellite direct-to-mobile calls in partnership with LEO satellite provider Lynk.
Vodafone meanwhile has launched LEO satellite trials in Turkey with local operator partner SatCo.
It is a major coup for Telstra to be first among Australia-based Telcos to announce a specific service, however longer term, LEO satellites will allow Optus and Vodafone to be more formidable competition in rural and regional Australia, as LEO satellites will give them a reach that they don’t enjoy due to their lack of ground-based cellular infrastructure compared to Telstra.
Further, the Australian telco market will be opening up to increased international competition if offshore telcos want to join in. In March, ChannelNews reported that Amazon was gearing to take on the NBN with a fast satellite-based internet service.
Nevertheless LEO satellites are a fillip for Telstra in light of the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission’s (ACCC) decision late last year to veto a deal between Telstra and TPG Telecom to consolidate their presence in rural and fringe areas of the country through an infrastructure and service swap.
The coming of LEO satellite services also will be a test for the ACCC. To what extent does its jurisdiction cover LEO-satellite-based communications, particularly when it involves telecommunication services provided by foreign companies from space?
References:
We’re working with Starlink to connect more people in remote Australia
Telstra to partner with Elon Musk’s Starlink for satellite calls and broadband
Musk’s SpaceX and T-Mobile plan to connect mobile phones to LEO satellites in 2023
During a live media event Thursday afternoon, T-Mobile’s Mike Sievert and SpaceX’s Elon Musk announced a new partnership that’s intended to connect T-Mobile sold phones to a new constellation of SpaceX’s Starlink satellites. The result, according to the companies, will be the elimination of all cellular dead zones around the U.S.
“It’s a lot like putting a cellular tower in the sky,” Sievert said, adding that the “vast majority” of T-Mobile’s existing phones would be supported by the service. Meaning, customers will not need to purchase new phones in order to connect them to Starlink’s second-generation satellites.
Sievert said that T-Mobile expects to offer the service for no additional charge on its more expensive plans. For customers on its cheaper plans, he said they may need to pay an additional monthly charge in order to be able to access satellite coverage.
Starlink’s satellites will use T-Mobile’s mid-band spectrum to create a new network. Most phones used by the company’s customers will be compatible with the new service, which will start with texting services in a beta phase beginning by the end of next year. The companies did not say when it might launch commercially.
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/WSL6VTEO3FONZGAOYYYFER22AU.jpg)
T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert at a joint news conference at Space X facility in Brownsville, TX
REUTERS/Adrees Latif
SpaceX has launched nearly 3,000 low-Earth-orbiting (LEO) Starlink satellites since 2019, handily outpacing rivals OneWeb and Amazon.com Inc’s Project Kuiper. Starlink recently suffered a major setback when the FCC rejected the company’s application for almost $900 million in government subsidies. The agency ruled that Starlink’s service likely wouldn’t be able to meet the agency’s speed and service requirements.
SpaceX’s next-generation Starlink satellites, the first of which are planned to launch on SpaceX’s next-generation Starship rocket whenever it is fully developed, will have larger antennae that will allow connectivity directly to mobile phones on the T-mobile network, Musk said.
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/D53NNDMLVVKBDL27U25YAODCXA.jpg)
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/VX32JK5RMZMCHJKYGKRH3TNOMU.jpg)
SpaceX Starbase, in Brownsville, Texas, U.S., August 25, 2022. REUTERS/Adrees Latif
Meanwhile, U.S telecom firms are in a race to build up the mid-band portion of their 5G networks to catch up with T-Mobile, which bagged a chunky 2.5 GHz of mid-band spectrum thanks to a buyout of rival Sprint.
Mid-band or C-Band has proven to be perfect for 5G, as it provides a good balance of capacity and coverage. T-Mobile said it aims to pursue voice and data coverage after the texting services beta phase.
Others in the Mix:
Satellite communications firm AST SpaceMobile Inc is also building a global cellular broadband network in space that will operate with mobile devices without the need for additional hardware. AST SpaceMobile is relying on SpaceX’s rockets to get its satellites into orbit, having pivoted away from a plan to use Russian rockets after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
“Elon [Musk] and Mike [Sievert, of T-Mobile] helped the world focus attention on the huge market opportunity for SpaceMobile, the only planned space-based cellular broadband network,” AST SpaceMobile CEO Abel Avellan wrote on LinkedIn yesterday. “BlueWalker 3 … is scheduled for launch within weeks!”
Meanwhile, Verizon and AT&T each have their own satellite plans: Verizon plans to use Amazon’s planned Project Kuiper satellites to connect its rural cell towers to the Internet, and AT&T is planning a similar setup with OneWeb’s own growing constellation of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
In 2020, AT&T agreed to let startup AST SpaceMobile use its Band 5 spectrum to test transmissions from its BlueWalker 1 satellite to devices on the ground. AST SpaceMobile is now hoping to launch its new BlueWalker 3 prototype later next month. However, as reported by SpaceNews, supply chain issues delayed the launch of AST SpaceMobile’s first operational satellite by about six months, to late 2023.
AST SpaceMobile’s main rival, Lynk, already has one operational satellite in orbit for phone connections. As noted by Ars Technica, the company is hoping to receive FCC approval to offer satellite-to-phone services across 35 countries by the end of this year.
“Elon said it’s hard, and it’s only been done in the lab, but Lynk has done it in space already,” Lynk’s Charles Miller told the publication yesterday. “We’re the only company in the world that has done that.”
Lynk hasn’t yet announced an agreement with a major U.S. network operator, though it has agreements with a number of international operators. Lynk tested its services in the U.S. with Smith Bagley, a tiny wireless network operator offering services under the Cellular One brand in East Arizona.
“There are significant regulatory hurdles to clear, as the FCC is reviewing SpaceX’s request to launch a constellation of 30,000 Gen2 satellites, while other LEO proposals including Amazon’s Project Kuiper (with whom Verizon is collaborating) and AST SpaceMobile (financial backing from Vodafone and a commercial agreement with AT&T) are also working DC as well as international agencies to put some rules in place for this latest chapter of the Space Race,” Raymond James analysts wrote in a note to investors.
References:
UPDATE: Apple iPhone 14 text messages via Globalstar LEO satellites starting Nov 2022:
France’s Eutelsat nears deal to buy UK satellite internet company OneWeb
From the Financial Times:
The UK government is set to become a minority shareholder in a listed French business, as France’s Eutelsat nears a deal to acquire OneWeb, the satellite internet company rescued from bankruptcy by Boris Johnson’s government. According to people involved, a deal will be announced as soon as Monday and involve a takeover of OneWeb by Eutelsat, which already owns a 24 per cent stake in the UK-based company.
Expecting heavy political scrutiny, the deal will be presented publicly as a merger of equals. Combining the two companies will bring together the UK, French and Chinese governments as well as Indian billionaire Sunil Bharti Mittal as common shareholders in one of the world’s biggest satellite operators. Recommended The Big Read The corporate feud over satellites that pitted the west against China The French state owns a 20 per cent stake and China’s sovereign wealth fund owns 5 per cent in Eutelsat.
The UK has just under 18 per cent of OneWeb. After the deal, shareholders from both sides will be diluted. Paris-listed Eutelsat has a market value of €2.4bn and has roughly €3bn of net debt. In its most recent funding round, OneWeb was valued at $3.4bn. The deal values the UK government’s OneWeb stake at $600mn, two people with knowledge of the details said, which is $100mn more than it initially invested in 2020. Mittal, who has a 30 per cent stake in OneWeb, will be one of the largest shareholders in the combined group.
The UK will retain its special rights over OneWeb as part of the deal. Those rights include a veto over certain customers deemed undesirable for national security reasons as well as a say on supply chain and launch decisions. One UK official said that Eutelsat would seek a secondary listing on the London market. By merging with Eutelsat, OneWeb’s backers will have support for the huge amount of funding still required to deliver the company’s second generation satellite network.

The greater financial firepower will be needed in the competition with Elon Musk’s Starlink and Jeff Bezos’ Project Kuiper for low earth orbit, the new frontier for commercial space. OneWeb, which has 428 satellites in orbit, was a pioneer in the field but its current technology is acknowledged to be out of date. Musk’s Starlink has more than 2,000 satellites in orbit with newer technology. “The deal recognises that this is a highly competitive global race. It will allow the two companies to compete with SpaceX and emerging rivals from China as well. This is a good story for Britain,” the official said. Falling launch costs and cheaper satellites are enticing hundreds of private companies into a global space market estimated to be worth $1tn by 2040. The UK’s initial investment into OneWeb in 2020 was highly controversial and championed by Johnson’s former adviser Dominic Cummings.
The government ignored advice from senior officials when it decided to invest $500mn alongside $500mn from Bharti Global, part of the conglomerate controlled by Mittal, to bring the business out of Chapter 11 bankruptcy in the US. OneWeb collapsed in 2020 after its main backer SoftBank refused to fund yet another financing round, in a sign of significant cash funding requirements needed to take low earth orbit constellations to commercial operation. SoftBank still remains a substantial shareholder in OneWeb. Since its bankruptcy the group has raised $2.7bn. Eutelsat paid $550mn for a 24 per cent stake in OneWeb last year. Rothschild is working with Eutelsat, while Barclays is advising OneWeb, people close to the deal said. Bloomberg earlier reported on this deal.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
From Bloomberg:
Musk’s Starlink fleet of more than 1,500 satellites launched in the past three years by SpaceX has created an unprecedented challenge for rivals, leading to a wave of consolidation in the sector.
Last year, Viasat Inc. agreed to purchase Inmarsat Group Holdings Ltd. for $4 billion, creating the world’s biggest geostationary satellite company. Eutelsat itself rejected a takeover bid from billionaire Patrick Drahi that valued it at 2.8 billion euros.
OneWeb emerged from bankruptcy in 2020 in bailout by the UK with the help of Mittal, signaling a more interventionist industrial strategy by the government after Brexit. A deal with Eutelsat would be a rare example of a UK and a French company merging, and one that involves two state-backed companies shows how much the two governments are getting involved in the telecommunications industry.
The company was established in 2012 to build a constellation of small satellites in low-earth orbit, beaming internet connections to isolated places. OneWeb raised $3.4 billion from SoftBank Group Corp., Airbus SE and other big names before collapsing when lead investors pulled their money at the height of the coronavirus pandemic.
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/47219d82-1995-4555-ba13-48223364fa15
FCC allows SpaceX to connect Starlink to boats, planes, moving vehicles
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) on Thursday authorized Elon Musk’s SpaceX to use its Starlink satellite internet network with moving vehicles, green-lighting the company’s plan to expand broadband offerings to commercial airlines, shipping vessels and trucks.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Starlink, a fast-growing constellation of internet-beaming satellites in orbit, has long sought to grow its customer base from individual broadband users in rural, internet-poor locations to enterprise customers in the potentially lucrative automotive, shipping and airline sectors.
“Authorizing a new class of terminals for SpaceX’s satellite system will expand the range of broadband capabilities to meet the growing user demands that now require connectivity while on the move,” the FCC said in its authorization published Thursday, echoing plans outlined in SpaceX’s request for the approval early last year.
SpaceX has steadily launched some 2,700 Starlink satellites to low-Earth orbit since 2019 and has amassed hundreds of thousands of subscribers, including many who pay $110 a month for broadband internet using $599 self-install terminal kits.
The Hawthorne, California-based space company has focused heavily in recent years on courting airlines for in-flight WiFi via Starlink backhaul, having inked its first such deals in recent months with Hawaiian Airlines and semi-private jet service JSX. Delta Airlines has reportedly run some tests with SpaceX/Starlink.
“We’re obsessive about the passenger experience,” Jonathan Hofeller, Starlink’s commercial sales chief, said at an aviation conference earlier this month. “We’re going to be on planes here very shortly, so hopefully passengers are wowed by the experience.”
SpaceX’s proposal for ESIMs includes spectrum in the range of 12.2-12.7GHz – a slice of spectrum generally known as the 12GHz band. RS Access (a company funded by Michael Dell’s investment firm) and Dish Network opposed SpaceX’s proposed use of the 12GHz band based on interference concerns, but the FCC is still analyzing it and has yet to make a final ruling.
However, the FCC has concluded that authority of operations in the 12GHz band serves the public interest, as it will expand broadband into unserved and underserved areas. As a condition of the FCC’s approval, ESIM operations of SpaceX “must accept any interference received from both current and future services authorized” in the 12GHz band “and must not cause harmful interference to any authorized service, whether licensed or not,” the FCC’s Sullivan explained.
The FCC’s CONCLUSION (from the order):
We conclude that grant of SpaceX’s requests for ESIM authorizations and Kepler’s request for ESV authority, including for operations in the 12.2-12.7 GHz band, as conditioned and set forth herein, will serve the public interest by enabling SpaceX and Kepler to offer expanded broadband capabilities and serve unserved and underserved areas.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“Authorizing a new class of terminals for SpaceX’s satellite system will expand the range of broadband capabilities to meet the growing user demands that now require connectivity while on the move, whether driving an RV across the country, moving a freighter from Europe to a US port, or while on a domestic or international flight,” the FCC’s international bureau chief, Tom Sullivan, wrote in the order (PDF).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
SpaceX, under an earlier experimental FCC license, has been testing aircraft-tailored Starlink terminals on Gulfstream jets and U.S. military aircraft.
Elon Musk, the founder and CEO of SpaceX, has previously said that the types of vehicles Starlink was expected to be used with pursuant to Thursday’s authorization were aircraft, ships, large trucks and RVs. Musk, also the CEO of electric car maker Tesla Inc, had said he didn’t see “connecting Tesla cars to Starlink, as our terminal is much too big.”

Photo credit: Panther Media GmbH / Alamy Stock Photo
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
FCC clearance will enable Starlink to pursue connectivity agreements more aggressively in markets such as aviation, which is already covered by competitors such as Viasat and Hughes Network Systems. Those companies rely on a much smaller number of geosynchronous (GEO) satellites sitting at higher orbits than Starlink’s LEO constellation. However, Hughes Network Systems is also in the LEO business through its partnership with and investment in OneWeb.
Competition in the low-Earth orbiting satellite internet sector is fierce between SpaceX, satellite operator OneWeb, and Jeff Bezos’s Kuiper project, a unit of e-commerce giant Amazon.com which is planning to launch the first prototype satellites of its own broadband network later this year.
References:
LEO satellite status report, Starlink’s progress, dealing with space junk
There are currently 4,852 operating satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) from some eighty nations, though roughly half are U.S. commercial and government/military satellites. They are essential for everything from nuclear command and control, climate observation to GPS, and the internet, streaming video, and ATMs. Moreover, an already crowded earth orbit is getting worse. The private sector is driving the new space economy enabled by new technologies to miniaturize satellites, like the aforementioned cubesats. Google and Elon Musk’s SpaceX alone plan to launch some 50,000 cubesats in this decade.

Currently, Starlink (owned by SpaceX) has approximately 2,200 small satellites in LEO and working. That’s about half of SpaceX’s planned first-generation network of 4,408 Starlink satellites.
The 4,400 satellites will be spread among five different orbital “shells” at different altitudes and inclinations. SpaceX, founded and led by Elon Musk, has stated it eventually intends to launch as many as 42,000 satellites.

An explosion of private-sector space business—from satellite launches and space shuttles to the quest for mining asteroids and planets—has blurred the line between civilian and military activities, racing ahead of any duly considered global regulation. Dealing with space junk, however, is the most promising area for cooperation. The threat of space debris to all nations’ vital economic and national security assets in space—democracy-autocracy polarization notwithstanding—would, like climate change, seem such an instance.
Last November, Russia shot a missile into space to test its anti-satellite technology to see if it could destroy or incapacitate one of its own orbiting satellites. It did. The U.S. State Department says that missile smashed the Russian spacecraft into 1,500 large pieces and hundreds of thousands of smaller fragments, which resulted in a dangerous cloud of debris. That forced the crew aboard the ISS (International Space Station) to take shelter in their escape pops, SpaceX’s Dragon capsule. The resulting debris passed close to the ISS, but didn’t hit it. The crew was fine, but the incident highlighted just how big of a problem space debris can be.
In mid April, U.S. vice president Kamala Harris said the US would not conduct tests like this and called on other countries to do the same, but that promise won’t reduce the space junk already out there. Missile tests are just one way that space debris is created. Sometimes used rockets and old satellites are intentionally left up in space threatening to hit satellites or space rockets. And the more of it that space junk floating around, the harder it will be to avoid.
The U.S. Department of Defense’s Space Surveillance Network is the premier mechanism for monitoring space junk. Russia has some orbital monitoring capacity, but few other states do. Moreover, in addition to its unrivaled space surveillance capacity to monitor debris, the United States already has Spacing Sharing Agreements with over 100 nations to provide data and notifications to avoid collisions. These are important global public goods that can provide diplomatic leverage for shaping space rules and standards on space debris. The United States had given a heads-up to China about such risks during the Obama administration, according to well-placed sources.
In addition, private sector firms and startups in Japan, the United States, and Europe are devising ways to remove space debris, in what appears to be a coming sector of the space economy. The U.S. Space Force’s technology arm is already exploring the possibility of funding private firms to remove space debris. There are a range of methods of space junk removal being developed from satellite magnets, nets, harpoons, and even spider-like webs. These are all likely future contractors, bearing the risks of research and development.
International cooperation will be needed to effectively clean up space junk. There are only a handful of high-performance space-faring states—the United States, Russia, China, the EU, Japan, and India. As discussed above, the United States is well-positioned as first among equals to launch an ad hoc public-private coalition of space powers partnering with the private sector to pool resources and (non-national security-sensitive) capabilities to better monitor and clean up space debris and seek mutually acceptable codes of conduct and rules for such activities.
Robert Manning and Peter Wilson suggest the methods and procedures should be based an open architecture with adherence to the principle of form follows function: open to emerging space powers—South Korea, Brazil, Israel, and others.
References:
https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/satellite-database
https://nationalinterest.org/feature/coming-anarchy-outer-space-201934
https://arstechnica.com/video/watch/the-space-junk-problem
Viasat reports record quarterly revenues; launch of ViaSat-3 satellites in late summer 2022
Viasat posted record fiscal third quarter revenues of $720 million, up 25% year-over-year, boosted by its recent acquisitions of RigNet and Euro Broadband Infrastructure (EBI), as well as growth in its in-flight connectivity (IFC) business. Nevertheless, the provider of satellite and wireless networking technology reported a loss of $6.6 million in its fiscal third quarter. Virgin Atlantic was an important new in-flight connectivity (IFC) customer while the company continued to expand their fixed broadband presence internationally.
Satellite services unit revenues increased 40% to a record $310 million, while government systems revenues rose 2% to $270 million. Commercial Networks revenues rose 55% to $140 million, driven by mobile IFC terminal deliveries and the performance of its ground antenna systems business.
However, Viasat’s plan to provide global coverage with a set of new, high-capacity ViaSat-3 satellites has fallen a little behind schedule. The launch of the first of three satellites, set to cover the Americas, is now expected to happen in the late summer rather than in the first half of 2022.
The delay was due to a “modest slippage in our supply chain” fueled in part by the pandemic, Rick Baldridge, Viasat’s president and CEO, said on the company’s earnings call. “We’ve been working through limited availability of specific, critical skill workers.”
If the current plan holds, Viasat hopes to have the first ViaSat-3 satellite in service before the end of 2022. Future ViaSat-3 satellites are poised to cover the European, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) and Asia-Pacific regions.
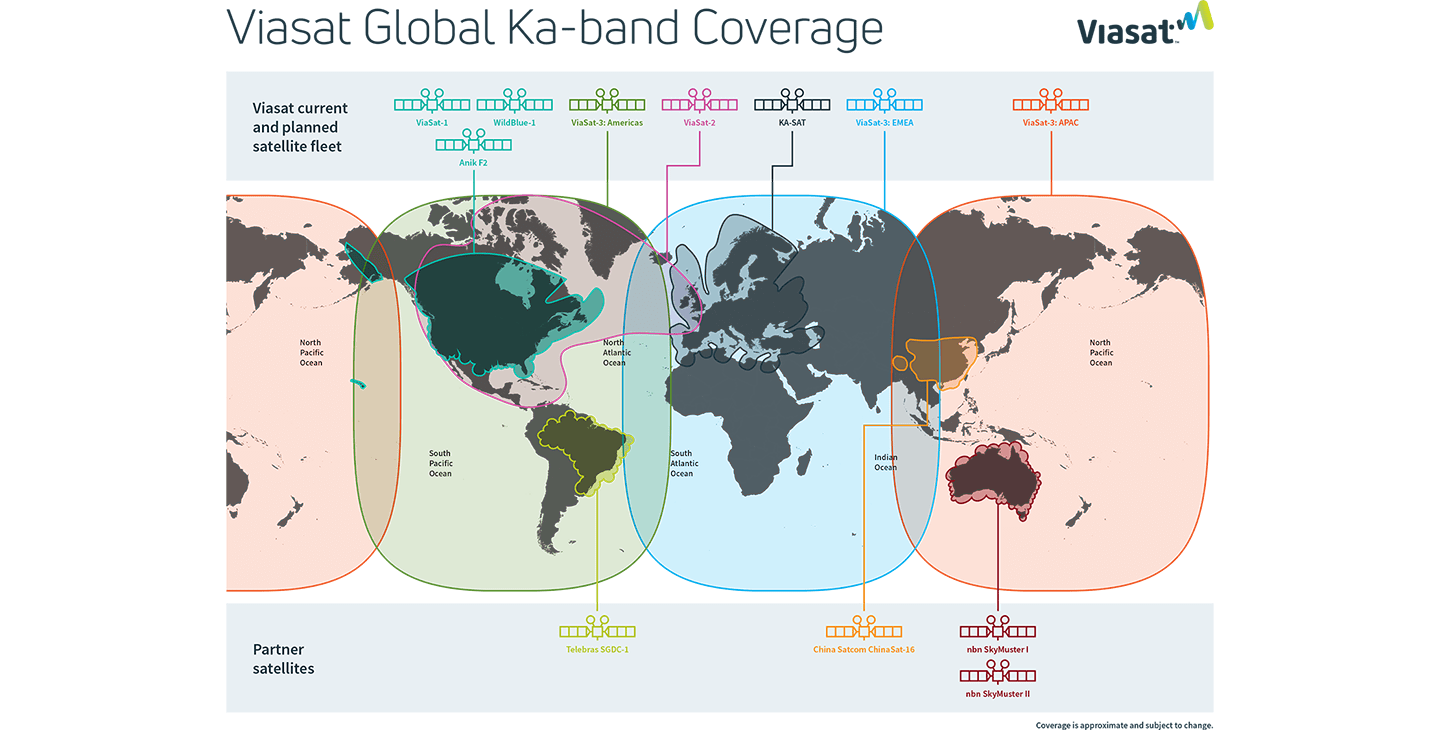
Viasat executives said the company is making good progress with alpha testing of a space-ground integration system for ViaSat-3, and they don’t expect the scheduling delay on the first ViaSat-3 satellite to materially impact Viasat’s financial guidance.
The payload module for the second ViaSat-3 satellite (for the EMEA region) is at Viasat’s facilities, with about 95% of the payload units now installed, the company said.
Jeff Baumgartner of Light Reading wrote about ViaSat-3 competition:
How much of a competitive impact Viasat’s residential satellite broadband service is seeing from FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) or even Starlink is difficult to pinpoint. Viasat no longer reports U.S. subscriber numbers as it expands that piece of the business globally. However, the company did note there was a “slight decrease” in its U.S. subscriber base in its fiscal third quarter as Viasat reallocates satellite bandwidth for mobile services.
Viasat execs aren’t overly concerned about a new, faster and pricier “Premium” tier from Starlink [1.] that will start to reach business customers and other high-capacity users in the second quarter of 2022.
Note 1. Starlink Premium promises to deliver up to 500Mb/sec, but is very expensive. It sells for $500 per month and requires customers to also pay $2,500 for the satellite router and a new antenna outfitted with double the capacity of its predecessor. Starlink Premium, a service targeted to businesses and other users that require more speed and capacity, also requires customers to put up a $500 fully refundable deposit.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Viasat expects its proposed deal for Inmarsat to close by the end of 2022. The company was named the 2021 Global Satellite Business of the Year, by Euroconsult at the World Satellite Business Week Summit.
References:
https://investors.viasat.com/static-files/05cbc97c-8c9b-4a5f-a59c-762b4afaade9
https://www.viasat.com/space-innovation/satellite-fleet/global-satellite-internet/
China’s answer to Starlink: GalaxySpace planning to launch 1,000 LEO satellites & deliver 5G from space?
Chinese state media is reporting that start-up satellite Internet firm GalaxySpace is planning to launch 1,000 low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, ultimately aiming to compete with SpaceX’s high-profile Starlink constellation.
GalaxySpace was founded in 2016. The company says it’s “committed to mass produce low-cost, high-performance small satellite through agile and fast-iterative development mode, and build the world’s leading LEO broadband satellite constellation and a global coverage with 5G communication network. Our mission is to improve the network connection condition of all regions and individuals, and to provide cost-effective, efficient and convenient broadband networks and services.Providing more accessible knowledge, more equal and extensive information, simpler and convenient communication and more development opportunities for everyone. The mission of GalaxySpace is to Creating global converged 5G communication network.”
Image Credit: GalaxySpace
According to the South China Morning Post (via Yahoo), the first batch of six satellites have already been produced, tested, and delivered to an undisclosed launch site. Beijing-based start-up GalaxySpace, has said it wants to extend China’s 5G coverage around the world and compete with Starlink, owned by Elon Musk’s firm SpaceX, in the market for high-speed internet services in remote areas. Of course, GalaxySpace’s new constellation of satellites will have quite a bit of catching up with Starlink, which has already launched around 2,000 LEO “birds,” with plans to increase the constellation size to 42,000. Starlink says they offer speeds of up to 110Mbps for consumer use.
According to Chinese media reports, GalaxySpace’s differentiating factor is that it will be the first constellation to deliver 5G connectivity to consumers, potentially offering download speeds of over 500Mbps. That’s an interesting claim, as there are no standards or implementation specs for 5G from anywhere in space. ITU-R M.2150 (formerly IMT 2020.specs) only covers terrestrial 5G services.
Naturally, like all satellite connectivity services, the quality of service will potentially be reduced significantly by poor weather. However, GalaxySpace claims that they will be able to deliver at least 80Mbps second even in the worst possible weather, according to their research.
5G is already prolific throughout China, according to the CCP (if you believe them). Recent figures suggest that by the end of 2021 there were 730 million 5G subscribers in China, over half the total population. As a result, GalaxySpace’s 5G services will likely be offered primarily to overseas companies as well as Chinese government and military activities.
But GalaxySpace is not China’s only growing broadband constellation. Both the Hongyan and Hongyun projects – owned by the state-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation and China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation, respectively – have been launching test satellites since as early as 2018.
Hongyan is aiming for 324 total satellites in its constellation, while Hongyun will have 157, with the two constellations operating at different altitudes and with different frequencies.
In 2021, with Starlink’s rise to prominence, Chinese authorities were reportedly considering making “major changes” to both the Hongyan and Hongyun projects. What these changes might be is unclear, but it seems likely to be some sort of acceleration in deployment and perhaps scale; China has said repeatedly in recent month that it fears Starlink’s dominance of this emerging industry could represent a threat to national security, especially if these devices are being used clandestinely by the US military.
Last year, Zhu Kaiding, a space engineer from the China Academy of Space Technology, which is working with GalaxySpace on the project, wrote in an academic article that the rise of Starlink had caused a Chinese satellite production line to increase its productivity by more than a third.
In addition to commercial LEO satellite Internet service rivalry, China has identified Starlink, which has signed multimillion dollar contracts with the U.S. military, as a threat to China’s national security. In 2020, researchers with the Chinese National University of Defense Technology estimated that it could increase the average global satellite communication bandwidth available to the U.S. military from 5Mbps to 500Mbps. The researchers also warned that existing anti-satellite weapons technology would find it virtually impossible to destroy a constellation the size of Starlink.
Zhu Kaiding, a space engineer from the China Academy of Space Technology, which is working with GalaxySpace on the project, said the Chinese project was struggling to keep pace with Starlink, which according to Musk is producing six satellites a day.
Zhu did not disclose how quickly China was producing satellites, but in a paper published in domestic journal Aerospace Industry Management in October last year, he said the Starlink program had forced a satellite assembly line in China to increase its productivity by more than a third. Zhu and colleagues have said that more than half the routine checks carried out at the launch site of high-frequency operations have been cancelled to save time.
The new satellites also use many components produced by private companies that have not previously been involved in Chinese space projects – a move that helped reduce the total hardware price of a high-speed internet satellite by more than 80 per cent.
Zhu said that the race against Starlink had put enormous pressure on China’s space industry, because “the technology is complex, the competition fierce, the deadlines tight and the workloads heavy.”
It is likely that the number of civilian users of satellite internet service in China will be limited – most urban residents can access 5G through their phone and broadband services are available in most rural areas – so the most likely customers are overseas companies or the Chinese government and military.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Stepping away from the geopolitical dimension of the satellite broadband space race, it is worth noting that the potential negatives for introducing such an enormous number of satellites into LEO could have for society, from Kessler syndrome caused by the build-up of space debris to the obstruction of terrestrial observatories. In fact, just this week there was a new study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, suggests that Starlink satellites are hindering the detection of near-Earth asteroids.
“There is a growing concern about an impact of low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellite constellations on ground-based astronomical observations, in particular, on wide-field surveys in the optical and infrared,” explained the study.
In 2020, SpaceX had responded to astronomers initial concerns about Starlink disrupting their imagine technology by attaching visors to their new satellites to dampen their brightness. This new study, however, would suggest that this problem is only going to be further exacerbated as the various players continue to launch devices into orbit throughout this year.
References:
https://www.totaltele.com/512227/Is-GalaxySpace-Chinas-answer-to-Starlink
https://www.yahoo.com/now/china-start-building-5g-satellite-093000905.html
http://www.yinhe.ht/aboutusEn.html
Starlink’s huge ambition and deployment plan may clash with reality
Ookla: Starlink’s Satellite Internet service vs competitors around the world
Starlink Internet could be a game changer with 100 megabytes per second download speed
PCMag Study: Starlink speed and latency top satellite Internet from Hughes and Viasat’s Exede
Starlink to explore collaboration with Indian telcos for broadband internet services
Starlink’s huge ambition and deployment plan may clash with reality
Starlink’s first mission of 2022 launched another 49 satellites into orbit, extending its grand total to nearly 2,000. But since completing its first orbital shell of about 1,600 satellites last May, “Starlink’s launch frequency has slowed dramatically with only four rocket launches over the past seven months, or roughly one every seven weeks,” explained Craig Moffett, principal analyst at MoffettNathanson in a note to clients. Craig wrote:
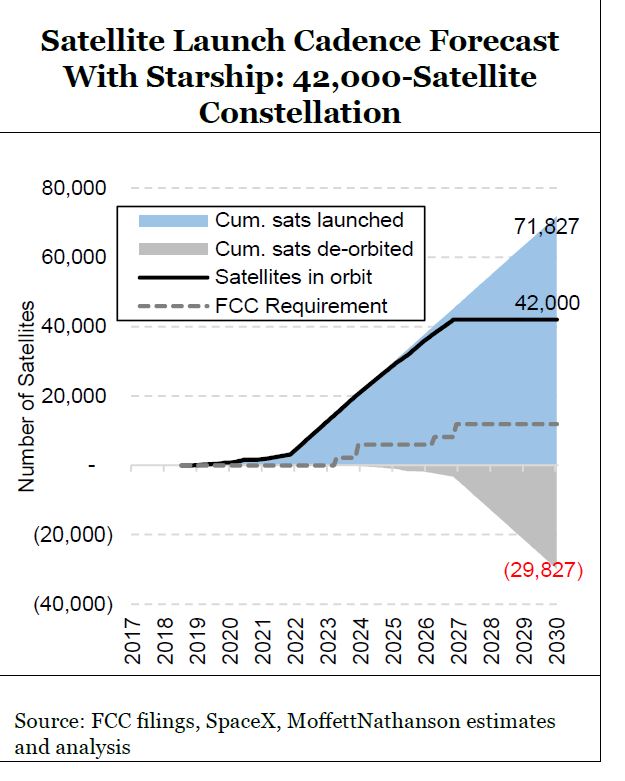
Starlink’s ambition is huge (a constellation of as many as 42,000 satellites). And the implied valuation for the still-private company is huge ($100B+ for all of SpaceX).
This “hugeness” has captured investors’ imaginations and no doubt hugeness itself is very much part of its appeal. But we haven’t yet seen investors come to grips with all of the implications of this bigness. We were struck by Elon Musk’s recent tweet conceding a “genuine risk of bankruptcy” – immediately dismissed by some as hyperbole – and it got us thinking about scale, and risk, in ways we really hadn’t considered before.
Moffett notes that the new Starlink V1.5 satellites are heavier, leading to fewer satellites per launch. “At a payload of 50 satellites per launch for Falcon 9 rockets – down from 60 per launch for V1.0 satellites – SpaceX would need to drastically increase launch frequency to once every seven days for five consecutive years just to launch the satellites required for their planned constellation of ~12,000 by their FCC deadline in 2027.”
In low-Earth orbit, satellites will drift back to Earth and burn up on re-entry. Assuming the satellites have an average lifespan of five years, the number of launches to simply replace expiring satellites will, by year five, be as large as the number of launches required over the next five years to grow the constellation. By the end of 2030, just nine years from now, they would have had to launch nearly 23,000 satellites in support of a 12,000 bird constellation. Assuming a Falcon 9 payload of 50 satellites, that would imply 48 launches each year – roughly one every seven days – just to sustain a constellation of 12,000 satellites even after the constellation is “finished.”
Privately held SpaceX (Starlink’s owner) will also need to strongly increase manufacturing capacity and manage tricky supply chain logistics to meet the needs for Starlink, as well as for SpaceX’s clients.
Based on $30 million per launch, Moffett estimates that it would cost about $15 billion to build a constellation of 30,000 satellites, with satellite replacement (production and launch) alone costing more than $3.6 billion per year. Please see chart below.
Starlink hopes to beef up its capabilities with Starship, a larger launch vehicle that’s had its share of problems, with an orbital test flight that could take place as soon as March. However, Craig suggests that Starship isn’t necessarily the answer to the problem, considering that new V2.0 satellites will be perhaps four times as massive as previous generation Starlink LEO satellites.
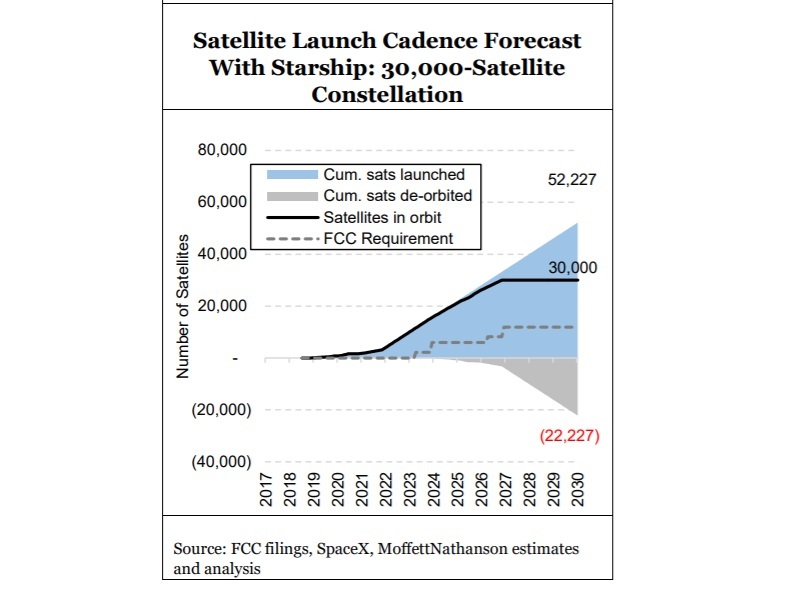
In November 2021, Elon Musk distributed a companywide email stating that a production crisis centered on the Starship rocket engine puts SpaceX on a path to “genuine risk of bankruptcy if we cannot achieve a Starship flight rate of at least once every two weeks next year.”
However, the costs will be very high. Moffett says the “sustenance” cost of the constellation, before considering any costs associated with overhead, engineering, ground facilities, network operations centers, or end-user support, installation, and/or maintenance, could tally $5B per year as per this chart:
Satellite projects are, by their very nature, huge. A defining characteristic of big infrastructure investments is that they demand that investors be confident about the success and payoffs from infrastructures that may take as much as a decade to build.
Moffett is concerned that investors [1.] have yet to “come to grips with all of the implications” of the audaciousness of the Starlink’s huge ambitions.
Note 1. It’s important to note that Starlink is part of SpaceX, which is still a privately owned company. As of October 2021, Barron’s said that “Elon Musk owns roughly 50% of SpaceX.” It is not known who or whom owns the other half of SpaceX
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/elon-musk-net-worth-trillionaire-51634679420?tesla=y