Morgan Stanley: Hello Europe, 5G is on the line!
by Emmet Kelly, Head of European Telecoms Research for Morgan Stanley
Introduction
5G technology promises to deliver faster download speeds, a far more efficient use of the mobile spectrum and denser networks with fewer white spots. For both industries and consumers, 5G will better enable technology like the Internet of Things to power smart factories, drive connected cars and use wireless locators to find a lost pet or house keys.
Despite high anticipation for 5G, one of the key questions is launch timing. Some U.S. operators have already rolled out limited 5G services in select U.S. cities, and operators in China, South Korea and Japan are prepping to launch 5G in the next 6 to 18 months. However, the 5G outlook in Europe is still somewhat of a question mark, with 2021-22 often cited as a launch date. Some industry observers say European telcos are sending a weak signal on 5G launch dates. But the new technology could launch earlier than expected.
Delays for Europe?
Why are European telcos broadcasting such a weak signal on 5G? First, 4G has hardly been a financial success for operators in Europe, which begs the question: “Why rush to 5G?” Indeed, European mobile-service revenues have declined by more than 25% since 4G was first rolled out seven to eight years ago.
Second, European operators may decide that waiting is the best strategy, since a delayed rollout will likely bring cheaper 5G kit prices, and a greater selection of 5G handsets. European telco balance sheets are also more stretched now than they were in 2010, so cheaper 5G kits could help margins.
Lastly, immediate use cases for 5G have yet to emerge, with the possible exception of Fixed Wireless Access, which would make 5G a replacement for wireline broadband.
…Or Perhaps Not?
That said, an alternative view is emerging that 5G could launch in Europe earlier than some expect. Telcos may note that early adopters of 4G saw decent market-share gains of up to two percentage points and may seek to replicate this success with early 5G adoption.
Additionally, some European government bodies have noted that the high expense of 5G could spark wireless consolidation. If mobile consolidation happens, 5G would likely emerge soon afterward.
A final consideration for telcos: Could 5G reveal the next killer app? For example, the launch of 4G laid the groundwork for wireless video to emerge unexpectedly as the predominant use case. Abundant 5G use cases have yet to reveal themselves, to which some industry watchers say: “Build the network, and the killer apps will come.”
References:
https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/europe-5G-launch-2019
https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/us-5G-rollouts-2018?cid=228977584:428065928:99793987
Verizon CFO: “5G” Home Fixed Wireless Exceeds Promised Speeds; Partnerships with Video Content Providers
Verizon is pleased with the performance of its fixed wireless network, “5G Home,”* which has offered better speeds than promised in “a lot of cases,” said Chief Financial Officer Matthew Ellis. Although the fixed wireless service was introduced in four initial markets using non-standard equipment, Verizon plans “to transition to the global standard (?) as soon as equipment is available,” Ellis said. Later, Verizon expects to offer Verizon 5G Home outside its traditional local service territory.
Ellis made his comments at the Morgan Stanley European Technology, Media & Telecom Conference in Barcelona.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
* IMPORTANT NOTE: As we’ve repeatedly explained, Verizon’s “5G” fixed wireless network is based on a proprietary spec. More importantly there is no standard 5G fixed wireless access because it is not being considered (i.e. no use case) for ITU-R IMT 2020. There are NO FUTURE STANDARDS imminent for 5G fixed wireless access. Instead, ALL SO CALLED 5G FIXED WIRELESS OFFERINGS ARE PROPRIETARY WITH NO INTEROPERABILITY!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“The product works exactly as expected,” said Ellis in a transcript from the conference published by Seeking Alpha. “And in some cases – a lot of cases – at speeds higher than the minimums that we promised in the commercial offerings.”
When Verizon 5G Home was announced, the company said the offering would support typical network speeds around 300 Mbps and up to 1 Gbps peak speed. The service sells for $50 monthly with a qualifying Verizon Wireless service or $70 a month for non-Verizon Wireless users.
Verizon has said that it sees a potential market of 30 million homes for Verizon 5G Home, and although some industry observers see that as overly optimistic, Ellis said “we certainly still see line of sight to getting to 30 million households in the U.S. with that product over the next few years.”
Ellis said Verizon launched the service initially in only four markets because the equipment the company will use initially to support the offering is not based on standards. The company made the decision to launch with non-standard equipment in order to get to market quickly.
“We want to transition to the global standard as soon as equipment is available,” he said.
In 2019, he said, “you’ll see more activity… than this year” involving Verizon 5G Home. A big piece of deployment plans is “getting the fiber in the ground in a number of cities to hook up the 5G network.”
The fiber deployment is particularly important considering that Verizon is deploying 5G in the 28 GHz band – a strategy that will help maximize bandwidth but over relatively short distances, requiring extensive backhaul infrastructure. As equipment becomes available, Verizon’s 5G network will support both fixed and mobile service, and backhaul costs will be shared across both services, thereby enhancing the business case for both offerings, Ellis noted.
“You should assume we’ll start in a city in the central area, and once we get enough scale in that city, we’ll launch the network in that city and then the build moves out within that city limit into suburban areas and so on,” he explained. “And as we do, we’ll just add homes toward the 30 million number.”
Ellis offered some commentary about Verizon’s decision to offer a YouTube over-the-top video service to 5G Home customers. He noted that when Verizon launched FiOS fiber broadband service, the decision was made to curate a traditional pay-TV offering to be delivered over the same platform. But as content costs have outpaced what Verizon can charge for video service, the company has moved away from that model.
With Verizon 5G Home, he said, “we felt the right approach . . . was to say ‘there are some viable OTT offerings – and if you’ve got a great broadband experience, which is what our 5G Home product is, OTT is the right way to deliver the content that the customer wants to have.’”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
From the Wall Street Journal: Banking on 5G
Verizon’s biggest transaction to date was the $130 billion purchase of full control of Verizon Wireless in 2013. Executives have stressed to analysts and investors in recent months that they are focused primarily on building out the carrier’s 5G network—which they say will generate additional revenue by powering new technology used in factories, hospitals and cities.
Verizon explored, but didn’t ultimately pursue, acquisitions of companies such as CBS Corp. , and this year told investors it isn’t interested in buying a content creator. Instead of acquiring content, it is offering its first 5G customers live channels, movies and shows through streaming partnerships with Apple TV and Google’s YouTube TV.
The carrier is in discussions with Apple and Google about partnerships that could extend the video services to a broader group of its cable and wireless subscribers and include some content from Verizon’s Oath digital-media unit, according to people familiar with those discussions. Those plans could be announced as soon as this month, the people said.
Sajod Moradi, a senior credit analyst at Macquarie Investment Management, says Verizon’s partnerships will allow it to benefit from expanded content offerings without creating the pressure to generate excess cash flow to pay down debt.
Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg said in a recent interview the carrier was exploring ways to apply 5G technology to the media, augmented-reality and virtual-reality brands within the unit.
References:
https://www.telecompetitor.com/cfo-verizon-5g-home-fixed-wireless-exceeds-promised-speeds/
https://www.wsj.com/articles/at-t-and-verizon-pursue-different-paths-into-the-future-1541999131
KDDI to launch limited 5G-based services in 2019; full 5G in 2020
Japanese network operator KDDI has announced plans to offer a limited range of 5G-based services in 2019, before a full-fledged 5G launch in 2020. During a conference call with investors and analysts, KDDI president Makoto Takahashi said the company’s initial 5G services will be in the areas of high-definition images and drone based security.
In 2020, KDDI plans a full-fledged 5G launch to support the upcoming Tokyo Olympic and Paralympic Games.
“In limited areas, we are aiming at distributing high-resolution images and drone security. In 2020, in a full-fledged launch manner, we are planning to provide 5G in areas of Tokyo for the Olympic and Parlympic Games and in areas in accordance with the request of municipalities and our partner companies,” the executive said.
“5G is actually the extension of 4G LTE technology. So, we are thinking of adding software functions which are common to 4G, and we are trying to share the facilities with other companies, so that we do a capex investment efficiently, to reinforce [the]network with a view to [the]IoT era,” Takashashi added. Translation: to fund the extensive capex needed to roll out 5G and the IoT, KDDI is introducing a new model involving collaboration with the competition.
In the lead up to the launch, KDDI has been involved in 5G trials with Ericsson and Samsung. Last year, KDDI and Ericsson signed an agreement for a 5G proof-of-concept trial in the 4.5-GHz band in cities across Japan. KDDI also recently signed an agreement with Japanese commerce giant Rakuten through which the latter will use KDDI’s 4G network for the provision of mobile services. The agreement will enable Rakuten to offer a nationwide LTE service from launch. The services will be provided until March 2026, which will give the e-commerce firm time to deploy its own network.

Japan’s KDDI plans to launch limited 5G services in 2019
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In April, KDDI signed an agreement with Japanese e-commerce giant Rakuten to provide the use of its 4G network for the planned launch of Rakuten Mobile Network in October next year.
Under the agreement, KDDI will provide Rakuten with network roaming, while Rakuten will provide payments as well as its logistics expertise, Takahashi said.
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20181109/5g/japan-kddi-launch-limited-5g-services-2019
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/kddi-launch-limited-5g-based-services-2019
5G Security Issues Raise Mission Critical Questions & Issues
The type of AKA associated with 5G (via 3GPP- not ITU-R) should ensure that a device and a 5G network can authenticate each other while maintaining a confidential data exchange and keeping the user’s identity and location private. However, the researchers say, in its current state, the AKA could not fulfill those security aims because the requirements it sets forth are not sufficiently precise.
The team of researchers emphasized their belief that the AKA security for 5G would be superior to the AKA used in 3G and 4G network protocols. It still has gaps, though, including one that shows a phone’s presence in the vicinity without disclosing its owner’s identity. Moreover, this vulnerable version of the AKA could result in a person getting wrongfully charged for a third party’s usage of the 5G network.
The published paper about these findings recommends fixes. They include explicitly requiring intended security properties currently missing from the AKA and modifying the key-confirmation component so it offers a provably secure solution. Overall, the researchers say the AKA does not adequately protect privacy from active attackers but admit remedying that problem would not be straightforward.
In an attempt to implement more security in the AKA, the researchers have reached out to 3GPP and hope to engage in a joint effort to improve the protocol before 5G’s widespread rollout. Also, the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security, or ENISA, released a different report warning that identified flaws with signaling protocols on the 2G, 3G and 4G networks could appear in the 5G network.
Ericsson show there could be 3.5 billion Internet of Things units by 2023 — equalling five times the number of connected devices used now. Additionally, the company forecasts that 5G networks will spur the growth of Internet-connected devices.
People became familiar with the security weaknesses of IoT devices when cybercriminals first targeted them with distributed denial of service attacks several years ago.
An insecure 5G network sets the stage for increasingly widespread attacks due to 5G’s high-speed bandwidth, which increases the available attack points. It’s not difficult to imagine a business using IoT sensors within a factory setting and getting shut down due to a DDoS attack.
Chip architecture company Arm is working on a software stack that would let IoT devices run with SIM card chips, thereby making them similar to smartphones with mobile data plans. Then, it would not be necessary to connect IoT devices via Wi-Fi. However, hackers can attack SIM cards and make them unusable. They can also distribute malware through text messages during SIM card attacks.
It’s too soon to say whether hackers will exploit SIM vulnerabilities in IoT devices that may eventually include them, but the possibility is there. In any case, it’s evident that the opportunities 5G offers could spur hackers’ efforts to launch increasingly devastating attacks using methods people already know, as well as wholly new techniques.
“5G doesn’t necessarily changes the risk factors we have today,” said Tom Lally, vice president of sales for data storage and management company, DataSpan, Inc. “But it is going to exponentially increase the threat vectors and opportunities for attackers to exploit.”
“5G is going to enable businesses to connect more and more devices at higher speeds so more data can be consumed at much faster rates,” he says. “Thus, increasing the capacity and data flows in and out of the datacenter. So if you have more devices connected and more traffic flows, then you have more potential vulnerabilities derived from the increase in new vectors.”
“It’s going to become more important than ever to have proper monitoring, be able to identify attacks once inside, and have the capability to respond effectively, to remediate any potential issue,” says Lally. “At the end of the day, you’re still looking for anomalies, you’re just going to have more. So the ability to swiftly identify and respond will be critical to minimizing risk.”
It is both valuable and admirable that researchers endeavored to bring the security concerns mentioned here to light. However, it’s crucial for people to remember that 5G is a pioneering technology. Besides these potential problems, there are inevitable risks not anticipated yet in these early stages.
Conversely, there are unforeseen benefits that are more specific than the advantages so often highlighted in media coverage of the 5G network. For example, some of the inventions people rely on soon might not have been possible to develop on older networks. In order to enjoy all those advantages to the fullest, it’s necessary to continually prioritize 5G network security.
References:
UPDATE:
The real work on 5G security is being done by 3GPP with technical specification (TS) 33.501 Security architecture and procedures for 5G system being the foundation 5G security document. That 3GPP spec was first published in Release 16, but the latest version dated 16 December 2020 is targeted at Release 17. You can see all versions of that spec here.
3GPP’s 5G security architecture is designed to integrate 4G equivalent security. In addition, the reassessment of other security threats such as attacks on radio interfaces, signaling plane, user plane, masquerading, privacy, replay, bidding down, man-in-the-middle and inter-operator security issues have also been taken in to account for 5G and will lead to further security enhancements.
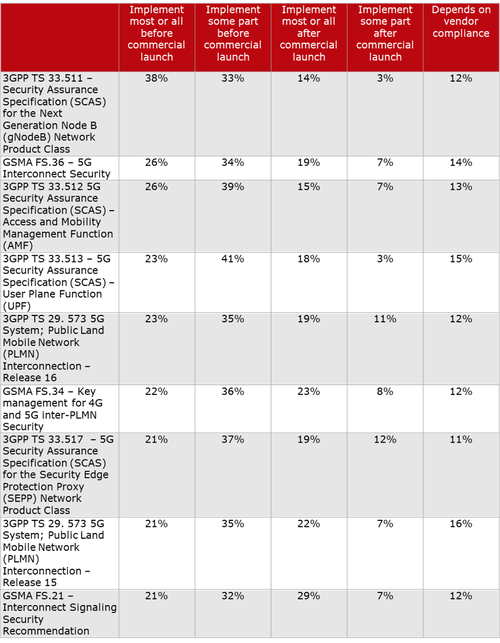
Another important 3GPP Security spec is TS 33.51 Security Assurance Specification (SCAS) for the next generation Node B (gNodeB) network product class, which is part of Release 16. The latest version is dated Sept 25, 2020.
Here’s a chart on 3GPP and GSMA specs on 5G Security, courtesy of Heavy Reading:
Samsung deploying small cells in large volumes for Reliance Jio in India
Samsung Networks is deploying small cells in large volume for indoor coverage for Mukesh Ambani-led Reliance Jio, which is set to have 99% population coverage soon in the country, according a Samsung executive.
“We have seen drive happening on indoor small cells. But that doesn’t mean that outdoor isn’t happening. Outdoor is happening at a good speed basis the site availability and so on… We will continue to expand on this piece of the network [indoor] because there are places where it’s more value to go that way,” Srini Sundararajan, Senior Vice President and Head of Networks Business at Samsung India, told ET.
“Jio tells us what their network requirements are, and we support…indoor always volume looks larger because devices are smaller and are easy to deploy and are self-configured,” he added.
Samsung Networks had earlier this year obtained a new 4G LTE network expansion contract from its sole customer in India, Reliance Jio, to increase the telco’s 4G network penetration from around 75% to 99% by Diwali this year.
The South Korean company is the sole 4G equipment provider to Jio with contracts to supply wireless base station equipment for over 140,000 sites for pan-India coverage last year, ET had earlier reported.
Image courtesy of Economic Times Telecom (India)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sundararajan said that Jio is expanding its networks for both coverage and capacity needs in the country. “It has to be both. There are still parts of the country we need to increase the coverage. Some of the hilly areas or remote areas. For every project, there is a certain percentage of sites for coverage and a large percentage is for capacity,” he added.
For capacity, Jio has started commercial deployment of massive mimo technology in areas where it is not able to add new sites easily.
In addition to 4G wireless equipment, Samsung is also providing packet core technology to Jio. The executive said that the virtualised packet core will play a crucial role in the 5G scenario. Samsung is currently preparing to conduct 5G field trials in New Delhi in the first quarter of the next year, and is working closely with the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
“We have a lot to offer similar to what we did on 4G, and which is why we said that we will partner with the DoT. We are directly partnering with the DoT to ensure that we listen to the needs of the government,” the executive said.
He added that the government’s involvement in these 5G field trials is very crucial for the successful commercial roll out since there will be 5G use cases that will have “societal value” along with the business value.
“The government is very proactively enabling and promoting to grow the 5G network. They are very aware that it is the ecosystem, and not just a vendor or operator. So they tend to bring different players into it to ensure that we are able to provide a high-value system for the country,” he added.
Samsung will be conducting the trial using the millimeter wave (mmwave) spectrum even as other vendors like Huawei plan to conduct trials in the mid-band. Sundararajan said that the millimeter wave band will offer a large chunk of spectrum that can result in uses cases like fixed wireless access (FWA) with huge capacity for data services. “We need to have the technology in the mmwave to enable the true vision of the government,” he said.
Samsung is currently doing 3.5Ghz trials in the mid-band in South Korea, and in the US, we are doing mmwave trials. “We are technology agnostic, but use cases will drive the adoption of one of these bands,” he said.
References:
Reliance Jio Blankets India with Inexpensive 4G Service; Where are the Profits?
India Selects Cisco, Samsung, Nokia, Ericsson for 5G trials; Bars Huawei and ZTE
India’s DoT Creates Dedicated 5G Technology Test Bed after Ericsson 5G Demonstration
5G smartphone prototype tested on Swisscom’s 5G network in Lucerne
Swiss network operator Swisscom, Ericsson, Qualcomm and Taiwanese wireless product device manufacturer WNC have claimed a 5G milestone with the first test of a 5G smartphone prototype on a live network. The companies used Swisscom’s 5G network, equipped with Ericsson’s 5G new radio hardware and software solutions, for a data transfer test using a Qualcomm smartphone prototype powered by the company’s Snapdragon™ X50 5G modem and RF subsystem. During the trial in Lucerne, a prototype hotspot device developed by WNC (Wistron NeWeb Corporation) was also successfully tested on the live network. That device also used the Qualcomm Snapdragon™ X50 5G modem.
Swisscom’s live pilot 5G network is operating on the 3.5-GHz band under a test license for use case field trials. Selected parts of Lucerne, Bern, Geneva and Zurich have joined Burgdorf in being connected live to the network on the test frequency. By the end of 2019, Swisscom plans to gradually roll out 5G to 60 cities and communities across Switzerland.
Arun Bansal, President Ericsson Europe and Latin America, says: “Ericsson, as a strategic partner, is proud to support Swisscom with its ambitious expansion of the 5G network. Together, Ericsson and Swisscom are kick-starting the 5G network rollout in Switzerland and preparing industries for 5G use cases that will benefit the whole economy.”

Swisscom CEO Urs Schaeppi said validation on a live network is an important step towards ensuring the first 5G smartphones reach the market by the middle of next year.
“One year ago, in cooperation with Ericsson, we presented the first laboratory applications. Today, we are taking the next step by presenting a 5G smartphone prototype for the first time in real conditions on our 5G network. This modem, or chipset, will soon be inside the first 5G smartphones.”
Jeffrey Gau, Chief Executive Officer, Wistron NeWeb Corporation, said: “In February, we selected the Snapdragon X50 5G NR modem family for our 3GPP-compliant 5G NR device product launches in 2019. Today is the next step in accelerating 5G market development. WNC is proud to be here today, with our partners at Qualcomm Technologies, Swisscom and Ericsson on this momentous occasion for the industry.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Swisscom to expand the 5G network across Switzerland
Looking to the future, Swisscom is not only bringing the 5G network to cities, but also to rural and tourist areas for the benefit of all. Urs Schaeppi says: “Though many applications are in the pipeline, they are still at an early stage. Back when 3G was launched, people doubted whether mobile Internet was necessary at all. Today, we know that mobile applications on 3G and 4G have revolutionised our daily lives. Now we’ve reached the same point with 5G.” Swisscom is shaping 5G development and plays an active role in standardisation through its work on international committees. Around the globe, countries and telecom providers are hatching ambitious plans for 5G expansion. In Switzerland, however, comparatively restrictive ONIR limits that were originally set in 1999 present an obstacle to a swift, extensive and profitable rollout. It is up to politicians and administrations to quickly adapt the underlying framework.
Illustration: Examples of potential 5G applications in Lucerne
From first aid to supporting the fire service with drones and new event experiences, combined mobility, smart farming or tourism products; these are just some of the possibilities that 5G opens up.
The illustration may be used without restriction; it may be used in part or full and can be edited as desired. An open .psd file is available on request. Please contact [email protected].
References:
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/ericsson-tests-5g-smartphone-prototype-live-network
Lessons Learned: Consumers want whole-home Wi-Fi service from ISPs
European fixed broadband providers are now scrambling to deliver gigabit speeds to their customers. But as they do, they are running into a fresh set of challenges, particularly in the home WiFi environment. How are providers and their vendor partners managing their new gigabit services and making sure that customers get what they’re promised? How can they improve the home WiFi experience?
Faster Wi-Fi connectivity is no longer impressing consumers, who want better connections throughout their homes, executives said at the Cable Next-Gen Europe event in London on November 6th. Panelists at a session titled: Managing 1 Gig Services & WiFi– Lessons Learned suggested ISP deployment of powerful lines of WiFi gateways would be required. For customers with larger homes, providing WiFi extenders that communicate with those gateways and a system that is all underpinned by cloud-based software and (often) a mesh-based architecture that can enhance and improve connectivity based on how that traffic is traversing the home’s WiFi network.
Owning the home WiFi network — or at least having deeper visibility into the WiFi network and providing systems that can understand changing traffic conditions and steer tablets, PCs and other devices to the optimal band or channel — could also prove to be a major operational benefit to cable operators and other ISPs. Since consumers tend to call the ISP whenever WiFi-related troubles arise, having this additional management layer is helpful in troubleshooting problems and reducing the need for costly truck rolls.
Though WiFi speed continues to be a key use case for gigabit services as consumers check to see if they are indeed getting what they pay for, there’s also an “expectation problem” that needs to be resolved because consumers expect high speeds to be delivered beyond the home gateway, said Michael Clegg, VP of global sales at Plume Design Inc. , a WiFi software and device maker that counts Comcast Corp. among its financial backers and deployment partners.
Stofa of Denmark is also moving ahead with 1-Gig deployments, but has likewise found that providing solid in-home WiFi performance and coverage is more important than ever, given that most of the devices that connect to the Internet in the home are doing so with WiFi, Uffe Callesen, lead architect at Stofa, said. However, it’s difficult to stay ahead of the technology curve with WiFi given the presence of a large mix of legacy devices that use an older version of the standard, he added.
And though few, if any, end devices require or use a full 1 Gbit/s connection, providing solid connectivity to every part of the customer’s home has become a paramount focus for service providers, Clegg pointed out.
Frode Elverum of Norway’s Get says whole-home Wi-Fi offerings can be a point of market differentiation for internet service providers.
Panelists here also did not view 5G, which is starting to emerge as a fixed wireless alternative broadband connection, as a significant threat to WiFi, particularly when it comes to in-home connectivity
“You’ll see a WiFi tail on the back end of 5G,” Clegg said, noting that some spectrum used for 5G services isn’t all that “friendly” in the home.
And the general story with residential 1 Gbit/s broadband services has not changed much — customer adoption of such speeds remains relatively low and, for now, have served primarily as a competitive response against rivals that run FTTP networks.
Norway’s Get started with a soft-launch of gigabit service and plans to ramp things up a bit more in early 2019 as it looks to put 1-Gig into its most attractive TV and broadband bundles. However, few customers need 1-Gig. “It’s more about the competitive positioning of our offering,” Elverum said.
“1-Gig, as a tier, is used really as a marketing tool,” agreed Eddy Mötter, CTO for Access Network, Solution Sales Department at Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd . While that’s the case today, it’s inevitable that apps and services that will require gigabit speeds will emerge. “That [capacity] space will be filled,” Challinor said, predicting that 1-Gig broadband will become the “de facto norm” within five to ten years.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/mobile/carrier-wifi/why-isps-are-high-on-whole-home-wifi/d/d-id/744575
Oracle Confirms Research: China Telecom Misdirected U.S. Internet traffic thru China
China Telecom is the largest fixed line operator in China, state owned, and bidding to become the third telecommunications network operator in the Philippines. Two weeks ago, researchers found that the company has been hacking into internet networks in the United States and hijacking data from countless users, a study has found.
The research, conducted jointly by scholars from the US Naval War College and Tel Aviv University, discovered that the China government, acting through China Telecom, has been engaged in data hacking even though it had entered into a pact with the U.S. in 2015 to stop cyber operations aimed at intellectual property theft.
Oracle’s Internet Intelligence division has just confirmed the findings of the academic paper published two weeks ago that accused China of “hijacking the vital internet backbone of western countries.”
Doug Madory, Director of Oracle’s Internet Analysis division (formerly Dyn), confirmed that China Telecom has, indeed, engaged in internet traffic “misdirection.” “I don’t intend to address the paper’s claims around the motivations of these actions,” said Madori. “However, there is truth to the assertion that China Telecom (whether intentionally or not) has misdirected internet traffic (including out of the United States) in recent years. I know because I expended a great deal of effort to stop it in 2017,” Madori said.

Image Courtesy of Oracle
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Madori then goes on to detail several of China Telecom’s BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) route “misdirections,” most of which have involved hijacking US-to-US traffic and sending it via mainland China before returning it to the U.S.
Verizon APAC errors had a knock-on effect, Madori explained: “Verizon APAC … were announcing [routes] to the internet on behalf of their customers. A couple of AS hops away, China Telecom was mishandling them – announcing them in a manner that would cause internet traffic destined for those IP address ranges to flow back through China Telecom’s network.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Indeed, the researchers found that China Telecom uses BGPs in order to carry out their data intrusions. Created in the early 1980s, BGP protocols do not feature any security controls, often resulting in misdirected traffic through “bad BGPs”. The majority of these cases are attributed to configuration mistakes.
However, researchers found that China Telecom has been deliberately hijacking BGP routes to send legitimate traffic through malicious servers.
They described the state-owned telco as “one of the most determined BGP hijackers in the international community.”
In order to validate their findings, the researchers built a route tracing system to monitor BGP announcements, allowing them to distinguish between normal, accidental patterns and deliberate ones.
They concluded that China Telecom was responsible for patterns of BGP behavior that “suggest malicious intent, precisely because of their unusual transit characteristics -namely the lengthened routes and the abnormal durations.”
“[China Telecom] has already relatively seamlessly hijacked the domestic US and cross-US traffic and redirected it to China over days, weeks, and months,” the researchers said.
“The prevalence of and demonstrated ease with which one can simply redirect and copy data by controlling key transit nodes buried in a nation’s infrastructure requires an urgent policy response,” they warned.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The routing snafu involving domestic US Internet traffic coincided with a larger misdirection that started in late 2015 and lasted for about two and a half years, Oracle’s Madory said in a blog post published Monday. The misdirection was the result of AS4134, the autonomous system belonging to China Telecom, incorrectly handling the routing announcements of AS703, Verizon’s Asia-Pacific AS. The mishandled routing announcements caused several international carriers—including Telia’s AS1299, Tata’s AS6453, GTT’s AS3257, and Vodafone’s AS1273—to send data destined for Verizon Asia-Pacific through China Telecom, rather than using the normal multinational telecoms.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Ahead of the third telco player’s selection Wednesday (November 7), Senators Grace Poe and Francis Escudero already voiced concerns about the possible threats to national security and data privacy in case China Telecom becomes the winner of the bidding.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://internetintel.oracle.com/blog-single.html?id=China+Telecom%27s+Internet+Traffic+Misdirection
https://www.zdnet.com/article/oracle-confirms-china-telecom-internet-traffic-misdirections/
GSMA 5G Spectrum Guide vs WRC-19 vs FCC 5G FAST Plan
In a new ‘industry position,’ mobile trade association GSMA states its views on spectrum needed for 5G mobile networks. The GSMA 5G Spectrum Guide executive summary talks about a new generation of wireless tech opening up a bunch of new opportunities, but that won’t be possible unless governments and regulators do a much better job of giving wireless network operators the swathes of spectrum they will need to deliver on the promise of 5G.
“Operators urgently need more spectrum to deliver the endless array of services that 5G will enable – our 5G future depends heavily on the decisions governments are making in the next year as we head into WRC-19,” said Brett Tarnutzer, Head of Spectrum at GSMA.
Editor’s Note:
WRC-19 refers to the World Radiocommunications Conference 2019. It’s a rare opportunity for organizations such as various ITU-R committees and the GSMA to propose spectrum to be used for various worldwide wireless applications. As this author has stated many, many times in numerous techblog posts, WRC-19 will confirm the frequencies to be used by all ITU-R IMT networks, including IMT 2020.
- revise the Radio Regulations and any associated Frequency assignment and allotment Plans;
- address any radiocommunication matter of worldwide character;
- instruct the Radio Regulations Board and the Radiocommunication Bureau, and review their activities;
- determine Questions for study by the Radiocommunication Assembly and its Study Groups in preparation for future Radiocommunication Conferences.
The next ITU Inter-regional Workshop on WRC-19 Preparation – Geneva, Switzerland, 20-22 November 2018. Details are here. The results of the ITU-R studies included in the Draft CPM Report to WRC-19 will be presented to the Workshop, as well as the status of regional preparations for CPM19-2, RA-19 and WRC-19.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Without strong government support to allocate sufficient spectrum to next generation mobile services, it will be impossible to achieve the global scale that will make 5G affordable and accessible for everyone. There is a real opportunity for innovation from 5G, but this hinges on governments focusing on making enough spectrum available, not maximising auction revenues for short term gains.”
GSMA 5G spectrum guide includes:
5G Spectrum Policy Positions (Updated)
The 5G spectrum guide starts with the GSMA’s key policy positions. They focus on areas where governments, regulators and the mobile industry should cooperate to make 5G a success.
Click here to download the updated full position paper in English or French. An updated version in Spanish will arrive shortly.
IMT Spectrum Between 24.25 and 86 GHz (Updated)
WRC-19 will be vital to realising the vision for 5G. The work at WRC-19 (centred around AI 1.13) will look at spectrum for mobile broadband in frequencies between 24.25 and 86 GHz.
Download the updated position paper in English here. There are also updated versions in French and Spanish. They are available here and here.
26 GHz and 28 GHz are both needed for 5G (Updated)
In this infographic we take a look at countries and regions that are trialling and supporting 26 GHz and or 28 GHz. It also details bands plans and use cases.
An updated version of the infographic is available in English here. The new version will shortly arrive in French and Spanish. The old versions are available here and here.
Considerations for the 3.5 GHz IMT range
Operators need new spectrum to keep up with growing mobile data and coverage demands. The 3.5 GHz IMT range offers an ideal opportunity to meet this demand. The band will be one of the first frequencies to carry 5G traffic, but first it must be licensed.
Download the report in English here,
The 5G era in the US
This report from GSMA Intelligence explores the current landscape and the future outlook for 5G in the US. It focuses on network deployment, spectrum, use cases, and policy and regulation.
The full report is available here
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“Governments and regulators have a major role to play in ensuring that consumers get the best outcome from 5G,” said GSMA’s Tarnutzer. “Once spectrum is allocated to mobile at WRC, licensing that spectrum at a national level, as history has shown, can take up to 10 years. Therefore, it is essential that governments take the right action now,” he added
That GSMA still feels the need to spell out the importance of radio spectrum to governments and regulators is somewhat astonishing, considering what a redundant and rhetorical issue that should be. Evidently, GSMA hopes that government regulators will be galvanized to make a strong case for their respective spectrum positions.
Here’s the GSMA’s list of demands for spectrum:
1. 5G needs wider frequency bands to support higher speeds and larger amounts of traffic. Regulators that make available 80-100 MHz of spectrum per operator in prime 5G mid-bands (e.g. 3.5 GHz) and around 1 GHz per operator in vital millimeter wave bands (i.e. above 24 GHz), will best support the very fastest 5G services.
2. 5G needs spectrum within three key frequency ranges to deliver widespread coverage and support all use cases:
- Sub-1GHz spectrum to extend high-speed 5G mobile broadband coverage across urban, suburban and rural areas and to help support Internet of Things (IoT) services
- Spectrum from 1-6 GHz to offer a good mix of coverage and capacity for 5G services
- Spectrum above 6 GHz for 5G services such as ultra-high-speed mobile broadband
3. It is essential that governments support the 26 GHz, 40 GHz (37-43.5 GHz) and 66-71 GHz bands for mobile at WRC-19. A sufficient amount of harmonised 5G spectrum in these bands is critical to enabling the fastest 5G speeds, low-cost devices and international roaming and to minimising cross-border interference.
4. Governments and regulators should avoid inflating 5G spectrum prices (e.g. setting high auction reserve prices) as they risk limiting network investment and driving up the cost of services.
5. Regulators should avoid setting aside spectrum for verticals in key mobile spectrum bands; sharing approaches, such as leasing, are better options where vertical industries require access to spectrum.
References:
https://www.apnews.com/b77934ab658f4ad685d55678a8fe7c59
https://www.gsma.com/spectrum/5g-spectrum-guide/
Indigo Cable System to boost connectivity in SE Asia & Australasia when it launches later this year
The Indigo Consortium has confirmed that it has landed the Indigo Cable System, which will link Australia’s East and West coasts, in Coogoo Beach, Sydney. In September, operators launched the Indigo Cable System from Floreat Beach in Perth, on Australia’s West Coast. Once complete, the Indigo Cable System will connect Australia’s East and West Coasts and then provide onward connectivity to a number of high profile destinations in South East Asia, including, Singapore and Jakarta, Indonesia.
The 9,200km Indigo Cable System will be comprised of two fiber pairs and will be able to support data transfers of 36Tbps. The Indigo Cable Consortium is comprised of AARNet, Google, Indosat Ooredoo, Singtel, SubPartners, and Telstra.
“The landing of INDIGO Central cable by Optus is a landmark development which will boost Australia’s communications ecosystem with much-needed high-speed capacity and network diversity. Together with INDIGO West, the next generation INDIGO Central data superhighway will enhance Singtel and Optus’ subsea networks, creating a cable ring connecting Australia to Singapore, through Southeast Asia, across the Pacific and back to Australia,” said Singtel’s Vice President, Carrier Services, Group Enterprise Ooi Seng Keat.
“This new data superhighway will complement our existing global links to Asia, US, Europe, Australia and the Middle East and allow Singtel and [Australian subsidiary] Optus to meet the growing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications as well as boost network diversity and resilience.”
Telstra head of North Asia and global wholesale Paul Abfalter added that the cable will connect to the operator’s extensive terrestrial infrastructure for onward connectivity in Australia.
“Our vast subsea network is a key part of our international growth strategy and we will continue to invest in additional capacity to meet the increasing demand for data and maintain our network leadership in the Asia-Pacific region.” he said.
References:
https://subpartners.net/indigo.html
https://www.submarinenetworks.com/systems/asia-australia/indigo
https://www.totaltele.com/501509/Singtel-Telstra-and-partners-land-Indigo-Cable-in-Sydney
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/indigo-cable-lands-western-australia
My story: Connecting Australians to the world, from the ’80s to the ‘Tera Era’




