Author: Alan Weissberger
China Telecom launches 5G standalone cloud native network with Tianyi Cloud
China Telecom claims it has launched what it says is the world’s largest 5G standalone (SA) network. Executives announced the start of commercial 5G SA operations during a company virtual conference last week and said their 5G SA network is currently supported by 30 devices, with 100 expected by year-end.
China Telecom’s 5G SA end-to-end capability testing with Tencent and Huawei was completed in September. Earlier in the week, China Telecom said it will offer 5G SA services to over 300 cities in China at a press event held with Qualcomm at Guangzhou, China.
Like all the other telcos on the path to 5G SA (only T-Mobile US has deployed it), China Telecom’s is said to be 5G SA is a cloud native network called the “Tianyi Cloud.” Company leaders said it’s 5G SA cloud network can guarantee “five-nines reliability,” secure network slicing and latency of below 5ms. In particular:
With the popularization of cloud computing, hybrid multi-cloud has become the new normal for cloud migration. It is just necessary to realize high-speed network interconnection and unified management between multi- clouds. The full-stack hybrid cloud launched by Tianyi Cloud realizes the same technical architecture of the underlying cloud platform and has no cloud capabilities. It extends and covers the deployment of three scenarios: edge, private cloud, and industry cloud. At the same time, it provides first-line multi-cloud capabilities, a dedicated line connects multiple mainstream public cloud service providers at the same time, and high-speed interconnection between public and private clouds can also be realized. In addition, it is worth mentioning that Tianyi Cloud’s full-stack hybrid cloud has been adapted to national production and production at the chip, hardware, and operating system levels, and has the ability to provide national production and service services.
The new generation of cloud-native database developed by Tianyi Cloud completely independently developed and technically tackled key problems. It successfully realized the de-IOE of China Telecom’s core IT system database. Telecom users and billion-level terminal equipment access. Through continuous upgrading and evolution, Tianyi Cloud’s new generation of cloud-native database has reached financial-level data security and high reliability, and has continuously broken through the limits of scale and performance, while being compatible with a complete database ecological chain, so as to meet customers’ diverse data service needs.
Also, China Telecom officially launched the “Cloud Terminal” plan at the event. Tianyi Cloud, as the base of the cloud terminal strategy, has independently created a cloud computer through computing in the cloud, data in the cloud, application in the cloud, security in the cloud, and imagination in the end mode. And cloud mobile phone products.
President and COO Li Zhengmao said the arrival of the 5G era provided the opportunity and the technical ability for the integration of cloud and the network.
In terms of 5G cloud integration, Hu Zhiqiang said:
“In the 5G era, cloud-network integration has entered a new realm. Cloud-network integration is the goal that Tianyi Cloud pursues.” On the one hand, Tianyi Cloud launched an intelligent edge video cloud to break through the bottleneck of ultra-high-definition real-time encoding technology. At the same time, it has real-time scheduling capabilities of millions of video streams. On the other hand, 5G is a cloud-based network. Tianyi Cloud provides 99.999% reliability guarantee and exclusive slice data security, achieving a comprehensive TCO reduction of more than 90%, and a delay of less than 5ms.”
A white paper presented at last week’s event describes China Telecom’s cloud-network integration as driven by open sharing, open network capabilities, multi-network access 5G and SD-WAN support. The China Telecom paper said the company was a hybrid multi-cloud strategy, integrating Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, AWS, Azure and others into its aggregation platform.
In conclusion, Hu Zhiqiang said: “China Telecom Tianyi Cloud will continue to strengthen technological innovation, strengthen open cooperation, and accelerate the construction of a digital China and a smart society, and make greater contributions with partners.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
http://www.c114.com.cn/news/117/a1143514.html
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/china-telecom-gets-cracking-on-5g-standalone/d/d-id/765464?
China says it has deployed 700,000 5G base stations this year; Huawei’s forecast
Bank of America: OpenRAN primer with global 5G implications
Written by Multiple Bank of America Research Analysts
Introduction:
OpenRAN turns base stations using proprietary hardware into software running on common off-the-shelf hardware. Tal Liani views this trend as a continuation of ongoing forces in the broader IT and hardware markets – a shift to virtualized hardware, merchant silicon and general software disruption of proprietary hardware markets.
With 78% of the cellular base station/ RAN market controlled by Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia, OpenRAN represents an opportunity for software-only vendors like Altiostar, Parallel Wireless and Mavenir to offer traditional as well as new carriers such as Rakuten and DISH the technology to build cost effective networks with no legacy equipment consideration. OpenRAN is ideally deployed in a virtualized or cloud-based architecture, offering a high degree of automation as well as enabling vendor mixing/matching to reduce costs of innovation and increase efficiencies.
$35bn RAN market set for new competition, disruption:
Radio Access Networks (RANs) represent the largest category of hardware technology, estimated at just under $35bn in 2020. The market is highly concentrated, with 78% controlled by Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia. OpenRAN is disrupting the market, enabling vendor mixing and matching, greater competition, and introducing new entrants via standardization, separation of software and hardware, and by turning certain elements into independent applications.
Early days for OpenRAN, likely limited impact in near-term:
OpenRAN is still in its early days, representing ~1% of the total RAN market in 2020 and ~6% projected by 2024. These estimates are preliminary though, and like any other disruptive technology, deployments could gain momentum as they are adopted by key carriers. To date, the biggest OpenRAN advocates are new carriers, like Rakuten and DISH, which are utilizing the technology to build cost effective networks having no legacy equipment considerations. Tier-1 carriers are taking a more measured approach with legacy architectures/vendors still offering better economics. Yet, at the same time, most leading carriers are testing OpenRAN and some already deploy it on a small scale. For example, Verizon‘s 5G upgrade is partially done with Ericsson‘s proprietary approach and partially with Samsung‘s OpenRAN solution. We also see interest from European carriers, with OpenRAN providing an efficient way to replace Huawei equipment.
Importance of semis, commodity hardware on the rise:
On the vendor side, OpenRAN represents new opportunities for software-only vendors like Altiostar, Parallel Wireless, and Mavenir, hardware providers like Fujitsu and leading semi vendors like Intel and Qualcomm. Nokia and Ericsson partially support OpenRAN, given its disruptive nature, focusing instead on proprietary software-based solutions, like virtualized (vRAN) or Cloud RAN. However, as momentum grows, we expect all leading vendors to support OpenRAN, similar to trends seen in Switching and Routing. We expect the legacy Radio vendors to offset the negative implications of OpenRAN via a growing focus on software, applications and expansion into adjacent markets.
Open Radio Access Networks, or OpenRAN, is an emerging trend that is set to shake up the roughly $40bn 4G/5G infrastructure market. We view this trend as a continuation of ongoing forces in the broader IT and Telecom Hardware markets, such as the shift to virtualized software, whitebox hardware, merchant silicon, and general software disruption of the proprietary hardware markets. We have witnessed similar efforts to open and standardize other networking markets such as Ethernet Switching and IP Routing, however, the complexity, performance demands, and tight vendor controls in the Mobile Infrastructure market have left the Radio Access Networks proprietary thus far. 5G deployments represent an entry point and a catalyst for OpenRAN, and our deep dive aims to explore the potential opportunities and disruption across vendors and sectors that service the RAN market.
Our note is organized into 5 main sections: 1) drivers of OpenRAN deployments vs the challenges, 2) introduction to the Radio Access Market, which describes the technical components, leading vendors, and market dynamics of the traditional RAN market, 3) an OpenRAN 101 section that outlines the architectural changes, new vendors, and growth forecasts, 4) the impact of OpenRAN, and opportunities related to adjacent areas of technology, such as semiconductors, and lastly 5) OpenRAN traction by geographic region.
Ultimately, we see three key takeaways for investors: 1) we flag that OpenRAN and Virtualized/Cloud RAN are separate trends that are coming together to form the attractiveness of Open and Virtualized RAN (vRAN), 2) it remains early for OpenRAN, which is expected to represent less than 1% of RAN spending in 2020 and grow to only 6% of the total market by 2024, and 3) OpenRAN creates opportunities for legacy and new vendors, in our view. We quantify the disruptive potential on page 33, and compare the OpenRAN phenomenon to what happened in the virtualized Evolved Pack Core (EPC) market. We also view OpenRAN as an enabling technology for global carriers to replace Huawei in certain areas, either through growing share of Nokia and Ericsson, or via the introduction of new vendors.
A key benefit of OpenRAN is new innovation in the radio access market, with newer software companies such as Altiostar pushing incumbent vendors to begin disaggregating their software from hardware and support industry groups dedicated to developing OpenRAN technology, such as the O-RAN Alliance. OpenRAN itself also encourages innovation via its open interfaces, and the enablement of third party vendors to add new solutions. OpenRAN is ideally deployed in a virtualized and cloud-based architecture, offering a high degree of automation, increasing efficiencies and reducing costs. Currently, OpenRAN development is supported by a wide range of semiconductor, hardware, testing, systems integration, and software companies, helping foster innovation in each domain and cooperation toward a more ‘hyperscale-like‘ network. As we have seen in other areas of cloud networking and technology, open ecosystems often foster greater innovation.
Less vendor lock-in to create more competition:
Another key driver for OpenRAN interest is the ability to avoid vendor lock-in. Following years of vendor consolidation in the Mobile Infrastructure market, there are only four leading equipment provider choices: Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, and ZTE to a lesser extent. On top of limited choice, it is notoriously difficult to switch vendors, requiring expensive and labor-intensive equipment swaps from the radio head to the baseband data center infrastructure. In some cases, the equipment swap cost burden falls on the carrier and in some cases vendors provide such services as part of the sales/services strategies. Ultimately, the lack of choice and difficulty in switching vendors create a market rife with equipment vendor lock-in.
Swapping out Huawei represents a major catalyst:
As the market has consolidated, political pressures versus Chinese vendors‘ role in 5G (see note on Huawei pressure and risk) further limit vendor choice to only 2-3 firms in some regions. Therefore, global pushback against Huawei/ZTE may be one of the largest drivers of OpenRAN adoption, pulling forward the timing of operator decisions on RAN architectures. Huawei has gained significant share in the $38bn market over the last seven years, now representing 34% of the total market, and government support for removing the vendor from networks has grown in recent months. The UK government recently instituted a policy banning UK carriers from buying new Huawei equipment beginning in 2021, and all Huawei equipment must be removed from UK networks by 2027. Other regions of Europe such as Belgium, Poland, and Sweden have also recently shied away from Huawei.
Importantly, replacing Huawei brings large costs, both from losing Huawei as a competitor (Huawei known for its attractive price/performance) and equipment swaps. As a result, the US government is beginning to take steps to help developing countries within Africa and the Middle East fund the costly replacement of Huawei/traditional equipment. Specifically, the US Agency for International Development is spearheading the effort, while the US State Department continues to pressure US allies to displace Huawei and ZTE equipment from their networks. In our view, the replacement of Chinese RAN technology could open up a $35bn market to both incumbent and new vendors, and the replacement of network vendors‘ architectures offers an attractive opportunity for carries to re-architect the Access network utilizing modernization and virtualization, which are both drivers for OpenRAN. The US government has also explored investing in OpenRAN technologies to help US software/hardware/semi vendors play more of a role in cellular networks.
Open RAN Cost Savings:
Opening the interfaces between the baseband unit (BBU) and remote radio unit (RRU) helps increase competition, lowers the switching costs, and likely saves carrier capex to some degree. However, we believe the real benefits related to the OpenRAN vision come to fruition when the architecture becomes virtualized or cloud OpenRAN (often referred to as Open vRAN). In Open vRAN, carriers first save on equipment capex as the baseband unit software runs on commodity off the shelf (COTS) hardware (i.e., x86 servers) rather than proprietary integrated hardware. Software can be purchased from new vendors and the equipment can be provided by vendors such as Quanta Computer. High degree of competition for the RRU component and the hardware commoditization for the BBU component could result in potential capex savings of 40-50%. Installation and integration services can also potentially be brought in house or outsourced to a longer list of competitors, adding RAN installation savings that are typically part of capex (see Exhibit 3).
The second area of carrier total cost of ownership (TCO) savings is related to the maintenance and operating expense. By copying the efficient cloud models of hyperscalers and centralizing/standardizing the foundation of the RAN, carriers stand to run more efficient data center operations. The software-defined approach also adds to network agility and automation. Through better agility and automation, carriers save on the management, maintenance, and upgrades for the network. Early reports suggest potential 31% operating expense savings as a result (see Exhibit 4).
OpenRAN Industry groups:
1. Telecom Infra Project (TIP):
TIP was formed in February 2016, with Facebook playing a central role. Major vendor Nokia is also part of the group. Japanese members include NTT, KDDI, SoftBank, Rakuten Mobile, NEC and Fujitsu. TIP‘s goal is to create mobile networks using open and disaggregated solutions. The scope of the group‘s work extends from OpenRAN to include the backhaul portion of the network, core network architecture and other areas.
TIP and O-RAN Alliance announced a liaison agreement in February 2020. Under the agreement, the groups will share information, reference respective specifications and collaborate on testing.
2. O-RAN Alliance:
O-RAN Alliance was formed in February 2018 through a merger between x-RAN Forum and C-RAN Alliance. Japanese members include NTT DoCoMo, KDDI, SoftBank, Fujitsu and NEC. In May 2020, O-RAN Alliance and GSMA, an industry body representing MNOs, agreed to collaborate on opening up 5G networks.
Major vendors Ericsson and Nokia are also part of the O-RAN Alliance. However, they appear to be taking a slightly different stance on OpenRAN. In February 2019, some members of O-RAN Alliance announced new open fronthaul specifications and related testing. Nokia is mentioned in the announcement, but Ericsson is absent. Nokia believes open standards are a viable option for RU-DU, but is doubtful about the effectiveness for the CU-DU interface.
The O-RAN Alliance is focused on efforts to standardize technologies. NTT DoCoMo is expected to play a key role in the standardization process. In September 2019, DoCoMo announced it had achieved interoperability with equipment from different vendors in a 4G/5G demo project. Vendors in the demo were Nokia, Fujitsu and NEC. As widely reported, Fujitsu has teamed up with Ericsson and NEC is collaborating with Samsung in OpenRAN technology.
India’s Telco and Infrastructure Groups: Fiber Optic Network Growth Essential
Growth in fiber optic network deployments are essential to further improve the quality of telecom services and support the surging mobile Internet demand as well as have potential to bring substantial social and economic benefits to consumers, businesses and state governments, India’s telco and infrastructure groups said. The Delhi-based telecom body represents Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea.
“Growth of fibre is the foremost priority for the ongoing exponential increase in data demand and improved quality of services,” the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) director-general SP Kochhar told ETTelecom.
Currently, India has an optical fiber-based network spanning across 28 lakh (100,000) kilometres as against the target set up by the National Broadband Mission to deploy as much as 50 lakh kilometres of optical fiber by 2024.
Kochhar’s views were seconded by the Towers and Infrastructure Providers Association (Taipa) that lobbies for companies such as Bharti Infratel, American Tower Corporation (ATC) India, Ascend Telecom Infrastructure, Indus Towers and Sterlite Technologies.
“The fiberisation of existing telecom infrastructure has the potential to bring substantial social and economic benefits to governments, citizens and businesses through an increase in productivity, competitiveness, improvements in service delivery, and optimal use of scarce resources like spectrum,” Tilak Raj Dua, director-general at Taipa said.
Editor’s Note:
The National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) is a project initiated in 2011 and funded by Universal Service Obligation Fund to provide broadband connectivity to over 200,000 gram panchayats of India at an initial cost of ₹200 billion (US$2.8 billion). This is to be achieved utilizing the existing optical fiber and extending it to the Gram Panchayats and Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), is a special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), PSU set up under companies act by Govt of India under Rule 1956 has been registered on Feb 25, 2012 for management and Operation of NOFN. More info at: http://www.bbnl.nic.in/index1.aspx?lsid=13&lev=1&lid=13&langid=1

Indian Railways Fiber Optic Network Map
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The pan India average of fiber to the tower ratio presently stands at 32% as against the target of 70% by 2024, envisaged by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), according to Taipa statistics.
Following the progression in the fourth-generation (4G) network deployments over the last couple of years, and the upcoming fifth-generation (5G) cellular technology, experts caution that low fiberization would eventually impact the service delivery, and a uniform policy across the country is much needed.
“In the last four years we have not had an increase in backhaul spectrum, hence, we are dealing with constrained factors and have to manage the quality of services based on existing capacity, for everybody’s good,” Kochhar said.
Coai said that the increased fiberization would meet the present requirement of bandwidth and future technologies such as 5G, and other emerging technologies,” Kochhar said and added that the early allocation of E and V bands to meet the backhaul requirements is also being considered by the government.
Dua further said that in order to address the increased data consumption in rural and urban areas and remote working following the Covid-19 outbreak, the role of fiberisation to propel digitalisation has increased multifold.
India, according to Crisil needs a tectonic shift in the fiberization landscape, and investment in fiberised backhaul infrastructure providing unlimited capacity and higher data speeds has to gain further traction if 5G has to become a reality.
Sandeep Aggarwal, co-chairman of the Telecom Equipment and Services Export Promotion Council (Tepc) believes that it is imperative to have a robust fibre infrastructure in the country to complement the next-generation or 4G and 5G technologies in line with the National Digital Communications Policy (NDCP) unveiled in 2018.
Former telecom secretary Shyamal Ghosh-headed Tepc represents Aksh Optifibre, Birla Cables, Paramount Wires & Cables, Himachal Futuristic Communications, Finolex Cables and Polycab Wires.
“With nearly 3 million kilometres of optic fibre cable (OFC) presently deployed, India will need to further enhance the footprint with an average of 2-kilometre of fibre per person,” Aggarwal said and added that more than 1 million kilometres of cable TV (CATV) fibre has been laid over the last one year in the country.
Private and public sector entities such as Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea, Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) and RailTel majorly contribute to the current fibre footprint in the country in addition to Centre’s ambitious BharatNet program that further aims to deploy nearly 8 lakh kilometres of fibre network separately.
There is a need to adopt new business models such as hiving off fibre assets via the Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) model that will help in reducing capital expense requirements and allowing telecom operators to focus on topline growth opportunities, according to Aggarwal.
Billionaire Mukesh Ambani-owned Reliance Jio and Sunil Mittal-driven Bharti Airtel have already sold-off their fiber verticals to become financially-nimble pure-play telecom services companies.
Taipa’s Dua feels that the upcoming cities would be built on the basis of readily available optical fiber cables, and next-generation telecom infrastructure and technologies like 5G.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
ICRA: Indian Telecom Industry Must Migrate from Copper to Dense Fiber Optic Networks
China says it has deployed 700,000 5G base stations this year; Huawei’s forecast
China has announced it has built nearly 700,000 5G base stations this year, exceeding its original target of 500,000, South China Morning Post reports. That’s more than twice the number of 5G base stations in the rest of the world combined, according to China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) vice-minister Liu Liehong.
The vice-minister said there are currently more than 180 million devices operating on China’s 5G network.
“The good infrastructure has spurred a range of new 5G-based applications,” Liu said in remarks reported by Chinese media Sina News. “For instance, the smart education sector has witnessed the emergence of new education models such as ultra-high-resolution, remote interactive teaching powered by 5G, immersive teaching with augmented and virtual reality technology and hologram classrooms during the Covid-19 pandemic.”
To achieve complete coverage, China will need 10 million 5G base stations in total, which involves an overall investment of CNY 2 trillion (approximately USD 280 billion) of investment, according to Zhang Yunyong, CPPCC member and president of the China Unicom Research Institute.
Chinese President Xi Jinping has singled out 5G networks and data centres as top priorities in the country’s plans to invest in “new infrastructure”. The next-generation network is considered a fundamental element of China’s new digital infrastructure, aimed at driving greater connectivity for consumers and businesses.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The latest analysts’ estimate from Jefferies, put the total number of 5G base stations across the country at 650,000. Their data projected China’s three major telecommunications network operators to have up to 750,000 5G base stations by the end of this year.
Analysts said that although the 5G base station roll out has been impressive, it was still only a fraction compared with China’s huge base of 1.2 billion 4G users, creating a situation where consumers have been reluctant to upgrade to more costly 5G plans because there are no killer apps and must-have consumer services.
South Korea, the first country in the world to provide 5G services, has 115,000 base stations in operation, according to government data in April. The South Korean government recently announced that the number of 5G service users across the country reached 8.65 million in August.
The global 5G network infrastructure market is expected to nearly double to USD 8.1 billion in 2020, according a report from Gartner.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Huawei Technologies expects 5G users to account for 20% of total mobile users in China and South Korea by the end of June 2021, Ryan Ding, president of Huawei’s carrier business group, said during a presentation at the company’s Global Mobile Broad Forum in Shanghai, China.
The executive said that 5G adoption was happening faster than some of the initial predictions in China, with operator China Mobile now having 130 million 5G subscribers, ahead of its target of 100 million for the year.
“5G is developing much faster than previous generations. Currently, there are more than 100 commercial 5G networks worldwide, and budget 5G mobile phones have dropped to CNY1,000 ($151). This is driving up the number of 5G users around the world, and leading carriers are already benefitting from 5G data plans. They are seeing an increase in the ARPU of 5G users through multi-metric service packages and upgraded services like 5G messaging and enriched calling,” Ding said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
5G users to account for 20% of China’s mobile base by June 2021: Huawei
Altiostar and NEC demonstrate front haul at India’s first O-RAN Alliance plugfest hosted by Bharti Airtel
Altiostar and NEC today said that they participated in the first plugfest event in the India region for the O-RAN ALLIANCE. Hosted by Bharti Airtel (“Airtel”), India’s largest integrated telecommunications services provider, the goal of the O-RAN Plugfest was to test and demonstrate the growing maturity of the O-RAN ecosystem.
Bharti Airtel plugfest was in partnership with telecom players like Altiostar, Altran, ASOCS, Mavenir, NEC, Sterlite Technologies (STL), VVDN, among others to demonstrate emerging technologies such as 5G.
“We are committed to evolving our network through an open architecture and are delighted to partner with the O-RAN community. This offers a great opportunity to Indian organizations with innovative hardware, software, and services capabilities to build a “’ Make in India – O-RAN solution’ – for Indian and global markets.” said Randeep Sekhon, CTO, Bharti Airtel.
The Indian telco is currently working with various US and Japanese vendors like Altiostar and NEC to develop OpenRAN based 5G telecom equipment, ETTelecom exclusively reported recently.
Airtel revealed that it is engaging with “Disruptive Telecom Equipment Vendors” to develop innovative solutions customized to Airtel’s requirements based on OpenRAN technology. “As a TSDSI Member, Airtel has proposed a new study Item on “Adoption of O-RAN Specification by TSDSI and contribution towards the development of India.
Specific use cases within the TSDSI Network Study Group (SG-N). Airtel will be submitting contributions in the form of a Study Report on O-RAN in SGN, and will also be collaborating with industry partners on the subject,” the telco had said.
“Testing and integration are crucial for developing a commercially available open RAN ecosystem and that’s why the O-RAN Alliance provides its member companies with an efficient global plugfest framework, which complements the O-RAN specification effort as well as the O-RAN Software Community,” said Andre Fuetsch, Chairman of the O-RAN Alliance and Chief Technology Officer of AT&T.
The telco has been a member of the O-RAN Alliance since its establishment in 2018. The first India edition of O-RAN Plugfest is part of Airtel’s commitment to building an open technology ecosystem, including O-RAN-based deployments, said the telco in an official statement.
It was also the first operator in India to commercially deploy a virtual RAN solution based on disaggregated and open architecture defined by the O-RAN Alliance.
Airtel, Altiostar and NEC teamed up for this project to demonstrate the world’s first interoperability testing and integration of massive MIMO radio units (O-RU) and virtualized distributed units (O-DU) running on commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) servers. The project featured a commercial end-to-end Open Fronthaul interface based on O-RAN specifications. This demonstration was comprised of control, user, synchronization and management plane protocols, including 3GPP RCT and performance cases.
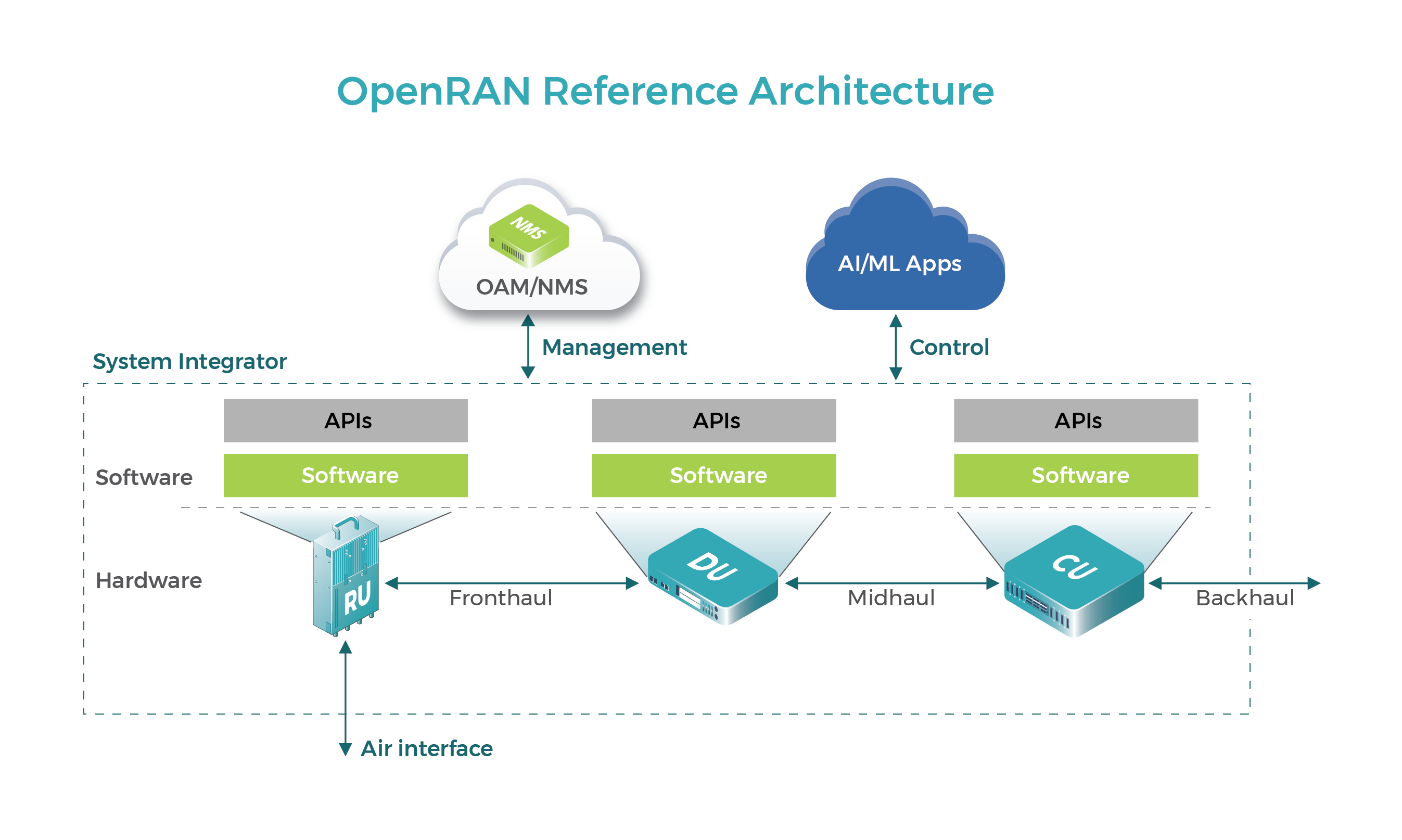
The purpose and scope of this demonstration was to show O-RAN option 7.2x split integration between a virtualized O-DU from Altiostar and an NR O-RU (i.e. 5G radio unit) from NEC. The demonstration also showed how this integrated setup can be used in an end-to-end EN-DC network setup (i.e. 5G non standalone architecture).
Going forward, Altiostar and NEC will continue to jointly drive new levels of openness in radio access networks (RAN) and across next-generation 5G networks.
“Today’s 4G and 5G radio access networks are undergoing a profound transformation, as the wireless industry is shifting to an open and cloud-native architecture that is being driven by vendors such as Altiostar and NEC, who are at the forefront of providing software and radio solutions based on O-RAN standards,” said Anil Sawkar, Vice President of Engineering and Operations at Altiostar. “Dozens of greenfield and brownfield wireless operators worldwide are trialling and deploying O-RAN networks as they realize the benefits of this new approach, including reduced costs, increased automation, and faster time to market with services.”
“Providing open innovations that conform to industry standards in the radio access network is critical to accelerating our customers’ journey towards Open RAN deployment and provisioning of more flexible and efficient networks that meet the requirements of cutting edge 5G use cases,” said Kazuhiko Harasaki, Deputy General Manager, Service Provider Solutions Division, NEC Corporation. “It is NEC’s honor to contribute to interoperability verification initiatives in India towards Open RAN innovation.”
Airtel has been a member of the O-RAN ALLIANCE since its inception in 2018. Airtel was the first operator in India to commercially deploy a virtual RAN solution based on a disaggregated and open architecture defined by O-RAN. “We are delighted to partner with the global O-RAN community. Our engagement with Altiostar and NEC for demonstrating O-RAN O-DU and O-RU, 5G RCT and E2E performance is another step forward towards building 5G systems with open network architecture,” said Randeep Sekhon, CTO at Bharti Airtel.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Altiostar:
Based outside Boston, Altiostar provides 4G and 5G open virtualized RAN (Open vRAN) software that supports open interfaces and virtualizes the baseband unit to build a disaggregated multi-vendor, web-scale, cloud-native mobile network. Operators can add intelligence, quickly adapt the network for different services and automate operations to rapidly scale the network and reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Altiostar collaborates with a growing ecosystem of partners to support a diverse Open RAN supply chain. The Altiostar Open vRAN solution based on O-RAN standards has been deployed globally, including the world’s first cloud-native commercial-scale mobile network with Rakuten Mobile in Japan. For more information, visit www.altiostar.com.
About NEC Corporation:
NEC Corporation has established itself as a leader in the integration of IT and network technologies while promoting the brand statement of “Orchestrating a brighter world.” NEC enables businesses and communities to adapt to rapid changes taking place in both society and the market as it provides for the social values of safety, security, fairness and efficiency to promote a more sustainable world where everyone has the chance to reach their full potential. For more information, visit NEC at http://www.nec.com.
About Airtel:
Headquartered in India, Airtel is a global telecommunications company with operations in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa. The company ranks amongst the top three mobile operators globally and its mobile network covers a population of over two billion people. Airtel is India’s largest integrated telecom provider and the second largest mobile operator in Africa. At the end of September 2020, Airtel had approx. 440 mn customers across its operations.
Airtel’s portfolio includes high speed 4G/4.5G mobile broadband, Airtel Xstream Fiber that promises speeds up to 1Gbps, converged digital TV solutions through the Airtel Xstream 4K Hybrid Box, digital payments through Airtel Payments Bank as well as an integrated suite of services across connectivity, collaboration, cloud and security that serves over one million businesses.
Airtel’s OTT services include Airtel Thanks app for self-care, Airtel Xstream app for video, Wynk Music for entertainment and Airtel BlueJeans for video conferencing. In addition, Airtel has forged strategic partnerships with hundreds of companies across the world to enable the Airtel platform to deliver an array of consumer and enterprise services.
References:
GSA forms new 4G and 5G Fixed Wireless Access Forum; FWA Market Review & Analysis
The Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) today announced the establishment of the GSA 4G-5G Fixed Wireless Access Forum to bring together leading chipset, module, and terminal vendors – as well as other telecommunications industry representatives, who wish to promote 4G and 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) technology, products and services – to report on progress of FWA deployments, identify use cases and encourage global adoption.
The GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum will build on the work done by the recently formed GSA Fixed Wireless Access Working Group to coordinate industry initiatives to deliver fixed wireless broadband services based on LTE and 5G access networks. The founding members of the FWA Working Group are Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, Samsung and ZTE. Membership to GSA Working Groups is open to all GSA Executive and Ordinary Members.
Underpinning the work of the new GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum is GSA’s research and role as the voice of the mobile ecosystem. GSA publishes regular industry reports and market data determine the extent and nature of fixed wireless access broadband service availability based on LTE or 5G around the world. As part of its industry advocacy,
GSA’s research team will share its latest global fixed wireless access update in its next GSA Snapshot Webinar on 24 November (16:00 GMT). Details on how to register for and attend the free webinar are available here https://gsacom.com/webinar-fixed-wireless-access/

Joe Barrett, President, Global mobile Suppliers Association, commented: “In a relatively short space of time, fixed wireless broadband access has become a mainstream service. Today we see hundreds of operators selling LTE-based fixed wireless access services around the world, and dozens more already live with 5G FWA services for home or business broadband. In addition, fixed wireless access device vendors have grown to over 100 globally and against this backdrop of real and significant market demand, the onus is on the FWA community to work together to drive business success.

“GSA has an unrivalled track record and experience in bringing together vendors, regulators and operators from across the 4G and 5G ecosystems and the formation of the new GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum will bring this experience to Fixed Wireless Access to help accelerate its development globally,” Barrett continued.
The scope of the new GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum includes:
· Sharing trends in the industry, identifying directions in technical development, accumulating and promoting successful experiences
· Improving the 4G and 5G FWA technologies required to provide wireless broadband connection solutions with increased performance and cost-effectiveness
· Fostering collaboration among FWA suppliers to improve the industry’s ecosystem and ensure business success
· Promoting the success of the FWA industry to accelerate the provisioning of broadband access to anyone, anywhere
The new GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum and Fixed Wireless Access Working Group is a key pillar of GSA’s growing industry advocacy; this work also includes the GSA Spectrum Group, the largest single spectrum advocacy team in the mobile industry representing the vendor ecosystem in 4G and 5G spectrum discussions with governments, regulators and other policy makers.
Membership and participation in the GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum is open to chipset, module, and terminal vendors, together with industry representatives from across the telecommunications ecosystem who wish to promote Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) technology, products and services.
For more information or a GSA 4G-5G FWA Forum Application Forum, please email [email protected].
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About GSA:
GSA is the voice of the global mobile ecosystem representing companies engaged in the supply of infrastructure, semiconductors, test equipment, devices, applications and mobile support services. The organization plays a central role in promoting 3GPP technology, advocating spectrum policies and stimulating IMT industry development. The association is a single source of information for industry reports and market intelligence
The GSA GAMBoD database is a unique search and analysis tool that has been developed to enable searches of LTE and 5G devices and new global data on Mobile Broadband Networks, Technologies and Spectrum (NTS). Results are presented as a list or in charts. Charts may be inserted into documents or presentations, subject to accreditation of GSA as the source.
GAMBoD is a resource dedicated to promoting the success and growth of the Mobile Broadband (MBB) industry and ecosystem and is fully available to all employees of GSA Executive and Ordinary Member companies and GSA Associates who subscribe to the service.
- More information on GAMBoD is available at: https://gsacom.com/gambod/
- Press Release for New GSA FWA Forum: https://gsacom.com/press-release/new-gsa-fwa-forum/
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
STL Partners — FWA Market Review and Analysis:
Today, fixed-wireless access (FWA) is used for perhaps 8-9% of broadband connections globally, although this varies significantly by definition, country and region. There are various use cases (see below), but generally FWA is deployed in areas without good fixed broadband options, or by mobile-only operators trying to add an additional fixed revenue stream, where they have spare capacity.
FWA via 4G -LTE using licensed spectrum has already experienced rapid growth of in numerous markets, such as South Africa, Japan, Sri Lanka, Italy, and the Philippines. This past week, T-Mobile announced an expansion of their 4G FWA called Home Internet service.
This growth has been driven by the combined impact of mobile network operators (MNOs) commercialising FWA services to households in underserved urban areas, the slow pace of fibre roll-out in some countries, government subsidies for rural broadband, and improvements in network planning tools and customer premise equipment with easier self-install options.According to STL Partners’ latest research and market forecasts, 5G is likely to have a major impact for operators in the coming years, especially from 2022 onwards as more spectrum becomes available to more operators, and equipment prices fall.
Nonetheless, 4G – LTE will continue to be more important than 5G in the FWA market overall at a global level over the next 5 years; the technology is much further down the cost- and experience curve, as well as using existing network infrastructure and spectrum.
Historically, most FWA has required an external antenna and professional installation on each individual house, although it also gets deployed for multi-dwelling units (MDUs, i.e. apartment blocks) as well as some non-residential premises like shops and schools. More recently, self-installed indoor CPE with varying levels of price and sophistication has helped broaden the market, enabling customers to get terminals at retail stores or delivered direct to their home for immediate use.
Looking forward, the arrival of 5G mass-market equipment and larger swathes of mmWave and new mid-band spectrum – both licensed and unlicensed – is changing the landscape again, with the potential for fibre-rivalling speeds, sometimes at gigabit-grade.
STL believes that the biggest changes and opportunities catalysed by 5G FWA will be:
• Alternative source of gigabit broadband in urban areas without fibre, or with poor competition and pricing.
• Mobile-only operators will target attractive demographic or sub-regional niches that fit with their existing and planned 5G footprint.
• Fixed and fixed-mobile converged broadband providers will use 5G FWA as a backup or enhancement for fixed-line services.
• The growing democratisation of 5G, with better support of unlicensed spectrum, plus cloud-delivered core networks and edge offload, will broaden its range beyond traditional MNOs to some wireless internet service providers (WISPs), cable operators, and others.
• Local licensing and new tranches of unlicensed spectrum will create options for municipalities, education agencies, and other public-sector bodies to offer 5G FWA for home-schooling, telemedicine, and other applications.
• In the longer term (2023 onwards) improved mmWave technology, including repeaters and other forms of signal-booster, could expand the addressable market for gigabit FWA.
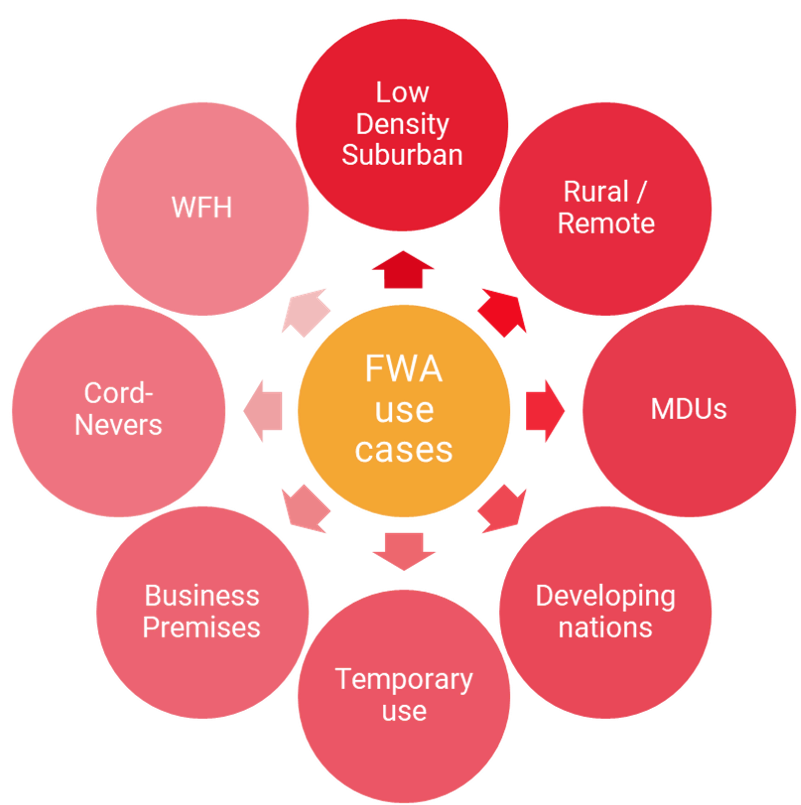
FWA Use Cases…. Source STL Partners
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
T‑Mobile expands Home Internet to over 130 additional cities
Huawei and Cambridge Wireless plan private 5G testbed in Cambridge, UK
Huawei and Cambridge Wireless have partnered to deploy and build a private 5G testbed at the Cambridge Science Park. This marks the start of a 3-year partnership which will include digital training, joint events and business support.
This will be the UK city’s first 5G mobile private network, and will support companies with the R&D and application of new digital technologies in areas such as remote surgery, autonomous vehicles and clean energy. The 5G testbed will go live in January 2021. Owned by Cambridge University, the Cambridge Science Park currently has over 120 technology companies and scale-ups.
“We are constantly working to provide value to CW members,” said Simon Mead, CEO of Cambridge Wireless. “As home to one of the world’s most advanced R&D ecosystems, Cambridge is perfectly positioned for the rollout of next-generation wireless technology and we’re delighted to be driving this initiative with our partners.
“We hope to bring something unique to the Science Park to accelerate use cases and development of this technology. We invite ambitious businesses to get involved, and through this exciting 3-year partnership with Huawei, we will support their 5G innovation journey.”
Victor Zhang, vice-president at Huawei, commented: “Huawei’s success is built on a relentless drive for innovation and we are able to keep pushing the boundaries of technology when we partner with those who share this ambition.
“The Cambridge eco-system is recognised as a global leader in technology, and we are excited to work with the talent and vision in this eco-system. We hope to enable Cambridge Wireless members to reach new heights by allowing them access to our state-of-the-art equipment and markets, including China and beyond.
“Our commitment to the UK and industry remains as strong as ever and we will continue to offer our expertise and technology to our partners to promote connections and innovation.”

To find out more and how to get involved, please contact:
Abhi Naha CCO CW (Cambridge Wireless)
Tel: +44(0)1223 967 101 | Mob: +44(0)773 886 2501
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About CW (Cambridge Wireless)
CW is the leading international community for companies involved in the research, development and application of wireless and mobile, internet, semiconductor, hardware and software technologies.
With an active community of over 1000 technology companies ranging from major network operators and device manufacturers to innovative start-ups and universities, CW stimulates debate and collaboration, harnesses and shares knowledge, and helps to build connections between academia and industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Huawei
Founded in 1987, Huawei is a leading global provider of information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure and smart devices. We are committed to bringing digital to every person, home and organization for a fully connected, intelligent world. Huawei’s end-to-end portfolio of products, solutions and services are both competitive and secure. Through open collaboration with ecosystem partners, we create lasting value for our customers, working to empower people, enrich home life, and inspire innovation in organizations of all shapes and sizes. At Huawei, innovation puts the customer first. We invest heavily in fundamental research, concentrating on technological breakthroughs that drive the world forward. We have nearly 194,000 employees, and we operate in more than 170 countries and regions, serving more than three billion people around the world. Founded in 1987, Huawei is a private company fully owned by its employees.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.huawei.com/uk/news/uk/2020/cambridge%20wireless%20partnership
WSJ: Samsung (not Ericsson or Nokia) best alternative to Huawei for 5G network equipment
By Elizabeth Koh
The Trump administration’s campaign pressuring allies to avoid 5G equipment made by Huawei Technologies Co. always had a hometown hitch: The U.S. doesn’t have a domestic manufacturer to rival the Chinese company. The best alternative may be South Korea’s Samsung Electronics
Samsung makes all of its network gear domestically and in India. That distinguishes it from its European rivals, Ericsson AB and Nokia Corp. , which both have significant manufacturing operations in China. Beijing has weighed retaliating against Nokia and Ericsson for any action by European Union members against Huawei by barring them from sending their Chinese-made products abroad, according to people familiar with the matter. Were that to happen, it could slow deliveries by the European companies in an already-competitive 5G rollout. The Chinese Foreign Ministry has denied considering that option.
Samsung already has some unique ties with the U.S. beyond the home appliances filling American homes. The company long ago won Pentagon clearance for government use of Samsung devices equipped with its Knox security software, which allows users to safeguard sensitive data on their phones and for years was overseen by a former Pentagon chief information officer. Devices with Knox software are used by military personnel in the U.S., U.K. and Canada.
The South Korean firm two years ago opened a new, seven-story office in Washington just a mile from Capitol Hill. Along with Nokia and Ericsson, Samsung drew an invitation for a planned White House strategy meeting on 5G in April that has been delayed indefinitely.
Samsung is far better known as the world’s largest producer of smartphones and televisions. But the firm is making a big push to turn its sleepy networks business into a 5G winner. Its differentiator is its product range, covering all aspects of 5G, from smartphones to base stations to the underlying chips that make network connections possible.
Samsung is one of four major 5G players. Huawei controls about a third of the 5G network market, trailed by Ericsson with a fourth and Nokia with about a fifth, according to market tracker Dell’Oro. Samsung has roughly 13%.
After flirting for years with major U.S. telecom carriers with limited success, Samsung is pushing hard—and succeeding—in its efforts to get a second look with Huawei off the table.
In September, Samsung announced it had signed a $6.65 billion deal with the largest U.S. wireless carrier, Verizon Communications Inc., the Korean company’s biggest such contract to date. Samsung, which is a secondary equipment vendor to AT&T Inc. and T-Mobile US Inc., is also still pursuing bigger deals with those carriers. Carriers often use multiple vendors for network infrastructure so they don’t rely on a single source of equipment.

Samsung’s 5G momentum is building just as the U.S. rollout is expected to hit another gear following Apple’s recent introduction of its first 5G phones.
PHOTO: GEORGE FREY/REUTERS
But Samsung is still, in part, relying on Ericsson and Nokia tripping up to bolster its case, says Ryan Koontz, a senior research analyst for Rosenblatt Securities, a New York-based brokerage firm.
Nokia, for example, was Verizon’s primary equipment vendor before the Samsung deal, Mr. Koontz says. But several problems—including a recent stumble with a key computer chip for 5G deployment—likely hurt Nokia’s relationship with the carrier for years, he says. Neither Nokia nor Verizon commented for this article. Ericsson, meanwhile, is just emerging from a costly yearslong restructuring, though it has recently returned to profitability.
“Samsung’s timing is perfect,” Mr. Koontz says. “The 5G programs are set up for a banner year.” Samsung’s 5G momentum is building just as the U.S. rollout is expected to hit another gear following Apple Inc.’s recent introduction of its first-ever lineup of 5G iPhones. The new iPhones are expected to boost sales of 5G-capable handsets to 20% of all U.S. phone sales in 2020, according to market tracker Counterpoint Research. That would mean substantially more subscribers to motivate the nation’s three main carriers to speed the expansion of their 5G networks. All three have some 5G coverage now, though some of the fastest service remains limited to certain cities.
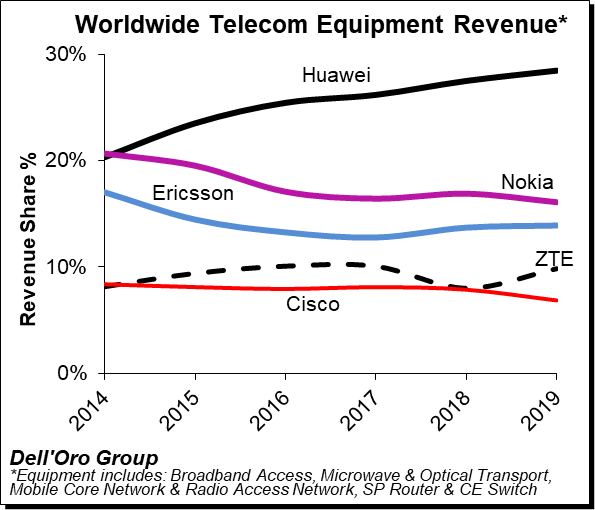
Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, and Cisco comprised 28% (28%), 16% (17%), 14% (14%), 10% (8%), 7% (8%), respectively.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Samsung ships one out of every five smartphones shipped globally. The company has sought to leverage its wide base of users as an asset for its network business, touting its experience building 5G phones and its devices’ ability to interact smoothly with its end-to-end network offerings. Controlling the network infrastructure throughout, Samsung says, ensures faster speeds.
Samsung’s push to broaden its network business is unprecedented for the industry, because it has such a small presence for existing 4G LTE and 3G networks globally, industry analysts say. Network gear traditionally builds on the equipment laid down for previous wireless standards, meaning bigger players in the network industry have enjoyed a solid starting advantage.
Even with Huawei forcibly stripped out of the network market, operators must weigh the significant cost and effort that would be required to tear out their existing equipment for another company’s new network. In the U.K., backing away from Huawei could delay its 5G rollout for years, and operators could pay billions to replace their hardware, the British minister in charge of digital issues, Oliver Dowden, has said.
Should Samsung succeed in making its case in the U.S., the payoff in the form of a substantial revenue increase likely wouldn’t emerge until late next year, analysts say. But Samsung is unlikely to see another upstart challenger making a similar case while the U.S. lags behind in making network equipment at home.
“There’s not a lot of choices for some networking equipment,” says Stan Adams, deputy general counsel at the Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit Center for Democracy and Technology. “If there are concerns about security and foreign-made networking equipment, that’s going to be a problem until we change our manufacturing base.”
Ms. Koh is a Wall Street Journal reporter based in Seoul. She can be reached at [email protected].
Deutsche Telekom in joint venture with SK Telecom for 5G in-building experiences
“The partnership between SKT and Deutsche Telekom is very meaningful at a time when the world is heavily affected by the Covid-19 pandemic,” said Park Jung-ho, CEO of SK Telecom. “The deepened bond between the two companies will play an important role as a bridge between Asia and Europe and lead us to new technologies that can bring greater value to humanity.”

Tim Höttges, CEO Deutsche Telekom, Park Jung-ho, CEO SK Telecom and their teams at a joint video conference.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom have been working closely since 2016 to lead innovations in ICT, seeing the sharing of fixed and wireless technologies. In May 2020, the two firms announced a collaboration to expand the global 5G ecosystem by accelerating 5G deployment in Europe. As part of this, they constructed a Network Engineer Exchange Programme that will see them exchange their respective technological expertise once the situation with Covid-19 improves.
T‑Mobile expands Home Internet to over 130 additional cities
T-Mobile US will increase its Home Internet service to more than 130 additional cities and towns across Michigan, Minnesota, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, West Virginia and Wisconsin. The move comes after it massively expanded its home broadband pilot to more than 20 million households in October.
The $50/month Home Internet pilot service will be deployed in underserved rural markets — through LTE-based coverage, with 5G service coming soon. The company says that only 63 percent of adults in rural America currently have access to high-speed internet.
“Home broadband has been broken for far too long, especially for those in rural areas, and it’s time that cable and telco ISPs have some competition,” said Dow Draper, T-Mobile EVP, Emerging Products. “We’ve already brought T-Mobile Home Internet access to millions of customers who have been underserved by the competition. But we’re just getting started. As we’ve seen in our first few months together with Sprint, our combined network will continue to unlock benefits for our customers, laying the groundwork to bring 5G to Home Internet soon.”
T-Mobile Home Internet is just $50/month all-in and features many of the same benefits that have made T-Mobile the fastest growing wireless provider for the past seven years:
- Self-installation. That means there’s no need for installers to come to your home.
- Taxes and fees included.
- No annual service contracts.
- No maddening “introductory” price offers. What you pay at sign-up is what you’ll pay as long as you have service.
- No hardware rental, sign-up fee or installation costs (because set-up is so easy!).
- No data caps.
- Customer support from the team that consistently ranks #1 in customer service satisfaction year after year.

Now that customers have had access to T-Mobile Home Internet since 2019, the reviews are in … and the feedback speaks for itself. Customers give T-Mobile Home Internet an average Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 42, compared to -75 (that’s a negative 75!) for their previous provider. Seventy-three percent report saving money with T-Mobile Home Internet, with 50% saving more than $30 per month (that’s $360 annually!).
The Home Internet pilot provides home broadband on the Un-carrier’s LTE network. With additional capacity unlocked by the merger with Sprint, T-Mobile is preparing to launch 5G Home Internet commercially nationwide, covering more than 50% of U.S. households within six years and providing a badly needed alternative to incumbent cable and telco ISPs.
Home broadband is one of the most uncompetitive and hated industries in America. Rural areas in particular lack options: more than three-quarters have no high-speed broadband service or only one option available. And when there’s no choice, customers suffer. It’s no wonder internet service providers have the second lowest customer satisfaction ratings out of 46 industries, beating cable and satellite TV companies by just one point according to the ACSI (American Customer Satisfaction Index)!
T-Mobile Home Internet service is available on a first-come, first-served basis, where coverage is eligible, based on equipment inventory and local network capacity, which is expanding all the time. For more information on T-Mobile Home Internet or to check availability for your home in these areas, visit t-mobile.com/isp.
Reference:




