FTTP
AT&T CEO John Stankey: 30M or more locations could be passed by AT&T fiber
AT&T CEO John Stankey was interviewed by Brett Feldman, Goldman’s U.S. telecom and cable analyst. AT&T is both a telecom and media company. We focus on the former for the IEEE Techblog. Here are selected telecom related comments Stankey made (BOLD font emphasis added):
We’re pulling (market) share back from our two largest competitors (Verizon and T-Mobile). I feel good about how we’re doing that. There’s more to be done as we invest in fiber, and we can compliment our wireless business with fiber. There’s opportunities for us to take communications further than what we’ve traditionally done at AT&T. And I think that business should be recognized for being a leading global communications business, like it is, very uniquely positioned with more fiber than any other communications company on the face of the planet, with a great wireless asset domestically in the U.S. and in Mexico, an opportunity to bring those things together, and run it incredibly effectively as a focused business. I think we’ve got a great story there.
I think AT&T is in a great position moving forward. I think the industry frankly is in a great position. I think there’s tremendous promise right now in what ubiquitous high capacity bandwidth with the kind of capabilities that 5G brings in terms of the density that it can afford, the number of devices, the ability to use technology to do things like network slice (requires 5G SA core network which Microsoft is building for AT&T) and begin to differentiate the network. I think this is going to be great for society. I think this is going to be great for the U.S. economy as a whole. If I had to bet, we don’t have the numbers for 2021, certainly can’t project 2022, but I have a sense of where this industry is going. (This author totally disagrees, largely because real, standards based 5G has yet to be deployed as there is only a standard for the RAN which doesn’t meet URLLC performance requirements. No standard for 5G SA core network.).
We’re probably going to see record infrastructure investment coming out of this industry in this period of time. And I think it’s going to equip the United States and our economy and our infrastructure in a way that we’ve never seen. I think that’s going to be incredibly powerful. And I think it’s not only going to be good for AT&T, because I think we have the right kind of wherewithal and the right kind of capability to be right alongside others that are investing at a high clip to bring that infrastructure forward. I think we’ll do just fine with where we are there. I believe when unleashed we have some of the best network minds in the country. I believe that dense fiber footprint that we have that’s denser than anybody else in the United States when engineered properly on top of a great spectrum assets and a great wireless business, it’s going to make our combined product offer and our business even better and more capable to deal with what customers need to do. So, I feel really comfortable about that. And I can do nothing more than not ask you to look at my prognostications, but look at how we’re performing in the market today.
We’ve now started doing some things quietly behind the scenes. We have another muscle to build here, which is how do we begin to work on software to differentiate our products and services in a way that makes our product better than what our competitors can do, because we do have a different asset base, and we are able to serve every corner of the market from the largest of enterprises to the smallest apartment somewhere in the United States. And I don’t think we’ve done as much as we can do in that vein, to actually make that real for our customers and the right products and the right services and the right offers. And so, rebuilding that product engine that we can do that and begin to differentiate allows us to do things that won’t necessarily just hinge on, can I get an attractive handset?
Brett Feldman: I believe your fiber network passes something around 15 million customer locations right now, you’re targeting to ultimately get to 30 million by 2025, that would still only be about half roughly half of the customer locations in the AT&T wireline footprint. Question we’ve gotten is how did you decide what the right target was? Why is it 30? And what really dictates the pace at which you build out fiber?
Stankey replied: Getting this kind of an engine (fiber optic build-out) ramped up to go from building 3 million to 4 million to 5 million homes (locations) past, working through the supply chain, all the logistics that are necessary to build network, it’s not a real simple undertaking. And as I’ve said, my goal is I feel very comfortable, we have places we can go to build 30 million homes (he really means residential and business locations combined) right now on an owned and operated basis, that have very attractive returns in the mid to upper teens. We’re demonstrating every day with our existing base, that we can operate that more effectively, we’ve now crossed over places where we have scale where we’re taking cost out of the business based on fiber replacement, the old infrastructure, we’re seeing that flow through in lower call rates, lower repair rates, better churn, all those things are going to continue to give us goodness moving forward.

Do I think there’s a magic number of 30? No, I don’t. I think there’s a combination of things. One is unlike the investment base, to recognize the good work we’ve been doing. And then in fact, we are building and adding value back to our shareholders. And when they start to recognize that in the form of the equity in the stock, do I believe my credibility and the team’s credibility goes up? Yes, do I believe there’s going to be other opportunities for us to come out, as we hit those scaling metrics that we have in place, the supply chain metrics that we might be able to go in and say, there’s more that we could possibly attack, I’d love to be in that position to do that. And I’ve kind of put that out as a challenge to the management team to say the only thing that stands in the way between you doing 30 million and doing more is your execution and performance.
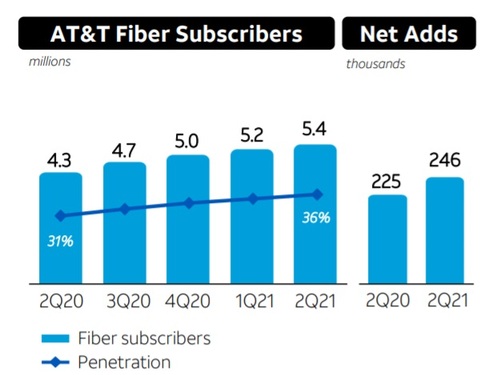
Brett Feldman: Speaking of execution, execution really has two pieces. It’s deploying the network, and then it’s driving penetration of that network. I believe you had about 5.4 million fiber subscribers as of your most recent quarters, that’s about 35% penetration [1.]. What do you think is the right target for your fiber penetration and how are you going to get there?
Note 1. Fiber-based broadband has clearly established itself as a growth engine for AT&T, which added another 246,000 fiber subscribers in Q2 2021, ending the period with 5.43 million. With about 80% of new fiber subscriber additions new to AT&T, overall broadband revenue growth at the company has finally surpassed declines in its legacy, non-fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) broadband business.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Stankey replied: If I look what’s happening right now, and kind of where we are in our maturity scale, one of the things I’m most excited about is our new net adds to fiber right now good, almost 80% of them are new to AT&T. So, we’ve now gotten to this place where we’ve been managing the base. And we’re now shifting over where got a lot of new customers coming in. And in fact, as you saw last quarter, we’re starting to get ourselves to a point where that consumer business is a growth business today, despite the legacy drag on historic telecom products, parts and the like of legacy data products, that the fiber growth is beginning to outstrip that where we have real growth in that business. And we’re now starting to turn that corner real EBITDA growth in that business. And so, I would tell you as I step back from that, we’re going to see consistent growth. But I’m not going to be happy until we have a 50:50 share split in places where there’s two capable broadband providers. And I think there’s no reason with the product is capable as what we have out there and how fiber performs and what we’re able to do and the differentials we see in our customer satisfaction to our most significant competitor often cable in those markets, we were looking at 10, 15 points of difference in satisfaction levels, between other players in the market and ourselves, that we shouldn’t be able to achieve that over time.
Brett Feldman: You had earlier made a slight adjustment to your fiber deployment for this year, you were hoping to do 3 million homes, it’s going to be closer to two and half million and you noted some of the well reported supply chain issues as being a factor. Any update there, is there any further disruption in your supply chains and your ability to secure labor?
Stankey replied:
And we’re talking about what’s probably effectively about a 90 day delay for us to hit those numbers, and really primarily in this case, got to fiber assemblies. The way fibers built in the distribution network is we engineer it, we provide detailed engineering to our manufacturer, the manufacturer in the manufacturing facility, pre-splices and pre-assembles some of that fiber before we receive it. So, when it goes in, we’re doing less field splicing. And we’re able to basically put it up in the air or bring it through infrastructure in a way that lowers labor costs coming in. And we’re having some supply issues in the factory partly labor driven because of COVID, individuals getting sick not being able to run enough shifts, and carry through and partly some raw material issues. But those have been worked through right now our deliveries over the last 30 days have tracked to what our expectations are.
So, we feel like we’re through that dynamic right now. We should be fine with it. But look the supply chain is fragile at all levels. It’s fragile on everything. Last week, it was the number of generators, we’re deploying for power backup on cell sites, there’s, we’re going to miss a target on some of those by a couple 100 because there’s a resin base connector in the harness and we can’t get the resin. And that resin base connector, it’s a $15,000 generator that’s been held up on something that’s $0.25 part, you see these things popping up, left and right, every corner of the business. So, I don’t know what next week brings, we’re aggressively managing it. We’ve got a great supply chain organization. We’re a scaled provider, with all of our vendors. So, we lean into that, we were able to work through the fiber dynamics because we are the largest consumer of fiber in the United States. We use that ability and that expertise to make sure we get what we need to move through. So, I feel we’re managing through it, okay. I don’t think there’s anything around the challenges we’re dealing with, it gives me concern on guidance where we stand right now, but it’s going to be choppy and a little bumpy moving forward on some of these things as we move through the years.
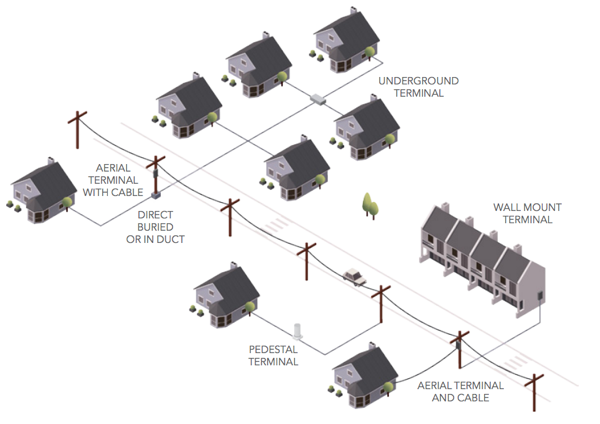
Typical fiber optic deployment to multiple homes via underground and aerial cable
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Stankey wouldn’t say how the proposed U.S. infrastructure bill might also alter AT&T’s outlook in a way that encourages the company to explore a buildout that goes beyond 30 million locations.
“There’s a degree of uncertainty there,” he said of the bill. “But in its current form [and if] it does actually make its way into law, that’s going to change the landscape of the broadband business in this country … It will also change my posture and point of view on where we should be playing as a company.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/08/12/atts-fiber-buildout-reduced-due-to-supply-constraints/
AT&T’s fiber buildout reduced due to supply constraints
AT&T has experienced recent disruptions in the supply of fiber optic cable, which has caused the company to trim back its planned fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) buildout for 2021, according to senior EVP and CFO Pascal Desroches.
AT&T had previously said it would build out its fiber network to an additional 3 million homes passed this year. But that’s now been reduced by 1/2 million.
“Since the start of the third quarter, we are seeing dislocation across the board, including in fiber supply. We’re probably going to come in a little bit light of 3 million homes passed, probably around 2.5 million,” Desroches said Tuesday at the Oppenheimer Technology, Internet & Communications Conference, according to this transcript.

An AT&T technician working on a fiber project
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Specifically, this is what Pascal said:
But since the start of the third quarter, we are seeing dislocation across the board, including in fiber supply. And as a result of those dislocations, we had previously provided guidance of 3 million homes past this year (unedited- very bad grammar). We’re probably going to come in a little bit in light of that, probably around 2.5 million. We don’t think it’s going to impact us long term. But I think it’s really important context because if we’re feeling the pain of this, I can only imagine what others in the industry are experiencing.
John Stankey (AT&T CEO) has always been a believer in fiber. I think when he took over he identified that as a priority area because he understood from a technology standpoint, there is no better technology for connectivity. And therefore, in a world where the demands for symmetrical speed are increasing significantly, this is the technology to bet heavily on. And so we have a great position, and we are leaning into adding to that position. So it’s really a function of when you — and I think others are now recognizing it as a result of what you’ve seen in the last year in the pandemic, the need to do what we’re doing now, 2-way communication can only happen with symmetrical speed. So I think everyone has had an aha moment, like we need to deploy fiber. And so we’ve long believed that. John has long believed that, and this is just really leading into that opportunity.
As we deploy fiber, our goal is to get at least 40% penetration on homes passed. And we think in certain markets, we’ll have an opportunity to do better than that. And the other thing that is great about is when you lay fiber, you lay fiber to a community where there is both homes and businesses. So it also helps boost returns in your enterprise business. And so that’s why it is so critical that we roll this out because the ability to grow both your enterprise and your consumer business is attractive. And we think these investments will provide us with mid-teen returns over time.
I know we’re largest fiber purchaser in the country. And we have prices that are at the best and most competitive among the industry. So we feel really good about the ability to secure inventory, fiber inventory and at attractive price points and the ability to execute and the build-out at scale, something that many others don’t have.
Oppenheimer moderator question: “Can you talk a little bit about where your supply comes from, I guess, both the fiber and the optical components or any other key suppliers? Is that U.S. sourced? Or is it a lot of it outsourced internationally?”
Pascal’s answer: “It is a U.S. company which has locations both domestically and outside the U.S.” [We suspect that it’s Corning].
AT&T typically has had no problem getting fiber at a low cost, Desroches said. “We’re the largest fiber purchaser in the country and we have prices that are the best and most competitive in the industry,” he said. “We feel really good about the ability to secure fiber inventory at attractive price points and the ability to execute the buildout at scale, something that many others don’t have.”
AT&T expects to catch up to its original fiber-construction estimates in the years after 2021, largely because of what Desroches called its “preferred place in the supply chain” and “committed pricing.” As AT&T said in a news release yesterday, AT&T is “working closely with the broader fiber ecosystem to address this near-term dislocation” and “is confident it will achieve the company’s target of 30 million customer locations passed by the end of 2025.”
AT&T added another 246,000 fiber broadband subs in Q2 2021, extending its total to 5.43 million, and said last month it was on pace to add about 1 million net fiber subscribers for all of 2021.
AT&T has estimated that nearly 80% of new fiber subscribers are also new AT&T customers, reversing a previous trend that saw a sizable portion of its FTTP customer net adds coming from upgrades of existing AT&T high-speed Internet customers on older VDSL and DSL platforms (which have been largely discontinued).
Speaking on AT&T’s 2Q-2021 earnings call last month, Desroches stated that the company’s consumer wireline business had reached a “major inflection point” as broadband revenues continue to surpass legacy declines. Meanwhile, AT&T’s broadband average revenue per user (ARPU) reached $54.76 in Q2 2021, improving from $51.61 in the year-ago period.
References:
Will AT&T’s huge fiber build-out win broadband market share from cablecos/MSOs?
Telefonica España to activate XGS-PON network in 2022; DELTA Fiber to follow in Netherlands
Telefonica España will begin the commercial deployment of a 10 Gbps fiber broadband network using XGS-PON technology in Spain in the first half of 2022, reports website bandaancha.eu.
The gradual rollout is part of Telefonica’s ‘Banda Ancha Abierta‘ (Open Broadband) project to install an efficient, open, scalable and virtualized network model that will facilitate fixed-mobile convergence (fixed access with mobile backhaul), Multi-access Edge Computing capabilities ( MEC), and the deployment of third-party applications.
Telefónica’s FTTH network in Spain passes 26.1 million homes as of June 2021, for which 4,726,700 clients are served through the Movistar and O2 brands. In addition, there are 2,801,700 clients of other operators served through indirect fiber optics.

The introduction of XGS-PON will introduce two new lambdas or wavelengths on the existing GPON fiber infrastructure. The same fiber cable will carry wavelengths corresponding to GPON and in parallel new colors of the laser for XGS-PON so that the two technologies do not interfere with each other.
XGS-PON raises the available throughput for an entire fiber branch to 10 Gbps downstream and 10 Gbps upstream for up to 64 client endpoints. That will permit Telefonica to commercialize speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps symmetric and, in the medium term, up to 10 Gbps.
XGS-PON requires new customer premises equipment. Telefónica customers have been waiting for years for the new XHGU router that the operator announced in 2018 and that is compatible with XG-PON, in addition to bringing high-penetration WiFi 6.
With the arrival of XGS-PON, Movistar will begin to distribute this new router or temporarily provide an ONT XGS-PON.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
In a related story, DELTA Fiber has attracted 2 billion euros to back a planned roll-out of XGS-PON technology throughout the Netherlands. The 10G PON deployment will expand DELTA Fiber’s network to 2 million fiber connections in 2025. It currently expects to reach 1 million connections by the end of this year.
The company expects to begin rolling out XGS-PON this September. It will use the technology exclusively in its future builds with an eye toward making gigabit broadband widely available.
DELTA Fiber also said it plans to deploy 25G PON in the future. Along these lines, the company recently announced a partnership with Proximus of Belgium to deploy fiber to the home networks in Flanders. Proximus has already adopted 25G PON technology.
References:
https://bandaancha.eu/articulos/movistar-actualizara-velocidad-red-fibra-9973
FTTH Council Europe: FTTH/B reaches nearly 183 million (>50% of all homes)
Europe has passed over half of homes able to receive fiber broadband. According to the latest figures compiled by Idate for the FTTH Council Europe, 52.5% of homes will be covered by FTTH/B at the end of September 2020. That’s up from 49.9% a year earlier.
FTTH Council Europe revealed the following:
• Number of homes passed by fiber (FTTH/B) reaches nearly 183 million homes in EU39.
• Europe’s fiber footprint (number of homes passed) expanded the most in the past year in France (+4.6M homes passed), Italy (+2.8M), Germany (+2.7M) and the UK (+1.7M).
• Three countries are accounting for almost 60% of homes left to be passed with fiber in the EU27+UK region.
• FTTH/B Coverage in Europe surpasses more than half of total homes.
• 16.6% growth in the number of fiber subscribers.
• Iceland leads the European FTTH/B league table second year in a row. 70.7% of its households having fiber connections. Belarus (70.4%) and Spain (62.6%) came in second and third.
• Belgium, Israel, Malta and Cyprus enter the FTTH/B ranking for the first time.
The above figures cover 39 countries across Europe, where nearly 183 million homes have fibre access. For the EU and UK alone, penetration reached 43.8 percent in September, up from 39.4 percent a year earlier.
The report also shows fiber take-up is accelerating, with a subscriber penetration of 44.9 percent of lines in the 39 countries, compared to 43 percent in September 2019. In total there were 81.9 million FTTH/B subscribers in September 2020, up 16.6 percent from a year earlier. Annual growth was again strongest in France, with nearly 2.8 million subscribers added in the 12 months, followed by Russia with 1.7 million and Spain with 1.4 million.
The countries with the highest fiber penetration across Europe are Iceland and Belarus, with over 70 percent of households using fiber broadband. Spain and Sweden are at over 60 percent, and Norway, Lithuania and Portugal over 50 percent.
“The telecoms sector can play a critical role in Europe’s ability to meet its sustainability commitments
by reshaping how Europeans work, live and do business. As the most sustainable telecommunication
infrastructure technology, full fibre is a prerequisite to achieve the European Green Deal and make the
European Union’s economy more sustainable. Competitive investments in this technology should,
therefore, remain a high political priority and we look forward to working with the EU institutions,
national governments and NRAs towards removing barriers in a way to full-fibre Europe” said Vincent
Garnier, Director General of the FTTH Council Europe.
About the FTTH Council Europe:
The FTTH Council Europe is an industry organization with a mission to advance ubiquitous full fibre based connectivity to the whole of Europe. Our vision is that fiber connectivity will transform and
enhance the way we live, do business and interact, connecting everyone and everything,
everywhere.
Fiber is the future-proof, climate-friendly infrastructure which is a crucial prerequisite for
safeguarding Europe’s global competitiveness while playing a leading global role in sustainability.
The FTTH Council Europe consists of more than 150 member companies.
Contacts:
Eric Joyce, Chair, Market Intelligence Committee
[email protected]
Sergejs Mikaeljans. Communications and Public Affairs Officer
[email protected] Tel: +32 474 81 04 54
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, BT has increased its its total FTTP network build target from 20 million to 25 million premises by December 2026, with Openreach working to connect up to 4 million premises a year.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ftthcouncil.eu/documents/Fibre_Market_Panorama_2021_PR_final.pdf
https://register.gotowebinar.com/register/2424555495368131344 (webinar registration)
PON’s Vulnerability to Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
by Shrihari Pandit
Introduction:
The dominant architecture used in fiber optic deployment -Passive Optical Networks (PONs) may be vulnerable to attack. It is important to bring attention to this under-appreciated weakness and discuss what steps are possible to protect fiber infrastructure.
As various PON technologies are long standing and widely deployed, this is a matter of no small concern. PONs are widely deployed by Verizon FiOS, AT&T U-verse and many others.
The PON architecture is a hodgepodge of old and new technologies, hardware and strategy, limited budget and often is not overseen by a single team.
In this article we describe how fiber optic infrastructure based on PONs may be open to potential denial of service (DoS) attacks via optical signal injections. Security experts warn that this is a growing issue, which could take down entire sectors of PON segments.
Considering the ever increasing state-sponsored and non-state-actor cyber attacks, these types of vulnerabilities that allow for massive disruption for large groups of people are very attractive targets.
PON Overview:
The cost advantages of PON architecture make it the overwhelming choice for FTTH deployments. PON allows wireline network providers to deliver service to businesses and homes without having to install costly active electronics on roads, curb-side or even within buildings themselves.
Active electronics, on the other hand, add cost and create operational complexity as deployments scale. The conveniences and differentiators of PONs are precisely what opens up the floodgates to serious vulnerabilities.
PONs are fundamentally susceptible due to the architecture from the passive optical splitter (POS) to the optical network unit (ONU) within the overall network infrastructure. The POS component of the network functions like a bridge, allowing any and all communications to transverse without the ability to filter, limit or restrict flow.
The fiber optic market currently boasts 585.9 million subscribers worldwide, with that number set to grow to 897.8 million subscribers by 2021.
The industry has moved to upgrade 1st generation GPONs and EPONs to next-generation PONs, like NG-PON2 (the favorite), XG-PON1 and XGS-PON. For example, Verizon uses the Calix AXOS E9-2 Intelligent Edge System for large-scale NG-PON2 deployments that began in the first quarter of 2018.
However, with subscriber density significantly increasing per PON segment, the risks increase as more subscribers are affected by a cyber attack on a single fiber.
Sidebar: NG-PON2
NG-PON2 combines multiple signals onto a single optical fiber by using the different wavelengths of laser light (wave division multiplexing), and then splits transmission into time slots (time division multiplexing), in order to further increase capacity. NG-PON2 is illustrated in the figure below.

Legend:
OLT =Optical Line Termination ONT =Optical Network Termination
NGPON2 has three key advantages for operators:
1. Cost
Firstly, it can co-exist with existing GPON and NGPON1 systems and is able to use existing PON-capable outside plant. Since the cost of PON FTTH roll out is 70 per cent accounted for by the optical distribution network (ODN), this is significant. Operators have a clear upgrade path from where they are now, until well into the future.
2. Speed
Initially NGPON2 will provide a minimum of 40 Gb/s downstream capacity, produced by four 10 Gb/s signals on different wavelengths in the O-band multiplexed together in the central office with a 10 Gb/s total upstream capacity. This capability can be doubled to provide 80 Gb/s downstream and 20 Gb/s upstream in the “extended” NGPON2.
3. Symmetrical upstream/downstream capacity
Both the basic and extended implementations are designed to appeal to domestic consumers where gigabit downstream speeds may be needed but more modest upstream needs prevail. For business users with data mirroring and similar requirements, a symmetric implementation will be provided giving 40/40 and 80/80 Gb/s capacity respectively.
………………………………………………………………………………………
The Essence of a PON Cyber Attack:
Given the flashpoints around the globe, it doesn’t take much imagination to envision how state and non-state actors might want to cause such a chaotic and widespread disruption.
If a “cyber criminal” gains access to the underlying fiber, they could inject a wideband optical signal to disrupt communications for all subscribers attached to the PON segment.
Alternatively, at your home the adversary could manipulate the ONU’s optical subsystem to transmit abnormal PON signals and impact service to all subs on that segment. Communications including internet, voice and even analog TV signals that operate on nearby wavelengths would be susceptible to these serious DoS attacks.
Possible Solutions, Preventive Methods and Procedures:
So, what can be done with current equipment without a massive and costly fiber optic network overhaul? The unfortunate answer is that an overarching vulnerability will always exist as long as the passive components are in place. A reactionary process is the best and only option.
The current primary solution for operators is to reduce the number of subscribers per PON segment as a way to manage risks. If an attack was detected, the network operator would be able to localize the source and identify and disconnect the bad actor from the network. But it’s easier said than done.
This sort of manual process is not ideal. Extensive PON outages means spending the time and money to send personnel to optical line terminals to check each individual port until the attacker is found. The installation of active electronics on each PON segment or near PON subscribers is unrealistic and impractical. That undertaking would actually be more costly in terms of time, money and location.
The best ongoing solution is that operators should consider installing passive tap points per PON segment. Each can be independently routed back and managed at a provider’s operations center and allow operators to effectively analyze segments and detect unusual optical light levels that may signal an attack.
At that point the operator could physically dispatch techs on-site to continue the localization and resolution process while ensuring other non-threatening users remain unaffected. This solution is to effectively take a reactionary restriction and make it as automatic and proactive as currently possible.
Conclusions:
P2MP (point to multi-point) architecture has become the most popular solution for FTTH and FTTP. Yet there needs to be a severe increase in awareness to potential PON vulnerability into the next generation.
If we can catalyze the telecom industry to develop methods and measures to protect infrastructure, such crippling network security issues will be stopped before widespread exploits occur.
The industry needs to address these concerns sooner rather than later or else be left without effective countermeasures against these very real threats.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-a-denial-of-service-attack-dos
https://s2.ist.psu.edu/paper/ddos-chap-gu-june-07.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G93I_v2pa24
……………………………………………………………………………….
About Shrihari Pandit:
Shrihari Pandit is the President and CEO of Stealth Communications, the NYC-based ISP he co-founded in 1995. Stealth, having built its own fiber-optic network throughout the city, provides high-bandwidth connectivity services to a broad roster of customers in business, education and government.
Prior to Stealth, Mr. Pandit was a network-security consultant to various software and telecom companies, including MCI, Sprint and Sun Microsystems. He also served as an independent consultant to several U.S. agencies, including NASA and the National Infrastructure Protection Center (NIPC), now part of the Department of Homeland Security.
Swisscom achieves 50 Gbps on a fixed PON connection – a world first!
Swisscom has achieved transmission speeds of 50 Gbps in a real PON (Passive Optical Network) environment test – a world first, according to the company. Swisscom has upgraded existing OLT (Optical Line Termination) hardware with a 50 Gbps PON Line Card prototype to reach a download speed of 50 Gbps and an upload speed of 25 Gbps on a fixed network.
The PON technology can be ready to market and deployed in around two years, according to Swisscom. It can be an option for business customers initially. Progressive network virtualization will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements.
The 10 Gbps service is expected to be sufficient for the residential mass market for several years yet, the company said. The 50 Gbps option allows for flexible deployment using existing fibre-optic infrastructure.
Markus Reber, Head of Swisscom Networks, said: “There is no question that the bandwidth need will continue to increase over the coming years. That’s why, here at Swisscom, we are already considering how our technology needs to develop to ensure that Switzerland continues to be ready to take advantage of the latest digital services with the best possible experience in the future. The results of testing based on PON technology and architecture clearly demonstrate that we have some powerful options available.”
“In my opinion, PON with 50 Gbit/s will be an option for the business customer market initially. Progressive network virtualisation will enable companies to use the bandwidth they need on a flexible basis in line with their requirements, for instance. In contrast, the 10 Gbit/s already available in the residential mass market should be more than enough for several years to come. However, the 50 Gbit/s option offers even more opportunities, as it allows the existing fibre optic infrastructure to be deployed in a more versatile way. As an example, the technology will soon facilitate access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, as the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households. With a transmission speed of 50 Gbit/s, there is ample bandwidth available.”
The technology also will support fiber optic access to mobile communication masts, particularly for 5G, since the same network can be used as the one already built to connect households.
Swisscom says that “over the coming years, the development of digital applications will result in a similar growth in bandwidth need as seen in recent years, when it increased more than tenfold within a decade. Swisscom is therefore investing in network expansion on an ongoing basis, deploying the latest innovative technologies to do so and safeguarding Switzerland’s high degree of digital competitiveness.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In April 2020, market research powerhouse Omdia (owned by Informa) forecast that In the 2018-2025 timeframe, the PON market will see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% to be worth $8.4 billion by 2025. “This market remains in an upswing as operators continue to expand and upgrade their fiber-based access networks for both residential and non-residential subscribers and applications,” states the Omdia team in their report (published prior to the global impact of COVID-19, it should be noted).
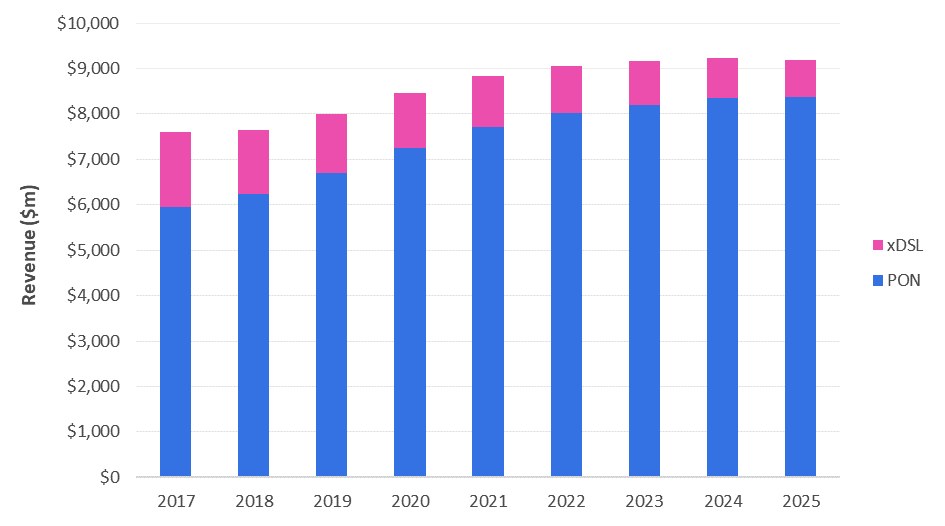
Omdia: PON and xDSL/Gfast equipment market by major segment, 2017–2025
Growth in the PON market will be driven by increasing demand for next-generation PON equipment, including 10G GPON, 10G EPON, NG-PON2 and 25G/50G PON, according to Omdia: By 2021, most GPON OLT (optical line terminal) shipments are expected to be 10G.
Omdia expects demand for NG-PON2 equipment (which is expensive because it includes tunable lasers) is expected to be limited, with significant deployments anticipated only by one major operator, Verizon.
In Western Europe, PON investments are only just starting: That market is set for a CAGR of 16.5% to be worth $1.6 billion in 2025.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.swisscom.ch/en/about/news/2020/10/08-weltpremiere.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/swisscom-reaches-50-gbps-in-real-network-environment–1357116
http://www.broadbandworldnews.com/document.asp?doc_id=758638
AT&T ends DSL sales while CWA criticizes AT&T’s broadband deployments
AT&T: DSL is Dead:
According to a message board post on DSL Reports, AT&T notified customers on billing statements in August that effective Oct. 1 it would no longer accept new orders for its copper-based DSL service. The notice also said that existing DSL subs will no longer be able to make speed changes to their respective DSL service.
The message board author wrote:
“On my August AT&T statement, traditional DSL is officially grandfathered effective October 1st. No new orders (moves, installs, speed change, etc.). Hopefully they will still allow promos….”
That’s no surprise to this author. AT&T’s DSL subscriber base has been eroding steadily – losing almost 350,000 subs over the past couple of years. In Q2 2020, AT&T shed 23,000 DSL subs, ending the period with just 463,000.
“We are focused on enhancing our network with more advanced, higher speed technologies like fiber and wireless, which consumers are demanding,” AT&T said in a statement. “We’re beginning to phase out outdated services like DSL and new orders for the service will no longer be supported after October 1. Current DSL customers will be able to continue their existing service or where possible upgrade to our 100% fiber network.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T Fiber Update:
AT&T also announced three new price points for its AT&T Fiber tiers and said that all new and existing AT&T Fiber Internet 100, Internet 300 and Internet 1000 subscribers would enjoy unlimited data without additional charges. AT&T Fiber started offering the new deals as a standalone product with no annual contracts for new customers on Sunday.
As of Q2-2020, AT&T had 4.3 million AT&T Fiber customers with nearly two million of them on 1-gigabit speeds. Overall, AT&T has about 15.3 million broadband subscribers while Charter has 28 million and Comcast has over 29 million.
AT&T’s fiber tier announcement comes after AT&T CEO John Stankey told a Goldman Sachs investor conference in September that “priority number one” is investing in fiber for 5G and FTTP services.
The new prices are also an indication that AT&T intends to ramp up its drive on FTTP sales in the wake of a recent study showing that many of AT&T’s new subs were coming from existing customers upgrading to fiber rather than from gaining market share from cable Internet operators (MSOs).
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
CWA Calls Out AT&T’s broadband efforts:
Coincidently today, the Communications Workers of America (CWA) criticized AT&T’s lack of fiber deployments. The report, co-authored with the National Inclusion Alliance (NDIA) stated:
AT&T is making the digital divide worse and failing its customers and workers by not investing in crucial buildout of fiber-optic infrastructure that is the standard for broadband networks worldwide. The company’s recent job cuts — more than 40,000 since 2018 — are devastating communities and hobbling the company’s ability to meet the critical need for broadband infrastructure.
An in-depth analysis of AT&T’s network shows the company has made fiber available to fewer than a third of households in its footprint, halting most residential deployment after mid-2019. The analysis also shows that 28% of households in AT&T’s footprint do not have access to service that meets the FCC’s standard for high-speed internet, and in rural counties 72% of households lack this access. In some places, AT&T is decommissioning its outdated DSL networks and leaving customers with no option but wireless service, which is not a substitute for wireline service.
In all, AT&T has made fiber-to-the-home available for fewer than one-third of the households in its network. AT&T’s employees — many of whom are Communications Workers of America (CWA) members — know that the company could be doing much more to connect its customers to high-speed Internet if it invested in upgrading its wireline network with fiber. They know the company’s recent job cuts — more than 40,000 since 2018 — are devastating communities and hobbling the company’s ability to meet the critical need for broadband infrastructure.
CWA recommends that AT&T dedicate a substantial share of its free cash flow to investment in next-generation networks across rural and urban communities, make its low-income product offerings available widely, and stop laying off its skilled, unionized workers and outsourcing work to low-wage, irresponsible subcontractors.
Editor’s Note:
According to CWA, AT&T has deployed fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) to only 28% of the households in its fiber coverage area as of the end of June 30, 2019.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The CWA/NDIA report said AT&T has targeted more affluent, non-rural areas for its fiber upgrades. Houses with fiber have a median income that’s 34% higher than those with DSL only. Across the rural counties in AT&T’s 21-state footprint, only a miniscule 5% have access to fiber, according to the report.
According to the report, 14.93 million—out of almost 53 million households—have access to AT&T’s fiber service. Among states, AT&T’s FTTH build out is the lowest in Michigan with 14% have access followed by Mississippi (15%) and Arkansas (16%).
“AT&T is also failing to make fiber available to the majority of its customer base in cities,” according to the report. “While most of AT&T’s fiber build has focused on urban areas—96 percent of households with access to fiber in AT&T’s footprint are in predominantly urban counties—the company hasn’t built enough fiber to reach the majority of urban residents. Seventy percent of households in urban counties still lack access to fiber from AT&T because the company has made fiber available to only 14.7 million households out of 48.4 million total households in these counties.”
The report also said there were many areas in AT&T’s footprint where it doesn’t offer the Federal Communications Commission’s “broadband” definition of 25 Mbps downstream and 3 Mbps upstream.
“For 28% of the households in its network footprint, AT&T’s internet service does not meet the FCC’s 25/3 Mbps benchmark to be considered broadband,” the report said. A key recommendation is that “AT&T must upgrade its network in rural communities to meet the FCC’s broadband definition, at least, and renew its efforts to deploy next-generation fiber.”
The report noted that in some areas where AT&T doesn’t provide faster speeds, cable operators, such as Comcast and Charter do.
“Even where that access is available from another provider—typically a cable provider—consumers are deprived of the benefits of competition in price, choice and service quality,” the report said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AT&T is counting on fiber for both residential and commercial services, including AT&T TV. In order to win over customers from cable operators, AT&T has paired its 1-Gig service with AT&T TV.
Regarding DSL, the report states: “AT&T’s poor maintenance of its DSL networks, with limited capacity for new connections, results in would-be new customers in some areas being denied service entirely or told they can only subscribe to fixed wireless service (a 4G wireless connection for home use, designed for rural areas).”
As expected, AT&T refuted the claims made in the CWA/NDIA report in a statement to FierceTelecom and Broadband World News on Monday afternoon.
“Our investment decisions are based on the capacity needs of our network and demand for our services. We do not ‘redline’ internet access and any suggestion that we do is wrong. We have invested more in the United States over the past 5 years (2015-2019) than any other public company. We have spent more than $125 billion in our U.S. wireless and wireline networks, including capital investments and acquisition of wireless spectrum and operations. Our 5G network provides high-speed internet access nationwide, our fiber network serves more 18 million customer locations and we continue to invest to expand both networks.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
New Fiber Optics Market Report:
Finally, a new report by Technavio forecasts that the global fiber optics market size will grow by USD 2.44 billion during 2020-2024, progressing at a CAGR of almost 5% throughout the forecast period.
Image Credit: Technavio
The increase in the number of FTTH homes and subscribers is the key factor driving the market growth. A higher number of customers are opting for fiber optic connections to leverage broadband services. This reduces the requirements for customer premises equipment (CPE) and distribution point unit (DPU).
References:
https://cwa-union.org/sites/default/files/20201005attdigitalredlining.pdf
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/cwa-calls-out-at-t-s-lack-fiber-its-dsl-footprint
http://www.broadbandworldnews.com/document.asp?doc_id=764417
AT&T CEO: Fiber, Stories and (Video) Content to drive future revenues and growth
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20201005005444/en/
Broadband Forum and LAN Laboratory Expand Certification Program to include XGS-PON
As demand for fiber networks continues to grow, the Broadband Forum has expanded its BBF.247 Optical Network Unit (ONU) Certification Program to include XGS-PON.
This latest update extends the program to a variety of key features needed by operators deploying XGS-PON networks. The certification is just one piece of Broadband Forum’s vision to provide network operators with the tools, open specifications, and open source references necessary to bring new services and technologies to their customers more rapidly. Certified ONU products can be deployed quickly, with improved interoperability to existing Optical Line Terminal (OLT) equipment already deployed. Similarly, certified ONU products will also work directly with newer Broadband Forum specifications, including the forthcoming virtual OMCI specifications and software defined access networks.
The XGS-PON extensions add to the BBF.247 G-PON initiative – which has now certified nearly 100 products since its launch in 2011. The new test plan will see ONUs undergo rigorous testing at Broadband Forum’s official certification program test laboratory Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN Laboratory), using MT2’s ONU testing solution. The work will confirm conformance to the latest PON ITU-T standards, providing network operators with assurance that they can deliver efficient networks and a high-quality customer experience. New additions to the technology are also now tested, including extended OMCI messages format, Enhanced Unicast & Multicast Operations, and Capacity Tests & Performance Monitoring. This increases the number of certification test cases by more than 50% compared to the previous version.
Eight products, including single or multi-user port ONUs/L2 and Residential Gateways from Altice Labs, CommScope, Huawei, Humax, KAONMEDIA, Sagemcom, Sercomm and ZTE have already been certified under the new BBF.247 certification program.
“The introduction of XGS-PON certification by Broadband Forum is a significant and positive step for the PON ecosystem as interoperability will encourage growth,” said Jaeseok Kim, Head of Infra Planning at SK Broadband. “This will become increasingly important as more operators look to upgrade existing network to meet consumer demand for Gigabit + speeds.”
Claudio Mathys, Product Manager Wireline Access Networks at Swisscom (Schweiz) AG, added: “Establishing interoperability and testing requirements are key elements in a liberated market. The introduction of XGS-PON from Swisscom as a technology leader – in conjunction with the certification and testing program from Broadband Forum – will significantly enhance the confidence from our competitors for CPE certification as based on industry standards and independent references. Achieving Broadband Forum certification is the entry ticket for connectivity to our network. We will definitely avoid the painful experience made with xDSL interoperability/complexity – right from the beginning.”
Hugues Le Bras, Network Engineer in Fixed Access Networks at Orange, said: “The role of interoperability and standards has only become more important as broadband grows in popularity and operators upgrade their networks to meet consumer demand. Orange already requests BBF.247 certification for each ONU deployed on the field. However, this expansion of Broadband Forum’s certification program will give us confidence when deploying next-generation technology that will enable the future era of connectivity. The latest additions to the certification also bring new features, such as flexibility and monitoring, which are essential for Orange throughout the ONU life.”
A future XGS-PON interoperability test event will take place at LAN Laboratory, in Tauxigny, France, from October 5 to 9, 2020, allowing vendors worldwide to exercise their OLT or Optical Network Terminal (ONT) solutions against each other. The event will give all equipment vendors the opportunity to improve the interoperability of their products by testing them against the other solutions presented at the event.
“Our existing G-PON certification has made a significant impact on ensuring products meet standards, and this latest expansion of the program will give operators the confidence to roll out mass XGS-PON deployments,” said Robin Mersh, CEO at Broadband Forum. “We now want to instill this same assurance in the industry for upcoming ITU PON technology, including XGS-PON and NG-PON2. XGS-PON is a major step in network evolution, supporting the expansion of 5G and through BBF.247 certification, we can ensure network interoperability.”
Thierry Doligez, Director of LAN Laboratory, said: “Both operators and vendors increasingly recognize the importance of certification in order to speed up deployment and we are proud to partner with Broadband Forum on this extension of its G-PON certification program. As operators move to upgrade their networks to meet increasing consumer demand, the new testing will make sure they are investing in trusted products which will guarantee a certain level of service. ONU manufacturers will also benefit from this substantial program update as it will give them the chance to prove their conformance against enhanced features.”
For more information or to actively get involved with Broadband Forum’s work on higher speed PON technologies, visit: www.broadband-forum.org.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
BBF.247 certification program is open to all GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON ONU products with Ethernet Interfaces and is based on the Broadband Forum’s TP-247/IR-247 test plan. It tests conformance to TR-156 and TR-280 using OMCI as defined in the ITU G.988, which are the most critical standards to interoperable implementations.
The Broadband Forum has reviewed and authorized the following independent testing agency to administer the approved BBF.247 tests and assess eligibility of products for the Broadband Forum Certification. For more information or to schedule testing, please contact the laboratory directly:
- LAN www.lanpark.eu
-
- Since 2009, the BBF has collaborated with FSAN (Full Service Access Network) on interoperability testing plugfests on the physical, TC and upper layers for GPON, with FSAN leading on the first two and BBF on the last.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Broadband Forum
Broadband Forum is the communications industry’s leading organization focused on accelerating broadband innovation, standards, and ecosystem development. Our members’ passion – delivering on the promise of broadband by enabling smarter and faster broadband networks and a thriving broadband ecosystem.
A non-profit industry organization composed of the industry’s leading broadband operators, vendors, and thought leaders, our work to date has been the foundation for broadband’s global proliferation and innovation. For example, the Forum’s flagship TR-069 CPE WAN Management Protocol has nearly 1 billion installations worldwide.
Broadband Forum working groups collaborate to define best practices for global networks, enable new revenue-generating service and content delivery, establish technology migration strategies, and engineer critical device, service & development management tools in the home and business IP networking infrastructure. We develop multi-service broadband packet networking specifications addressing architecture, device and service management, software data models, interoperability and certification in the broadband market.
Our free technical reports and white papers can be found at https://www.broadband-forum.org/
About Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN Laboratory)
The Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN) is a unique independent laboratory specialized in conformance, interoperability and coexistence tests of devices deployed by telecom operators in the access and home networks (DSL, G-PON, Broadband-PLC, …), by DSOs in Smartgrids networks using powerline communications (G3-PLC), and by the industry in video security networks (E&PoC). LAN also offers on-demand test services dedicated to PON network operators, addressing their needs in terms of pre-deployment qualification tests for each specific network they operate. LAN is one of the Broadband Forum’s Approved Test Laboratory (ATL), the unique one accredited by the Broadband Forum to conduct the worldwide recognized BBF.247 certification tests for G-PON, XG-PON and XGS-PON terminals.
For more information on Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques, please go to www.lanpark.eu, follow @Laboratoire_LAN on Twitter, or send an Email to [email protected].
About MT2
MT2 leads the industry in FTTH G-PON and XGS-PON network test, offering troubleshoot, monitoring deep analysis of products, and ‘single-click’ automated test suite solutions. MT2’s analyzers and OLT emulators have the unique powerful features to allow the user to simply ‘software-select’, and switch between GPON, XG-PON, XGS-PON or NG-PON2, all within the same single system. MT2 ensures the complicated protocols and subscriber internet access traffic complies with every spec, automatically, using a powerful and intuitive user interface, high precision and innovative design. MT2 actively contributes to the Broadband Forum activity, as a test-tool vendor, and developed its FTTH automated test suites for functionality and performance testing, covering BBF.247, TR-309 and TR-255, critical to ensure system quality and full validation of any operator’s FFTH network.
For more information on MT2, please go to www.mt2.fr, follow MT2ftth on LinkedIn, or send an Email to [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Openreach on benefit of FTTP in UK; Full Fiber rollouts increasing
A new report commissioned by UK fixed line infrastructure provider Openreach has concluded the UK would be £59 billion better off with full FTTP.
The report -‘Full fibre broadband: A platform for growth’ – was compiled by the Centre for Economics and Business Research (CEBR). The conclusion is that if the UK were to achieve ubiquitous fibre to the premises (FTTP) by 2025, UK productivity would increase by almost £59 billion, due to smarter ways of working and better public services made possible by FTTP.
It appears that the CEBR had a look at the effect FTTP has had in places where it’s already available and scaled that up to the whole country. It also tried to factor in other disruptive technological events such as mass ICT and even railways to get a sense of the transformative effect of everyone having faster broadband than they currently do.
“Full fibre is a vehicle to turbocharge our economy post-Brexit, with the power to renew towns and communities across the UK,” said Openreach CEO Clive Selley. “We’re proud to be leading the way with over 1.8 million homes and businesses already having access to our full fibre network. We’re currently building full fibre to around 22,000 premises a week– which is one every 28 seconds. But we want to go even faster and further – to 15 million premises and beyond if we can get the right conditions to invest.”
“Through our Fibre First programme, Openreach is now building to 103 locations across the UK and we’re on track to build to four million premises by March 2021. With the right policies and regulation, we can build a better, more reliable broadband network faster than any other country in the world and unlock the benefits for the whole UK. If that doesn’t happen, then many people will be locked out of a more connected future and the UK could lose its status as a global digital leader.”
Openreach believes the telecoms sector should be exempt from paying business rates for the foreseeable future, be granted better access to blocks of flats and other such buildings and get a regulatory environment more conducive to investment.
To read the full report as well as Openreach’s thoughts on how the roll-out of full FTTP can be speeded up, please click here.
To some extent Openreach is pushing at an open door here, since no one thinks faster broadband is a bad idea. This report is just part of the ongoing lobbying campaign to get the UK state to be a bit more helpful when it comes to fibre infrastructure and, presumably, to maintain the momentum created by Boris Johnson’s enthusiasm for fibre.
Meanwhile, the pace of Openreach full fiber roll-outs is increasing. There are now 1,604,178 premises where the Openreach FTTP services can be ordered from assorted retailers. This is an increase of 110,247 compared to the previous month and gives a build rate of 25,724 premises a week.
Splits for Openreach FTTP and changed in category since 12th September 2019:
- 463,391 premises via BDUK/gap funded or other rural intervention (increase of 10, reality in the 6000-7000 range)
- 764,521 premises in Fibre First areas (increase of 129,876)
- 270,774 premises via New Build since January 2016 (increase of 29,784)
- 107,468 premises via commercial/old roll-out (decrease of 47,447)
The big take-away should be for the increasing number of full fibre operators both big and small, that if you need high levels of take-up to sustain your business model in the short to medium term you need to do a lot of community engagement and pricing needs to be the same or lower than the price people are paying today even if your speeds are significantly higher.
…………………………………………………………………………..
About Openreach:
Openreach works on behalf of communications providers to build and maintain the UK’s digital network — the lines, poles and cables used to provide phone, broadband and TV services. We don’t provide phone, broadband or TV services directly to consumers. To get these services, you should contact a communications provider below to find out about the packages they can offer you.
References:
https://www.openreach.com/full-fibre-impact
http://telecoms.com/500272/openreach-explains-why-fttp-is-such-a-great-idea/
https://www.thinkbroadband.com/news/8565-pace-of-openreach-full-fibre-roll-out-may-be-increasing
https://www.openreach.com/fibre-broadband/fttp-providers



