Uncategorized
Beijing Internet Institute: IPv6 leads Internet into a new era after 12+ years of wavering
Well, it’s certainly about time for IPv6! The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has been going on for at least 12 years (See New Urgency to Move to IPv6 as Last Block of IPv4 Addresses are Allocated, published Feb 6, 2011!).
IPv6 is the first and might be the last upgrade of the global network in the coming decades. The development of IPv6 and IPv6 derivative and convergence technology standards will meet the objective requirements of the continuous expansion of the future network, facilitate the digital transformation in multiple fields, and become a new track of global digital technology innovation. In light of this, the “Global IPv6 Development and Standard Evolution Symposium and the Release Ceremony of the 2022 IPv6 Support White Paper,” held by the IPv6 Forum and the China Future Internet Engineering Center (CFIEC) on January 5, 2023.
The event accumulates global experts from global organizations from IPv6 Forum, CFIEC, Asia-Pacific Internet Network Information Center (APNIC), China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), China Communication Standardization Association (CCSA), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), European Telecommunications Standardization Association IPv6 Enhanced Innovation Working Group (ETSI IPE). Experts discuss the development vitality and opportunities of IPv6 under the new turning point of digital economy, strengthen the in-depth cooperation between different organizations, establish a perfect IPv6 and derived and fusion technology standards. accelerating large-scale deployment of IPv6 globally in the “global IPv6 development” and “IPv6 standard evolution” dimensions.

IPv6 is leading the development of the Internet
IPv6 provides more innovation capacity and development space for network infrastructure. Wu Hequan, academician of the CAE Member, summarizes the current development trend and characteristics of IPv6 at the meeting. He believes that the global Internet development has entered the dominant period of IPv6, which mainly presents three characteristics: first, the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is accelerating; Second, from IPv4/IPv6 dual stack to IPv6 only; Third, IPv6 is developing towards IPv6+, with the developing IPv6 address space capabilities and fully integrating with the new generation of IT. IPv6 is playing an active role.
Liu Dong, Vice President of IPv6 Forum, introduced the development of the global IPv6 deployment in general: “The global IPv6 deployment speeds up to a new level in 2022. Countries or regions with a combined IPv6 deployment rate of around 30% or above account for more than half of the world. IPv6 deployment rate in 26 countries exceeded 40%, an increase of 9% compared with 2021; 37 countries have deployment rates exceeding 30%; The deployment rate of 51 countries exceeded 20%. IPv6-only has become a global consensus. The IPv6 applications and users will grow rapidly in the future ”
Sharing the development of IPv6 deployment in the Asia-Pacific region at the conference, Pan Guangliang, Director of Basic Resource Services at the Asia Pacific Internet Network Information Center (APNIC), puts, “The growth of the Internet has not stopped and will not stop. As more and more devices connects to the Internet, IPv6 is the way to go and is growing globally, with Asia seeing strong growth in overall IPv6 capability. According to APNIC statistics, the IPv6 support capacity in Asia exceeds the global average level by nearly 40%. Several countries such as China, India and Malaysia have witnessed rapid IPv6 development. In the next few years, the deployment of IPv6 will continue to improve, and more innovative applications based on IPv6 will appear ”
The development of IPv6 in China is outstanding. Gao Wei, director of the Internet Center of the Standards Institute of the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, points out at the conference: “China is among the first countries in the world to carry out research, standard setting, application development and large-scale commercialization of IPv6 and next-generation Internet technologies. By December 2022, the number of IPv6 users in China has reached 717.7 million, with IPv6 traffic on fixed networks accounting for 12% and mobile networks 46%, showing a good momentum of development. IPv6 transformation achieves monumental success especially in the cloud platform, to achieve the new era of IPv6 traffic increase to provide strong support.”
IPv6 standard evolves from IPv6-Only to “cloud network”, “computing network” and “security”
In the era of digital economy, the integration of the Internet and the economy continues to deepen, and industrial digitalization with digital industrialization have become opportunities for all industries to score a new chapter. As an important starting point of digital transformation, standard is more conducive to opening up a leading advantage in the changing situation. The research, development and creation of IPv6 and its derived and converged technical standards are closely related to the development and deployment of IPv6. With the accelerated deployment of IPv6, the international standardization of IPv6 has entered a new stage and came across new changes.
Zhao Huiling, chairman of CCSA TC3 Technical Committee of China Communications Standardization Association, says that after 20 years of development, the current IPv6 standards have formed a systematic and standardized trend, covering five categories of standards: resources, networks, applications, security and transition. The standards at this stage can meet the needs of IPv6 network construction, but the security standards and application standards still have a lot to catch up. She also proposes four key directions for the creation of IPv6 industry standards in the new stage:
- First, in the field of cloud network integration, IPv6 supports the deep integration of new resources such as cloud network edge intelligent collaboration and data computing power;
- Second, in the field of IOT, IPv6 supports seamless global coverage, and anyone can communicate with anyone at any place and any time.
- Third, in the field of intelligent operation and maintenance, IPv6 supports end-to-end network quality assurance to ensure that the demands of the cloud on the network in enterprise production scenarios are met.
- Fourth, in the field of security and credibility, IPv6 supports end-to-end security endogenous mechanisms, adaptive security frameworks and security atomic capabilities, security defense, detection, and response prediction.
Li Zhenbin, member of the IETF Internet Architecture Committee (IAB) and Huawei’s chief IP protocol expert, also mentions that, “As the data communication industry moves towards the intelligent connection era of IPv6+, IETF has also gradually carried out various IPv6 standardization work, including the IPv6+1.0 (SRv6) standard, the IPv6+2.0 (5G&Cloud) standard Important achievements have been made in relevant standards. At this stage, IPv6 provides more differentiated service capabilities. Cloud network and computing network become the key applications of IPv6. Through IPv6 expansion and APN and other technologies, personalized networks can be realized and diverse computing power requirements can be met. In terms of APN6, we have signed a standard manuscript with several operators to successfully promote BOF at IETF, which will be the key direction of future technology innovation and standard creation. In addition, the general tunnel encapsulation technology GIP6 based on IPv6 also deserves further attention. ”
After years of deployment and penetration, IPv6 has entered a golden age of IPv6-Only evolution. When introducing the development of IPv6 at ETSI, Xie Chongfeng, Vice Chairman of ISG at ETSI IPE (IPv6 Enhanced innovation) and senior expert on IPv6 at China Academy of Telecommunication Research, says that network infrastructure is multi-domain and multi-scenario. To this end, we should actively promote the multi-domainIPv6-Only network architecture and technical requirements, in the form of a standard in the industry consensus, which will help operators, OTT, and service and devices manufacturers to buildIPv6-Only networks, and promote network infrastructure towards IPv6-Only.
The Release of 2022 Global IPv6 Support White Paper:
This seminar is not only a rare multilateral interaction and exchange between domestic and foreign organizations and experts on IPv6 development and standards, but also a demonstration of the fruitful results achieved in promoting IPv6 globally in the past year. At the meeting, the 2022 Global IPv6 Support White Paper jointly prepared by the IPv6 Forum and CFIEC was officially released. Latif Ladid, the president of the IPv6 Forum, says at the release ceremony that the white paper is based on the latest progress of global IPv6 technology, the number of global users, the network and domain name system, international operators, websites, cloud services Network equipment and other parties elaborate on the global IPv6 support and make multi-dimensional and multi-dimensional statistics to comprehensively, objectively and accurately reflect the global IPv6 development. At the same time, the IPv6 Forum also selected “IPv6 Outstanding Contribution Enterprises” and “IPv6 Pioneer Enterprises” in 2022 based on the white paper. Latif Latid gives awards to five enterprises including Cisco, Huawei, HP, H3C and D-Link, with the “IPv6 Outstanding Contribution Enterprise” award, and ten enterprises, Dell, IBM, TOPSEC, QI-ANXIN, Allied Telesis, Panasonic, Microsoft, ZTE, China Mobile and TP Link, receive the “IPv6 Pioneer Enterprise” award. Yang Wu, chief architect of the H3C Router product line, Zhu Keyi, head of the Huawei Digital Communication Standards and Patent Department, and Han Minglei, an expert on TUPSEC protocol conversion products, also shared the latest IPv6 solutions and products at the meeting.
Liu Dong, Vice President of the IPv6 Forum and director of CFIEC, illustrates: “At the beginning of the year, it is a great pleasure to meet with you online. Through your sharing, we can see that we have made progress in two important dimensions, ‘Global IPv6 Development’ and ‘IPv6 Standard Evolution’, and formed a large number of new achievements. In the future, our various organizations will continue to deepen cooperation and make use of advantages. While moving towards IPv6-Only, the first is to maintain continuous innovation and improve the IPv6 network value; The second is to actively expand the innovative application of IPv6 in the context of the Internet of Everything. The third is to create and improve new technical standards for the sustainable development of IPv6. Let us accelerate the global IPv6 scale deployment, and let IPv6 and the Internet benefit everyone. ”
SOURCE Beijing Internet Institute
References:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/the-internet-has-entered-the-new-era-led-by-ipv6-301716195.html
Akamai: U.S. Internet speeds increased 22% YoY; IPv6 adoption is a conundrum
New Urgency to Move to IPv6 as Last Block of IPv4 Addresses are Allocated

Ookla: Fixed Broadband Speeds Increasing Faster than Mobile: 28.4% vs 16.8%
A new report from Ookla shows that fixed broadband speeds are gaining faster than mobile speeds globally. Speedtest Global Index™, tracks countries’ internet speeds and the overall global median internet speeds which are increasing across the world as countries continue to invest in fiber and 5G. Fixed broadband download speeds increased by 28% over the past year. That’s compared to a nearly 17% increase for mobile speeds, according to Speedtest Global Index™ data from November 2021 to November 2022.
Here are selected charts from their report:





Ookla is excited to see how global speeds and rankings change over the next year as individual countries and their providers choose to invest and expand different technologies, particularly in 5G and fiber. Be sure to track your country’s and check in on our monthly updates on the Speedtest Global Index. If you want more in-depth analyses and updates, subscribe to Ookla Insights™.
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/global-index-internet-speed-growth-2022
Ookla: State of 5G Worldwide in 2022 & Countries Where 5G is Not Available
Performance analysis of big 3 U.S. mobile operators; 5G is disappointing customers
Hindu businessline: Indian telcos deployed 33,000 5G base stations in 2022
As 2022 nears an end, India based telcos like Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel have deployed about 33,000 base stations for 5G services. Sources in India’s Department of Telecommunications told businessline that the telcos deployed around 10,000 base stations in December, taking the cumulative number of base stations deployed for 5G services to about 33,000.
[For another report on 5G base stations in India see; 20,980 base stations installed for 5G, about 2,500 being set up per week, Government tells Rajya Sabha | Headlines (devdiscourse.com)]
Telecom operators commenced deploying the 5G network after Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated 5G services on October 2. Only Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel have commenced 5G capex, as debt-laden Vodafone Idea is still trying to raise additional funds to commence capital expenditure for its 5G network.

Quoting the Ministry of Communications report to the Rajya Sabha, businessline reported last week that the telcos had deployed about 21,000 base stations for 5G services till November 26. According to senior DoT officials, the telcos have added more than 10,000 additional base stations to that number.
Since operators need to deploy 2–6 base stations per tower, the number of telecom towers for 5G has not increased substantially in the past three months. The two operators alone would have deployed 3,000 to 4,000 telecom towers for 5G services.

While telcos have commenced deploying 5G towers in the majority of Indian States, the national capital Delhi is experiencing the fastest deployment of 5G services. Almost a third of all the base stations deployed are located in Delhi. Therefore, users in Delhi NCR will experience the best 5G services.
References:
Telecom operators deploy 33,000 5G base stations this year – The Hindu BusinessLine
Cheerleading from 5G Americas contradicts disappointing financial results from 5G telcos
Chris Pearson, President of 5G Americas said,”5G continues to make significant progress throughout the world. The foundation of this new era of innovation is spectrum, standards (lack thereof?) and a growing ecosystem of key technologies that are being adopted by operators, vendors and end users.”
With 75 countries reporting 5G connections, most recent data from Omdia suggests 433 million global 5G connections were added from Q3 2021 to Q3 2022, almost doubling connections from 489 million to 922 million. Overall, those figures represent 14.4 percent sequential quarterly growth from 806 million in Q2 2022 to 921 million in Q3 2022. Global 5G connections are forecast to again accelerate in 2023, approaching 2 billion and reaching 5.9 billion by the end of 2027.
North America is a leader in the uptake of wireless 5G connections with a total of 108 million 5G and 506 million LTE connections by the end of Q3 2022. 5G penetration of the population in the North American market is approaching 30 percent, as the region added 14 million 5G connections for the quarter – a gain of 15.47 percent over Q2 2022. Overall, a total of 137 million 5G connections is projected to come from North America by the end of 2022, bolstered by strong 5G smartphone shipments in the US. IDC predicts the US 5G smartphone market will reach 118.1 million units shipped in 2022, showing a 27% increase from 2021.
Kristin Paulin, Principal Analyst at Omdia said, “There is still much more to come from 5G that will drive growth. Expanding mid-band coverage will bring a better 5G experience, balancing coverage and speed. And the standalone 5G deployments in progress will enable new applications that take 5G to the next level.”
In comparison, 4G LTE is expected to remain strong in Latin America and the Caribbean through the end of 2022. In Q3 2022, there were 530 million 4G LTE connections, representing 2.14 percent quarterly growth with the addition of 11 million new LTE subscriptions. Latin America and the Caribbean is projected to have 22 million 5G connections by year end of 2022, and 399 million by 2027.
According to Jose Otero, Vice President of Caribbean and Latin America for 5G Americas, “With over half a billion connections, 4G LTE is the foundation of mobile wireless connectivity throughout the Latin America region. Yet, as we look forward to the future, 5G will begin to play a bigger and bigger role for citizens in the region as deployments and connections increase significantly.”
Overall, the number of 5G commercial networks globally has reached 250, according to data from TeleGeography and 5G Americas. That number is expected to reach 253 by the end of 2022 and 397 by the end of 2025 representing strong 5G network investment growth in many regions throughout the world.
The number of 5G and 4G LTE network deployments as of December 14, 2022, are summarized below:
5G:
- Global: 250
- North America: 14
- Caribbean and Latin America: 28
4G LTE:
- Global: 702
- North America: 17
- Caribbean and Latin America: 131
Visit www.5GAmericas.org for more information, statistical charts, infographic and a list of LTE and 5G deployments by operator and region. Subscriber and forecast data is provided by Omdia and deployment data by TeleGeography (GlobalComm).
About 5G Americas: The Voice of 5G and LTE for the Americas
5G Americas is an industry trade organization composed of leading telecommunications service providers and manufacturers. The organization’s mission is to facilitate and advocate for the advancement and transformation of LTE, 5G and beyond throughout the Americas. 5G Americas is invested in developing a connected wireless community while leading 5G development for all the Americas. 5G Americas is headquartered in Bellevue, Washington. More information is available at 5G Americas’ website and Twitter.
5G Americas’ Board of Governors Members include Airspan Networks Inc., Antel, AT&T, Ciena, Cisco, Crown Castle, Ericsson, Intel, Liberty Latin America, Mavenir, Nokia, Qualcomm Incorporated, Samsung, Shaw Communications Inc., T-Mobile US, Inc., Telefónica, VMware, and WOM.
Contacts
5G Americas
Viet Nguyen
+1 206 218 6393
[email protected]
Nokia to open 5G and 6G research lab in Amadora, Portugal
Nokia today announced the opening of a new research and development center focused on 5G and future 6G mobile network technology at its Portuguese campus in Amadora. The center will create employment across several different disciplines and advance research in technologies that are vital components of current 5G and future 6G networks. Last year, Nokia signed a deal with the Portuguese government to open a Global Business Services Center and participate in initiatives that promote digital skills. Apparently, this is part of that industry initiative.
The research and development center will create multiple highly skilled jobs focusing on the advanced development of software to support mobile networks. The center will oversee the full cycle of embedded and real-time software development from early analysis to final delivery. It will bring together professionals from diverse technical disciplines, including software engineers, product owners, and technical leads to work alongside teams around the world.
Tommi Uitto, President of Nokia Mobile Networks, said: “The new research and development center in Portugal demonstrates Nokia’s continued investment in the future of wireless communications. The center’s vital work will continue to expand the possibilities of mobile networks, critical for seamlessly connecting people, businesses, and industries. Importantly, this will be a hub for innovation, reinforcing our 5G technology leadership and helping to realize our ambition to become a 6G pioneer.”
Sérgio Catalão, Country Manager, of Nokia Portugal, said: “The announcement made today is a testament to the continued solid operation of Nokia in the country, reinforced once again by a collaboration with the Portuguese Government. This project reinforces our commitment to supporting Portugal’s digital transformation with our market-leading technology by working in close cooperation with academia, as well as bolstering our team with the best talent.”
A vibrant technology ecosystem, highly skilled talent pool, country stability, and location in Europe were contributing factors for Nokia to locate the research and development center in Portugal. The company has been an important innovation hub for Nokia globally through its units in Amadora and Aveiro and hosts services centers that remotely manage broadband networks for some of the leading global operators. The center follows a strategic agreement signed last year with the Portuguese government to open a Global Business Services Center and participate in initiatives that promote digital skills. The company has close to 2,800 employees in the country.


Comment & Analysis:
There are quite a few on these new 5G/6G Research Centers being opened all over the world. We wonder what “research will actually be done” as detailed programs have not been disclosed. Ericsson announced last week that it was investing heavily in a new research facility in the UK. The objective is to conduct research projects that ultimately contribute to the global development of 6G. Focus areas include network resilience and security, AI, cognitive networks, and energy efficiency.
We think the research efforts should be directed at solving the problems of 5G such as an implementation standard for 5G SA Core networks to facilitate multi-vendor interoperability of both hardware and software. Another urgent 5G issue is to reduce the huge power consumption of 5G base stations, especially for mmW frequencies.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/news/releases/2022/11/28/nokia-to-open-new-5g-and-6g-research-and-development-center-in-portugal/
FCC Releases New National Broadband Maps & FCC Speed Test App
At long last, the FCC has released the first public version of its National Broadband Map. The new map is consequential as it will inform how many millions or billions of dollars each state and territory gets from the federal government for broadband infrastructure.
The broadband map’s release follows an effort that began in September to give Internet service providers (ISPs) and local governments an opportunity to review and challenge broadband data findings. That followed an initial FCC broadband data collection process that began in June. IEEE Techblog summarized that and more in this post.
“Today is an important milestone in our effort to help everyone, everywhere get specific information about what broadband options are available for their homes, and pinpointing places in the country where communities do not have the service they need,” said Chairwoman Rosenworcel. “Our pre-production draft maps are a first step in a long-term effort to continuously improve our data as consumers, providers and others share information with us. By painting a more accurate picture of where broadband is and is not, local, state, and federal partners can better work together to ensure no one is left on the wrong side of the digital divide.”
The public will be able to view the maps at broadbandmap.fcc.gov and search for their address to see information about the fixed and mobile services that internet providers report are available there. If the fixed internet services shown are not available at the user’s location, they may file a challenge with the FCC directly through the map interface to correct the information.
Map users will also be able correct information about their location and add their location to the map if it is missing. The draft map will also allow users to view the mobile wireless coverage reported by cellular service providers.

The FCC also announced the launch of an updated version of the FCC Speed Test App that will enable users to quickly compare the performance and coverage of their mobile networks to that reported by their provider. The app allows users to submit their mobile speed test data in support of a challenge to a wireless service provider’s claimed coverage.
Today’s debut marks the start of the public’s ability to offer challenges as well. The FCC has asked for challenges to the map data to be submitted between now and January 13, 2023, so that corrections can be included in a finalized version of the map.
The final version of the map will be used to distribute funding from the Broadband, Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program in summer 2023. As determined by the Department of Commerce last year, each state will get an initial $100 million from the $42.5 billion BEAD program, with additional funding to be distributed based on the number of unserved and underserved locations, according to the new national broadband map.
Members of the public, along with local governments and providers, will now be able to submit two different types of challenges: location (for example, incorrect location address, incorrect location unit count, etc.) and availability (for example, if the map incorrectly lists a certain provider or broadband technology as available).
While the FCC will continue collecting crowdsourced speed data for fixed speeds, that data is not part of the challenge process. Rather, the map is relying on maximum available advertised speeds.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-releases-new-national-broadband-maps
https://broadbandmap.fcc.gov/home
Additional information sources:
- New users can download the FCC Speed Test App in both the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
- Existing app users should update the app to gain these new features.
- A video tutorial and more information on how to submit challenges is available at fcc.gov/BroadbandData/consumers.
- For more information about the BDC, please visit the Broadband Data Collection website at fcc.gov/BroadbandData.
Cable One invests $50 million in Ziply Fiber after its JV called Clearwire Fiber
Cable One [1.] has invested $50 million to acquire a minority stake in northwestern U.S. wireline network operator Ziply Fiber [2.]. Although the investment was made on September 6th, it was first announced Thursday November 3rd when Cable One Chair and CEO Julie Laulis revealed the investment during the company’s Q3 2022 earnings call. She referred to Ziply Fiber as Cable One’s “newest strategic growth partner.” A Ziply representative confirmed the sum from Cable One was part of the $450 million in new funding it announced on September 8th.
Note 1. Cable One is an American broadband communications provider. Under the Sparklight brand, it provides service to 21 states and 900,000 residential and business customers. It is headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona, though it does not serve that metro area.
Note 2. Ziply Fiber was formed from the acquisition of Frontier Communications operations in Washington, Oregon and Montana. Ziply has an ambitious fiber buildout/upgrade plan with the launch of symmetrical, multi-gigabit broadband speed tiers.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In a 10-Q filing, Cable One stated it invested an initial $22.2 million in Ziply in November 2022 and expects to invest the remaining $27.8 million before the end of September 2023. Its investment netted the company less than a 10% equity interest in Ziply.
“We are investing alongside proven operational and financial leaders that we have maintained long-term trusted relationships with and they continue to demonstrate the ability to deliver strong results and shareholder returns that align with our rigorous standards,” a Cable One spokesman told Light Reading.


Other highlights from Cable One’s Q3-2022 results and earnings call:
- Total revenues were $424.7 million in the third quarter of 2022 compared to $430.2 million in the third quarter of 2021. Year-over-year, residential data revenues increased 6.3% and business services revenues decreased 11.5%. Revenues for the third quarter of 2022 included $4.9 million from CableAmerica(1) operations. Revenues for the third quarter of 2021 included $16.3 million from operations that were contributed to Clearwave Fiber(1) and from the Divested Operations, of which a substantial majority consisted of business services revenues.
- Net income was $70.6 million in the third quarter of 2022, an increase of 35.1% year-over-year. Adjusted EBITDA was $224.6 million in the third quarter of 2022, an increase of 1.9% year-over-year. Net profit margin was 16.6% and Adjusted EBITDA margin(2) was 52.9%.
- Revenues decreased $5.5 million, or 1.3%, to $424.7 million for the third quarter of 2022 due primarily to the contribution of operations to Clearwave Fiber and the disposition of the Divested Operations during 2022 that collectively generated $16.3 million of revenues in the prior year quarter, predominantly consisting of business services revenues, and decreases in residential video and residential voice revenues. The decrease was partially offset by increases in higher margin residential data and business services revenues from continuing operations and the addition of CableAmerica operations.
- Cable One, like other cable operators, is seeing a slowdown in consumer move activity across its footprint. The operator posted an organic gain of just 1,800 broadband subs in the quarter, according to MoffettNathanson, a division of SVB Securities.
- Sell-in for 1-Gig service has accelerated to nearly 32%.
- Cable One’s average revenue per user (ARPU) rose 15%, to $80.46, as customers migrated to faster, higher-priced services or took an unlimited data plan.
- Rate increases are “absolutely on the table,” Laulis said.
- Average data usage reached about 580 gigabytes per month in Q3, up 19% year-over-year.
- Cable One, which has DOCSIS 4.0 on its roadmap, has tested symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds, but did not say when it might launch such services.
- FWA adoption in Cable One’s markets “remains low,” Laulis said.
- Video losses hit 18,000, widened from a year-ago loss of 8,000. Reflecting Cable One’s de-emphasis on video and its laser-focus on broadband, the company’s video base eroded by another 28% year-over-year.
At the start of 2022, Cable One along with three private equity companies formed a joint venture called Clearwave Fiber, aiming to reach 500,000 rural locations by 2027. Cable One contributed assets from its Illinois-focused Clearwave Communications and South Carolina-based Hargray Communications businesses as part of the deal. Shortly after its formation, Clearwave Fiber acquired the assets of Kansas-based operator RG Fiber to gain a foothold in the state.
Earlier this week, Clearwave Fiber revealed it has already crossed the 100,000 passings mark. By the end of this year, the company said its services will be available in a total of 35 markets across four states: Illinois, Kansas, Georgia and Florida.
References:
Cable One joint venture to expand fiber based internet access via FTTP
Ziply Fiber deploys 2 Gig & 5 Gig fiber internet tiers in 60 cities – AT&T can now top that!
Frontier Communications and Ziply Fiber to raise funds for fiber optic network buildouts
https://www.lightreading.com/cable-tech/cable-one-invests-$50m-in-ziply-fiber/d/d-id/781591
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/broadband/cable-one-doubles-down-fiber-50m-ziply-investment
LightCounting: Optical components market to hit $20 billion by 2027+ Ethernet Switch ASIC Market Booms
|
The optical communications industry entered 2020 with very strong momentum. Demand for DWDM, Ethernet, and wireless fronthaul connectivity surged at the end of 2019, and major shifts to work-at-home and school-at-home in 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic created even stronger demand for faster, more ubiquitous, higher reliability networks.
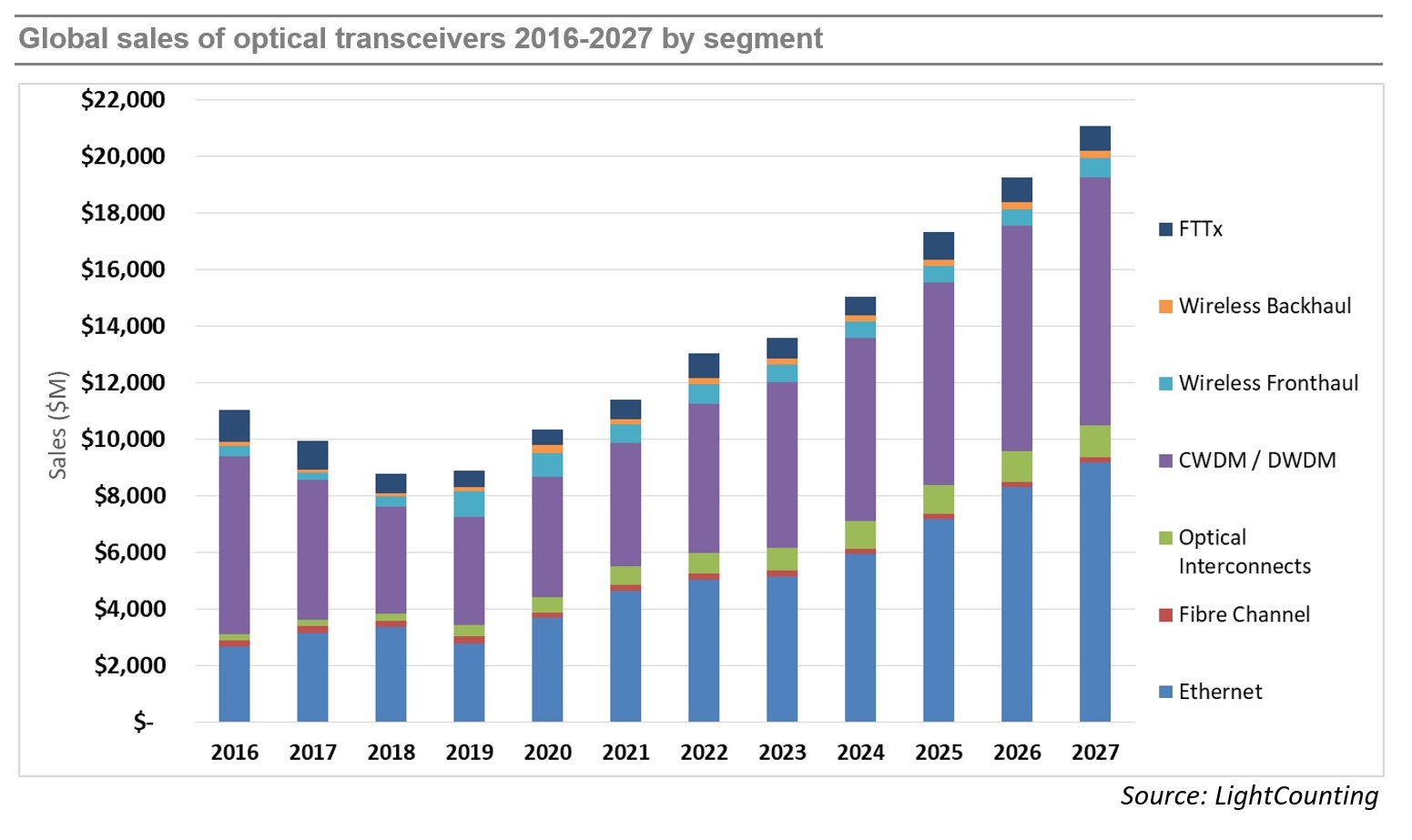
While supply chain disruptions continued, the industry was able to largely overcome them, and the market for optical components and modules saw strong growth in 2020 and 2021, as shown in the figure below. Light Counting believes the transceiver market is on track for another year of strong (14%) revenue growth in 2022, after increasing by 10% in 2021, and 17% in 2020. However, market growth is projected to slow to 4% in 2023, prior to recovering in 2024-2025.
Demand for optics is strong across all market segments, but continuing bottlenecks in the global supply chain negatively impacted sales of 400G DR4 and 100G DR1+ transceivers to Amazon in the first 9 month of 2022. Meta increased its deployments of optics sharply this year, but its latest forecast for 2023 has been reduced substantially. We suspect that Amazon and other cloud companies may moderate their investments in 2023, if the current economic slowdown continues to negatively impact their advertising, streaming, and retail businesses.
|
  |
|
LightCounting’s latest forecast projects a 11% CAGR in 2022-2027, not very different from the 13% CAGR in the forecast published in October 2021. Strong sales of DWDM and Ethernet optics accounted for most of the market growth in 2021 and these segments are projected to lead the growth in 2022-2027. Sales of optical interconnects, mostly Active Optical Cables (AOCs), will also increase at double digit rates over the next 5 years. PON sales for FTTx networks will remain steady, as the China market ends its 10G cycle and North America and Europe ramp up 10G PON deployments, driven by government funding programs. 25G and 50G PON provide new growth later in the forecast period. Wireless fronthaul is one area of weakness, since 5G network deployments in China are reaching completion. This segment will return to growth in 2026-2027 with the onset of 6G deployments (which we don’t think will happen till many years later).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
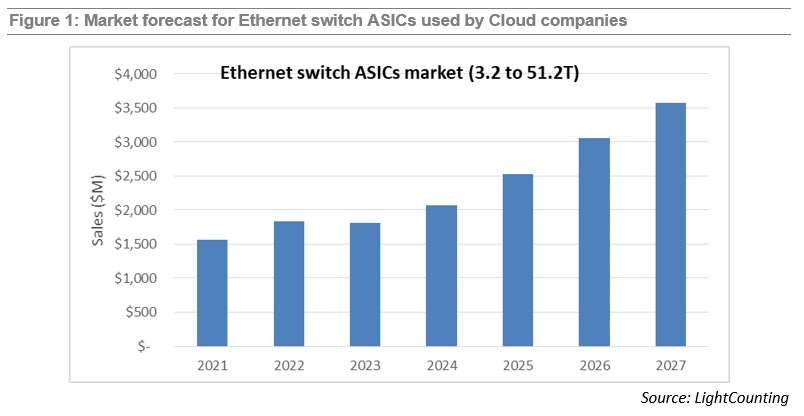
Demand for Ethernet switches from Cloud companies created a new market segment for very high bandwidth switches and switch ASICs. It also transformed the industry supply chain as Cloud companies started using internally designed Ethernet switches and opening these “white box” designs to a broader community. LightCounting’s report on Ethernet switch ASICs was first published in April 2022, and today the first update has been released. The report covers the most interesting segment of the switching ASIC market – high bandwidth (3.2T and above), low latency chips deployed in Cloud datacenters. The report offers brief profiles of the leading suppliers of merchant switch ASIC and system integrators, offering products to Cloud companies, and includes a forecast for sales of 3.2 to 51.2T switch ASICs. The updated report now includes 3.2T/6.4T chips in addition to the higher speed products. This change added close to $1 billion to the total market size compared to our April estimate. The forecast includes chips sold in the merchant market as well as chips used by Cisco in their own equipment (captive market). A lower forecast for 2023 compared to our April 2022 edition reflects reduced guidance by the leading Cloud companies for datacenter upgrades planned for next year. Despite a reduced forecast, the overall market is expected to roughly double in size from $1.8 billion in 2023 to $3.6 billion in 2027.
References:
|
Highlights of GSA Private-Mobile-Networks August 2022 report
A new report by the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), the Private-Mobile-Networks August 2022 report, has identified 66 MNO’s and 70 countries/territories where organisations are involved with private mobile network projects. This equates to 889 organisations deploying LTE or 5G Private Mobile Networks (PMN) in one or more locations – up from 794 reported in June 2022.
Manufacturing is the major adopter of Private Mobile Networks with 165 identified companies, growth of almost 50% from the end of 2021, with other strong interest from education, mining, and power utilities sectors.
LTE is the dominant technology, used in 672 of the private mobile networks for which GSA has data, whilst 5G is being deployed by 354 organisations. 5G Standalone currently accounts for just thirty-seven deployments.
The USA leads the way with the most organisations deploying private networks based on LTE or 5G, followed by Germany, China, the UK, and Japan.
Joe Barrett, President of the Global mobile Suppliers Association called private mobile networks a microcosm of the wider 4G and 5G ecosystem and reported “a strong positive correlation between liberalised spectrum and the adoption of private mobile networks.”
An executive summary of the report is available from the GSA website based on dataset of over 50 equipment vendors, 66 operators and 70 countries and territories.
References:
https://totaltele.com/private-mobile-network-deployments-now-in-70-countries/
5G Optical Transceiver Market Trends and Technologies
by Fayre Fan (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
The fiber optic transceiver is the core component of optical communications. It is used to realize optical-to-electrical conversion. The transmitter converts the electrical signal into an optical signal, while the receiver does the reverse – it converts the optical signal into an electrical signal.
Increasingly, fiber optics is being used for the transport of 5G signals to and from the edge of the carrier’s wide area network. Optical transceivers are the basic component of 5G backhaul, midhaul and fronthaul. Their cost accounts for 50%~70% of the total 5G network costs.
Low cost is the key appeal of the 5G optical transceivers. The industry has carried out extensive research on 5G optical module technology, and currently, there are many solutions.
Increasing demands for 5G transceivers: low cost is the key to 5G optical module:
The growth of optical modules in the 5G network mainly comes from three factors:
- More base stations are needed in the high-frequency band.
- Larger bandwidth is required for high-speed rates.
- More connections are required for added midhaul transmission links.
Global top suppliers of 5G base stations include Huawei (China), Ericson (Sweden), Nokia (Finland), ZTE (China), and Samsung (Korea). China is the largest 5G market, which has captured about 74% of the market, followed by Korea and Europe.
The development of the global 5G network market stimulates the increasing demand for 5G optical transceivers. According to the forecast data from Lightcounting, the global market share of 5G fronthaul transceivers will reach 657/632/593 million dollars in 2022~2024. 5G midhaul and backhaul transceivers will reach 242/245/247 million dollars respectively. Therefore, reducing cost is a key objective of 5G transceiver development. Here’s an illustration of backhaul, midhaul and fronthaul:


5G fronthaul -demand for 25G BiDi transceiver:
In the 4G fronthaul network, the most commonly used transceivers are single-mode 10G duplex transceivers. 5G network has higher requirements for the data rate and optical interface of transceivers. In consideration of saving fiber resources and maintaining high-precision synchronization of uplink and downlink, the simplex bi-directional (BiDi) transceiver allowing data transmitting and receiving over one single fiber, is superior to duplex transceivers. Moreover, considering the 5G download rate is at least 10 times higher than that of the 4G network, the 25 Gbit/s data rate is also necessary for the 5G fronthaul transceivers. Taken together, 25G BiDi transceivers are needed for 5G fronthaul networks.
Optical Transceivers for 5G Front-Haul
| Data Rate | Form Type | Transmission Distance | Wavelength | Modulation Format | Transmitter & Receiver |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 70~100m | 850nm | NRZ | VCSEL+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 300m | 1310nm | NRZ | FP/DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 10km | 1310nm | NRZ | DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 BiDi | 10/15/20km | 1270/1330nm | NRZ/PAM4 | DFB+PIN/APD |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 10km | CWDM | NRZ | DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | Tunable SFP28 | 10/20km | DWDM | NRZ | EML+PIN |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 70~100m | 850nm | NRZ | VCSELs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | 4WDM-10 | NRZ | DFBs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | 1310nm | PAM4/DMT | EML+PIN |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 10km | CWDM4 | NRZ | DFBs+PINs |
5G midhaul and backhaul – demand for 50G/100G/200G/400G transceivers:
The 5G midhaul and backhaul are mainly carried through the metro access layer, convergence layer, and core layer. For the access layer, 50G/100G transceivers are commonly used. For example, 50G PAM4 transceiver is a cost-effective solution for 5G midhaul and backhaul. It is based on 25G optical components and PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4-level) modulation. For the convergence layer and core layer, 100G/200G/400Gb/s DWDM transceivers are mainly used. And low-cost coherent 100G/200G/400G transceivers are welcomed, which mainly use QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation and DSP (Digital Signal Processing) technology.
Optical Transceivers for 5G Mid-Haul/Back-Haul
| Data Rate | Form Type | Transmission Distance | Wavelength | Modulation Format | Transmitter & Receiver |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 40km | 1310nm | NRZ | EML+APD |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28/SFP56 | 10km | 1310nm | PAM4 | EML/DFB+PIN |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 10km | 1270/1330nm | PAM4 | EML/DFB+PIN |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28/SFP56 | 40km | 1330nm | PAM4 | EML+APD |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 40km | 1295.56/1309.14nm | PAM4 | EML+APD |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | CWDM/LWDM | NRZ | DFBs/EMLs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 40km | LWDM | NRZ | EMLs+APDs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10/20km | DWDM | PAM4/DMT | EMLs+PINs |
| 100/200/400Gbit/s | CFP2-DCO | 80~120km | DWDM | PM QPSK/8-QAM/16-QAM | IC-TROSA+ITLA |
| 200/400Gbit/s | OSFP/QSFP-DD | 2/10km | LWDM | PAM4 | EMLs+PINs |
Technological innovations of 5G transceivers:
Optical transceiver-related technology mainly includes packaging technology and optoelectronic components technology.
In terms of packaging technology, 5G transceivers can adopt existing mature packaging technologies. For example, since 25G BiDi has a similar optical structure to that of 10G BiDi, the common TO-CAN (transistor-outline-can) package can be used to save cost.
The most vital technological innovation aims at optoelectronic components technology. The technological innovation of optoelectronic devices mainly aims at these goals: function expansion, data rate increase, and cost reduction.
Function expansion innovation of laser chips example: industrial-grade laser chips no longer require temperature control devices, the laser chip used in the non-airtight environment no longer requires the expensive airtight package, the laser chip with a small divergence angle no longer requires an expensive non-spherical lens, anti-reflection laser chips no longer require isolators, etc. Those technologies simplify the packaging of the optical module, also providing higher reliability and lower cost.
Data rate increase innovation includes example: the 50G PAM4 optical module uses a 25G baud rate laser/detector, and an electrical chip with high linearity. Compared with the 25G NRZ (non-return to zero) optical module, it allows for higher bandwidth.
Cost reduction innovation example: coherent 100G transceiver, it reduces the cost on the premise of meeting the transmission distance requirement within 200km.
Ultimately, the key technologies of 5G optical modules are mainly reflected in the innovation of optoelectronic chips. The specific technologies include:
- Industrial temperature grade high-speed laser chip technology
- High linearity 25G baud rate DFB chip and EML chip technology
- Low-cost 25G wavelength tunable laser chip technology
- Low-cost coherent 100G/200G/400G optical transceiver technology
For example, Marvell and OE Solutions recently announced a collaboration to deliver the industry’s first production-ready 100G QSFP-DD optical modules optimized for 5G backhaul and Metro Access applications.
In conclusion, 5G optical transceivers will play a more important role in the entire optical module market compared with the 4G era. Technological innovation will be the main driver to realize the low-cost 5G optical modules.
References:
https://www.researchreportsworld.com/global-5g-base-station-sales-market-21017689