NEC and Mavenir collaborate to deliver 5G Open vRAN platform
NEC Corp. and Mavenir entered a collaboration agreement to deliver a 5G Open virtualized RAN (vRAN) platform to the Japanese enterprise market. This move will open up Local/Private 5G Network opportunities for enterprises, regional authorities and other organizations, according to the companies.
Under this collaboration, NEC and Mavenir said they will jointly work on 5G Open vRAN and Local 5G business developments and create a simple and cost-efficient ecosystem in the market. The collaboration will bring together NEC’s expertise in IT, network and system integration and Mavenir’s cloud-native network technology.
Editor’s Note:
Moving to a virtual RAN (vRAN) may offer operators important benefits, including a reduced capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operational expenditure (OPEX) over time. Additionally, RAN transformation can be boosted by network functions virtualization (NFV) technology, which changes the typical network architecture from hardware-based to software-defined infrastructure and decouples the baseband functions from the underlying hardware. In turn, the architecture is more flexible, agile, and easier to maintain, allowing operators to launch new services to market faster than ever before.
Cisco created and announced Open vRAN at Mobile World Congress 2018. Conversations with key network operator customers, as well as our partners, made it apparent that something needed to change and they thought we could help. Since then, it’s been a whirlwind ride – working with customers to better define this future and the key elements, building solutions with our partners, innovating in the market to explore new service designs, and contributing to the process of defining industry specifications.
On that last topic, sometimes there is a little confusion between Open vRAN and O-RAN due to the similar names and similar principles. The naming similarity was coincidental, but not surprising, given both are fairly descriptive of the opportunity. O-RAN (Open RAN Alliance) describes themselves well on their website: “The O-RAN Alliance was founded by operators to clearly define requirements and help build a supply chain eco-system to realize its objectives.” They have extensive details available on their website and in their whitepaper.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Mavenir delivers an Open vRAN platform that provides strategic differentiation by enabling multi-source Remote Radio Units (RRUs) to interwork with the virtualized, containerized, Cloud Base Band software over Ethernet Fronthaul (FH), using the O-RAN open interface, overcoming the traditional constraints of the proprietary walled garden specifications used by the other traditional equipment vendors.

“We are excited to collaborate with NEC, as we move together toward open, virtualized networks,” said Pardeep Kohli, Mavenir’s President and CEO. “Mavenir’s vRAN and NEC’s radio naturally come together to quickly and easily bring new and innovative solutions to the Japanese Enterprise Market.”
NEC actively promotes an open, virtualized infrastructure model in support of the 5G era, using IT, orchestration and network expertise. Moreover, the NEC ecosystem contributes to vRAN via inter-operability testing between multiple vendors’ equipment that is compliant with O-RAN fronthaul specifications.

“The combination of advanced assets and expertise from Mavenir and NEC will enable us to offer end-to-end one-stop 5G Open vRAN and Local/Private 5G solutions, including an advanced 5G network solution for the ecosystem, and vertical solutions that meet the needs of a great variety of Enterprise customers.” said Nozomu Watanabe, senior vice president at NEC.
This joint collaboration will continue to provide value-added products for customers worldwide. An overview of this collaboration will be introduced during MWC Barcelona 2020 (assuming the event is not cancelled as is rumored now) at the NEC booth, Hall 3, 3M30.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Mavenir:
Mavenir is the industry’s only end-to-end, cloud-native Network Software Provider focused on accelerating software network transformation and redefining network economics for Communications Service Providers (CSPs) by offering a comprehensive end-to-end product portfolio across every layer of the network infrastructure stack. From 5G application/service layers to packet core and RAN, Mavenir leads the way in evolved, cloud-native networking solutions enabling innovative and secure experiences for end users. Leveraging industry-leading firsts in VoLTE, VoWiFi, Advanced Messaging (RCS), Multi-ID, vEPC and OpenRAN vRAN, Mavenir accelerates network transformation for more than 250+ CSP customers in over 140 countries, which serve over 50% of the world’s subscribers.
We embrace disruptive, innovative technology architectures and business models that drive service agility, flexibility, and velocity. With solutions that propel NFV evolution to achieve webscale economics, Mavenir offers solutions to help CSPs with revenue generation, cost reduction, and revenue protection. Learn more at www.mavenir.com
References:
https://mavenir.com/press-releases/nec-and-mavenir-deliver-5g-open-vran-solution/
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/nec-mavenir-collaborate-to-deliver-5g-open-vran-platform–1326379
https://blogs.cisco.com/sp/the-open-vran-wave-is-building
Point Topic: Fixed Broadband Tariff Report for Q4 2019
|
U.S. District Judge approves T-Mobile- Sprint merger; New T-Mo will be #2 wireless carrier in U.S.
A federal judge has ruled in favor of T-Mobile USA’s merger with Sprint, despite evidence presented that showed the deal will likely erode competition, raise U.S. wireless data prices, and result in significant layoffs as redundant jobs are eliminated. U.S. District Judge Victor Marrero concluded the T-Mobile USA merger with Sprint, worth $26 billion when it was struck two years ago, wasn’t likely to substantially lessen competition, and rejected the main arguments by a group of states seeking to block the deal as anti-competitive. The judge praised T-Mobile in his ruling, calling it “a maverick that has spurred the two largest players in its industry to make numerous pro-consumer changes” and describing its business strategy as “undeniably successful.
Judge Marrero wrote:
“While Sprint has made valiant attempts to stay competitive in a rapidly developing and capital-intensive market, the overwhelming view both within Sprint and in the wider industry is that Sprint is falling farther and farther short of the targets it must hit to remain relevant as a significant competitor.”
“Finally, the FCC and DOJ have closely scrutinized this transaction and expended considerable energy and resources to arrange the entry of Dish as a fourth nationwide competitor, based on its successful history in other consumer industries and its vast holdings of spectrum, the most critical resource needed to compete in the RMWTS markets.”
“Dish’s statements at trial persuade the court that the new firm will take advantage of this opportunity, aggressively competing in the RMWTS markets to the benefit of price-conscious consumers and opening for consumer use a broad range of spectrum that had heretofore remained fallow.”
The two companies said they would move forward to finalize their long-delayed merger. The deal’s current terms offer Sprint shareholders new stock equal to 0.10256 of one T-Mobile share.
“Today was a huge victory for this merger… and now we are FINALLY able to focus on the last steps to get this merger done!” cheered T-Mobile CEO John Legere (pictured below) in a press release.

The states might decide to appeal the ruling and another U.S. district judge in Washington must approve the existing Justice Department arrangement. Letitia James, New York’s attorney general, said the states disagreed with the decision and would review their options. “There is no doubt that reducing the mobile market from four to three will be bad for consumers, bad for workers and bad for innovation,” Ms. James said.
The two companies also need clearance from California’s Public Utilities Commission and face a private antitrust suit challenging the merger. A judge in the Northern District of California ruled in January 2020 that the case could proceed if the carriers overcame the state-led challenge.
T-Mobile and Sprint hope to close the merger by April 1st. The two telcos have spent more than seven years pursuing a combination in some form. They abandoned previous attempts in 2013 and 2017 before their boards struck an agreement in early 2018 that would allow T-Mobile to take over its smaller rival, creating a company closer in size to Verizon and AT&T.
The new T-Mobile would be a formidable rival to Verizon and AT&T, the two largest wireless carriers in the country. In fact, the total number of “New T-Mobile” wireless subscribers will be more than AT&T currently has.
The “New T-Mobile” will be strengthened by a massive stockpile of wireless radio licenses held by Sprint. Those spectrum holdings allow the new company to serve more customers with high-speed internet service on the go, putting pressure on AT&T and Verizon to match them as carriers upgrade to faster 5G mobile networks.
The court victory also benefits T-Mobile parent Deutsche Telekom AG and Japan’s SoftBank Group Corp., Sprint’s majority owner. SoftBank Chairman Masayoshi Son, a billionaire investor who upended the telecom business in Japan, had been seeking a way to rescue an investment that proved less successful in the U.S.
Tuesday’s court verdict will test the idea that three big players will compete as effectively as four did. Dish enters the market with fewer customers than Sprint, making it a distant No. 4 in the consumer-cellular business.
Dish Chairman Charlie Ergen testified during the trial that his Englewood, Colo., company was better equipped to compete than Sprint. His new wireless service will ride over T-Mobile’s network at first, though customers will eventually use a new cellphone system Dish is required to build over seven years.
Quotes from opponents of the deal:
“We are profoundly disappointed that the judge approved a merger that will harm communities of color and low-income communities across California,” said Greenlining Institute Technology Equity Director Paul Goodman, in a statement.
“While the court may think it unlikely for a newly entrenched trio of enormous wireless carriers to collude rather than compete, the history of broken and abandoned merger promises from these companies – to say nothing of the mountains of evidence and expert analysis in this trial – say otherwise,” said Free Press Vice President of Policy and General Counsel Matt Wood, in a statement.
“The Rural Wireless Association disagrees with Judge Marrero’s decision to approve this deal, which has been consistently and drastically altered from what was originally proposed in early 2018, and now includes Dish, a company that has zero experience operating as a facilities-based mobile wireless carrier network as the savior for wireless competition,” the association said in a statement.
Quotes from supporters of the deal:
“I’m pleased with the district court’s decision. The T-Mobile-Sprint merger will help close the digital divide and secure United States leadership in 5G,” said FCC Chairman Ajit Pai in a statement.
“We appreciate Judge Marrero’s thorough evaluation of this merger. The ruling, in addition to the DOJ and FCC approvals, accelerates our ability to deploy the nation’s first virtualized, standalone 5G network and bring 5G to America,” said Dish Network’s Charlie Ergen in a statement. “We are eager to begin serving Boost customers while aggressively growing the business as a new competitor, bringing lower prices, greater choice and more innovation to consumers. We look forward to the Boost employees and dealers joining the Dish family.
Analyst Opinions:
“This is clearly a big win for T-Mobile, which will now how [sic] a superior spectrum position which it can use to launch 5G and handle even higher growth,” wrote the Wall Street research analysts at Lightshed in a post. “We also see this as a big win for Dish based on what we have learned about its MVNO terms. It’s not great news for Verizon, given that it removes Sprint and Dish’s spectrum as an alternative, created a new competitor in Dish and has empowered T-Mobile with the tools to deliver a superior network experience to consumers.”
“We view a deal as initially negative to AT&T/Verizon despite our view that consolidation should help to further rationalize the competitive/pricing environment long term considering T-Mobile is likely to be aggressive at least early on to help validate the premise of the deal which is it will result in more favorable pricing for consumers,” wrote the Wall Street analysts at Cowen in a note to investors.
“Dish will need to execute on a myriad of levels including building a cloud-native nationwide network followed by the operational challenges that come with competing against three very well entrenched wireless players,” the Cowen analysts added.
“The wireless industry is going to get tougher. Cable would have had a much easier time sucking subscribers out of Verizon and AT&T in a four-carrier market with a capacity constrained T-Mobile. Now they are going to have to fight T-Mobile for every one of those subs, and industry pricing is likely headed lower,” wrote the Wall Street analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors.
However, the New Street analysts pointed out that cable companies may also see some silver lining in the merger of Sprint and T-Mobile, if it is ultimately approved. “Cable will have one more company competing for its MVNO business. We have been surprised the companies haven’t announced new MVNO terms with Verizon or AT&T; negotiations were in full force in October / November last year. Perhaps they have been waiting to see what T-Mobile might offer them if the deal went through. Altice will be the most immediate winner; their MVNO with Sprint now moves to a much better network.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Addendum from Robin Hood Snacks:
|
Here’s the history of this complex courtship:
Sprint has been lagging rivals for a while… so the judge doesn’t think this deal will substantially hurt competition. Plus, regulators will make sure that Dish Network enters the game as a viable new service provider. Sprint will have to sell Dish 9M customers, but that’ll still be a distant competitor to the Big 3. |
|
THE TAKEAWAY
|
|
We have a three-opoly on our hands… Here’s the pecking order now: Verizon #1, New T-Mobile #2, and AT&T #3. And a three-opoly could affect your bill:
|
Verizon enters 5G market in Europe with London tech lab to open this April
Verizon Communications plans to advance its 5G efforts by opening a 5G tech lab in London this April as a way of displaying the services the company can offer. The production studio and showroom, Verizon’s first outside the U.S., is also aimed at attracting partners for 5G-related projects. The new Verizon lab will showcase services enabled by 5G wireless broadband and invites partners to collaborate on developing new ways to use it. The studio will use 5G to speed up data-intensive content production like motion-capture for entertainment and marketing. It’s all part of the company’s bet on the new tech.
- New facility offers first Verizon 5G-enabled development and collaboration space outside the United States
- Showcases existing 5G use cases and experiences & offers co-creation space for 5G-enabled application development
- 5G-enabled production studio brings next-generation content experiences to Verizon Media customers
- European investment enables Verizon to more easily share 5G leadership and expertise with companies based outside the U.S.
- Co-located Verizon Business & Media expertise offers unique, holistic approach to both 5G infrastructure & content
“Verizon has proven expertise in delivering 5G in the U.S.,” said Tami Erwin, Group CEO, Verizon Business. “One of the best ways of unleashing the true possibilities of 5G is getting it into the hands of innovators and visionaries. Our London facility enables our international customers to benefit from this expertise as they look to deploy 5G-enabled applications and experiences.”
“We’ve pretty much bet the company on this — it’s not like we’re dabbling,” said Toby Redshaw, vice president of innovation at Verizon’s business unit.
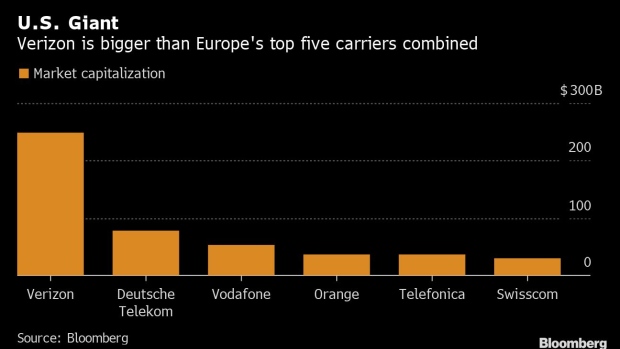
The outlook is still early, uncertain and competitive for these 5G services. And European carriers will have significant home field advantages: they already have relationships with the continent’s biggest businesses, local cultural and regulatory know-how, and own more local network assets.
But Redshaw says Verizon’s advantages include a head start from testing 5G in the field for years back in the U.S., and its larger scale. He was visiting London for the lab’s opening and to woo prospective clients, and said he’s had recent conversations with a Formula One team and other businesses. The company said the fresh London investment is “significant” but declined to give a number.
Examples of tech on display include cybersecurity visualization software, which lets a user fly around a virtual 3D landscape that represents their company’s network to spot potential anomalies. A service called BriefCam can instantly crunch reams of video and apply searches for a range of objects, such as all the red cars in a day’s worth of traffic footage, something a police force could find useful.
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-expands-international-5g-ecosystem
https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/verizon-muscles-into-europe-s-5g-race-with-u-k-outpost-1.1387674
Importance of FCC C Band Auction for 5G in the U.S.
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai has described the commission’s plan for its auction of a portion of the C-band — the 4Ghz to 8GHz radio frequencies used mostly for consumer satellite transmissions, but in the future for 5G mobile broadband.
The FCC wants to auction off the bottom 280MHz (the 3.7 – 4.2Ghz range) of the C-band and reserve 20Mhz of the band above that threshold for further needs. Both the FCC and current satellite operators say this will still leave enough spectrum for the operators to provide the same level of service that we have today.
The C-band is a valuable block of very underutilized spectrum. Portions of it are also a great addition to mobile operators who want to roll out 5G using the mid-band spectrum.
The 3.7 to 4.2Ghz range of the C band would offer a great balance of range and capacity which is important when carriers want to offer any real nationwide 5G service. A combination of low-band, mid-band, and upper millimeter-wave bands would offer carriers plenty of spectrum to maintain existing networks and add 5G expansion from coast to coast, and that’s what carriers and the current FCC wants to see happen.
Executives from Verizon, AT&T and T-Mobile stated their support for Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Ajit Pai’s proposal to get C-band spectrum cleared and available for a public auction, a plan that immediately saw backlash from some senators and public interest groups.
The network operators’ support isn’t surprising given they’ve been pressing for more mid-band spectrum for 5G and lobbying for quick action on C-band spectrum specifically, but they’re all coming at it from different places.
Currently, four satellite operators provide the majority of C-band satellite service in the U.S. — Intelsat, SES, Eutelsat, and Telesat. These are the companies that provide the actual satellite broadcast that you might be paying another company for and reach well over 100 million homes.
The satellites and ground equipment need to be changed so that they use the upper 200MHz of the C-band to transmit at the same level of service we’re all used to. The cost of this relocation is expected to be in the $3 billion to $5 billion range and will be covered by the auction winners.
The FCC would like this relocation, which is expected to be finished by September 2025, to be expedited. It proposes what chairman Pai calls “accelerated relocation payments.” These would also be paid by the winning bidders, but only if the satellite operators meet a specific schedule: free the lowest 100MHz of the spectrum by September 2021 and the remaining 180MHz by September 2023. Should this occur, the fees would include these expedition bonuses and rise to $9.7 billion.
Chairman Pai says that this is almost necessary if the U.S. wants to be competitive with the rest of the world when it comes to 5G:
“It is in the public interest to make available frequency in the C-band as quickly as possible as part of a national priority to promote American leadership in 5G. To get the job done quickly, we need to align the private interest of satellite companies with the public interest.”
Pai also notes that these are simply FCC proposals and that Congress can overrule any or all of them.
While acknowledging that Congress can have the final say, Pai also stated the regulations that allow the FCC to make these decisions.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Section 316 of the Federal Communications Act grants authority to modify any licenses granted to current holders of C-band spectrum, section 309 allows the FCC to auction the lower 280MHz of the spectrum for “flexible” use, section 303 allows the FCC to set new rules and regulations for the technical usage of the C-band, and Title 3 allows the FCC to require the auction winners to pay any and all relocations fees.
Pai also suggested that he hopes Congress will make a small override to the proposed FCC recommendations and offer 10% of the proceeds to rural broadband initiatives. This is a promise Pai has made and championed for since placed as FCC chair, yet so far we’ve seen no movement from carriers or to regulations.
If there is to be any real nationwide 5G network that’s reliable and stand-alone, we’ll have to see plenty of spectrum reallocation. Some, like this news, will be authorization for new use cases and others will be carriers repurposing existing holdings. It will take a lot of work before any country has a full 5G nationwide network.
References:
https://www.multichannel.com/news/c-band-auction-timetable-plan-faces-challenges
T-Mobile Earnings Beat + 5G Network Status + 600 MHz and Spectrum Position
T-Mobile US beat analysts’ estimates for quarterly revenue and profit on Thursday, as the wireless carrier added more mobile phone subscribers to its monthly plans, some of which come bundled with a Netflix Inc service.
The third-largest U.S. wireless carrier by subscribers has been awaiting a decision on its proposed merger with Sprint Corp. The two U.S. telcos delivered closing arguments in a federal court last month against a multi-state lawsuit that argues the merger will increase prices for the consumers.
T-Mobile’s fourth-quarter net income rose to $751 million from $640 million, a year earlier. Excluding items, the company earned 87 cents, beating analysts’ average estimate of 83 cents. Revenue rose to $11.88 billion from $11.45 billion, edging past analysts’ average estimate of $11.83 billion, according to IBES data from Refinitiv.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Highlights from the T-Mobile Investor Factbook website:
Strong Customer Growth:
• 1.9 million total net additions in Q4 2019 – 7.0 million in 2019 – 6th year in a row of more than 5 million total net additions
• 1.3 million branded postpaid net additions in Q4 2019, best in industry – 4.5 million in 2019, best in industry
• 1.0 million branded postpaid phone net additions in Q4 2019, best in industry – 3.1 million in 2019, best in industry
• 77,000 branded prepaid net additions in Q4 2019 – 339,000 in 2019
• Branded postpaid phone churn of 1.01% in Q4 2019, up 2 bps YoY – 0.89% in 2019, down 12 bps from 2018
First Nationwide 5G Network:
• Launched the first nationwide 5G network utilizing 600 MHz spectrum, forming the foundational 5G coverage layer for
New T-Mobile; network covers more than 200 million people and more than 5,000 cities and towns
• 4G LTE on 600 MHz now covers 248 million people and 1.5 million square miles
• Currently, more than 33 million 600 MHz compatible devices already on our network
Strong Standalone Outlook for 2020:
• Branded postpaid net additions of 2.6 to 3.6 million
• Net income is not available on a forward-looking basis(2)
• Adjusted EBITDA target of $13.7 to $14.0 billion, which includes leasing revenues of $450 to $550 million
• Cash purchases of property and equipment, including capitalized interest of approximately $400 million, are expected
to be $5.9 to $6.2 billion. Cash purchases of property and equipment, excluding capitalized interest, are expected to
be $5.5 to $5.8 billion
• In Q1 2020, pre-close merger-related costs are expected to be $200 to $300 million before taxes
• Net cash provided by operating activities, excluding payments for merger-related costs and any settlement of interest
rate swaps, is expected to be in the range of $7.9 to $8.5 billion
• Free Cash Flow, excluding payments for merger-related costs and any settlement of interest rate swaps, is expected
to be in the range of $5.4 to $5.8 billion
Total Customers:
• Total net customer additions were 1,863,000 in Q4 2019, compared to 1,747,000 in Q3 2019 and 2,402,000 in Q4 2018. This is the 27th consecutive quarter in which TMobile added more than one million total net customers.
• T-Mobile ended Q4 2019 with 86.0 million total customers, of which 67.9 million were total branded customers.
• For the full-year 2019, total net customer additions were 7,011,000 compared to 7,044,000 in 2018. This was the sixth consecutive year in which total net customer additions exceeded 5 million.
______________________________________________________________
5G NETWORK:
On December 2, 2019, T-Mobile launched America’s first nationwide 5G network, including prepaid 5G with Metro by T-Mobile, covering more than 200 million people and more than 5,000 cities and towns across over 1 million square miles with 5G. In addition, we introduced two new 600 MHz 5G capable superphones, the exclusive OnePlus 7T Pro 5G McLaren and the Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G and anticipate offering an industry-leading smartphone portfolio built to work on nationwide 5G in 2020. This 5G network is our foundational layer of 5G coverage on 600 MHz low-band spectrum.
Should we close our merger with Sprint, we will rapidly deploy 5G on Sprint’s 2.5 GHz spectrum, completing the “layer cake” of spectrum and providing consumers with an unmatched 5G experience. On June 28, 2019, T-Mobile introduced its 5G network using high-band millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum in conjunction with the introduction of our first 5G handset, the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G. The 5G network on mmWave spectrum has been rolled out in parts of seven cities (New York City, Los Angeles, Dallas, Atlanta, Cleveland, Las Vegas and Miami).
600 MHz Spectrum:
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile owned a nationwide average of 31 MHz of 600 MHz low-band spectrum. In total, T-Mobile owns approximately 41 MHz of low-band spectrum (600 MHz and 700 MHz). The spectrum covers 100% of the U.S.
- As of the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile had cleared 275 million POPs and expects to clear the remaining 600 MHz spectrum POPs in 2020.
- T-Mobile continues its deployment of LTE on 600 MHz spectrum using 5G-ready equipment. At the end of Q4 2019, we were live with 4G LTE in nearly 8,900 cities and towns in 49 states and Puerto Rico covering 1.5 million square miles and 248 million POPs.
- Combining 600 and 700 MHz spectrum, we have deployed 4G LTE in low-band spectrum to 316 million POPs.
Currently, more than 33 million devices on T-Mobile’s network are compatible with 600 MHz spectrum.
Spectrum Position:
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile owned an average of 111 MHz of spectrum nationwide, not including mmWave spectrum. The spectrum comprises an average of 31 MHz in the 600 MHz band, 10 MHz in the 700 MHz band, 29 MHz in the 1900 MHz PCS band, and 41 MHz in the AWS band. On June 3, 2019, the FCC announced the results of Auctions 101 (28 GHz spectrum) and 102 (24 GHz spectrum). In the combined auctions, T-Mobile spent $842 million to more than quadruple its nationwide average total mmWave spectrum holdings from 104 MHz to 471 MHz.
- We will evaluate future spectrum purchases in upcoming auctions and in the secondary market to further augment our current spectrum position. We are not aware of any such spectrum purchase options that come close to matching the efficiencies and synergies possible from merging with Sprint.
Network Coverage Growth:
- T-Mobile continues to expand its coverage breadth and covered 327 million people with 4G LTE at the end of Q4 2019.
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile had equipment deployed on approximately 66,000 macro cell sites and 25,000 small cell/ distributed antenna system sites.
Network Capacity Growth:
- Due to industry spectrum limitations (especially in mid-band), T-Mobile continues to make efforts to expand its capacity and increase the quality of its network through the re-farming of existing spectrum and implementation of new technologies including Voice over LTE (“VoLTE”), Carrier Aggregation, 4×4 multiple-input and multiple-output (“MIMO”), 256 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (“QAM”) and License Assisted Access (“LAA”).
- VoLTE comprised 90% of total voice calls in Q4 2019, flat with 90% in Q3 2019 and up from 87% in Q4 2018. Carrier aggregation is live for T-Mobile customers in 969 markets, up from 956 markets in Q3 2019 and 923 in Q4 2018.
- 4×4 MIMO is currently available in 708 markets, up from 683 markets in Q3 2019 and 564 in Q4 2018.
- T-Mobile customers have 256 QAM available across the Un-carrier’s entire 4G LTE footprint.
Source: Opensignal USA Mobile Network Experience Report January 2020, based on data collection period from 9/16/2019 to 12/14/2019 - T-Mobile is the first carrier globally to have rolled out the combination of carrier aggregation, 4×4 MIMO and 256 QAM. This trifecta of standards has been rolled out to 701 markets, up from 674 markets in Q3 2019 and 549 markets in Q4 2018.
- LAA has been deployed to 30 cities including Atlanta, Austin, Chicago, Denver, Houston, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, Philadelphia, Sacramento, San Diego, Seattle, and Washington, DC.
Network Speed:
- Based on data from Opensignal for Q4 2019, T-Mobile’s average download speed was 25.8 Mbps, AT&T at 27.5 Mbps, Verizon at 25.3 Mbps, and Sprint at 23.9 Mbps.
- Based on data from Opensignal for Q4 2019, T-Mobile’s average upload speed was 8.6 Mbps, compared to Verizon at 7.9 Mbps, AT&T at 6.0 Mbps, and Sprint at 2.7 Mbps.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://investor.t-mobile.com/financial-performance/quarterly-results/default.aspx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CHPuI289U-Q&feature=youtu.be
U.S. government & tech companies to create software standards for 5G telecommunications networks
The White House wants U.S. tech firms to collaborate on one or more 5G infrastructure software standard(s). The plan would build on efforts by some U.S. telecom and technology companies to agree on common engineering standards that would allow 5G software developers to run code on machines that come from nearly any hardware manufacturer.
That would reduce, if not eliminate, reliance on Huawei equipment.according to Larry Kudlow, Director of the National Economic Council. That would reduce, if not eliminate, reliance on Huawei equipment. The U.S. contends Huawei has strong links to the Chinese military, making use of its equipment a national-security risk. Huawei has denied such links and says it operates independently of the Chinese government.
“The big-picture concept is to have all of the U.S. 5G architecture and infrastructure done by American firms, principally [1],” Larry Kudlow said in an interview with the Wall Street Journal. “That also could include Nokia and Ericsson because they have big U.S. presences.”
Note 1.: That is highly unlikely to happen, because there are ZERO U.S. firms producing 5G infrastructure. The only non-Asian 5G infrastructure equipment makers are Nokia and Ericsson- both headquartered in Europe. 5G network operators AT&T and Verizon are working with Cloud Service Providers, Microsoft and Amazon, respectively on integration of mobile edge computing with their 5G networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T, Microsoft and Dell [2] are among the companies working with the administration on the project. “Dell and Microsoft are now moving very rapidly to develop software and cloud capabilities that will, in fact, replace a lot of the equipment,” Mr. Kudlow said. “To quote Michael Dell, ‘Software is eating the hardware in 5G.’
Note 2.: None of those companies are now or will in the future make 5G infrastructure. AT&T is a network operator that purchases 5G infrastructure equipment, Microsoft is primarily a Cloud Service Provider (AZURE), while Dell is an IT infrastructure company that primarily sells to enterprise data center customers.
Kudlow is likely referring to virtualization of the 5G radio access and 5G core networks when he mentioned “software and cloud capabilities that will, in fact, replace a lot of the equipment.” Yet there’s already a lot of work that’s been done in vRAN and cloud RAN (sometimes referred to as “cloud native radio access networks.”
For open source cellular hardware, there is an OpenRAN project within the O-RAN Alliance, which involves disaggregating a cellular Base Station into its constituent components and defining interfaces between those. The Open Network Foundation (ONF) is collaborating with the O-RAN Alliance to generate open source software for that project. There are also several RAN projects within the Telecom Infrastructure Project (TIP), including OpenRAN, vRAN Fronthaul and OpenRAN 5G NR Base Station.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
White House officials say they are taking the effort seriously because of the potential value of 5G technology to the broader economy. Industry boosters say the new 5G engineering standard will power an “Internet of Things” in which factories, household appliances and vehicles are connected in the way mobile phones are now. They say 5G can do for future tech startups what 4G technology did for smartphone apps like Uber Technologies Inc. and Snapchat Inc., building a foundation for future innovation.

“Talk is a good start,” said Roger Entner, an analyst for industry researcher Recon Analytics. “But in the end it needs action. More funding will accelerate everything.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Similar U.S. government initiatives and proposals:
The effort appears to line up very closely with a new program at the U.S. military’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) called “Open Programmable Secure 5G” (OPS-5G). As noted by Data Centre Dynamics, the program promises to “create open source software and systems enabling secure 5G and subsequent mobile networks such as 6G. The signature security advantage of open source software is increased code visibility, meaning that code can be examined, analyzed and audited, either manually or with automated tools. In addition, the portability of open source serves, as a desired side-effect, to decouple the hardware and software ecosystems. This significantly raises the difficulty of a supply-chain attack and eases the introduction of innovative hardware into the market.”
U.S. lawmakers have proposed funding research and development into open 5G software standards. A bipartisan group of senators in January proposed tapping proceeds from the Federal Communications Commission’s coming spectrum license auctions to pay for research grants into those technologies. The administration is looking into those efforts but hasn’t yet decided whether to back them, Mr. Kudlow said.
If U.S. and European companies work separately, it could take longer to develop world-beating technology. If they work together, it could raise antitrust concerns. However, Kudlow said he didn’t believe antitrust would be an issue, saying the companies would compete in providing 5G technology. “We’re taking a coordinating role among leading companies,” he said.
He didn’t provide a specific time frame, though others in the government have said they expect to have a system running within 18 months. Earlier, the White House considered subsidizing a new hardware competitor to Huawei or backing a government-owned 5G network but rejected both.
President Trump is squarely behind the effort, said Kudlow, who is leading the initiative as director of the National Economic Council.
“The president kept saying to me, ‘Can’t we just put it (5G) under one simple infrastructure?’” Kudlow said. “We’re trying to create an American soup-to-nuts infrastructure for 5G. He kept hearing that Huawei seems to be able to do it.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Huawei’s threat to U.S. and European tech companies:
Paul Triolo, head of global technology policy at the Eurasia Group, a business consulting firm agreed that Huawei has a formidable lead in 5G technology. “The problem is you’re starting late in the game to fix this problem,” Mr. Triolo said of the U.S. effort. He added that the initiative could also threaten Nokia and Ericsson by making their machines into commodities, Mr. Triolo said.
Perhaps the most insightful proceeding on Huawei and the Chinese threat to 5G in the US is playing out at the FCC, the US government agency charged with oversight of telecom networks. That agency is considering a proposal that would bar the purchase of Huawei equipment among US companies that receive government subsidies for network buildouts in rural areas. The FCC is also evaluating its own rip-and-replace program of existing Huawei equipment in US networks.
However, unlike some of the other Trump administration efforts against Huawei, the FCC’s proceeding is being held in the open, with publicly available comments from all the companies involved in the issue.
Huawei is the world’s largest supplier of wireless networking equipment, yet it generates less than 1% of its revenue from the US market, according to research and consulting firm GlobalData.
Huawei has denied any links to Beijing, but the Chinese government is largely responsible for Huawei’s success due to the immense funding it funneled to the company and the measures it took to block competitors from impeding Huawei’s rise in the China market. As a result, Huawei became a telecom juggernaut not just in China, but all over the world. Now, the US is trying to adopt a similar strategy to promote US firms, and it wants to do so ahead of more widespread rollout of next-gen 5G networks in the coming years.
“If the US wants 5G hardware and software developed by a US or European company, the government should encourage companies to begin negotiations with Huawei to license our 5G technology,” Huawei’s US security lead Andy Purdy told the WSJ. Purdy says that Huawei’s intellectual property is integral to fast 5G deployment, and that without it, “the combined product will be one to two years behind the comparable Huawei products in terms of functionality and assurance.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-pushing-effort-to-develop-5g-alternative-to-huawei-11580831592
GSA: Number of 5G devices has doubled in last 5 months!
Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) today reported that the number of announced 5G devices has broken the 200 barrier for the first time. With 208 5G devices now announced from 78 vendors, the number of commercial devices has more than doubled in the last five months, having surpassed the milestone of 100 devices from 41 vendors in August 2019.
“During 2019, the number of announced 5G devices grew rapidly, starting with a few announcements and then gathering pace as operators in various parts of the world launched their first commercial 5G services,” commented Joe Barrett, President, GSA.
“This growth has continued into 2020 with the number of announced 5G devices exceeding 200 for the first time. Not only is this a symbolic milestone, but it also means we are starting to be able to identify trends in spectrum support and form factors. The diversity of both further reinforces how the industry is working hard to deliver on the 5G promise to markets and operators around the globe.”
- The latest market data reveals that over two-thirds (66.8%) of all announced 5G devices are identified as supporting sub-6 GHz spectrum bands.
- Only 17 of the commercially available devices (around 29% of them) are known to support services operating in mmWave spectrum.
- Slightly more than 27% of all announced devices are known to support both mmWave and sub-6 GHz spectrum bands. The bands known to be most supported by announced 5G devices are n78, n41, n79 and n77.
Part of the GSA Analyzer for Mobile Broadband Devices (GAMBoD) database, the GSA’s 5G device tracking reports global device launches across the 5G ecosystem and contains key details about device form factors, features and support for spectrum bands. Access to the GAMBoD database is only available to GSA Members and to GSA Associates subscribing to the service.
The January 2020 5G Ecosystem Report containing summary statistics can be downloaded for free from https://gsacom.com/paper/5g-device-ecosystem-report-february-2020/?utm=devicereports5g.
By the end of January 2020, GSA had identified:
o 69 CPE devices (indoor and outdoor, including two Verizon-spec compliant devices not meeting 3GPP 5G standards) at least 12 of which are now believed to be commercially available
o 62 phones, at least 35 of which are now commercially available.
o 35 modules
o 14 hotspots (including regional variants), at least nine of which are now commercially available
o 5 laptops (notebooks)
o 4 routers
o 3 robots
o 3 televisions
o 3 tablets
o 2 snap-on dongles/adapters
o 2 drones
o 2 head-mounted displays
o 2 USB terminals/dongles
o 1 switch
o 1 vending machine
GAMBoD is a unique search and analysis tool that has been developed by GSA to enable searches of mobile broadband devices and new global data on Mobile Broadband Networks, Technologies and Spectrum (NTS). The 5G devices database contains details about device form factors, features, and support for spectrum bands. Results are presented as a list or in charts. Charts may be inserted into documents or presentations, subject to accreditation of GSA as the source.
GAMBoD is a resource dedicated to promoting the success and growth of the Mobile Broadband (MBB) industry and ecosystem and is fully available to all employees of GSA Executive and Ordinary Member companies and GSA Associates who subscribe to the service.
About GSA
GSA is the voice of the mobile vendor ecosystem representing companies engaged in the supply of infrastructure, semiconductors, test equipment, devices, applications and mobile support services. GSA actively promotes the 3GPP technology road-map – 3G, 4G, 5G – and is a single source of information resource for industry reports and market intelligence. The GSA Executive board comprises of Ericsson, Huawei, Intel, Nokia, Qualcomm, and Samsung.
GSA Membership is open to all companies participating in the mobile ecosystem and operators, companies and government bodies can get access to GAMBoD by subscribing as an Associate. More details can be found at https://gsacom.com/gsa-membership
News/updates: RSS Feed: https://gsacom.com/rss-feeds/
GSA LinkedIn group: www.linkedin.com/groups?gid=2313721
Twitter: www.twitter.com/gsacom
Vodafone tests 5G Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) in its Dusseldorf lab
Vodafone announced that it has conducted what it claims is the world’s first test of 5G Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), based on a combination of two low spectrum bands in its VIP lab in Dusseldorf, Germany. The company used simultaneously the 700MHz and 800MHz bands on a 5G non-standalone device. The frequency in the 800MHz range was used as the “anchor band”, while the 700MHz frequencies were shared between 4G and 5G.
The tests were conducted with suppliers Ericsson, Huawei and Qualcomm which used its Snapdragon X55 5G modem (which supports 5G NR mmWave and sub-6 GHz spectrum bands and can deliver speeds of up to 7 Gbps over 5G and 2.5 Gbps on Cat 22 LTE).
Vodafone claims this is a world first in cellular radio. 2G, 3G and 4G standards were initially rolled out on dedicated blocks of spectrum, which meant that re-allocating for the next generation was an extremely slow – not to mention expensive – process. With dynamic spectrum sharing, this can be done overnight with a simple software upgrade.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

DSS allows network operators to deliver both 4G and 5G within the same spectrum, enabling a smooth transition between the two technologies and therefore a more cost-effective rollout. While the technology has already been demonstrated, the unique aspect of last month’s test was the simultaneous use of two low frequency bands (700MHz and 800MHz) on a 5G non-standalone device. 800MHz was used as the “anchor band” while 700MHz was shared dynamically between 4G and 5G, allowing operators to seamlessly allocate spectrum resources according to demands on the network.
Without DSS, an operator that has 20 MHz of mid-band spectrum would have to split that spectrum in two. In other words, they would have to allocate 10 MHz of spectrum to 4G LTE and cram all their LTE users into that 10 MHz of spectrum. Then the remaining 10 MHz of AWS spectrum could be used for 5G, even though initially there will only be a minimal number of 5G users.
With DSS, an operator doesn’t have to split that mid-band spectrum or have a dedicated spectrum for either 4G LTE or 5G. Instead, they can share that 20 MHz of spectrum between the two technologies.
For operators, DSS technology means they will be able to unleash the potential of 5G quicker, both for consumers and in industry, and ensure coverage over a wider area than ever before. It will also lay the foundations for the future technologies that will rely on 5G.
How does DSS benefit for the end-user? Most importantly, it means better 5G coverage, with lower latency and higher quality (in addition to faster download speeds) for consumers sooner. DSS on low bands will also be significant in enabling low latency applications and deeper in-building coverage.
Dynamic spectrum sharing will no doubt play an integral role in ensuring a seamless global rollout of 5G and this test is a significant step towards offering this next-generation connectivity for all. Through industry collaboration such as these, we can make that leap sooner, revolutionising the lives of consumers and enabling business innovation across the globe.
References:
https://www.vodafone.com/perspectives/blog/dynamic-spectrum-sharing
Juniper Research: Network Operators to Spend Billions on AI Solutions
A new study from Juniper Research has found that total network operator spending on AI solutions will exceed $15 billion by 2024; rising from $3 billion in 2020. The research identifies network optimisation and fraud mitigation solutions as the most highly sought-after AI based services over the next 4 years. AI-based solutions automate network functionalities including routing, traffic management and predictive maintenance solutions.
For more insights, download our free whitepaper, How AI Analytics will Boost Operators’ Revenue.
Network Optimisation & Fraud Prevention Driving Adoption in Developed Markets
The new research, AI Strategies for Network Operators: Key Use Cases & Monetisation Models 2020-2024, found that operators in developed regions, such as North America and Europe, would account for over 40% of AI spend by 2024, despite only accounting for less than 20% of global subscribers. It predicts that growing demand for operational efficiencies will drive operators in these regions to increase their overall investment into AI over the next 4 years.
The research urges operators to embrace a holistic approach to AI implementation across service operations, rather than applying separate AI strategies to individual use cases. It suggests network operators leverage AI to unify internal data resources and encourage cross-functional insight sharing into network efficiencies to maximise the benefits of collaboration across internal teams.
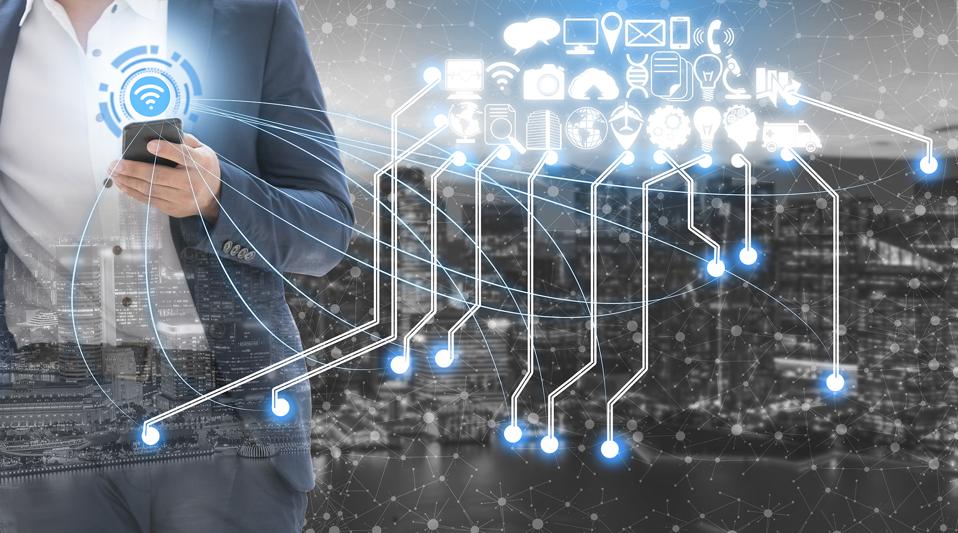

The research predicts that AI spend by Emerging Markets operators will exceed $5 billion by 2024, rising from only $900 million in 2020. It found that this growth will be driven largely by operators exploring early use cases of AI before expanding the presence of AI in their networks to include more comprehensive services.
The report forecasts that Indian Subcontinent and Africa & Middle East will experience the highest growth in spend on AI services, with operator spend in both regions forecast to grow over 550% over the next 4 years. It anticipates that operators in these regions will initially invest in AI-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) solutions that yield immediate benefits.
Related post:



