Indigo Cable System to boost connectivity in SE Asia & Australasia when it launches later this year
The Indigo Consortium has confirmed that it has landed the Indigo Cable System, which will link Australia’s East and West coasts, in Coogoo Beach, Sydney. In September, operators launched the Indigo Cable System from Floreat Beach in Perth, on Australia’s West Coast. Once complete, the Indigo Cable System will connect Australia’s East and West Coasts and then provide onward connectivity to a number of high profile destinations in South East Asia, including, Singapore and Jakarta, Indonesia.
The 9,200km Indigo Cable System will be comprised of two fiber pairs and will be able to support data transfers of 36Tbps. The Indigo Cable Consortium is comprised of AARNet, Google, Indosat Ooredoo, Singtel, SubPartners, and Telstra.
“The landing of INDIGO Central cable by Optus is a landmark development which will boost Australia’s communications ecosystem with much-needed high-speed capacity and network diversity. Together with INDIGO West, the next generation INDIGO Central data superhighway will enhance Singtel and Optus’ subsea networks, creating a cable ring connecting Australia to Singapore, through Southeast Asia, across the Pacific and back to Australia,” said Singtel’s Vice President, Carrier Services, Group Enterprise Ooi Seng Keat.
“This new data superhighway will complement our existing global links to Asia, US, Europe, Australia and the Middle East and allow Singtel and [Australian subsidiary] Optus to meet the growing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications as well as boost network diversity and resilience.”
Telstra head of North Asia and global wholesale Paul Abfalter added that the cable will connect to the operator’s extensive terrestrial infrastructure for onward connectivity in Australia.
“Our vast subsea network is a key part of our international growth strategy and we will continue to invest in additional capacity to meet the increasing demand for data and maintain our network leadership in the Asia-Pacific region.” he said.
References:
https://subpartners.net/indigo.html
https://www.submarinenetworks.com/systems/asia-australia/indigo
https://www.totaltele.com/501509/Singtel-Telstra-and-partners-land-Indigo-Cable-in-Sydney
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/indigo-cable-lands-western-australia
My story: Connecting Australians to the world, from the ’80s to the ‘Tera Era’
ITU-T SG15: G.mtn Metro Transport Network + Transport Support for IMT2020/5G Networks
ZTE and China Mobile report that standardization work for a multi company January 2018 contribution on Slicing Packet Network (SPN) technology was approved as a future ITU-T recommendation for “Metro Transport Networks” (G.mtn) at the October 8-19, 2018 ITU-T SG15 meeting in Geneva.
ITU-T SG15 Q11 focused much of the October meeting on topics related to IMT2020/5G transport networks, and approved three new work items including two related to that area. The new IMT-2020/5G Transport-related work items are both targeted at metro networks, including transport of RAN traffic. They are G.mtn “Interfaces for a metro transport network,” which is a new transport technology, and G.709.25-50 “25G and 50G OTN interfaces” that is an extension to the OTN. The other new work item is G.Sup.sub1G “Sub 1 Gbit/s services transport over OTN” that describes existing and new mappings for sub-Gbit/s clients over OTN.
SPN is a multi-service network platform that can meet new requirements of the 5G transport, data center interconnection, enterprise customer services, residential access network services. The SPN technology endeavors to provide: low latency, high bandwidth, ultra-high-precision synchronization, flexible management and control, and low cost.
At the October ITU-T SG15 plenary session in Geneva, Chinese network operators, equipment vendors, and research institutes submitted several proposals for 5G network transport technology solutions. From Contribution 1034 by China Mobile and other China resident companies: A proposal to initiate a new work item on Management Aspects for SPN:
Slicing Channel Layer (SCL) is defined as a path layer. Many SPN contributions have been presented in previous ITU-T SG15 meetings which clearly showed that SPN can be an appropriate candidate solution for 5G transport.,,
It is proposed that Q12, Q14 start a new work item on management aspects for 5G transport networks. It shall address management aspects of SPN network elements containing transport functions for the SCL and SPL layers. The same management architecture and tools for traditional transport networks such as MPLS-TP and OTN shall be reused as much as possible. The management functions for fault management, configuration management and performance monitoring shall be specified.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Based on the above proposals (led by China Mobile), ITU-T SG 15 approved G.mtn standard initialization of the SPN forwarding plane technology. China Mobile persuaded industry experts attending the SG 15 meeting that SPN has advantages in terms of 5G transport capability, key technical feasibility and industrialization, ZTE and China Mobile said in a statement.
………………………………………………………………………………..
Transport Network support of 5G: An updated version of Technical Report GSTR-TN5G, Transport network support of IMT-2020/5G, was agreed. This report captures requirements for Transport Network support of 5G mobile fronthaul, middle-haul, and backhaul networks. A new Recommendation was completed on Radio over fiber systems, and a new Supplement on 5G Wireless Fronthaul Requirements in a PON Context. New Recommendations G.8262.1 and Amendment 2 to G.8273.2 that specify new clocks to support synchronization for IMT-2020/5G were consented.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/press-center/news/201811/20181102
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/itu-t-created-new-work-item-gmtn-spn-weiqiang-cheng
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/itu-t-initializes-gmtn-standardization
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/studygroups/2017-2020/15/Pages/exec-sum-201810.aspx
Sapio Research Survey: 20% have SD-WAN project, but 48% of those are proof of concept
In a survey of 200 senior IT and networking managers in the US and the UK, Sapio Research found 20% of respondents said they have a software-defined WAN project in progress, while 32% haven’t explored the technology and 27% may look at it in the future. About one-third of respondents said they wanted to reduce network costs and to better manage their network infrastructure. The research study found that 48% of those are running SD-WAN proof of concept at select sites or other limited deployments. That means only about 10% are transitioning fully to SD-WAN.
The survey was commissioned by Teneo and based on input from 200 senior IT and networking managers evenly split between the U.S. and U.K. The companies have worldwide operations and revenues between $127 million and $38 billion. The survey found that 32% have not yet explored the technology, though 27% may do so in the future.
When senior IT professionals were asked why they were considering SD-WAN, the most common reason was the increasing complexity of network infrastructure and performance tasks (cited by 36% of interviewees), closely followed by the need to cut network costs (34%) and the need for better management of network infrastructures (also 34%). Increasing pressure on both company resources and budgets as IT team look after more complex network infrastructures is driving companies to examine SD-WAN’s potential.
Exactly half of companies questioned say that deploying and managing networking infrastructure is time-consuming. Interviewees estimate that these upkeep tasks take up 36% of their overall IT budget. One third of the survey (33%) admit that they had used ‘as a Service’ models from external providers to keep on top of maintenance tasks.
Researchers also found that companies are blending connectivity options to get necessary bandwidth: nearly four in ten (38%) of interviewees want to add more MPLS, 22% want more Internet connectivity, and 20% want to add more Internet and MPLS combined. Under one in five (17%) said their needs were satisfied.
Half of the respondents pointed to the time-consuming nature of deploying and managing a network as their main driver. Overall, those interviewed said that upkeep consumes as much as 36% of their IT budgets. One-third said that they have used “as-a-service” platforms to keep pace. Varied offerings have emerged. “Due to the immaturity of the SD-WAN space each vendor has come to the market with a different strategy,” wrote Steve Evans, Teneo’s vice president of solutions engineering in response to emailed questions from FierceTelecom. “We are seeing this converge in some areas. However, there are still noticeable differences between the major players in the space. I would not say that the vendors do not know what to bring to market. I think it’s more that some vendors favor particular features over others.”
The SD-WANs enterprises deploy will look different from one another, according to the survey. Thirty-eight percent of respondents want to add MPLS, 22% want to add broadband and 20% want to add both. Seventeen percent are happy with their current connectivity.
It is perhaps surprising that companies want to add MPLS, since reducing costs is seen as a key driver of SD-WAN. “SD-WAN is not about removing MPLS, although there can be cost benefits,” Evans wrote. “With the reliability of Internet circuits or broadband improving, the usage of MPLS will still have a place until people are comfortable with running business critical applications over circuits with no SLAs.”
Evens did point to cost savings of using broadband where it makes sense. “We have seen SD-WAN being used to enable businesses to utilize all of the MPLS bandwidth they are paying for to improve service for critical applications and then augment this bandwidth with the cheaper options for less important traffic, thus removing the expensive backup circuits and gaining more bandwidth for less cost,” wrote Evans.
There still is a learning curve for both vendors and end users. “The challenge around understanding SD-WAN is that vendors are all talking features and that they all fit every situation,” Evans wrote. “They are not starting with what the customer is trying to achieve and then showing how their technology would fit the needs. There is also a misunderstanding on what is meant by certain features and in comparing how well one solution executes on a feature.”
Progress is being made, however. “More and more businesses already have a basic understanding of SD-WAN and are able to articulate their requirements, but some are still looking to get an understanding of the market and the technology,” according to Evans. “Both groups need help understanding exactly how their requirements map to the available SD-WAN technologies.”
Another element that is not yet clear is who companies prefer to work with. Thirty-nine percent of survey respondents want to partner with a global network vendor, 24% with a telecommunication partner and 24% with a management consultancy.
The survey found that 8% of respondents are considering specialist SD-WAN vendors, 3% are considering specialist integrators of SD-WAN and 3% will use multiple partners.
“Network managers are looking at SD-WAN strategies to run multiple networking environments in standardised ways – whether the underlying motivation is greater simplicity, cost efficiency or transforming critical applications’ performance across their company’s operations,” said Marc Sollars, CTO of Teneo.
“Many firms are clearly putting a toe in the water on SD-WAN, or doing a proof of concept, but it’s still very hard to say when this test phase will start to translate into enterprise-level implementations,” added Sollars. “In many ways, the broad range of choice that SD-WAN brings is what’s causing companies to hesitate over their decisions.”
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/research-sd-wan-drivers-strategies-are-broad-and-deep
AT&T exec: SD-WAN is “killer app” after MEF says they will define SD-WAN service
AT&T exec: SD-WAN is “killer app” after MEF says they will define SD-WAN service
AT&T’s Josh Goodell at MEF 18 conference in LA: “SD-WAN is the killer app — we’re deploying 28,000 end points, it has really exploded.” Really? We’re from Missouri= show me
Meanwhile, the MEF has definesd an SD-WAN service and its various attributes. With strong support from service provider and technology provider members, MEF currently is on track to ratify and publicly release its MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Definition standard in 1Q 2019. SD-WAN service standardization will enable a wide range of ecosystem stakeholders to use the same terminology when buying, selling, assessing, deploying, and delivering SD-WAN services. The SD-WAN service definition is a foundational step for accelerating sales, market adoption, and certification of MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services orchestrated across a global ecosystem of automated networks.
SD-WAN Service Standardization
SD-WAN service standardization is being conducted within the context of the MEF 3.0 Global Services Framework. It is part of a transformational initiative to standardize a complete family of dynamic Carrier Ethernet (CE), IP, Optical Transport, SD-WAN, security, and other virtualized services that will be orchestrated over programmable networks using LSO (Lifecycle Service Orchestration) APIs.
MEF’s SD-WAN service definition specification describes requirements for an application-aware, over-the-top WAN connectivity service that uses policies to determine how application flows are forwarded over multiple underlay networks irrespective of the underlying technologies.
“MEF’s groundbreaking work in standardizing an SD-WAN service addresses one of the biggest obstacles impacting SD-WAN service market growth,” said Nan Chen, President, MEF. “In a recent joint MEF and Vertical Systems Group survey of service providers worldwide, nearly 80% of respondents identified the lack of an industry-standard service definition as a significant challenge for service providers to offer or migrate to SD-WAN services. MEF’s SD-WAN service standardization will undoubtedly accelerate sales of SD-WAN products and services like MEF accomplished with Carrier Ethernet service standardization.”
Just as the industry has benefited from MEF standardization of CE services – which now exceed an estimated $50 billion in annual revenues globally – there are numerous potential benefits associated with a common SD-WAN service definition. These include, among other things:
- Reducing market confusion about service components, core capabilities, and related concepts, thus saving valuable time given the scarce availability of skilled personnel.
- Enabling service providers and technology providers to focus on providing a core set of common capabilities and then building on that core resulting in differentiated offerings.
- Facilitating inclusion of SD-WAN services in standardized LSO architectures, thereby advancing efforts to orchestrate MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services across multiple providers.
- Paving the way for creation and implementation of SD-WAN services certification, which will give users confidence that a service meets a fundamental set of requirements.
SD-WAN Implementation
MEF member companies are involved in multiple SD-WAN implementation-related initiatives that can be leveraged to provide feedback on standardization requirements and create software-oriented artifacts that can be used to accelerate efforts to orchestrate standardized SD-WAN services. These initiatives include the MEF 3.0 Multi-Vendor SD-WAN Implementation project, the MEF18 LSO Hackathon, and several SD-WAN Proof of Concept (PoC) demonstrations at MEF18.
The MEF18 LSO Hackathon is focused on developing and validating data models for SD-WAN services. This presents a unique opportunity for those involved in technical aspects of SD-WAN services and products to learn in a hands-on way about the latest SD-WAN service and LSO standardization work at MEF as well as the related API and YANG work at ONF and IETF.
Three MEF18 PoC demonstrations directly related to LSO-enabled orchestration of SD-WAN services include:
- Zero Touch Services with Secure SD-WAN
- Towards a Multi-Vendor Orchestrated SD-WAN – LSO-enabled Solution with Open Source Orchestrator and Container-based uCPEs
- Instantiation and Delivery of SD-WAN over a Virtualized and Orchestrated Wholesale Carrier Ethernet Access Service.
MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Service Certification
MEF currently plans to introduce a pilot version of certification for MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services in the first half of 2019. This certification will test a set of service attributes and their behaviors defined in the upcoming SD-WAN standard and described in detail in the MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Service Certification Blueprint.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
…………………………………………………………………………………
Cisco Virtual Networking Index report: Enterprise SD-WAN growth will increase five-fold by 2022:
5G interoperability tests using Alef Mobitech’s mobile edge platform
Several major tech companies and an unnamed global mobile carrier have declared their tests of 5G interoperability a success. Alef Mobitech‘s mobile edge platform for the technology can be “reliably deployed into national mobile networks as a seamless, transparent overlay on their existing 4G infrastructure,” Alef says. HP, Cisco, Nokia, Huawei, Dell and Ericsson conducted the tests with Alef and a “tier-one global mobile carrier” that remains anonymous.
Editor’s Note:
Alef Mobitech, launched in 2013, is a Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) products and services provider. Alef is transforming the Mobile Internet through its MEC platform. The company has offices in New Jersey. India and Brazil.
Alef Mobitech provides value-added services at the edge of the mobile network. Mobile edge computing allows us to physically locate products and services closer to users. Alef makes your network faster and more responsive. New and existing networks benefit from our edge architecture. We provide market differentiation and new revenue opportunities to mobile carriers and developers.

Key Alef characteristics:
- Offers a first-of-its-kind MEC Platform that allows applications and network services to work in tandem.
- Utilizes optimized mobility at the Radio Edge to provide a richer, more responsive and relevant delivery of multi-media applications.
- Simplifies distribution and delivery across multiple markets.
- Through key partnerships, these applications will benefit from a speedier and richer mobile internet experience.
- Reduces complexity and enhances speed to market via a Managed Service offering. Creates a more immersive, interactive, and intelligent Mobile Internet.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The tests, which used Alef’s edge computing platform, were completed across New Jersey, Sao Paulo, and Mumbai. According to Alef, the tests show its platform can be “reliably deployed into national mobile networks as a seamless, transparent overlay on their existing 4G infrastructure”.
“The interoperability testing included standard billing interfaces — both pre-paid and post-paid, for voice and data services — and a comprehensive revenue assurance test regimen,” Alef said.
“Alef also demonstrated comprehensive interconnects with existing operations, administration, maintenance, and provisioning systems … throughout all of this testing, zero changes to the existing infrastructure were required.”
The announcement followed Samsung, Ericsson, and Nokia last week syncing their 5G equipment in partnership with SK Telecom in Korea, interoperating Samsung’s 5G Non-standalone (NSA) switchboard with Ericsson and Nokia’s 5G base stations.
In July, Huawei, Intel, and China Mobile also worked on 5G interoperability and development testing (IODT), which they said would help accelerate the commercialisation of 5G networking equipment globally.
Intel and Huawei had in February used Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2018 to conduct the world’s first 5G NR over-the-air interoperability public demonstration after Huawei had announced partnering with Intel on interoperability trials based on 3GPP standards back in September 2017.
At the end of December, Ericsson kicked off 5G interoperability trials with Australian mobile carrier Telstra; United States carriers T-Mobile, Verizon, Sprint, and AT&T; Japanese carrier NTT DoCoMo; Korean carrier SK Telecom; and European carriers Vodafone and Orange, as well as smartphone chip giant Qualcomm.
https://www.zdnet.com/article/5g-mobile-edge-tests-completed-by-global-tech-giants/
Calix touts GigaSpire as smart home solution for ISPs
To do so, broadband Internet providers will need to go to battle with a wide variety of companies who are now aiming to capture growing smart home revenue as their own, including blue chip technology companies like Google and Amazon. Those two are joined by a growing number of device manufacturers from well known brands like Netgear and Linksys to emerging smart home ecosystem enablers like Ring and Iris.
Patching all of these platforms together can be challenging and frustrating to end customers, and service providers often get the brunt of this frustration in the form of tech support inquiries, whether it’s the provider’s fault or not. Many providers have ventured into managed Wi-Fi services to help curtail this issue, while hoping to generate additional revenue in the process. GigaSpire takes this strategy much further, according to Calix.
In an analyst briefing, Calix EVP of Field Operations Michael Weening says GigaSpire far surpasses any Wi-Fi gateway platform that end customers can buy from any retail or online environment.

GigaSpire Platform (Source: Calix)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
GigaSpire runs Calix’s EXOS operating system, which was introduced last year and extends their AXOS access operating system platform into the customer premises. Other GigaSpire features include:
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) capable, with up to 12 Wi-Fi streams
- Intelligent bandwidth optimization using MU-MIMO technology
- Universal and managed IoT supporting Zigbee, ZWave, combo BlueTooth Low-Energy and BlueTooth Classic
- Amazon Alexa is integrated into the GigaSpire MAX
- Instrumentation and analytics providing telemetry, performance and behavioral analytics that CSPs can leverage through the Calix Cloud
Calix also intends to build an ecosystem of smart home applications that will ride the GigaSpire platform, allowing service providers to offer and perhaps monetize smart home IoT applications. Examples provided include smart home device management, home security and network security.
Two Calix customers are acting as launch customers for GigaSpire, including Nebraska-based Allo Communications and Dubai-based du.
“Calix has been a great partner as we’ve built up our home Wi-Fi enabling the best connectivity but also the best customer service through ongoing network management,” said Brad Moline, president and CEO of ALLO Communications in press release. “This new smart home solution is anticipated to build on that connectivity advantage and really put it to use by delivering customized and differentiated service bundles to our subscribers.”
Smart Home-as-a-Service Goals
Calix’s goal with GigaSpire is to create an end-to-end smart home platform that service providers can take to the residential market and offer smart home-as-a-service. Whether that’s through better integration of existing smart home applications customer’s already have, or by introducing new ones through a smart home app ecosystem enabled through Calix designated partners. Calix will extend the GigaSpire platform to the SMB segment with a business focused smart IoT platform in 2019.
References:
WSJ Interview with John Donovan: Inside AT&T’s Plan for 5G Technology
Wireless telcos are counting on 5G’s capabilities to broaden their customer base beyond phones to new machines like driverless cars and factory robots. AT&T executives are so enticed by the promise of mixed-reality goggles, which superimpose images in users’ field of vision, that they invested in visor maker Magic Leap to help develop a market for the devices (see below for details).
AT&T is in a race to launch 5G services faster than its rivals, though each is taking a different path to get there. Verizon Communications tried to get the jump on its competition with its own pre-5G (fixed wireless broadband) standard. AT&T directed its research toward internationally recognized specifications (i.e. 3GPP which is not a standards organization)—hoping that doing so will make its service more adaptable as the technology matures.
The chief executive of AT&T’s communications division, John Donovan, spoke with The Wall Street Journal about AT&T’s plans for 5G, among other things. Here are edited excerpts of the conversation.
WSJ: There’s been a lot of talk about 5G technology. When it comes, what will it look like?
MR. DONOVAN: You’ll start to see handsets rolling out as early as the first quarter of 2019, but much more probably and in more volume when you start to look at the back half of ’19. Things will be compatible with not only 5G but also all of the prior generations. With nonstandards technology, [that kind of backward compatibility] is not typically the case. That’s why we didn’t waste too much time on the nonstandard version like some of our competitors.
WSJ: It sounds like there’s a bit of a chicken-and-egg problem. If you don’t know what consumers are going to want 5G service for, how do you know where to build the network first?
MR. DONOVAN: We think that the 5G network is going to be most impactful for most consumers and businesses based on specific use cases. One would be retail. With this 5G network, you’re going to be able to get centimeter-level accuracy on location. These potential use cases include recognizing consumers entering the store, alerting the concierge or manager to provide a personalized experience [and showing] product features on adjacent digital signage or scanning and displaying product features within the store app on the consumer’s mobile device. Those are the kinds of things we think are going to drive this, as opposed to saying, “Hey, I’ve got a phone and it’s faster, look at mine, it’s got this 5G tag up in the corner.”

Research and Deployment:
Milestones in the evolution and rollout of 5G technology

……………………………………………………………………………………….
We’ve made two announcements so far. One is in robotic manufacturing in Austin, Texas, with Samsung. And we have an exclusive for the Magic Leap mixed-reality goggles.
The speed of 5G means the next generation of goggles will be smaller, lighter and cheaper. When we did the announcement with Magic Leap, one of the things we announced is that DirecTV Now will be one of the apps available on the goggles. So, you put the goggles on and you can project four televisions onto the wall.
It’s mind-blowing to think about creating an 80-inch television from a set of goggles.
WSJ: When 5G comes to my cellphone, am I going to pay more for a plan?
MR. DONOVAN: That’s to be determined. I think that’s something that collectively the industry’s going to try to innovate around. When we went from megabits and text-message plans to unlimited in the 4G network, there wasn’t a lot of incremental revenue. But 4G dropped our costs dramatically, so it improved our margins.
With 5G, you can never call these things until you get into the marketplace. Most would say now that it’s going to carry a premium because it’s so superior in some of the things it can do. But that premium may be that you have three new devices in your home that have small connection fees, and not necessarily that you have an iPhone in your hand and the plan it’s on costs more.
WSJ: Looking back on past generations of wireless, as networks mature, it gets harder to tell the networks apart, at least in the consumer’s mind. How do you try to distinguish yourself from the other guys?
MR. DONOVAN: Generally, we’ve hit a point with networks that there’s “good enough.” The analogy I use is oxygen. You’ll notice if it’s not there. But if it is there, in its highest state it’s invisible. How do you make it visible? Your people. I love the idea when it’s about the people in the stores, the call centers, your sales rep. We’re more likely to win in a world differentiated around people than marginally differentiated by machines.
WSJ: Should the number of stores be growing? Do you think we need more places to buy phones?
MR. DONOVAN: Yes, but I don’t want to build a store that you have to go to. I want to go to where you already are. So, if you look at our retail growth this year, it’ll be in kiosks, pop-up stores and trucks. If you’re in a brand new [apartment] and you want to deal with fiber and a family plan and television, wouldn’t it be great if you had a pop-up store that’s in the lobby right near the leasing office, you can get all of that stuff done, and a year later the store is gone because the building’s leased up?
The future of retail is that you need to be where the people already are. The idea that you’re going to run a television commercial, have them get off the couch and go call an 800 number, or get off the couch and go to a store, is no longer the case.
If you take the wireless business, even up to three to five years ago, you could run a promotion on television and generate volume by people going to your store. Today, the customer’s perception is that’s an industry offer. They would never say, “That’s a T-Mobile offer, I’m going to go to the store and get it done.” They go from there to Google and they start searching. Or the other thing is they go entirely in social. So their friends say, “You know what, you need to switch to AT&T and here’s why.”
Those two things didn’t even exist five years ago from a standpoint of how we marketed.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Mr. FitzGerald is a Wall Street Journal reporter in Washington. Email[email protected].
Appeared in the October 30, 2018, WSJ print edition as ‘What’s Behind AT&T’s Plan for 5G Technology.’
……………………………………………………………………………….
India Mobile Congress 2018: Telecom Equipment Vendors to Invest over Rs 4,000 crore in India; Samsung in Spotlight
IEEE President Jim Jefferies speaking at India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telecom Equipment Vendors Investment in India:
Telecom equipment makers including Cisco, Samsung, Ericsson, Nokia, Intel and Sterlite Tech (from India) will be investing more than Rs 4,000 [1] crore in India, announced Telecom Minister Manoj Sinha Saturday at the third day of the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018. That investment commitment is in line with India Prime Minister Narendra Modi‘s goal to achieve a capital gain of $100 billion (about Rs 7 lakh crore) by 2022. The amount invested will increase further, said Sinha, adding that the investment commitment shown by the equipment manufacturers is a part of government’s ambitious policy target to achieve Rs 7 lakh crore worth of investment by 2022. Sinha said discussions and announcements at IMC show that India is ready for the emerging 5G services. The 5G technology (based on the forthcoming IMT 2020 standard) would facilitate massive machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and has many other applications.
Note 1. 4000 crores (= 400000 lakhs) is equal to 40000 million (40 billion). 40,000,000,000 INR is equal to 544,400,000 USD @ 73.48 Indian rupees to 1 US dollar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These are the first set of investments flowing in after the announcement of National Digital Communications Policy. In August this year, the India Cabinet has approved the National Digital Communications Policy 2018 that aims to attract $100 billion of investment and creation of 4 million jobs in next four years, in addition to an aggressive focus on next-generation of technologies. However, the investments will be made over a period of next one-two years, according Telecom Secretary Aruna Sundararajan.
Among all these telecom equipment makers, Sterlite Tech is the only homegrown (Indian) company that locally produces end-to-end optic fiber gear, a critical digital infrastructure required to increase 4G-LTE footprint and enabler of upcoming “5G” technology roll-outs.
Meanwhile, Korea’s Samsung, Sweden’s Ericsson, Finland’s Nokia and the US-based Cisco have already partnered with India service operators and the telecom department to conduct field trials and demonstrate India-specific 5G use cases.
Industry experts discussed challenges in the digital communications during the three-day India Mobile Congress 2018 event, which saw participation from 20 countries and 300 companies, Sinha said. Sinha added that discussions and announcements at the event show India is ready for the emerging 5G services. The 5G technology could facilitate massive machine-to-machine communications and has multiple usages.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The India Mobile Congress 2018 was organized jointly by the India DoT and industry group Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) which represents telcos such as Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea as well as gear makers such as Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Cisco and Samsung.
Sundararajan said IMC has generated more enthusiasm around 5G and the government has already committed to be at par with the world in launching this next generation services. “We have already demonstrated government intent that India does not miss the 5G bus. We have already started to take initial set of action to make an enabling environment. We expect actual allocations of spectrum (for 5G services) to begin in the second half of next year,” Sundararajan added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Samsung in IMC 2018 Spotlight:
At IMC 2018, Samsung announced its plan for India’s first large-scale 5G trial, scheduled to take place in the first quarter of 2019 in collaboration with the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
In his keynote speech at the event, Youngky Kim, President and Head of Networks Business at Samsung Electronics, said, “Samsung will pave the way for 5G to unlock the full potential of India together with industry leaders. We are witnessing a rise in adoption of new technologies, inspired by ‘Digital India’ and spurred by the transition to 4G.’
“Our partnership with Reliance Jio has empowered millions, making their everyday lives better. Our roadmap for 5G showcases our strong commitment to India. We will continue to be a partner in Government of India’s Digital India mission,” said HC Hong, President and CEO, Samsung Electronics SouthWest Asia. Leading Disruptive Changes Using 4G in Digital India Since 2012, Samsung has been a key partner of the Indian telecommunications industry. During President Kim’s keynote speech at the IMC, he said that Samsung has successfully built the world’s largest greenfield and the most advanced 4G LTE networks nationwide by partnering with Reliance Jio.
At IMC 2018, Samsung showcased how its 5G solutions can enable a variety of 5G-powered business models and scenarios, including: 5G home broadband services, Smart Cities and Smart Agriculture.
Samsung’s 5G Skyship (see photo below), which was developed in partnership with Korea Telecom, was flying over the exhibition center to demonstrate first response use cases. Samsung says it has been a pioneer in developing 5G solutions using its technology and experience. With its successful development of the first commercial ASIC-based 5G modems and mmWave RFICs, the company has been manufacturing compact-sized 5G radio and router devices and CPEs.
 Photo provided by KT shows an unmanned airship using “high-end 5G” technology at the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018 in New Delhi
Photo provided by KT shows an unmanned airship using “high-end 5G” technology at the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018 in New Delhi
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung says its years of commitment to R&D investments since 2000 have come to fruition, as the company has been selected by the world’s leading operators such Verizon, AT&T, Sprint and SK Telecom for both 4G and 5G solutions and services. At the root of this achievement are Samsung’s end-to-end solutions spanning network equipment, devices, chip sets and the world’s-first regulatory approval of 5G equipment by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Samsung will continue its legacy of 4G LTE to enable digital transformation and provide a seamless path to 5G.
Fujitsu, Ericsson form 5G partnership focused on Japanese market
Fujitsu has entered a strategic partnership with Ericsson aimed at delivering joint end-to-end 5G solutions, initially for the Japanese market. The two companies plan to combine their radio access and core network portfolios to deliver 5G mobile network services and solutions across Japan before expanding to other markets worldwide. The companies will also collaborate on R&D activities related to 5G. This agreement comes shortly after NEC and Samsung announced their own 5G partnership aimed at developing end-to-end 5G system solutions.
Fujitsu has been collaborating on open standards activities driven by major operators and aims to achieve interoperability for its radio access products. According to Fujitsu EVP of network business Tango Matsumoto, this partnership will support that aim.
“Through this partnership with Ericsson, we will provide flexible 5G network systems that are open and standard compliant, and will leverage our expertise in wireless technologies and network integration to a wide range of customers in and outside of Japan,” he said. “From (enhanced) mobile broadband, expected to be the first widespread use case of 5G, to the IoT and beyond, this partnership holds out the promise of exciting new business opportunities,” he added.
Ericsson EVP of networks Fredrik Jejdling added that the partnership will support the company’s efforts to carve out a share of the Japanese 5G market.
“Our global expertise in 5G combined with our understanding of the local market puts us in an excellent position to support the introduction of 5G in Japan,” he said. “By working closely with operators and partners, we are creating solutions that will bring successful use cases and applications to the market. With Fujitsu we get an excellent partner to accelerate this development.”
Fujitsu’s previous work on 5G saw it last year kick off a field trial of its 5G ultra high-density distributed antenna technology and tests of simultaneous high-speed transmission of high-res video using the antenna system, in partnership with Japanese carrier NTT DoCoMo.
Ericsson has the second-biggest share of global base-station sales — approaching 30%, according to IHS Markit. Ericsson’s equipment is already being used in parts of the U.S. that are rolling out 5G service.
Fujitsu, which does most of its business in Japan, holds less than a 1% global base station market share. Fujitsu and Fujitsu Laboratories, which have been working on 5G trials with NTT DoCoMo since 2014, have also collaborated with NTT DoCoMo on evaluating communications speed for distributed antennas deployed at multiple outdoor locations.
Reference:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/2018/10/fujitsu-and-ericsson-team-up-on-5g-partnership
3GPP Workshop: IMT 2020 Submission to ITU-R WP5D and Timelines for 5G Standards Completion
3GPP RAN for IMT 2020, by Balazs Bertenyi, Chairman of 3GPP RAN (Nokia):
The Workshop on 3GPP submission towards IMT-2020 was held in Brussels, Belgium, October 24-25, 2018, hosted by the European Commission. The meeting was intended to inform the Independent Evaluation Groups and the industry in general about the 5G mobile communication system and corresponding evaluations that 3GPP has and will submit as a candidate for IMT-2020 to ITU-R. The workshop also had a live streaming service kindly provided by the host and announced shortly before the meeting via the 3GPP web page (see reference below) and the RAN reflector.
Introduction:
3GPP has been working extremely hard to bring 5G NR standards to the industry in an accelerated manner. Non-standalone 5G NR (New Radio) was completed in December 2017, and the corresponding ASN.1 has been stabilized in June/2018.
Standalone 5G NR was completed in June 2018, and the corresponding ASN.1 scheduled to be frozen in September/2018.
Some of the architecture options to facilitate migration from LTE to 5G NR will be completed in December 2018 and will still be within 3GPP Release 15.
3GPP has also approved the work program for Release 16 containing a host of new and enhanced functionalities for 5G NR. The target completion for Release 16 is December/2019.
3GPP submission to IMT2020 (ITU-R WP5D) will contain both Release 15 and (mostly) Release 16 functionality.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
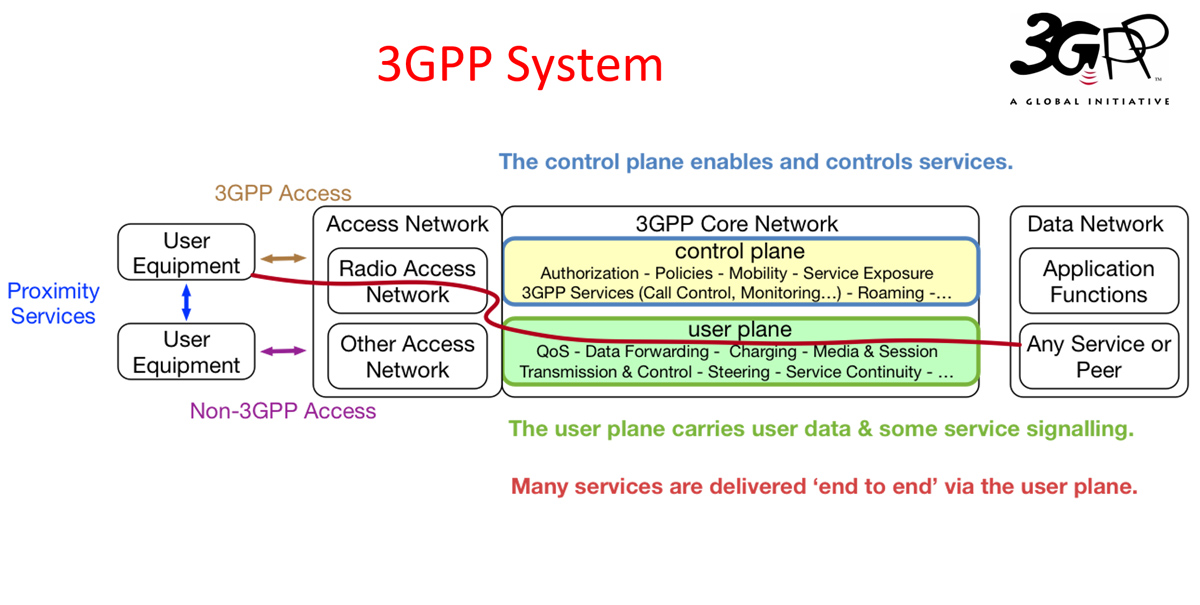
Software- and Service-centric Transformation:
One CoreNetwork fits all => Open & Flexible Enabler
Telecom Operators => Multiple Stakeholders
Phones => Things
Procedures => Services
Static Topology => On-demand Resources
Dedicated Hardware => Orchestrated Resources
Network Function => Virtualization
Single Network => Slice
5G Core Technologies (subset):
Orchestration and Virtualization (NFV) – de-couple logical function from hardware
Slicing – logical end-2-end networks tailed to customer needs
Edge Computing (MEC) – resources where they are needed (URLLC)
Exposure (API) – 3rd party access to 5G services
Service Based Architecture (SBA) – stateless, open, flexible
Harmonized Protocols & Access Agnostic – generic solutions
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
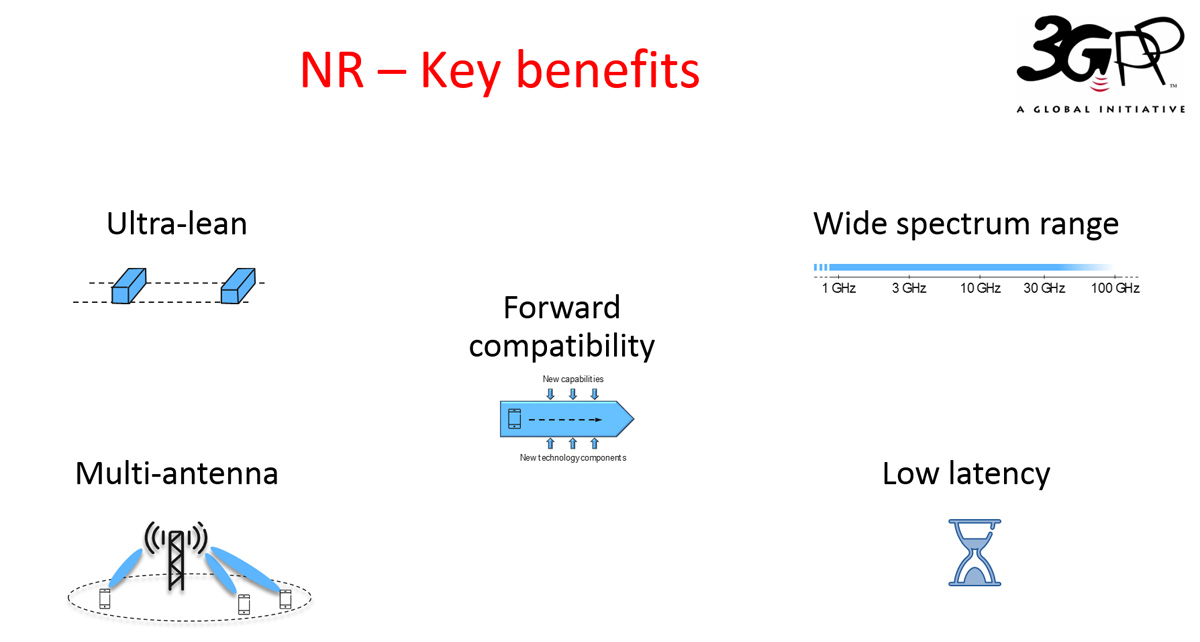
Physical Layer:
· NR addresses a broad range of use cases with a flexible physical layer structure
· Key enablers include
o Ultra-lean design
o Operability in a wide spectrum range
o Low latency
o Forward compatible design
o Advanced multi-antenna techniques
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Comparison of NR-MIMO vs LTE MIMO
|
|
LTE Rel-8 |
LTE-A Pro Rel-15 |
NR Rel-15 |
|
Purpose |
Spectral efficiency enhancement |
Spectral efficiency enhancement |
– Coverage enhancement – Spectral efficiency enhancement |
|
Multi-beam operation |
No specification support |
No specification support |
– Beam measurement, reporting – Beam indication – Beam failure recovery |
|
Uplink transmission |
– Up to 4 layers per UE – Up to 8 layers for MU-MIMO (cyclic shifts for ZC-sequence) |
– Up to 4 layers per UE – Up to 8 layers for MU-MIMO |
– Up to 4 layers per UE – Up to 12 layers for MU-MIMO (orthogonal ports) |
|
Downlink transmission |
Up to 4 layers per UE |
– Up to 8 layers per UE – Up to 4 layers for MU-MIMO (orthogonal ports) |
– Up to 8 layers per UE – Up to 12 layers for MU-MIMO (orthogonal ports) |
|
Reference signal |
– Fixed pattern, overhead – Up to 4 TX antenna ports (CRS) |
– Fixed pattern, overhead – Up to 32 TX antenna ports (CSI-RS) |
– Configurable pattern, overhead – Up to 32 TX antenna ports (CSI-RS) – Support for above 6GHz |
3GPP ……………………
””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””
IMT-2020 – Final submission
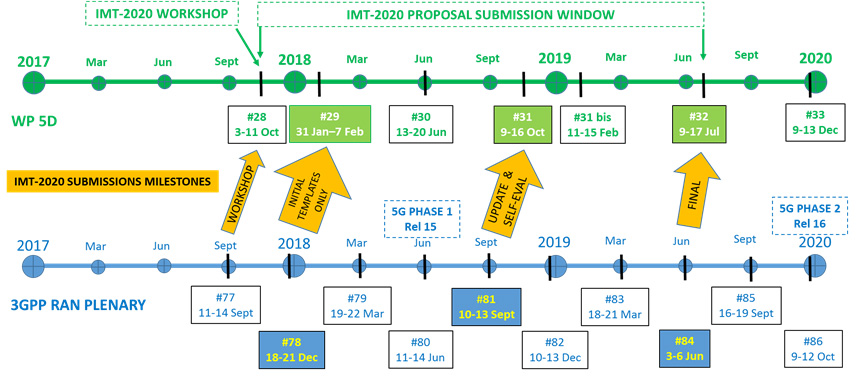
- Calibration for self evaluation
- Prepare and finalize initial description template information that is to be submitted to ITU-R WP 5D#29.
Step 2: From early 2018 to Sep 2018, targeting “update & self eval” submission in Sep 2018
- Performance evaluation against eMBB, mMTC and URLLC requirements and test environments for NR and LTE features.
- Update description template and prepare compliance template according to self evaluation results.
- Provide description template, compliance template, and self evaluation results based on Rel-15 in Sep 2018.
Step 3: From Sep 2018 to June 2019, targeting “Final” submission in June 2019
- Performance evaluation update by taking into account Rel-16 updates in addition to Rel-15
- Update description template and compliance template to take into account Rel-16 updates in addition to Rel-15
- Provide description template, compliance template, and self evaluation results based on Rel-15 and Rel-16 in June 2019.
”””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””””
Let’s compare that with the ITU-R WP5D Timeline Technology Aspects WG (RIT, SRIT): Note IMT 2020 items in the workplan!
|
July 2019 |
[Geneva] WP 5D #32 |
• Finalize draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.MS/MSS.2GHz] • Further update/Finalize draft new Report/Recommendation ITU-R • Finalize draft new Report/Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT.3300 MHz RLS] • Finalize Doc. IMT-2020/YYY Input Submissions Summary • Finalize revision of Recommendation M.2012 • Finalize Addendum 5 to Circular Letter IMT‑2020 • Workshop on evaluation of IMT-2020 terrestrial radio interfaces |
|
December 2019 |
[Geneva] WP 5D #33 (max 5 day meeting) |
• Focus meeting on evaluation – review of external activities in Independent Evaluation groups through interim evaluation reports |
|
February 2020 |
[TBD] WP 5D #34 |
• Finalize Doc. IMT-2020/ZZZ Evaluation Reports Summary • Finalize Doc. IMT-2020/VVV Process and use of GCS • Finalize Addendum 6 to Circular Letter IMT‑2020 • Finalize draft new Report M.[IMT.AAS] • Finalize draft new Report ITU-R M.[HAPS-IMT] |
|
June 2020 |
[TBD] WP 5D #35 |
• Finalize draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT-2020.OUTCOME] • Finalize Addendum 7 to Circular Letter IMT‑2020 |
|
October 2020 |
[TBD] WP 5D #36 |
• Finalize draft new Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT‑2020.SPECS] • Finalize Addendum 8 to Circular Letter IMT‑2020 |
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Now let’s examine the ITU-R WP5D Oct 2018 meeting input contributions related to IMT 2020:
[Note the tremendous support of companies backing 3GPP]
|
[1050] Preliminary description template and self-evaluation of 3GPP 5G candidate for inclusion in IMT-2020 – multiple companies co-authored this contribution! |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
|
Updated submission of candidate IMT-2020 Radio Interface Technology |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
||
|
Consideration on IMT-2020 evaluation process |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
|
Proposed preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT_EXPERIENCES] |
GENERAL ASPECTS |
|
Proposals on workplan and document template for process and the use of Global Core Specification (GCS), references and related certifications in conjunction with Recommendation ITU‑R M.[IMT-2020.SPECS] |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
|
Proposals on working document towards IMT-2020/VVV and its workplan |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
||
|
Second submission of a candidate technology of IMT-2020 |
TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS |
|
Proposal on continuity of development of working document towards a preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.EXPERIENCES] – National [approaches, best practices and/or] experience of some countries in which certain frequency band(s) are allocated to mobile services and identified for IMT systems related to technical, operational and regulatory/procedural aspects |
GENERAL ASPECTS |
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Below is a chart of the organizations that have indicated they will submit candidate IMT 2020 RITs to ITU-R WP5D. The list includes: 3GPP, China, Korea, ETSI/DECT Forum, and the India Standards organization (TSDSI). ALL BUT THE ETSI/DECT Forum will be based on 3GPP New Radio (NR) for the core RIT PHY layer.
References:
http://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/1976-imt_2020
http://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/1987-imt2020_workshop
http://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/1994-copatibility
Busting a Myth: 3GPP Roadmap to true 5G (IMT 2020) vs AT&T “standards-based 5G” in Austin, TX




