Samsung
UPDATED: Huawei now #1 global smartphone vendor
Despite the severe U.S. restrictions on Huawei, the company has succeeded in taking the top spot in the global smartphone market, according to figures from Canalys. The market research firm estimates Huawei shipped more smartphones worldwide than any other vendor for the first time in Q2 2020, marking the first quarter in nine years that a company other than Samsung or Apple led the market.
Note, however, that global smartphone sales DECLINED in the second quarter. Huawei shipped an estimated 55.8 million devices in the quarter, down 5 percent year on year. Samsung came second with 53.7 million smartphones, down 30 percent from a year earlier.
Huawei’s resilience was due to its strong position in China, where its shipments rose 8 percent in Q2. This offset an estimated 27 percent fall in its shipments abroad. Canalys estimates over 70 percent of Huawei’s smartphone sales are now in mainland China. That helps explains why the company can be so successful in selling smartphones, despite not being able to use licensed Google Android and associated apps on its latest flagship devices (that’s because Huawei was placed on the U.S. Entity list last year).
Canalys said the situation would likely not have happened without the Covid-19 pandemic. Huawei profited from the strong recovery in the Chinese economy, while Samsung has a very small presence in China, with less than 1 percent market share, and suffered from the restrictions in key markets such as the US, India, Brazil and Europe.

“This is a remarkable result that few people would have predicted a year ago,” said Canalys Senior Analyst Ben Stanton. “If it wasn’t for COVID-19, it wouldn’t have happened. Huawei has taken full advantage of the Chinese economic recovery to reignite its smartphone business. Samsung has a very small presence in China, with less than 1% market share, and has seen its core markets, such as Brazil, India, the United States and Europe, ravaged by outbreaks and subsequent lockdowns.”
“Taking first place is very important for Huawei,” said Canalys Analyst Mo Jia. “It is desperate to showcase its brand strength to domestic consumers, component suppliers and developers. It needs to convince them to invest, and will broadcast the message of its success far and wide in the coming months. But it will be hard for Huawei to maintain its lead in the long term. Its major channel partners in key regions, such as Europe, are increasingly wary of ranging Huawei devices, taking on fewer models, and bringing in new brands to reduce risk. Strength in China alone will not be enough to sustain Huawei at the top once the global economy starts to recover.”
As a result, it will be hard for Huawei to maintain its lead in the long term. Its major channel partners in key regions such as Europe are increasingly wary of stocking Huawei devices, taking on fewer models and bringing in new brands to reduce risk, as per the above Canalys quote from analyst Mo Jia.
Separately, Gartner estimates that 10% of smartphone shipments, or about 220 million units in 2020, will have 5G capability, but they’ll work on “5G” networks with a LTE core (5G NSA).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Addendum:
Huawei’s just announced global licensing agreement with Qualcomm grants Huawei back rights to some of the San Diego-based company’s patents effective Jan. 1, 2020. It remains to be seen if Huawei will design smartphone components that use those patents in their next generation of 5G endpoint devices.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.canalys.com/newsroom/Canalys-huawei-samsung-worldwide-smartphone-market-q2-2020
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Update- August 3, 2020:
According to market research firm Omdia, overall Q2-2020 smartphone shipment volume was down a hefty 15.7%, year-on-year, to 229.7 million units.
Samsung will certainly hope there are better times ahead. Omdia figures show the South Korean behemoth lost its #1 position in Q2, dislodged by Huawei. Samsung’s Q2 shipments plummeted nearly 28%, year-on-year, to 54.3 million.
Many of Samsung’s most important markets, were significantly impacted by COVID-19, especially emerging markets, which apparently accounted for more than 70% of Samsung’s overall shipments in 2019.
For its part, Samsung is hopeful of a Q3 smartphone recovery, helped by the launch of new flagship models, including the Galaxy Note and a new foldable phone.
Huawei, helped by a resurgent domestic market in China, snagged a 20% global smartphone share during Q2 (55.8 million units), up from an 18% market share the previous quarter. Year-on-year, Huawei’s Q2 shipment units were down a comparatively modest 4.9%.
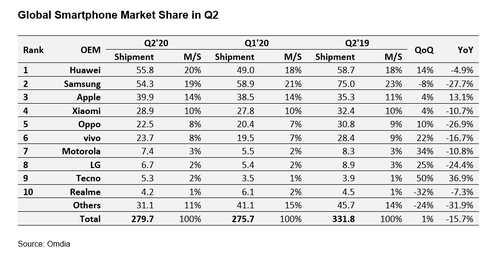
Apple was one of the few OEMs to increase Q2 shipment volumes, year-on-year (up 13.1%, to 39.9 million units). The iPhone SE, a model with mid-range pricing, coupled with the iPhone 11, helped Apple expand its unit shipments, and cement its third-spot position with a market share of 14% (up from 11% in Q2 2019).
“With the launch of the iPhone SE in April, Apple has released a long-desired product, with an attractive price,” said Jusy Hong, director of smartphone research at Omdia.
“For existing iPhone users who needed to upgrade their smartphones in the second quarter, the new SE represented an affordable option that does not require a large downpayment or high monthly repayment rates,” added Hong.
Reference:
https://www.lightreading.com/huawei-apple-buck-q2-smartphone-trends—report/d/d-id/762886?
Samsung acquires network services provider TWS; SK-Telecom launches Global MEC Task Force
1. Samsung Acquires Network Services Provider TeleWorld Solutions to Accelerate U.S. 5G Network Expansion
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. today announced the completion of an agreement to acquire TeleWorld Solutions (TWS), a network services provider headquartered in Chantilly, VA.

TWS provides network design, testing and optimization services to mobile service and cable operators, equipment OEMs and other companies across the U.S. With network builds associated with 5G and 4G LTE enhancements advancing in the U.S, the acquisition will address the need for end-to-end support in delivering network solutions.
TWS, a privately owned company, will operate as a wholly owned subsidiary of Samsung Electronics America, Inc. The service offerings and customers of TWS complement Samsung’s growth among networks infrastructure clients. With competencies in radio frequency (RF) and network design service—as well as installation, testing, and optimization services—TWS will continue to serve its existing customers and clients they currently support with Samsung. The TWS leadership team will continue to manage the business and, together with Samsung, address the network upgrade cycle occurring in the US.
With a growing position in the US networks industry, along with its 5G technology leadership, Samsung Networks has collaborated with major U.S. network operators to fulfill 5G’s network expansion. As its growth continues through network operator agreements and enterprises seeking their own cellular networks, the combination of Samsung and TWS will help customers address next-generation demands.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. SK Telecom Joins Forces with Bridge Alliance Members for Cooperation in 5G MEC
SK Telecom today announced the launch of the ‘Global MEC Task Force’ with Bridge Alliance member operators, including Singtel, Globe, Taiwan Mobile and PCCW Global, for cooperation in 5G mobile edge computing (MEC).
SK Telecom will share its lessons-learned in 5G and MEC areas with other members that are preparing to launch 5G, while making joint efforts for the development of MEC technologies and services. The company will also play a leading role in setting international MEC standards to build an interoperable MEC platform.
MEC is being highlighted as a key technology that can improve the performance of ultra-low latency services such as cloud gaming, smart factory and autonomous driving by creating a shortcut for mobile data communications.
Through the task force, SK Telecom expects to lead the expansion of the 5G MEC ecosystem to the Asian countries, and develop valuable overseas market opportunities for its 5G technologies/services including MEC.
As the first chair of the task force, SK Telecom will be hosting the first MEC workshop with Bridge Alliance from January 13 to 15 at its headquarters located in Seoul, Korea. The workshop will identify potential regional MEC-based use cases, and discuss business models and commercialization plans.
The company will introduce its 5G strategies, 5G MEC-based use cases including smart factory, and 5G clusters including ‘LoL Park.’
“As the global 5G pioneer, SK Telecom is committed to contribute to the expansion of the global 5G ecosystem,” said Lee Kang-won, Vice President and Head of Cloud Labs of SK Telecom. “SK Telecom will work closely with Bridge Alliance Member Operators to help accelerate their progress in 5G and MEC, and create a pan-Asian 5G MEC ecosystem.”
“As the role of telecommunications companies is expanding beyond simply providing mobile connectivity to offering new values based on infrastructure, Bridge Alliance believes that this cooperation will serve as a key driver for realizing win-win business opportunities to all members,” said Ong Geok Chwee, CEO of Bridge Alliance.Photo: (from left) Ha Min-yong, VP and Head of Global Alliance Group, SK Telecom, Ong Geok Chwee, CEO of Bridge Alliance, and Lee Kang-won, VP and Head of Cloud Labs, SK Telecom.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or [email protected]
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?page.page=1&idx=1439&page.type=all&page.keyword=
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Samsung #1 in Global 5G smartphone sales with 6.7 Million Galaxy 5G Devices in 2019
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. said that it shipped more than 6.7 million Galaxy 5G smartphones globally in 2019, giving consumers the ability to experience next-generation speed and performance. As of November 2019, Samsung accounted for 53.9% of the global 5G smartphone market and led the industry in offering consumers five Galaxy 5G devices globally, including the Galaxy S10 5G, Note10 5G and Note10+ 5G, as well as the recently launched Galaxy A90 5G and Galaxy Fold 5G.
The 6.7 million in Samsung 5G smartphone sales eclipses the 4 million target the firm set itself, though as its main Android competitor (Huawei) is being stifled by political friction, it is hardly surprising Samsung has stormed into the lead. Note also that Apple has not announced a 5G smartphone and probably will not do so till late 2020. In the absence of main competitors, Samsung is maintaining its leadership position in the 5G segment as well as 4G-LTE.
“Consumers can’t wait to experience 5G and we are proud to offer a diverse portfolio of devices that deliver the best 5G experience possible,” said TM Roh, President and Head of Research and Development at IT & Mobile Communications Division, Samsung Electronics. “For Samsung, 2020 will be the year of Galaxy 5G and we are excited to bring 5G to even more device categories and introduce people to mobile experiences they never thought possible,” he added.
The Galaxy Tab S6 5G, which will be available in Korea in the first quarter of 2020, will be the world’s first 5G tablet bringing ultra-fast speeds together with the power and performance of the Galaxy Tab series. With its premium display, multimedia capabilities and now, 5G, the Galaxy Tab S6 5G offers high-quality video conferencing, as well as a premium experience for watching live and pre-recorded video streams or playing cloud and online games with friends.

“5G smartphones contributed to 1% of global smartphone sales in 2019. However, 2020 will be the breakout year, with 5G smartphones poised to grow 1,687% with contribution rising to 18% of the total global smartphone sales volumes,” said Neil Shah, VP of Research at Counterpoint Research. “Samsung has been one of the leading players catalyzing the 5G market development in 2019 with end-to-end 5G offerings from 3GPP standards contribution, semiconductors, mobile devices to networking equipment. With tremendous 5G growth opportunities on the horizon, Samsung, over the next decade, is in a great position to capitalize by further investing and building on the early lead and momentum, ” Shah added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sidebar: Qualcomm or Samsung 5G silicon in future 5G devices?
It has become widely accepted that the latest Qualcomm chipset features in the majority of flagship smartphone devices throughout the year. Only two smartphone makers – Samsung and Huawei – have said they were making their own 5G chipsets which would be integrated into their 5G smartphones. Will Samsung use both its own silicon as well as Qualcomm’s in future 5G devices?
Over the next few months Qualcomm will begin shipping both the Snapdragon 865 and Snapdragon 765 chipsets. The Snapdragon 865 is more powerful, though 5G is on a separate modem, potentially decreasing the power efficiency of devices. The Snapdragon 765 has 5G connectivity integrated, though is notably less powerful. Whichever chipset OEMs elect for, there will be a trade-off to stomach.
Looking at the rumours spreading through the press, it does appear many of the smartphone manufacturers are electing for the Snapdragon 865 and a paired 5G modem in the device. Samsung’s Galaxy S11, Sony Xperia 2 and the Google Pixel 5 are only some of the launches suggested to feature the Snapdragon 865 as opposed to its 5G integrated sister chipset.
With Mobile World Congress 2020 in Barcelona just two months away, there is amble opportunity for new 5G devices to be launched prior, during and just after the event. It will be interesting to see what 5G silicon is used in them.
Incomplete (or non existent) 5G Standards:
Of critical importance is that there are currently no standards for 5G implementations. The closest is IMT 2020.SPECS which won’t be completed and approved till November 23-24, 2020 ITU-R SG5 meeting or later. That spec will likely not include the 5G packet core (5GC), network slicing, virtualization, automation/orchestration/provisioning, network management, security, etc which will either be proprietary or use 4G LTE infrastructure. It also might not include signaling, ultra low latency or ultra high reliability, depending on completion of those items in 3GPP Release 16 and its disposition to ITU-R WP 5D.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
For nearly a decade, Samsung has worked to bring 5G from the lab to real life by working closely with carrier partners, regulatory groups and government agencies to develop the best 5G experience possible. As a leading contributor to industry groups like 3GPP and O-RAN Alliance, Samsung is committed to an open, collaborative approach to networking, which has helped to accelerate delivery of 5G to consumers and businesses. Over the past year, in addition to launching a robust 5G device portfolio, the company reached several historical milestones including providing network equipment for the world’s first 5G commercial service in Korea as well as working closely with global carrier partners to expand 5G networks and introduce 5G experiences and use cases.
In the year ahead, Samsung says they will continue to lead the market in 5G innovation by introducing new advancements that will improve the speed, performance and security of Galaxy 5G devices even further. In 2020, these advancements will give even more people access to new mobile experiences that change the way they watch and interact with movies, TV and sports, play games and talk with friends and family.
For more information about Samsung Galaxy 5G devices please visit news.samsung.com/us/galaxy-5g/, www.samsungmobilepress.com or www.samsung.com/galaxy.
References:
https://news.samsung.com/us/samsung-galaxy-5g-devices-shipping-more-than-6-million-2019/
https://telecoms.com/501580/samsung-claims-the-5g-lead-after-6-7-million-shipments/
https://www.extremetech.com/mobile/304091-samsung-shipped-over-6-7-million-5g-phones-in-2019
Samsung makes major progress in 5G network equipment sales; seeks to leverage first mover advantage to lead in 5G
Overview:
Telecommunications network equipment sold to wireless network providers has always been a minor part of Samsung’s business, especially compared to memory chips and mobile phones – two sectors where it leads the world (also #1 in total semiconductor revenue and #1 or #2 silicon foundry vs TSMC). Last year, Samsung held only a 6.6% share of the overall telecom equipment market, compared with Huawei’s 31%. It ranked fifth in global sales of wireless base stations.
In fact, the South Korean conglomerate’s information technology and mobile communications business declined 7% last year to $87 billion, of which an estimated $85 billion was mobile device sales and $2 billion was network infrastructure. SK Telecom is probably Samsung’s biggest customer for network gear. In the U.S., Samsung sells its 5G network equipment (base stations/small cells) to AT&T, Verizon and Sprint (Samsung is also a part of the Sprint Spark initiative).
Yet this year, Samsung is benefiting from a first-mover advantage in with South Korea deploying nationwide commercial (pre-standard) 5G networks in April and leading the world in 5G subscribers. So the company’s initial 5G success story relies on its dominant positions in the South Korean and U.S. markets, where 5G services were launched earlier than in other regions. RCR wireless said this past April that Samsung Electronics had sold 53,000 5G base stations to Korean carriers.

Samsung also hopes to capitalize on Huawei’s U.S. ban and U.S. government attempts to bar it from other countries 5G networks. Yet despite Washington’s ban, the Chinese tech giant has so far won fifty (or more) 5G contracts from countries including Switzerland, the United Kingdom, Finland and even South Korea, according to a media report that quoted Ryan Ding, the president of Huawei’s Carrier Business Group. Huawei is also extremely well positioned thanks to the launch of Chinese 5G services early this month. It offers both price competitiveness and a technological edge, according to network operators that have tested Huawei’s gear. It also is the holder of the largest number of telecommunications equipment patents.
Kim Young-ki, the head of Samsung Electronics’ network business division, said last June that Samsung would capture more than 20% of the global 5G equipment market by 2020. And since Kim’s statement, Samsung has made major inroads. It now supplies 5G equipment to two of the three of the world’s first 5G service providers, SK Telecom and KT, both in South Korea, where (as noted above) nationwide 5G services began in April. Samsung also supplied the first 5G-enabled smartphones.
Beyond South Korea, Samsung provides 5G gear to AT&T, Verizon and Sprint in the U.S., which both run limited 5G services. Test supplies of Samsung 5G equipment have been provided to Telefonica of Germany, as well as AT&T and T-Mobile of the US. However, Samsung declined to comment to Asia Times on how those tests are proceeding.
In October, Samsung won a contract to supply 5G mobile network equipment to KDDI, Japan’s second-largest telecommunications company. It did not reveal the details of the deal, but local media reports said the 5G equipment supplied by Samsung was expected to be worth US$2 billion over the next five years.
Also in October, Samsung showcased advanced LTE and 5G technologies used in combination in dual-connected mode networks with Reliance Jio Infocomm of India at the India Mobile Congress 2019. Experts say India is not ready to launch 5G services, but Samsung is keen to pave the way in cooperation with Jio.
“Samsung has been working in close cooperation with Jio to bring a digital transformation including transition to 4G throughout India for seven years,” Paul Kyungwhoon Cheun, Executive Vice-President and Head of Network Business at Samsung, said in a press release. “Samsung and Jio will continue to join forces in bringing next-generation innovation across the country, harnessing the full 5G potential in driving further growth of digital India.”

According to the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea, Samsung took 36% of global sales of 5G network equipment in the first quarter of this year – the top position – followed by Ericsson and Huawei, both with 28%, and Nokia with 14%. That improvement illustrates how far Samsung Electronics has come in the 5G market.
“Now, Samsung is posting a higher 5G equipment market share than its competitors as only a few countries, such as Korea and the US, have commercialized 5G service,” an unnamed industry expert told Asia Times. “We need to see how Samsung performs in the future … it is not likely to maintain its current position as more and more countries commercialize 5G services.” The expert added that 5G services will be launched in about 50 countries next year, creating new battlegrounds for the sector’s players to fight on.
Samsung’s 5G Future:
Gaining early traction in major markets is crucial for wireless network equipment makers. “Telecommunication service providers tend to keep their relations with existing suppliers once their network is set,” Kim Jong-ki of the Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade told Asia Times. “It’s too early to speak of the future of Samsung’s 5G telecommunication business, but Samsung indeed has the potential to be a strong contender.
“Samsung’s participation in the world’s first commercialization of 5G network in Korea is a valuable asset for Samsung, and Samsung has R&D power and enough patents in the key area of 5G telecommunication – though its total number of patents does not match Huawei’s,” Kim added.
Pundits say that in addition to Samsung’s first-mover advantage, its position as an end-to-end 5G solution provider and its immunity to security concerns in the US are further strengths. Washington’s blacklisting of Huawei offers Samsung a particularly juicy opportunity to seize a major bridgehead in the world’s largest economy.
“Samsung’s telecommunications equipment business is expected to perform better in the 5G era [than in previous eras] as it took the initiative in the newly growing 5G market, as seen in its global market share in the first quarter of this year,” the expert said. “Now, Samsung’s position looks different from that in the 4G gear market.”
Moreover, there appears to be backing for aggressive moves into the sector at the very pinnacle of the electronics conglomerate – a critical factor in Korea’s family-dominated business groups.
“Samsung’s changed stance on the telecommunication equipment business is also expected to enhance competitiveness,” the expert added. “Lee Jae-yong, the heir of the Samsung business group, has shown a will to promote the business.”
Samsung states on its website:
While the IMT-2020 goals play a pivotal role in directing research and development, 5G networks will need to go far beyond numerical improvements in order to meet the requirements of evolving network usage that we are seeing today. Indeed, while 5G networks will enable the delivery of some very impressive services to the traditional mobile subscriber, dozens of previously unconnected industries are now incubating ideas that will completely transform the role of mobile telecommunications in today’s society.
In order to support these services, 5G radio access networks (5G RAN) will need to be flexible. They will need to be able to adapt to a wide range of different service requirements so that network and third party service providers alike can deploy new applications, services and devices seamlessly and sustainably. Through the evolution of the radio air interface, the implementation of ‘software-defined’ principles and more, the 5G RAN will enable transparent connectivity for a new generation of information-driven users and industries.
5G radio access deployments will be characterized by their highly dense, throughput focused and software-driven nature. Foremost among the differences between 5G and LTE will be the logical separation of each component of the 5G fNB (future NodeB). In particular, we will see the baseband split, with the lower layers of the 5G protocol stack merging with the radio unit to form a new element called the Access Unit (AU).
In an interview with an Ovum analyst, Samsung’s Dongsoo Park, PhD said:
“Having Korea as our home base affords us an incredible opportunity to commercialize the latest technology, which are reinforced by our current presence in the U.S., Japan, Europe, Southeast Asia, the Middle East and Russia. Our recent collaboration with Jio India further promotes Samsung’s firm commitment to the infrastructure business.”
We couldn’t agree more and are eager to see if Samsung can leverage that first mover advantage and potential Huawei blacklisting to gain share in the 5G network infrastructure market.
References:
https://www.asiatimes.com/2019/11/article/samsung-takes-on-huawei-in-race-for-5g-dominance/
https://www.samsung.com/global/business/networks/insights/5g-radio-access/
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics MOU for 8K TV connected via a 5G Network
SK Telecom (SKT) today announced that it signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Samsung Electronics to jointly develop and commercialize the world’s first 5G-8K TV. SKT said the 5G-8K TV will revolutionize users’ television-watching experience by directly receiving 8K video over SK Telecom’s ultra-low latency and ultra-wideband 5G network.
SKT launched its 5G service simultaneously with its rival Korean cellular carriers in early April. Korea’s largest mobile operator by subscribers said it reached the 1 million 5G subscriber milestone on 21 August.
*8K (7680×4320 resolution) is the highest resolution currently in existence, a fourfold enhancement of UHD standard.
SK Telecom plans to apply Mobile Edge Computing and Network-Based Media Processing to its pre-standard 5G network to realize seamless transmission of 8K video. Samsung Electronics will apply its 8K AI Upscaling and next-generation codec technologies to upgrade full HD and UHD images to 8K resolution. The company will also equip 8K TVs with 5G dongles to support direct transmission of 8K resolution video content.

Park Jin-hyo, second from left, who heads SK Telecom’s ICT Technology Center, and Lee Hee-man, right, who heads Samsung Electronics’ VD Service PM Group, with other officials after signing a MOU to develop 8K TV powered by 5G networks. / Courtesy of SK Telecom.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Viewers will be able to watch video content of POOQ* and oksusu at 8K resolution.
*POOQ is an over-the-top video subscription service offering programs on terrestrial TV. It is a joint platform of Korea’s terrestrial broadcasters.
The two companies have also agreed to jointly evolve 5G-8K TV further to deliver a new user experience by working together in the areas including eSpace, SK Telecom’s hyper-space platform for replicating the real world in cyberspace, and 5G Sero TV, a 5G-based television that can be rotated both horizontally and vertically to provide a smartphone-like UX for TV users.
Moreover, they plan to develop B2B business models in areas of smart office and digital signage by adding 5G connectivity to televisions and displays.
SK Telecom introduced technologies related to ‘5G connected screen’ at an MPEG held in July 2019 and was designated as the NBMP (Network Based Media Processing) chair company to lead international standardization of 5G connected screen related technologies. To this end, SK Telecom will newly open Hyper Media Lab under its ICT R&D Center.
“The 5G-8K TV is the culmination of ultra-low latency 5G networks combined with ultra-high definition TV technology,” said Park Jin-hyo, Chief Technology Officer and Head of ICT R&D Center at SK Telecom. “5G technology will help make the world of hyper media a reality.”
Samsung Electronics will utilize artificial intelligence features that upscale lower-quality content to appear close to 8K resolution. Samsung will equip its 8K TV with a small piece of hardware, called a dongle, to support wireless reception of 8K images.
Qualcomm, Samsung, and Huawei announce 5G SoCs at IFA in Berlin
The Berlin-based IFA consumer electronics show keynotes from Qualcomm, Huawei, and Samsung illustrated the telecom supplier industry’s strong dedication to 5G System on a Chip (SoC). Yet this comes more than one year before the IMT 2020 Radio Interface Technology (RIT) standard has been completed and six months (or more) before 3GPP Release 16 (which will specify ultra low latency and ultra high reliability) has been finalized. Hence, we wonder if major revisions of announced 5G SoC’s and chipsets will be required in IMT 2020 standard endpoint devices?
Qualcomm President Cristiano Amon’s keynote presentation described the company’s 5G strategy, which is focused in part on driving access to 5G end point devices. Amon promised to bring 5G mobile phones to the masses with a high-end modem and said Qualcomm chips would also power mid-price 5G devices reaching the market next year.
Qualcomm’s second-generation X55 modem supports 5G at both sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave frequencies and supports peak downlink speeds of 7 Gbps and peak uplink speeds of 3 Gbps.
Notable in Qualcomm’s IFA presentation is support for dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) across the 6-, 7- and 8-series Snapdragon mobile platforms. In addition to bringing down the price point on 5G phones, this fits with operators plans to rapidly scale coverage in 2020 by using DSS, which lets LTE and 5G operate in the same band at the same time. More on DSS (Ericsson and Qualcomm 5G data call) in this techblog post.
As wireless network providers introduce or expand their 5G network offerings, “We need to enable the operators to have that ecosystem ready so you can start providing new devices with dynamic spectrum sharing… We want all the users to have the benefit of this technology,” Amon told the IFA audience.
To make that 5G ecosystem possible, Amon announced Qualcomm would bring its portfolio of 5G mobile platforms out of just the 8-series and into the 7- and 6-series in 2020. Amon said a dozen OEMs were already onboard. with the 5G-enabled 7-series. “We are going to bring 5G to scale with our many partners.”
“Qualcomm have done a phenomenal job to drive the 5G ecosystem,” said industry analyst Paolo Pescatore. “It’s going faster than anyone could have ever imagined.”
–>We certainly agree with that comment – Qualcomm has done a splendid job, but much more work remains before an IMT 2020 chipset/SoC is introduced – most likely in mid 2021. Qualcomm will likely be partnering with carriers to market new devices. It’s typical for operators to market subsidized handsets in the United States, but much less so in Europe.

Image courtesy of Qualcomm.
5G chipsets from Qualcomm, the world’s biggest supplier of mobile phone chips, now run on five devices from Samsung Electronics, including the $1,299 Galaxy S10 5G model and the new $2,000 Galaxy Fold. Samsung is the world’s #1 smartphone maker. It has also put Qualcomm chips in its lower-priced A90 5G model, which had used Samsung chips in an earlier version.
Amon said that Qualcomm plans to add 5G capabilities to its lower-cost Snapdragon 6 and 7 series devices, which could make 5G phones available at lower prices than the current models, which are mostly flagship devices priced at a premium. Qualcomm’s 6 and 7 series Snapdragon chips are found in devices from Lenovo Group Ltd’s Motorola, Xiaomi Corp, Oppo and Vivo that retail in the $300 range.
Indeed, virtually all flagship 5G mobile devices launched in 2019 in Europe and beyond are built on the Qualcomm’s ®Snapdragon™ 855 Mobile Platform. Such semiconductor market dominance is unprecedented in this author’s 52 years of experience.
“The transition to 5G is going to be faster than earlier transitions,” Amon told Reuters on the sidelines of the IFA consumer electronics fair in Berlin. “Now we have to bring it to everyone.”
Conversely, this author believes the transition to mass market/high volume 5G (based on IMT 2020 standards), will be much longer than earlier transitions, e.g. from 3G to 4G.
More than 20 network operators and a similar number of smartphone makers – from the United States to Europe to China – are launching 5G services and handsets. Amon estimated there were 2.2 billion mobile users that could upgrade to 5G. Again, we don’t think that will happen till there’s real 5G interoperability and roaming, which will require all devices and base stations to support IMT 2020 RITs/SRITs at a minimum!
Unlike rivals, Qualcomm is designing its chipsets to handle frequencies “from A to Z,” said Amon at IFA, adding that flexibility to switch between 4G networks and new 5G networks was critical.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Qualcomm’s 5G chipset competition is limited:
1. 5G chips from Taiwan based Mediatek can only handle sub-6 bands, reducing the cost and complexity of the chips and phone designs. There really are no other 5G merchant market silicon vendors. Mediatek’s 5G chip supports Standalone (SA) and Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G infrastructure, but it only supports sub-6GHz spectrum.
“Everything about this chip is designed for the first wave of flagship 5G devices. The leading-edge technology in this chipset makes it the most powerful 5G SoC announced to date and puts MediaTek at the forefront of 5G SoC design,” said MediaTek President Joe Chen. “MediaTek will power rollouts of 5G premium level devices,” Chen added.
2. China state owned Unisoc announced the MAKALU 5G technology platform and its first 5G Modem IVY510 at MWC2019 in Barcelona, but that company is not represented in ITU-R WP5D meetings where IMT 2020 RIT/SRITs are being standardized. UNISOC IVY510 is the first 5G Modem of UNISOC based on the MAKALU technology platform, produced with TSMC’s 12nm process. As the first 2G/3G/4G/5G multimode platform of UNISOC, IVY510 complies to the latest 3GPP R15 spec, supports Sub-6GHz 5G spectrum with a channel bandwidth of 100MHz, which is a highly integrated, high performance, low power 5G platform, and supports both standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) network configurations to meet communication and networking requirements during different stages of 5G deployment.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung announced the Exynos 980 eight-nanometer mobile processor with an integrated 5G modem capable of sub-6 GHz downlink speeds of 2.55 Gbps and 1.28 Gbps uplink.
ENDC refers to 5G/LTE dual connectivity and, based on 3GPP documents, stands for E-UTRAN New Radio-Dual Connectivity. Essentially ENDC allows user equipment to connect to an LTE eNodeB that acts as a master node and a 5G gNodeB that acts as a secondary node. Sprint, for instance, uses this to deploy LTE and 5G in its 2.5 GHz spectrum at the same time; a complement to the split-mode manner the carrier configures its massive MIMO radios. Samsung said that ENDC provides peak speeds of 3.55 Gbps downstream and $2.55 Gbps upstream.

Image courtesy of Samsung Electronics.
“With the introduction of our 5G modem last year, Samsung has been driving in the 5G revolution and paved the way towards the next step in mobility,” said Ben Hur, vice president of System LSI marketing at Samsung Electronics. “With the 5G-integrated Exynos 980, Samsung is pushing to make 5G more accessible to a wider range of users and continues to lead innovation in the mobile 5G market,” he added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Huawei’s Richard Yu reviewed the specs of the Kirin 990, which the company called “the world’s first 5G SoC,” a disputed claim. Yu touted the Kirin 990 chipset at IFA: “It’s the world’s most powerful 5G system on a chip. It’s the world’s most powerful 5G modem.”
The Kirin 990 5G is built on a seven-nanometer semiconductor manufacturing process. It includes silicon technologies from previous iterations of the Kirin line as well as the Balong line.

Richard Yu, CEO of Huawei’s consumer business group, presents at IFA. Image courtesy of Huawei.
The updated Kirin is set to power Huawei’s upcoming flagship smartphone the Mate 30, which will be officially announced at a Sept. 19th launch event in Munich, Germany. According to specs provided by Huawei, the Kirin 990 packs more than 10 billion transistors. It can theoretically support downlink speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps and uplink speeds of 1.25 Gbps upstream. The chip set has an adaptive receiver that enables it to switch between 4G and 5G where coverage of the faster technology is weak. And, to save energy, it has a ‘big core’ to handle powerful computing tasks with the support of artificial intelligence, and a ‘tiny core’ for less demanding operation.
Huawei probably won’t sell the Kirin SoC on the semiconductor merchant market, but rather use it internally in its 5G endpoint devices (mostly 5G smart phones- for now). The latest Kirin does not support millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies, which provide multi-gigabit-per-second speeds at the expense of much shorter range/distance. The U.S. has auctioned more millimeter wave frequencies than any other country while AT&T and Verizon are using it in their pre-IMT 2020 standard 5G deployments. Again, mmWave has a much shorter range than mid and lower band spectrum, but has higher data-carrying capacity. Currently, millimeter wave-based 5G networks are more or less limited to the U.S. market where regulatory issues make it very difficult for Huawei to sell anything, including smartphones.
Indeed, due to U.S. trade sanctions, Huawei’s 5G-ready Mate 30 smartphone, scheduled to be launched on Sept. 19, won’t be able to run the official version of Google’s Android operating system and app services if U.S. sanctions remain in place. That eliminates the entire Android app ecosystem which include pre-installing the Google Play store and a suite of popular apps such as Google Maps that buyers would expect to be available from the moment they turn on their new phone and synch it with their profile. Huawei’s fallback option would be to run the devices on its home-grown Harmony operating system, although company officials and analysts say it is not yet ready for prime time.
All that makes it highly unlikely Huawei will be able to sell any 5G smartphone outside of China.
“Qualcomm has a scale advantage,” said Ben Wood, analyst at CCS Insight. “Huawei’s commitment to continue innovating on silicon is really impressive, especially given the geopolitical headwinds they are facing. “But at the end of the day, it’s a single-vendor solution. And, even if they had aspirations to sell the chipset, that is getting more difficult all the time,” Wood added.
References:
https://ca.reuters.com/article/idCAKCN1VR1HT-OCATC
https://www.reuters.com/article/qualcomm-5g-idUSL2N25W1K5
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20190907/5g/huawei-samsung-5g-ifa
Samsung (with AT&T) Tests How 5G Can Improve Chip-Making
By Sara Castellanos of the Wall Street Journal
Samsung Electronics Co. is testing how 5G wireless networks can speed up connections at its chip-making factory in Austin, Texas, a pilot that aims to prove 5G is more than a buzzword. The company is experimenting with the new technology to show what ultra-fast speeds can do at its Austin chip factory
The company has teamed up with AT&T Inc. ’s communications division to develop a customized 5G network to experiment with how it could be used in chip manufacturing.
The fifth generation of cellular networking, 5G is designed to replace current 4G technology, also known as LTE. The ultrafast speeds and reduced lag that will come with 5G will buttress new applications such as augmented reality and self-driving cars. Peak download speeds using 5G are expected to be about 100 times as fast as with 4G.
The transformation that will come from widespread commercial 5G deployments in manufacturing, logistics, transportation and energy is still about a decade away, experts have said. That’s partly because it will take time to roll out the infrastructure to achieve full 5G coverage.
In the meantime, Samsung and other companies are testing 5G’s potential in limited pilots to show what the technology can do.
“We’re still in the experimentation phase, but we’re hopeful there’s value,” said Alok Shah, vice president of networks strategy, business development and marketing at Samsung Electronics America, the company’s U.S. unit.
Factories will be a big beneficiary of 5G connections, said Andre Fuetsch, chief technology officer for AT&T Communications, AT&T’s biggest division.
“We see 5G being a great solution for solving a lot of the Wi-Fi issues that typical factories have today,” he said. The technology, for example, could be used on manufacturing floors to power more reliable connections for computer-vision-scanning equipment that checks product quality.
AT&T has also rolled out consumer 5G networks in about 20 U.S. cities.
Samsung Electronics America and AT&T have invested millions of dollars in 5G innovation at Samsung’s chip-manufacturing facility in Austin. Thousands of employees work at the chip factory, which is the size of about 10 football fields, Mr. Shah said.
Chip-making uses a lot of water and toxic chemicals; 5G could help chip factories cut waste and alert workers to safety hazards.
For example, 5G would allow more sensors to be installed to detect air quality, Mr. Shah said. Streaming real-time data from the sensors over 5G networks would mean that a control center can immediately detect serious air-quality hazards and move people out of harm’s way. Sensors in factories today can’t rely on existing wireless networks to pass along warnings to a control center, Mr. Shah said.
“Being able to put thousands of sensors within a relatively small space is hard for other [networking] technologies to support,” Mr. Shah said. Certain networks can only support a finite number of devices. Fifth-generation wireless networks could support 1 million devices per square kilometer, up from about 100,000 devices per square kilometer with 4G LTE, he said.
Sensors on pumps and valves could also stream data about water usage over 5G networks so the facility can improve the efficiency of its water usage in real time and reduce waste.
Using 5G connections, workers could also learn how to repair equipment on the factory floor through augmented and virtual-reality headsets without any buffering or lags.
Other companies including New York Times Co. and German engineering firm Robert Bosch GmbH are testing 5G in pilots. The market for 5G, including related network infrastructure, is forecast to grow to $26 billion in 2022 from $528 million in 2018, according to research firm International Data Corp.
The tests are often “showcase demonstration pieces,” useful for proving that 5G could generate revenue through new services or make processes more efficient, said Jason Leigh, research manager for mobility and 5G at IDC.
“The sooner you can get something tangible, it makes it easier to have that discussion at a C-suite and board level about what 5G really is, and it’s not just this fad,” Mr. Leigh said.
Write to Sara Castellanos at [email protected]
https://www.wsj.com/articles/samsung-tests-how-5g-can-improve-chip-making-11565813658
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last September, AT&T and Samsung created the US’s first manufacturing-focused 5G “Innovation Zone” in Austin, TX. The zone, designed to test 5th generation wireless broadband technology, will be on Samsung Austin Semiconductor’s 160-acre campus in north Austin. The site will feature AT&T’s 5G wireless technology along with Samsung’s 5G network equipment, according to an announcement Wednesday from the two companies.
Technology experts say 5G — which is essentially ultra high-speed wireless connections — will not only power future waves of mobile devices, but also will evolve technology in other industries like automotive and health care. Companies expect 5G to be up to 100 times faster than the current 4G networks.
“This collaboration with Samsung Electronics America and AT&T will help us test how a 5G network can improve mobility, performance and efficiencies within our plant,” Sang-Pil Sim, president of Samsung Austin Semiconductor, said in a statement.
South Korea-based Samsung has operated in Austin since 1997. About 3,000 employees work in the 2.45 million-square-foot Austin chip making plant. Samsung has invested $17 billion in its Austin campus through the years.
SK Telecom and Samsung Bring South Korea Closer to 5G Standalone Commercialization
The two companies successfully completed interoperability test between 5G Standalone Core and Commercial Network Solutions (based on 3GPP Release 15 which is not 3GPP’s final submission to ITU-R for IMT 2020 RIT/SRITs.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics today announced the successful completion of South Korea’s first interoperability assessment between 5G Standalone (SA) Core and other commercial network systems over a pre-standard 5G network. This successful result brings the two companies one step closer to 5G SA commercialization.
The 5G SA Core, jointly developed by SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics, not only supports technologies including network slicing and function modularization based on 3GPP standards, but also offers additional functions that operators have been using since LTE, include billing, subscriber management and operational convenience system. The interoperability assessment is the final stage for verifying the validity of 5G SA data transmission, signifying that the SA system is ready to be launched for commercial service.
Both companies implemented several cutting-edge technologies in the 5G SA Core that has been used for the interoperability. The technologies include Data Parallel Processing technology that performs QoS and transmission control simultaneously; Data Acceleration technology that classifies and distributes similar traffic types; and Path Optimization technology that automatically delivers data traffic to Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) platform.
“Along with the initial phase of NSA rollout, SK Telecom has been continuously focusing on researching and developing the SA technology in order to provide customers a differentiated service quality with innovative products, which will be launched in the first half of next year,” said Park Jin-hyo, Chief Technology Officer and Head of ICT R&D Center at SK Telecom. “By strengthening bilateral collaboration with Samsung, SK Telecom will drive and lead highly innovative 5G technologies and solutions.”
“The fundamental structure of 5G SA is built on a completely new configuration, successfully delivering the most optimized 5G service to customers and enterprises across numerous industries,” said Jaeho Jeon, Executive Vice President and Head of R&D, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Maintaining Korea’s leadership in network innovations through continuous investments in next-generation technologies is important to Samsung and SK Telecom, and the companies will continue to collaborate on developing and commercializing 5G SA.”
Once 5G SA is commercialized, data processing efficient will be improved by threefold, allowing efficient control for supporting massive data traffic. Moreover, 5G SA system is highly optimized for emerging next generation services such as Autonomous driving, Smart Factory, Smart Farm, and AR/VR.
For the past five years, the two companies have been collaborating on LTE and 5G development, which ultimately led to this successful 5G SA Core interoperability test. Some of other accomplishments include the commercialization of Virtualized LTE Core and Packet Optimization system; and they have completed the development of 3GPP Rel. 15 based SA Core in July last year, and successfully launched 5G NSA commercial service in April this year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom is the largest mobile operator in Korea with nearly 50 percent of the market share. As the pioneer of all generations of mobile networks, the company has commercialized the fifth generation (5G) network on December 1, 2018 and announced the first 5G smartphone subscribers on April 3, 2019. With its world’s best 5G, SK Telecom is set to realize the Age of Hyper-Innovation by transforming the way customers work, live and play.
Building on its strength in mobile services, the company is also creating unprecedented value in diverse ICT-related markets including media, security and commerce.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
For more information, please contact:
[email protected] or [email protected].
Media Contact
Yong-jae Lee
SK Telecom Co. Ltd.
(822) 6100 3838
(8210) 3129 6880
Irene Kim
SK Telecom Co. Ltd.
(822) 6100 3867
(8210) 8936 0062
Ha-young Lee
BCW Korea
(822) 3782 6421
Samsung deploying small cells in large volumes for Reliance Jio in India
Samsung Networks is deploying small cells in large volume for indoor coverage for Mukesh Ambani-led Reliance Jio, which is set to have 99% population coverage soon in the country, according a Samsung executive.
“We have seen drive happening on indoor small cells. But that doesn’t mean that outdoor isn’t happening. Outdoor is happening at a good speed basis the site availability and so on… We will continue to expand on this piece of the network [indoor] because there are places where it’s more value to go that way,” Srini Sundararajan, Senior Vice President and Head of Networks Business at Samsung India, told ET.
“Jio tells us what their network requirements are, and we support…indoor always volume looks larger because devices are smaller and are easy to deploy and are self-configured,” he added.
Samsung Networks had earlier this year obtained a new 4G LTE network expansion contract from its sole customer in India, Reliance Jio, to increase the telco’s 4G network penetration from around 75% to 99% by Diwali this year.
The South Korean company is the sole 4G equipment provider to Jio with contracts to supply wireless base station equipment for over 140,000 sites for pan-India coverage last year, ET had earlier reported.
Image courtesy of Economic Times Telecom (India)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sundararajan said that Jio is expanding its networks for both coverage and capacity needs in the country. “It has to be both. There are still parts of the country we need to increase the coverage. Some of the hilly areas or remote areas. For every project, there is a certain percentage of sites for coverage and a large percentage is for capacity,” he added.
For capacity, Jio has started commercial deployment of massive mimo technology in areas where it is not able to add new sites easily.
In addition to 4G wireless equipment, Samsung is also providing packet core technology to Jio. The executive said that the virtualised packet core will play a crucial role in the 5G scenario. Samsung is currently preparing to conduct 5G field trials in New Delhi in the first quarter of the next year, and is working closely with the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
“We have a lot to offer similar to what we did on 4G, and which is why we said that we will partner with the DoT. We are directly partnering with the DoT to ensure that we listen to the needs of the government,” the executive said.
He added that the government’s involvement in these 5G field trials is very crucial for the successful commercial roll out since there will be 5G use cases that will have “societal value” along with the business value.
“The government is very proactively enabling and promoting to grow the 5G network. They are very aware that it is the ecosystem, and not just a vendor or operator. So they tend to bring different players into it to ensure that we are able to provide a high-value system for the country,” he added.
Samsung will be conducting the trial using the millimeter wave (mmwave) spectrum even as other vendors like Huawei plan to conduct trials in the mid-band. Sundararajan said that the millimeter wave band will offer a large chunk of spectrum that can result in uses cases like fixed wireless access (FWA) with huge capacity for data services. “We need to have the technology in the mmwave to enable the true vision of the government,” he said.
Samsung is currently doing 3.5Ghz trials in the mid-band in South Korea, and in the US, we are doing mmwave trials. “We are technology agnostic, but use cases will drive the adoption of one of these bands,” he said.
References:
Reliance Jio Blankets India with Inexpensive 4G Service; Where are the Profits?
India Selects Cisco, Samsung, Nokia, Ericsson for 5G trials; Bars Huawei and ZTE
India’s DoT Creates Dedicated 5G Technology Test Bed after Ericsson 5G Demonstration
India Mobile Congress 2018: Telecom Equipment Vendors to Invest over Rs 4,000 crore in India; Samsung in Spotlight
IEEE President Jim Jefferies speaking at India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telecom Equipment Vendors Investment in India:
Telecom equipment makers including Cisco, Samsung, Ericsson, Nokia, Intel and Sterlite Tech (from India) will be investing more than Rs 4,000 [1] crore in India, announced Telecom Minister Manoj Sinha Saturday at the third day of the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018. That investment commitment is in line with India Prime Minister Narendra Modi‘s goal to achieve a capital gain of $100 billion (about Rs 7 lakh crore) by 2022. The amount invested will increase further, said Sinha, adding that the investment commitment shown by the equipment manufacturers is a part of government’s ambitious policy target to achieve Rs 7 lakh crore worth of investment by 2022. Sinha said discussions and announcements at IMC show that India is ready for the emerging 5G services. The 5G technology (based on the forthcoming IMT 2020 standard) would facilitate massive machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and has many other applications.
Note 1. 4000 crores (= 400000 lakhs) is equal to 40000 million (40 billion). 40,000,000,000 INR is equal to 544,400,000 USD @ 73.48 Indian rupees to 1 US dollar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These are the first set of investments flowing in after the announcement of National Digital Communications Policy. In August this year, the India Cabinet has approved the National Digital Communications Policy 2018 that aims to attract $100 billion of investment and creation of 4 million jobs in next four years, in addition to an aggressive focus on next-generation of technologies. However, the investments will be made over a period of next one-two years, according Telecom Secretary Aruna Sundararajan.
Among all these telecom equipment makers, Sterlite Tech is the only homegrown (Indian) company that locally produces end-to-end optic fiber gear, a critical digital infrastructure required to increase 4G-LTE footprint and enabler of upcoming “5G” technology roll-outs.
Meanwhile, Korea’s Samsung, Sweden’s Ericsson, Finland’s Nokia and the US-based Cisco have already partnered with India service operators and the telecom department to conduct field trials and demonstrate India-specific 5G use cases.
Industry experts discussed challenges in the digital communications during the three-day India Mobile Congress 2018 event, which saw participation from 20 countries and 300 companies, Sinha said. Sinha added that discussions and announcements at the event show India is ready for the emerging 5G services. The 5G technology could facilitate massive machine-to-machine communications and has multiple usages.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The India Mobile Congress 2018 was organized jointly by the India DoT and industry group Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) which represents telcos such as Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea as well as gear makers such as Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Cisco and Samsung.
Sundararajan said IMC has generated more enthusiasm around 5G and the government has already committed to be at par with the world in launching this next generation services. “We have already demonstrated government intent that India does not miss the 5G bus. We have already started to take initial set of action to make an enabling environment. We expect actual allocations of spectrum (for 5G services) to begin in the second half of next year,” Sundararajan added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Samsung in IMC 2018 Spotlight:
At IMC 2018, Samsung announced its plan for India’s first large-scale 5G trial, scheduled to take place in the first quarter of 2019 in collaboration with the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
In his keynote speech at the event, Youngky Kim, President and Head of Networks Business at Samsung Electronics, said, “Samsung will pave the way for 5G to unlock the full potential of India together with industry leaders. We are witnessing a rise in adoption of new technologies, inspired by ‘Digital India’ and spurred by the transition to 4G.’
“Our partnership with Reliance Jio has empowered millions, making their everyday lives better. Our roadmap for 5G showcases our strong commitment to India. We will continue to be a partner in Government of India’s Digital India mission,” said HC Hong, President and CEO, Samsung Electronics SouthWest Asia. Leading Disruptive Changes Using 4G in Digital India Since 2012, Samsung has been a key partner of the Indian telecommunications industry. During President Kim’s keynote speech at the IMC, he said that Samsung has successfully built the world’s largest greenfield and the most advanced 4G LTE networks nationwide by partnering with Reliance Jio.
At IMC 2018, Samsung showcased how its 5G solutions can enable a variety of 5G-powered business models and scenarios, including: 5G home broadband services, Smart Cities and Smart Agriculture.
Samsung’s 5G Skyship (see photo below), which was developed in partnership with Korea Telecom, was flying over the exhibition center to demonstrate first response use cases. Samsung says it has been a pioneer in developing 5G solutions using its technology and experience. With its successful development of the first commercial ASIC-based 5G modems and mmWave RFICs, the company has been manufacturing compact-sized 5G radio and router devices and CPEs.
 Photo provided by KT shows an unmanned airship using “high-end 5G” technology at the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018 in New Delhi
Photo provided by KT shows an unmanned airship using “high-end 5G” technology at the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2018 in New Delhi
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung says its years of commitment to R&D investments since 2000 have come to fruition, as the company has been selected by the world’s leading operators such Verizon, AT&T, Sprint and SK Telecom for both 4G and 5G solutions and services. At the root of this achievement are Samsung’s end-to-end solutions spanning network equipment, devices, chip sets and the world’s-first regulatory approval of 5G equipment by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Samsung will continue its legacy of 4G LTE to enable digital transformation and provide a seamless path to 5G.




