Month: December 2017
Verizon, Qualcomm, and Ericsson collaborate on successful Massive MIMO Trial
Verizon said in a press release that it completed the first successful FDD (Frequency Division Duplexing) massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) trial with a fully compatible customer device thanks to its collaboration with Ericsson and Qualcomm. The trial included the use of the latest Ericsson massive MIMO software and hardware along with a mobile test device powered by Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 845 Mobile Platform with an X20 LTE modem.
According to the aforementioned press release:
Massive MIMO is a key technology component in the evolution towards 5G. It has the potential of greatly improving network capacity and the customer’s experience. To realize the gains, both the network and devices need to support new TM9 [1] functionality which leverages advanced beam forming schemes between the network equipment and the mobile device. This will raise network spectral efficiency and customer speeds.
Note 1. In 3GPP Release-10 (LTE-Advanced) Transmission Mode 9 (TM9) was introduced. TM9 is designed to help reduce interference between base stations to maximise signal stability and boost performance. The new TM-9 enables the enhancement of network capabilities and performance with minimum addition of overhead. More information on TM9 is here.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Qualcomm introduced the 845 Mobile Platform at the Snapdragon Summit in Hawaii in early December. The trial comes after Verizon and Ericsson deployed massive MIMO on the wireless carrier’s Irvine, Ca network in late October.
“We don’t wait for the future, we build it. And this is another great example of moving the industry forward,” Verizon Chief Network Engineer and Head of Wireless Networks Nicola Palmer said in the release. “Massive MIMO is a critical component of our 4G LTE Advancements and will play an important role in 5G technology that will result in single digit latency and scalability in the billions of connections,” he added.
Joe Glynn, vice president, business development at Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. said: “This milestone further demonstrates Qualcomm Technologies’ leadership and commitment to continually bring innovative technologies to consumers to improve their mobile experiences. We look forward to continuing our work with Verizon and Ericsson to push the limits of LTE while ushering in a world of 5G.”
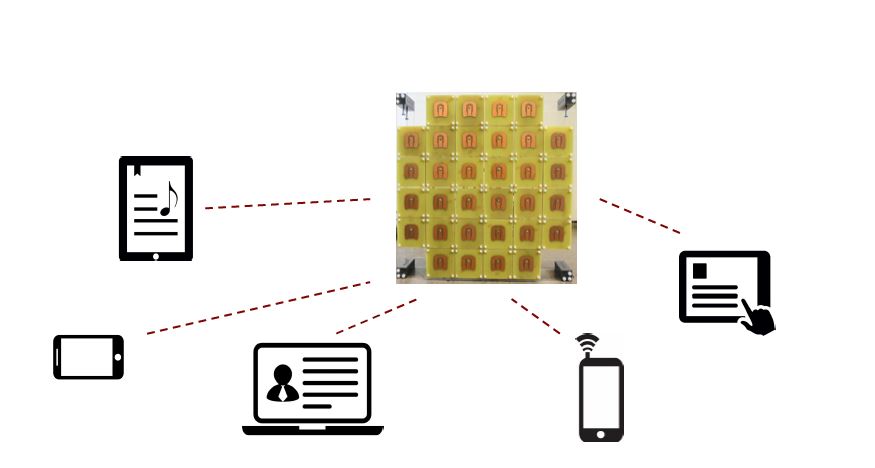
Massive MIMO is an LTE Advanced (4G) technology which has been described as being akin to a set of focused flashlights targeting users rather than a single floodlight. The high number of transmitters enables more possible signal paths and beam forming, which directs the beam from the cell site directly to where the customer is located, dramatically cutting down on interference.
Figure 1. Massive MIMO exploits large antenna arrays to spatially multiplex many terminals.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
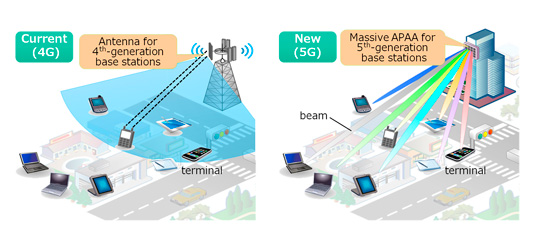
Figure 2. Active Phased Array Antenna (APAA) shown above right in 5G base stations. The combination of analog beam forming via APAA and digital MIMO signal processing for the multi-beam multiplexing is believed to be one of the promising approaches for reducing the complexity and power consumption of 5G base stations. However, that has yet to be proven in a commercial 5G deployment.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In October, Verizon and Ericsson announced they had achieved a milestone in LTE Advanced technologies by completing their first deployment of FDD massive MIMO on Verizon’s wireless network in Irvine, California. Massive MIMO improves both spectral and energy efficiency, increasing network capacity for currently compatible devices in the market. Customers experience higher and more consistent speeds when using apps and uploading and downloading files.
Ericsson’s massive MIMO portfolio is expected to be available next year, putting it in line with commercial smartphones with the TM9 compatible chipset, which are expected to hit the market in the first half of 2018.
The past year saw a lot of talk around massive MIMO, which is considered by many to be a foundation technology for 5G. At the inaugural Mobile World Congress Americas in September, Sprint and Ericsson unveiled results of 2.5 GHz massive MIMO field tests conducted in Seattle and Plano, Texas, using Sprint’s spectrum and Ericsson’s radios.
- In early September, Ericsson said massive MIMO was part of a trial with T-Mobile US using mid-band FDD spectrum on three sites in Baltimore, Maryland.
- In February, Blue Danube Systems announced the completion of commercial trials using its massive MIMO technology in licensed FDD LTE spectrum with AT&T and Shentel.
Niklas Heuveldop, Head of Market Area North America, Ericsson, said: “Advanced Antenna Systems and Massive MIMO are key technology enablers for 5G, and 4G LTE service providers and end users will also benefit from the superior capacity and network performance these technologies enable. The latest trial is another important step in the collaboration we have with Verizon and Qualcomm Technologies to further evolve 4G and prepare the network for 5G.”
The Ericsson Massive MIMO portfolio is expected to be available next year, putting it well in line with commercial smartphones with the TM9 compatible chipset, which are expected to hit the markets in the first half of 2018.
References:
http://www.samsung.com/global/business-images/insights/2017/Massive-MIMO-Comes-of-Age-0.pdf
http://www.ni.com/white-paper/52382/en/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2017/10/17/mimo-starting-to-realize-its-full-potential-in-lte-networks/
https://www.everythingrf.com/News/details/2639-zte-completes-massive-mimo-tests-for-imt-2020-5g
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03993.pdf
India’s DoT Creates Dedicated 5G Technology Test Bed after Ericsson 5G Demonstration
India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has firmed up plans to set up a 5G test bed that will be anchored by Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras, where this author presented several guest lectures in December 1990. According to a DoT official, the test bed is expected to be operational within the next six months.
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) too is soon expected to issue a set of recommendations to the Center that would enable companies wanting to conduct research experiments for the latest generation of mobile telephony to do so domestically. A senior TRAI official told the Indian Express newspaper that these recommendations would be a part of the suggestions on ease of doing business that the regulator is in process of issuing to the government.
“We need to have an ecosystem in India itself, which is simple so that experiments can be conducted. We should have sand-boxing, and licensing for experimentation on 5G technology here. For experiment purposes, we should have a light-touch system, where if some company wants to research, it should be able to get a license to do so,” the (unnamed) official said. “If these experiments were happening here, our officials would have been training here itself instead of China. We are soon going to give recommendations to the government on this issue,” the official added.
To accelerate research and development of technologies as well as specifications related to 5G, the Center has set up a high-level forum comprising officials from the DoT, the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, and the Department of Science & Technology, with representatives from industry and academia. The high-level forum, set up in September, is expected to evaluate and approve roadmaps and action plans with a broader target of rolling out 5G in India by 2020, which is the aim for most global telecom companies for launch of commercial 5G services.
India has traditionally been behind the curve in adoption of mobile technologies, especially in when the global standards for 3G and 4G were being set. One of the key objectives behind setting up the high-level forum on 5G was for India to be able to participate in the process being undertaken by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) in creating standards for 5G (IMT 2020), which is expected to be a key driver of technological growth in form of artificial intelligence, internet of things, etc.
The high-level forum will also work towards accelerated deployment of 5G for specific use cases in India, and these will include the development of road map related to emerging technologies, testing, and trials. It will also aim to strengthen domestic telecom equipment manufacturing necessary for the technology. As per a presentation prepared by the DoT, the targets set for the forum suggest that local manufacturers should be able to capture 50 per cent of Indian market and 10 per cent of global market over next five to seven years. The aforementioned DoT official said that the proposed 5G test bed at IIT Madras will play the role of a key enabler for research and development of domestic manufacturing of 5G equipment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Earlier in December, Ericsson demonstrated a 5.75Gbps “5G” network setup in Mumbai, India. In their live demonstration at at a trade show, the company showcased “essential technologies on the road to 5G.” One highlight was Gigabit LTE (1 GBPS download speeds) with License Assisted Access+ (LAA) technology. The LAA live demo highlighted the technology’s ability to leverage wireless network resources using higher frequency bands on a small cell architecture. Other technology innovations presented in the Ericsson showcase included advancements in Radio Network Evolution, 5G Ready Transport and Network Slicing.
+License Assisted Access is a LTE feature that leverages the 5 GHz unlicensed band in combination with licensed spectrum to deliver a performance boost for mobile device users. For more on LAA, please visit here.

Ericsson estimates that mobile data traffic in India will grow by 11 times by 2023.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In a recently released Ericsson 5G Business Potential Report, 5G will enable a $27 billion revenue opportunity for Indian telecom operators by 2026. The largest opportunity will be seen in sectors like manufacturing, energy and utilities followed by public safety and health sectors. This will be over and above the revenue generated from traditional services which are expected to grow up to $63 billion by 2026.
Key findings from the Ericsson report:
- Industry digitalization investments are growing and generating revenue for ICT players worth an estimated USD 3.3 trillion by 2026
- Operators can benefit from an additional 34 percent revenue from 5G-enabled market opportunities by 2026
- 5G has the potential to deliver unparalleled benefits to society and businesses
- The time is now to start creating a 5G business
3GPP Approves “5G” New Radio spec with tremendous industry support
“Today the 3GPP TSG RAN Plenary Meeting in Lisbon, Portugal successfully completed the first implementable 5G NR specification. AT&T, BT, China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Fujitsu, Huawei, Intel, KT Corporation, LG Electronics, LG Uplus, MediaTek Inc., NEC Corporation, Nokia, NTT DOCOMO, Orange, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Samsung Electronics, SK Telecom, Sony Mobile Communications Inc., Sprint, TIM, Telefonica, Telia Company, T-Mobile USA, Verizon, Vodafone, and ZTE have made a statement that the completion of the first 5G NR standard has set the stage for the global mobile industry to start full-scale development of 5G NR for large-scale trials and commercial deployments as early as in 2019.

On February 27, 2017 in Barcelona, global mobile industry leaders announced their support for the acceleration of the 5G NR standardization schedule, which introduced an intermediate milestone to complete the first implementable specification for Non-Standalone 5G NR operation. As a result of this announcement, the schedule acceleration was agreed at the 3GPP RAN Plenary Meeting on March 9 in Dubrovnik, Croatia. This first specification was completed as part of 3GPP Release 15. Widespread commercial deployment is expected to start next year.
The completion of the 3GPP New Radio specification is an essential milestone to enable cost-effective and full-scale development of 5G NR, which will greatly enhance the capabilities of 3GPP systems, as well as facilitate the creation of vertical market opportunities. 3GPP plans to continue to develop Release 15, including the addition of support for Standalone 5G NR operation also agreed upon by 3GPP in Dubrovnik. The 5G NR lower layer specifications have been designed so that they can support Standalone and Non-Standalone 5G NR operation in a unified way, to ensure that 3GPP benefits the global industry with a large-scale single 5G NR ecosystem. We express our appreciation for the tremendous efforts that 3GPP has dedicated to accomplishing this challenging standardization schedule.”

Editor’s Note:
3GPP NR spec is NOT a standard as 3GPP itself says it’s not a standards body. More importantly, NR is one of several Radio Interface Technologies that will be presented to ITU-R WP 5D for evaluation and selection of the true 5G/IMT 2020 standard for the Radio Access Network.
3GPP is an engineering organization that develops technical specifications – not standards. “The 3GPP Technical Specifications and Technical Reports have, in themselves, no legal standing. They only become “official” when transposed into corresponding publications of the Partner Organizations (or the national / regional standards body acting as publisher for the Partner). At this point, the specifications are referred to as UMTS within ETSI and FOMA within ARIB/TTC.”
http://www.3gpp.org/specifications/63-official-publications
“3GPP specification” cover all GSM (including GPRS and EDGE), W-CDMA (including HSPA) and LTE (including LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro) specifications, and the emerging 5G specifications.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telecom Company Support:
AT&T
“We’re proud to see the completion of this set of standards. Reaching this milestone enables the next phase of equipment availability and movement to interoperability testing and early 5G availability,” said Hank Kafka, VP Access Architecture and Analytics at AT&T. “It showcases the dedication and leadership of the industry participants in 3GPP to follow through on accelerating standards to allow for faster technology deployments.”
BT
“BT welcomes the first significant step to 5G deployment and we remain excited about the further innovations that 5G will bring.” said Neil J. McRae, Chief Architect at BT, “We are proud to have played a part in this and BT is committed to continuing to drive further 5G standardisation at pace to benefit our customers and communities.”
China Mobile
“The first version of 5G NR not only provides a NSA solution for 5G deployment but also completes the common part of NSA and SA, which lay a solid foundation for a global unified 5G system with global market scale. We believe the next important milestone that is SA standard providing end to end 5G new capability could be completed by June of 2018, which is very crucial to enable the operators to explore the enterprise and vertical markets. China Mobile is actively working with industry partners for 5G commercialization in year of 2020 and providing various services to customer.” said Zhengmao Li, EVP of China Mobile Group.
China Telecom
“China Telecom is proud of being part of the 3GPP standard efforts that led to the completion of the first implementable 5G new radio specification. We expect that this important milestone, together with the SA part to be completed later, will promote and accelerate the development of 5G products, trials and commercial deployment in the coming years,” said Liu Guiqing, EVP of China Telecom. “With this successful completion of the 5G new radio standard, China Telecom plans to lead the 5G effort by launching field trials in many major cities in China as early as 2018, and prepare for the possible commercialization thereafter.”
China Unicom
Guanglu Shao, EVP of China Unicom Group, said: “It is the significant step for both 3GPP and the whole industry. This first version of 5G NR standardization provides essential functionalities for NSA and SA deployment, which are equally important for operators. We believe in that the industry could joint together further to make 5G more advanced for both human and vertical societies. We welcome the 5G era’s coming, and will continue collaborate with industry partners to make successful 5G commercialization.”
Deutsche Telekom
“We view both the Non-Standalone and Standalone modes of New Radio as equally important for the completeness of the 5G standard specification. This timely finalization of NSA is one important step on that journey and in the development of the 5G ecosystem,” said Bruno Jacobfeuerborn, CTO Deutsche Telekom. “It is crucial that the industry now redoubles its focus on the Standalone mode to achieve progress towards a full 5G system, so we can bring key 5G innovations such as network slicing to our customers.”
Ericsson
Erik Ekudden, CTO at Ericsson, said: “3GPP has done a tremendous job to complete the first 5G specifications according to industry demand and expectations. As a prime contributor to 5G standardization, Ericsson has worked with industry partners in the evolution of mobile technology to a global network platform for consumers and enterprises. Our research team has worked on 5G since 2010 including early 5G testbed efforts created together with these industry partners. The open contribution-driven specification work and the rapid completion of the first 5G standards for global deployment demonstrates the strength of the 5G eco-system.”
Fujitsu
Masayuki Seno, EVP and Head of Network Products Business Unit at Fujitsu, said: “I’m very pleased that the first 5G NR standard has been completed today. Fujitsu will accelerate development of 5G NR products based on the first 3GPP 5G NR specifications and provide them to worldwide markets to support our customers’ trials and commercial deployments.”
Huawei
Yang Chaobin, president of Huawei 5G product line, said: “As one of the key players, Huawei has committed to develop a single global 5G standard. With the a successful cooperation and join efforts with global organizations including governments, regulatory agencies, research organizations, academia, industries, and many more sectors, 3GPP 5G NR standardization Phase 1 has been completed with great progress. Huawei will keep working with global partners to bring 5G into the period of large-scale global commercial deployment from 2018.”
Intel
“We are pleased to work in cooperation and close alignment with global mobile industry leaders to support the new 3GPP Non-Standalone 5G NR standard and to accelerate the first NR trials,” said Asha Keddy, Intel vice president and general manager, Next Generation and Standards. “As part of this coordinated effort, Intel will continue to play a leading role across the network, cloud and client devices; and with our first commercial 5G modems, we will help the ecosystem lead the way to 5G deployments worldwide.”
KT Corporation
Dongmyun Lee, Chief Technology Officer and Head of Institute of Convergence Technology, KT said: “As one of the 5G leaders, we are greatly excited to witness the first ever release of 5G NR NSA specification that the whole industry including KT has endeavored to achieve in recent years and therefore make a strong commitment to finally bring full-scale services of the true 5G standards to commercial market as early as 2019.”
KT expects that such 3GPP’s efforts meeting the market needs will further accelerate the realization of the 4th Industrial Revolution for telecommunication industry.”
LG Electronics
I.P. Park, Chief Technology Officer, said: “LG Electronics is pleased to be one of key contributors to the first global 5G NR standard completed in a timely manner, which will play a pivotal role in enabling innovative IoT services and expediting the convergence of diverse industry sectors. Along with continued contributions to evolved 5G standards, we will make all the efforts to introduce new innovative 5G convergence products and services in the market.”
LG Uplus
Joosik Choi, Head of 5G Strategy Planning, said: “We would like to thank to 3GPP and all companies for great effort on initial 5G NR NSA standard which will accelerate promising future. As one of the big contributor for RF analysis on LTE band, 3.5GHz and 28GHz dual connectivity operation, LG Uplus will keep endeavor for bring 5G NR deployment and advanced standard into industry for this ecosystem.”
MediaTek Inc.
“The milestone reached is significant as it is an important step towards making 5G NR a commercial reality,” said Dr. Kevin Jou, Corporate Sr. Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, MediaTek. “As a leading baseband chip provider, MediaTek has actively contributed to the standardization of 5G NR and will continue to do so. With the standard becoming stable, our focus is now on delivering viable commercial solutions that will enable the use of 5G NR technology to its full potential.”
NEC Corporation
Atsuo Kawamura, executive vice president and head of the Telecom Carrier Business Unit at NEC Corporation, said: “Completion of Non-Standalone 5G NR standardization is a significant milestone for the realization of full-scale 5G services. NEC is strongly committed to driving the progress of standardization for a global mobile system, and believes future 5G services will benefit society in an unprecedented manner by utilizing advanced information and communications technologies. NEC is creating secure and intelligent technologies to realize such services.”
Nokia
Marcus Weldon, president of Nokia Bell Labs and chief technology officer, Nokia, said: “This is a key milestone in bringing 5G to market, and one in which Nokia is proud to have played a significant role. 5G will advance new possibilities for the role of wireless technology in society, leading to dynamic innovation in mobile broadband and in industrial automation for industry 4.0, enabling the creation of exciting new applications that connect and control our physical and digital worlds.”
NTT DOCOMO
Dr. Hiroshi Nakamura, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, NTT DOCOMO said: “I would like to express my deepest gratitude for 3GPP’s great effort to successfully complete the first release of 5G NR specification six months ahead of schedule. NTT DOCOMO has made tremendous contributions to the standardization as a world-leading mobile operator. We have been collaborating with various partners across industries to co-create 5G services through ‘5G Trial Sites’ since this May. This completion will accelerate these activities and we will launch 5G services with Non-Standalone 5G NR by 2020.”
Orange
Arnaud Vamparys, SVP Radio Networks said: “Orange welcomes this inaugural first release of a worldwide standard for 5G. With subsequent 3GPP releases expected from mid 2018 that will accelerate application and IoT development, Orange sees a myriad of opportunities to deliver a differentiated and high quality network, and is therefore fully committed to working with the industry to roll out 5G.”
Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
“We are excited to be part of this significant milestone, and to once again be at the forefront making the 5G vision a reality in 2019,” said Cristiano Amon, executive vice president, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and president, Qualcomm CDMA Technologies. “We look forward to continue working with our mobile industry peers to bring 5G NR commercial networks and devices in 2019 in smartphone and other form factors, for both sub-6Ghz and mmWave frequency bands, and to continue developing 5G technologies to connect new industries and enable new services and user experiences in the years to come.”
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
DJ Koh, President and Head of IT and Mobile Communications Division at Samsung Electronics, said: “As a global leader in the mobile industry, Samsung has been collaborating with the whole industry to achieve this milestone in 5G standards. With the completion of 5G NSA NR standard, we will be able to expedite 5G commercial deployments including chipsets, devices and network equipment. Samsung will continue making every effort to deliver complete Rel-15 NR standards. Rel-15 NR and its further evolution will be a key milestone for the industry to meet the increasing global demand for enhanced mobile broadband services and exploring new business opportunities and services inspired by 5G.”
SK Telecom
“Having global 3GPP 5G NR standard by 2017 is one of key milestones to bring 5G into early commercial service in 2019”, said Jinhyo Park, EVP, Head of ICT R&D Center, “SK Telecom is proud to be one of key contributors to the accelerated 3GPP 5G NSA-NR standardization. We will continue to work on further development of 3GPP 5G NR to ensure readiness for early 5G commercial deployment.”
Sony Mobile Communications Inc.
Mr. Izumi Kawanishi, Director, EVP, Sony Mobile Communications Inc., said: “Sony has been part of the 5G NR and NSA standardization and recognizes the progress in 3GPP to reach this important milestone with features targeting evolved mobile broadband and ultra low latency communications. Sony Mobile is ready for full-scale development of 5G NR smartphones to take benefit of the opportunities offered by the new standard.”
Sprint
“We’re excited to help usher in the next generation of wireless networks that will drive new levels of innovation and progress around the world,” said Dr. John Saw, Sprint CTO.”We congratulate 3GPP and its delegates on this important milestone, and we look forward to working with our industry partners to deploy 5G NR in our 2.5 GHz (NR band n41) spectrum.”
TIM
Mr. Giovanni Ferigo, CTO, said: “TIM has already defined a sound track towards 5G and is collaborating with key industry players, municipalities and public Institutions to unleash the full potential of 5G for people and vertical markets by 2020 expanding the footprint of LTE-A. The extraordinary work done in 3GPP in a few months to keep the promise of a first set of standards coping with the strict requirements of a new radio interface is a fundamental step in this roadmap. We are looking forward to contributing to the next 3GPP milestones which will complete the work on Release 15.”
Telefonica
Mr. Enrique Blanco, Telefónica’s Global Systems and Networks Director, said: “Telefónica greatly appreciates the efforts made by the industry for completing this major milestone towards 5G. Telefónica acknowledges the full potential of 5G, and encourages the industry to keep developing ambitious ideas in order to deliver outstanding connectivity and bring the best possible experience to our customers. Telefónica is fully committed to working with the industry in this direction.”
Telia Company
“We are happy to see that the acceleration of 5G standardization that we and the whole industry called for in February has been achieved. This allows for the early commercial deployments needed to open up for innovation and new business opportunities that our customers expect from us”, says Mauro Costa, Director Network Architecture & Strategy, Telia Company. “In order for the industry and society to take advantage of the full potential of 5G, it is vital that the standardization now continues with a focus to complete also the stand alone version.”
T-Mobile USA
“This is an important moment and a crucial development toward making 5G NR happen,” said Neville Ray, Chief Technology Officer for T-Mobile US. “At T-Mobile, we’re committed to drive a 5G rollout across the US in 2020, and the efforts of 3GPP will help us to realize this great win for our customers.”
Verizon
“Verizon is delighted that the 3GPP is moving quickly to release a global standard for mobile 5G,” said Ed Chan, Chief Technology Architect and Network Planning.”With this important 3GPP milestone, Verizon is once again well positioned to deliver next-generation technology to customers just as we did with 4G LTE.”
Vodafone
Luke Ibbetson, Head of Vodafone Group R&D said: “Completion of the 5G standard six months earlier than originally anticipated is a significant milestone that should enable compliant network infrastructure and phones to be delivered in line with our requirements. This first version of 5G will build on the success of 4G, providing fast and highly efficient mobile broadband services to our customers and setting the foundation for the Gigabit Society.”
ZTE
Mr. Xu Huijun, CTO of ZTE Corporation, said: “The completion of the Non-Standalone 5G NR standardization is a critical milestone in the industry. I really appreciate 3GPP’s efforts in meeting this challenging schedule. As one of the contributors to the 5G standards-making process, ZTE will partner with the fellow mobile industry players to commit to accelerating the 5G NR large-scale trials and deployments.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
http://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/1931-industry_pr_5g
IHS Markit: Telecom Revenue +1.1%; CAPEX -1.8% in 2017
Despite unabated exponential growth in network usage, global telecom revenue is on track to grow just 1.1 percent in 2017 over the prior year, according to a new report [1] by business information provider IHS Markit.
Global economic growth prospects, meanwhile, are looking up. IHS Markit macroeconomic indicators point to moderate global economic growth of 3.2 percent for 2017, up from 2.5 percent in 2016, and world real gross domestic product (GDP) is projected to increase 3.2 percent in 2018 and 3.1 percent in 2019.
“Although the telecom sector has been resilient, revenue growth in developed and developing economies has slowed dramatically due to saturation and fierce competition,” said Stéphane Téral, executive director of research and analysis and advisor at IHS Markit. “At this point, every region is showing revenue growth in the low single digits when not declining, and there is no direct positive correlation between slow economic expansion and anemic telecom revenue growth or decline as seen year after year in Europe, for instance.”
China alone is tamping down global telecom capex in 2017:
IHS Markit forecasts a 1.8 percent year-over-year decline in global telecom capital expenditures (capex) in 2017, mainly a result of a 13 percent year-over-year falloff in Chinese telecom capex. Asia Pacific outspends every other region in the world on telecom equipment.
“Call it precision investment, strategically focused investment or tactical investment, but all three of China’s service providers — China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom — scaled back their 2017 spending plans, and the end result is another double-digit drop in China’s telecom capex bucket, with mobile infrastructure hit the hardest,” Téral said. “Bringing down capital intensity to reasonable levels of 15 to 20 percent is the chief goal of these operators.”
The virtualization trend:
A transformation is underway in service provider networks, epitomized by software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV), which involve the automation of processes such as customer interaction, as well as the addition of more telemetry and analytics with feedback loops into network operations, operations and business support systems, and service assurance.
“Many service providers have deployed new architectural options — including content delivery networks, distributed broadband network gateways, distributed mini data centers in smart central offices, and video optimization,” said Michael Howard, executive director of research and analysis for carrier networks at IHS Markit. “Nearly all operators are madly learning how to use SDN and NFV, and the growing deployments today bring us to declare 2017 as The Year of SDN and NFV.”
Data is the new oil, and AI is the engine:
Big data is becoming more manageable, and operators are leveraging subscriber and network intelligence to support the automation and optimization of their networks using SDN, NFV and initial forays into using analytics, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
“Forward-thinking operators are experimenting with how to use anonymized subscriber data and analytics to create targeted services and broker this information to third parties such as retailers and internet content providers like Google,” Téral said. “No matter their size, market or current level of digitization, service providers need to rethink their roles in the new age of information and reset the strategies needed to capitalize on this opportunity.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Note 1. The Telecom Trends & Drivers Market Report is published twice annually by IHS-Markit to provide analysis of global and regional market trends and conditions affecting service providers, subscribers, and the global economy. These roughly 40- page reports assess the state of the telecom industry, telling the story of what’s going on now and what we expect in the near and long term, illustrated with charts, graphs, tables, and written analysis. These critical analysis reports are a foundation piece for all market forecasts.
The reports include top takeaways on the economic health of the global telecom/datacom space; regional and global trends, drivers, and analysis for the service provider network sector in the context of the overall economy; financial analysis of the world’s top 10 service providers (revenue growth, capital intensities, free cash flow, debt level); regional enterprise and carrier spending trends; top-level service provider and subscriber forecasts; macroeconomic drivers; and key economic statistics (e.g., unemployment, OECD indicators, GDP growth). The reports are informed by all of IHS Technology research, from market share and forecasts to surveys with telecom service providers and small, medium, and large businesses.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
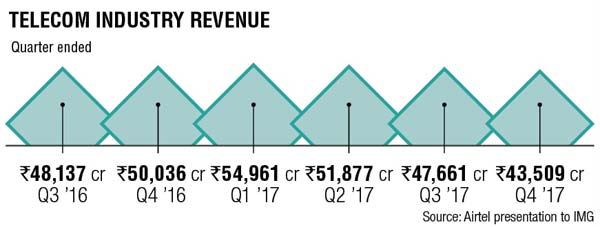
The chart below from Bharti Airtel (India’s largest telecom company) shows that telecom industry revenue has declined in 2017 Q2, Q3, and Q4 with only Q1 showing positive growth.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Optical Network Equipment Vendors:
In a service provider survey report on Optical Networking and equipment vendors, IHS-Markit found Ciena, Huawei and Nokia as the three most popular optical networking equipment vendors. The report also highlighted Data Center Interconnection (DCI) is a huge growth opportunity.
IHS-Markit predicts DCI will be a significant driver for the optical equipment market, surging from 19 percent of overall equipment sales at mid-2017 to nearly 30 percent by 2021.
Ciena was deemed the top DCI vendor by 39 percent of those surveyed by IHS-Markit. Cisco, Coriant, and Infinera each garnered 36 percent of the votes.Last year Ciena reportedly won a DCI deal from rival ADVA Optical, which had a negative impact on ADVA’s operational results.
Ciena also topped the list of top (optical) transport software-defined networking (SDN) vendors, with 46 percent of those surveyed citing the company as a leader in the segment. Adams noted that while this market was still in its early days, Ciena’s continued integration of its Blue Planet software platform with its optical equipment products was driving differentiation in the market.
Cisco attracted the second most votes in terms of transport SDN leadership, followed by Nokia and Infinera.
Fiber Broadband Association: 1.4M Fiber Miles Needed for 5G in Top 25 U.S. Metros
The Fiber Broadband Association (FBA) has issued a very optimistic fiber deployment forecast, which calls for approximately 1.4 million miles of fiber in the top 25 metro markets in the U.S. That’s driven in large part by carriers’ 5G wireless deployment plans, which will require fiber backhaul, especially for small cells.
The FBA, formerly known as the Fiber to the Home Council Americas, promotes fiber deployment to homes, business and “to everywhere,” the organization notes in a new report titled “The Road to 5G is Paved with Fiber.”
The report also makes a case for why the FBA believes fixed 5G as the only connection to a home will not be the norm.
FBA’s Fiber Deployment Forecast:
In the report, the FBA spells out the assumptions that drove its fiber deployment forecast and cites sources for those assumptions:
- While macrocells are roughly .5 to 25 miles apart, 5G will require small cells located between 200 and 1,000 feet apart
- To deliver gigabit peak speeds to each user, the minimum downlink speed to each small cell will need to be 20 Gbps and the uplink peak data rate will need to be 10 Gbps
- 5G may require 60 small cells to cover one square mile
- The top 25 U.S. metro markets cover approximately 174,000 square miles
The 1.4-million fiber-mile forecast could be on the low side if multiple carriers want to build competing networks, the FBA notes.
Pessimistic on Fixed 5G:
“We do not believe fixed 5G to the home – as the only connection to the home – will become the norm,” the FBA argues in the new report. Tell that to Verizon and AT&T which are planning to deploy some form of 5G fixed wireless to residences.
The report’s author notes that home network connections may need to support multiple 4K and soon 8K video streams, hundreds of in-home internet-connected devices and multiple virtual reality and augmented reality (VR/AR) users, which will require higher bandwidths than can be delivered by 5G under current development standards.
Additionally, the report argues that the millimeter wave signals that will be used for some 5G deployments do not penetrate exterior walls and would require a receiver attached to an exterior wall, requiring additional hardware costs and ongoing energy and maintenance costs. It’s worth noting, though, that results from early 5G trials are showing that the technology is not as limited as wireless experts initially expected it to be and both AT&T and Verizon have ambitious plans for fixed 5G.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Cignal AI reported that North America metro WDM sales grew with increased spending by cloud and colo customers, offsetting weakness in the long-haul WDM market. Cisco and Ciena were the main beneficiaries of this shift to metro WDM, with Cisco realizing double-digits year-over-year growth related to cloud/colo shipments and growth in its NCS 4000 revenue. Significant shipments for metro WDM applications resulted in global coherent 100G port shipments exceeding 100,000 units in the quarter.
EMEA revenue dropped almost 20 percent year-over-year in 3Q17. Huawei, one of the top vendors in the region, experienced a very sharp decline and provided negative guidance into 2018. This data point, as well as others, compelled Cignal AI to reduce its forecast for EMEA for this year and 2018. Cignal AI expects to see weak spending trends among tier-1 customers in the region. Cignal AI also cut its 2018 forecast for China based on ongoing uncertainty tied to regional spending and a stall in revenue growth in 3Q17.
- Last quarter was the weakest YoY revenue growth recorded in China in over 4 years as momentum from 2Q17 spending failed to continue into the third quarter. Spending trends in the region remain difficult to predict.
- Revenue in the rest of Asia (RoAPAC) eased following breakout results in India during 2Q17 though spending remains at historically high levels.
- Quarterly coherent 100G+ port shipments broke 100k units for the first time on a global basis. 100G+ Port shipments in China were flat QoQ and are substantially up YoY
LightCounting’s 3Q 2017 Optical Market Update + China’s Optical Network Comeback?
I. Light Counting’s 3Q2017 Market Update:
In its newly released “December 2017 Quarterly Market Update” LightCounting LLC states that demand for optical communications technology in 3Q 2017 followed what has been a year-long trend: Telecom/network service provider spending declined year-on-year while data center operators increased their investments in fiber optic infrastructure.
The decline in telecom optical network spending hit the optical components segment hardest, but was negative for vendors selling to telcos which can be seen from the chart below:

In 3Q 2017, data center use of optical communications technology was considerably more than that of telecom/network service providers.
Source: LightCounting LLC
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Chinese carriers (see companion piece below) followed through on their announced plans to trim spending. LightCounting reports that China Telecom will continue to cut capex in 2018. Elsewhere in the world, only Orange looks like it will spend more this year than last among LightCounting’s list of top 15 telecom service providers.
Upticks in 100G DWDM transponders and WSS module sales paled in comparison to the declines experienced in the FTTx and wireless front haul markets, both sequentially and annually (see “Demand for FTTx, wireless optics declines from 2016: LightCounting”).
LightCounting says that check-ins with semiconductor vendors such as Analog Devices, Qualcomm, and Xilinx revealed increased activity in wireless/cellular communications, including 4.5G and 5G projects. This information leads the market research firm to expect initial commercial deployments of next generation wireless technologies in 2018, which in turn should boost the demand for optical front haul technology.
Optical vendors with exposure to the data center and internet content provider markets fared better than long haul/DWDM vendors. For example, Alibaba, Facebook, and Google increased their infrastructure spends by 142%, 62% and 39%, respectively, leading to overall spending records in the space during the quarter. Facebook plans to double capex in 2018, leading to hopes that data center optical spending growth is sustainable.
Optical transceiver vendors benefited during the quarter, which Applied Optoelectronics seeing a 27% increase in revenues and Innolight a 94% boom versus 3Q16. Shipments of PSM4 and CWDM4 100GbE modules set records during the quarter. However, 100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 optical transceiver demand in the third quarter of 2017 proved softer than LightCounting expected.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
LightCounting LLC says:
Our analysis is based on confidential sales data provided by leading suppliers and offers a unique port-based view of the industry.
References:
https://www.lightcounting.com/News_121317.cfm
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/optical-networking-market
…………………………………………………………………………………..
II. China’s Optical Market Comeback (via Barron’s on-line), by Tiernan Ray
China’s optical fiber market is coming back, but slowly, according to a note this morning from Rosenblatt Securities analyst Jun Zhang, who follows shares of laser vendor Oclaro, Acacia Communications, Applied Optoelectronics, and other vendors.
“Demand in China is stabilizing and slightly improving,” writes Zhang, “but we do not see a broad acceleration in China’s recovery yet.
“Chinese vendors recently concluded 2018 component and module procure- ments. Therefore, optical module and component suppliers should have base- line procurement contracts from Chinese vendors for 2018.”
The tricky part, indicates Zhang, is that Chinese buyers of components are increasingly coming up with their own internal components, which is going to dent some of the demand:
Instead of over promising volume to suppliers, we believe Chinese vendors offered baseline procurement volume estimates for 2018. Additionally, we believe these current procurement forecasts do not include any upside from initial 5G deployments in 2H18. However, line and client side module procurements from Chinese vendors are all down YoY due to internal sourcing. Therefore, due to conservative forecasts and increasing competition in the module market, most optical suppliers will likely continue to speak conservatively on China demand.
Zhang goes through what to expect, and it’s quite a mixed bag for various different vendors:
As we expected, ZTE is attempting to increase its internal sourcing for line side CFP2 DCO modules in 2018. Therefore, Acacia’s business could be negatively impacted in 2018 by ZTE. On the other hand, we believe there’s a chance Acacia can qualify at Huawei for DSP in 2018, but we see no signs yet. Intel’s CWDM4 has been qualified at Facebook and could have a sizeable market share, similar to the share size we expect InnoLight to also have at Facebook in 2018. However, Applied Optoelectronics shares are down significantly at Facebook in 2018 likely putting its CQ4 guidance at risk […]
NeoPhotonics could be up YoY, Lumentum flat YoY, Oclaro down slightly YoY, and Acacia down YoY. We also estimate Huawei and ZTE’s 100G ports to grow to 150K and 35K from 130K and 45K, respectively, in 2018. FiberHome recently saw a large share gain at China Unicom and we expect it to double its 100G port shipments in 2018 from a small basis.
FCC Votes to Reverse Net Neutrality & No Longer Regulate Broadband Internet Services
Overview:
By a 3 to 2 vote along party lines, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) voted on Thursday to dismantle landmark rules regulating the businesses that connect consumers to the internet, granting broadband ISPs the power to potentially reshape Americans’ online experiences. The agency scrapped the so-called net neutrality regulations that prohibited broadband providers from blocking websites or charging for higher-quality service or certain content. The federal government will also no longer regulate high-speed internet delivery as if it were a utility, like phone service. The upshot is that the “Restoring Internet Freedom” order passed today, removes the FCC as a regulator of the broadband industry and relegates rules that prevented blocking and throttling content to the honor system.
That means a consumer or business is helpless if they have a complaint against an ISP or broadband service provider although there’s lip service saying that “the FCC and FTC will securely share consumer complaints pertaining to the subject matter of the Internet Freedom Order’s requirements to the extent feasible…….” FTC enforcement action is mentioned, but from our experience the FTC does nothing when it receives a complaint! They don’t even contact the business you’re complaining about (like the BBB does).
From the FCC’s Memorandum of Understanding (bold font added– see other FCC.gov references below):
(1) Pursuant to the FCC’s authority under the Communications Act of 1934, as amended, on December 14, 2017, the FCC adopted a Declaratory Ruling, Report and Order, and Order in the proceeding Restoring Internet Freedom, WC Docket No. 17-108, Declaratory Ruling, Report and Order, Order, FCC 17-166 (Dec. 14, 2017) (“Internet Freedom Order”), which, in principal part, restores broadband Internet access service to its Title I information service classification,reinstates the private mobile service classification of mobile broadband Internet access service, and returns to the Transparency Rule the FCC adopted in 2010 with certain limited modifications to promote additional transparency. As authority for the Transparency Rule, the FCC relies on Section 257 of the Communications Act, among other provisions, which requires the FCC to identify and eliminate market entry barriers for entrepreneurs and other small businesses in the provision and ownership of telecommunications services and information services and to report to Congress on how such marketplace barriers have been addressed by regulation or could be addressed by recommended statutory changes; and
(2) Congress has directed the FTC to, among other things, prevent unfair methods of competition and unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, 15 U.S.C. § 45, and has charged the FTC with enforcing a number of other specific rules and statutes.
Therefore, it is agreed that:
1. Consistent with its jurisdiction and to fulfill its duties under Section 257 of the Communications Act, among other provisions, the FCC will monitor the broadband market and identify market entry barriers by, among other activities, reviewing informal complaints filed by consumers, and will investigate and take enforcement action as appropriate with respect to failures by an Internet service provider to comply, in whole or in part, with the Internet Freedom Order’s requirements to file with the FCC or display on a publicly available, easily accessible website the specified subjects of disclosure.
2. Consistent with its jurisdiction, the FTC will investigate and take enforcement action as appropriate against Internet service providers for unfair, deceptive, or otherwise unlawful acts or practices, including but not limited to, actions pertaining to the accuracy of the disclosures such providers make pursuant to the Internet Freedom Order’s requirements, as well as their marketing, advertising, and promotional activities.
3. Consistent with each agency’s jurisdiction and to maximize the resources of each agency, at the regular coordination meeting established by the Agencies’ 2015 Memorandum of Understanding, the Agencies will discuss potential investigations against Internet Service Providers that could arise under each agency’s jurisdiction, and coordinate such activities to promote consistency in law enforcement and to prevent duplicate or conflicting actions, to the extent appropriate and consistent with law.
4. To further support coordination and cooperation on these matters, the Agencies will continue to work together to protect consumers, including through:
• Consultation on investigations or enforcement actions that implicate the jurisdiction of the other agency;
• Sharing of relevant investigative techniques and tools, intelligence, technical and legal expertise, and best practices in response to reasonable requests for such assistance from either Agency; and
• Collaboration on consumer and industry outreach and education efforts, as appropriate.
5. The FCC and FTC will securely share consumer complaints pertaining to the subject matter of the Internet Freedom Order’s requirements to the extent feasible and subject to the Agencies’ requirements and policies governing, among other things, the protection of confidential, personally identifiable, or nonpublic information.
6. The Agencies may coordinate and cooperate to develop guidance to assist consumers’ understanding of Internet service provider practices.
7. In seeking to encourage and facilitate the enforcement of applicable law, the Agencies recognize that decisions by one agency to take or withhold action are not, except by operation of law, binding on or intended to restrict action by the other agency.
8. To ensure the effective exchange of information between the Agencies, the persons signing below and their successors shall be deemed Designated Liaison Officers to serve as the primary sources of contact for each agency. Formal meetings between appropriate senior officials of both Agencies to exchange views on matters of common interest and responsibility shall be held from time to time, as determined to be necessary by such liaison officers…..blah, blah, blah!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analysis:
The action reversed the agency’s 2015 decision, during the Obama administration, to better protect Americans as they have migrated to the internet for most communications. It will take a couple of weeks for the changes go into effect, but groups opposed to the action have already announced plans to sue the agency to restore the net neutrality regulations. Those suits could take many months to be resolved.
FCC chairman Ajit Pai said the rollback of the rules would eventually help consumers because broadband providers like AT&T and Comcast could offer people a wider variety of service options. We are helping consumers and promoting competition,” Mr. Pai said in a speech before the vote. “Broadband providers will have more incentive to build networks, especially to under-served areas.” We think that’s disingenuous nonsense!
The discarding of net neutrality regulations is the most significant and controversial action by the F.C.C. under Mr. Pai. In his first 11 months as chairman, he has lifted media ownership limits, eased caps on how much broadband providers can charge business customers and cut back on a low-income broadband program that was slated to be expanded to nationwide carriers.
His plan for the net neutrality rules, first outlined early this year, set off a flurry of opposition. Critics of the changes say that consumers may have more difficulty finding content online and that start-ups will have to pay to reach consumers. In the past week, there have been hundreds of protests across the country, and many websites have encouraged users to speak up against the repeal. After the vote, numerous groups said they planned to file a lawsuit challenging the change.
As expected, the five FCC commissioners were fiercely divided along party lines. In front of a room packed with reporters and television cameras from the major TV networks, the two Democratic commissioners warned of consumer harms to come from the changes.
Mignon Clyburn, one of the Democratic commissioners, presented two accordion folders full of letters in protest to the changes, and accused the three Republican commissioners of defying the wishes of millions of Americans. “I dissent, because I am among the millions outraged,” said Ms. Clyburn. “Outraged, because the F.C.C. pulls its own teeth, abdicating responsibility to protect the nation’s broadband consumers.”
“I dissent from this rash decision to roll back net neutrality rules,” said FCC Commissioner Rosenworcel. “I dissent from the corrupt process that has brought us to this point. And I dissent from the contempt this agency has shown our citizens in pursuing this path today. This decision puts the Federal Communications Commission on the wrong side of history, the wrong side of the law, and the wrong side of the American public.”
On the other hand, Brendan Carr, a Republican FCC commissioner, said it was a “great day” and dismissed “apocalyptic” warnings. “I’m proud to end this two-year experiment with heavy-handed regulation,” Mr. Carr added.
During Mr. Pai’s speech before the vote, security guards entered the meeting room at the F.C.C. headquarters and told everyone to evacuate. Commissioners were ushered out a back door. The hearing restarted a short time later. That shows you how unpopular the repeal of Internet Neutrality really is!
Despite all the uproar, it is unclear how much will change for internet users. The rules were essentially a protective measure, largely meant to prevent telecom companies from favoring some sites over others. And major telecom companies have promised consumers that their experiences online would not change.
Mr. Pai and his Republican colleagues have echoed the comments of telecom companies, who have told regulators that they weren’t expanding and upgrading their networks as quickly as they wanted to since the creation of the rules in 2015.
“There is a lot of misinformation that this is the ‘end of the world as we know it’ for the internet,” Comcast’s senior executive vice president, David Cohen, wrote in a blog post this week. “Our internet service is not going to change.” We certainly hope so!
But with the F.C.C. making clear that it will no longer oversee the behavior of broadband providers, telecom experts say, the companies could feel freer to come up with new offerings, such as faster tiers of service for business partners such as HBO’s streaming service or Fox News. Such prioritization could stifle certain political voices or give the telecom conglomerates with media assets an edge over rivals.
Is this net neutrality repeal set in stone? Not necessarily. The repeal could be overturned in court or by Congress. A Democratic senator is already working on legislation. Net neutrality advocates are also saying they’ll push ahead with both options to fight the repeal. In order for the repeal to go into effect, it must be approved by the Office of Management and Budget — a process that could take several months.
Other Voices:
Consumer groups, start-ups and many small businesses say there are examples of net neutrality violations by companies, such as when AT&T blocked FaceTime on iPhones using its network.
These critics of Mr. Pai, who was nominated by President Trump, say there isn’t enough competition in the broadband market to trust that the companies will try to offer the best services for customers. The providers have the incentive to begin charging websites to reach consumers, a strong business model when there are few places for consumers to turn when they don’t like those practices.
“Let’s remember why we have these rules in the first place,” said Michael Beckerman, president of the Internet Association, a trade group that represents big tech firms such as Google and Facebook. “There is little competition in the broadband service market.”
Mr. Beckerman said his group was weighing legal action against the commission. Public interest groups including Public Knowledge and the National Hispanic Media Coalition said they planned to challenge Mr. Pai’s order in court. Eric T. Schneiderman, the New York attorney general, also said he would file a lawsuit.
Dozens of Democratic lawmakers, and some Republicans, have pushed for Congress to pass a law on the issue, if only to prevent it from flaring up every couple of years at the F.C.C. — and then leading to a court challenge.
One Republican commissioner, Mike O’Reilly, said he supported a federal law created by Congress for net neutrality. But he said any law should protect the ability of companies to charge for faster lanes, a practice known as “paid prioritization.” Any legislation action appears to be far off, however, and numerous online companies warned that the changes approved on Thursday should be taken seriously.
“If we don’t have net neutrality protections that enforce tenets of fairness online, you give internet service providers the ability to choose winners and losers,” Steve Huffman, chief executive of Reddit, said in an interview. “This is not hyperbole.”
Netflix, which has been relatively quiet in recent weeks about its opposition to the change, said that the decision “is the beginning of a longer legal battle.” Netflix via Twitter (tweet) at 10:26 AM – Dec 14, 2017:
“We’re disappointed in the decision to gut #NetNeutrality protections that ushered in an unprecedented era of innovation, creativity & civic engagement. This is the beginning of a longer legal battle. Netflix stands w/ innovators, large & small, to oppose this misguided FCC order.”
This author totally agrees with Netflix! Let us know how you feel by leaving a comment in the box below this post. It can be anonymous if you like and your email address won’t be published! Thanks, Alan
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
| FCC Acts To Restore Internet Freedom (from FCC.gov website): | |||
| Reverses Title II Framework, Increases Transparency to Protect Consumers, Spur Investment, Innovation, and Competition | |||
| Documents: | |||
| Word : DOC-348261A1.docx DOC-348261A2.docx DOC-348261A3.docx DOC-348261A4.docx DOC-348261A5.docx DOC-348261A6.docx | |||
| PDF : DOC-348261A1.pdf DOC-348261A2.pdf DOC-348261A3.pdf DOC-348261A4.pdf DOC-348261A5.pdf DOC-348261A6.pdf | |||
| Text : DOC-348261A1.txt DOC-348261A2.txt DOC-348261A3.txt DOC-348261A4.txt DOC-348261A5.txt DOC-348261A6.txt | |||
| 12/14/2017 | |||
| Restoring Internet Freedom FCC-FTC Memorandum Of Understanding | |||
| . | |||
| Documents: | |||
| PDF : DOC-348275A1.pdf | |||
| Text : DOC-348275A1.txt | |||
Greg Wyler- OneWeb Satellite-Internet CEO- Telecom Man of the Year + $500M more from Softbank
Greg Wyler, the entrepreneur and CEO of satellite internet company OneWeb, has won the Fierce Wireless “Most Powerful Person In Telecom” tournament for 2017, just edging past T-Mobile CEO John Legere during this weekend’s final matchup and beating other industry notables like Ericsson’s Borje Ekholm, Apple’s Tim Cook and Verizon’s Lowell McAdam.
This past Sunday afternoon, Legere urged his almost 5 million Twitter followers to vote for OneWeb’s Wyler instead of himself:
Gartner Analysis & Predictions: Enterprise Network Infrastructure and Services
by : Bjarne Munch | To Chee Eng | Greg Young | Danellie Young | Vivek Bhalla | Andrew Lerner |Danilo Ciscato of Gartner Group
Overview:
This new Gartner Group report is on the key impacts of digital business, cloud and orchestration strategies. In particular, IT leaders must continue to focus on meeting enterprise needs for expanded WAN connectivity, application performance and improved network agility, without compromising performance.
Key Findings:
- As enterprises increasingly rely on the internet for WAN connectivity, they are challenged by the unpredictable nature of internet services.
- Enterprises seeking more agile WAN services continue to be blocked by network service providers’ terms and conditions.
- Enterprises seeking more agile network solutions continue to be hampered by manual processes and cultural resistance.
- Enterprise’s moving applications to public cloud services frequently struggle with application performance issues.
Recommendations:
IT leaders responsible for infrastructure agility should:
- Reduce the business impact of internet downtime by deploying redundant WAN connectivity such as hybrid WAN for business-critical activities.
- Improve WAN service agility by negotiating total contractual spend instead of monthly or annual spend.
- Improve agility of internal network solutions by introducing automation of all operations using a step-wise approach.
- Ensure the performance of cloud-based applications by using carriers’ cloud connect services instead of unpredictable internet services.
- Improve alignment between business objectives and network solutions by selectively deploying intent-based network solutions.
Strategic Planning Assumptions:
Within the next five years, there will be a major internet outage that impacts more than 100 million users for longer than 24 hours.
- By 2021, 25% of enterprise telecom contracts will evolve to allow for greater flexibility such as canceling services or introducing new services within the contract period, up from less than 5% today.
- By 2021, productized network automation (NA) tools will be utilized by 55% of organizations, up from less than 15% today.
- By YE20, more than 30% of organizations will connect to cloud providers using alternatives to the public internet, which is a major increase from 5% in 3Q17.
- By 2020, more than 1,000 large enterprises will use intent-based networking systems in production, up from less than 15 today.
Analysis:
Gartner Group has five predictions that represent fundamental changes that are emerging in key network domains, from internal networking to cloud services and WAN services.
two key aspects that the majority of Gartner clients struggle with:
- The increased interest in utilizing the internet for WAN connectivity continues to raise concerns about the performance of public internet services and performance of applications deployed in public cloud services. We discuss the risk that enterprises encounter due to the unpredictable nature of the internet, and we discuss how an enterprise can use MPLS to connect directly to public cloud services instead of using the internet.
- Enterprises continue to need new business solutions deployed faster, but remain hampered by the inability of network solutions and network services to respond fast enough and rectify performance issues fast enough. We discuss three options to improve network operations as well as network services.

Source: Gartner (December 2017)
Strategic Planning Assumptions
Strategic Planning Assumption: Within the next five years, there will be a major internet outage that impacts more than 100 million users for longer than 24 hours.
Analysis by: Andrew Lerner, Greg Young
Key Findings:
- We are increasingly seeing organizations use the internet as a WAN, and estimate that approximately 20% of Gartner clients in many geographic regions have at least some critical branch locations entirely connected via the internet.
- Most IT teams don’t have a detailed understanding of the multitude of applications and services that are being used on the public internet and/or their criticality. This is because of years of line of business (LOB)-centric buying and the proliferation of SaaS.
- While the internet is highly resilient, there are specific infrastructure and technology hot spots that, if compromised, could threaten the internet as a whole or large portions of it. This could be the result of natural disasters, man-made accidents or intentional acts.
- Natural disasters and man-made acts that could impact large portions of the internet include earthquakes, solar flares, electronic pulses, meteors, tsunamis, hurricanes, major cable cuts and network operator errors.
- Intentional acts include hacktivism, terrorism toward critical infrastructure, and/or coordinated distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, attacks against carrier- and ISP-specific components, and protocols (e.g., SS7).
While the probability of each of these events individually is small, the likelihood that at least some of them will occur over an extended period of time is actually surprisingly high. For example, even if there is only a 1% chance that any of the 11 examples identified above results in an outage within a year, there is a statistical likelihood of over 45% that at least one of them will occur over a five-year period. Further, to date, there have been indications that the internet is vulnerable to sizable outages:
- In 2008, millions of users and large portions of the Middle East and India were impacted by a cable cut. 1
- In 2016, a large DDOS attack resulted in many large e-commerce sites going down, including Twitter, Netflix, Reddit and CNN. 2
- In 2015, Telekom Malaysia created a routing problem that rendered much of the Level 3 network unavailable. 3
- It has been widely reported that 70% of all internet traffic goes thru Northern Virginia 4 and, while this might be an overstated, there’s no doubt that there are several major chokepoints in the internet infrastructure.
Market Implications:
At a minimum, an extended and widespread internet outage would cause dramatic revenue loss for enterprises, and could even create life-threating situations depending on what business the organizations is in. Initially, many organizations often brush this off by saying, “Well there’s not much we can do about it anyway” or “If there is a large internet outage due to a natural disaster, then personal safety is the priority and the enterprise connectivity is the least of our concerns.” However, there are very specific and actionable items that infrastructure and operations (I&O) leaders should take to mitigate the impact of a large outage.
Strategic Planning Assumption: By 2021, 25% of enterprise telecom contracts will evolve to allow for greater flexibility such as canceling services or introducing new services within the contract period, up from less than 5% today.
Analysis by: Danellie Young
Key Findings:
- Enterprise telecom contracts are typically fixed in both term duration and for the services required for procurement.
- Most larger revenue contracts ($1 million annually) require the enterprise to agree to minimum revenue commitments on an annual basis.
- Major WAN decisions are made by 31% to 47% of enterprises each year, including equipment refresh or carrier renegotiations (assuming the refresh cycle on routers is six years, and the average enterprise WAN service contract is three years).
- A large majority of enterprises are struggling with the cost, performance and flexibility of their traditional WAN contracts, further exacerbated by the proliferation of public cloud applications.
Market Implications:
Enterprise telecom contracts remain rigid and fixed, with specified services required to ensure compliance. Typically such contracts penalize customers when services are disconnected midterm. Enterprise telecom contracts are typically negotiated on 36-month cycles, based on either full-term or revenue commitments. Revenue commitments are set based on monthly spend, annual spend or total contract spending. Upon meeting the contract’s revenue commitment, the enterprise can then renegotiate or consider alternative services or providers since their financial obligation has been met. Terminating contracts early for convenience will typically levy penalties on the enterprise. These penalties range from 100% of the monthly recurring charges (MRCs) to a percentage of the MRCs to a declining portion through the remainder of the term (i.e., 100% in the first 12 months, 75% in months 13 to 24 and 50% through the end of the term).
Currently, contracts are split between term and revenue commit contracts, whereby most of the revenue commitments are made on an annualized basis. Alternatively, a small number (5%) are offered or negotiated with total contract values tied to them. Total contract revenue commitments enable the enterprise to meet the obligation earlier in their contract and provide the opportunity to negotiate new lower rates and a new contract, and to solicit competitive proposals before the full 36-month cycle terminates.
In addition to traditional voice and data services, many networking vendors now offer SD-WAN functionality products, while carriers and managed service providers (MSPs) are beginning to launch and roll out managed SD-WAN services as an alternative to managed routers. Contract flexibility will be needed to allow the enterprise the flexibility to migrate to new solutions, without financial risk or paying early termination fees on services. Thus, while we anticipate rapid adoption of SD-WAN and virtualized customer premises equipment (vCPE) solutions in the enterprise, SD-WAN by itself will not improve contractual conditions.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5G Americas: LTE & LPWANs leading to ‘Massive Internet of Things’ + IDC’s IoT Forecast
A new by 5G Americas whitepaper, titled “LTE Progress Leading to the 5G Massive Internet of Things”is an overview of the technological advancements that will support the expanding IoT vertical markets, including connected cars and wearables. The term Massive IoT (MIoT) has been recently created by the telecom industry to refer to the connection for potentially large number of devices and machines that will call for further definition in the standards for LTE and later for 5G.
The generic requirements for IoT are low cost, energy efficiency, ubiquitous coverage, and scalability (ability to support a large number of connected machines in a network). To legacy operators, IoT services should ideally be able to leverage their existing infrastructure and co-exist with other services. In the 3GPP Release
13 standard, eMTC and NB-IoT were introduced. These technologies met the above generic IoT requirements. They support in-band or guard band operations. Device cost and complexity are reduced. A large quantity of IoT devices can be supported in a network while battery life is extended. Many of the related features were covered in the 5G Americas whitepaper, LTE and 5G Technologies Enabling the Internet of Things.

Jean Au, staff manager, technical marketing, Qualcomm Technologies, and co-leader of the whitepaper said: “Some cellular service providers in the U.S. are already adding more IoT connections than mobile phone connections, and the efforts at 3GPP in defining standards for the successful deployment of a wide variety of services across multiple industries will contribute to the growing success for consumers and the enterprise.”
At present, low-power wide area networks (LPWANs) are already gaining popularity and it is expected that cellular-based technologies including LTE-M (Machine) and Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) will emerge as the foremost standards for LPWA by 2020.
Wireless network operators will have the option to choose from several Cellular IoT (CIoT) technologies depending on their spectrum portfolio, legacy networks and requirements of the services they offer.
Vicki Livingston, head of communications, 5G Americas, said:
“There will be a wide range of IoT use cases in the future, and the market is now expanding toward both Massive IoT deployment as well as more advanced solutions that may be categorized as Critical IoT.”
According to Research and Markets, the global IoT platform market will grow at a CAGR of 31.79 percent from 2017 to 2021. The large number of active IoT devices collect data through sensors and actuators and transmit the back to a centralized location. The IoT platform empowers the end-user to make informed decisions using the data. Together with design innovations in 5G architectures, cloud-native edge computing platforms ensure Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications can be run in a cost-effective manner.
References:
http://www.5gamericas.org/files/3514/8121/4832/Enabling_IoT_WP_12.8.16_FINAL.pdf
………………………………………………………………………………………
Addendum: IDC’s IoT Forecast
Worldwide spending on the Internet of Things (IoT) is forecast to reach $772.5 billion in 2018, an increase of 14.6% over the $674 billion that will be spent in 2017. A new update to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Semiannual Internet of Things Spending Guide forecasts worldwide IoT spending to sustain a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.4% through the 2017-2021 forecast period surpassing the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and reaching $1.1 trillion in 2021.
IoT hardware will be the largest technology category in 2018 with $239 billion going largely toward modules and sensors along with some spending on infrastructure and security. Services will be the second largest technology category, followed by software and connectivity. Software spending will be led by application software along with analytics software, IoT platforms, and security software. Software will also be the fastest growing technology segment with a five-year CAGR of 16.1%. Services spending will also grow at a faster rate than overall spending with a CAGR of 15.1% and will nearly equal hardware spending by the end of the forecast.
“By 2021, more than 55% of spending on IoT projects will be for software and services. This is directly in line with results from IDC’s 2017 Global IoT Decision Maker Survey where organizations indicate that software and services are the key areas of focused investment for their IoT projects,” said Carrie MacGillivray, vice president, Internet of Things and Mobility at IDC. “Software creates the foundation upon which IoT applications and use cases can be realized. However, it is the services that help bring all the technology elements together to create a comprehensive solution that will benefit organizations and help them achieve a quicker time to value.”
The industries that are expected to spend the most on IoT solutions in 2018 are manufacturing ($189 billion), transportation ($85 billion), and utilities ($73 billion). IoT spending among manufacturers will be largely focused on solutions that support manufacturing operations and production asset management. In transportation, two thirds of IoT spending will go toward freight monitoring, followed by fleet management. IoT spending in the utilities industry will be dominated by smart grids for electricity, gas, and water. Cross-Industry IoT spending, which represent use cases common to all industries, such as connected vehicles and smart buildings, will be nearly $92 billion in 2018 and rank among the top areas of spending throughout the five-year forecast.
“Consumer IoT spending will reach $62 billion in 2018, making it the fourth largest industry segment. The leading consumer use cases will be related to the smart home, including home automation, security, and smart appliances,” said Marcus Torchia, research director, Customer Insights & Analysis. “Smart appliances will experience strong spending growth over the five-year forecast period and will help to make consumer the fastest growing industry segment with an overall CAGR of 21.0%.”
Asia/Pacific (excluding Japan) (APeJ) will be the geographic region with the most IoT spending in 2018 – $312 billion – followed by North America (the United States and Canada) at $203 billion and Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) at $171 billion. China will be the country with the largest IoT spending total in 2018 ($209 billion), driven by investments from manufacturing, utilities, and government. IoT spending in the United States will total $194 billion in 2018, led by manufacturing, transportation, and the consumer segment. Japan ($68 billion) and Korea ($29 billion) will be the third and fourth largest countries in 2018, with IoT spending largely driven by the manufacturing industry. Latin America will deliver the fastest overall growth in IoT spending with a five-year CAGR of 28.3%.
The Worldwide Semiannual Internet of Things Spending Guide forecasts IoT spending for 14technologies and 54 use cases across 20 vertical industries in eight regions and 53 countries. Unlike any other research in the industry, the comprehensive spending guide was designed to help vendors clearly understand the industry-specific opportunity for IoT technologies today.
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS43295217