Month: September 2022
Mavenir and NEC deploy Massive MIMO on Orange’s 5G SA network in France
Mavenir and NEC Corporation (NEC) have deployed massive MIMO (mMIMO) on Orange’s 5G standalone (SA) experimental network in France.
Mavenir’s cloud-native Open virtualized Radio Access Network (Open vRAN) software has been deployed on Orange’s cloud infrastructure with NEC’s 32T32R mMIMO active antenna unit (AAU) to deliver high capacity and enhanced coverage. Interoperability between radios and virtualized Distributed Units (vDUs) over the O-RAN Alliance Open Fronthaul Interface is key to Open RAN’s ability to simplify the deployment of multi-vendor networks and eliminate vendor lock-in.
The technologies have been deployed at the Orange Gardens campus in Chatillon near Paris, and are part of the extension of project Pikeo – Orange’s cloud-based and fully automated 5G SA experimental network, also called Pikeo at this site.
“Mavenir and NEC’s successful Open RAN deployment of mMIMO on Orange’s Innovation 5G SA experimental network is a major stepping stone on the road towards Open RAN deployments and illustrates Orange’s commitment to support the development of multi-vendor Open RAN solutions with innovative partners. Our Open RAN Integration Centre, open to our partners worldwide, contributes to the development of a strong Open RAN ecosystem in Europe,” said Arnaud Vamparys, SVP Radio Access Networks and Microwaves at Orange.
The deployment includes Mavenir’s cloud-native Open virtualized Radio Access Network (Open vRAN) software rolled out across Orange’s cloud infrastructure with NEC’s 32T32R mMIMO active antenna unit (AAU) to deliver high capacity and enhanced coverage.
“Deploying 5G SA mMIMO is a significant milestone in developing Open RAN and transitioning from virtualized to cloudified networks,” said Hubert de Pesquidoux, executive chairman of Mavenir.
“We are very proud of our continuing collaboration with Orange, NEC and other companies that are proving the potential of the multi-vendor, cloud-native, standards-based approach.”
The deployment forms part of the extension of project Pikeo – Orange’s cloud-based and fully automated 5G SA experimental network.
“The latest deployment of Open RAN mMIMO in Europe is another milestone for Open RAN and one that required close collaboration and tight integration between multiple vendors. This synergy is exactly what Open RAN needs to successfully deliver on its promise of a truly open multi-vendor ecosystem,” said Naohisa Matsuda, general manager of NEC’s 5G strategy and business.
“Forward-thinking mobile operators like Orange are showcasing the potential of Open RAN mMIMO. This is the right time for the mobile industry to follow the blueprint set by industry-leading operators to move to the new era of Open RAN-powered connectivity.”
About Mavenir:
Mavenir is building the future of networks and pioneering advanced technology, focusing on the vision of a single, software-based automated network that runs on any cloud. As the industry’s only end-to-end, cloud-native network software provider, Mavenir is focused on transforming the way the world connects, accelerating software network transformation for 250+ Communications Service Providers and Enterprises in over 120 countries, which serve more than 50% of the world’s subscribers.
About NEC Corporation:
NEC Corporation has established itself as a leader in the integration of IT and network technologies while promoting the brand statement of “Orchestrating a brighter world.” NEC enables businesses and communities to adapt to rapid changes taking place in both society and the market as it provides for the social values of safety, security, fairness and efficiency to promote a more sustainable world where everyone has the chance to reach their full potential. For more information, visit NEC.
References:
Comcast to roll out DOCSIS 4.0 and Multi-Gig speeds in 2023; Fiber (not FWA) is the real competitor
Comcast is on a path to deliver 10Gbps connectivity. Speaking at a Bank of America investor conference on September 8th, Comcast EVP and Deputy CFO and Treasurer Jason Armstrong said the cable network operator will be in the market with DOCSIS 4.0 and offering symmetrical multi-gig broadband in the second half of 2023. Currently, upload speeds top out at 200 Mbps.
Armstrong said: “Comcast fiber connectivity has gone from 0% to 40% sort of across our footprint in a fairly linear fashion. And in that time frame, we’ve become America’s number one broadband provider, 32 million subs. I would tell you in the last couple of years through the pandemic, we added three million subscribers in an environment where fiber was actually picking up in terms of the presence in the markets that served against us….Fixed wireless access (FWA) is newer, but longer term, fiber is the real long-term competitor. And it always has been. Our view hasn’t changed. It’s a very viable competitor.”
“And longer term, if you think about it, any secular trend out there, whether it’s AR, VR, Metaverse, low latency gaming, the move from linear to streaming, every one of those is — those are bandwidth talks. That’s going to continue to move up usage profiles across the network. Those are all trends that work in our favor.”
Comcast said rollouts of its 2-gig offering are underway in Colorado Springs, Colorado; Augusta, Georgia; and Panama City Beach, Florida. It added the service will be available in a total of 34 markets by the end of 2022 and to more than 50 million locations across the country by the end of 2025. Comcast already offers speeds of up to 1.2 Gbps across its entire cable network using DOCSIS 3.1 technology and has been rolling out mid-split upgrades over the past several months in preparation for an update to DOCSIS 4.0. Speeds of up to 6 Gbps are already available to certain Xfinity fiber customers.

Elad Nafshi, EVP and Chief Network Officer at Comcast Cable, told Fierce Telecom the faster speeds will be available on any DOCSIS 3.1 modem, meaning no upgrades will be required. Elad noted the company’s recent launch of a Wi-Fi 6E router which will deliver the best user experience. According to Nafshi, the mid-split upgrades are just one small piece of the work it has put into enabling the new speed tier. He pointed to its deployment of a virtual cable modem termination system (vCMTS) as well as digital nodes and digital optics as critical pieces of the puzzle which also lay the groundwork for its future DOCSIS 4.0 rollout.
“The way we’re delivering the increased upstream speeds is by, for the very first time, launching DOCSIS 3.1 in the upstream. It’s by relying on the Octave platform that enables us to truly optimize the delivery of those greater upstream speeds by leveraging those new upstream frequencies in order to deliver on this product. Extending additional DOCSIS 3.1 channels, which enable us to deliver the 2-gig speeds as well. There’s a lot of firsts coming to market here,” he explained.
References:
https://www.xfinity.com/support/articles/requirements-to-run-xfinity-internet-speeds-over-1-gbps
Intel and Broadcom complete first Wi-Fi 7 cross-vendor demonstration with speeds over 5 Gbps
Intel and Broadcom held what they say is the industry’s first cross–vendor demonstration of Wi–Fi 7 [1.], with over-the-air speeds above 5 Gbps. The trial used an Intel® Core™ processor-based laptop with a Wi-Fi 7 solution connected to a Broadcom Wi-Fi 7 access point.
Note 1. Wi-Fi 7 is the 7th generation WiFi standard or IEEE 802.11be. The official IEEE 802.11be title is “Standard for Information technology–Telecommunications and information exchange between systems Local and metropolitan area networks–Specific requirements – Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. Amendment: Enhancements for Extremely High Throughput (EHT).” The scope of this standard is to define one medium access control (MAC) and several physical layer (PHY) specifications for wireless connectivity for fixed, portable, and moving stations (STAs) within a local area. The purpose of this standard is to provide wireless connectivity for fixed, portable, and moving stations within a local area. This standard also offers regulatory bodies a means of standardizing access to one or more frequency bands for the purpose of local area. It is dependent on IEEE802.11ax, often referred to as WiFi 6 or 6E.
In summary, WiFi 7 is an extremely high throughput wireless network that uses 2.4Ghz, 5Ghz, and 6Ghz frequency bands. Wi-Fi 7 leverages advanced technology to maximize overall capacity, decrease latency and increase speed to every device.
“We are proud to highlight how next-generation Wi-Fi 7 can make new mobile PC experiences possible. Industry collaboration is essential to ensure we deliver on the promises of this new wireless technology. We would like to thank our colleagues at Broadcom for their great technical cooperation, which helped enable this unprecedented, first-of-its-kind demonstration of ultra-high speed and ultra-low latency Wi-Fi 7,” said Carlos Cordeiro, Intel Fellow and Wireless CTO, Client Computing Group, Intel.
Vijay Nagarajan, vice president, Wireless Connectivity Division, Broadcom, said, “Today’s milestone sends a clear message: the ecosystem is ready and Wi-Fi 7 is here to deliver extraordinary capacity and blazing fast speeds to extend gigabit broadband. The reliable, low latency communication provided by Wi-Fi 7 is a key element of Broadcom’s vision for connecting everything as the Internet evolves to its next iteration replete with immersive experiences. Industry collaboration is key to making this unprecedented connectivity a reality and we were delighted to work with Intel to achieve another industry first.”
Wi-Fi 7 is the platform for the next 10 years of wireless experiences, which require higher speeds, lower latency, improved reliability and greater capacity. Wi-Fi 7 leverages new features including wider 320 MHz channels in unlicensed 6GHz spectrum, higher order 4K QAM data modulation, simultaneous connections across multiple bands with multi-link operation and improved channel utilization efficiency with multi-resource unit puncturing.
Wi-Fi 7’s deterministic operation enables new product classes, including augmented and virtual reality, ultra-high-definition 16K media streaming, and super-responsive and reliable gaming, while supporting large numbers of connected devices in the home or office. And with Wi-Fi 7’s greatly increased speeds, broadband subscribers will get full value from their multi-gigabit internet plans.
“Wi-Fi 7 is the most powerful and capable Wi-Fi protocol yet and will allow Wi-Fi to continue to serve the most demanding applications in the consumer and vertical markets with the highest level of determinism yet,” said Phil Solis, Research Director, Connectivity at IDC. “Interoperability testing between Intel and Broadcom will enable the development of products that can be used in the test beds for official Wi-Fi Alliance certification testing.”
Intel and Broadcom provide the full network that is essential to help maximize Wi-Fi 7’s potential and deliver end-to-end experiences to the wider Wi-Fi marketplace.
“As longtime WBA board members, Broadcom and Intel have been instrumental in pioneering Wi-Fi 6 and 6E. Now they’re leading the way again with Wi-Fi 7, which leverages the rapidly growing availability of 6 GHz spectrum in multiple countries across APAC, EMEA, Latin America and the U.S. Their successful trial is a milestone toward bringing Wi-Fi 7’s double-digit gigabit speeds, ultra-low latency, carrier-grade resilience and other next-generation capabilities to consumers and businesses worldwide. Enterprise and residential networks will also greatly benefit from the advanced capabilities of Wi-Fi 7,” said Tiago Rodrigues, CEO of the Wireless Broadband Alliance.
Broadcom and Intel say they will continue to show the additional capabilities of Wi-Fi 7.
WHAT DOES QUALCOMM HAVE TO SAY ABOUT WIFI 7?
“Qualcomm Technologies’ Wi-Fi 7 solutions push the boundaries of what Wi-Fi can do, with enhanced speeds, latency and network capacity plus support for advanced features like 320MHz channels, 4K QAM and advanced multi-link implementations such as High Band Simultaneous Multi-Link.”
References:
Intel and Broadcom Achieve First Cross-Vendor Wi-Fi 7 Demo
Intel Wi-Fi 7 page and Broadcom Wi-Fi 7 page
AT&T continues to add customers in key focus areas- 5G and fiber
Pascal Desroches, senior executive vice president and chief financial officer, AT&T spoke today at the Bank of America Media, Communications and Entertainment Conference where he provided an update to shareholders. Desroches reiterated that AT&T continues to take a disciplined and return-focused approach to growth and investment and made the following points:
- The company continues to add customers in its strategic focus areas of 5G and fiber. Overall industry postpaid phone volumes remain healthy, and AT&T has continued to see solid demand with continued low postpaid phone churn. In addition, AT&T’s consistent, disciplined and simple go-to-market approach continues to attract high-value customers. Desroches indicated that the impacts of recent pricing action on churn are within AT&T’s expected range and the company continues to expect that the pricing changes will be accretive in the back half of the year.
- AT&T continues to expand its fiber footprint and has the ability to serve 18 million customer locations in more than 100 metro areas with AT&T Fiber. Desroches shared he’s pleased with the increasing penetration rates for new fiber build. As AT&T expands to new markets, the company has seen first-year penetration rates about two times greater than historical norms.
- Desroches noted that AT&T is not seeing any material incremental shift in its cash collection cycles, which are within the company’s expectations and largely consistent with normal pre-pandemic levels.
- While the current macroeconomic environment has reduced visibility into economic trends going into next year, Desroches reiterated expectations for improved cash conversion in 2023 compared to 2022. Factors driving the company’s outlook for improved cash conversion include expectations for better service revenue levels exiting 2023 — from both a larger customer base and higher ARPUs — lower interest costs and the benefits from continued transformation savings.
- Expectations for improved cash conversion off this year’s free cash flow guidance of the $14 billion range provide more than sufficient financial flexibility to meet AT&T’s financial obligations – including its annual dividend commitment of $8 billion, or $1.11 per common share – even after factoring in the company’s above historical capital investment levels.

Contacts
Brittany Siwald
AT&T Corporate Communications
Phone: (214) 202-6630
Email: [email protected]
Dell’Oro Worldwide Wireless LAN market at new high in 2Q-2022; IDC reports 20.4% annual growth for enterprise segment
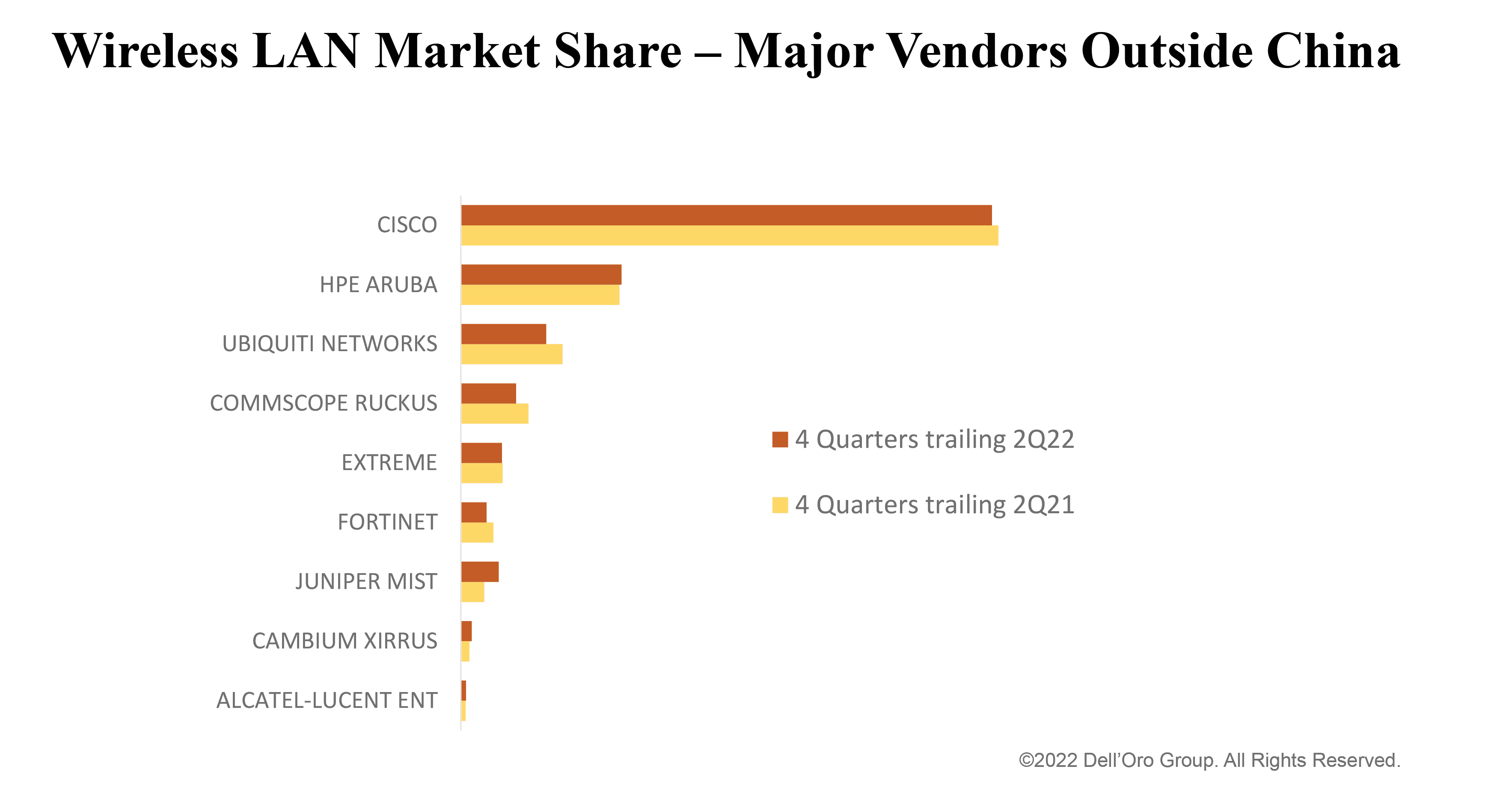
1. According to Dell’Oro Group’s Wireless LAN Quarterly Report, the Wireless LAN market reached a new high in the second quarter, eclipsing $2 Billion, with HPE Aruba and Juniper Mist overcoming supply constraints to contribute over two thirds of the shipment growth outside China. Enterprises saw a 10 percent increase in average prices compared to last year, boosting manufacturers’ revenues and helping to defray additional costs.
“HPE and Juniper really pulled rabbits out of their hats this quarter ̶ Aruba and Mist represent the majority of the growth in units shipped outside China,” says Siân Morgan, Wireless LAN Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “It’s like a game of whack-a-mole for the manufacturers. They’ll get their hands on one particular access point component and then another shortage will pop up. We’re expecting shipments to be lumpy through the next few quarters.”
Cisco has promised shipments ‘en masse’ for enterprises, and all of the manufacturers are busy finding creative solutions: redesigning products, using brokerage firms, or bypassing component distributors.
“Wireless LAN solutions have also become more expensive for enterprises. It’s very rare to see such a long stretch of quarters with year-over-year price increases. It’s a combination of higher-end products being available, including the new Wi-Fi 6E technology, as well as a general move by the manufacturers to cover their escalating costs. Looking ahead we have to ask ourselves how long the market will bear these higher prices,” added Morgan.
Additional highlights from the 2Q 2022 Wireless LAN Quarterly Report:
- The Wireless LAN market saw two distinct phenomena driving the growth: one in China, and another one in the markets outside China.
- In light of the China lockdowns, the Wireless LAN market in China showed surprising strength with both Huawei and H3C pulling in strong quarters.
- Wi-Fi 6E shipments accelerated this quarter, as another half dozen vendors started shipping products supporting the new 6 GHz band. However, now in its fourth quarter of product availability, Wi-Fi 6E is lagging the adoption rate of the prior two generations of Wi-Fi.
- Revenue from public cloud-managed APs has outpaced the market. The cloud-managed AP business is still dominated by Cisco – although this quarter, Juniper grabbed an outsized market share in cloud-managed Wireless LAN.
Sian wrote in an email to this author, “It is difficult to judge changes in market share based on one or two quarters, given that supply constraints are making shipment volumes choppy. To understand how the market is unfolding it is useful to look at market share based on trailing four-quarter averages, which are shown in the chart below.
Dell’Oro note earlier this year that supply chain issues increased vendor backlogs by up to 15-times normal levels. “Many enterprises have planned network upgrades and the popular connection is Wi-Fi. The trouble is getting it. Several manufacturers announced that components from second and third-tier suppliers became the bottleneck in 1Q22,” said Tam Dell’Oro, Founder, CEO and Wireless LAN Analyst. “Supply constraints have resulted in highly volatile quarterly performance vendor-to-vendor depending on whether or not they have all the components. For example, sales may be up 20 percent in one quarter and down 20 percent the next. Another item, which could potentially cause delays, that we are keeping our eye on are the contract negotiations between the west coast dockworkers union and the Maritime Association,” added Dell’Oro.
The Dell’Oro Group Wireless LAN Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the Enterprise Outdoor and Indoor markets, Wireless LAN Controllers with tables containing manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and unit shipments by the following wireless standards: 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6 and 6E [6 GHz]), 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) Wave 1 vs. Wave 2, and historic IEEE 802.11 standards. The Enterprise market is portrayed by Public Cloud vs. Premises and Private Cloud deployments, as well as by ten Vertical markets and by Customer Size. To purchase these reports, please contact us by email at [email protected].
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. IDC reports that the enterprise segment of the worldwide wireless local area network (WLAN) market continued its strong growth in the second quarter of 2022 (2Q22), increasing 20.4% year over year to $2.1 billion. That’s according to the IDC report: “Worldwide Quarterly Wireless LAN Tracker.”
The 20.4% annualized growth builds on the enterprise WLAN market growing 17.1% year over year in the first quarter of 2022. In the first half of 2022, the enterprise WLAN market has grown 18.4% compared to the first half of 2021. Growth in the enterprise WLAN market continues to be driven by the latest Wi-Fi standard, known as Wi-Fi 6 or 802.11ax. Wi-Fi 6 access points (AP) made up 76.5% of the revenues in the Dependent AP segment and accounted for 62.7% of unit shipments within the segment. Wi-Fi 5 products, also known as 802.11ac, made up the remaining balance of Dependent AP sales.
The consumer segment of the WLAN market declined 3.5% year over year in 2Q22, with the quarter’s unit shipments remaining relatively flat at 0.6% growth compared to the first quarter of 2022. Adoption of Wi-Fi 6 continues in the consumer segment of the WLAN market too: In 2Q22, Wi-Fi 6 made up 33.5% of the market’s revenues.
“The enterprise WLAN market continues to grow at a rapid clip, emphasizing the importance of wireless technology in the network and digital transformation goals of organizations across the globe,” said Brandon Butler, research manager, Enterprise Networks at IDC. “The enterprise WLAN market is not immune to challenges however, with the supply chain disruptions and component shortages being notable examples. But strong demand for wireless refreshes to Wi-Fi 6 – and increasingly to Wi-Fi 6E – is buoying the market and leading to strong growth rates.”
The enterprise WLAN market had mixed results across the globe. In the United States, the market increased 15.7% annually, while in Latin America the market grew 47.7% from a year earlier. In Canada the market declined 1.6%. In Western Europe, the market increased 45.4%, but in Central and Eastern Europe, the market declined 20.6%. Within Central and Eastern Europe, Russia’s market declined 73.2% as the Russia-Ukraine war rages on. In the Middle East & Africa, the market rose 23.2%. In the Asia/Pacific region, excluding Japan and China, the market rose 26.5%, while in the People’s Republic of China the market increased 8.7% year over year. In Japan the market rose 6.2%.
Vendor highlights (note that Juniper Mist is NOT mentioned by IDC as a leading wireless LAN vendor):
- Cisco’s enterprise WLAN revenues increased 19.3% year over year in 2Q22 to $792.0 million, giving the company market share of 37.7%, compared to market share of 41.5% in the previous quarter, 1Q22.
- HPE-Aruba revenues rose 48.6% year over year in 2Q22, giving the company market share of 14.9%, down from 16.5% in the first quarter.
- Ubiquiti enterprise WLAN revenues increased 10.5% year over year in 2Q22, giving the company 7.9% market share in the quarter, up from 7.1% in 1Q22.
- Huawei enterprise WLAN revenues rose 20.0% year over year in 2Q22, giving the company 8.5% market share, up from 4.6% market share in the previous quarter.
- H3C revenues increased 16.4% year over year in 2Q22, giving the company market share of 4.6%, up from 4.3% in 1Q22.
The IDC Worldwide Quarterly Wireless LAN Tracker provides total market size and vendor share data in an easy-to-use Excel Pivot Table format. The geographic coverage includes nine major regions (USA, Canada, Latin America, People’s Republic of China, Asia/Pacific (excluding Japan & China), Japan, Western Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and Middle East and Africa) and 60 countries. The WLAN market is further segmented by product class, product type, product, standard, and location. Measurement for the WLAN market is provided in vendor revenue, value, and unit shipments.
About IDC Trackers:
IDC Tracker products provide accurate and timely market size, vendor share, and forecasts for hundreds of technology markets from more than 100 countries around the globe. Using proprietary tools and research processes, IDC’s Trackers are updated on a semiannual, quarterly, and monthly basis. Tracker results are delivered to clients in user-friendly Excel deliverables and on-line query tools.
References:
HPE Aruba and Juniper Mist Navigate Component Shortages to Gain Share, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS49663322
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=IDC_P23464
T-Mobile sells Sprint wireline business to Cogent for $1
T-Mobile will sell its wireline business, acquired from Sprint, to Cogent Communications Holdings Inc for $1, while taking a $1 billion charge on the transaction. The deal includes a $700 million contract under which Cogent will provide transit services to T-Mobile for 4-1/2 years after the deal closes. Cogent and T-Mobile expect to close the deal in or prior to December 2023.
T-Mobile has been turning its attention away from the wireline business that includes assets from its $26 billion acquisition of Sprint Corp in 2020. The decline of Sprint’s wireline business has been astounding to this author. For years, Sprint was the leader in wireline technologies like X.25, Primary Rate ISDN, Frame Relay, ATM, Carrier Ethernet and MPLS. Their optical network was second to none and was used as a backbone network for many carriers, including AT&T.
The deal for the Sprint wireline assets, a unit formerly known as Sprint Global Markets Group, provides a range of services, including MPLS (Cogent plans to convert those to VPLS and WAN), DIA (dedicated Internet access) and transit, wavelength and colocation services. The unit generated roughly $560 million in revenues in 2021 and has about 1,300 employees. In North America, the unit operates approximately 19,000 long-haul route miles, 1,300 metro route miles, and some 16,800 route miles of leased dark fiber. Total wireline business revenue was $739 million last year, according to Reuters.
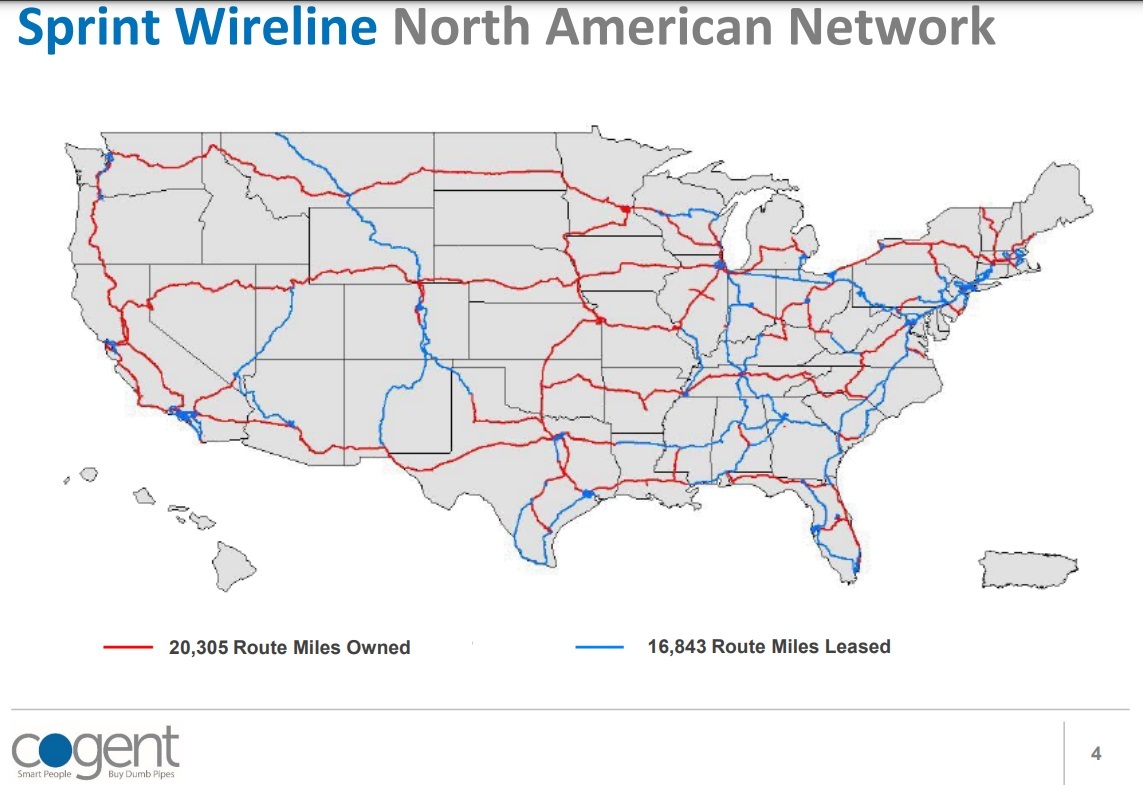
In the most recent earnings call, T-Mobile Chief Executive Michael Sievert said the company was no longer using Sprint infrastructure to support its wireless business and that an asset review was underway.
“We think that T-Mobile must be receiving some sort of discount on the IP transit services that they will be buying from Cogent contractually, and they will save on the costs that they’d otherwise have to keep, maintain and improve (the infrastructure),” said Michael Ashley Schulman, partner and chief investment officer at Running Point Capital Advisors.
For Cogent, the deal provides a U.S. long-haul network that could eventually replace its current leased network and help expand the company’s product set to consumers and enterprises.
Cogent expects its revenue base to be about $1.1 billion, or 180% of its current $600 million run rate, CEO Dave Schaeffer said on a conference call. He outlined several strategic benefits from the deal, noting it will increase its fiber footprint and boost scale in the DIA, transit, virtual private networks and colocation/data centers markets.
The deal also paves the way for Cogent to enter the North American market for wavelength sales, and compete with market leaders Lumen and Zayo. Cogent, which is also looking to enter the market for dark fiber sales, said it also stands to gain international operating licenses in India and Malaysia, where it has no presence today.
Among other benefits, Cogent will also acquire a legacy Sprint customer base of about 1,400 businesses that, it claims, fall outside Cogent’s typical customer profile.
Cogent expects to offer customers the ability to migrate from their legacy MPLS VPN solutions to modern Ethernet / VPLS or SD-WAN / DIA solutions for their corporate needs. Cogent also expects to facilitate the migration of netcentric internet access customers from the T-Mobile Wireline Business (legacy Sprint) AS1239 to Cogent’s AS174.
Cogent expects its revenue base, post-close, to be $1.1 billion, or 180% of its current $600 million run-rate. Cogent likewise expects its multi-year revenue growth post-close will be 5% to 7% annually, with targeted aggregate revenue of over $1.5 billion by 2028.
A newly formed direct subsidiary of Cogent will consummate the acquisition. Cogent does not plan to issue new debt or equity in order to finance the acquisition, and the transaction is not expected to be dilutive to Cogent’s existing stockholders. Cogent plans to maintain its current dividend per share, which is expected to continue to increase over time.
Morgan Stanley served as the financial adviser for Cogent, while Houlihan Lokey was T-Mobile’s financial adviser.
References:
https://www.cogentco.com/en/about-cogent/events/3565-cogent-investor-call
China Mobile Partners With ZTE for World’s First 5G Non Terrestrial Network Field Trial
 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, ZTE says they’ve produced the industry’s smallest 5G Core network product, dubbed the Mini5GC. The new Mini5GC features miniaturization, light weight, simple networking and ultra-high integration. The company states that it can well facilitate safe production, flexible adjustment of work sites, and efficient and accurate emergency rescue in mining areas.
References:
https://sdnfv.zte.com.cn/en/news/2022/2/ZTE-5G-Common-Core-Aims-to-Improve-Digital-Economy
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/products/core_network/packet_core/202003251501/5G-Common-Core
FCC to release U.S. broadband maps in November 2022
Today, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) confirmed that its first data collection window for the broadband serviceable location fabric has closed. The agency also said it is targeting November 2022 for a public release of a first draft of the new map.
“For the first time ever, we have collected extensive location-by-location data on precisely where broadband services are available, and now we are ready to get to work and start developing new and improved broadband maps,” wrote Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel in a note on Friday afternoon. This comes after FCC work over the past 18 months to update and improve their broadband maps.
What’s next for the FCC’s broadband maps:
- FCC is targeting November 2022 for release of the first draft of the map.
- The Fabric challenge process will begin in 10 days.
- The Fabric is the first-ever national dataset capturing individual locations that should have fixed broadband service availability. It is the product of integrating multiple data sources for each state and territory—in other words, hundreds of data sources. These data sources include, among other things, address records, tax assessment records, imagery and building footprints, Census data, land use records, parcel boundaries, and geo-spatial road and street data. Our old broadband maps, in contrast, lacked any of this location-specific information.
- Broadband providers reported their own availability data to the locations identified in the Fabric.
- The FCC is continually working to improve our Fabric through additional data sources, such as LIDAR data and new satellite and aerial imagery sources, as they become available and through our upcoming challenge processes.
- States, local governments, Tribal governments, and providers can now access the initial Fabric data, and, in 10 days we will open up a window for them to challenge this data.
In a public notice, the FCC set some parameters for that process, writing: “We remind governments, service providers, and other entities and organizations planning to submit challenges that the Fabric is intended to identify BSLs as defined by the Commission, which will not necessarily include all structures at a particular location or parcel.” The FCC will host a webinar on September 7, at 2 p.m. ET, “to assist state, local, and Tribal governments, service providers, and other entities who intend to submit bulk challenges, or proposed corrections, to the location data in the Fabric,” it said.
Once the maps are released, FCC will open a process for the public and other stakeholders to make challenges directly through the map interface.
Looking ahead, there’s one more important thing to note about the new maps. When the first draft is released, it will provide a far more accurate picture of broadband availability in the United States than our old maps ever did. That’s worth celebrating. But our work will in no way be done. That’s because these maps are iterative. They are designed to updated, refined, and improved over time.
Broadband providers are constantly updating and expanding their networks. We have set up a process to make sure our maps will reflect these changes and yield more precise data over time. We have also built a process in which state, local and Tribal governments, other third parties and, perhaps most importantly, consumers, will be able to give us feedback on the maps and help us continually improve and refine the data we receive from providers. All of this will require persistent effort—from the agency, providers, and other stakeholders. The Commission is committed to doing this hard work and keeping the public informed of our efforts every step of the way.
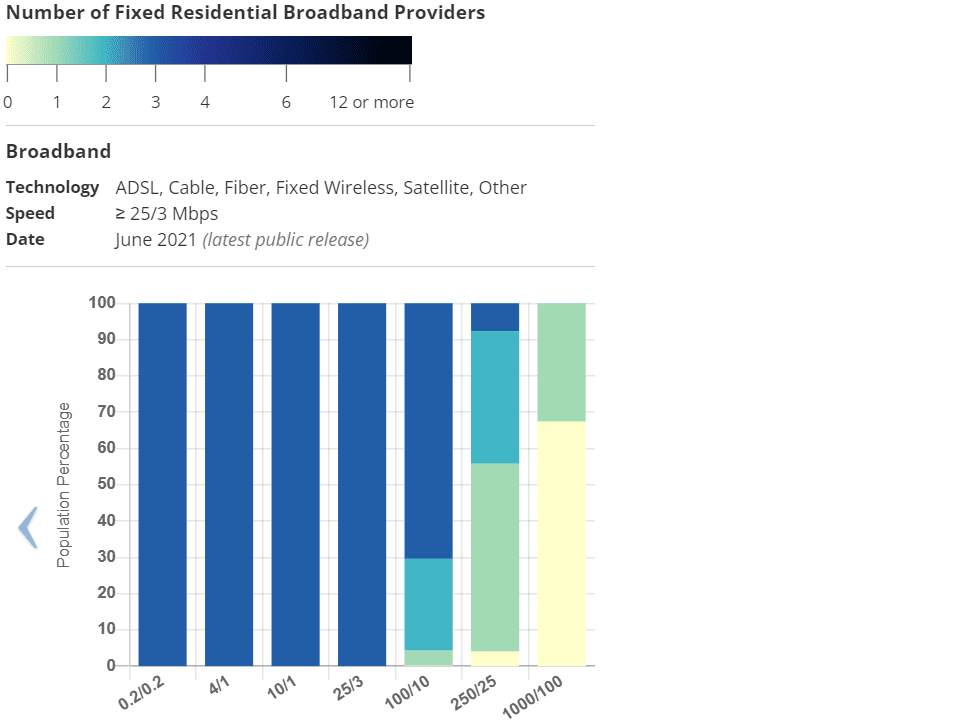
Here’s the most current broadband map for Santa Clara County, CA (oven referred to as Silicon Valley and previously as the Valley of Hearts Delight):
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/news-events/notes/2022/09/02/another-step-toward-better-broadband-maps
https://www.fcc.gov/document/start-bulk-fabric-challenge-process-announced
Carrier Ethernet Market Assessment and MEF 3.0 Certification
Disclaimer: This is an update to our August 24, 2022 post that includes a new report on the Global Carrier Ethernet Market and the status of MEF 3.0 certification for Carrier Ethernet and SD-WAN.
Chart from: https://reportsexpress.com/carrier-ethernet-services-market-report-4/
To date, 80 global service and technology providers now offer MEF 3.0-certified Carrier Ethernet (CE) and SD-WAN solutions. In addition, more than 8,000 professionals from 500+ companies around the globe have earned MEF professional certifications in Carrier Ethernet, SD-WAN, and SDN/NFV. Five of the six top companies ranked on Vertical Systems Group’s 2021 U.S. Carrier Managed SD-WAN Leaderboard—AT&T, Comcast Business, Verizon, Lumen, and Windstream—have achieved MEF 3.0 SD-WAN certification (see complete list below), and each of these providers employs professionals with MEF-SDCP training and certification.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..Lumen Technologies ranked first in Vertical Systems Group’s mid-year US Carrier Ethernet Leaderboard. VSG’s rank order is based on retail port share as of June 30, 2022: Lumen, AT&T, Spectrum Enterprise, Verizon, Comcast Business and Cox Business. To qualify for a rank on this LEADERBOARD, network providers must have four percent (4%) or more of the U.S. retail Ethernet services market. VSG analyzes Ethernet port share based on six service segments that service providers deliver to enterprise customers: Ethernet DIA (Dedicated Internet Access), E-Access to IP/MPLS VPN, Ethernet Private Lines, Ethernet Virtual Private Lines, Metro LAN and WAN VPLS (Virtual Private LAN service).
Challenge Tier citations were attained by the following six companies (in alphabetical order): Altice USA, Cogent, Frontier, GTT, Windstream and Zayo. The Challenge Tier includes providers with between 1% and 4% share of the U.S. retail Ethernet market.

“Share rankings on the U.S. Ethernet LEADERBOARD remain unchanged for the first half of 2022, however a shakeup is possible by the end of the year,” said Rick Malone, principal of Vertical Systems Group. “Escalating requirements for Gigabit Ethernet services – and particularly 100+Gbps – are spurring capacity upgrades and intensifying competition among fiber-based providers.”
Research Highlights:
- Lumen continues to hold the top rank on the Mid-2022 U.S. Ethernet LEADERBOARD based on port share.
- Our latest Ethernet research shows that port shares are tightening between several of the market leading providers.
- Dedicated Internet/Cloud Access (DIA) was the fastest growing Ethernet service for the first half of 2022 and is on pace to be the largest Ethernet service overall by year-end based on billable U.S. customer installations. Primary Ethernet DIA applications are connectivity for Cloud services and Managed SD-WANs.
- Market demand is rising for Ethernet services ranging up to 100+ Gbps. Customers requiring higher bandwidth connectivity are also evaluating alternatives to Ethernet, including Wavelength and Dark Fiber services.
- Ethernet service providers continue to grapple with supply chain challenges, including lengthy lead times and shortages of the supplies necessary for customer deployments and backbone network operations.
- Lumen and Verizon are the only LEADERBOARD companies with MEF 3.0 Carrier Ethernet (CE) certification.
The Market Player tier includes all providers with port share below 1%. Companies in the Market Player tier include the following providers (in alphabetical order): ACD, AireSpring, Alaska Communications, Alta Fiber, American Telesis, Arelion, Armstrong Business Solutions, Astound Business, Breezeline, BT Global Services, Centracom, Consolidated Communications, Conterra, Crown Castle, Douglas Fast Net, DQE Communications, ExteNet Systems, Fatbeam, FiberLight, First Digital, FirstLight, Flo Networks, Fusion Connect, Global Cloud Xchange, Great Plains Communications, Hunter Communications, Intelsat, Logix Fiber Networks, LS Networks, MetTel, Midco, Momentum Telecom, NTT, Orange Business, Pilot Fiber, PS Lightwave, Ritter Communications, Segra, Shentel Business, Silver Star Telecom, Sparklight Business, Syringa, T-Mobile, Tata, TDS Telecom, TPx, Unite Private Networks, Uniti, US Signal, WOW!Business, Ziply Fiber and other companies selling retail Ethernet services in the U.S. market.
Market shares are measured based on the number of billable retail customer ports installed. Vertical Systems Group’s Ethernet port share analysis includes six service segments based on what service providers are offering and enterprise customers are purchasing as follows: Ethernet DIA (Dedicated Internet Access), E-Access to IP/MPLS VPN, Ethernet Private Lines, Ethernet Virtual Private Lines, Metro LAN, and WAN VPLS.
@Ethernet is available now exclusively by subscription to an ENS Research Program. Research data includes the market share detail that powers the U.S. and Global Provider Carrier Ethernet Services LEADERBOARD results. Contact us for more information and pricing.
Vertical Systems Group: Mid-2022 U.S. Carrier Ethernet Leaders; Change is Coming
https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/08/30/2506924/0/en/MEF-3-0-Certification-Growth-Fueled-by-Acceleration-of-Global-Enterprise-Digital-Transformation.html
5G Optical Transceiver Market Trends and Technologies
by Fayre Fan (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
The fiber optic transceiver is the core component of optical communications. It is used to realize optical-to-electrical conversion. The transmitter converts the electrical signal into an optical signal, while the receiver does the reverse – it converts the optical signal into an electrical signal.
Increasingly, fiber optics is being used for the transport of 5G signals to and from the edge of the carrier’s wide area network. Optical transceivers are the basic component of 5G backhaul, midhaul and fronthaul. Their cost accounts for 50%~70% of the total 5G network costs.
Low cost is the key appeal of the 5G optical transceivers. The industry has carried out extensive research on 5G optical module technology, and currently, there are many solutions.
Increasing demands for 5G transceivers: low cost is the key to 5G optical module:
The growth of optical modules in the 5G network mainly comes from three factors:
- More base stations are needed in the high-frequency band.
- Larger bandwidth is required for high-speed rates.
- More connections are required for added midhaul transmission links.
Global top suppliers of 5G base stations include Huawei (China), Ericson (Sweden), Nokia (Finland), ZTE (China), and Samsung (Korea). China is the largest 5G market, which has captured about 74% of the market, followed by Korea and Europe.
The development of the global 5G network market stimulates the increasing demand for 5G optical transceivers. According to the forecast data from Lightcounting, the global market share of 5G fronthaul transceivers will reach 657/632/593 million dollars in 2022~2024. 5G midhaul and backhaul transceivers will reach 242/245/247 million dollars respectively. Therefore, reducing cost is a key objective of 5G transceiver development. Here’s an illustration of backhaul, midhaul and fronthaul:

5G fronthaul -demand for 25G BiDi transceiver:
In the 4G fronthaul network, the most commonly used transceivers are single-mode 10G duplex transceivers. 5G network has higher requirements for the data rate and optical interface of transceivers. In consideration of saving fiber resources and maintaining high-precision synchronization of uplink and downlink, the simplex bi-directional (BiDi) transceiver allowing data transmitting and receiving over one single fiber, is superior to duplex transceivers. Moreover, considering the 5G download rate is at least 10 times higher than that of the 4G network, the 25 Gbit/s data rate is also necessary for the 5G fronthaul transceivers. Taken together, 25G BiDi transceivers are needed for 5G fronthaul networks.
Optical Transceivers for 5G Front-Haul
| Data Rate | Form Type | Transmission Distance | Wavelength | Modulation Format | Transmitter & Receiver |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 70~100m | 850nm | NRZ | VCSEL+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 300m | 1310nm | NRZ | FP/DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 10km | 1310nm | NRZ | DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 BiDi | 10/15/20km | 1270/1330nm | NRZ/PAM4 | DFB+PIN/APD |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 10km | CWDM | NRZ | DFB+PIN |
| 25Gbit/s | Tunable SFP28 | 10/20km | DWDM | NRZ | EML+PIN |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 70~100m | 850nm | NRZ | VCSELs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | 4WDM-10 | NRZ | DFBs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | 1310nm | PAM4/DMT | EML+PIN |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 10km | CWDM4 | NRZ | DFBs+PINs |
5G midhaul and backhaul – demand for 50G/100G/200G/400G transceivers:
The 5G midhaul and backhaul are mainly carried through the metro access layer, convergence layer, and core layer. For the access layer, 50G/100G transceivers are commonly used. For example, 50G PAM4 transceiver is a cost-effective solution for 5G midhaul and backhaul. It is based on 25G optical components and PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4-level) modulation. For the convergence layer and core layer, 100G/200G/400Gb/s DWDM transceivers are mainly used. And low-cost coherent 100G/200G/400G transceivers are welcomed, which mainly use QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation and DSP (Digital Signal Processing) technology.
Optical Transceivers for 5G Mid-Haul/Back-Haul
| Data Rate | Form Type | Transmission Distance | Wavelength | Modulation Format | Transmitter & Receiver |
| 25Gbit/s | SFP28 | 40km | 1310nm | NRZ | EML+APD |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28/SFP56 | 10km | 1310nm | PAM4 | EML/DFB+PIN |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 10km | 1270/1330nm | PAM4 | EML/DFB+PIN |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28/SFP56 | 40km | 1330nm | PAM4 | EML+APD |
| 50Gbit/s | QSFP28 BiDi | 40km | 1295.56/1309.14nm | PAM4 | EML+APD |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10km | CWDM/LWDM | NRZ | DFBs/EMLs+PINs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 40km | LWDM | NRZ | EMLs+APDs |
| 100Gbit/s | QSFP28 | 10/20km | DWDM | PAM4/DMT | EMLs+PINs |
| 100/200/400Gbit/s | CFP2-DCO | 80~120km | DWDM | PM QPSK/8-QAM/16-QAM | IC-TROSA+ITLA |
| 200/400Gbit/s | OSFP/QSFP-DD | 2/10km | LWDM | PAM4 | EMLs+PINs |
Technological innovations of 5G transceivers:
Optical transceiver-related technology mainly includes packaging technology and optoelectronic components technology.
In terms of packaging technology, 5G transceivers can adopt existing mature packaging technologies. For example, since 25G BiDi has a similar optical structure to that of 10G BiDi, the common TO-CAN (transistor-outline-can) package can be used to save cost.
The most vital technological innovation aims at optoelectronic components technology. The technological innovation of optoelectronic devices mainly aims at these goals: function expansion, data rate increase, and cost reduction.
Function expansion innovation of laser chips example: industrial-grade laser chips no longer require temperature control devices, the laser chip used in the non-airtight environment no longer requires the expensive airtight package, the laser chip with a small divergence angle no longer requires an expensive non-spherical lens, anti-reflection laser chips no longer require isolators, etc. Those technologies simplify the packaging of the optical module, also providing higher reliability and lower cost.
Data rate increase innovation includes example: the 50G PAM4 optical module uses a 25G baud rate laser/detector, and an electrical chip with high linearity. Compared with the 25G NRZ (non-return to zero) optical module, it allows for higher bandwidth.
Cost reduction innovation example: coherent 100G transceiver, it reduces the cost on the premise of meeting the transmission distance requirement within 200km.
Ultimately, the key technologies of 5G optical modules are mainly reflected in the innovation of optoelectronic chips. The specific technologies include:
- Industrial temperature grade high-speed laser chip technology
- High linearity 25G baud rate DFB chip and EML chip technology
- Low-cost 25G wavelength tunable laser chip technology
- Low-cost coherent 100G/200G/400G optical transceiver technology
For example, Marvell and OE Solutions recently announced a collaboration to deliver the industry’s first production-ready 100G QSFP-DD optical modules optimized for 5G backhaul and Metro Access applications.
In conclusion, 5G optical transceivers will play a more important role in the entire optical module market compared with the 4G era. Technological innovation will be the main driver to realize the low-cost 5G optical modules.
References:
https://www.researchreportsworld.com/global-5g-base-station-sales-market-21017689