Author: Alan Weissberger
Samsung in OpenRAN deal with NTT DOCOMO; unveils 28GHz Radio Unit (RU)
Samsung Electronics announced the company is supplying a variety of 5G radios to support NTT DOCOMO’s Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) expansion. Samsung will now provide a range of Open RAN-compliant 5G radios covering all of the Time Division Duplex (TDD) spectrum bands held by the operator.
This builds upon the two companies’ 5G agreement previously-announced in March 2021, in which NTT DOCOMO selected Samsung as its 5G network solutions provider. Samsung now adds new radios — including 3.7GHz, 4.5GHz and 28GHz — to its existing 3.4GHz radio support for NTT DOCOMO.

This expanded portfolio from Samsung will enable NTT DOCOMO to leverage its broad range of spectrum across Japan to build a versatile 5G network for diversifying their services offered to consumers and businesses. The companies have also been testing the interoperability of these new radios with basebands from various vendors in NTT DOCOMO’s commercial network environment.
“We have been collaborating with Samsung since the beginning of 5G and through our Open RAN expansion, and we are excited to continue extending our scope of vision together,” said Masafumi Masuda, Vice President and General Manager of the Radio Access Network Development Department at NTT DOCOMO. “Solidifying our global leadership, we will continue to build momentum around our Open RAN innovation and to provide highly scalable and flexible networks to respond quickly to the evolving demands of our customers.”
“Japan is home to one of the world’s most densely populated areas with numerous skyscrapers and complex infrastructure. Samsung’s industry-leading 5G radios portfolio meets the demands of low-footprint, low-weight solutions, while also ensuring reliable service quality,” said Satoshi Iwao, Vice President and Head of Network Division at Samsung Electronics Japan. “As NTT DOCOMO continues to accelerate its Open RAN innovation, we look forward to working together to deliver a richer experience to consumers and generating new business opportunities.”
With this announcement, Samsung introduces its new 28GHz Radio Unit (RU) for the first time — as a new addition to its portfolio of leading mmWave solutions. This RU, which weighs less than 4.5kg (~10lbs), features a light and compact form factor with very low power consumption, enabling flexible deployments in various scenarios. Additionally, Samsung’s 3.4GHz, 3.7GHz and 4.5GHz radios are also Open RAN-compliant and designed to deliver high performance and reliability.
Last month, Samsung won a contract with NTT East to provide cloud-native 5G core and RAN equipment to the provider’s private 5G network platform. That deal followed on an agreement earlier this year for Samsung to power the operator’s private 5G network services in the east areas of Japan, and followed trials of Samsung’s 5G standalone (SA) network core in test environments.
Samsung also secured a deal with Comcast to activate the cable giant’s deep spectrum holdings and become an infrastructure-owning 5G cellular operator targeting market heavyweights Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile US. Comcast will use Samsung’s 5G RAN equipment for its Xfinity Mobile service, including a newly developed 5G Strand Small Cell that is designed to be mounted on Comcast’s existing aerial cable lines. This all-in-one piece of equipment is central to the deployment as it will allow Comcast to mount cellular antennas where it’s already running cable connections for wireless backhaul.
A recent Dell’Oro Group report noted the vendor has been gaining RAN market share at the expense of its China-based rivals Huawei and ZTE outside of their home country. This could accelerate as the U.S. Federal Communications Commission adopted new rules prohibiting domestic telecommunication operators from acquiring and using networking and other equipment from China-based vendors, including Huawei.
“While commercial Open RAN revenues continue to surprise on the upside, the underlying message that we have communicated now for some time now has not changed and remains mixed,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President with the Dell’Oro Group. “Early adopters are embracing the movement towards more openness but at the same time, there is more uncertainty when it comes to the early majority operator and the implications for the broader RAN supplier landscape now with non-multi vendor deployments driving a significant portion of the year-to-date Open RAN market,” continued Pongratz.
Additional Open RAN highlights from the Dell’Oro’s 3Q 2022 RAN report:
- Top 4 Open RAN revenue suppliers for the 1Q22-3Q22 period include Samsung, Fujitsu, NEC, and Mavenir.
- Trials are on the rise globally, however, North America and the Asia Pacific regions are still dominating the commercial revenue mix over the 1Q22-3Q22 period, accounting for more than 95 percent of the market.
- More than 80 percent of the year-to-date growth is driven by the North America region, supported by large scale non-Massive MIMO and Massive MIMO macro deployments.
- The rise of Open RAN has so far had a limited impact on the broader RAN (proprietary and Open RAN) market concentration. The data contained in the report suggest that the collective RAN share of the top 5 RAN suppliers (Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Samsung) declined by less than one percentage point between 2021 and 1Q22-3Q22.
- Short-term projections have been revised upward to reflect the higher baseline – Open RAN is now projected to account for 6 to 10 percent of the RAN market in 2023. Open RAN growth rates, however, are expected to decelerate next year, reflecting the likelihood that the sum of new brownfield deployments will be able to offset more challenging comparisons with the early adopters.
Samsung says they have pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
NTT DOCOMO began commercial 5G services in early 2020, and included open RAN-compliant equipment provided by Fujitsu, NEC, and Nokia. The carrier more recently signed a partnership with South Korea’s SK Telecom (SKT) to develop new 5G and 6G cellular technologies and deployment plans taking advantage of open and virtualized RAN (vRAN) technology.
NTT DOCOMO is Japan’s leading mobile operator with over 85 million subscriptions, is one of the world’s foremost contributors to 3G, 4G and 5G mobile network technologies. Beyond core communications services, DOCOMO is challenging new frontiers in collaboration with a growing number of entities (“+d” partners), creating exciting and convenient value-added services that change the way people live and work. Under a medium-term plan toward 2020 and beyond, DOCOMO is pioneering a leading-edge 5G network to facilitate innovative services.
References:
https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-electronics-expands-5g-radio-support-for-ntt-docomo
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/docomo-deepens-samsung-5g-ran-drive/2022/12/
https://www.docomo.ne.jp/english/
Ericsson: Over 300 million Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) connections by 2028
According to Ericsson, total global FWA [1.] subscriptions will grow at 19 percent year-on-year during the 2022 to 2028 period to reach more than 300 million by 2028, the vast majority of which will be based on 5G.
Note 1. FWA is a connection that provides primary broadband access through mobile network-enabled customer premises equipment (CPE). This includes various form factors of CPE, such as indoor (desktop and window) and outdoor (rooftop and wall-mounted). It does not include portable battery-based Wi-Fi routers or dongles.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The use of FWA for home and even business broadband is proving to be a major early use case for 5G, especially in regions where the fixed broadband market is lacking. FWA growth is in part driven by India and will also come in other emerging markets. Its data shows that almost 40 percent of 5G FWA launches came in emerging markets in the past year, with services now on offer in densely populated countries like Mexico, South Africa and the Philippines.
Key findings:
- More than three-quarters of service providers surveyed in over 100 countries are now offering Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) services.
- Nearly one-third of service providers now offer FWA over 5G, compared to one-fifth a year ago.
- The number of 5G FWA connections are expected to grow to around 235 million by 2028, representing almost 80 percent of the total FWA connections.

Source: Ericsson
“Following the 5G spectrum auction in India in July, a major service provider has expressed a goal to serve 100 million homes and millions of businesses with 5G FWA services,” Ericsson stated. 5G has only just come to market in India; its big operators launched services in early October. But operators are rolling out the technology at pace and with the price of 5G smartphones coming down, customer numbers will go up. 5G subscriptions in the India region – which includes Nepal and Bhutan – should reach 31 million by the end of this year and 690 million by end-2028, accounting for more than half of all mobile subscriptions – 1.3 billion – by that date.
“Higher volumes of 5G FWA in large high-growth countries such as India have the potential to drive economies of scale for the overall 5G FWA ecosystem, resulting in affordable CPE that will have a positive impact across low-income markets,” Ericsson added.
Globally, 5G subscriptions will hit 5 billion by the end of 2028, Ericsson predicts, despite the economic challenges much of the world is facing.
Service providers together added 110 million 5G subscriptions in the July-September period, bringing the worldwide total to around 870 million. With that sort of uptake, the 1 billion by year-end figure looks comfortably attainable, and will come two years earlier than the same milestone following the launch of 4G. Growth is being driven by device availability, falling prices and large-scale deployments in China, Ericsson said.
Ericsson added that North East Asia as a whole and North America are witnessing strong 5G growth, with penetration in those markets likely to reach around the 35 percent mark by the end of this year. Given that the world’s first 5G launches came in the US and in Korea back in 2019, it makes sense that those areas are leading the way in terms of uptake.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/dataforecasts/fwa-outlook
https://www.ericsson.com/en/fixed-wireless-access#
Research & Markets: 5G FWA Global Market to hit $38.17B by 2026 for a CAGR of 87.1%
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
JC Market Research: 5G FWA market to reach $21.7 billion in 2029 for a CAGR of 65.6%
Juniper Research: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to Generate $2.5 Billion in Global Network Operator Revenue by 2023
5G FWA launched by South Africa’s Telkom, rather than 5G Mobile
Samsung achieves record speeds over 10km 5G mmWave FWA trial in Australia
Verizon and WiPro in Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) partnership
Verizon Business, today announced a global Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) partnership with Wipro Limited, an India based technology services and consulting company, that will accelerate the network modernization and cloud transformation journey for businesses. Wipro’s Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) solution, powered by Verizon Business will include a range of pre-configured and tested service chains on a subscription-based consumption model, designed to drive network consumption infrastructure on demand. The multi-year partnership will enable Wipro to transition customers from legacy cycles of deploying hardware, applications and services to an automated, self-healing, and highly secure network service environment.
Massimo Peselli, Senior Vice President and Chief Revenue Officer, Global Enterprise and Public Sector for Verizon Business said: “Many organizations want to get out of endless technology refresh cycles but they face the twin challenges of traditional hardware and fixed infrastructures. Our partnership with Wipro will enable businesses to future-proof their network in a manner that is more flexible, agile and predictive, centered around their specific needs.”
“This is a network-as-a-service partnership that includes managed services, hardware and security for the global market,” said Sowmyanarayan Sampath, executive vice president and CEO of Verizon Business. “The bulk of Wipro’s customers are global, and the system integrator caters to industry verticals such as retail and energy with a strong value system. We have a logical go-to-market strategy,” Sampath added.
A recent IDC survey of over 400 technology-buying decision makers across the globe revealed that 69% of respondents are planning a network transformation investment in the next 12 months. NaaS has increasingly begun challenging legacy commercial models that require large upfront capital costs by providing more flexible, subscription-based services that can more easily be modified as needs change. The technology has accelerated the implementation of new digital technologies such as AI/ML, 5G, IoT, advanced robotics, blockchain, AR/VR, and voice-assistance.
Jo Debecker, Senior Vice President & Global Head, Cloud and Infrastructure Services, Wipro Limited commented: “Our joint NaaS offering brings together two industry leaders to drive this unique value proposition that will help our customers keep pace with changing demands of the cloud and network infrastructure while achieving operational efficiencies and agility at scale.”
Today’s agreement brings together two network industry leaders.
- Verizon has been named a Leader in Gartner® Magic Quadrant Network Services, Global for the last 16 years and manages more than 4,300 networks globally.
- Wipro is a Leader in Gartner® Magic Quadrant for Managed Network Services and manages over 500+ Network and data center facilities across geographies and different industries.
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-business-wipro-partner
https://www.naasenterprisesurvey.com/#executive-summary
India’s COAI joins 4 European telcos in demanding OTT players pay to use their networks
India Telecom industry body Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) has reiterated that over-the-top (OTT) players should pay telcos for using their network. The payment can be done directly to the telecom firms on mutually agreed terms and in case a mutual agreement is not reached, an appropriate licensing and regulatory framework should be formed which governs the contribution of OTT players towards creation of network infrastructure.
The association has highlighted that globally, the desirability of OTTs making a “fair contribution” to network costs of telecom firms has gained momentum. For instance, the European Commission (EU) is advocating for formalizing due legislation for OTT players to share the network investment burden of the telecom players in a proportionate manner.
The EU continues to express concern that there are big tech companies who generate a lot of data traffic but do not invest towards building infrastructure. The governments of France, Italy and Spain sent a joint paper to the European commission in August 2022, requesting for the swift development of a legislative proposal in this regard. Similar sentiments have been expressed by representatives of the US regulator FCC and in Australia, a world-first law was passed in Feb 2022, aimed at making tech giants pay for news content on their digital platforms, COAI said.
“We wish to submit that any entity which creates a property or infrastructure by investing funds, is entitled to take usage charges (rent /lease charges, etc.) from the user of that property or infrastructure who uses the same for commercial purposes,” COAI said in a letter to India’s Telecom Secretary K Rajaraman.
Further, the association stressed that the government needs to provide a legal framework and empowerment for enabling such entity to charge any user that uses its service/infrastructure on a reasonable basis. The telecom body had demanded the same thing while submitting its comments on the draft telecom bill to the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), which is currently working on a revised draft of the bill. The COAI has suggested a few methods that can be used for making such payments. As per COAI, OTT players can pay telecom firms by way of an equivalent of “usage charge” for the actual traffic carried by these OTTs on telcos’ network which can be easily measured. The usage charge is to be mutually agreed between the telecom firms and OTT players and paid directly to the telcos. The definition of the “usage charge” may be clearly mentioned in the Telecom Bill itself.
“If a mutual agreement is not reached, then an appropriate licensing and regulatory framework should be in place which governs the contribution of OTT players towards creation of network infrastructure,” COAI said. Please refer to this video for more details on the proposed Telecom Bill.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In February, four major European telcos are demanding legislation at European Union level to force the platforms, aka Big Tech, over-the-top (OTT) providers or hyperscalers, to pay their fair share of network investments. Timotheus Höttges, CEO of Deutsche Telekom (DT), Stéphane Richard, outgoing chairman and CEO of Orange, José María Álvarez-Pallete, chairman and CEO of Telefónica and Nick Read, CEO of Vodafone, penned a joint statement saying the current situation is simply not sustainable.
Citing the Sandvine Global Internet Phenomena Report from January 2022, they point out that video streaming, gaming and social media “originated by a few digital content platforms” accounts for over 70% of all traffic running over the networks.
“The investment burden must be shared in a more proportionate way,” the four CEOs insist. “Digital platforms are profiting from hyper scaling business models at little cost while network operators shoulder the required investments in connectivity. At the same time our retail markets are in perpetual decline in terms of profitability.”
They also warn that Europe risks falling behind other regions of the world if it does not take steps now, “ultimately degrading the quality of experience for all consumers.”
While the CEOs of DT, Orange, Telefónica and Vodafone have taken heart from recent commitments by the European Commission to ensure that all market players make a “fair and proportionate contribution” to infrastructure costs, they want legislators “to introduce rules at EU level to make this principle a reality.”
“The clock is ticking loudly, particularly given the huge investments still required to achieve the connectivity targets for 2030 set by the European Commission in its Communication on the European Digital Decade. Without an equitable solution, we will not get there,” the statement concluded.
References:
https://www.sandvine.com/phenomena
Vodafone UK opens Edge Innovation Lab; partners with AWS for distributed MEC zone in Manchester
Vodafone-UK has opened a new Edge Innovation Lab in MediaCity, Salford – the first of its kind in the UK. The lab will support the development of Manchester, and the surrounding region, into a Northern digital powerhouse, according to the company. The lab will give enterprises in the region an opportunity to trial new use cases that rely on real-time connectivity.
In addition to equipping the lab with dedicated MEC servers, Vodafone has also partnered with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to deploy a distributed MEC zone in Manchester, which will presumably give enterprises a taste of what ‘real-world’ performance might look like. Voda has also roped in IBM’s IT spin-off Kyndryl to offer customers professional and managed MEC and cloud services.
Spending on edge-related hardware, software and services is expected to reach $176 billion worldwide this year, according to IDC, rising to $274 billion by 2025. With figures like this doing the rounds, it’s little wonder that Vodafone is keen to get enterprise customers to buy into the concept.
“The lab offers innovators the opportunity to experiment with next-generation technologies and bring to life ideas that could revolutionise the way we do business and deliver public services,” said Nick Gliddon, UK business director at Vodafone, in a statement. “It will place Manchester and the surrounding region at the centre of the next stage of digital revolution.”
MEC technology enables real time data processing at the network edge, allowing for the creation of low latency services that would not be possible on today’s traditional network infrastructure. This offers innovators in the Greater Manchester area an opportunity to be at the forefront of next generation digital services.
By installing specialist servers either in Vodafone or customer facilities, applications are able to respond to command significantly faster. This time applications take to respond, known as latency, is a barrier for next generation innovations that require almost instantaneous reactions, or are powered by artificial intelligence. When combined with 5G, latency could be reduced to speeds faster than the human brain processes information.
Use cases enabled by MEC include autonomous vehicles, autonomous operations in factories, immersive augmented and virtual reality, remote medicine, cloud gaming and drone transport.
Vodafone has deployed Dedicated MEC servers at the Edge Innovation Lab and has launched a Distributed MEC zone in the Manchester area in partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS), as part of their AWS Wavelength Zone infrastructure. Vodafone will also showcase Mixed Reality and Visual Inspection services at the lab. Vodafone has partnered with Kyndryl to offer customers professional and managed services for dedicated MEC and wider cloud-managed services to Vodafone customers.
Tosca Colangeli, president, Kyndryl UK&I, said: “We are excited, as part of our strategic partnership with Vodafone, to be supporting the Edge Innovation Lab in Salford and to use the facility as inspiration and co-creation for our joint customer engagements.
“We expect edge technologies to increasingly become an enabler of business outcomes, allowing end users – and machines – and industries including manufacturing, energy and retail, to reap the benefits of traditional cloud computing while gaining advantages such as reduced data latency, better data autonomy and enhanced security.”
This builds on Vodafone’s four-year partnership with HOST in MediaCity, where the lab will be located.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Opinion —Nick Wood of telecoms.com wrote:
Barely a day goes by at the moment without someone opening a lab somewhere.
- Monday saw Nokia cut the ribbon on a 5G and 6G research facility at its campus in Amadora, Portugal. Its focus is software, specifically embedded and real-time software. It wants to employ 100 staff over the next two years.
- Last Tuesday, Ericsson revealed plans to spend tens of millions of pounds over the course of the next decade on a UK-based 6G research programme. A team of researchers, academics, PhD students and CSP and industry partners will look at aspects like network resilience and security, AI, cognitive networks and energy efficiency.
- A day later, UK-based Colt strengthened its partnership with IBM by opening an Industry 4.0 lab, also in the UK. It will offer enterprises in the manufacturing sector hands-on experience with various applications enabled by their respective cloud and edge networking solutions in an effort to lower barriers to adoption and generate a bit of business for Colt and IBM along the way.
- A couple of weeks ago, Orange Belgium opened its second 5G lab. The first is based in Antwerp, but this new one is in Liège, and will focus on standalone (SA) 5G use cases.
The growing number of labs showcasing what can be done with 5G and related tech like MEC and slicing only goes to show just how desperate the industry is to evolve beyond enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and into new service categories that will hopefully generate more revenue. Meanwhile, Nokia and Ericsson researching 6G is just prudent planning on their part – they need to have something expensive to sell to operators in 10 years time.
Whatever the motivation, it seems to be a good time to be in the lab-building business.
References:
Nokia to open 5G and 6G research lab in Amadora, Portugal
Nokia today announced the opening of a new research and development center focused on 5G and future 6G mobile network technology at its Portuguese campus in Amadora. The center will create employment across several different disciplines and advance research in technologies that are vital components of current 5G and future 6G networks. Last year, Nokia signed a deal with the Portuguese government to open a Global Business Services Center and participate in initiatives that promote digital skills. Apparently, this is part of that industry initiative.
The research and development center will create multiple highly skilled jobs focusing on the advanced development of software to support mobile networks. The center will oversee the full cycle of embedded and real-time software development from early analysis to final delivery. It will bring together professionals from diverse technical disciplines, including software engineers, product owners, and technical leads to work alongside teams around the world.
Tommi Uitto, President of Nokia Mobile Networks, said: “The new research and development center in Portugal demonstrates Nokia’s continued investment in the future of wireless communications. The center’s vital work will continue to expand the possibilities of mobile networks, critical for seamlessly connecting people, businesses, and industries. Importantly, this will be a hub for innovation, reinforcing our 5G technology leadership and helping to realize our ambition to become a 6G pioneer.”
Sérgio Catalão, Country Manager, of Nokia Portugal, said: “The announcement made today is a testament to the continued solid operation of Nokia in the country, reinforced once again by a collaboration with the Portuguese Government. This project reinforces our commitment to supporting Portugal’s digital transformation with our market-leading technology by working in close cooperation with academia, as well as bolstering our team with the best talent.”
A vibrant technology ecosystem, highly skilled talent pool, country stability, and location in Europe were contributing factors for Nokia to locate the research and development center in Portugal. The company has been an important innovation hub for Nokia globally through its units in Amadora and Aveiro and hosts services centers that remotely manage broadband networks for some of the leading global operators. The center follows a strategic agreement signed last year with the Portuguese government to open a Global Business Services Center and participate in initiatives that promote digital skills. The company has close to 2,800 employees in the country.

Comment & Analysis:
There are quite a few on these new 5G/6G Research Centers being opened all over the world. We wonder what “research will actually be done” as detailed programs have not been disclosed. Ericsson announced last week that it was investing heavily in a new research facility in the UK. The objective is to conduct research projects that ultimately contribute to the global development of 6G. Focus areas include network resilience and security, AI, cognitive networks, and energy efficiency.
We think the research efforts should be directed at solving the problems of 5G such as an implementation standard for 5G SA Core networks to facilitate multi-vendor interoperability of both hardware and software. Another urgent 5G issue is to reduce the huge power consumption of 5G base stations, especially for mmW frequencies.
References:
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/news/releases/2022/11/28/nokia-to-open-new-5g-and-6g-research-and-development-center-in-portugal/
ETSI Telemetry Standard for Optical Access Networks to enhance FTTP QoE
As the scale and services offered through the Optical Access Networks increase, it is crucial to maintain network good operation and performance. To achieve this, the Optical Access Network monitoring can be improved when compared to existing traditional methods via automated real-time data collection. Telemetry enables this and transmits data from the optical line terminal (OLT) – i.e., the device at the endpoint of a passive optical network – in real-time to provide information to the data collection platform.
With the new ETSI specification ETSI GS F5G-011 defining Telemetry Framework and Requirements for Access Networks, service providers and operators benefit from the advantages of real-time monitoring with scale, speed and automation using telemetry. The data retrieved by telemetry, together with analytics and AI, will ultimately offer end users an optimized quality of experience (QoE) for their fiber to the home (FTTH) network, unlocking the potential of the fifth generation of fixed networks (F5G). Note that F5G is based on fiber access- not wireless/cellular access.
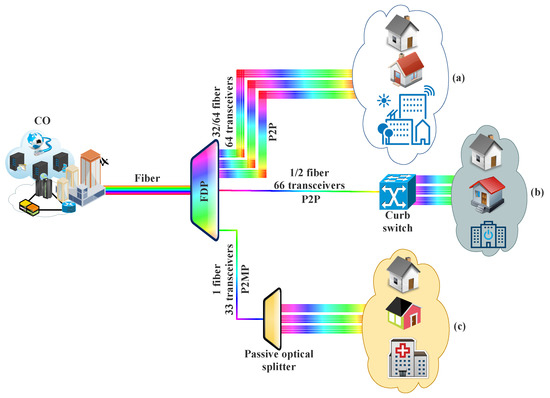
Today, the Access Network deployment is based on a traditional data pulling methods, such as Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), syslog and Command-Line Interface (CLI) to pull data from the OLT to monitor Optical Access Network and troubleshoot any issues. The interface uses proprietary management information bases (MIBs) from different OLT equipment vendors, making automation a difficult task. Each request to pull data is therefore resource intensive and impacts the performance of the OLT, adding complexity because there is more than one pull request per OLT. The pulling method does not efficiently scale.
With the flexibility of telemetry, which uses the push method to continuously stream data from the OLT, the data of interest can be selected from the OLT and transmitted it in a structured format to a data collection platform for monitoring, AI-based analytics and visualization.
Telemetry introduces finer granular data points and more frequent data streaming in the Optical Access Network. It enables better performance monitoring and therefore better control over large Access Networks. Telemetry data can assist in the prediction of network problems and take preventative actions without impacting the performance of the OLT. The operators can gain better visibility and insight into the network. They can also enhance the network operational performance by using data analytics.
“Telemetry technology opens the door to big data and machine learning methods application in the Access Network and brings a clear benefit to end users,” outlines Luca Pesando, Chair of the ETSI F5G group which developed this standard. “In the Group Specification, we also showcase examples of implementation of the telemetry system as we recommend it, already at the stage of Proof of Concept so that operators can leverage the potential of this new telemetry architecture,” he adds.
Requirements of F5G QoE (from ETSI GS F5G 005 V1.1.1 (2022-03):
- The F5G network shall support telemetry.
- The F5G network shall support the capability of telemetry to frequently send measured data.
- The F5G network shall support the capability of telemetry to export fine grained statistics.
- The F5G network telemetry interface shall support per-slice QoS measurement data.
- The F5G network shall support end-to-end QoE assessment in the CPN, Access Network, Aggregation Network, and Core Network.
- The F5G network shall support AI-based QoE assessment based on measured network or application performance data.
- The F5G CPN shall provide a mechanism to improve QoE in the customer premises network (residential, enterprise, verticals).
- The F5G service and underlay plane shall support network-layer QoS measurement mechanisms to support QoE assessment and management.
- The F5G service and underlay plane shall support application-layer QoS measurement mechanisms to support QoE assessment and management.
The ETSI F5G Industry Specification Group is working on 10 other specifications and will soon release F5G PON (Passive Optical Networks) for industrial applications and an F5G security architecture. If you’re interested, feel free to join us and contact [email protected]
About ETSI:
ETSI provides members with an open and inclusive environment to support the development, ratification, and testing of globally applicable standards for ICT systems and services across all sectors of industry and society. We are a non-profit body, with more than 900 member organizations worldwide, drawn from over 60 countries and five continents. The members comprise a diversified pool of large and small private companies, research entities, academia, government, and public organizations. ETSI is officially recognized by the EU as a European Standardization Organization (ESO). For more information, please visit us at https://www.etsi.org/
Press contact:
Claire Boyer
Tel.: +33 (0)6 87 60 84 40
Email: [email protected]
References:
ETSI – New ETSI Telemetry Standard Improves Automation for better End-User Quality of Experience
https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/F5G/001_099/005/01.01.01_60/gs_F5G005v010101p.pdf
Nokia Executive: India to Have Fastest 5G Rollout in the World; 5Gi/LMLC Missing!
While speaking at an event organized by the Foreign Correspondent Club on Friday evening, Nokia India Head of Marketing and Corporate Affairs, Amit Marwah said India is going to record the fastest 5G rollout in the world and it is going to have the biggest success of the next -generation telecom service with the support of the government.
“We (India) are not late, we are at the right time. In the rest of the country compared to other countries where the ecosystem has to develop. We have a 5G-ready ecosystem. We have 10 per cent of smartphones in India which are 5G ready. India is going to witness the fastest rollout of 5G which will be at least three times faster than what we have seen in 4G,” Marwah said. The 5G services will progressively cover the entire country over the next couple of years — Reliance Jio promises to do that by December 2023 and Bharti Airtel by March 2024.
Marwah said telecom manufacturing is becoming robust in India backed by the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme. “We were part of PLI 1.0. We were one of the only companies that met and exceeded our target of PLI 1.0. We let go-off that scheme and let go-off the incentive of one year because PLI 2.0 was even more interesting. Volumes and scale in India are increasing so much that you have let go for one year. We re-applied for PLI f2.0 and today we are part of PLI 2.0 which means we are investing more, adding more lines and adding more products,” he said.
The PLI scheme offers up to 20 times incentive on incremental sales of telecom equipment made in India. The government has added additional incentives for designing products in India in the second version of the PLI scheme. Marwah said that manufacturing is on a very positive note in India across the sectors but definitely in telecom.
“The only challenge right now is the availability of fabs which are semiconductors. 60-80 per cent of what we manufacture requires semiconductors. That is the area where we still need to work on. There is still some kind of infiltration of equipment in telecom from neighboring countries which need to have a little more vigilance and kind of stopping at the customs,” Marwah added.
Note: In October, Nokia announced that it had won a multi-year deal with Reliance Jio India to build one of the largest 5G networks in the world.
Department of Telecom, Deputy Director General (Policy) YGSC Kishore Babu said that the 5G adoption and applications are expected to be more diverse in India compared to other countries. “However, most of the use cases across the world remind us we may have to innovate to meet most of the requirements in the coming months and years,” Babu said.
Tech Mahindra, Chief Strategy Officer and Head of Growth, Jagdish Mitra said 5G is the biggest opportunity in technology so far, for India to bridge what we have typically referred to as Bharat and India.
“We have 62 per cent of our workforce in the agriculture sector, and 5G presents us with a huge opportunity to convert that into the most profitable segment. We can enable high yields by producing smarter networks and delivering products to the farmers,” Mitra said.
Telecom Sector Skill Council, CEO, Arvind Bali said close to 25 lakh people need to be reskilled and up-skilled in the field of telecom in the next few years because there is a shift from 4G to 5G.
“We need to have at least one lakh technicians and engineers, in the next few years, who have been trained specifically on 5G courses for the new job requirements and we at TSSC are setting up Centers of Excellence and training labs with the help of the industry. 5G is going to open up big requirements for a talented workforce and we are training the youth in new-age technologies,” Bali said. He added that TSSC is also developing all the curriculum and the digital content for training people to meet the industry requirement.


End Note: Despite all the hype and hoopla about 5G in India, none of the 5G network announcements have stated support for 5Gi which is part of the ITU-R M.2150 5G standard for RIT/SRITs. The 5Gi standard uses Low Mobility Large Cell (LMLC) to extend 5G connectivity and the range of a base station. It does so by using bands of the spectrum, which are lower than 5G’s operational bands but offers a high-range waveform. Ideally, the 5G frequency band ranges from 700MHz to 52GHz, but 5Gi can go lower than 700MHz and up to 36GHz without sacrificing the range. 5Gi was contributed to ITU-R WP 5D by TSDSI and backed by the Indian government.
LMLC technology increases the inter cell site distance to 6 km from the 3GPPs 1.7 km, which should make the deployment cost-effective. Also, the 5Gi standard reduces the mobility speed from 3 km/h to 30 km/h to make 5G network usage satisfactory to India’s scenario. In contrast, the 3GPP RIT/SRIT in the ITU M.2150 5G standard has maintained the mobility requirement between 120 km/h to 500 km/h, which is inconceivable in India.
One year ago, Vodafone Idea said it was working with a “few companies” to prepare for trials using 5Gi. “We are already working with a few companies. As and when the product is ready, we will be keen and will be doing trials and deploy accordingly” Jagbir Singh, chief technology officer (CTO) of Vi said at the time. He didn’t divulge details of the partners are. At this time, Vodafone Idea has not stated when it would deploy 5G– only that it would be 5G NSA (with a LTE anchor for everything other than the radio access network).
References:
India’s TSDSI candidate IMT 2020 RIT with Low Mobility Large Cell (LMLC) for rural coverage of 5G services
At long last: India enters 5G era as carriers spend $ billions but don’t support 5Gi
Vodafone Idea to use 5Gi (ITU M.2150-LMLC) in trials
https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/R-REC-M.2150-1-202202-I!!PDF-E.pdf (ITU-R 5G RIT/SRIT standard is M.2150)
FCC bans Huawei, ZTE, China based connected camera and 2-way radio makers
On Friday, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) banned Huawei Technologies Co. and ZTE Corp. from selling electronics in the U.S. by regulators who say they pose a security risk, continuing a years-long effort to limit the reach of Chinese telecommunications companies into U.S. telecommunications networks.
The FCC also named connected-camera makers Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co. and Dahua Technology Co., as well as two-way radio manufacturer Hytera Communications Corp.
“The FCC is committed to protecting our national security by ensuring that untrustworthy communications equipment is not authorized for use within our borders, and we are continuing that work here,” Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in a news release. “These new rules are an important part of our ongoing actions to protect the American people from national security threats involving telecommunications.”
“On March 12, 2021, we published the first-ever list of communications and services that pose an unacceptable risk to national security as required under the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act. This initial Covered List included equipment from the Chinese companies Huawei, ZTE, Hytera, Hikvision, and Dahua. Since then, we’ve added equipment and services from five additional entities. Last year I also proposed stricter data breach reporting rules and worked with the Department of State to improve how we coordinate national security issues related to submarine cable licenses.”
In the 4-0 vote, the FCC concluded the products pose a risk to data security. Past efforts to curb Chinese access include export controls to cut off key, sophisticated equipment and software. Recently US officials have weighed restrictions on TikTok over fears Chinese authorities could access US user data via the video sharing app.
“This is a culminating action,” said Klon Kitchen, a senior fellow at the Washington-based American Enterprise Institute, a public-policy think tank. “Things that began under Trump are now being carried out. The Biden administration is continuing to turn the screws on these companies because the threat isn’t changing.”
Hikvision said its video security products “present no security threat to the United States and there is no technical or legal justification for the Federal Communications Commission’s decision.” The company said the ruling will “make it more harmful and more expensive for US small businesses, local authorities, school districts, and individual consumers to protect themselves, their homes, businesses and property.”
Huawei declined to comment, while Dahua, Hytera and ZTE didn’t respond to emails sent outside normal business hours in China.
The looming FCC move didn’t come up in the bilateral meeting between US President Joe Biden and Chinese President Xi Jinping in Indonesia last week, a US official said, speaking on condition of anonymity. Biden did discuss technology issues more broadly with Xi and was clear that the US will continue to take action to protect its national security, the official said.
“This is the death knell for all of them for their US operations,” said Conor Healy, director of government research for the Bethlehem, Pennsylvania-based surveillance research group IPVM. “They won’t be able to introduce any new products into the US.”
Dahua and Hikvision stand to be affected most since their cameras are widely used, often by government agencies with many facilities to monitor, Healy said. Agencies including police also use handheld Hytera radios, he said.
In its order, the FCC also asked for comment on whether to revoke existing equipment authorization, Rosenworcel said in an online statement.
According to Healy, merchants could be stuck with gear that’s illegal to sell.
In 2018, Congress voted to stop federal agencies from buying gear from the five companies named by the FCC. The agency said earlier that the companies aren’t eligible to receive federal subsidies, and also has barred Chinese phone companies from doing business in the U.S.
The order released Friday was required under the Secure Equipment Act – a bill President Biden signed into law on November 2021.
The big picture: Huawei and ZTE are two of the world’s biggest suppliers of telecom equipment.
- Countries including Canada, Britain and Australia have ramped up restrictions against the use of 5G technologies from Huawei and ZTE in recent years.
- Huawei executives have previously said the company does not give data to the Chinese government and that its equipment is not compromised.
- The company’s chief security officer Andy Purdy has also argued that a ban would hurt American jobs because it spends over $11 billion a year from American suppliers.
References:
https://www.axios.com/2022/11/25/fcc-bans-huawei-zte-equipment-national-security
Research & Markets: 5G FWA Global Market to hit $38.17B by 2026 for a CAGR of 87.1%
The global 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) market is expected to grow from $1642.62 million in 2021 to $3074.07 million in 2022 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 87.1%, according to a new Research & Markets report. The change in growth trend is mainly due to the companies stabilizing their output after catering to the demand that grew exponentially during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021. The market is expected to reach $38173.20 million in 2026 at a CAGR of 87.1%.
The main types of 5G fixed wireless access are hardware and services. Hardware refers to physical parts that enable fixed wireless access such as mobile phones and devices that have MIMO antenna technology built into the device for the mmWave frequencies. 5G small cell networks and RAN towers are the most important hardware elements of 5G technology infrastructure. The different demographics include urban, semi-urban and rural. It is implemented in various market segments such as residential, commercial, industrial and government.
North America was the largest region in the 5G fixed wireless access market in 2021. Europe was the second largest market in 5G fixed wireless access market. The regions covered in this report are Asia-Pacific, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, North America, South America, Middle East and Africa.

Image Credit: Everything RF
The increasing adoption of 5G networks is expected to fuel the growth of the 5G fixed wireless access market in the coming years. 5G is the fifth generation of mobile data technology designed to significantly improve wireless network speed and flexibility. With the introduction of 5G, mobile technology can meet the demands of fixed-line networks and price ranges. According to Future Networks, a UK-based telecommunications company 5G will account for 1.2 billion connections by the end of 2025. Moreover, according to vXchnge, a US-based company that offers data centers and colocation services, 5G networks will cover 40% of the world and handle 25% of all mobile traffic data by 2024. Therefore, the increasing adoption of 5G networks drives the growth of the 5G fixed wireless access.
Technological innovations are shaping the 5G fixed wireless access market. Major companies operating in the 5G fixed wireless access sector is focused on developing technological solutions for 5G fixed wireless access. For instance, in February 2020, Huawei, a China-based telecommunications equipment company launched LampSite EE based on Huawei’s 5G technology. LampSite EE is the business version of 5G LampSite for industrial scenarios. The version is an update from Huawei’s pioneer LampSite 5G indoor radio connectivity solution, and it is geared toward smart manufacturing, smart hospitals, smart transportation, and smart warehouses, among other industries.
References:
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
JC Market Research: 5G FWA market to reach $21.7 billion in 2029 for a CAGR of 65.6%
Juniper Research: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to Generate $2.5 Billion in Global Network Operator Revenue by 2023
https://www.everythingrf.com/community/what-is-fixed-wireless-access



