Author: Alan Weissberger
Highlights of CTIA’s 2021 Annual Wireless Industry Survey
The U.S. cellular industry invested $30 billion in 2020 to power America’s world-leading wireless networks, according to CTIA’s 2021 Annual Wireless Industry Survey. This represents a five-year high and the third straight year of increasing capital expenditures (CAPEX), pushing cumulative mobile telecom industry investment over $600 billion.
The U.S. accounted for 18% of global mobile telecom CAPEX last year, while being only 4% of the world’s population and 6% of all global mobile connections.
Important CTIA survey results:
- Mobile speeds increased 50% in the past year.
- 5G networks nationwide now cover over 300 million people.
- 5G for home broadband services—capable of over 100M b/sec downstream—are deployed in communities across the country.
- Increases in wireless data use, cell sites and data-only devices—indicators of the ongoing shift to the “5G Economy.”
Other highlights:
- Sustained Wireless Investment. Over the past five years, wireless providers have invested nearly $140 billion, and over the life of the wireless industry, total capital investment is over $601 billion. This investment is in addition to the almost $200 billion in payments to the government for the spectrum needed to power wireless networks.
- America’s Demand for Wireless Data Continues to Grow. In 2020, mobile wireless data traffic topped 42 trillion megabytes, a 208% increase since 2016. Over the past decade, America’s wireless users drove a 108x increase in mobile data traffic—an amount equal to Gen Z’s 72 million members streaming TikToks for over 586 hours each.
- Wireless Providers Are Building the Infrastructure for Our Country’s Future. Over the past five years, operational cell sites have increased over 35%—and in just the two years since the implementation of historic federal siting reforms, more cell sites have been sited than the previous seven years combined. Now numbering over 417,000, these sites provide the physical platform for the U.S. 5G Economy.
- Providers’ Messaging Platforms See Continued Growth. Total carrier messaging traffic (SMS + MMS) reached 2.2 trillion, an increase of more than 119 billion over 2019, driven by a 28% jump in MMS messages as users send more GIFs, videos and other multimedia.
- Internet of Things More Than Two-Fifths of All Devices. Data-only devices—think smartwatches, hotspots, and medical sensors, for instance—now represent 41% of all estimated devices. Totaling over 190M, these data-only devices have grown 272% since 2013.
“These numbers show that while we were social distancing last year, U.S. wireless providers were busy both ensuring that wireless networks handled skyrocketing demand and constructing 5G networks, the foundation for our country’s post-pandemic recovery,” said Meredith Attwell Baker, CTIA’s President and CEO.
………………………………………………………………………………………..
U.S. Wireless Industry Continues to Lead the World in Capex:
The U.S. wireless industry’s investment in 2020 represents, once again, 18% of the world’s total mobile capex—even though the U.S. has just 4.3% of the world’s population and 5.9% of the world’s mobile connections. That means that for two years in a row, the U.S. accounted for nearly one-fifth of global wireless capex.
Building More Cell Sites to Support 5G Economy:
America’s cell sites provide the physical platform that enables technological innovation in the U.S. 5G Economy, driving broader coverage and capacity to meet increasing consumer demand. By the end of 2020, over 417,000 cell sites were built and operational, an increase of 35% since 2016—and in just the two years since the implementation of historic federal siting reforms, more cell sites have been built than the previous seven years combined.

Source: CTIA
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Licensed Spectrum Investment Continues to Grow:
U.S. wireless networks depend on licensed spectrum, which enables providers to deliver faster speeds and higher capacity to consumers. The wireless industry invested ~$85 billion in the two auctions the FCC launched in 2020—airwaves that will be the foundation for the U.S. 5G Economy for years to come, creating millions of jobs and sparking hundreds of billions of dollars in economic growth.
The $82 billion C-band auction revenue represents the largest investment in a spectrum auction to date and brings the total to more than $200 billion in payments to the government for the spectrum needed to power wireless networks and carry the increasing volumes of services used by consumers across the country.
5G Rollouts Continue:
Since 5G was launched in 2019, three nationwide networks—and regional provider networks across the U.S.—already cover 300 million Americans, up from 200 million last year and amounting to over 90% of the entire country. 5G networks are also being built out and expanding faster than 4G. The first 5G network achieved nationwide coverage 2x as fast as 4G, and all three major providers built nationwide networks 42% faster than 4G.
Large national operators and small local start-ups are also bringing 5G for home broadband (also known as 5G fixed wireless) services to millions of homes across the country, including in unserved and underserved communities.
Mobile Wireless Data Traffic Continues to Increase:
Mobile wireless data traffic had another record year, topping 42 trillion MBs—a 208% increase since 2016. Over the past decade, Americans have driven a 108x increase in mobile data traffic.
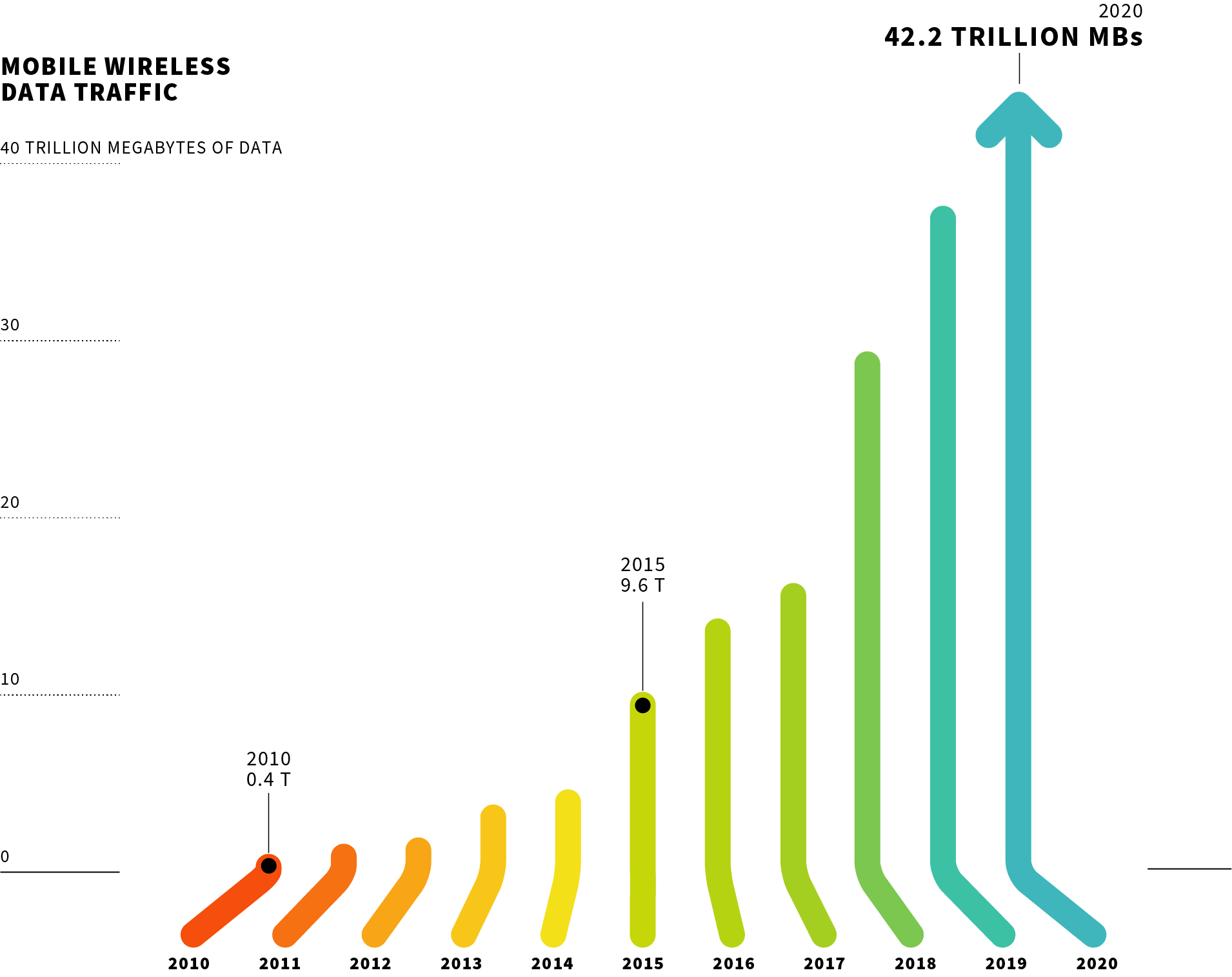
Source: CTIA
……………………………………………………………………………………
Continued Growth of Data-Only Devices:
5G is driving our nation’s transition to the Internet of Things, where medical sensors, smartwatches, hotspots, and other IoT devices usher us into the “connected-everything” era. Data-only devices rose to 190.4 million in 2020, now representing 41.3 percent of all estimated devices. Data-only devices have grown 272 percent since 2013. Overall wireless connections grew to 468.9 million.
References:
Telcos Loss: Private 5G & MEC/5G SA Core Network – Cloud Giants Take Market Share
The Case for Private 5G:
Some organizations do not want telcos involved in 5G. Instead, they have bought their own spectrum licenses and plan to build and operate private 5G networks.
According to a research report by the Beyond by BearingPoint and Omdia, only 16% of enterprise projects are telco-led, while a fifth of businesses plan a do-it-yourself 5G private network approach.
Private 5G networks offer much more robust security as they need not be connected to the larger telecom network, and hence are attractive to companies which have very high security requirements, such as power plants and other critical infrastructure.
Private 5G networks are also highly customizable and can therefore be built to exact company specifications as opposed to having to select from telco offerings. Also, wireless data can be managed and analyzed internally.
Given that 5G SA/ Core network deployments will take years and will all be different, private networks can deliver robust connectivity now. Another important advantage is that many private 5G networks are being designed to operate indoors as well as outdoors.
Indeed, the survey found that 5G is clearly seen as primarily a B2B or B2B2X opportunity. 72.8% of telcos believe that most 5G revenues will be derived from B2B, B2B2C or Government/ smart cities opportunities. The challenge for telcos is to capture some of that market, less it all goes to private 5G network equipment suppliers, like Nokia, Cisco and NEC.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Telco Partnerships with Public Cloud Service Providers:
Most 5G network operators are teaming up with public cloud giants (AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud) for either multi-access edge computing (MEC) and/or implementation of (non-standardized) 5G SA core networks. That business partnership requires telcos to split revenues with those cloud giants and/or pay them a fee.
This growing list of CSA-Public Cloud partnerships continue to grow. We’ve summarized many of them in previous IEEE Techblog posts (see References below).
The biggest risk is that such partnerships diminish the telco’s role in 5G as all the intelligence and key functions are implemented by the cloud providers. That once again, relegates the CSPs to dumb pipe providers (of only the radio access network [RAN]), which only provide 2 way wireless transport.
Research conducted by Beyond by BearingPoint and Omdia (a sister company of Light Reading owned by Informa) revealed that hyper-scaler cloud service providers have “accelerated their push into network activities” during the pandemic, even as that has “exposed some limitations of communications service providers (CSPs) when it comes to capabilities to create new agreements at speed.”

Expect AWS, Azure and Google Cloud to accelerate their push to take over all the intelligence/smarts in a 5G network, including such highly touted functions as “network slicing,” service registration & discovery, network automation, authentication, security and many more which are ONLY possible with a 5G SA core network.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/the-core/standalone-shaping-up-to-be-5gs-next-big-flop/a/d-id/771094
https://www.bearingpointbeyond.com/en/industries/5g/5g-insights/5g-enterprise/
German Telecom Regulator awards 5G private network licenses in the 3.7GHz to 3.8GHz band
Samsung introduces 5G mmWave small cell for indoor use with Verizon as 1st customer
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
Analysis of Dish Network – AWS partnership to build 5G Open RAN cloud native network
Cloud Service Providers Increase Telecom Revenue; Telcos Move to Cloud Native
TIM with Google and Ericsson will launch first ‘5G Cloud Network’ in Italy
Spain’s Correos to be a MVNO & offer cloud + fiber services
According to reports from Spain news sites La Información and Expansión, the group’s Correos telecom division is preparing to launch a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) and also intends to offer fiber services and a local cloud storage offering.

Correos, chaired by Juan Manuel Serrano, has been developing scenarios for three years to take advantage of its extensive network of offices to diversify the business. It has already closed agreements with banking, energy and telco entities.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
The Correos Telecom website certainly indicates that something important will happen. The reports say the new services could be launched as soon as this week.
The new mobile phone service and high-speed fiber connection will be announced this week and made available to the Group’s employees imminently, thus complying with the first phase of implementation of this new strategy championed by Correos Telecom.
Speculation about a potential Correos MVNO has been around since at least December 2020, when El Pais said the Spanish postal service intended to follow in the footsteps of its French and Italian counterparts by launching its own mobile and Internet services.
Few other details are available as yet, although the reports suggest that fixed and mobile services will initially be targeted at the post office’s own workers and eventually rolled out to anyone who wants them.
La Información said Correos Telecom will offer the group’s 53,000 employees a wide range of mobile phone options as well as two packages of fixed and mobile services, with TV to be added at a later stage.
It’s not clear which mobile network would host any Correos MVNO. A likely contender could be Spain’s fourth-largest operator Másmóvil, the aggressively expansionist group that recently launched a takeover bid for Basque operator Euskaltel.
Másmóvil is already playing host for Sweno, the new MVNO that is due to be launched in collaboration with El Corte Inglés any time soon. Unveiled in March, the Sweno MVNO is expected to offer mobile and fiber services on a converged basis, although there seems to have been some delay in getting the joint products off the ground.
Sweno is an existing El Corte Inglés brand that is being re-purposed for the telecoms offering.
Másmóvil will add to an already brimming pot of marques. As well as Másmóvil itself, the group provides services under the Yoigo, Pepephone, HitsMobile, Lebara, Lycamobile and Llamaya brands.
Másmóvil has become an increasingly a potential competitor of Orange Spain, Telefónica (Movistar) and Vodafone Spain. If the Euskaltel deal goes through, Másmóvil will gain a larger slice of the market. Traditionally a regional player, Euskaltel branched out nationally last year under the Virgin brand.
Spain has been a highly competitive market for years, driven by an early and aggressive move by Telefónica into converged offerings of fixed, mobile and TV services.
All four operators now provide services under their own low-cost brands, such as Telefónica’s Tuenti and O2 Spain; Vodafone’s Lowi; and Orange’s Amena and Simyo.
It certainly remains to be seen how new low-cost offerings from the likes of Correos and El Corte Inglés will be positioned, although the suggestion that Correos will initially target its own workforce would certainly provide it with a ready-made audience.
………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.expansion.com/empresas/distribucion/2021/07/23/60f9db08468aeb73428b4612.html
TV Broadcasts on 5G Networks: Telefónica and DVB Project
Telefónica said that the transmission followed a year of trials that had resulted in the capability of delivering a live stream over 5G with a reduction in latency to up to 0.8 seconds, or 25% less than the normal broadcast latency.
The telco said that the pilot was part of a set of 5G initiatives led by the Galician regional government’s Axencia para a Modernización Tecnolóxica de Galicia (Amtega) to place the region at the forefront of the development of mobile broadband technology.
Sara González, director of technology and media support at CRTVG said that “the drive for innovation of the Corporación Radio e Televisión de Galicia is being realised in projects like this, with the exploration of new technologies that can be applied to improve our live broadcasts and retransmissions”.
She said that the use of 5G “will enable us to improve the reliability of retransmissions, improve the quality of the transmitted image thanks to its great bandwidth and reduce latency.”
References:
Galicia Television broadcasts live with Telefónica’s 5G | News | Infrastructures
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Work has already commenced in its Technical Module to provide extensions to the relevant existing specifications – including DVB-I service discovery and DVB-DASH – to address the use cases and requirements collected and agreed by the Commercial Module.

Earlier this month, the DVB Steering Board approved the publication of the commercial requirements (DVB Bluebook C100). The document not only provides a set of 70 technical and procedural requirements, but also introduces key elements of 5G networks and systems related to media distribution including 5G Broadcast, 5G Media Streaming and other ongoing activities in 3GPP. In particular, LTE-based 5G Broadcast provides all functionalities to operate classical TV services including receive-only, free-to-air and high-power high-tower network infrastructures. The commercial requirements were developed based on six guiding use cases, all documented in an annex to BlueBook C100.
5G-based technologies promise to enable content and service providers to access mobile devices, typically interfacing with installable apps. 5G-based distribution to other types of receivers, such as moving vehicles, devices connected to roof-top mounted antennas or 5G-based home gateways, is not excluded. A particular benefit of DVB-I services over 5G is the ability to support integrated DVB-I hybrid services, i.e., services for which the basic broadcast distribution is augmented with unicast for extended service coverage, lower distribution costs, improved quality and additional user experiences.
The commercial requirements themselves are structured in technical and procedural aspects. Generally, the requirements ask for specifications to support different Rel-16-based 5G operation modes, namely 5G Broadcast, unicast-based 5G Media Streaming, concurrent delivery of the same service over both modes, and hybrid DVB-I services. In all cases it is expected that the specifications reuse existing DVB technologies to the extent possible and provide commonalities with other IP-based DVB delivery means.
The requirements are clustered in different service-operation phases, namely provisioning, announcement and detection, components, distribution and delivery, quality and monitoring, as well as client-related aspects. While they are extensive and detailed, it is expected that many are already covered by the existing DVB-I specification or would only demand minor extensions. This is a benefit of the original DVB-I design to provide a TV service platform independent of the access layer.
C100 explicitly addresses different aspects related to collaboration. This is a key issue for potentially successful operation of DVB services over 5G, as broadcast service providers and 5G network operators need to collaborate to beneficially use DVB-I functionalities and 5G functionalities for DVB-I service distribution. This aspect is addressed in the requirements by asking the technical group to provide specifications for network and client-side interfaces and APIs to formalise the communication across these two business domains.
Secondly, the DVB-I over 5G system is expected to align with common industry practices, for example those developed in 3GPP, 5G-MAG or other organizations that contribute to successful deployment of media and TV services over 5G.
Finally, an important aspect in the development of DVB specifications is the availability of Verification and Validation (V&V) tools. Collaborative efforts with other organizations such as 5G-MAG, 3GPP or DASH-IF are expected to be initiated in order to support reference and interoperability efforts. As an example, the newly established 5G-MAG Reference Tool project may create synergies with V&V tools for DVB-I over 5G.
DVB concludes by saying that DVB Updates to relevant DVB specifications to fully support DVB-I over 5G are expected to be completed in Q3 2022. However, with expected continuous extensions of 5G technologies in upcoming releases, the first release of DVB-I over 5G may be only the starting point in a long-lasting endeavor to enhance DVB-based TV services by also leveraging 5G-based distribution systems.
Samsung’s Voice over 5G NR (VoNR) Now Available on M1’s 5G SA Network

The VoNR call service fully utilizes 5G SA architecture for an improved high definition quality call experience, while providing 5G speeds for data-driven activities throughout the duration of the voice calls In comparison to calls made on the 5G non-standalone (NSA) network, which rides on existing 4G networks, the VoNR service boasts faster call setup time and seamless voice call continuity, presenting M1 customers with the true 5G experience. M1 customers will be able to enjoy the benefits of VoNR service as M1 gears up for its 5G SA market trial launch on the 27th of July.
The two companies said that VoNR service will open up numerous 5G SA-enabled data services and provide the baseline for quality video conferencing or augmented and virtual reality features, offering a glimpse into the possible connectivity solutions 5G SA will enable M1 to bring to its subscribers. This author is quite skeptical of that claim.
The underlying technology relies on the network having a 5G Core and IMS architecture (IP Multimedia Subsystem, a standard used for voice over LTE (VoLTE) and now voice over 5G networks). M1 also said it was the world’s first to implement VoNR, although that claim also was made by Deutsche Telekom, who implemented VoNR using multiple 5G vendors.
According to M1, VoNR offers faster call setup times, more seamless voice call continuity, and an improved high definition quality call experience when compared to calls made via 5G non-standalone (5G NSA) networks. [5G NSA technology relies on a 4G- LTE anchor for everything except data transmission.]
The new VoNR feature will be available as an over-the-air update to compatible 5G Samsung devices on M1’s 5G Booster Plan, on top of getting data speeds “almost five times faster than 4G.”
Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra, S21+ and S21 customers on M1 network will be amongst the first in the world to enjoy the benefits of the VoNR network via an over-the-air software update on M1’s 5G Booster Plan. Customers can also look forward to seamless connectivity with an ultra-fast data speed rate that is almost five times faster than 4G. Furthermore, paired with Samsung’s 5G compatible devices, multi-tasking is possible with remarkable productivity improvement.
“We have once again reached a groundbreaking milestone in our 5G SA journey – to be the first in the world to successfully support VoNR service on our 5G SA network. We are glad to work with a like-minded partner like Samsung to achieve high quality call and better 5G experience for our customers. With M1’s imminent market trial of the 5G SA network, we are excited to leverage 5G SA’s low latency, ultra-responsive, highly secured and high-throughput mobile connectivity to deliver high performance and reliable 5G services for our consumers and enterprises. This step in our 5G implementation journey is in line with the Keppel Group’s Vision 2030, which includes enhancing connectivity for communities,” said Mr. Denis Seek, Chief Technical Officer, M1.
“Samsung is proud to play a pioneering role in placing Singapore at the forefront of network technology innovation, turning on next-generation service in the country. Committed to inspiring the world and shaping the future with transformative ideas and technologies, we are taking a meaningful step in realising the full potential of 5G for consumers and industries. With VoNR, we look forward to delivering more transformative experiences to customers and businesses with M1,” said Ms. Sarah Chua, Vice-President, IT and mobile, Samsung Electronics Singapore.
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network Market 5 Year Forecast
In a revision of its Mobile Core Network 5-Year Forecast report, Dell’Oro Group predicts the Mobile Core Network (MCN) to have an overall revenue compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3% from 2020 to 2025. MCN includes 4G Evolved Packet Core (EPC), IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) and the 5G SA Core Network.
The Dell Oro report estimates the 5G portion of the MCN market to have a 33% CAGR. Strong growth in 5G Core network offsets corresponding declines in 4G and IMS core revenue.
Report Highlights:
- The cumulative investment is expected to be over $50B from 2021 to 2025, with regional shares in the range for North America – 18% to 23%; Europe, Middle East, and Africa – 30% to 35%; Asia Pacific – 40% to 45%; and Caribbean and Latin America – 5% to 10%.
- By the year 2025, MCN functions associated with 5G are expected to represent over 70% of the revenue mix between 4G and 5G MCN functions.
- 5G Core builds by the three incumbent service providers for 5G Standalone (5G SA) networks in China are continuing to exceed our expectations. In addition, in 2021, the new Chinese communications service provider, China Broadcasting Network (CBN) will be beginning construction of its 5G SA network.
- Deployments of more 5G SA networks are expected in the latter half of 2021 in Australia, Germany, Japan, South Korea, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. AT&T and Verizon should begin in earnest in 2022 and 2023 with their 5G SA networks. Geographic coverage is minimal at launch and is expected to grow throughout the forecast period.
“China was all the action in 2020,” Dave Bolan, research director at Dell’Oro Group for MCN, told Light Reading via email. He expects that trend to continue, especially in the first half of the forecast period. Bolan points out that phase one of the 5G SA rollout in China amounted to over $1 billion in 5GC contracts, and the pace of rollout is accelerating with phase two. Phase three is now being readied.
Dell’Oro does not yet provide vendor market share for MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing formerly known as Mobile Edge Computing), but Bolan said Huawei and ZTE, given the size of China’s market, are currently in the lead.
In an email to this author, Bolan wrote:
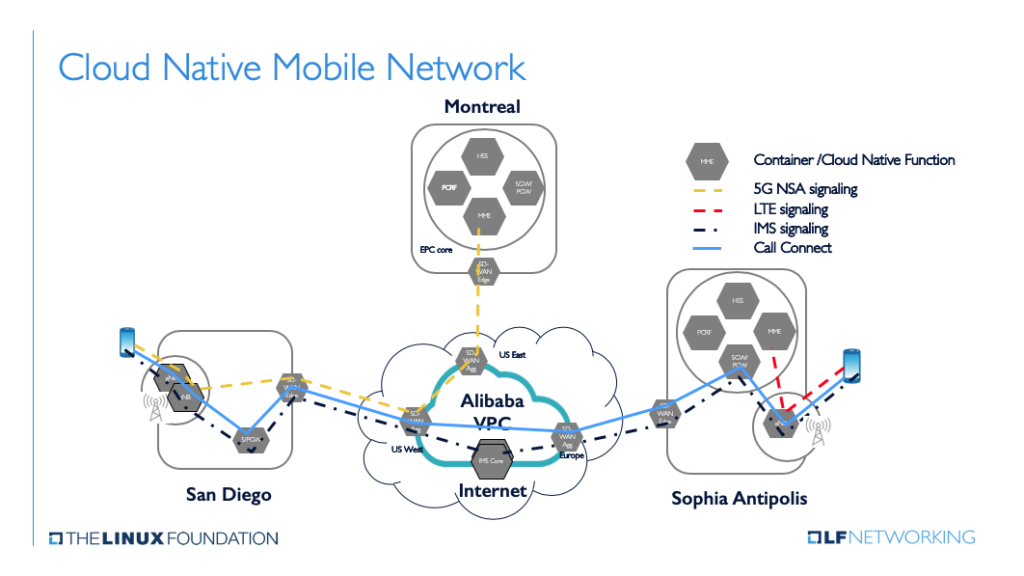
“All of 5G Core network will be Cloud-Native [1.], mostly Container-based. Except there are different cloud-native versions and container versions, not making it truly open. Anyone that wants to put their core on the public cloud will have to customize it for each cloud platform.
Same may be true for the NFVI ((network functions virtualization infrastructure) if it runs on – x86, AMD, ARM, or Nvidia processors – and couple that with the different 5G UPF (user plane function) acceleration techniques, it gets complex very quickly.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note 1. Cloud native, in essence, means the MCN software has been designed for cloud deployment. The software is built up of independent microservices and can run on a container platform, like Kubernetes. In addition to the traditional cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), many IT vendors have developed 5G cloud native software. The list includes, VMware, Oracle, Cisco, HPE, Mavenir, Samsung, Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, ZTE, NEC, and Dell Technologies (partnering with either Affirmed Networks or Nokia).
……………………………………………………………………………………………
“The basic network to get the 5G core up and running is the focus today,” Bolan told Light Reading. “NSSF [network slicing service function] and NEF [network exposure function] will come in the second half of the forecast.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
5-Year Forecast: Mobile Core Network Market Revenues CAGR Projected at 3 Percent from 2020 to 2025
https://www.lightreading.com/the-core/5g-core-spend-is-on-roll-says-delloro/d/d-id/771043?
https://www.opnfv.org/resources/5g-cloud-native-network
Shift from SDN to SD-WANs to SASE Explained; Network Virtualization’s important role
Disclaimer:
The IEEE Techblog has not covered this topic for a very long time, because there are no standards or accepted specifications for any type of SD-WAN or SASE interoperability. Those networks are all supplied by a single vendor, but that hasn’t stopped them from gaining market share, especially from legacy IP-MPLS VPNs. That’s even though functionality differs for each vendor’s SD-WAN or SASE offering and there is no interoperability, especially from one provider’s SD-WAN to another’s.
Explanations:
SD-WANs use Application-aware routing across the WAN, whereas classical SDN used a centralized controller to compute routes at the Network layer for the Control plane with “L2/L3 packet forwarding engines” in the Data Plane. The SDN Control and Data planes are separated with the “OpenFlow” API used to communicate between them.
NFV is not about routing but virtualizing network functions (“virtual appliances”) that would otherwise be implemented in hardware-firmware boxes.
Network virtualization (defined below) has played a key role in the popularity of SD-WAN and SASE, even though that network paradigm was not included in the original definition of SDN in which no overlay networks were permitted. (That was referred to as “SDN Washing” from 2011-2014, by SDN strongman Guru Parulker, now Executive Director of the Open Network Foundation.)
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Discussion:
At many data networking industry conferences and events from 2011 to 2014, participants claimed that Software Defined Networks (SDNs) would usher in a whole new era for networking. One colleague of mine said it would be “a new epoch for networking.” Instead, there were various versions of SDNs, used primarily by hyper-scale cloud service providers (most notably Google and Microsoft) and a few large telcos (e.g. NTT, AT&T). But SDN never spread to enterprise or campus networks.
When SDN fizzled out, the industry’s focus shifted to Software Defined WANs (SD-WANs), which provides user control of a virtual network overlay via the Application layer. There are three components to a SD-WAN:
- SD-WAN edge is where the network endpoints reside. This can be a branch office, a remote data center, or cloud platform.
- SD-WAN Orchestrator is the virtualized manager for network, overseeing traffic and applying policy and protocol set by operators.
- SD-WAN Controller centralizes management, and enables operators to see the network through a single software interface, and set policy for the orchestrator to execute.
In addition, there are three main types of SD-WAN architecture: on-premises, cloud-enabled, and cloud-enabled with a backbone.
SD-WANs continue to roll out in many different shapes, forms and flavors, without any standards for any type of interoperability (e.g no UNI, NNI, Interface to legacy IP-MPLS VPNs, etc). Even the definition and certification by the MEF (Metro Ethernet Forum) has failed to catch on so there is no uniform functionality between one SD-WAN and another.
Because of its virtualized network architecture [1.], SD-WANs don’t require specific hardware for specialized network functions. Instead, the infrastructure is made of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) equipment, also known as white-boxes. Therefore, all SD-WAN products are 100% software based.
Note 1. Network virtualization is the process of transforming network functions into software and disconnecting them from the hardware they traditionally run on. The software still consumes the hardware’s resources, but is a separate entity that can be changed, moved, and segmented while the hardware remains the same.
The virtualized and software-based version of the network is an overlay on top of the physical network infrastructure. The physical network’s devices like switches and routers still perform tasks like packet forwarding, while how to forward those packets is handled by the software running on the switches and routers.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Meanwhile a newer entry known as Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) has garnered a lot of media attention. This Gartner-coined product category, which combines elements of SD-WAN, cloud-based security, and edge computing, has gained significant traction in the two years since its inception.
SASE’s remote access functionality and low barrier to entry made it an attractive option for enterprises trying to cope with the rapid shift to remote work due to the pandemic. Within months of the first lockdown orders going into effect, nearly every SD-WAN and security vendor had announced a SASE security architecture, either through internal development, partnerships, or acquisitions.
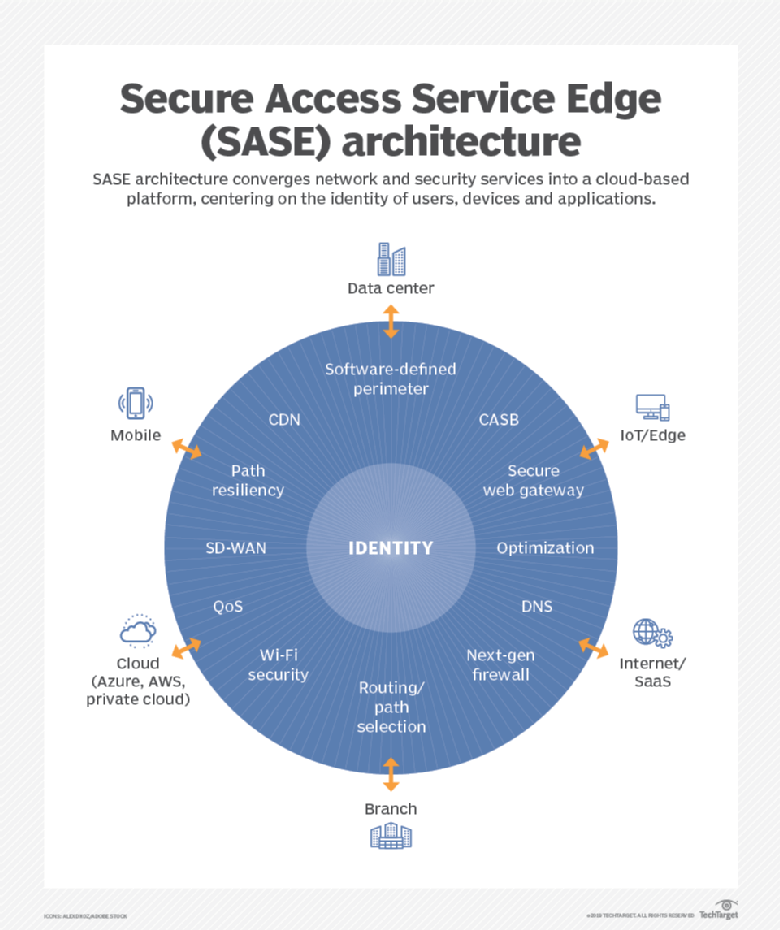
SASE is the convergence of wide area networking, or WAN, and network security services like CASB (Cloud Assisted Security Broker), FWaaS (Firewall as a Service) and Zero Trust, into a single, cloud-delivered service model.
According to Gartner, “SASE capabilities are delivered as a service based upon the identity of the entity, real-time context, enterprise security/compliance policies and continuous assessment of risk/trust throughout the sessions. Identities of entities can be associated with people, groups of people (branch offices), devices, applications, services, IoT systems or edge computing locations.”
Gartner forecasts that, “by 2024, at least 40% of enterprises will have explicit strategies to adopt SASE, up from less than 1% at year-end 2018.”
A SASE architecture identifies users and devices, applies policy-based security, and delivers secure access to the appropriate application or data. This approach allows organizations to apply secure access no matter where their users, applications or devices are located.
According to Cisco’s latest CISO Survival Guide, almost all (98%) CISOs plan to spend money on secure access service edge (SASE), and 55% of them intend to prioritize 25% to 75% of future IT security budgets on it, according to
Cisco surveyed more than 100 CISOs and security leaders for this report. The biggest shift for CISOs this year is toward SASE, following the pandemic and related trend of working from anywhere in the world, said Dug Song, chief strategy officer at Cisco Secure.
“I think hybrid work is here to stay,” Song told SDxCentral in an interview. Most organizations have decided to maintain flexible work for employees even post-pandemic, which requires changes to their IT security programs.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Many industry experts say SASE services must be built on a cloud-native architecture (like 5G SA core network) and distributed across multiple edge locations.
While several vendors including Cisco and Fortinet have rejected the cloud native approach, arguing that networking and security appliances still have a role to play both at the branch and the edge, it’s a principle that’s reflected in Gartner’s own literature and wholeheartedly embraced by VMware, CATO and other SASE vendors.
Specifically, VMware offers a cloud-native SASE architecture that has combined multiple solutions in it such as SD-WAN Gateways, VMware Secure Access, ZTNA solution, SWG, CASB, AND VMware NSX Firewall. VMware delivers all these solutions through PoPs. It delivers the network and security services in an intrinsic or sequenced manner.
Cato CMO Yishay Yovel told SDxCentral, “The feeling I have is that a lot of the market is trying to talk about SASE now in a generic way, like everybody has everything, or everybody has the same capabilities, and it doesn’t matter exactly how they’re done.”
Yovel also said that just because a vendor claims to offer the full SASE software stack, doesn’t mean it’s been implemented in a way that’s scalable.
Many of the SASE functions — cloud-based firewalls in particular — are compute-intensive, they usually have to be run in cloud data centers and can’t run on the cloud provider’s more numerous content delivery network edge locations.
This dramatically limits the number of locations a SASE vendor can offer if relying on public cloud infrastructure. For example, Google Cloud claims services in 146 edge locations around the globe, but only operates 21 global data centers, which it refers to as regions.
Scalability and availability are another challenge, Yovel noted. In many cases, these virtual appliances aren’t multi-tenant and have to be assigned to a specific customer account, resulting in additional resources being required should the customer bump up against the limits of a single instance.
Yovel argues that unless a vendor’s SASE software stack is unified, customers may miss out on the ability to share context across multiple security or network functions. He explained that many functions, SD-WAN for example, are only aware of certain contexts like what application is being used, but this context could be used in conjunction with other contextual information like time, location, or identity to inform other parts of the SASE stack.
“We collect all the context elements. It doesn’t matter which part of these engines need them. Everything is built into a unified thing,” Yovel said.
The bottom line for today’s cybersecurity professionals is that both zero trust and SASE networking trends should be watched closely and integrated into forward-looking enterprise network architectural decisions.
…………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/networking/sd-wan/definitions/software-defined-sdn-wan/
https://start.paloaltonetworks.com/gartner-report-roadmap-for-sase-convergence.html
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-sase
https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/top-sase-vendors/
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/cato-ribs-palo-alto-networks-other-sase-imposters/2021/07/
https://www.sdxcentral.com/networking/sd-wan/
https://www.sdxcentral.com/networking/nfv/definitions/network-virtualization-and-how-it-works/
https://searchcloudsecurity.techtarget.com/tip/Why-its-SASE-and-zero-trust-not-SASE-vs-zero-trust
AT&T Earnings, Revenue, Subscriber Additions Beat Forecasts
AT&T reported Q1 FY 2021 earnings results that beat analyst expectations. Revenue surpassed forecasts, up 7.6% from the year-ago quarter to $44.0 billion, reflecting partial recovery from the prior-year effects of the initial Covid-19 outbreak.
Higher revenues from WarnerMedia, Mobility (1.), Mexico, and Consumer Wireline more than offset declines in domestic video and Business Wireline and the sale of AT&T’s activities in Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Note 1. Mobility (aka Wireless) is AT&T’s largest and most important business, accounting for 43% of consolidated revenues, and fully 67% of pro-forma revenues post divestitures. Business and Consumer broadband wireline are also important segments for the telco, which is greatly expanding its fiber optic footprint. AT&T expects 1 million Consumer Fiber net adds for the full year 2021.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
The telco added 789,000 net new postpaid wireless phone subscribers in the second quarter, a major turnaround from the 151,000 subscribers it shed in the year-ago quarter.
After showing such a strong recovery in second-quarter results at its wireless and media businesses, AT&T raised its full-year outlook. The company now expects 2-3% comparable sales growth this year, compared to an earlier forecast for 1 percent. This excludes the impact of the pending spin-off of DirecTV, which should be completed in the coming weeks.
However, everything was not all wine and roses for AT&T. Operating profit dropped to $3.3 billion from $3.5 billion a year ago, due to a bigger writedown on Vrio and higher programming costs from the return of sports.
Net adjusted profit increased to $1.5 billion from $1.2 billion, helped by financial gains, and adjusted EPS totaled 89 cents, up 7.2% year-on-year. Analysts had projected AT&T earnings of 79 cents a share on revenue of $42.64 billion. A year earlier, AT&T earned 83 cents a share on revenue of $41.1 billion.
Operating cash flow fell by around $1.1 billion from a year ago to $10.9 billion, with capex at $4.0 billion and content spend of $5.3 billion. Free cash flow totaled $7.0 billion. With net debt down by around $0.9 billion compared to March, AT&T finished the period with leverage of 3.15x adjusted EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization).
For the full year 2021, AT&T now expects adjusted EPS (Earnings Per Share) to grow in the low- to mid-single digits with capex at around $17 billion.
During its earnings call, AT&T CFO Pascal Desroches said the operator reached a “major inflection point in our consumer wireline business,” with broadband revenue growth now surpassing legacy declines.
“The story with Fiber remains much the same. We continue to see solid subscriber growth with most of those customers new to AT&T. And broadband revenues grew more than 8%. HBO Max continues to exceed our expectations. Having surpassed the lower end of our global subscriber target 6 months ahead of plan, we are now raising our expectations to 70 million to 73 million global subscribers by the end of the year. We also launched our domestic ad-supported version of HBO Max as well as our international offering in 39 Latin American territories at the end of the quarter. That sets us up for additional customer growth as our addressable market expand.”
“We expect profitability trends to improve,” he continued. “We saw they improved from Q1 to Q2 and we expect that to continue as we make our way through the back part of the year.”
“Our Fiber growth continues to be solid. We added 246,000 Fiber customers in the quarter. Broadband ARPU grew by 6.1% year-over-year. Our aggregate fiber penetration rate is now more than 36%, up from about 31% a year ago. And nearly 80% of net adds are new AT&T broadband customers. We’ve reached a major inflection point in our Consumer Wireline business. Broadband revenue growth now surpasses legacy declines.”
AT&T CEO John Stankey noted its consumer fiber subscriber base increased by more than 1 million customers since the same quarter a year ago. The operator ended the quarter with 5.43 million fiber customers, up from 4.32 million in Q2 2020.
Jeff McElfresh, CEO of AT&T’s Communications division, reiterated on the call it expects to reach 3 million new locations with fiber in 2021 and tipped this new build to spur accelerated net additions in Q3 and Q4.
“The first two quarters of this year have essentially been built selling into our aged fiber footprint from a prior build,” he said. “We are currently deploying some of the early stages of our next 3 million build that we disclosed for this year…the bulk of that inventory is going to come online towards the back half of the year. So my expectations are that our net add performance takes a step up as that inventory comes online.”
………………………………………………………………………………..
Quotes:
“We expect Dish to be successful in the market,” explained Jeff McElfresh, the CEO of AT&T Communications, which houses the company’s 5G and fiber operations. “And so the competitive dynamics aren’t changed here. Rather, we get to participate in their success at this point.”
“We’re going to enjoy some anchor tenant benefits from that,” he said of the company’s new deal with Microsoft. “We’re not disclosing any specific financial details, but one thing that we are not doing … We’re not outsourcing our core network functions. We are relying upon Microsoft to develop a scaled compute and storage capability at the edge while we retain control of our network stack and the kinds of services that we’re going to offer to the market.” McElfresh explained that the transaction will allow AT&T to focus on its services rather than the nitty gritty details of maintaining its network operations.
“It just continues to prove to be sustainable,” McElfresh said of AT&T’s free phone promotion, which has not dragged down AT&T’s earnings or profits. “We’ve remained consistent in our offer construct… This model is sustainable.”
Analyst colleague Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson wrote:
When AT&T first embarked on their disastrous detour into the Media business, the wireless industry was in the throes of a brutal price war. It was hard to read the company’s moves as anything other than an intentional diversification away from wireless.
As it happened, the wireless industry started getting better right around the time that AT&T moved to buy Time Warner. That was no coincidence. AT&T’s need to focus on debt reduction at the time was the principal reason the industry pulled back from the brink.
Three years later, the wireless industry is still doing well. Industry subscriber growth across post-paid and pre-paid combined has soared to an improbable 5x population growth, and the very strong unit growth reported by AT&T and Verizon over the past two days suggests that it’s not slowing down for now.
Yes, AT&T’s solid growth comes with the asterisk of extreme promotions that are still suppressing EBITDA – AT&T’s EBITDA growth is lagging well behind Verizon’s, despite much faster unit growth. But, all in all, their results in Q2 were inarguably very strong.
But in jettisoning their Media and other non-core assets now, AT&T risks pivoting back to wireless at a time when this is as good as it gets. Competitive intensity in the wireless industry appears poised to be getting stronger (for all mobile carriers).
Just as AT&T, in retrospect, diversified away from Wireless at the bottom, are they diving back in at the top?
“It’s always difficult to parse the market reaction to such a tangle of businesses (we are looking forward to AT&T being a telecom company again),” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors. “Taken together, the business that will constitute the future AT&T beat on revenue and subs (phone adds spectacular),” added the New Street analysts.
“AT&T added 789,000 postpaid phone subs in the quarter, well ahead of our 325,000 forecast, with the beat roughly evenly split between better gross adds and lower churn (0.69% vs our 0.80%), indicating that the company’s retention efforts continued to be effective in the quarter,” wrote the financial analysts with Evercore in a note to investors.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2021/second_quarter_2021_results.html
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/financial/at-t-adds-246k-fiber-subs-q2-tips-momentum-to-accelerate-h2
Intel working with Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel on 5G for India
Intel said that it is helping Reliance Jio make the transition from 4G to 5G as part of their 5G infrastructure deal. Intel and Jio are collaborating in the areas of 5G radio, core, cloud, edge and artificial intelligence.
“…our collaboration spans those areas, and it’s co.innovation. So, we have got our engineering and business unit teams working closely with Reliance Jio in those areas. And we are committed towards helping customers and partners like Reliance Jio to make the transition from 4G to 5G,” Prakash Mallya, vice president and MD of sales, marketing and communications group at Intel told ET.
Intel’s investment arm, Intel Capital, had in 2020 invested Rs 1,894.50 crore to buy a 0.39% equity stake in Jio Platforms.
Separately, Bharti Airtel Wednesday said it is collaborating with Intel for working towards 5G network development by leveraging Virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN) and O-RAN technologies.
This is Intel’s second 5G-related partnership in India. As per the above, Intel is collaborating with Reliance Jio to help India’s #1 telco with its 5G network development, including in the areas of 5G radio, core, cloud, edge, and artificial intelligence.

Airtel will deploy Intel’s 3rd-generation Xeon Scalable processors, FPGAs, and eASICS, and Ethernet 800 series across its network to build a foundation for rolling out wide-scale 5G, mobile edge computing (MEC) and network slicing which requires a 5G SA core network.
The partnership will also allow Airtel to tap into the hyperconnected world where Industry 4.0, cloud gaming, and virtual/augmented reality (VR/AR) become an integral part of daily lives, according to an official statement.
Earlier this year, Airtel became the first telecom operator in India to demonstrate 5G over a live network in Hyderabad using liberalized spectrum.
The Sunil Mittal-led Bharti is also conducting 5G trials in major cities such as Gurgaon’s Cyber Hub in the Millennium city and in Mumbai’s Phoenix Mall in Lower Parel, in partnership with Swedish Ericsson and Finland’s Nokia, respectively, ET previously reported.
Airtel also entered into a partnership with Tata Sons and Tata Consultancy Services to deploy OpenRAN 5G solutions, including radio and core. It plans to begin pilot in January 2022.
Jio has developed and tested its homegrown 5G solutions together with its partners in India and plans to export the solutions to global markets once proven at a pan-India scale.
Prakash Mallya, vice president and MD of sales, marketing and communications group at Intel recently told ET that the company is helping Indian telecom operators. On Jio partnership, he said that Intel is helping the Mukesh Ambani-led telco transition from 4G to 5G as part of their 5G infrastructure deal.
Intel’s investment arm, Intel Capital, had in 2020 invested India Rupees 1,894.50 crore to buy a 0.39% equity stake in Jio Platforms.
Randeep Sekhon, CTO – Bharti Airtel said, “Airtel is delighted to have Intel as a part of its rapidly expanding partner ecosystem for 5G. Intel’s cutting-edge technologies and experience will contribute immensely to Airtel’s mission of serving India with world-class 5G services. We also look forward to working with Intel and home-grown companies to unlock India’s potential as a global 5G hub.”
“Airtel is delivering their next-generation enhanced network with a breadth of Intel technology, including Intel Xeon Scalable processors and FlexRAN software to optimize RAN workloads with embedded intelligence, to scale their infrastructure and deliver on the promise of a connected India,” Dan Rodriguez, Intel corporate vice president, Network Platforms Group said in a joint statement.
References:
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/5g-business-opportunity-infographic.html
Ericsson & MediaTek near 500 Mbps upload in mmWave carrier aggregation tests
Ericsson announced a new upload speed record with 5G on mmWave spectrum – double the current upload speeds and the fastest recorded to date.
In a four-component carrier uplink aggregation tests with MediaTek, a peak throughput rate of 495 Mbps was achieved. This included 425 Mbps on 5G New Radio (5G RAN) test and a 70 Mbps on 4G-LTE test.
The demo performed in June used pre-commercial software on a device containing a MediaTek M80 5G chipset. The lab tests used Ericsson RAN Compute baseband 6648 with the AIR 5331 millimeter wave radio. Four carriers of 100 MHz each in the 39 GHz band were used for non-standalone 5G, along with 20 MHz in the 1,900 MHz band for LTE (more in Tech Details below).
Ericsson said the test of uplink carrier aggregation is the first of its kind, as the industry previously focused more on boosting download speeds. The increased adoption in the past year of home working and schooling has driven the use of applications like videoconferencing that require also fast upload speeds.
Upload speed dictates how quickly data is sent from the computer or handheld device to the internet. This includes uploading files, such as photos and videos to social media or collaborative worksites. Upload speeds are also crucial to the image and sound quality of video conferencing. Strong uplink means less or even none of those frozen screens, or broken audio, when using apps like Skype or Microsoft Teams. Similarly, faster uplink improves voice over internet protocol (VoIP) calls and online gaming experience.
Hannes Ekström, Head of Product Line 5G RAN at Ericsson, said: “We continue to build on our previous successes, breaking our own record in upload speed. With a peak rate of close to 500 Mbps, we’ve demonstrated in this latest milestone with MediaTek how unprecedented data speeds can be delivered in uplink using mmWave and carrier aggregation. This means our customers can enhance their 5G offerings with higher uplink data rates, vastly improving user experience.”
JS Pan, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnership at MediaTek, said: “This world’s first demonstration of an industry-leading mmWave uplink technology in partnership with Ericsson, shows MediaTek is again establishing 5G milestones and pushing the envelope of its capabilities. 5G mmWave connectivity helps boost network coverage and capacity, faster performance, and introduces more diverse use cases.”
This latest technology milestone follows a single user multiple input multiple output (SU-MIMO demo in April 2021 when Ericsson delivered a single user uplink data rate of 315 Mbps, 15-20 times faster than current typical uplink speed.
Tech details:
Ericsson and MediaTek integrated four component carrier, each of 100 MHz, in the uplink using non-standalone architecture (aggregating 8x100MHz in the downlink and 4×100 MHz in the uplink). The integration carried out in a lab setting resulted in a throughput of 495 Mbps (425 Mbps in 5G plus 70 Mbps in 4G), doubling the current uplink speed on the market.
The test was done using the 39 GHz spectrum of NR (400 MHz) and combining it with a single carrier of LTE 1900 MHz spectrum (20 MHz). The whole bandwidth was then aggregated using the LTE and NR links, realizing a total throughput of close to 500 Mbps.
RELATED LINKS
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2021/7/ericsson-and-mediatek-achieve-mmwave-uplink-record



