Author: Alan Weissberger
Vodafone-Espana trial: 5G connected drone (UAS) enables Guardia Civil to improve surveillance in rural areas
Vodafone Spain has completed a trial with the Guardia Civil military police force to evaluate the viability of using 5G networks to improve surveillance using remote-controlled drones.
The pilot test consisted of using the 5G network to improve communication of the UAS (unmanned aerial vehicle systems) drone for surveillance tasks in rural areas or areas with difficult access. The drone was remotely-controlled by the Guardia Civil.
The Tarsis fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle system of local provider Aertec Solutions coupled with a 5G smartphone for both high-definition and 4k camera communications, as well as flight command management.
Vodafone said its 5G network provided the maximum bandwidth and minimum latency required for the transmission of high-quality images and control signals in real time, allowing specialist pilots to operate the drone remotely from a control center.
In order to carry out teleoperation safely, it was necessary to broadcast high quality images from cameras installed in the UAS and to send remote control actions or reference coordinates by the pilot.
The pilot trial was the latest test in the Andalucia 5G initiative which has been promoted by Spain’s ICT development agency Red.es, which is being developed by Vodafone and Huawei.
This is one of the two projects that Spain’s Government has promoted through the first public call for aid to 5G pilots, resolved in the spring of 2019.
Presented in November 2019 in Seville, it includes 35 use cases that will apply the benefits of 5G technology in the sectors of energy, industry, smart cities, tourism, agriculture, health and dependency, security, emergencies and defense, society and digital economy.
Vodafone said the project’s budget is EUR 25.4 million, including EUR 6.3 million from Red.es. It will cover the provinces of Seville, Jaen, Malaga, Cadiz and Huelva.
References:
https://www.saladeprensa.vodafone.es/c/notas-prensa/np_piloto_5G_dron_Guardia_Civil/
https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-54797917
Google Cloud and Intel partner for 5G Cloud Native Core & Edge Networking
Google Cloud and Intel plan to collaborate to develop cloud-native 5G core, 5G services and edge networking for network operators, enterprises, and the growing pool of vendors involved in mobile networks.
The partnership spans three main areas focused on:
- Accelerating the ability of communications service providers to deploy their virtualized radio access network (RAN) and open RAN solutions with next-generation infrastructure and hardware.
- Launching new lab environments to help communications service providers innovate for cloud native-based 5G networks.
- Making it easier for communications service providers to deliver business applications to the network edge.
“The next wave of network transformation is fueled by 5G and is driving a rapid transition to cloud native technologies,” said Dan Rodriguez, Intel corporate vice president and general manager of the Network Platforms Group, in a press release. “As communications service providers build out their cloud infrastructure, our efforts with Google Cloud and the broader ecosystem will help them deliver agile, scalable solutions for emerging 5G and edge use cases.”
The partnership’s cloud native 5G objectives will be “across the telecommunications stack, with application providers, carriers and communications service providers, hardware providers, and global telecoms,” according to the press release, to decrease the cost and time-to-market needed for the telecommunications industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Last March, Google Cloud announced a telecommunications industry strategy that focused on cloud capabilities with 5G connectivity and this builds upon that plan.
Google Cloud recently announced an initiative to deliver 200+ partner applications to the edge via Google Cloud’s network and 5G.
Opinion:
Partnerships like this one will be increasingly necessary to build 5G cloud native core networks and services (like network slicing), because there are no implementation specific standards (more below).
Ericsson wrote in a blog post:
“Of course, the implementation of a fully cloud native network will take considerable time and the new and legacy infrastructure will have to co-exist in a hybrid mode to begin with. Nevertheless, depending on your market requirements, it is important to start the journey towards a cloud native 5G Core now and focus future investments in accordance with the new target architecture. This is also the reason why we have re-designed our EPC software to also be cloud native and created a solution we call the Ericsson dual-mode 5G Core.”
“The new 5GC will live together with EPC for a considerable time and it’s important to define an evolution path that is smooth and cost efficient, while still supporting your business strategy and ambitions. We have developed a solution we call dual-mode 5G Core, where 5GC and EPC live together under one common O&M system for efficient TCO. This enables a smooth migration at your own pace and in accordance with your business needs.”
Images Courtesy of Ericsson
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
3GPP High Level Specs on 5G Network Architecture/5G Core:
The high level 3GPP technical specs for 5G Core (5GC) call for a service based architecture (SBA), which is designed for cloud native deployment.
These three 3GPP Technical Specs (TS’s) are the basis for 5G core networks, but they do not specify implementation details:
- 23.501 System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)
- 23.502 Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)
- 23.503 Policy and charging control framework for the 5G System (5GS); Stage 2
The ETSI standard is a transliteration of 3GPP TS 23.501: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/123500_123599/123501/15.03.00_60/ts_123501v150300p.pdf
From section 4.2.1:
“The 5G architecture is defined as service-based and the interaction between network functions is represented in two ways.
– A service-based representation, where network functions (e.g. AMF) within the Control Plane enables other authorized network functions to access their services. This representation also includes point-to-point reference points where necessary.
– A reference point representation, shows the interaction exist between the NF services in the network functions described by point-to-point reference point (e.g. N11) between any two network functions (e.g. AMF and SMF).
Service-based interfaces are listed in clause 4.2.6.
Reference points are listed in clause 4.2.7.
Network functions within the 5GC Control Plane shall only use service-based interfaces for their interactions.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
More information on use cases and the full news release can be found on Google’s website.
More Context: 5G & Wireless Communications at Intel
Intel Partner Stories: Intel Customer Spotlight on Intel.com | Partner Stories on Intel Newsroom
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2020/10/building-a-cloud-native-5g-core-the-guide-series
Intel, Google Cloud Aim to Advance 5G Networks, Edge Innovations
Apple is new smartphone king, but market declined 5% in 4Q 2020
Apple doesn’t report unit sales for its devices. However, the company said revenue from iPhones grew by 17% in the fourth quarter of calendar 2020 on a year-over-year basis to $65.6 billion. Apple’s business is seasonal, and the quarter ending in December is usually the company’s biggest in terms of sales.
“The sales of more 5G smartphones and lower-to-mid-tier smartphones minimized the market decline in the fourth quarter of 2020,” said Anshul Gupta, senior research director at Gartner. “Even as consumers remained cautious in their spending and held off on some discretionary purchases, 5G smartphones and pro-camera features encouraged some end users to purchase new smartphones or upgrade their current smartphones in the quarter.”
Table 1. Worldwide Top 5 Smartphone Sales to End Users by Vendor in 4Q20 (Thousands of Units)
| Vendor | 4Q20
Sales |
4Q20 Market Share (%) | 4Q19
Sales |
4Q19 Market Share (%) | 4Q20-4Q19 Growth (%) |
| Apple | 79,942.7 | 20.8 | 69,550.6 | 17.1 | 14.9 |
| Samsung | 62,117.0 | 16.2 | 70,404.4 | 17.3 | -11.8 |
| Xiaomi | 43,430.3 | 11.3 | 32,446.9 | 8.0 | 33.9 |
| OPPO | 34,373.7 | 8.9 | 30,452.5 | 7.5 | 12.9 |
| Huawei | 34,315.7 | 8.9 | 58,301.6 | 14.3 | -41.1 |
| Others | 130,442.8 | 33.9 | 145,482.1 | 35.8 | -10.3 |
| Total | 384,622.3 | 100.0 | 406,638.1 | 100.0 | -5.4 |
Due to rounding, some figures may not add up precisely to the totals shown.
Source: Gartner (February 2021)
Full Year 2020 Results:
Samsung experienced a year-on-year decline of 14.6% in 2020, but this did not prevent it from retaining its No. 1 global smartphone vendor position in full year results. It faced tough competition from regional smartphone vendors such as Xiaomi, OPPO and Vivo as these brands grew more aggressive in global markets. In 2020, Apple and Xiaomi were the only two smartphone vendors of the top five ranking to experience growth.
Huawei recorded the highest decline among the top five smartphone vendors which made it lose the No. 2 position to Apple in 2020 (see Table 2). The impact of the ban on use of Google applications on Huawei’s smartphones was detrimental to Huawei’s performance in the year and negatively affected sales.
Table 2. Worldwide Top 5 Smartphone Sales to End Users by Vendor in 2020 (Thousands of Units)
| Vendor | 2020
Sales |
2020
Market Share (%) |
2019
Sales |
2019
Market Share (%) |
2020-2019
Growth (%) |
| Samsung | 253,025.0 | 18.8 | 296,194.0 | 19.2 | -14.6 |
| Apple | 199,847.3 | 14.8 | 193,475.1 | 12.6 | 3.3 |
| Huawei | 182,610.2 | 13.5 | 240,615.5 | 15.6 | -24.1 |
| Xiaomi | 145,802.7 | 10.8 | 126,049.2 | 8.2 | 15.7 |
| OPPO | 111,785.2 | 8.3 | 118,693.2 | 7.7 | -5.8 |
| Others | 454,799.4 | 33.7 | 565,630.0 | 36.7 | -19.6 |
| Total | 1,347,869.8 | 100.0 | 1,540,657.0 | 100.0 | -12.5 |
Due to rounding, some figures may not add up precisely to the totals shown.
Source: Gartner (February 2021)
“In 2021, the availability of lower end 5G smartphones and innovative features will be deciding factors for end users to upgrade their existing smartphones,” said Mr. Gupta. “The rising demand for affordable 5G smartphones outside China will boost smartphone sales in 2021.”
Deutsche Telekom tests 5G SA network via “Telekom cloud infrastructure”
Deutsche Telekom has started testing the “standalone” (SA) version of 5G, setting up its first 5G SA antenna site in the town of Garching, near Munich. The site will be the first in Germany with 5G core network technology, which has yet to be standardized.
The antenna site will soon be connected to a 5G Standalone core network. The core network will be implemented via a Telekom cloud infrastructure. The hallmark of 5G Standalone is that the infrastructure in the core network will also be fully upgraded to a new, cloud-based 5G architecture. This is the next evolution of 5G and also a prerequisite for new deployment options.
Deutsche Telekom has already achieved 68% coverage of the German population with non-standalone (NSA) version of 5G, which uses the existing 4G-LTE network as an anchor for all non radio aspects.
“It is important for us to be at the forefront of the further innovation steps of 5G,” says Claudia Nemat, Board Member for Technology and Innovation at Telekom. “To ensure that our customers can take advantage of technologies such as network slicing or edge computing in the future, we continue to actively drive the development of 5G and its features.”
With 5G Standalone, the network structure and architecture is changing. The 5G technology currently deployed in Germany is based on the 5G Non-Standalone (5G NSA) network architecture. This means that today’s 5G offerings are still technically dependent on a simultaneously available 4G network (LTE) and virtually “piggyback” on this network, i.e., they do not yet function completely independently.
“5G standalone is one of the goals for us with 5G,” said Walter Goldenits, head of technology at Telekom Deutschland. “The network innovation in Garching is initially the first step for us into the 5G SA live network. It helps us to gain necessary and important experience with 5G SA. A rollout in the area will then also depend on the requirements of our customers. Technology and the market will play a joint role in further development.”
There are currently no terminals for customers that support 5G standalone. Telekom is therefore conducting the first tests with special development software on commercially available devices. The goal is to test various connections and applications that function completely standalone and without the support of 4G in the coming weeks.
“The further roll-out of 5G is the preparation of our network for the next steps in 5G development. We will use every opportunity to make 5G even faster and develop it further,” says Walter Goldenits.

Image courtesy of Samsung
…………………………………………………………………………
Last month, Samsung and Deutsche Telekom conducted their first 5G SA trial in Pilsen, the Czech Republic, verifying performance of 5G SA multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output (MU-MIMO) technologies.
The trial used Samsung’s latest end-to-end 5G SA solutions. In the SA trial, the two companies achieved outstanding results with the MU-MIMO technology using Samsung’s 3.5GHz Massive MIMO radio. The spectrum efficiency was tripled in comparison to that of LTE under realistic conditions and the throughput was increased by about 2.5 times of SU-MIMO (Single-User MIMO).
“We are pleased to collaborate with Samsung to verify the performance of its 5G SA solution,” said Alex Choi, SVP Strategy & Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom. “Together with strong partners we are consistently introducing advanced technical capabilities into our network, and we are very excited about the potential of 5G SA networks to further accelerate the 5G evolution.”
Samsung also said: “5G SA architecture enables mobile operators to have more efficient and simple network operations, while empowering 5G networks to deliver immersive user experiences and new business models for enterprises.”
References:
https://www.telekom.com/en/media/media-information/archive/telekom-tests-5g-standalone-619118
https://www.samsung.com/global/business/networks/products/core/cloud-core/
https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20210128009500320
Dell’Oro Group: RAN market revenues at new record high
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, preliminary estimates suggest that the 2G-5G radio access network (RAN) market ended the year 2020 on a high note, with the full year 2020 revenues marking a new record since we started tracking the program in the year 2000.
“While we correctly identified the overall trajectory of the market going into the year and maintained the positive outlook even as the pandemic intensified and economists adjusted their GDP projections sharply downward,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst with the Dell’Oro Group. “We also need to recognize that we completely underestimated the magnitude and the breadth of the ascent in the fourth quarter and for the full year 2020, reflecting stronger than expected results in multiple regions,” Pongratz added.
Additional highlights from the 4Q 2020 RAN report:
- Initial estimates suggest that vendor rankings remained stable between 2019 and 2020, while revenue shares were impacted to some degree by the state of the 5G rollouts in China and North America.
- Ericsson and Nokia maintained their No. 1 and No. 2 RAN revenues rankings excluding China. Both suppliers improved their RAN revenue shares outside of China, accounting for 35 percent to 40 percent and 25 percent to 30 percent of the overall RAN market, respectively.
- Huawei maintained its No. 1 ranking for the global RAN market, reflecting share gains in China.
Dell’Oro Group’s RAN Quarterly Report offers a complete overview of the RAN industry, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, transceivers or RF carrier shipments, macro cell and small cell BTS shipments for 5G NR Millimeter Wave, 5G NR Sub 6 GHz, and LTE. The report tracks the RAN market by region and includes market data for Massive MIMO. The report also includes a four-quarter outlook. To purchase this report, please contact us by email at [email protected].
In December 2020, Dell’Oro forecast the overall RAN market to advance for a fourth consecutive year in 2021. In North America, low-band activity is expected to remain elevated while mid-band activity is projected to improve. However, the timing of the C-band availability remains uncertain (especially since there was no FCC requirement for C-band spectrum bidders to actually build and deploy cellular networks).
5G core capex should grow at a faster pace than 5G NR (RAN/RIT) revenues. Dell’Oro believes that the 5G Core/5G RAN revenue ratio will trend below historical core/RAN averages in the initial 5G wave and then gradually improve as operators start embracing 5G SA.
Small Cells to Account for 10% to 20% of Total RAN
The global growth outlook for small cells – including sub 6 GHz and mmWave – remains favorable, underpinning projections the technology will play an increasingly important role supporting the overall RAN network as operators and enterprises navigate new technologies, spectrum bands, and use cases.
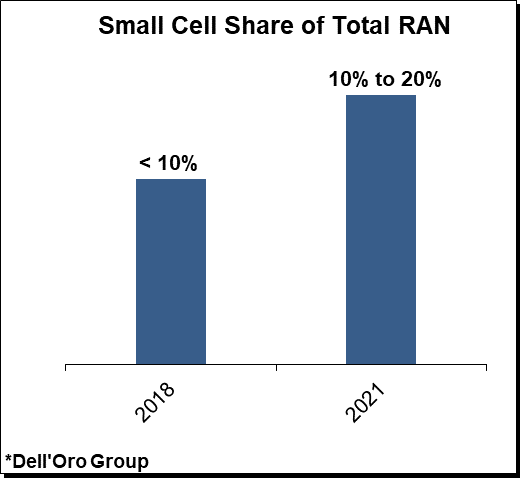
Small cell RAN revenues are projected to approach 10% to 20% of the overall RAN market in 2021. Within the small cell mix, Sub 6 GHz capex is expected to characterize the lion share of the investments, driven partly by the reduced gap between macro and small cell radios associated with upper mid-band deployments.
Open RAN to Account for 1% to 2% of Total RAN Market in 2021
Open RAN and Virtual RAN continues to gain momentum, bolstered by Ericsson now formalizing its support with its Cloud-RAN announcement. The uptake remains mixed between the various Open RAN segments, as noted with Dell’Oro’s 3Q20 Open RAN update. These trends are expected to extend into 2021, with adoption accelerating in some RAN settings while the uptake remains weak in other RAN segments.
Huawei: 5G Technology Illuminates the Future + Huawei analysis
On the eve of MWC Shanghai 2021, Ryan Ding, CEO and President of Huawei’s Carrier Business Group, talked about “5G technology lights up the future.”
“2020 has been a difficult year. During that period, Huawei worked closely with our customers,” said Ding.
In 2020, Huawei supported the stable operations of more than 300 networks in more than 170 countries and helped operators offer online services and minimize the impact of the pandemic on their businesses. In collaboration with Huawei, the operators attracted 22 million new residential wireless broadband users around the world. Thanks to this, people can easily access telemedicine services and work from home.
“5G developed faster than we expected.” More than 140 commercial 5G networks have been implemented in 59 countries.
According to Ding, more than 50% of these networks were built by Huawei. The ecosystem is also developing. In China , more than 68% of the smartphones distributed in 2020 were 5G phones. More than 200 industrial 5G modules and devices are currently available, supporting 5G applications in a wide range of industries.

Huawei’s Ryan Deng talking up 5G
According to reports prepared in 2020 by market research firms such as IHS, P3, OpenSignal and Meqyas, the best 5G networks in Seoul, Amsterdam, Madrid, Zurich, Hong Kong and Riyadh were the ones that Huawei built.
Ding highlighted that a good experience on the web is the foundation of commercial success and that these six cities are only the tip of the iceberg of its purpose of collaborative innovation with the operators.
For example, by implementing Huawei’s AAU 64T64R and market-leading multi-antenna algorithms, LG u + achieved greater spectrum efficiency and a network experience more than 25% better than other carriers. With Huawei’s Blade AAU, which can operate in the Sub3G and C bands, Sunrise reduced site acquisition time from 24 months to just 6 months and was the only operator with 5 consecutive outstanding ratings in Switzerland.
5G is becoming part of the core production processes of industries. Looking ahead, Ding was optimistic about the prospect of a large-scale deployment of 5G industrial applications in 2021.
5G applications have been incorporated in more than 20 industries including manufacturing, healthcare, education and logistics. The manager pointed to examples of sectors in China where industrial 5G applications are already proving their value, such as in coal mining and steel fabrication and production, where the adoption of 5G technology has made production safer, smarter and more efficient. He also stressed: “5G is no longer exclusive to pioneer users, but aims to improve our daily lives. 2021 will be the 1st year with large-scale industrial 5G applications.
Operators will need new capabilities in planning areas network operations, implementation, maintenance, optimization and operations to achieve zero-to-one progress and replicate one-to-many success.
At the next MWC Shanghai, Huawei will hold in-depth exhibitions and discussions on these topics with stakeholders. of the sector, both online and through means that do not require connection. We will continue to innovate to help our customers develop the best 5G networks and achieve greater business success.”
SOURCE: Huawei
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analysis by Iain Morris of Light Reading:
Of today’s 140 “live” 5G networks, Huawei built more than half, said Ryan Ding, the head of Huawei’s networks division, during the company’s traditional briefing before the annual MWC Shanghai show (normally scheduled for June, it switched places with the bigger Barcelona show this year due to coronavirus).
Huawei can rely on a domestic market that has awarded almost 90% of all mobile infrastructure business to Chinese vendors. When the number of 5G base stations in a country hits 700,000, as it did last year in China, any pain elsewhere becomes tolerable. Several hundred thousand more are planned in 2021. Contrast that with Europe, where the entire region in 2019 hosted fewer than half a million mobile sites, according to Ernst & Young.
Even in Europe, Huawei’s networks business has not suffered as badly as it might have done. Several big countries have resisted political pressure to copy the UK and exclude Huawei from the future 5G market. They include Germany, where Huawei last year accounted for more than half the country’s mobile infrastructure. Its government undoubtedly fears the ramifications of a ban for exports of cars and machine tools to China.
Huawei’s massive fixed-line business has also been allowed to chug on outside the UK, which is now weighing a final decision. Smaller than the radio access networks business, broadband products still generated more than $8.4 billion in global revenues last year, according to Omdia, a sister company to Light Reading. Some 43% of that went to Huawei. In France, where authorities have indicated they will not renew licenses for Huawei’s mobile equipment, Orange counts Huawei as one of its two main broadband vendors (the other being Nokia).
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Several European operators, including Deutsche Telekom, Orange and Spain’s Telefónica, have previously bought Huawei equipment for the cloud services they offer to their business customers. “Huawei provides standards servers (with the so-called x86 architecture) for the Open Telekom Cloud,” said a Deutsche Telekom spokesperson, in an email to Light Reading, when asked if that equipment remained in use.
Reference:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/huawei-is-proving-as-hard-to-stop-as-movie-supervillain
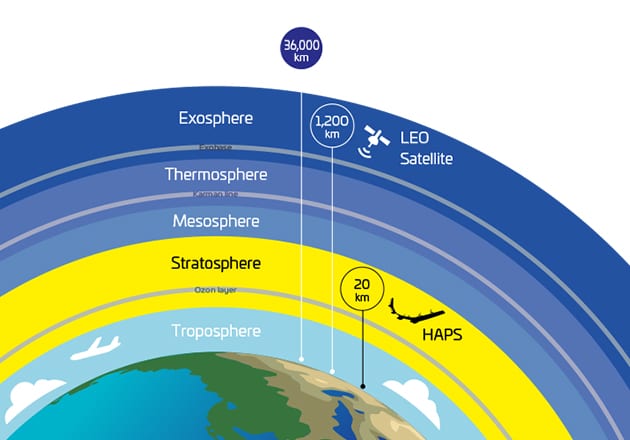
ITU-R Future Report: high altitude platform stations as IMT base stations (HIBS)
Introduction:
A High Altitude Platform Station (HAPS) is a wireless network node that operates in the stratosphere at an of altitude around 20 km and is instrumental for providing communication services. Precipitated by technological innovations in the areas of autonomous avionics, array antennas, solar panel efficiency levels, and battery energy densities, and fueled by flourishing industry ecosystems, the HAPS has emerged as an indispensable component of next-generations of wireless networks.
High-altitude platform station (HAPS) systems can potentially be used to provide both fixed broadband connectivity for end users and transmission links between the mobile and core networks for backhauling traffic. Both types of HAPS applications would enable wireless broadband deployment in remote areas, including in mountainous, coastal and desert areas.
In some situations, HAPS may be rapidly deployed for disaster recovery communications, particularly because the use of inter-HAPS links allows the provision of services with minimal ground network infrastructure.
ITU Radio Regulations (RR) define HAPS as radio stations located on an object at an altitude of 20-50 kilometres and at a specified, nominal, fixed point relative to the Earth.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
An ITU-R “work in progress” report will describe spectrum needs, usage and deployment scenarios, and technical and operational characteristics for the use of high altitude platform stations as IMT base stations (HIBS) for mobile service in certain frequency bands below 2.7 GHz already identified for IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications). In particular, the report will explain the technical and operational characteristics of HIBS in the bands 694‑960 MHz, 1710-1885 MHz, 1885-1980 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz, 2110-2170 MHz and 2500-2690 MHz to be used in sharing and compatibility studies under WRC-23 agenda item 1.4.
HAPSMobile’s Sunglider can cover 200 km at a distance of 20 km above the Earth in the stratosphere.
Image courtesy of HAPSMobile
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
IMT systems have evolved significantly in terms of spectrum identification, network deployment, and radio access technology, with the standardization of IMT-Advanced (4G) and IMT-2020 (5G).
At the same time, recent advances in battery and solar-panel technologies could enable HIBS to provide low latency mobile broadband connectivity to underserved communities, and in rural and remote areas, over a large geographic footprint.
These technological advances could enable HIBS, using the same frequency bands as ground-based IMT base stations, to be used as a part of, and complement terrestrial IMT networks. Existing user equipment (UE), which already supports a variety of frequency bands identified for IMT, could be served by both HIBS and ground-based IMT base stations. HIBS will therefore require new identifications to use certain frequency bands below 2.7 GHz already identified for IMT, considering potential HIBS deployment scenarios and its technical and operational characteristics, while taking into account sharing and compatibility with existing applications and services under WRC-23 Agenda 1.4.
Recognizing this, WRC-19 adopted Resolution 247 to consider “the use of HIBS in the mobile service in certain frequency bands below 2.7 GHz already identified for IMT, on a global or regional level.”
Basic concepts of HIBS applications:
HIBS (high altitude platform station as IMT base station) is defined in No. 1.66A as a “A station located on an object at an altitude of 20 to 50 km and at a specified, nominal, fixed point relative to the Earth.”
It’s important to recognize that HIBS can provide low latency mobile connectivity to unserved areas, including rural and remote areas, over a large footprint ( around 31,500 km2).
HIBS can enhance terrestrial IMT networks with so-called “super macro cells” that complement the existing ground-based deployment methods (e.g. macro cell, micro cell).
HIBS are intended to be used as a part of, and complement to, terrestrial IMT networks, using the same frequency bands as ground-based IMT base stations. In this sense, the UE to be served, whether by HIBS or ground-based IMT base stations, are the same. HIBS applications could provide flexibility and broaden the use of the existing IMT bands to complement coverage and support different use cases, while taking into account sharing and compatibility with existing applications and services.
Such use of spectrum by HIBS would require new identifications for HAPS as IMT base stations are required similar to those in RR no. 5.388A established at WRC-2000. Modifications to the IMT identification under RR No. 5.286AA, 5.317A, 5.341A, 5.341B, 5.341C, 5.346, 5.346A, 5.384A and 5.388 are outside the scope of WRC-23 Agenda Item 1.4.
The amount of spectrum needed in a given deployment scenario would depend on a number of factors and in the following section, examples of spectrum needs for HIBS applications is provided under specific system characteristics and deployment scenarios.
Usage and deployment scenarios:
The aim of HIBS is to provide internet access and services to the UE in remote area cases with quick deployment and less transmission loss.
Some HIBS applications communication usages foreseen are:
– Natural disaster relief missions, where communication for coordination and situation awareness across help and humanitarian aid organizations is needed.
– Fire detection, monitoring and firefighting missions to ensure communication between actors.
– Exploration missions with communication needs between exploration teams and regional home base.
Possible deployment scenarios:
HIBS would be deployed to provide connectivity to areas unserved and/or underserved by ground-based IMT base stations, such as:
– Areas where it is difficult to provide mobile connectivity using ground-based IMT base stations due to economic challenges (e.g. very small population covered, lack of backhaul connectivity and power supply, etc.).
– Areas covered by ground-based IMT base stations, but disruption to power supply and/or backhaul have resulted in a temporary lack of mobile connectivity.
– Unpopulated areas not covered by ground-based IMT base stations.
Mobile connectivity is becoming widespread, connecting objects (IoT: Internet of things, IoE: Internet of everything), as well as people.
Sensor networks which combine different types of sensors and IoT technology based on IMT systems (eMTC: enhanced Machine-Type Communication, NB-IoT: Narrowband IoT) are likely to be widely used in both populated and unpopulated areas. These areas are currently unserved and/or underserved.
Safety and security:
HIBS can help provide ubiquitous mobile coverage in unpopulated areas, thereby allowing users to get mobile connectivity regardless of time, place or circumstances. Thus, users will be able to make an emergency call wherever they are, in the case of a sudden car breakdown, getting lost or another problem.
In the aftermath of a natural disaster, communication networks can be restored quickly by using HIBS to cover these areas.
As they can connect to ordinary mobile phones that people carry all the time, HIBS are well suited for safety and security applications.
Internet of Things:
ICT is now widely used to help maintain and manage public infrastructure, such as roads, pavements, bridges and dams. Using a combination of IMT-based IoT technology and HIBS connectivity, infrastructure in both urban areas and rural/unpopulated areas can be managed on the same sensor network. The same approach can also be used to monitor natural processes, which are difficult for people to get close to, such as an active volcano.
Connected sensor networks can also support large-scale agriculture and livestock farming. The data they collect can be used for automation and the streamlining of processes, and can lead to innovation in this sector.
In this way, HIBS will be able to expand the reach of IoT services to support efficient management and maintenance of both public infrastructure and natural objects, while contributing to the development of the farming industry.
Event services:
HIBS can also be deployed above a venue, such as a stadium, a theme park, a resort, a tourist spot or exhibition place to provide more capacity to accommodate a temporary increase in demand. The rapid deployment of HIBS can augment the terrestrial network infrastructure to satisfy unusually high capacity requirements over short periods of time.
Frequency Bands:
HIBS will need additional and separate identification to use certain frequency bands below 2.7 GHz already identified for IMT taking into account sharing and compatibility with existing applications and services. Modifications to the identifications to IMT (5.286AA, 5.317A, 5.341A, 5.341B, 5.341C, 5.346, 5.346A, 5.384A and 5.388) in the Radio Regulations are outside the scope of WRC-23 Agenda Item 1.4. It may be possible for HIBS to employ the same band plans (see ITU-R Recommendation M.1036) as used by ground based IMT networks.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/backgrounders/Pages/High-altitude-platform-systems.aspx
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2007.15088.pdf
https://eepower.com/news/hapsmobile-and-apb-collaborate-to-develop-high-energy-density-batteries/#
https://www.engineering.com/story/haps-alliance-is-putting-5g-in-the-stratosphere
Report Linker: 5G Security Market to experience rapid growth through 2026
Report Linker forecasts that the global 5G security market will grow from USD 580 million in 2020 to USD 5,226 million by 2026, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 44.3% during the forecast period.
The 5G security market is gaining traction due to rising security concerns in the 5G networks, increasing ransomware attacks on IoT devices, rising attacks on critical infrastructure, and increasing IoT connections paved way for mMTC with enhanced security requirement. However, high cost of 5G security solutions will restrain the adoption by SMEs.
The implied negative flipside for operators and enterprises, of course, is that more money will have to be spent on tackling 5G vulnerabilities. The report pointedly notes that the high cost of 5G security solutions will limit adoption by SMEs.
Based on solution type, the DDoS protection solution segment is expected to grow with the fastest growth rate during the forecast period
The DDoS protection segment is projected to grow with the most rapid growth rate in 2020 to 2026.Enterprises use DDoS protection and mitigation solutions and services for adaptive defense against DDoS attacks.
These attacks further affect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of resources, which may result in billion-dollar losses for enterprises.
Enterprises segment to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Enterprises are undergoing digital transformation across different industries. Businesses are in various stages of implementing new technologies to develop new solutions, improve service delivery, increase operational efficiency, reduce cost, gain competitive advantage, and meet rising customer expectations. 5G will soon make it into the list of technologies enterprise will consider, with standalone 5G solutions that will enable various new industrial applications, such as robotics, big data analytics, IIoT and AR/VR in engineering and design, as well as new ways to provide remote support and training. As a result, enterprises will need 5G security mechanism to secure the entire network, applications, and devices.
Asia Pacific (APAC) region to record the highest growth and also account for largest markety share in the 5G security market
APAC region is set to dominate 5G, edge computing, blockchain, and 5G security technology, due to its size, diversity, and the strategic lead taken by countries, including Singapore, South Korea, China, Australia, and Japan.These countries have always supported and promoted industrial and technological growth.
Also, they possess a developed technological infrastructure, which is promoting the adoption of 5G security solutions across all industry verticals. Moreover, the region has become the center of attraction for major investments and business expansion opportunities.
While Reportlinker.com praises APAC for leading in 5G security, Europe is way behind if a recent report according to a report from the European Court of Auditors (ECA).
A year-long ECA probe into how European Union (EU) member states are dealing with 5G security found that while “member states have started to develop and implement necessary security measures to mitigate risks, they seem to be progressing at a different pace.”
More worryingly, Annemie Turtelboom, the ECA member leading the audit, indicated that some EU countries were bypassing supplier security checks in order to speed up 5G rollout.
………………………………………………………………………………………..
Companies such as ZTE (China), Samsung (South Korea), and Huawei (China) are heavily investing in the upcoming 5G technology and are initiating field trials together with some of the leading mobile service carriers, such as China Telecom (China), KT (South Korea), SK Telecom (South Korea), China Mobile (China), SoftBank (Japan), and China Unicom (China).
• By Company Type: Tier 1 – 62%, Tier 2 – 23%, and Tier 3 – 15%
• By Designation: C-level – 38%, Directors – 30%, and Others – 32%
• By Region: North America – 40%, Europe – 15%, APAC – 35%, and Rest of the World (RoW)– 10%
This research study outlines the market potential, market dynamics, and major vendors operating in the 5G security market. Key and innovative vendors in the 5G security market include A10 Networks (US), Akamai (US), Allot (Israel), AT&T (US), Avast (Czech Republic), Check Point (US), Cisco (US), Clavister (Sweden), Colt Technology (UK), Ericsson (Sweden), F5 Networks (US), ForgeRock (US), Fortinet (US), G+D Mobile Security (Germany), Huawei (China), Juniper Networks (US), Mobileum (US), Nokia (Finland), Palo Alto Networks (US), Positive Technologies (UK), Radware (Israel), Riscure (The Netherlands), Spirent (US), Trend Micro (Japan), and ZTE (China).
Research coverage
The market study covers the 5G security market across different segments. It aims at estimating the market size and the growth potential of this market across different segments based on component (solutions and services), network component security, architecture, end user, deployment type, vertical, and region.
The study also includes an in-depth competitive analysis of the key market players, along with their company profiles, key observations related to product and business offerings, recent developments, and key market strategies.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/security/5g-security-market-set-to-boom-report/d/d-id/767415?
Telefonica in 800 Gbps trial and network slicing pilot test

With this initiative the intention is also to begin building services for customers to be marketed via Telefónica’s 5G network. The project will thus enable Telefónica to obtain key results that will serve to drive the ecosystem and promote the interoperability and standardisation of this technology with a view to its marketing towards the end customer. Some of the sectors that can benefit the most from Network Slicing are the State Security Corps and Forces, media and communication, cars, industry and hotels.
5G Network Coverage Increases in Saudi Arabia; STC Selects Ericsson as Managed Service Provider
Saudi Arabia’s Communications and Information Technology Commission (CITC) has announced that seven additional cities and provinces were covered by 5G services in Q4 2020, bringing the total to 51 cities and provinces in various regions of Saudi Arabia.
CITC’s quarterly ‘Meqyas’ report highlighted that Zain led in terms of 5G footprint in the Kingdom, covering 44 cities and provinces, followed by the Saudi Telecom Company (STC) with 22 and Mobily with 21 cities and provinces.
STC recorded the highest average 5G download speed of up to 342.35Mbps, followed by Zain (338.12MB) and Mobily (220.86Mbps). The Meqyas report also revealed that Zain has deployed 5G services in all regions of the Kingdom except Makkah, in which Mobily recorded the best performance during Q4 2020.
Separately, STC announced the deployment of its 5G network in 47 cities around the country. It’s part of its plan to strengthen its leadership in reliable mobile coverage and deploy the largest 5G network in the Middle East. According to STC, phase 2 of the plan will increase 5G network coverage in Saudi Arabia to over 71 cities across the country.
As part of its infrastructure enhancement, the FTTH fiber optic network is also going to be expanded. This will enable higher broadband speeds and services to home and business users. In addition, STC has also confirmed that it has been expanding its global Internet Gateway, progressively growing the capacity of the network.
Eng. Haithem Al Faraj, SVP, technology and operations, STC, said: “STC will continue to pursue an aggressive 5G expansion, together with growth in its advanced 4G network.”

STC has selected Ericsson as its managed services provider in Saudi Arabia. As part of the agreement, Ericsson will deploy Ericsson Operations Engine to strengthen STC’s network operations with the latest technology solutions to transform operations to a predictive and proactive automated operation.
Ericsson will deploy its latest Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered software suite and machine learning tools and capabilities to provide an automated end-to-end managed operations service. The Ericsson Operation Engine will support activities in Network Operation, IT Operations and Field Support and Maintenance for stc’s networks, covering technology domains from the core to access, including 5G.
The suite will further empower stc to maintain its network quality at the highest level and deliver the best user experiences via transition towards a data-driven and proactive identification of network and performance issues.
The agreement will enable STC to succeed in its operational efficiency and digitization objectives in support of the Saudi Vision 2030.
Bader Abdullah Allhieb, Operations Vice President, STCs, says: “We are committed to providing a futuristic network that enables world-class experience for our customers in Saudi Arabia and this agreement shows our commitment in this direction. We are confident that this partnership with Ericsson will strengthen STC’s operational capabilities to improve our people’s quality of life and contributing to the economic and social development of Saudi Arabia in line with Saudi Vision 2030.”
Mathias Johansson, Vice President and Head of Saudi Arabia and Egypt, Ericsson Middle East and Africa, says: “Today’s network managed services agreement demonstrates STC’s continued confidence in our end-to-end solutions and IT operations. Through Ericsson Operations Engine, we will be able to develop data-driven insights to deliver enhanced performance focused on end-user experience. We will continue to work closely with STC to ensure consumers, enterprises and society benefit from the new experiences, services, and capabilities enabled by 5G.”
STC said it will continue to pursue its market leadership in the field of new and advanced technologies to achieve a significant and comprehensive expansion of its 5G network, while also developing its advanced 4G network.
References:
https://www.commsupdate.com/articles/2021/02/12/citc-51-cities-in-saudi-arabia-covered-by-5g/
https://www.itp.net/94380-stc-to-deploy-phase-2-of-5g-in-71-saudi-arabia-cities#:~:text=STC
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/stc-deploys-5g-network-in-over-47-cities–1372282
http://www.saudiarabiapr.com/pr.asp?pr=8911773