Author: Alan Weissberger
GSA FWA Report: 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks in the EU; Speeds revealed
GSA has been tracking the FWA broadband market to determine the evolving extent and nature of availability of services based on LTE or 5G technologies around the world. The number of network operators delivering FWA services varies widely by region, as Figures 3 and 4 show.
There are more operators marketing FWA services in Europe than any other region, particularly in the 27 countries that make up the EU, which has 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks. An operator’s decision about whether to offer services will depend on various factors: how well covered with fixed-line broadband services the country or territory is; whether there are many remote regions with little to no broadband availability; whether that operator provides a fixed network at all and how advanced that network is from a technology perspective; and whether its rivals have introduced a FWA service. Where one operator introduces such a service, its rivals often quickly follow.
FWA Service Speeds:
Operators are often opaque about the FWA service speeds their LTE and 5G customers should expect. We believe this is because actual network performance depends on distance from cell towers, speed of movement or local interference — from walls or other physical or electronic objects — and other factors.
Operators often do not provide speed information or are deliberately vague talking about the types of speed that LTE, LTE-Advanced and 5G can theoretically provide, mentioning the maximum theoretical speed a customer might get (in a perfect scenario), mentioning speeds measured by third parties or, occasionally, offering average speed information.
GSA collected information about the fastest download speeds quoted by operators for their FWA services where data was available. The maximum speeds promoted for LTE FWA services range from 1 Mbps to 2.5 Gbps. The average of the marketed maximum peak download speeds that GSA identified was 173.3 Mbps, up significantly from 155.2 Mbps in November 2022 (based on maximum speed data for 333 operators, up from 317 operators identified as promoting their LTE FWA speeds in November 2022).
Data on 5G FWA maximum download speeds was collected from 72 operators (compared with 36 in June 2021). Quoted peak speeds ranged from 10 Mbps to 5400 Mbps in the downlink, with half of them sitting in the 250Mbps to 2300 Mbps range. The average 5G FWA maximum peak download speed identified by GSA is 1077 Mbps, up significantly from 875 Mbps in November 2022 and from 863 Mbps in June 2022.
Where information was made available to GSA, the average or typical peak download speed marketed to customers was lower at an estimated 31.8 Mbps for LTE networks, compared with 32.7 Mbps in November 2022 and 38.5 Mbps at the end of 2020; and just over an estimated 236.2 Mbps for 5G FWA services, down from 248.3 Mbps in November 2022 and up from 147 Mbps in November 2020. It should be noted that the sample sizes of operators quoting their average speeds were much smaller than the sample sizes of those quoting maximum speeds, at 35 for LTE and 14 operators for 5G, and that some quoted average ranges (where we used the midpoint in the range).
Conclusions:
The promotion of LTE and 5G networks as a mainstream mechanism for the delivery of broadband services to homes and businesses is now well established, with lots of services available from network operators, supported by a wide range of devices from many vendors.
FWA services are being offered as an alternative or complement to fixed broadband; the nature of the message is dependent on whether an operator already owns a large fixed broadband network it wishes to continue to sell.
As more operator networks are upgraded to LTE-Advanced, as more 5G networks are built out and as more (particularly 5G) CPE devices are commercialised, GSA expects the number of FWA services to rise. This study will be updated in November 2023
Lumen, Google and Microsoft create ExaSwitch™ – a new on-demand, optical networking ecosystem
Lumen Technologies today announced a new network interconnection ecosystem called ExaSwitch™, created in collaboration with Google and Microsoft. This platform empowers organizations with high bandwidth needs to route their traffic dynamically and quickly between networks, and without third-party intervention.
This ExaSwitch project was created by the initial participants to route traffic between large internet and cloud networks. Early adopters include Lumen, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and an additional large cloud provider. The ExaSwitch ecosystem will continue to strengthen as additional participants join, making it easier to automate, scale and manage capacity between the members.
ExaSwitch users will be able to connect their edge sites, data centers and central offices to the platform. With a self-service portal, they can set up connections in 400G increments, which can then be consumed on demand in 100G increments. Lumen, the administrator for the initial ExaSwitch deployments, will be responsible for installing optical hardware at the location of each participant. Users can choose their own fiber source for connecting into ExaSwitch, which they can do either via the self-service portal or an application programming interface (API) portal managed by Lumen.
“The days of slow, legacy cross connects are over; ExaSwitch is the future of network interconnections,” said Andrew Dugan, Chief Technology Officer, Lumen. “Large network backbones no longer need a physical location to connect. Instead, optical switching will be used to establish high-capacity optical links between metro sites. And it’s so much more than just internet peering; it’s an on-demand network connection for quickly deploying needed capacity across all types of data traffic exchanges.”
“We like the ease, speed and cost efficiency of performing interconnects to network partners directly from our main sites,” said Steve Walter, Global VP of Network Operations, Google. “ExaSwitch provides an agile, on-demand platform using proven technology that achieves that.”
“Creating a geographically distributed yet automated interconnection platform creates so many options to improve connectivity, resiliency, and speed to add capacity on to one’s network,” said Frank Rey, Partner, Azure Networking, Microsoft. “We are pleased at the opportunity ExaSwitch has to change the interconnection ecosystem.”
The ExaSwitch administrator will install optical hardware at the preferred location for each participant, who will choose their own fiber source for connecting into ExaSwitch. When two participants agree to connect, they can join quickly through self-provisioning, or an API portal driven and managed by the administrator. The real-time capacity deployment allows them to easily order, modify and delete services as needed. Lumen is acting as the administrator for the initial deployments.
Key benefits:
- Participants use a self-service portal to configure and turn up connectivity with other participants much faster than they can now.
- Connections are set up in 400G increments and can be consumed on demand in 100G increments, with each site capable of up to 25.6 Tbps of optical cross connects.
- Participants will have the ability to connect their edge sites, data centers and central offices in major markets to gain diversity and save costs on cross connects.
“The ExaSwitch optical switching platform is an innovative on-demand ecosystem for automating, scaling and managing high-value interconnect services,” said Courtney Monroe, VP of Telecommunications Research for IDC. “It is poised to disrupt legacy manual platforms, as well as the way enterprises, and the IT ecosystem interconnect, procure and manage interconnectivity.”
Lumen is currently operating the ExaSwitch platform in three of the largest US interconnection hubs – Chicago, Dallas and Virginia – with plans to expand to all major markets in North America with large internet hubs. ISPs, cloud providers, large content providers and enterprises can go to http://exaswitch.net to learn more about ExaSwitch and how to join this growing ecosystem.
Lumen earlier this year completed 400G wavelength upgrades covering 70 U.S. markets. The company’s SVP of Core Network Solutions told Fierce Telecom in January a single 400G wave requires only two cross-connects, which offers “huge cost benefits for the customers.”
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen connects the world. We are dedicated to furthering human progress through technology by connecting people, data, and applications – quickly, securely, and effortlessly. Everything we do at Lumen takes advantage of our network strength. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to our edge cloud, security, and managed service capabilities, we meet our customers’ needs today and as they build for tomorrow. For news and insights visit news.lumen.com, LinkedIn: /lumentechnologies, Twitter: @lumentechco, Facebook: /lumentechnologies, Instagram: @lumentechnologies, and YouTube: /lumentechnologies.
SOURCE: Lumen Technologies
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/lumen-google-microsoft-unveil-new-optical-networking-platform
ACSI report: AT&T, Lumen and Google Fiber top ranked in fiber network customer satisfaction
Lumen to provide mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
Lumen: DDOS attacks on the rise with telcos accounting for 76% in 1Q-2022
Omdia: China Mobile tops 2023 digital strategy benchmark as telcos develop new services
Telecom operators around the world are embracing digital transformation and developing services in new sectors (beyond connectivity) to facilitate that megatrend. Omdia’s Service Provider Digital Strategy Benchmark report, which scores the digital strategies of 12 major global operator, identified the leaders as: China Mobile, SK Telecom, NTT DoCoMo, and Deutsche Telekom. With telecom operators all making a fair amount of noise about digital transformation, it’s useful to have a way of ranking their efforts and cutting through the marketing hype.

China Mobile scored 27.5 points out of a maximum of 35. It scored so highly due to the scale at which it has deployed high-speed broadband and subsequently used that infrastructure as platform to develop new services, Omdia explained.
“East Asian operators account for three of the top-four places in the benchmark, demonstrating that service providers in the region are among the most advanced in the world. China Mobile is showing a particularly impressive speed of change, with digital transformation services now accounting for more than 25% of service revenues,” said Dario Talmesio, Research Director, Service Provider Strategy & Regulation, at Omdia. “China Mobile is rapidly turning itself into a TechCo operator with an array of digital services beyond connectivity,” he added.
China Mobile reported a 30% year-on-year increase in digital transformation revenue for full-year 2022 to 207.6 billion yuan (US$29 billion), while overall telecommunications services revenues came in at CNY812.1 billion ($114 billion), up by 8.1%.
The China state owned telco itself attributed the growth in digital transformation revenue to “the rapid expansion of 5G applications, mobile cloud, digital content, smart home and other businesses,” and talked up its “remarkable results” in that area. “These services have become a key growth driver contributing to a more balanced, stable and healthy overall revenue structure,” it said in its annual results announcement.
SK Telecom’s position at number two in the ranking is based on its drive to reinvest itself as an AI company and its work to develop services in areas including the metaverse and urban air mobility, Omdia said.
When SK Telecom chief executive took the reins just over 18 months ago, he outlined plans to drive a 20% revenue hike between 2020 and 2025 essentially by transforming the telco into an AI and digital infrastructure company. Amongst other things, that meant turning the firm’s ifland metaverse into an open platform, and a year later the telco was able to announce that its metaverse platform had gone global.
It is working with a number of other operators on metaverse content and technology, including Singtel and NTT DoCoMo, the latter also performing well on digital transformation. Fairly generally, Omdia talks up DoCoMo’s strength in technology and digital services.
Omdia also picks out e& – the operator formerly known as Etisalat – for particular mention. The United Arab Emirates-based telco group ranks fifth in the benchmark.
“e&’s strong showing is based on its new strategy, unveiled in early 2022, of transforming itself into a global technology and investment group—a strategy that it is pursuing vigorously,” said Matthew Reed, Chief Analyst, Service Provider Markets, at Omdia.
The UAE telco reorganised itself under four pillars. The first covers its existing telecoms operations, but the second and third, E& life and e& enterprise, are responsible for new digital services and experiences in the consumer and business markets respectively. The fourth is about investment. The firm made many headlines with its decision to adopt e& as its new brand; the rebrand arguably overshadowed the strategic shift. But with that ampersand essentially standing for all the new sectors in addition to telecoms – next-gen technologies, digital experiences, financial services, the cloud, IoT, AI and so forth – it does make sense, and clearly e& is doing something right to find itself scoring 22 in the Omdia benchmark.
Bharti Airtel is ranked seventh in the 2023 benchmark, up from ninth place in 2022 following Airtel’s launch of 5G in India in late 2022 and as Airtel continues to develop its sizeable portfolio of digital services.
ABOUT OMDIA:
Omdia, part of Informa Tech, is a technology research and advisory group. Our deep knowledge of tech markets combined with our actionable insights empower organizations to make smart growth decisions.
References:
https://telecoms.com/522182/east-asian-telcos-ahead-on-digital-transformation/
Omdia: Consumer Telco Opportunity Challenged by Global Tech Giants
Omdia Surveys: PON will be a key part of network operator energy reduction strategies
Omdia forecasts weaker 5G market growth in near term, 4G to remain dominant
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
FT: A global satellite blackout is a real threat; how to counter a cyber-attack?
by John Thornhill, Innovation Editor at the Financial Times (FT)
What if the satellite communications networks encircling our planet ever go down? Mobile phones will stop working, navigation systems will crash, television screens will go dark and financial transactions will fail.
The three most likely ways this might happen are: an intense geomagnetic storm resulting from a solar flare like that which occurred in 1859, known as the Carrington event; a cascading collision of space debris, called the Kessler effect; or a deliberate cyber attack.
On Sunday, a SpaceX rocket blasted off from Cape Canaveral with a special payload designed to reduce the last of those dangers. On board was a US government Moonlighter satellite, described as “the world’s first and only hacking sandbox in space.”
Once the satellite is deployed, five so-called “white hat” — or ethical — hacking teams at the Hack-A-Sat 4 competition in Las Vegas will try to hijack the Moonlighter and win a $50,000 prize for exposing its vulnerabilities.
“With Moonlighter, we’re trying to get in front of the problem before it is a problem,” one project leader told The Register.
Last year, on the day Russia invaded Ukraine, hackers launched a malware attack against Viasat’s KA-SAT satellite. They temporarily disrupted the communications of thousands of broadband users in Ukraine, as well as in Poland, Italy and Germany, where 5,800 wind turbines were also affected.
“We are all aware that the first ‘shot’ in the current Ukraine conflict was a cyber attack against a U.S. space company,” Kemba Walden, America’s acting national cyber director, has said.
Leaked CIA intelligence, reported by the Financial Times this year, warned that China was also building sophisticated cyber weapons to “deny, exploit or hijack” enemy satellites. The U.S. has not revealed its own offensive capabilities in this domain. But it is not only Chinese spy balloons Washington is worrying about. Whereas space used to be solely the domain of nation states, private companies are increasingly dominating the game as launch costs fall and satellites shrink in size.
Last year, the U.S. launched 1,796 objects into space, 32 times more than in 2000. The lines between the military and civilian have also blurred as a result of dual-use applications, such as global positioning systems, making commercial satellites a target. And because of the difficulties of fixing satellites in space, designers add a lot of back-up parts, increasing the “attack surfaces” that hackers can exploit.

Viasat says it has learnt lessons from last year’s attack and has strengthened its defences. Basic cyber hygiene is essential in every link in the communications chain (the hackers accessed a misconfigured ground-based virtual private network appliance). Constant vigilance is required: the US company has been persistently attacked since the war began. And rapid response teams must be ready to re-establish control if a system is compromised.
“Anybody who claims perfect security is either lying or they do not know what they are talking about,” Craig Miller, Viasat’s president of government systems, tells me. “You have to be able to respond very quickly.”
There are three main ways to hack a satellite, according to James Pavur, a cyber security engineer at Istari, a US start-up. The first target is ground infrastructure, the most accessible attack surface but usually the best protected. Then, hackers can aim to intercept wireless communications between ground stations and the satellites — or spoof them. The third, and hardest, approach is to go after the “bird in orbit” by building, or exploiting, security backdoors in satellite components. So operators must secure their entire supply chain.
Most hacking attacks are hard to trace. Only four countries have the known capability to take out a satellite with a rocket — the US, China, India and Russia — although such attacks risk triggering the Kessler effect. But anyone from anywhere at any time can hack software. White hat hackers are a particularly valuable community in helping to secure critical satellite infrastructure, argues Pavur.
“There is a mindset of security through obscurity. But a sufficiently motivated adversary will find an ‘exploit’,” he says. Far better to discover those vulnerabilities first and fix them rather than trying to shelter in obscurity. The idea of crowdsourcing security sounds like an oxymoron. But white hat hackers have won round sceptics over the past decade. As software developers say: “Given enough eyeballs, all bugs are shallow.” That rule may even apply in space.
Write to: [email protected]
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/d5df1e81-f126-4a48-9a42-5b4aca842dcb
https://www.lse.ac.uk/ideas/projects/space-policy/publications/Cyberattacks-on-Satellites
https://interactive.satellitetoday.com/the-growing-risk-of-a-major-satellite-cyber-attack/
Wipro and Cisco Launch Managed Private 5G Network-as-a-Service Solution
Wipro has announced a managed private 5G-as-a-Service solution in partnership with Cisco. The new offering enables enterprise customers to achieve better business outcomes through the seamless integration of private 5G with their existing LAN/WAN/Cloud infrastructure.
Managed private 5G from Cisco and Wipro supports organizations looking to enjoy the advantages of a private 5G network without having to acquire, run, and maintain one. The as-a-service solution benefits enterprise customers by minimizing the risks associated with upfront capital expenditure (Capex) investments and expedites technology adoption as Wipro and Cisco take on the technical, operational, and commercial risks of implementing the solution.
“Private 5G is already enabling connectivity for a wide range of use cases in factories, supply chains, university and enterprise campuses, entertainment venues, hospitals, and more,” said Masum Mir, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Provider Mobility, Cisco Networking. “We’ve created a simplified and intuitive private 5G solution with Wipro, leveraging the advantages of 5G, IoT, Edge and Wi-Fi6 technologies to improve customer outcomes.”
The managed private 5G solution is built on Cisco’s 4G/5G mobile core technology and Internet of Things (IoT) portfolio – spanning IoT sensors and gateways, device management software, as well as monitoring tools and dashboards. The solution is seamlessly built, run, and managed by Wipro for customers. To support the partnership, Wipro has created a dedicated private 5G lab to build, test, and demonstrate industry use-cases.
“Wipro and Cisco have a long history of building secure networks for enterprises and industries,” said Jo Debecker, Global Head of Wipro FullStride Cloud. “We are both dedicated to the partnership and delivering a secure, cloud-managed private 5G service to our customers. Because it is an as-a-service solution, it provides maximum benefits while minimizing the human resources and costs associated with owning a private network.”
Lourdes Charles, Vice President, 5G / Connectivity Services, Wipro Limited said, “Private 5G integration will put organizations on the cusp of a new revolution. We are delighted to expand our long-standing strategic relationship between Cisco and Wipro to include managed private 5G solutions for enterprise customers. To simplify the customer experience, the solution will validate mission-critical use cases, operations Service-Level Agreements, and lifecycle management. Wipro is fully committed through our 5G Def-i platform, to assist customers with their private 5G networks through best-in-class technology, pricing, and performance.”
“Wipro believes Cisco is very well positioned with extensive products and services to provide the complete stack for enterprise-converged network and security solutions,” the firm noted in an email to SDxCentral. “Cisco also brings integration with enterprise infrastructure and applications.”
IoT Analytics recently ranked Cisco as one of the market’s top software providers, touting its Cisco Edge Intelligence and IoT security offerings. The analyst firm also noted that spending on IoT software hit $53 billion in 2022, with the installed base of connected IoT devices surging to 14.4 billion units. The firm expects that device number to surge to 30 billion units by 2027.
Wipro says that 5G cellular network for enterprise running on both licenses and shared spectrum lays the foundation for:
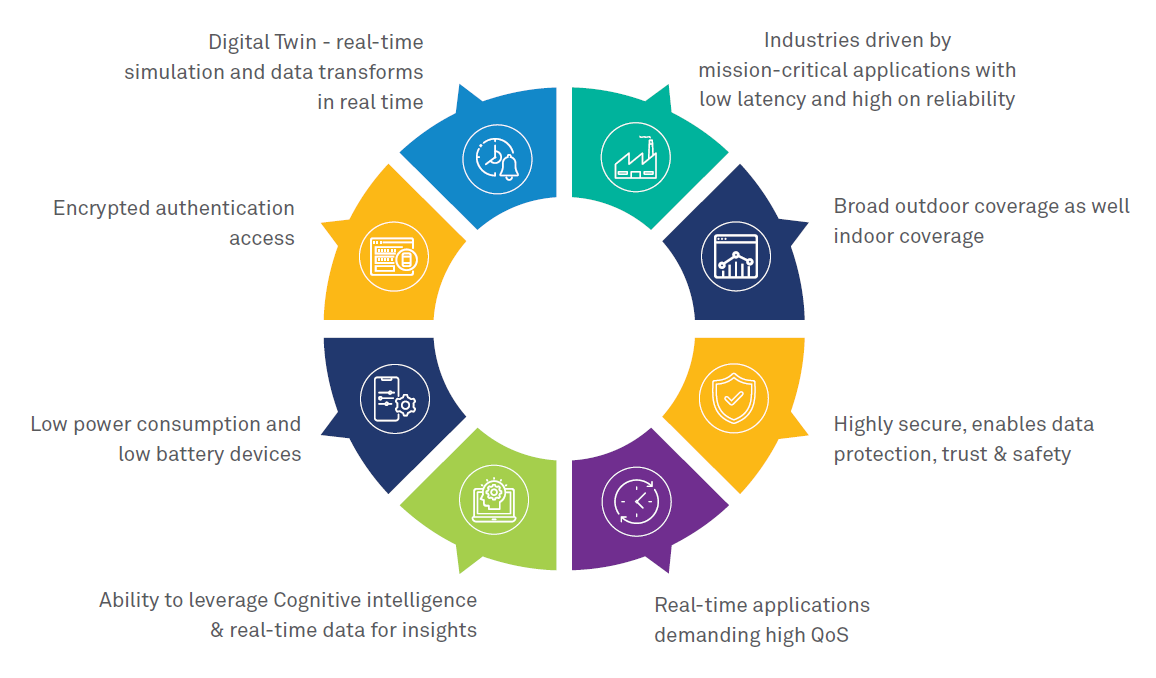
ABI Research this week reported that more than 1,000 enterprise private networks have been deployed worldwide, despite a slowdown in public proclamations.
“This is actually a good sign for the private networks market,” Leo Gergs, senior analyst for 5G Markets at ABI Research, wrote. “Enterprises are beginning to see the deployment of private cellular connectivity as a competitive advantage and, therefore, do not want to talk about it too openly. Which is important as the market moves from the experimental phase toward commercializing private network deployments.”
Gergs added that this growth has now placed more pressure on the telecommunications industry to ensure those networks can handle increasingly complex and revenue-generating use cases. “The telco industry urgently needs to deliver on promises made to the enterprise community now. Otherwise, enterprise 5G will enter the history books as the technology that always overpromised and under-delivered.”
United Kingdom-based managed service provider Logicalis recently deployed Cisco’s private network with Logicalis overseeing the on-site engineering, including site preparation, ordering of solution components, organization of the spectrum, SIM management, staging, creation of customer profiles and core and RAN installation.
Chris Calvert, VP of private wireless services for Logicalis US, explained that Cisco is providing its Private 5G platform, which includes the 4G/5G core network that Logicalis’s 4G LTE and 5G service requires. That core is available as a single standalone (SA) core or a high-availability three-server cluster.
“Cisco really wanted this to be a managed services-only solution,” Calvert said. “Basically, Logicalis is Cisco’s customer. The combination of the industry expertise and the fact that we have a large managed-services practice were really the driving forces behind Cisco selecting Logicalis as one of only two manufacturers that can actually provide this solution currently.”
About Wipro Limited:
Wipro Limited is a leading technology services and consulting company focused on building innovative solutions that address clients’ most complex digital transformation needs. Leveraging our holistic portfolio of capabilities in consulting, design, engineering, and operations, we help clients realize their boldest ambitions and build future-ready, sustainable businesses. With over 250,000 employees and business partners across 66 countries, we deliver on the promise of helping our customers, colleagues, and communities thrive in an ever-changing world. For additional information, visit us at www.wipro.com.
About Cisco:
Cisco offers an industry-leading portfolio of technology innovations. With networking, security, collaboration, cloud management, and more, we help to securely connect industries and communities. Information about Cisco’s products is here.
References:
Cisco’s Private 5G story: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kdsyhsXicNk
FTTH was ~60% of France fixed broadband market in Q1-2023
FTTH lines made up nearly 60% of French fixed broadband market in Q1-2023. FTTH subscriptions across mainland France and the overseas territories reached a 59.4% share of the country’s fixed broadband market at the end-March 2023, up by 10 percentage points from Q1 2022.


Viva La France!
According to the latest update from France regulator Arcep, the FTTH installed base added 895,000 net connections since December for a total of 19.02 million (+965,000 in Q4), representing a 22.8% increase year-on-year. As of March 31, 2023, 35.3 million premises (apartments, houses, offices, etc.) can be connected via FTTH i.e. a little over 80% of premises in the national territory. If you add cable internet that gives us 37.6 million locals who potentially have access to very high speed on wired networks in France. This represents a growth of approximately 3.6 million over the past year.
96% of Paris is connectable to optical fiber, but it’s only 50% in Lille. No explanation is given for this slowdown which is not in line with the France Very High Speed Plan which aims to generalize optical fiber throughout France by 2025.
Other high-speed networks (cable, VDSL and fixed wireless/LTE) continued to see their combined installed base decline quarter-on-quarter (-129,000) to stand at 3.25 million. As a result, the number of overall lines delivering download speeds of at least 30 Mbps reached 22.27 million at end-March.
The ADSL segment maintained its downward trend, leading to a further drop in connections delivering less than 30 Mbps. This brought the installed base across all fixed broadband networks to 32.04 million, up by 99,000 since December. This compares to with 63,000 market net additions in the previous quarter and 133,000 in Q1 2022.
Looking at progress in the ongoing fibre roll-outs, French operators brought FTTH connectivity to 840,000 million additional premises in the three months to March, for an overall footprint of 35.29 million. The pace of deployment slowed down from 1.3 million premises passed with fibre in the December quarter, and 1.1 million in Q1 2022.
On a year-on-year basis, the volume of new premises passed with fibre roughly halved across both densely populated metropolitan areas and mid-sized towns with privately funded roll-outs, while recording a 10% fall in public initiative fibre networks under deployment in rural communities. The latter reached a footprint of 12.8 million premises eligible for FTTH services at end-March, representing 610,000 additional premises since December.
Associated documents:
- Scorecard for fixed broadband and superfast broadband services – figures for Q1 2023
- Maconnexioninternet.arcep.fr, to obtain detailed information on fixed internet access coverage, particularly thanks to FttH rollout maps (which are also still available athttps://cartefibre.arcep.fr/)
- Open data:data on fibreand data on all access technologies
References:
FCC explores shared use of the 42 GHz band
The FCC voted Thursday to launch a proceeding to consider sharing models in 500 megahertz of spectrum in the 42 GHz band. The agency believes its examination could inform how the band might best be used —particularly by smaller wireless service providers— and provide guidance on future uses of sharing models in spectrum management.
FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel, who just returned this week from a quick trip to Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt for an ITU meeting, said that when she took over at the FCC, she believed the agency had overinvested in millimeter wave (mmWave) auctions and done too little to bring mid-band spectrum to market. She set out to change that, launching auctions in the 3.45 GHz and 2.5 GHz bands.
“With those successful mid-band efforts in the rear-view mirror, we are now turning back to millimeter wave,” Rosenworcel said in prepared remarks. “But this time we want to consider something different. In the 42 GHz band we have 500 megahertz of greenfield airwaves with no federal or commercial incumbencies. So we are putting out ideas. We are exploring non-exclusive access models. This could entail using a technology-based sensing mechanism to help operators actively detect and avoid one another. It could involve non-exclusive nationwide licenses that leverage a database to facilitate coexistence. It could also entail site-based licensing. To get even more out of this effort we ask if our approaches could be combined with shared-used models in other spectrum bands, like the lower 37 GHz band.”
“Our goal here is to come up with a new model to lower barriers, encourage competition and maximize the opportunities in millimeter wave spectrum. In short, it’s time to be creative. I look forward to the record that develops—and then look forward to sharing our creativity with the world.”
A Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) is in effect where the FCC will build a record on the benefits and drawbacks of implementing a shared licensing approach in the 42 GHz band. The NPRM proposes licensing the 42 GHz band as five 100 megahertz channels and seeks comment on other aspects of implementing a shared licensing approach, including coordination mechanisms, buildout requirements and technical rules.
Michael Calabrese, director of Wireless Future, Open Technology Institute at New America, said his organization agrees that a shared licensing framework is the best use of the 42 GHz band, making this spectrum available to a wide range of fixed wireless ISPs, enterprises and other users.
“Coordinated sharing will be particularly powerful if the FCC adopts a common framework for the lower 37 and 42 GHz bands, giving operators as much as 1100 megahertz of bandwidth,” he said in a statement provided to Fierce. “Fixed wireless deployments are exploding, adding options and competition for high-capacity broadband at lower prices. As open access bands, wide-channel millimeter wave spectrum can fuel and accelerate this positive trend.”
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/exploring-shared-use-42-425-ghz-band
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-393517A1.pdf
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/fcc-eyes-42-ghz-shared-use
KDDI Deploys DriveNets Network Cloud: The 1st Disaggregated, Cloud-Native IP Infrastructure Deployed in Japan
Israel based DriveNets announced today that Japanese telecommunications provider KDDI Corporation has successfully deployed DriveNets Network Cloud as its internet gateway peering router. DriveNets Network Cloud provides carrier-grade peering router connectivity across the KDDI network, enabling KDDI to scale its network and services quickly, while significantly reducing hardware requirements, lowering costs, and accelerating innovation. Additional applications will be deployed on DriveNets Network Cloud in the future.
“KDDI prides itself on deploying the most advanced and innovative technology solutions that allow us to anticipate and respond to the ever-changing usage trends, while providing considerable value to our customers,” said Kenji Kumaki, Ph.D. General Manager and Chief Architect, Technology Strategy & Planning, KDDI Corporation. “DriveNets Network Cloud enables us to quickly scale our network as needed, while controlling our costs effectively.”
“While many of Japan’s service providers have been aggressively pursuing the virtualization of network functions on their 4G and 5G networks, disaggregation of software and hardware in service providers’ routing infrastructure is just getting started,” said Ido Susan, DriveNets’ co-founder and CEO. “I am extremely proud that our Network Cloud solution was selected by KDDI, a leading innovative service provider, and is already deployed in their network, supporting the needs of KDDI‘s customers.”

The deployment of DriveNets Network Cloud on the KDDI network is the culmination of several years of testing and verification in KDDI‘s labs. It also reflects the growing adoption of disaggregated network architectures in service provider networks around the world.
“The move to disaggregated networking solutions will continue to be a prevailing trend in 2023 and beyond as savvy service providers try new technologies that can enable them to innovate faster and reduce costs. We are now seeing this technology also adopted in other high-scale networking environments, such as AI infrastructures,” said Susan.
DriveNets Run Almog wrote in an email, “KDDI is using white box devices from Delta. These are the “same” OCP compliant NCP devices which are deployed at AT&T (UFISpace in the AT&T case). they are using it as a peering router (vs. AT&T’s core use case). so this announcement is public indicative to several things: a 2nd Tier #1, another use case, and another ODM vendor, all in commercial deployments with our network cloud.”
DriveNets Inbar Lasser-Raab wrote in an email, “Getting a tier-1 SP to announce is very hard. They are cautious and our solution needs to be working and validated for some time before they are willing to talk about it. We are working on our next PR, but you never know when we’ll get the OK to release” ![]()
Compared to traditional routers that are comprised of software, hardware and chips from a single vendor, a DDBR solution combines software and equipment from multiple vendors, allowing service providers to break vendor lock and move to a new model that enables greater vendor choice and faster scale and introduction of new services through modern cloud design.
In addition to KDDI, DriveNets is already working with other service providers in Asia Pacific to meet the growing interest in its disaggregated networking solutions in the region. In mid-2021, the company established a Tokyo-based subsidiary to enhance its presence in the region.
DriveNets offers an architectural model similar to that of cloud hyperscalers, leading to better network economics and faster innovation. DriveNets Network Cloud includes an open ecosystem with elements from leading silicon vendors and original design manufacturers (ODMs), certified by DriveNets and empowered by our partners, which ensure the seamless integration of the solutions into providers’ networks.
About DriveNets:
DriveNets is a leader in cloud-native networking software and network disaggregation solutions. Founded at the end of 2015 and based in Israel, DriveNets transforms the way service and cloud providers build networks. DriveNets’ solution – Network Cloud – adapts the architectural and economic models of cloud to telco-grade networking. Network Cloud is a cloud-native software that runs over a shared physical infrastructure of white-boxes, radically simplifying the network’s operations, increasing network scale and elasticity and accelerating service innovation. DriveNets continues to deploy its Network Cloud with Tier 1 operators worldwide (like AT&T) and has raised more than $587 million in three funding rounds.
About KDDI:
KDDI is telecommunication service provider in Japan, offering 5G and IoT services to a multitude of individual and corporate customers within and outside Japan through its “au”, “UQ mobile” and “povo” brands. In the Mid-Term Management Strategy (FY23.3–FY25.3), KDDI is promoting the Satellite Growth Strategy to strengthen the 5G-driven evolution of its telecommunications business and the expansion of focus areas centered around telecommunications.
Specifically, KDDI is especially focusing on following five areas: DX (digital transformation), Finance, Energy, LX (life transformation) and Regional Co-Creation. In particular, to promote DX, KDDI is assisting corporate customers in bringing telecommunication into everything through IoT to organize an environment in which customers can enjoy using 5G without being aware of its presence, and in providing business platforms that meet industry-specific needs to support customers in creating businesses.
In addition, KDDI places “sustainability management” that aims to achieve the sustainable growth of society and the enhancement of corporate value together with our partners at the core of the Mid-Term Management Strategy. By harnessing the characteristics of 5G in order to bring about an evolution of the power to connect, KDDI is working toward an era of the creation of new value.
References:
https://drivenets.com/products/
IEEE/SCU SoE May 1st Virtual Panel Session: Open Source vs Proprietary Software Running on Disaggregated Hardware
DriveNets raises $262M to expand its cloud-based alternative to core network routers
AT&T Deploys Dis-Aggregated Core Router White Box with DriveNets Network Cloud software
DriveNets Network Cloud: Fully disaggregated software solution that runs on white boxes
KDDI claims world’s first 5G Standalone (SA) Open RAN site using Samsung vRAN and Fujitsu radio units
Cisco and AT&T to expand connectivity for hybrid workforces
Cisco and AT&T today announced new solutions to enhance connectivity and advance the calling landscape for hybrid workforces. Whether on the shop floor, the top floor, at the branch office, the home office, or the commute in between, the modern workforce is not tethered to a single space, device, or geography. With the new offerings, including Cisco’s Webex Calling and SD-WAN solutions alongside AT&T mobile network, businesses of any size can offer employees a simple, secure, consistent experience to thrive in any setting.
The companies today announced plans that will help ensure a seamless and reliable mobile-first collaboration experience, allowing users the flexibility to take calls across multiple devices while traveling for work, running errands, and more.
With the dramatic increase in the use of mobile phones as the primary business device, enterprises need connectivity solutions that are easy to manage, secure, and provide the flexibility and reliability desired for work from anywhere. This integration addresses this need with key features including:
- Single number mobile identity: Combining the capabilities of an AT&T wireless smartphone with the native integration of Webex Calling will provide greater functionality and flexibility for on-the-go communication.
- Reduce costs: This integration helps enterprise customers lower costs by reducing or eliminating the need for traditional fixed business lines.
- Crystal clear voice: AT&T Cloud Voice with Webex Go allows users to securely make and receive business calls using AT&T’s fast, reliable nationwide mobile network and seamlessly elevate calls to a fully immersive Webex collaboration experience across the Webex App and devices1, with capabilities like closed captioning, noise removal, and white boarding.
- Fast, efficient, and secure collaboration: AT&T and Cisco’s joint solution will increase the ability to effectively and securely collaborate no matter the location, resulting in improved knowledge sharing and faster decision making.
AT&T Cloud Voice with Webex Go2 will be available for all Webex Calling users from Cisco partners in the United States later this year.
SD-WAN Connectivity without Compromise:
Demand for unified experiences over secure connectivity to the cloud and site-to-site continues to surge. Cisco and AT&T are working together to bring secure on-demand connectivity for SD-WAN with add-on services that may include over mobile 5G and fiber broadband to businesses of every size.
For small and medium businesses, AT&T is launching a new self-service option to simplify and accelerate SD-WAN deployment. Businesses can now easily connect, protect, manage, and scale their networks using AT&T Business Wi-Fi with Cisco Meraki.
For larger enterprises, AT&T SD-WAN with Cisco is a fully managed connectivity solution with embedded security and analytics. Enterprises can now confidently connect a user or device to any application in their multicloud using a secure access service edge (SASE)-enabled architecture. This delivers integrated security and application optimization for end-to-end visibility.
Cisco will also provide the ability to embed AT&T wireless connectivity into Cisco devices enabling zero touch provisioning for Cisco and AT&T customers, through AT&T Control Center powered by Cisco.
“The network is at the core of the modern workforce. The ability to get things done is no longer reliant on where you are, but how you are connected,” said Jonathan Davidson, Executive Vice President and General Manager of Cisco Networking. “Hybrid work only works when there is a seamless, consistent, and secure experience for workers, regardless of location. Together with AT&T, we are giving businesses what they need to securely connect everything and everyone—wherever they are. Because when everything is connected, then anything is possible.”
“Mobility is key to enabling hybrid work. Businesses want a seamless and reliable communication experience,” said Mike Troiano, Senior Vice President, Business Products, AT&T. “At the heart of our collaboration with Cisco is a shared vision to empower organizations with secure connectivity, unmatched reliability, and deep network expertise. By deeply integrating our technology, businesses can be assured their communications are built on a solid foundation. Together we are unlocking new levels of productivity, agility, and connectivity— enabling teams to thrive in the modern work landscape.”

Webex Go with AT&T’s Mobile Network
About AT&T:
We help more than 100 million U.S. families, friends and neighbors, plus nearly 2.5 million businesses, connect to greater possibility. From the first phone call 140+ years ago to our 5G wireless and multi-gig internet offerings today, we @ATT innovate to improve lives. For more information about AT&T Inc. (NYSE:T), please visit us at about.att.com. Investors can learn more at investors.att.com.
About Cisco:
Cisco is the worldwide technology leader that securely connects everything to make anything possible. Our purpose is to power an inclusive future for all by helping our customers reimagine their applications, power hybrid work, secure their enterprise, transform their infrastructure, and meet their sustainability goals. Discover more on The Newsroom and follow us on Twitter at @Cisco.
Spark New Zealand partnering with Lynk Global to offer a satellite-to-mobile service
Spark, the leading telco in New Zealand, announced it is collaborating with Lynk Global to offer a satellite-to-mobile service, aiming to enhance connectivity for its customers. Later this year, selected customers will be offered a free trial of the service.
The satellite-to-mobile service will enable periodic text messaging throughout the day during the initial trial. However, as more commercial satellites are deployed, Spark intends to expand the service in 2024 to offer more regular connectivity. The ultimate goal is to provide voice and data services to customers once they become reliably available.
Spark said while satellite coverage cannot reach 100 percent due to the requirement of a clear line of sight to the sky, it offers an additional layer of resilience, especially in light of increasingly severe and frequent weather events caused by climate change. By leveraging satellite connectivity, Spark aims to extend its network reach to areas that are currently underserved by traditional mobile coverage.
According to the Spark press release, the trial period will provide an opportunity to refine and enhance the service in alignment with the increasing number of satellites in orbit. Integration into Spark’s network and regulatory approval are also essential steps before the service can be officially launched.

Photo Credit: Spark New Zealand
The collaboration with Lynk Global and the existing partnership with Netlinkz, which aims to provide satellite broadband services, are part of Spark’s broader strategy to leverage satellite technology as part of its connectivity offering to customers. Spark says it is actively working with various partners to expand the range of services it can deliver.
In a separate announcement last week, Spark revealed its partnership agreement with Netlinkz to provide Starlink business-grade satellite broadband to customers later this year. This initiative follows ongoing trials with a select number of New Zealand businesses.
Spark Product Director, Tessa Tierney, said, “We believe satellite has an important role to play in connecting Aotearoa New Zealand. While satellite can’t provide 100% coverage – as you need a clear line of sight to the sky to get connected2 – it certainly adds an additional layer of resilience, particularly now, as we face increasingly severe and frequent weather events due to climate change. And once there are more satellites launched and the service is available more broadly, it will allow our mobile customers to start to use their phones in more areas that aren’t reached by traditional mobile coverage.”
“We know that our customers will be eager to start using satellite messaging, but the technology is still evolving, so the service and experience will improve and expand as the number of satellites in the sky increases. That’s why we’ve chosen to trial this technology with some of our customers first, to make sure we can offer a great product to our customers when we make it widely available. We also need to integrate the technology into our network and achieve regulatory approval to launch the service. But we are excited to see the possibilities this creates for New Zealanders and will be working hard to make it widely available as soon as we can.
“This partnership with Lynk, and our partnership with NetLinkz to offer a satellite business connectivity service are part of Spark’s broader strategy to use satellite as a part of our connectivity offer to customers. We are continuing to work with these and other potential partners to broaden the services Spark can offer.”
Spark’s introduction of satellite-to-mobile services and business-grade satellite broadband underscores its commitment to enhancing connectivity options for customers across the country, particularly in underserved areas. Spark said further details, including eligibility criteria and timelines, will be disclosed in the coming months.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.sparknz.co.nz/news/Spark-to-launch-satellite-to-mobile-service/
Spark New Zealand to Launch Satellite-To-Mobile Service With Lynk Global




