FCC reports and orders
FCC updates subsea cable regulations; repeals 98 “outdated” broadcast rules and regulations
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is updating its regulations for subsea cables to enhance security and streamline the licensing process. The updates, adopted at an FCC open meeting on August 7th, aim to address national security concerns related to foreign adversaries (like Russia and China) and accelerate the deployment of these critical communication networks. This initiative, developed by the Office of International Affairs in collaboration with the Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau and the Enforcement Bureau, is intended to bolster national security. The new rules address potential vulnerabilities of subsea cables to foreign adversaries, recognizing their critical role in global internet traffic and financial transactions.
FCC Chairman Brendan Carr said that while the FCC often focuses on airwaves as vital but unseen infrastructure, submarine cables are just as essential. “They are the real unseen heroes of global communications. [The Commission] must facilitate, not frustrate the buildout of submarine cable industries.” Indeed, the vast global network of subsea cables carry ~ 99% of the world’s internet traffic and support more than $10 trillion in daily financial transactions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The risk of Russia- and China-backed attacks on undersea cables carrying international internet traffic is likely to rise amid a spate of incidents in the Baltic Sea and around Taiwan, according to a report by Recorded Future, a U.S. cybersecurity company. It singled out nine incidents in the Baltic Sea and off the coast of Taiwan in 2024 and 2025 as a harbinger for further disruptive activity. The report said that while genuine accidents remained likely to cause most undersea cable disruption, the Baltic and Taiwanese incidents pointed to increased malicious activity from Russia and China. “(Sabotage) Campaigns attributed to Russia in the North Atlantic-Baltic region and China in the western Pacific are likely to increase in frequency as tensions rise,” the company said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The FCC also repealed 98 “outdated” broadcast rules and regulations as part of a deregulation effort aimed at streamlining and modernizing the agency’s rules. These rules, deemed obsolete or unnecessary, included outdated requirements for testing equipment and authorization procedures, as well as provisions related to technologies like analog broadcasting that are no longer in use. The move is part of the FCC’s “Delete, Delete, Delete” docket, which seeks to identify and remove rules that no longer serve the public interest.
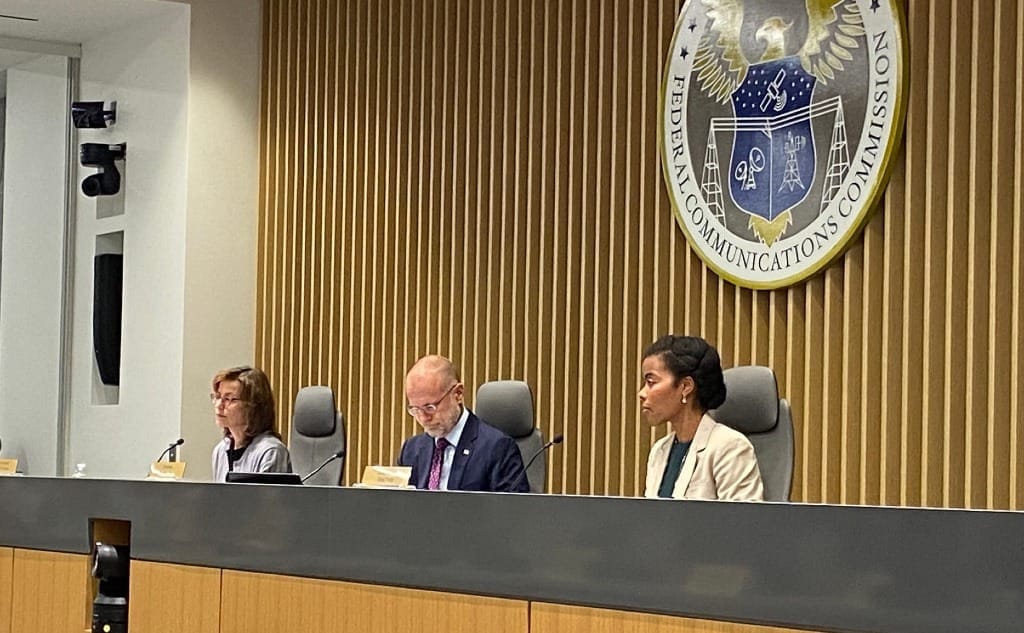

FCC Chairman Brendan Carr (middle) and Commissioners Olivia Trusty (right) and Anna Gomez (left) at the Open Meeting on August 7, 2025 in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: Broadband Breakfast/Patricia Blume.
Many of the repealed rules relate to analog-era technologies and practices that are no longer relevant in today’s digital broadcasting landscape. These rules cover various areas, such as obsolete subscription television rules, outdated equipment requirements from the 1970s, unnecessary authorization rules for standard practices, obsolete international broadcast provisions, and sections that were for reference only or were duplicative or reserved. In particular:
- The repealed rules covered equipment requirements for AM, FM, and TV stations that are now obsolete, as well as rules related to subscription television systems that operated on now-defunct analog technology.
- The FCC eliminated rules regarding international broadcasting that used outdated terms and procedures.
- Several sections that merely listed citations to outdated FCC orders, court decisions, and policies were also removed.
- The FCC eliminated a rule requiring FM stations to obtain authorization for stereophonic sound programs, which is now standard practice.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/August2025
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-deletes-outdated-broadcast-rules-and-requirements/carr-statement
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-413057A1.pdf
https://broadbandbreakfast.com/fcc-unanimously-approves-buildout-of-secure-submarine-cables/
New FCC Chairman Carr Seen Clarifying Space Rules and Streamlining Approvals Process
U.S. federal appeals court says FCC’s net neutrality/open internet rules are “unlawful”
Intentional or Accident: Russian fiber optic cable cut (1 of 3) by Chinese container ship under Baltic Sea
Sabotage or Accident: Was Russia or a fishing trawler responsible for Shetland Island cable cut?
Geopolitical tensions arise in Asia over subsea fiber optic cable projects; U.S. intervened to flip SeaMeWe-6 contractor
China seeks to control Asian subsea cable systems; SJC2 delayed, Apricot and Echo avoid South China Sea
Who will be the big bidders at upcoming FCC C-band and AWS auctions?
Under new chairman Brendan Carr, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plans to open up more C-band (3.98-4.2 GHz) spectrum for 5G, recalling a golden age of spectrum awards that brought in tens of billions of dollars. The first C-band auction, which drew to a close in early 2021, brought in a staggering US$94 billion. Verizon made headlines by shelling out $52.9 billion at the auction, including incentive payments and clearing costs, so naturally there is talk of whether it will look to repeat its performance in the next C-band sale. But until we have more information it’s all just speculation. “In 2020, the FCC conducted the most successful auction in history when it released 280 megahertz of mid-band spectrum in the C-band for 5G,” Carr wrote, in a blog post.
At its upcoming February 25, 2025 Open Commission Meeting, the FCC (among other things) will:
- Enhancing National Security Though the Auctioning of Spectrum Licenses
The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would update 10 year-old AWS-3 service-specific competitive bidding rules to bring those rules in line with current practice as the first step in fulfilling the Commission’s statutory obligation to initiate an auction of licenses for the AWS-3 spectrum in the Commission’s inventory by June 23, 2026, under the Spectrum and Secure Technology and Innovation Act. (GN Docket Nos. 25-70, 25-71, 13-185) - Exploring New Uses for Mid-Band Spectrum in the Upper C-band
The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry exploring whether, and if so how, we could free up additional mid-band spectrum for new services in the Upper C-band to meet projected spectrum demand, spur economic growth, and advance American security interests. (GN Docket No. 25-59)
CTIA – the U.S. wireless industry’s primary trade group – quickly cheered the news: “We applaud Chairman Carr for his swift action in exploring how best to make the upper C-band available for 5G wireless commercial use,” CTIA CEO Meredith Attwell Baker said in a statement. However, Carr didn’t specifically say whether that C-band 2.0 auction would be for 5G. “We will vote on a notice of inquiry that asks whether the commission should open up additional portions of the C-band (3.98-4.2 GHz) for more intensive use. We want to hear your views,” Carr wrote.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX and the major U.S. 5G telcos (AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile) have expressed interest in upper C-band spectrum. SpaceX said in January that the FCC should develop “a modernized sharing framework” for the upper C-band, presumably so that it could be used by both satellite operators (like SpaceX) and terrestrial operators (like AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile).
“Establishing a modernized sharing framework for the upper C-band that welcomes multiple new entrants is essential to solidify American leadership in 6G, which will interweave terrestrial and satellite networks into a seamless consumer experience,” SpaceX wrote. Politico noted that FCC’s Carr – has been developing ties to Musk.
“While the outcome is far from certain, we give an edge to the wireless interests,” wrote Blair Levin, a policy adviser to New Street Research and a former high-level FCC official, in a recent note to investors. “In this administration it appears that ‘whatever Elon wants, Elon gets.’ So, it is difficult to have conviction on the outcome.” Indeed, there are plenty of ways for the FCC to handle the upper C-band situation. Levin wrote, “There are multiple compromises available, such as allocating some to exclusive and some to satellite sharing or getting back more spectrum from the current users,” he wrote.
Other industry watchers are unsure about SpaceX vs wireless industry C-band spectrum bidding:
- “It’s unclear whether SpaceX could overcome the wireless lobby’s desire for more terrestrial spectrum,” analyst Tim Farrar, with TMF Associates, told Light Reading.
- “The upper C-band is an enormous opportunity to unleash additional spectrum for mobile 5G, for LEO [low-Earth orbit] satellite direct-to-device connectivity, or for a combination of both,” Michael Calabrese told Light Reading. Calabrese is director of the Wireless Future Project, which is part of New America’s Open Technology Institute think tank. Calabrese said that FCC Chairman Brendan Carr “is wise to open a notice of inquiry to explore what form of repurposing or sharing will best promote innovation and the connectivity needs of the future. The one certainty is that the 220 megahertz in C-band that was not repurposed five years ago should be a priority for reallocation to a higher and better use today.”
–>The previous C-band sale may have been the peak of wireless network operator spectrum spending, but we could see the big players pony up a significant amount of cash again in the next year or so at FCC auctions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mr. Carr also talked about an upcoming AWS-3 frequency auction, indicating that it is on track to take place by mid-2026 as required by law. In one of his first official statements as the new chairman of the FCC, Carr said he plans to auction AWS-3 spectrum before the end of next year. He added that the commission would consider holding another auction of C-band spectrum.
“This month, we will vote to kickstart the process for reauctioning a large number of AWS-3 spectrum licenses that have sat in inventory for years. This auction will be a win-win. It brings new spectrum into play for commercial use. And the proceeds from this auction will also cover the costs of the national security initiative known as “rip and replace”—an effort that is removing untrustworthy technology, like Huawei and ZTE gear, from networks. Specifically, our AWS-3 notice of proposed rulemaking will ensure that the Commission is on track to meet its statutory obligation to complete this auction by June 23, 2026.’
Those auctions will help pay for Rip and Replace (mostly Huawei network equipment) from U.S. telco networks. The Rip and Replace program was created in 2020 to remove Chinese components from U.S. wireless communications systems. The Rip and Replace fund needs an additional $3B in order to finish its mission.
AT&T is the most likely to spend big on the AWS-3 spectrum sale, given that it has less mid-band spectrum than its rivals, and CEO John Stankey has already expressed interest in the airwaves.
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/spectrum/new-fcc-chair-looks-to-repeat-c-band-mega-auction
https://broadbandbreakfast.com/fcc-to-vote-on-aws-auction-inquiry-into-upper-c-band-2/
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/could-elon-grab-some-of-5g-s-spectrum-
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/carr-hands-a-spectrum-gift-to-5g-industry
https://www.ctia.org/news/ctia-statement-on-chairman-carrs-announcement-on-upper-c-band
https://www.fcc.gov/February2025
Eric Schmidt: FCC C-Band Auction Dooms U.S. 5G Future
UPDATED: Mid-band Spectrum for 5G: FCC C-Band Auction at $80.9B Shattering Records
FCC Auction 110 for mid-band 5G spectrum gets $21.9B in winning bids
FCC Chairman Pai Reviews 5G FAST plan and importance of the C-Band (3.7 GHz to 4.2 GHz) auction
4 U.S. Mobile Operators offer C-band FCC proposal to address aircraft interference
FCC Auction 108 (2.5 GHz) ends with total proceeds << than expected; T-Mobile expected to be #1 spectrum buyer
FCC launches new 5G mid-band wireless spectrum auction (FCC Auction 108)
Bloomberg: 5G in the U.S. Has Been a $100 Billion Box Office Bomb
U.S. federal appeals court says FCC’s net neutrality/open internet rules are “unlawful”
U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit today struck down the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC’s) hard-fought and long-debated net neutrality/open internet rules. The FCC had sought to reinstate a sweeping policy established under President Obama that was designed to treat internet service as an essential public service, similar to a water or power utility. The court ruled that broadband communications, including broadband delivered via mobile networks, is classified as an “information” service rather than a more heavily regulated “telecommunications” service. That important distinction means the FCC lacks the authority to impose the current set of rules, the court’s three-judge panel found.
The court said a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling had removed a judicial framework that allowed courts to interpret rules with deference to the federal agency that created them. The 6th Circuit said the FCC did not have the statutory authority to change the classification of broadband internet to a telecommunications service. That role rests with Congress. The case was brought by the Ohio Telecom Association, a trade organization representing internet service providers (ISPs).
The negative ruling arrives about six months after the Sixth Circuit court stayed the FCC’s network neutrality rules, under current Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel, which aimed to resurrect broadband under a more heavily regulated Title II/telecommunications service classification. The FCC, under Rosenworcel, passed the current set of net neutrality rules in April 2024.

Backgrounder: Under the net neutrality rules, internet service providers (ISPs) would have been subjected to greater regulation. A Republican-led commission repealed the rules in 2017 during President-elect Donald Trump’s first term in office. Early last year, the FCC — then back under Democrat control — voted to formalize a national standard for internet service to prevent the blocking or slowing of information delivered over broadband internet lines. The core principle of open internet meant that internet service providers couldn’t discriminate among content suppliers. The order also would have given the FCC increased oversight to demand that internet providers respond to service outages or security breaches involving consumers’ data. The FCC cited national security, saying increased oversight was necessary for the commission to effectively crack down on foreign-owned companies that were deemed to be security threats.
“Using ‘the traditional tools of statutory construction’ … we hold that Broadband Internet Service Providers offer only an ‘information service’ … and therefore, the FCC lacks the statutory authority to impose its desired net-neutrality policies through the ‘telecommunications service’ provision of the Communications Act,” the Sixth Circuit court, based in Cincinnati, OH, said in its ruling.
“We conclude that Broadband Internet Service Providers at the very least offer consumers the ‘capability’ of ‘retrieving’ ‘information via telecommunications’,” the Sixth Circuit explained. “Accordingly, the FCC’s contrary conclusion is unlawful.”
The decision is another blow to an FCC that had fought for the rules to be reinstated under Rosenworcel and the outgoing Biden administration. The decision is a win for broadband service providers along with several organizations, including ACA Connects, CTIA, NCTA and USTelecom, that had argued against the rules, holding that the market has been thriving under a “light-touch regulatory framework.”
In a statement about the Sixth Circuit Court’s decision, FCC chairwoman Rosenworcel said:
“Consumers across the country have told us again and again that they want an internet that is fast, open, and fair. With this decision it is clear that Congress now needs to heed their call, take up the charge for net neutrality, and put open internet principles in federal law.”
However, the ruling is likely just the start of a larger wave of deregulatory shifts that’s expected to occur in 2025 and beyond under the new Trump administration. Incoming FCC Chairman Brendon Carr (see quote below) is the senior Republican on the five-member commission and has championed many of Trump’s causes. One of the authors of the Project 2025 policy paper, he has outlined plans to remove regulations conservatives consider overbearing or outdated. He will also wrestle with looming budget crunches and court rulings that threaten to erode the federal agency’s overall authority.
Some reactions to Thursday’s ruling:
1. “We hope that today’s decision will allow for a refocused conversation about effective ways to achieve national goals with respect to broadband access,” Mike Romano, EVP of NTCA – The Rural Broadband Association, said in a statement.
2. MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett noted in an emailed statement to investors that the broadband market has been concerned that if the FCC had the authority to impose Title II reclassification, it could open the door for the Commission to impose broadband price regulation. “That risk is now put to bed,” he said. The decision was of little surprise after the FCC’s ability to start enforcing the rules was delayed after the court put them on hold amid a review of the precedent set by the US Supreme Court’s decision last June to strike down the decades-old Chevon deference (a.k.a. the Loper Bright) decision. That decision stands to limit the power and authority of federal agencies, such as the FCC, in interpreting certain laws that are considered ambiguous. Notably, Chevron has played a significant role over the years in establishing the FCC’s authority to set and enforce network neutrality regulations. “Indeed, the reason we and others stopped worrying about Title II was because it was clear that the judicial principle of Chevron Deference wasn’t going to survive much longer,” Moffett wrote.
3. Free Press, a long-time network neutrality advocate, argued that the court wrongly rejected the FCC’s jurisdiction on the matter. “Beyond being a disappointing outcome, today’s 6th Circuit opinion is just plainly wrong at every level of analysis,” Matt Wood, VP of policy and general counsel at Free Press, said in a statement. “Today’s decision will let the incoming Trump FCC abdicate its responsibility to protect internet users against unscrupulous business practices … It’s rich to think of Donald Trump and Elon Musk’s hand-picked FCC chairman characterizing light-touch broadband rules as heavy-handed regulation, while scheming to force carriage of viewpoints favorable to Trump on the nation’s broadcast airwaves and social media sites.”
4. Statement from Tully Center for Free Speech on Net Neutrality Ruling:
As expected, FCC Commissioner & incoming FCC Chairman Brendon Carr (Republican) cheered news of the ruling by stating, “Over the past four years, the Biden Administration has worked to expand the government’s control over every feature of the Internet ecosystem. You can see it in the Biden Administration’s efforts to pressure social media companies into censoring the free speech rights of everyday Americans. You can see it in the Biden Administration’s demand that the FCC adopt ‘digital equity’ rules for the Internet—sweeping regulations that give the Commission nearly limitless powers over the Internet. And you can see it in the Biden Administration’s decision to impose so-called ‘net neutrality’ rules by applying Title II or utility-style regulations to the Internet.”
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/chairwoman-rosenworcel-sixth-circuit-court-net-neutrality-decision
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-408580A1.pdf
FCC restores net neutrality order, but court challenges loom large
Analysis: FCC attempt to restore Net Neutrality & U.S. standards for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
Aftermath of Salt Typhoon cyberattack: How to secure U.S. telecom networks?
Salt Typhoon Attack: On December 4, 2024, a top U.S. security agency representative confirmed reports that foreign actors, state-sponsored by the People’s Republic of China, infiltrated at least eight U.S. communications companies, compromising sensitive systems and exposing vulnerabilities in critical telecommunications infrastructure. This was part of a massive espionage campaign that has affected dozens of countries. Salt Typhoon has targeted telcos in dozens of countries for upward of two years, officials added.
Dated legacy network equipment and years of mergers and acquisitions are likely impeding the ability of telecommunications providers to prevent China inspired cyber-attacks. Until telecom operators fully secure their networks, China will keep finding ways to come back in, officials have warned.
- On Thursday, FCC chair Jessica Rosenworcel proposed a new annual certification requirement for telecom companies to prove they have an up-to-date cybersecurity risk management plan. More below.
- Senior Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency and FBI officials confirmed Tuesday that U.S. telcos are still struggling to keep the China-backed hackers out of their networks — and they have no timeline for when total eviction is possible.
FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel suggested ‘telecom carriers’ raise their network security methods and procedures: “The cybersecurity of our nation’s communications critical infrastructure is essential to promoting national security, public safety, and economic security,” said Rosenworcel. “As technology continues to advance, so does the capabilities of adversaries, which means the U.S. must adapt and reinforce our defenses. “While the Commission’s counterparts in the intelligence community are determining the scope and impact of the Salt Typhoon attack, we need to put in place a modern framework to help companies secure their networks and better prevent and respond to cyberattacks in the future.”
Rosenworcel’s plan is to make U.S. telcos submit some kind of annual certification to the FCC, proving their cybersecurity measures are up to scratch. The clear inference from the attack itself and all the subsequent attempts to shut the stable door after the horse has bolted is that those efforts currently fall short of the mark. Understandably, none of the specific deficiencies have been publicly detailed.
These proposed FCC measures have been made available to the five members of the Commission. They may choose to vote on them at any moment. If adopted, the Declaratory Ruling would take effect immediately. The Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, if adopted, would open for public comment the cybersecurity compliance framework, which is part of a broader effort to secure the nation’s communications infrastructure.
The FCC press release refers to a recent WSJ report based on an unpublished briefing from U.S. national security adviser Anne Neuberger, in which she detailed the scale of the Salt Typhoon attack. “The Chinese compromised private companies, exploiting vulnerabilities in their systems as part of a global Chinese campaign that’s affected dozens of countries around the world,” she was quoted as saying.

Illustration: Sarah Grillo/Axios
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Legacy network equipment and years of acquisitions have made it particularly difficult for telcos to patch every access point on their networks, Cliff Steinhauer, director of information security and engagement at the National Cybersecurity Alliance, told Axios.
- Many of the systems in question are nearly 50 years old — like landline systems — and they were “never meant for the type of sensitive data and reliance that we have on them right now,” he said.
- During an acquisition, a company could also miss a server when taking stock of all its newly acquired equipment, Steinhauer said. Network engineers are often inundated with security alerts that are hard to prioritize, he added.
- U.S. telecommunications carriers are required to provide a way for law enforcement to wiretap calls as needed — providing another entry point for adversaries.
Many of the security problems telcos face require simple fixes, like implementing multifactor authentication or maintaining activity logs.
- Even CISA’s recent guidance for securing networks focuses on the security basics.
- But to keep China out, telcos would have to make sure that every device — including their legacy physical equipment, online servers and employees’ computers — is patched.
Most high-profile cyberattacks across industries come down to the basics: a compute server that didn’t have multifactor authentication turned on or an employee who was tricked into sharing their password. Even if a company invests all of its resources in cybersecurity, it may not be enough to fend off a sophisticated nation-state like China.
- These actors are skilled at covering their tracks: They could delete activity logs, pose as legitimate users, and route their traffic through compromised computers in the U.S. so they aren’t detected.
- “You’ve got a persistent, motivated attacker with vast resources to poke and prod until they get in,” Mr. Steinhauer said.
References:
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-408015A1.pdf
https://www.axios.com/2024/12/06/telecom-cybersecurity-china-hack-us
WSJ: T-Mobile hacked by cyber-espionage group linked to Chinese Intelligence agency
NTIA and DoD report: Spectrum Sharing strategy for users of lower 37 GHz band
In a new 31-page report, the U.S. NTIA and the DoD offered spectrum sharing recommendations for federal and non-federal users in the lower 37GHz band. The NTIA is the government agency that handles federal usage of spectrum. The FCC handles commercial spectrum usage.
“The FCC, NTIA and DoD began discussions in 2020 on the details of a coordination mechanism. These discussions resulted in a draft sharing framework, based on first-in user rights,” the NTIA wrote in a press release. Here’s the backgrounder from NTIA:
- Building on prior collaborative efforts of NTIA, DoD, and the FCC, the findings reflect coordination across a range of government and industry stakeholders.
- The recommendations for a sharing framework take advantage of the physical characteristics of this band, which is well-suited for short-range and line-of-sight wireless applications.
- The report recognizes the need for flexible access tailored to both Federal and non-Federal user requirements to foster technological advances and policy innovation.
With limited incumbent uses, the band presents a “clean slate” for developing a new model for co-primary Federal and non-Federal access. Specifically, this spectrum supports the creation of very narrow, directed beams and limited propagation for ground communications, making robust forms of sharing possible.
- U.S. policymakers have long recognized the unique sharing opportunities of the Lower 37 GHz band, as well as the need to protect Federal sites, including 15 military sites, five National Aeronautics and Space Administration receiving earth station operations and two National Science Foundation sites.
- In coordination with NTIA, the FCC in 2016 adopted an Order that concluded that non-Federal fixed and mobile applications can share 37-38.6 GHz with DoD operations. The Order made the Lower 37 GHz band available for co-primary sharing, with both Federal and non-Federal users accessing the band by registering sites through a coordination mechanism.
- In 2019, the FCC established service rules addressing Federal sites for a 2020 auction in the 37 GHz band, with sharing rules for 37.0-37.6 GHz to be addressed at a later date. Among other things, the decision added one Federal site to the list of protected Federal sites in the 37 GHz band and limited future DoD access to the 37.6-38.6 GHz (Upper 37 GHz) band unless the Department could demonstrate that its operations cannot be accommodated in the Lower 37 GHz band.
- To enable an innovative sharing approach for the Lower 37 GHz band, the FCC, NTIA and DoD began discussions in 2020 on the details of a coordination mechanism. These discussions resulted in a draft sharing framework, based on first-in user rights.
- Following the release of the NSS Implementation Plan, the FCC released a 2024 Public Notice, that sought information on sharing issues in the Lower 37 GHz band, including how to accommodate various use cases through a coordination mechanism between Federal and non-Federal operators.

Image Credit: Dmytro Razinkov/Alamy Stock Photo
The NTIA outlined a detailed, two-phase sharing process for the 37GHz band: “The first phase would use simple propagation models to determine whether there are overlapping contours and permit operations to proceed in the absence of any overlap,” the NTIA wrote. “The second phase would apply in the event of overlap between a proposed site registration and an existing site already registered in the database and would require the parties to exchange more detailed data and attempt to coordinate their operations.” Next the FCC would have to implement the NTIA’s sharing recommendations.
Expected uses of the Lower 37 GHz band include data-intensive applications, such as high speed, low latency 5G services. Wireless operators view this spectrum as well-suited for providing additional bandwidth, for example during large events through indoor distributed antenna deployments. Industry also sees value in the band for addressing increased demand for mobile network capacity by offloading traffic from other bands.
- Potential use cases include fixed wireless access; high-capacity backhaul; cable supplement for Internet of things (IoT) networks and augmented reality applications; and mobile or private networks that support industrial IoT, smart factories and other high-bandwidth indoor communications applications.
- Federal users, including DoD, may leverage some of this same technology, including as part of potential additional adaptations to meet mission requirements (e.g., hardening).
- Although not being proposed for any specific frequency allocation at this time, DoD is evaluating additional use cases to meet military missions, including: (1) Unmanned Systems to provide terrestrial or maritime to aeronautical mobile and potentially space to aeronautical mobile (maritime, terrestrial) unmanned systems; and (2) Wireless Power Transfer to provide a variety of capabilities currently in development by military research labs to deliver power to wireless communication systems, mobile vehicles, surface and subsurface vehicles, and other potential uses cases.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/dod-agrees-to-spectrum-sharing-paradigm-in-37ghz
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
Big 5G Conference: 6G spectrum sharing should learn from CBRS experiences
mmWave Coalition on the need for very high frequency spectrum; DSA on dynamic spectrum sharing in response to NSF RFI
FCC restores net neutrality order, but court challenges loom large
The FCC voted on Thursday, April 25th along party lines to pass its order on Safeguarding and Securing the Open Internet, restoring net neutrality and reestablishing the Commission’s Title II authority over broadband services. The restored “net neutrality” rules prevent broadband internet service providers/ISPs (e.g. Comcast and AT&T) from favoring some sites and apps over others. The vote was taken at the FCC’s open meeting for the month of April. Democrats on the FCC voted to restore net neutrality and Title II rules. The issue will face inevitable court challenges and is likely to be reversed if Donald Trump wins the November presidential election.
As a result of the vote, the FCC restores fundamental authority to provide effective oversight over broadband service providers, giving the Commission essential tools to:
• Protect the Open Internet – Internet service providers will again be prohibited from blocking, throttling, or engaging in paid prioritization of lawful content, restoring the rules that were upheld by the D.C. Circuit in 2016.
• Safeguard National Security – The Commission will have the ability to revoke the authorizations of foreign-owned entities who pose a threat to national security to operate broadband networks in the U.S. The Commission has previously exercised this authority under section 214 of the Communications Act to revoke the operating authorities of four Chinese state-owned carriers to provide voice services in the U.S. Any provider without section 214 authorization for voice services must now also cease any fixed or mobile broadband service operations in the United States.
• Monitor Internet Service Outages – When workers cannot telework, students cannot study, or businesses cannot market their products because their internet service is out, the FCC can now play an active role.
Here are a few FCC commissioner comments:
“Broadband is now an essential service. Essential services, the ones we count on in every aspect of modern life, have some basic oversight. So let’s be clear about what we are doing today. This agency, the nation’s leading communications authority, believes every consumer deserves Internet access that is fast, open and fair. That is why we determine that the Federal Communications Commission should be able to assist consumers and take action when it comes to the most important communications of our time. And that’s broadband. This is common sense,” said FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel.
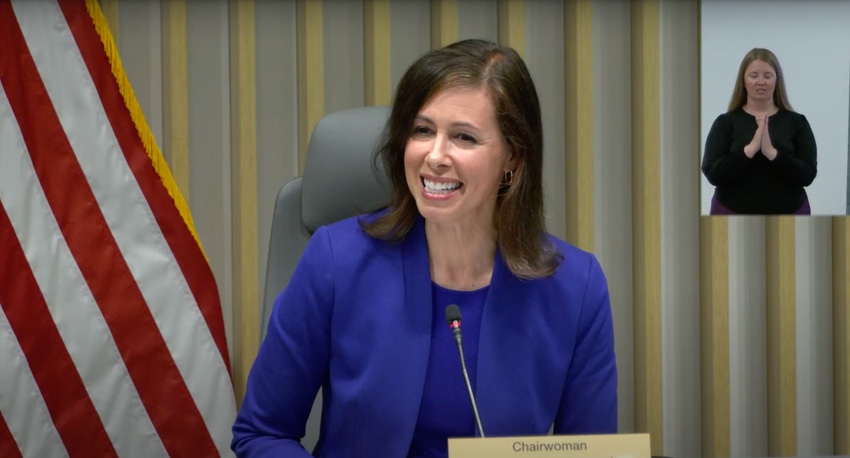

FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel presides at the FCC’s open meeting on Thursday, April 25, 2024.(SOURCE: FCC LIVESTREAM)
Republican FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr offered a different opinion during a nearly 35-minute diatribe:
“Today’s order is not about correcting a market failure. Broadband access is more vibrant and competitive than ever, no matter how you slice the reams of data,” said Carr. “Will ISPs invest as intensely when the rules of the road are opaque, when business choices can be second guessed without notice, when regulators reserve the right to dictate the rate of return or when upgrades and innovations require more and more paperwork and approvals? Uncertainty riddles every aspect of this order … I’m confident that we will right the ship, and I’m certain that the courts will overturn this unlawful power grab.”
The vote drew expected reactions from industry and consumer groups. Those in favor of the ruling celebrated, while still expressing dissatisfaction with a few “shortcomings” of the order. Andrew Jay Schwartzman, Senior Counselor at the Benton Institute for Broadband & Society said:
“Today’s vote provides welcome, if long overdue, protections for all Americans. Despite a few shortcomings, this is the most important thing the FCC can do to promote free speech, competition, public safety, and national security. The Benton Institute for Broadband & Society would have preferred that the Commission continued the debate on whether or not broadband providers should contribute to the Universal Service Fund and that it had taken a more proactive stance toward wireless companies’ efforts to create loopholes to avoid regulation of some 5G services. But those shortcomings do not change the fact that today is a great day for internet freedom.”
On the opposition front, industry trade groups called the rules “heavy-handed” and indicated their intent to file lawsuits.
“ACA Connects will continue to support efforts, including litigation, to overturn these heavy-handed, unnecessary utility-style regulations, which only serve to discourage development of robust and reliable broadband service for all Americans,” said Grant Spellmeyer, president and CEO of ACA Connects, in an emailed statement.
“WISPA is disappointed by today’s action to impose utility regulation on the broadband industry,” said Louis Peraertz, VP of policy for the fixed wireless trade group WISPA–The Association for Broadband Without Boundaries. “Once the final Order is published, WISPA will carefully review it and determine what legal recourse we should take in order to ensure that our members can continue to provide their local communities with reliable high speed broadband service.”
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-restores-net-neutrality
https://www.fcc.gov/net-neutrality
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/fcc-passes-net-neutrality-order-again-for-now
Analysis: FCC attempt to restore Net Neutrality & U.S. standards for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
FCC Votes to Reverse Net Neutrality & No Longer Regulate Broadband Internet Services
FCC legal advisor: Potential End of ACP Is the ‘Biggest Challenge’ Facing the Broadband Marketplace
On Wednesday April 17th, broadband officials and experts called for continued pressure to replenish the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) [1.]. Some panelists during Next Century Cities’ bipartisan tech policy conference also urged community leaders to engage with their state broadband offices as NTIA approves states’ plans for the broadband, equity, access and deployment program.
Note 1. The Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) is a benefit program from the FCC that helps households pay for broadband for work, school, and healthcare. The program is separate from the FCC’s Lifeline Program. The ACP is targeted at low-income families and individuals, and may include a one-time benefit of up to $100 for a phone or internet-capable device like a tablet, laptop, or desktop computer. The program also offers a monthly service discount and one device discount per household. The FCC said that unless lawmakers act to give the program additional funding, the full $30 discount will end at the end of April. The loss of ACP will hit poor people very hard and significantly widen the digital divide.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The biggest challenge facing the broadband marketplace right now is “the potential end of ACP next month,” said Hayley Steffen, legal adviser to Commissioner Anna Gomez. Ensuring the program is funded and continues is Gomez’s “highest priority right now,” Steffen said. FCC Consumer and Governmental Affairs Bureau Chief Alejandro Roark agreed, noting the program has “accomplished more over the past two years to bridge our country’s digital opportunity divide than any other standalone effort in our nation’s history.”
On Monday, a coalition of 271 civil-society groups and local, state and Tribal governments sent a letter to the U.S. House of Representatives that urges all members to sign a discharge petition to support the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) Extension Act. The legislation would provide an additional $7 billion to save a successful broadband-subsidy initiative.
Rep. Yvette Clarke, D-N.Y., is circulating a discharge petition (House Resolution 1119) in a bid to force a floor vote on her Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) Extension Act (HR-6929/S-3565), which would appropriate $7 billion to keep the ailing FCC broadband fund running through the end of FY 2024. ACP “has been a transformative force, empowering nearly 23 million American households in rural and urban communities with reliable, high-speed, and affordable broadband access,” Clarke said Wednesday in a statement.
“To continue this progress, I implore my colleagues to join me by signing the discharge petition. This will ensure [HR-6929] receives the vote it deserves” on the House floor. “We cannot turn our back on the progress made in closing the digital divide,” she said.
“Advocating in numbers is powerful,” said TDI CEO AnnMarie Killian. ACP “really requires that we take a stance and bring forth the importance of digital inclusion for all,” Killian said. DigitalC CEO Joshua Edmonds agreed, but “at the same time, we should walk and chew gum here and look at the value and potential of community-based networks, too.”
Affordability is “a key factor” for individuals with disabilities who rely on broadband for telecom relay services, Killian said, and the end of ACP could have a “significant impact on our economically disadvantaged consumers.” Fort Collins, Colorado, Broadband Executive Director Chad Crager encouraged local officials to start considering “another solution” to addressing affordability in their communities if ACP ends. “We hope it’s renewed” and extended, Crager said, but “the reality will not be forever.”
“This really is the moment for us to not give up” on advocating for ACP’s future, Roark said. ACP has been the FCC’s “best and most successful” effort at broadband affordability, Steffen said. Many households enrolled in the program will be eligible for the Lifeline benefit should ACP end, she said, but Lifeline is “definitely no replacement for ACP.” Roark also encouraged discussions on “how potentially ACP could be integrated into the USF framework.”
NTIA is “actively reviewing” states’ BEAD applications, Senior Policy Adviser Lukas Pietrzak said, noting that 48 states’ volume I proposals have already been approved (see 2403060046). “I have great expectations” for the states’ plans because “at the bare minimum, they did include Black community anchor institutions,” said Fallon Wilson, Multicultural Media, Telecom and Internet Council vice president-policy, citing states with several historically Black colleges and universities. The challenge now is ensuring the states’ plans are executed so that those institutions actually receive funding, Wilson said.
NTIA is also preparing to announce “in the next few weeks” how many applications it received for the second round of tribal broadband connectivity program funding, said Pietrzak. Projects funded by the middle-mile infrastructure grant program are “also starting to break ground in the spring and summer,” Pietrzak said, “which is exciting to see here.” He also noted that 20,000 devices have been distributed through the connecting minority communities program.
References:
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=853996&id=1940601
https://communicationsdaily.com/reference/2404100075?BC=bc_66205df7037e5
https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=aabc18cb-3e53-4085-bda8-42a894e71a08
Analysis: FCC attempt to restore Net Neutrality & U.S. standards for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection
FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel announced the tentative agenda for the April 2024 Open Meeting scheduled for 10:30 am EDT on Thursday, April 25, 2024. As part of the agenda, the Commission will consider a draft Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration (Order) that would restore Net Neutrality [1.] and bring back a national standard for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection.
Note 1. Net neutrality is a concept that internet service providers (ISPs) should treat all data on the internet equally. This means that ISPs should not block, slow down, or charge more money for access to certain websites or services. Net neutrality is important because it helps to ensure that everyone has equal access to the internet.
If the FCC order is approved, the Chairwoman’s proposal would ensure that broadband services are treated as an essential resource deserving of FCC oversight under Title II authority [2].
Note 2. U.S. carriers providing “telecommunications services,” are regulated under Title II. of the 1934 U.S. Communications Act.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
What the Declaratory Ruling and Order Would Do:
Classify broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service and classify mobile broadband Internet access service as a commercial mobile service.
Find that reclassification would provide the Commission with additional authority to safeguard national security, advance public safety, protect consumers, and facilitate broadband deployment.
Find that classification of broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service represents the best reading of the text of the Act, and that such reclassification accords with Commission and court precedent and is fully justified under the Commission’s long standing authority to classify services subject to its jurisdiction.
Establish broad, tailored forbearance—including no rate regulation, no tariffing, no unbundling of last-mile facilities, and no cost accounting rules—in the FCC’s application of Title II to broadband Internet access service providers (ISPs).
What the Report and Order Would Do:
Reinstate straightforward, clear rules that prohibit blocking, throttling, or engaging in paid or affiliated prioritization arrangements, and adopt certain enhancements to the transparency rule.
Reinstate a general conduct standard that prohibits unreasonable interference or unreasonable disadvantage to consumers or edge providers.
Make clear that the Commission will employ a case-by-case review under sections 201 and 202 to ensure that Internet traffic exchange practices do not harm the open Internet.
Establish a multi-faceted enforcement framework comprised of advisory opinions, enforcement advisories, Commission-initiated investigations, and informal and formal complaints.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Legal Opinions on FCC net neutrality draft order:
Legal experts and FCC watchers say the net neutrality draft order on the FCC’s April 25th open meeting agenda will face legal arguments similar to what the 2015 net neutrality order did, with many of the same parties involved.
Starting with a briefing for reporters the day before the draft order was released, the FCC argued the proposed rules would survive legal challenge. Net neutrality rules are “wildly popular,” Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in California last week, adding the draft rules are “court approved.” Rosenworcel said, “I want to make sure that they are again the law of the land.”
Major Questions:
The proposed order is “legally vulnerable,” Free State Foundation President Randolph May told Commissioner Brendan Carr, according to a filing Friday in docket 23-320. May said it was “extraordinary … for an agency to propose burdensome restrictive major regulatory mandates without any meaningful evidence of any present harm to consumers or competition.”
Daniel Deacon, assistant professor at the University of Michigan Law School, pointed to Justice Brett Kavanaugh’s dissent as a D.C. circuit judge in the 2017 en banc affirmation of the 2015 net neutrality rules. Kavanaugh argued that imposing net neutrality rules via Title II represents a “major” policy that requires clear congressional authorization under the major questions doctrine, and that such authorization was lacking, Deacon said: SCOTUS “could reach that conclusion regardless of what they end up doing in Loper Bright and Relentless.”
The commission tries to head off major questions arguments in the draft order. “We do not think the major-questions doctrine properly comes into play in this context at all,” it said. “We are simply following the best reading of the Communications Act, as demonstrated by the statute’s plain text, structure, and historical context: there is no call for deference to an interpretation that is not the statute’s most natural reading.”
The rules won’t “have the extraordinary economic and political effect required to implicate the major-questions doctrine,” according to the draft order.
While the rules “will have substantial benefits for the American public … not every regulatory action that has substantial effects is so momentous as to trigger the major-questions doctrine. The Internet will continue to sustain its enormous economic and social value under our actions today, just as it did under the 2015 Order.”
The pending net neutrality order “is the antithesis of the Supreme Court’s major-questions cases,” the FCC said. “There is nothing novel about the Commission’s exercise of its classification power here,” as the agency has exercised it numerous times, it said. “Regulating communications services and determining the proper regulatory classification of broadband falls squarely within the Federal Communications Commission’s wheelhouse,” the commission said.
Cato’s Skorup disagreed. The agency sees national security implications in net neutrality and finds that it’s important for free speech, “telegraphing they believe” it’s a major question, he said.
It’s unclear how the Supreme Court seemingly heading toward some change to its Chevron doctrine would play out in the inevitable appeal of the FCC’s order. The net neutrality issue isn’t about the FCC having superior insight into the nature of broadband but is a political question about oversight, said Douglas Holtz-Eakin, American Action Forum president. By the time a net neutrality case comes before the D.C. Circuit, there would likely be a SCOTUS ruling affecting Chevron, and the appellate court would have to be guided by it, he said.
CCIA’s Joyce said that even if SCOTUS rejects Chevron, that doesn’t apply to net neutrality, since it doesn’t involve a brand new and novel FCC action. “How can you possibly say that about whether broadband is a Title II service?” she asked. “This stuff is old.”
Some see a net neutrality legal fight charting new territory. The draft order is broader than 2015’s, with issues of national security and broadband contributing to Universal Service Fund (USF), so there are several different issues than were involved in the past, said Holtz-Eakin.
While it seems likely that SCOTUS will curtail or reject the Chevron doctrine sometime this summer, that isn’t going to deter the FCC, Skorup said. But it could change how the D.C. Circuit — which upheld the 2015 net neutrality order — approaches things, he said. Given SCOTUS reversals of the D.C. Circuit on federal agency deference issues, such as 2021’s Alabama Association of Realtors decision, “I would hope the D.C. Circuit would get the message … that it needs to apply more scrutiny than it is giving agencies currently,” he said.
“The net neutrality rule will undoubtedly be characterized by the reviewing court as a major question because it is an issue of ‘vast economic and political significance,’” emailed Thomas McGarity, University of Texas’ Lozano Long Professor in Administrative Law. “That being the case, Chevron will be inapplicable,” he said: “The court will only ask whether Congress has clearly authorized the agency to promulgate the rule. The clarity of the authorization will be the primary issue on appeal.”
Other lawyers said it’s not preordained that the order will be overturned.
“It’s important to remember that the only reason why broadband is an ‘information service’ is because of Chevron deference,” said Public Knowledge Senior Vice President Harold Feld. The 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in 2003 ruled that cable modem service was a telecom service, he said. SCOTUS’ 2005 Brand X decision, then “reversed the 9th Circuit on the grounds of Chevron deference. In 2019, the 2017 order rolling back the 2015 net neutrality rules survived a challenge at the D.C. circuit only because of precedent,” Feld said.
Two of the judges, Patricia Millett and Robert Wilkins, indicated they would have found the rollback order “arbitrary … but for Chevron and Brand X. One cannot help what activist judges will do,” but if the pending order is returned to the D.C. Circuit, “I would expect it to be affirmed,” Feld added.
The Supreme Court held in Brand X that the FCC has the discretion to decide how to classify broadband, emailed Benton Institute for Broadband & Society Senior Counselor Andrew Schwartzman.
“If, as is likely, the Chevron, and Brand X precedents will be modified to some degree this spring, and depending on what the Court says, the matter might then have to be resolved by analysis of the text,” he said.
Perkins Coie’s Martin said it’s likely the D.C. Circuit could affirm the FCC’s action again, as there’s consistent precedent that agency action on the matter is OK. However, if SCOTUS overturns Chevron, the appellate court may feel compelled to come out differently, he said. And if the D.C. Circuit overturns the FCC, SCOTUS could very well deny any subsequent cert petition by the agency, he said. Schwartzman questioned whether SCOTUS will ultimately hear the case. The court is “loath to overrule precedent unless absolutely necessary,” he said.
CTIA discussed concerns about how non-broadband internet access services are treated under the draft net neutrality order circulated by Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel. In meetings with staff for all five commissioners, CTIA asked the FCC to remove warnings not present in the 2015 order. Non-BIAS services, and network slicing, have emerged as major issues. The draft “favorably references non-BIAS use cases that ‘cannot be met over the Open Internet,’ but any suggestion that an offering that can function to some extent over BIAS must be offered over BIAS would be a dramatic shift from the 2015 framework,” said a filing posted Wednesday in docket 23-320. The draft also says the commission “will closely monitor any services that have a negative effect on the performance of BIAS in any given moment or the capacity available for BIAS over time” and that the commission “will be watchful of services that do not require isolated capacity.
CTIA said, “The 2015 Order did not set forth any of these rigid warnings, and for good reason. The net effect of such guidance could restrict the offering of non-BIAS services. Customers would lose out on choice and innovation, and networks would operate less efficiently.”
References:
Link to the Draft Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration: https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401676A1.pdf
Link to the April 25, 2024 Meeting webpage: https://www.fcc.gov/april-2024-open-commission-meeting
https://www.fcc.gov/document/promoting-fast-open-and-fair-internet
https://www.reuters.com/technology/fcc-vote-restore-net-neutrality-rules-reversing-trump-2024-04-02/
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
FCC Votes to Reverse Net Neutrality & No Longer Regulate Broadband Internet Services
Internet Association to Join Law Suits to Restore Net Neutrality
Is FCC Net Neutrality Rollback Coming? Will that spark cablcos investment in rural/ suburban areas?
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=851581&id=1935719
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
Introduction:
The FCC will take a series of steps to reestablish the commission’s net neutrality framework and reclassify broadband internet access service (BIAS) as a Communications Act Title II telecom service in a 434 page declaratory ruling and order which doesn’t resolve the issue of network slicing as a paid priority 5G service.
A draft of the items to be considered during the agency’s April meeting, released Thursday, would establish “broad” and “tailored” forbearance for ISPs. “Access to broadband Internet is now an unquestionable necessity. We also exercise broad forbearance for broadband providers as part of the Title II reclassification. Since the Commission’s abdication of authority over broadband in 2017, there has been no federal oversight over this vital service. This item would reestablish the Commission’s authority to protect consumers and safeguard the fair and open Internet, which protects free expression, encourages competition and innovation, and is critical to public safety and national security.”
Network Slicing:
The draft doesn’t make a final determination on how network slicing should be treated under the rules. Network slicing, which requires a 5G SA core network, enables 5G network operators to create multiple virtual networks on top of a shared network. How slicing should be treated has been hotly contested.
“To the extent network slicing falls outside of BIAS, we will closely monitor these uses to evaluate if they are providing the functional equivalent of BIAS, being used to evade our open Internet rules, or otherwise undermining investment, innovation, competition, or end-user benefits in the Internet ecosystem,” the draft said.
“The record reflects that the potential use cases for network slicing are still under development” and that carriers “are in the early stages of adopting the technique, with some moving more quickly than others. Given the nascent nature of network slicing, we conclude that it is not appropriate at this time to make a categorical determination regarding all network slicing and the services delivered through the use of network slicing.”
Yet the document also says it agrees with NCTA “that we ‘should not allow network slicing to be used to evade [the] Open Internet rules.’”
“The FCC declined to do what either side wanted” on slicing, New Street’s Blair Levin stated in a note to investors. “While this was not the clear, decisive win the wireless providers may have hoped for, we don’t believe this or a future FCC is likely to crack down on the primary uses of network slicing, which we understand to be network management techniques that better match wireless services to specific needs in ways that increase spectrum utilization.”
“The text left me rather confused more than reassured,” Digital Progress Institute President Joel Thayer said Friday. The commission seems interested in addressing slicing case by case, he said: “This does not bode well for consumer-facing uses of slicing as that tech starts to develop.”
One implication is the FCC might crack down on slicing if the agency sees it as a form of paid prioritization of network traffic, said Jonathan Cannon, R Street Institute policy counsel-technology and innovation and former aide to FCC Commissioner Nathan Simington.
The report and order would: “Reinstate straightforward, clear rules that prohibit blocking, throttling, or engaging in paid or affiliated prioritization arrangements, and adopt certain enhancements to the transparency rule.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new FCC order would adopt “conduct-based rules” in the commission’s net neutrality framework, establishing “bright-line rules to prohibit blocking, throttling, and paid prioritization” by ISPs. An accompanying draft report and order would also reinstate a general conduct standard and establish a “multi-faceted enforcement framework.”
The draft declaratory ruling would officially reclassify broadband as a Title II service, saying the step would allow the commission to “more effectively safeguard the open internet” and establish a nationwide framework. The draft would largely adopt the commission’s 2015 rules on forbearance, making clear that the record “does not convincingly show that imposing universal service contribution requirements on BIAS is necessary at this time.”
The commission in the draft defended reclassification as a national security matter, noting it has previously taken action under Title II to address national security threats against voice services. “The nation’s communications networks are critical infrastructure, and therefore too important to leave entirely to market forces that may sometimes, but not always, align with necessary national security measures,” the item said.
The draft declaratory ruling also addresses the impact of reclassification on the commission’s universal service goals under section 254 of the Communications Act. Reclassification “will put the commission on the firmest legal ground to promote the universal service goals of section 254 by enabling the commission and states to designate BIAS-only providers” as eligible telecom carriers, the draft said, adding that BIAS-only providers would be allowed to participate in the high-cost and Lifeline programs.
The draft elaborates on the importance of reclassifying broadband to the agency’s authorities under Section 214 of the Communications Act, another issue raised by industry (see 2403070040). Reclassification “enhances the Commission’s ability to protect the nation’s communications networks from entities that pose threats to national security and law enforcement.”
“We find that reclassification will significantly bolster the Commission’s ability to carry out its statutory responsibilities to safeguard national security and law enforcement,” the draft said: “There can be no question about the importance to our national security of maintaining the integrity of our critical infrastructure, including communications networks.” It noted that Congress created the FCC “for the purpose of the national defense.”
The agency dismissed arguments that reclassification isn’t justified for national security purposes: “The nation’s communications networks are critical infrastructure, and therefore too important to leave entirely to market forces that may sometimes, but not always, align with necessary national security measures.” Arguments about potential costs “are unpersuasive given that, at this point, they represent only speculation about hypothetical costs and burdens.”
A draft order on reconsideration included with Thursday’s item said the net neutrality order would resolve four outstanding petitions for reconsideration filed against the FCC’s 2020 net neutrality remand order by Incompas, California’s Santa Clara County, Public Knowledge, and jointly several public interest groups including Common Cause. “As a procedural matter, we find that we have effectively provided the relief sought by each of the Petitions through a combination of the 2023 Open Internet NPRM and today’s actions,” the draft order said. “In light of the Commission’s actions today, we grant in large part and otherwise dismiss as moot” all four petitions for reconsideration. “We agree with the petitioners that the Commission’s analysis in the [Restoring Internet Freedom] Order and RIF Remand Order was insufficient in addressing the public safety, pole attachment, and Lifeline-related repercussions of classifying BIAS as a Title I service,” the draft said.
House Commerce Committee ranking member Frank Pallone, D-N.J., and Communications Subcommittee ranking member Doris Matsui, D-Calif., praised Rosenworcel “for moving to finalize rules that reflect reality: broadband internet service is critical infrastructure and an indispensable part of American life, and it must be treated that way.” The FCC’s move for Title II reclassification shows the commission is “recognizing this reality and asserting its rightful authority over broadband providers in order to protect this vital service and the hundreds of millions who rely on it each day,” Pallone and Matsui said. The two lawmakers “have confidence that a court reviewing this action will uphold it, just as courts have done in the past.” Sens. Ed Markey, D-Mass., and Ron Wyden, D-Ore., also lauded the proposal Thursday after earlier urging Rosenworcel to prevent loopholes in the rules.
The House Commerce GOP majority was tight-lipped after the draft’s release Thursday. Republican members tweeted Wednesday that the net neutrality proposal showed the commission “continues pushing Biden’s Broadband Takeover by imposing unnecessary heavy-handed regulations.”
References:
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401676A1.pdf
https://communicationsdaily.com/reference/2404040064?BC=bc_661167bc293cd
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=847526&id=1928175
BT Group, Ericsson and Qualcomm demo network slicing on 5G SA core network in UK
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
FCC increases broadband speed benchmark (x-satellites) to 100/20 Mbit/s
The U.S. FCC voted this week to implement a 4x increase to its “broadband” benchmark, from 25/3 Mbit/s to 100/20 Mbit/s (download/upload speeds). The Commission’s Report was issued pursuant to section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996. The FCC concluded “that advanced telecommunications capability is not being deployed in a reasonable and timely fashion based on the total number of Americans.”
Using the agency’s Broadband Data Collection deployment data for the first time rather than FCC Form 477 data, the Report shows that, as of December 2022:
• Fixed terrestrial broadband service (excluding satellite) has not been physically deployed to approximately 24 million Americans, including almost 28% of Americans in rural areas, and more than 23% of people living on Tribal lands;
• Mobile 5G-NR (ITU-R M.2150/3GPP Release 16) coverage has not been physically deployed at minimum speeds of 35/3 Mbps to roughly 9% of all Americans, to almost 36% of Americans in rural areas, and to more than 20% of people living on Tribal lands;
• 45 million Americans lack access to both 100/20 Mbps fixed service and 35/3 Mbps mobile 5G-NR service; and
• Based on the new 1 Gbps per 1,000 students and staff short-term benchmark for schools and classrooms, 74% of school districts meet this goal.
The Report also sets a 1 Gbps/500 Mbps long-term goal for broadband speeds to give stakeholders a collective goal towards which to strive – a better, faster, more robust system of communication for American consumers.
FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in a statement discussing the agency’s new 100/20 Mbit/s benchmark.
“This fix is overdue. It aligns us with pandemic legislation like the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the work of our colleagues at other agencies. It also helps us better identify the extent to which low-income neighborhoods and rural communities are underserved. And because doing big things is in our DNA, we also adopt a long-term goal of 1 Gigabit down and 500 Megabits up.”
“One more thing. The law requires that we assess how reasonable and timely the deployment of broadband is in this country.”
Don’t expect much change. As noted by Engadget, U.S. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offering speeds under the new benchmark won’t be able to call their services “broadband” on the new telecom information labels the FCC will soon begin requiring. However, ISPs and network providers are not required to hit the FCC’s new 100/20 Mbit/s speeds.
Moreover, it will not impact the NTIA’s massive $42.45 billion Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program, which already requires 100/20 Mbit/s speeds on networks receiving government subsidies.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The FCC’s definition of broadband excludes satellites at a time of frenzied investments in Internet services from space. Championed by Elon Musk’s Starlink, companies ranging from Amazon to OneWeb to Telesat are planning similar low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations for space-based Internet.
Starlink’s parent company – SpaceX – this week conducted another test of its massive Starlink rocket. That rocket is in part intended to launch Starlink’s second generation satellites.
However, the FCC has excluded such satellite efforts from most of its broadband programs. For example, it rejected Starlink’s application for government funding through its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) program.
“It is evident that fixed wireless access (FWA) offerings already compete aggressively with traditional wired broadband services, and LEO satellite-based services are poised to do the same. Accordingly, all three should be treated as robust rivals within a single ‘home Internet’ product market,” wrote the Free State Foundation, another think tank.
According to FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr, a Republican, the agency specifically excludes Starlink from its overall efforts because he thinks President Biden dislikes SpaceX chief executive Elon Musk. “The Biden Administration is choosing to prioritize its political and ideological goals at the expense of connecting Americans,” Carr alleges.
With its roughly 5,000 satellites, Starlink currently offers median speeds of around 64 Mbit/s, according to Ookla, and counts around 2.6 million customers globally.
References:
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401205A1.pdf
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401205A2.pdf
BroadbandNow Research: Best & Worst States for Broadband Access
FCC proposes 100 Mbps download as U.S. minimum broadband speed
Fiber Connect 2023: Telcos vs Cablecos; fiber symmetric speeds vs. DOCSIS 4.0?
GAO: U.S. Broadband Benchmark Speeds Too Slow; FCC Should Analyze Small Business Speed Needs
FCC Says Broadband Deployment Lacking; Redefinition (25M/3M) Has Huge Implications for AT&T, Verizon & Comcast
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)


