Uncategorized
AFNR RF exposure study shows small increase in radiation in France
France’s spectrum agency ANFR [1.] has released a study (in French) of radio frequency (RF) exposure measurements collected in the immediate vicinity of 1,000 town halls across France during 2020. ANFR was requested by the Ministry of Ecological Transition (MTE) to renew the project to measure public exposure to electromagnetic waves over more than 1,000 town hall places. This campaign ran from March to December 2020 using the national monitoring of public exposure.
Note 1. AFNR:
AFNR, France’s National frequency agency, is a public administrative establishment that was created by the French 26 July 1996 telecommunications regulation Act giving it the mission of managing the French radio spectrum

The establishment was born through the merger of two main missions:
1. Inter-ministerial spectrum management, at the time within the remit of the Telecommunications Coordination committee and the Post and Telecommunications senior management;
2. The management and control of independent radio networks previously within the remit of the French National Radiocommunications Department
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
All the results are available at www.cartoradio.fr. This project of measurements follows on from the previous ones which were held in 2014 and 2017 in the same town hall squares. The cities were chosen during the first study for their representativeness of the French population. The objective of those studies was to provide an indicator of average radiation exposure at national level. The objective of this study is to present the exposure levels obtained in 2020 and to analyze their evolution since 2014.
The results of the current campaign are directly comparable with those collected in the same 1,000 locations in 2014 and in 2017, in order to analyze the evolution of radiation over time. The latest report shows a small increase in the average RF measurement compared to the previous campaign (0.54 V/m from 0.46 V/m in 2017). This follows the slight uplift reported between 2014 and 2017 (from 0.38 V/m to 0.46 V/m).
Commenting on mobile-related radiation, the agency said that exposure linked to LTE had increased marginally, while exposure linked to 2G/3G had remained broadly stable. The study was carried out before the launch of 5G in France.
The study was released alongside two other publications, summarizing the results from other measurements carried out by ANFR teams in France. Overall, these teams collected 4,700 data points in 2020 as part of their ongoing monitoring work on radiation exposure.
Earlier this month, the agency released the findings from a recent project focused on the 26 GHz millimeter-wave (mmWave) band, collecting measurements during the 5G pilot carried out by Orange and railway company SNCF at the train station in the city of Rennes. The study found that the exposure values were significantly lower than the regulatory limit of 61 V/m set for the 26 GHz band. They ranged from 0.4 V/m to 3.2 V/m depending on the conditions of the tests, which included both realistic and extreme scenarios.
The agency has also recently published the results of nearly 300 measurements collected near Linky smart meters last year, detecting values well below the regulatory limit.
References:
https://www.anfr.fr/fileadmin/mediatheque/documents/expace/20210716-campagne-mairies-2020.pdf
https://www.anfr.fr/fileadmin/mediatheque/documents/expace/study-exposure-paris14-english.pdf
https://www.anfr.fr/en/anfr/about-us/
Dell’Oro Group: Telecom equipment market advances in 1Q-2021; Top 7 vendors control 80% of the market
Preliminary estimates from Dell’Oro Group suggests the overall telecom equipment market – Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network, SP Router & Switch – started the year on a high note, advancing 15% year-over-year (Y/Y) in the 1st quarter of 2021, reflecting positive activity in multiple segments and regions, lighter comparisons, and a weaker US Dollar (USD).
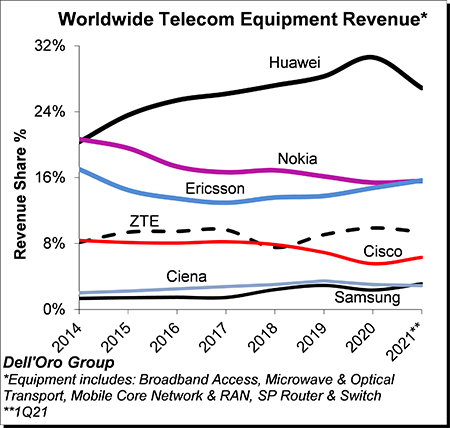
The analysis contained in these reports suggests the collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 1Q2021, with the top seven vendors comprising around ~80% of the total market. Not surprisingly, Huawei maintained its leading position. However, the gap between Nokia and Ericsson, which was around 5 percentage points back in 2015, continued to shrink and was essentially eliminated in the quarter. In addition, Samsung passed Ciena in the quarter to become the #6 supplier.
Excluding North America, we estimate Huawei’s revenue share was about 36% in the quarter, nearly the same as the combined share of Nokia, Ericsson, and ZTE.
Additional key takeaways from the 1Q2021 reporting period include:
- Following three consecutive years of growth between 2018 and 2020, preliminary readings suggest the positive momentum that characterized the overall telco market in much of 2020 extended into the first quarter, underpinned by double-digit growth on a Y/Y basis in both wireless and wireline technologies including Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, Mobile Core Network, RAN, and SP Router & Switch.
- In addition to easier comparisons due to poor market conditions in 1Q20 as a result of supply chain disruptions impacting some segments, positive developments in the North America and Asia Pacific regions, both of which recorded growth in excess of 15% Y/Y during the first quarter, helped to explain the output acceleration in the first quarter.
- Aggregate gains in the North America region were driven by double-digit expansion in Broadband Access, RAN, and SP Routers & Switch.
- The results in the quarter surprised on the upside by about 2%, underpinned by stronger than expected activity in multiple technology domains including Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, RAN, and SP Routers & Switch.
- The shift from 4G to 5G continued to accelerate at a torrid pace, impacting not just RAN investments but is also spurring operators to upgrade their core and transport networks.
- At a high level, the suppliers did not report any material impact from the ongoing supply chain shortages in the first quarter. At the same time, multiple vendors did indicate that the visibility going into the second half is more limited.
- Overall, the Dell’Oro analyst team is adjusting the aggregate forecast upward and now project the total telecom equipment market to advance 5% to 10% in 2021, up from 3% to 5% with the previous forecast.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Cisco was the top-ranked vendor for market share, followed by Huawei, Nokia, and Juniper.
- The SP Router and Switch market is forecasted to grow at a mid-single-digit rate in 2021.
- The adoption of 400 Gbps technologies is expected to drive double-digit growth for the SP Core Router market in 2021.
SiFi Networks is building 10G b/sec open access fiber networks in the U.S.
SiFi Networks is a privately owned, U.S. based company that builds and operates competitive fiber networks which service providers use to deliver first class service to their customers; internet, TV, phone and more. The company was founded in 2013 and operates using a wholesale model focused on getting carriers onboard as tenants. It is now offering 10 Gb/sec fiber access networks to U.S. operators, hoping to entice them to adopt a more European infrastructure model and sign on as tenants to its wholesale fiber network rather than building out the last mile themselves.
SiFi Networks is delivering open access fiber networks right across the US called FiberCities®, called so because fiber passes every single home and business in the city and Smart City access points are put in place as standard, developing a future proofed city for generations to come.
The company is a big advocate of dig once and only once, therefore removing costs and disruption that could be associated with future connectivity, and by operating the network independently of any end service provision it removes the requirement for others to go to the expense and disruption of building separate networks.
Earlier this month, the city of Salem, MA, signed a contract attracting over $35 million of private investment to create a citywide, fully fiber-based broadband network. The project will be privately funded by SiFi Networks, with no taxpayer subsidy. With projects like this, the company hopes to transform the U.S. broadband model by operating citywide networks that can be used by multiple service providers, mobile carriers and even the municipality itself.

SiFi president Scott Bradshaw told Fierce Telecom that SiFi has build commitments in place covering 13 cities across seven states. This will eventually yield a projected footprint of “well over” 40 million feet of fiber covering more than half a million homes and businesses, he said.
CEO Ben Bawtree-Jobson added it expects to announce several additional projects in the coming months. The CEO noted its open access network model is fairly revolutionary in the U.S. “It’s very much commonplace in other countries, in particular in Europe, but in the U.S. having last mile infrastructure that’s independently operated, that isn’t under the control of the service provider is a new model,” Bawtree-Jobson said.
Jeff Heynen, VP of broadband access and home networking at analyst firm Dell’Oro Group, explained in an email to Fierce this is primarily due to the “the legislative influence of the big telco and cable operators.” He said major incumbents like Verizon and AT&T “were able to successfully lobby legislators that they should own their networks and equipment because they bear the heavy cost of the initial deployment.” In states like North Carolina, these players even convinced lawmakers to “block the roll out of municipal fiber networks because they were argued to be unnecessary.”
While a handful of open fiber networks have sprung up in cities across the country, Heynen said, “The influence of the big carriers on legislation (local, state, and national) has limited their advance over the years.”
Bawtree-Jobson noted reactions to its offer have varied, with smaller ISPs “happy to get onto networks, share infrastructure and gain access to customers” without having to spend massive amounts in capex and opex. Incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs) are a tougher nut to crack, he said.
Bolstering its pitch, though, is SiFi’s plan to roll out 10 Gbps capabilities from day one. Bawtree-Jobson said the idea is to be “ahead of the game in terms of philosophy, thinking, concept. Ahead of the game in terms of network architecture. Ahead of the game in terms of network capability and speed as well.”
SiFi is planning to use micro-trenching for its fiber rollouts, which is expected to help accelerate its deployments. Bawtree-Jobson said depending on the size of the project, its city deployments are expected to take anywhere from two to five years to complete.
References:
https://sifinetworks.com/corporate/
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/sifi-networks-aims-to-bring-european-fiber-model-to-us
IDC forecasts $522B semiconductor market in 2021; robust growth in 5G; Samsung #1
Worldwide semiconductor revenue grew to $464 billion in 2020, an increase of 10.8% compared to 2019, according to the Semiconductor Applications Forecaster (SAF) from International Data Corporation (IDC). IDC forecasts the semiconductor market will reach $522 billion in 2021, a 12.5% year-over-year growth rate. IDC anticipates continued robust growth in consumer, computing, 5G, and automotive semiconductors.
Supply constraints will continue through 2021. While shortages initially occurred in automotive semiconductors, the impact is being felt across the board in semiconductors manufactured at older technology nodes. Much like a traffic jam and the ripple effect, a disruption on the semiconductor supply chain operating close to capacity will impact across the supply chain. The industry will continue to struggle to rebalance across different industry segments, while investment in capacity now will improve the industry’s resiliency in a few years. Looking forward to 2021, IDC sees continued strong growth in semiconductor sales worldwide as adoption of cloud technologies and demand for data and services remain unchanged. Global fiscal and monetary policy remain accommodative and will provide a tailwind for continued capital investments in long term infrastructure.
The market for semiconductors in Computing systems, such as PCs and servers, outpaced the overall semiconductor market, growing 17.3% year over year to $160 billion in 2020. “Demand for PC processors remains strong, especially in value-oriented segments,” said Shane Rau, research vice president, Computing Semiconductors. “The PC processors market looks strong through the first half and likely the whole year.” IDC forecasts Computing systems revenues will grow 7.7% to $173 billion in 2021.
Growth in Mobile Phone semiconductors was resilient in 2020. “Mobile phone shipments fell by more than ten percent in 2020, but mobile phone semiconductor revenues grew by 9.1% due to a shift to higher priced 5G semiconductors, more memory per phone, sensors, and RF support for more spectrum bands,” said Phil Solis, research director for Connectivity and Smartphone Semiconductors.
“2021 will be an especially important year for semiconductor vendors as 5G phones capture 34% of all mobile phone shipments while semiconductors for 5G phones will capture nearly two thirds of the revenue in the segment.” IDC forecasts mobile phone semiconductor revenues will grow by 23.3% in 2021 to $147 billion.
The Consumer semiconductor market segment rebounded in 2020. Robust sales of game consoles, tablets, wireless headphones and earbuds, smart watches, and OTT streaming media devices fueled segment growth by 7.7% year over year to $60 billion. “Apple, AMD, and Intel showed exceptional growth as consumers upgraded their digital spaces at home,” said Rudy Torrijos, research manager, Consumer Semiconductors. “New gaming consoles from Microsoft and Sony, continued strong sales of wearables from Apple, and the rise in smart home networks managed by Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant will accelerate growth in 2021 to 8.9% year over year.”
“Automotive sales recovered in the second half of 2020, but the supply constraints for the automotive semiconductor market for some products will last through 2021 as fires and fab shutdowns further impacted the automotive semiconductor market and it takes time for chips to move through the automotive ecosystem, specifically in the U.S. and Europe,” said Nina Turner, research manager, Automotive Semiconductors. For 2021, IDC forecasts that automotive semiconductor revenue will grow 13.6%.
“Overall, the semiconductor industry remains on track to deliver another strong year of growth as the super cycle that began at the end of 2019 strengthens this year,” said Mario Morales, program vice president, Semiconductors at IDC. “The markets remain narrowly focused on shortages across specific sectors of the supply chain, but what is more important to emphasize is how critical semiconductors are to every major system category and content growth that remains unabated.”
The IDC Worldwide Semiconductor Applications Forecaster (SAF) database serves as the basis for IDC’s semiconductor supply-side research, including our market forecasts and custom market models. This database contains revenue data collected from over 150 of the top semiconductor companies for 2015-2020 and forecasts for 2021-2025. Revenue for over twenty semiconductor device areas, five geographic regions, seven industry segments, and more than 65 end-device applications are included in the database and pivot tables.
For more information about the SAF, please contact Nina Turner at [email protected]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, IC Insights believes that Samsung will again replace Intel as the leading semiconductor producer beginning in the second quarter of this year.
Intel was the world’s top semiconductor manufacturer from 1993 through 2016. However, after nearly a quarter of a century, the semiconductor industry saw a new number-one supplier beginning in 2017 when the memory market surged and Samsung displaced Intel. This unseating marked a milestone achievement not only for Samsung, but also for all other competing semiconductor producers who had tried for years to supplant Intel as the world’s largest supplier, according to IC Insights.
Samsung held the leading semiconductor supplier spot for six quarters before the memory market collapsed in late 2018 and Intel once again became the leading IC supplier in the fourth quarter of 2018, IC Insights indicated. The memory market plunge was so steep in late 2018 and early 2019 that Samsung went from having 17% more revenue than Intel in third-quarter 2018 to having 18% less sales than Intel just two quarters later. Intel endured its own sales slump in the first quarter of 2019, although it was nowhere near the decline exhibited by the memory producers.
With the DRAM market on the rise and the NAND flash market forecast to gain momentum in the second half of the year, it appears likely that Samsung will once again position itself at the number-one semiconductor supplier for the full year 2021, IC Insights said.

References:
https://www.digitimes.com/news/a20210505PR201.html
T-Mobile 5G hype vs Craig Moffett: “We’re not in the 5G era yet”
T-Mobile US reported total revenues of $19.8 billion and service revenues of $14.2 billion in the last quarter. T-Mobile’s gain of 1.2M post-paid net additions was solidly ahead of Wall Street consensus of 1.0M, and was similar to last year’s pro forma gain of 1.3M. The company added 773K post-paid phone subscribers, dramatically better than last year’s pro-forma gain of just 104K, and blowing away consensus of 475K.
T-Mobile’s 773,000 postpaid phone customer additions during the first quarter handily beat AT&T’s 536,000 and Verizon’s loss of 178,000 customers, according to Walter Piecyk, a financial analyst at LightShed Partners. They continue to take market share. Their annual post-paid subscriber growth rate of 3.9% marks a sharp acceleration from the 2.7% growth rate reported last quarter.
T-Mobile has already migrated 20% of Sprint’s customers, and 50% of Sprint’s traffic (a doubling from
last quarter), to the much more robust T-Mobile network. The vast majority of Sprint customers
are already enjoying service benefits from access (even with legacy handsets) to T-Mobile’s
lower frequency spectrum bands.
T-Mobile: America’s Largest, Fastest and Most Reliable 5G Network Extends its Lead
- Extended Range 5G covers 295 million people across 1.6 million square miles, 4x more than Verizon and 2x more than AT&T
- Ultra Capacity 5G covers 140 million people and on track to cover 200 million people nationwide by the end of 2021
- Majority of independent third-party network benchmarking reports show T-Mobile as the clear leader in 5G speed and availability
- Network perception catching up to reality with a nearly 120 percent increase in consumers who view T-Mobile as “The 5G Company” since Q3 2019

Image Credit: T-Mobile
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On the company’s earnings call, T-Mobile US CEO Mike Sievert said that “discerning customers” are choosing T-Mobile’s new Magenta Max pricing plan, which offers few limits in the amount of 5G data that customers can consume. T-Mobile’s new Magenta Max customers consume 40% more data than its other 5G customers, and fully 70% more data than T-Mobile’s average 4G LTE customers.
“The take rate has just been amazing,” T-Mobile CFO Peter Osvaldik said of Magenta Max. “There are premium customers that are attracted to this premium network.”
“We’ve never been able to outrun the insatiable demand that customers have,” Sievert said of Internet service providers in general. “So when you provide the industry’s only true, unlimited plan, they do what they do, they use it up.”
According to Sievert, that indicates that T-Mobile’s 5G network will be a big winner. “We’re really starting to pull away from the pack. T-Mobile is positioned to maintain our 5G leadership for the duration of the 5G era.”
In a great example of braggadocio, Sievert said:
“We have again demonstrated that our unique winning formula and balanced approach enables us to grow share while delivering strong financial results. In our increasingly connected world, we recognize our role as stewards of this profitable company and industry, while continuing to use our Un-carrier DNA to bring change to wireless and broadband alike, to disrupt the status quo and ultimately benefit customers. And this quarter was no exception.”
T-Mobile said it now covers fully 140 million people with its 2.5GHz network, which it calls “ultra capacity.” By the end of this year, the company said that number will increase to 200 million people. Meantime, speeds available on that network will rise from an average of 300 Mbit/s today to up to 400 Mbit/s by the end of this year, the operator said. 5G speeds will continue to rise after that, according to T-Mobile’s network chief Neville Ray. “2022 is going to be even better,” he said.
Analyst Craig Moffett (who participated in the earnings call) put somewhat of a damper on all that 5G hype by stating: “But we’re not in the 5G era yet. We’re not even a year into the first generation of 5G iPhones. Less than 10% of Americans have 5G-enabled phones, and half of those probably only got a new phone because they needed a replacement. 5G isn’t really driving handset selection, or service provider selection, yet.”
“That T-Mobile continues to take share even in the twilight of the LTE era is reassuring. In a world of roughly comparable networks, they are competing on the basis of price alone… and they are taking share rapidly. In 5G, they will compete not only on the basis of the industry’s lowest prices, but also the industry’s best network. As we’ve said before, T-Mobile’s ‘worst to first’ story is a generational one. Networks don’t achieve advantage overnight, and they don’t lose it overnight, either. Ten and twenty-year cycles in telecom aren’t unusual.”
“T-Mobile’s brand, and its network, have been ascendant for years. But they have, up to now, achieved only parity. Their path to network superiority is potentially even longer, and, we suspect, even brighter.”
T-Mobile continues to increase market share even in the twilight of the LTE era is reassuring. In a
world of roughly comparable networks, they are competing on the basis of price alone… and they
are taking share rapidly. In 5G, they will compete not only on the basis of the industry’s lowest prices, but also the industry’s best network.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/t-mobile-reports-strong-first-quarter-2021-results
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/does-5g-make-difference-t-mobile-says-yes/d/d-id/769256?
Verizon Explores Sale of Media Assets; Wake up Call for AT&T?
According to the Wall Street Journal, Verizon Communications is exploring a sale of its media assets including Yahoo and AOL, as the telecommunications giant looks to exit an expensive and unsuccessful bet on digital media. The sales process, which includes private-equity firm Apollo Global Management Inc. (which owns Cox Media Group) could lead to a deal worth $4 billion to $5 billion, according to people familiar with the matter—assuming there is one.
Verizon splashed out billions of dollars assembling a portfolio of once-dominant websites, including AOL and Yahoo. Verizon bought AOL in 2015, and Yahoo in 2017. It then merged them into a new venture called Oath, paying more than $9 billion in total to acquire the pair. So the rumored sale would be a huge loss for Verizon, based on what it paid for those two media outlets.
The digital-media business ultimately failed to reach its target of $10 billion in annual revenue by 2020, and Verizon in 2018 wrote down about $4.5 billion of its value. Verizon has cut jobs in the unit, and in November agreed to sell its HuffPost news division to BuzzFeed Inc. That followed a 2019 agreement to sell the Tumblr blogging platform for a nominal sum to the owner of WordPress.
Verizon’s media business, which also includes Yahoo Finance and Yahoo Mail (used by AT&T-Yahoo Internet subscribers) as well as news sites TechCrunch and Engadget, generated $7 billion of revenue in 2020, down 5.6% from the previous year due to a sharp advertising pullback during the early months of the coronavirus pandemic. Business picked up in the second half and the unit has logged two consecutive quarters of double-digit growth, including a boost of 10%, to $1.9 billion, in the first quarter.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
SIDEBAR — Message to AT&T:
If the Verizon media sales go through, it should send a clear message to AT&T, which went heavily into debt when it purchased Time Warner (and to a lesser extent DirecTV). AT&T has already spun off off its TV assets. AT&T agreed to create a new company for its U.S. video business unit together with private equity firm TPG Capital. The company will be called New DirecTV and include: today’s Direct TV, U-verse TV and AT&T TV (AT&T’s OTT video service). Closing the TV units “sale” will reduce their observed rate of decline. In the most recent quarter, video revenue shrank by 9.2%. That hemorrhage will stop once the video sale is complete. Next stop is for AT&T to sell or spin off Time Warner to reduce it’s debt load.
It’s incomprehensible to this author, that AT&T’s wireline Internet subscribers (actually AT&T-Yahoo Internet) are dependent on Yahoo support for email and any other content issues, including log-in. When you click on https://att.net you are redirected to https://currently.att.yahoo.com/. Since the 2017 Verizon acquisition of Yahoo, there is no tech support from AT&T on any email or content issues you might have with your AT&T-Yahoo internet account. AT&T will only troubleshoot wireline connectivity issues- NOT email or internet content problems its subscribers might experience.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
By selling now, Verizon could raise needed cash at a time when valuations of similar assets are enjoying an upswing. The company this year committed about $53 billion to secure spectrum licenses that will support its ultrafast fifth-generation wireless network.
Indeed, Verizon was by far the biggest spender in January’s record-breaking FCC C-Band spectrum auction. The carrier bid nearly $45.5B, well ahead of still-heavy spending AT&T which paid $23.4B for that spectrum. Of course, there are huge additional build-out costs to actually deploy 5G over C-Band spectrum!
Verizon executives recently told investors that capital spending (CAPEX) this year on network equipment, fiber optic cables and the like could reach up to $21.5 billion.
Verizon has focused much of its recent attention lately on partnerships with streaming-video services like Disney+ and Hulu that can be bundled with its wireless and home-Internet plans.
Analyst Craig Moffett recently wrote in a note to clients:
“Verizon has, until now, taken a “wait-it-out” stance, perhaps out of confidence that AT&T’s (cellular network) promotional stance had to be transitory. Verizon’s short term results have suffered during this wait-it-out period; subscriber results have been weak.
Faced with AT&T’s ongoing retention marketing promotion, Verizon faces a lose-lose choice: either continue to lose subscribers (and face something still worse, when 5G comes around), or respond and their subscriber growth will recover, but their profitability will decline. There are no good options.
With longer term concerns about competitive positioning in 5G looming ever closer, we are
downgrading Verizon to Neutral.”
References:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/verizon-explores-sale-of-media-assets-11619642003
AT&T reports strong wireless growth in 1Q 2021; C Band ? Fiber footprint increases
AT&T reported strong wireless subscriber growth today. The company recorded $19.0 billion in mobility revenue, up 9.4% from a year earlier. While service revenue grew just 0.6%, with subscriber gains largely offset by continued pressure on international roaming amid the pandemic, AT&T’s equipment revenue rose 45.2% as AT&T benefited from a greater mix of higher priced smartphones. The latest results also benefitted from comparisons to those from a year-ago period that saw temporary store closures due to the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis.
The telecom/media recorded to 595,000 postpaid phone net additions for the quarter and a postpaid phone churn rate of 0.76%, which was down from 0.86% a year prior. Of the major wireless companies in the U.S., AT&T has been the most focused since the latest iPhone launch on offering promotions meant to drive upgrades from existing customers, rather than mostly targeting customers who would be switching from another carrier.
Impressively, AT&T added 235,000 AT&T Fiber customers in the 1st quarter of 2021, up from 209,000 in the year-ago period. Fiber penetration rose to 35% from 30% in Q1 2020.
During an earnings call, AT&T CEO John Stankey said the company added a total of more than 1 million fiber subscribers over the last four quarters, and was on track to build out fiber to 3 million consumer and business customer locations in 2021. He previously said AT&T was aiming to roll out fiber to 2 million new residential customers this year.
Reflecting on its progress thus far, Stankey said, “I like what I see in terms of our market position. If you look at things like lives, churn, customer satisfaction and net promoter scores and the actual performance of the product, they’re all great…I’ve not seen share movement on typical products like this as rapidly as we’re able to get share movement once we deploy an area.”
“We continued to excel in growing customer relationships in our market focus areas of mobility, fiber, and HBO Max,” said CEO John Stankey. “We had another strong quarter of postpaid phone net adds, higher gross adds, lower churn, and good growth in Mobility EBITDA.” AT&T posted 2.7 million total domestic HBO Max and HBO subscriber net adds, bringing total domestic subscribers to 44.2 million.
AT&T said it expects to spend $6 to $8 billion between 2022 and 2024 to deliver 5G services over its own midband C-band spectrum licenses. The company expects to cover up to 100 million people in “early” 2023, but that target generally trails the buildout plans of Verizon and T-Mobile.
“Global supply chains are stressed right now across the board. You ask the question, can you do the work? And people will give you comfortable answers,” Stankey said in response to questions about plans for C-band, timing and increased capex on AT&T’s first quarter earnings call.
“But I’m a little skittish,” Stankey acknowledged. “We’re seeing dynamics that are occurring in the global supply chain where unexpected things are popping up. And is it possible we could see certain element shortages that start to crop up as everybody’s racing to put stuff up on towers? It may.”
Stankey said that’s part of why he’s cautious about increasing guidance or making changes to C-band plans until there is a little momentum happening.
Likely as a result, Stankey expressed interest in purchasing additional midband spectrum licenses later this year during the FCC’s 3.45-3.55GHz spectrum auction. “I believe there could be an opportunity there,” he said.

Business Wireline, which accounts for 14% of AT&T’s consolidated revenues, saw weak results. This has historically been a highly cyclical business. Total Business Wireline revenue was $6.0B, down 3.5% YoY, a bit better than last quarter’s 4.1% decline. That result was considerably weaker than the expectation of a 3.5% decline.
As with peers, AT&T’s Business Wireline business has held up better than we would have expected during the COVID recession. Verizon noted last quarter that their own Business Wireline segment has been boosted by explosive growth in Public Sector revenues, driven in large measure by schools adjusting to the demands of remote learning, and they indicated that they expected some mean reversion. Perhaps, the CARES Act, which provides a huge amount of subsidy for schools and local governments, will soften (or even reverse) that blow.
AT&T Communications CEO Jeff McElfresh said that AT&T is “supportive” of President Joe Biden proposed infrastructure plan, which sets out to bring high-speed broadband to rural America, and that the company is “encouraging the government to do this in a smart way.” He argued that efforts to expand broadband access are “generally more impressive when you have scale backing the implementation” and that private-public partnerships, as well as collaboration within the telecommunications industry, can help drive success.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analyst Comments:
“AT&T appears to be ceding the field in wireless with a network plan that doesn’t even attempt to close the gap with T-Mobile and Verizon,” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to clients released shortly after AT&T disclosed its first quarter financial results. “As with results today, for a little longer AT&T may be able to stem the tide of losses through continued aggressive promotions and retention offers, but this can only go so long given other costly priorities (a massive investment in HBO, a doubling of the fiber footprint) amidst generally constrained resources. Moreover, if they allow the network gap to widen too far, they may not be able to keep subs at any price (as was the case with Sprint in later years).”
“AT&T is investing in mobile and HBO Max, as it promised, and at great cost,” wrote the financial analysts at Sanford C. Bernstein & Co. in a note to investors. “The problem is, there are not enough investment dollars to go around. We believe the share price fairly reflects the highly uncertain outlook, and we are watching … as the competitive environment evolves.”
Craig Moffett of MoffetNatanson wrote: “The broadband business requires big capital investments up front for gradual and steady returns later… but the payback period even for good investments is as much as ten years…. The C-Band auction was just the beginning. Verizon has already committed to an additional $10B of capex over the next three years, and Verizon was, by all accounts, far ahead of AT&T already in small cell densification. And what of their costly handset giveaways? Can they be sustained?”
“The problem, as ever, is s AT&T’s debt load. To maintain any pretense that they will be able to pay down debt and service their $15B per year dividend, they need to sustain free cash flow at current levels, or grow it even. But service revenue is still declining, and, despite solid cost controls in Q1, EBITDA is still declining as well (down 4.7% YoY).”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Performance analysis of big 3 U.S. mobile operators; 5G is disappointing customers
Speedtest Intelligence® from Ookla reveals T-Mobile was the fastest mobile operator in the United States during Q1 2021 with a Speed Score™ of 50.21 on modern chipsets. AT&T was second and Verizon Wireless third.
Note that this is the first quarter Ookla is reporting on the country as a whole, rather than using competitive geographies. Ookla says that expanding its focus to include rural areas will show drops in performance, decreasing speed and increasing latency when compared with prior reports.
In Q1 2021, T-Mobile had the fastest median 5G network download speed in the U.S. at 82.35 Mbps. AT&T was second at 76.60 Mbps and Verizon Wireless third at 67.24 Mbps. For a complete view of commercially available 5G deployments in the U.S. to-date, visit the Ookla 5G Map™.
Ookla discovered that during Q1 2021 that T-Mobile subscribers with 5G-capable devices were connected to a 5G service 65.4% of the time. 5G “time spent” on Verizon Wireless’ network was at 36.2% and at 31% on AT&T’s network.
In measuring each operator’s ability to provide consistent speeds, Ookla found that T-Mobile had the highest Consistency Score™ in the U.S. during Q1 2021, with 84.8% of results showing at least 5 Mbps download and 1 Mbps upload speeds. AT&T was second and Verizon Wireless third. All three U.S. mobile carriers were above 80% in terms of consistency.
Here’s the current status of Worldwide median 5G Speeds as of Q3-2022:

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Earlier this week a new report from becnhmarking company Rootmetrics found that T-Mobile US is leading in 5G availability across U.S. cities. Rootmetrics found that AT&T’s 5G provides the best performance, and AT&T and Verizon both won high marks for 5G reliability.
“While we’ve seen strong and improving 5G availability and speeds from the carriers in many cities, it’s important to keep in mind that with the major U.S. networks utilizing different types of spectrum for 5G, the 5G availability and speeds that consumers experience can vary a great deal for different carriers across or even within different markets,” Rootmetrics concluded.
Rootmetrics tested 5G networks in 45 cities across the U.S. between January and March of this year. It recorded at least some 5G availability from all three carriers in nearly all of them. T-Mobile US was the only carrier with a 5G network presence in all 45 of the cities, AT&T had 5G service in 44 out of the 45, and Rootmetrics saw 5G availability for Verizon in 43 out of the 45 cities.
The availability of T-Mobile’s 5G was one common theme across both testing reports. Rootmetrics’ testing, conducted in the first half of 2021, said that T-Mobile had 5G availability in all 45 of the markets it tested and showed the highest percentages of 5G availability in the most markets: More than 55% availability in 30 markets, with the lowest tested market being Sarasota, FL, where Rootmetrics’ testing showed T-Mo 5G available for a device to connect to only about 19% of the time.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Light Reading’s Mike Dano writes that “AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile offer unlimited 5G disappointment.” In a subhead titled, “T-Muddle” Dano writes:
In 2019, T-Mobile boasted that “5G speed will be up to 10x faster, compared to LTE.” But when it first launched its 5G network on its lowband 600MHz spectrum, speeds were only 20% faster than its LTE network. Then, after T-Mobile closed its acquisition of Sprint’s 2.5GHz midband spectrum, it quickly began offering 5G speeds up to 1Gbit/s. The operator even debuted a new 5G lexicon for its offerings: “5G Ultra Capacity” refers to its speedy 2.5GHz network, while “Extended Range 5G” refers to its slower 600MHz network.
So it would stand to reason that customers might want to see which flavor of T-Mobile 5G they can access, right? A quick check of T-Mobile’s coverage map reveals none of these details. The operator only offers a generic “5G” coverage layer that does not provide details about whether it’s 600MHz or 2.5GHz. One is slightly faster than LTE while the other provides average speeds of 300Mbit/s. Prospective T-Mobile customers are left in the dark.
T-Mobile isn’t the only operator seemingly content to hide behind 5G obfuscation. AT&T has debuted no fewer than three different 5G brands – 5G+, 5Ge and 5G – yet it does not offer any details to prospective customers about how it might charge for those offerings. The operator’s pricing plans mention only “5G” and do not specify whether that means 5G+, 5Ge or 5G, or all three.
Regarding Verizon’s 5G pricing plans, Dano stated:
The operator offers a truly dizzying array of 5G plans and pricing options – one observer described Verizon’s pricing plans as “a series of nesting dolls.”
In 5G, Verizon is reserving its faster “Ultra Wideband” technology only for its expensive unlimited plans. Customers on its cheapest Start Unlimited plan can either pay $10 extra for 5G specifically, or they can spend that same $10 to upgrade to a more expensive unlimited plan that offers 5G as well as other goodies, such as more mobile hotspot data. Why the two different upgrade options? “We always like to give customers choices,” explained a Verizon spokesperson.
But what that really means is that customers are simply left to fend for themselves. They’re left to pick from among a dizzying number of pricing options, all promising “unlimited” data, but all limiting that data in various ways. Customers are left to figure out why messages from iPhones to Android phones won’t show delivery receipts. They’re left to discover why they’re still receiving robocalls, and what they might need to do to block them. They’re left to uncover what kind of 5G they can get and whether it’s any different from 4G.
In conclusion, Dano says that “AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile continue to be very interested in outdoing one another in their 5G pricing schemes and big, new network claims.” However, they’re not succeeding in pleasing their customers who remain frustrated and disappointed.
Cartoon courtesy of long time IEEE contributor Geoff Thompson:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.speedtest.net/global-index/united-states#market-analysis
https://rootmetrics.com/en-US/content/5g-in-the-us-1H-2021
Starlink now covers all of UK; Plans to connect vehicles with satellite Internet service
Starlink has expanded to all regions of the United Kingdom. The SpaceX owned company’s satellite Internet service is still in beta and was previously available in only the southern England part of the UK. Today, the company announced an expansion to cover parts of Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and northern England. Starlink says users should currently expect data speeds to vary between 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s over the next several months, with brief periods of no connectivity whatsoever.
Starlink’s Email:
Starlink is now available in parts of Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and northern England, in addition to existing service areas in southern England.
During beta, users can expect to see data speeds vary from 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s over the next several months as we enhance the Starlink system. There will also be brief periods of no connectivity at all.
As we launch more satellites, install more ground stations and improve our networking software, data speed, latency and uptime will improve dramatically.
To check availability for your location, visit starlink.com and re-enter your service address. If Starlink is not yet available in your area, you can place a deposit to hold your space in line for future service.
The UK’s average download speed across all broadband providers is around 67.23Mb/s, but climbing as the rollout of full-fiber starts picking up pace again following a pandemic-induced slowdown.
Starlink wants to quickly deliver decent broadband connectivity to rural locations which have been left underserved due to the difficulties and cost of laying traditional fiber.
“This will transform rural WiFi,” says Compare Fibre’s co-founder Nathan Hill-Haimes. “We are really keen to stress the impact this can have on connecting rural locations with high-speed internet.”
A Starlink user from Devon told the Press Association: “If you need connectivity to run a business and if you need connectivity for communication, particularly in Covid times, £90 a month is quite justifiable.”

Starlink was issued a UK “Earth station network license” in November, an Ofcom spokesperson told CNBC. The £200 ($272) a year license allows Starlink to sell satellite dishes and other communications equipment in the U.K. so that people can pick up signals emitted by Starlink’s network of satellites.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, SpaceX wants to begin connecting large vehicles – from trucks to jets to ships – to its Starlink satellite Internet network, according to a request the company filed with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
“This application would serve the public interest by authorizing a new class of ground-based components for SpaceX’s satellite system that will expand the range of broadband capabilities available to moving vehicles throughout the United States and to moving vessels and aircraft worldwide,” SpaceX director of satellite policy David Goldman wrote in a letter to the FCC filed on Friday.
Starlink is the company’s capital-intensive project to build an interconnected internet network with thousands of satellites, known in the space industry as a constellation, designed to deliver high-speed internet to consumers anywhere on the planet.
To date SpaceX has launched more than 1,100 satellites for Starlink. In October, SpaceX began rolling out early service in a public beta to customers in the U.S., Canada and the U.K., with service priced at $99 a month. Additionally, in a late January update, SpaceX told the FCC that its Starlink beta now has more than 10,000 users.
The Starlink service also includes a $499 upfront cost for the hardware needed to connect to the network. Known as the Starlink Kit, it includes a user terminal (the small, dish-like antenna) and a Wi-Fi router.
SpaceX did not indicate in its filing Friday whether the Starlink user terminals for moving vehicles will have a different design than the dishes currently being shipped to early customers. But SpaceX said each “ESIM,” or Earth Station In Motion, is “electrically identical to its previously authorized consumer user terminals,” with added “mountings that allow them to be installed on vehicles, vessels and aircraft.”
The company also noted that it “will ensure installation” of the vehicle terminals through “qualified installers.” While SpaceX did not say whether those installers would be company employees, it continues to expand Starlink manufacturing and operations – including plans for a new equipment factory in Austin, Texas.
Over 1,000 Starlink satellites are currently in orbit of the total 12,000 satellites which have been authorized. Filings have been submitted to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) requesting permission to launch 30,000 additional Starlink satellites.
Increasing competition:
Starlink is, by far, the biggest satellite broadband deployment. However, rivals such as Amazon’s “Project Kuiper” will be looking to challenge the titleholder in the coming years.
Project Kuiper was given the green light by the FCC last year to launch 3,236 of its own satellites.
“We are doing an incredible amount of invention to deliver fast, reliable broadband at a price that makes sense for customers,” Rajeev Badyal, Vice President of Technology for Project Kuiper, said at the time.
SpaceX is currently launching around 60 satellites at a time and aims to have deployed 1,440 by late 2021 to provide near-global service.
“As we launch more satellites, install more ground stations and improve our networking software, data speed, latency and uptime will improve dramatically,” the company wrote in a release announcing Starlink’s expansion in the UK.
Starlink and Kuiper will also be competing against promising satellite broadband firm OneWeb.
OneWeb nearly collapsed after crucial funding was pulled last-minute during the first peak of the COVID-19 pandemic and filed Chapter 11 bankruptcy. However, the company was rescued following a $1bn (£800m) investment from the UK government and Bharti Global Ltd of India.
Kwasi Kwarteng, Secretary of State for Business, Energy, and Industrial Strategy, said: “Our investment in OneWeb is part of our continued commitment to the UK’s space sector, putting Britain at the forefront of the latest technological advances.”
Since the UK and Bharti’s investment, OneWeb has continued to receive large investments. In January, the company announced that it has raised $1.4 billion in total funding after securing investments from SoftBank Group and Hughes Network Systems.
Masayoshi Son, Chairman and CEO of SoftBank, commented: “We are excited to support OneWeb as it increases capacity and accelerates towards commercialization. We are thrilled to continue our partnership with Bharti, the UK government, and Hughes to help OneWeb deliver on its mission to transform internet access around the world.”
OneWeb is the smallest of the three satellite broadband firms but has launched 74 of its innovative ultrafast broadband satellites to date and plans to launch a total of 648 by the end of 2021.
Neil Masterson, CEO of OneWeb, said: “OneWeb’s mission is to connect everyone, everywhere. We have made rapid progress to re-start the business since emerging from Chapter 11 in November.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Assessment of COVID-19 impact on telecom industry; C-Band Spectrum Update
COVID-19 Impact on Telcos:
Source: Analysys Mason

The telecommunications industry has suffered limited damage as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Revenue figures for most network operators have fallen slightly, but few have encountered anything that is particularly severe or long-lasting. As a result, few telcos have made significant changes to their strategy.
However, some aspects of the telecoms sector have been significantly affected by the pandemic. The most obvious is business services; revenue in this segment declined sharply for most operators in 2020 and prospects for 2021 are uncertain. Operators may have to rethink important parts of their strategies related to these aspects.
The telecoms industry has been affected by the pandemic in many different ways, and have been grouped these into three main categories depicted in the figure below:
Summary of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the telecoms industry

Assumptions of a stable economy and a continuation of existing service and technology trends often underpin an operator’s strategic plan. For some of the services offered by operators, business services in particular, these assumptions look outdated and may need a rethink.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
C-Band Auction Update:
Source: MoffettNathanson Research
Heading into the FCC’s C-Band auction, Wall Street analysts saw Verizon as the leading bidder for 5G wireless radio spectrum. Bidding for licensed spectrum in the telecom industry’s most expensive auction ever reached more than $75 billion on Monday amid speculation over how much each of the big wireless telcos and cable companies have paid.
In a note to clients, analyst/colleague Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson is assuming that Verizon will end up being the largest buyer at the ongoing auction of mid-band spectrum targeted for new 5G deployments. As a result, Verizon’s balance sheet will be more heavily burdened and more of their future cash flows will be diverted to debt service so their future profits will be lower.
AT&T, on the other hand, will “be disadvantaged for a generation” if they don’t get a significant chunk of the mid-band spectrum being auctioned. Craig believes that AT&T was probably “one of the two big bidders that more or less backed away after round 24 or round 38.”
An important issue is “whether “winners” in this auction acquired reasonably uniform contiguous blocks, or whether they instead (worst case scenario) ended up with a patchwork of licenses and a hefty bill to burden the balance sheet. If so, will their footprints be largely erased by subsequent topping bids from others.”
With respect to using the purchased mid-band spectrum for accelerated 5G deployments, Craig wrote: “At best, the huge sums paid here for spectrum risk displacing the capital investment needed to put the acquired spectrum to use. At worst, they risk financially destabilizing one or more players.”
In conclusion, Craig asks if the large amounts of money being spent for an asset (licensed mid-band spectrum) that is best thought of as simply maintaining the status quo will be worth the price paid? “Again, the most important question is this: is anyone going to change their revenue forecast just because the industry had to spend twice as much as expected to buy spectrum for 5G.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Mid-band Spectrum for 5G: FCC C-Band Auction at $70B Shattering Records



