Uncategorized
ITU Virtual Digital World SME Awards for Connectivity, Smart Cities, e-Health, Digital Finance
- Connectivity – new approaches to increasing universal access to the internet
- Smart cities, smart living – improving urban life in areas such as energy, transport, planning, education
- E-health – improve healthcare through remote diagnosis and treatment
- Digital finance – increase access to the digital economy for the banked and unbanked
From very small satellite-powered remote IoT sensors to mobile finance for smallholder farmers, navigational platforms for smart public transit or portable electrocardiograms for remote diagnosis and much, much more, this virtual edition of the ITU Digital World Awards – open to all small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) worldwide – celebrated creativity and innovation in digital solutions meeting real-world needs.
- Astrome from India, using millimetre wave wireless communication to provide fibre-like backhaul capacity for 4G and 5G infrastructure, in the Connectivity category;
- BusMap from Viet Nam, providing smart public transit solutions through navigation algorithms and advanced user experience features for consumers, corporates and governments in the Smart cities, smart living category;
- Appy Saude from Angola, for their e-health platform identifying the nearest pharmacy location, best price and availability of medicines, in the E-health category;
- OKO Finance from Israel, providing smallholder farmers with crop insurance and access to digital financial tools through simple mobile technologies, in the Digital finance category.
Millimeter Wave Market Projected to reach 7.38B by 2027; 37% CAGR
The global telecom millimeter wave technology market size is projected to reach USD 7.38 billion by 2027, registering a CAGR of 37.01%.
Millimeter Waves (MMW) can transmit a large amount of data efficiently, operating in the electromagnetic spectrum of 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Millimeter waves are also known as Extremely High-Frequency (EHF) waves owing to its operational frequency spectrum. The property of transmitting a large amount of data has made the technology popular across the telecommunication application.
The MMW technology industry is prominently dependent on the applications in various verticals where it is used extensively. Major application areas include telecommunication, military and defense, security services, and medical and healthcare. Evolution of 5G technology is likely to occur over the coming years on account of recent developments and continuous research and progress in the telecom industry.
Millimeter waves are anticipated to play a vital role in the development of 5G technology on account of the technology’s demand for higher-bandwidth. The 5G technology is predicted to emerge in the coming years and the market is likely to witness its adoption significantly. Eventually, the demand for MMW technology is expected to boost, in turn, propelling the overall MMW technology market, particularly across the telecom industry.
Increased government funding and initiatives coupled with intensive R&D carried out from the military and private sectors are leading towards the improvement of the MMW technology. In addition, the E-band frequency segment having extensive application in the telecommunication sector is estimated to generate the highest revenue. The E-band frequency segment is projected to keep on dominating in the telecom industry owing to the growing telecom applications. Therefore, the overall telecom millimeter wave technology market is poised to witness significant growth worldwide over the forecast period at a notable pace.
Telecom Millimeter Wave Technology Market Report Highlights:
- North America accounted for the largest market share in the telecom MMW technology market owing to the technology’s early and greater adoption rate
- U.S. being the highest revenue generating country in 2019 in North America, the regional market is predicted to exhibit steady growth over the forecast period
- E-band frequency segment is anticipated to grow rapidly over the estimated duration owing to its extensive adoption in the telecom applications
- The telecom industry in the Asia Pacific is poised to expand substantially over the coming years, and the E-band frequency segment is likely to witness lucrative opportunity in the regional telecom industry
- Besides, growing urbanization in the Asia Pacific region and competition amongst the telecom service providers to offer superior quality of internet and other related services in order to enlarge customer base is another factor expected to drive the telecom MMW technology market
- Online streaming of high-quality videos, online gaming, and other entertainment stuff which demand high bandwidth and consume heavy data are again likely to fuel the overall demand for MMW technology in the telecom sector globally.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) communication systems have attracted significant interest regarding meeting the capacity requirements of the future 5G network. The mmWave systems have frequency ranges in between 30 and 300 GHz where a total of around 250 GHz bandwidths are available. Although the available bandwidth of mmWave frequencies is promising, the propagation characteristics are significantly different from microwave frequency bands in terms of path loss, diffraction and blockage, rain attenuation, atmospheric absorption, and foliage loss behaviors. In general, the overall loss of mmWave systems is significantly larger than that of microwave systems for a point-to-point link.
Fortunately, the small wavelengths of mmWave frequencies enable large numbers of antenna elements to be deployed in the same form factor thereby providing high spatial processing gains that can theoretically compensate for at least the isotropic path loss. Nevertheless, as mmWave systems are equipped with several antennas, a number of computation and implementation challenges arise to maintain the anticipated performance gain of mmWave systems. Toward this end, this chapter discusses key enabling techniques of the mmWave based 5G network from the link level perspective. The link level performance of the mmWave wireless system depends on a number of factors, including the transmission scheme (i.e., whether we employ beamforming, multiplexing, or both), the approach to identifying the channel, how to design the transmitted signal waveform structure and access strategies.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/millimeter-wave
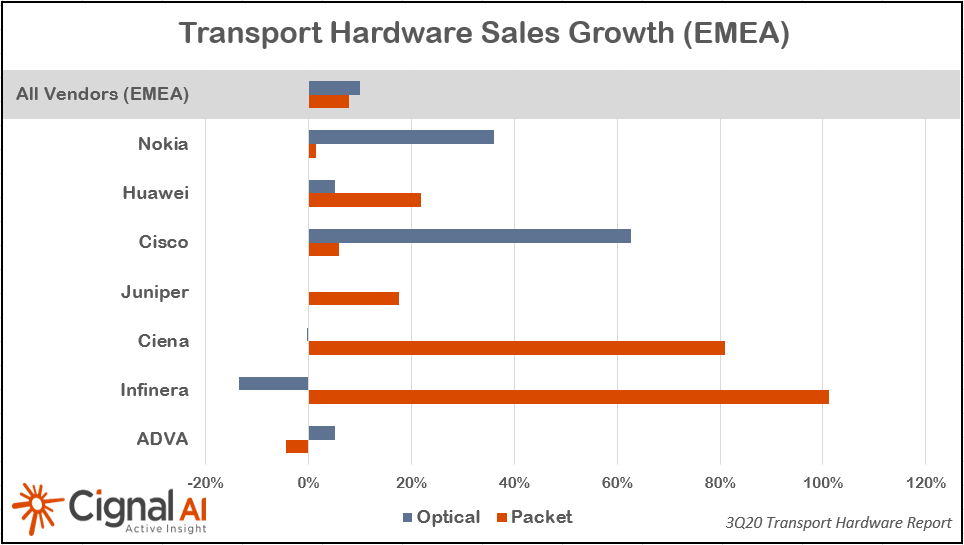
Dell’Oro and Cignal AI: Optical Transport Equipment Market Grows in 3Q 2020
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, the optical transport equipment revenue increased 9 percent year-over-year in 3Q 2020 reaching $3.8 billion. The market growth was largely attributed to higher demand in Asia Pacific.
“Sales slowed in North America following a strong first half of the year,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “Whether it was due to network demand caused by people working and studying from home or new projects at the beginning of the year, the demand for optical equipment in the region rose 11 percent in the first half of 2020. But I think there was enough concern surrounding the longevity of the pandemic that service providers grew cautious and refrained from overextending their capital. As a result, optical revenue in North America declined 7 percent in the third quarter,” continued Yu.
Growth in Asia Pacific more than offset the lower revenue in North America and Latin America. Optical revenue grew 22 percent year-over-year in Asia Pacific, driven largely by higher deployments in China and Japan. Also, with lockdown restrictions easing, some regions such as Middle East and Africa (MEA), significantly rebounded in the quarter following a sharp decline in 1H 2020. Sales in China, Japan, and MEA each grew over 25 percent.
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments (by speed including 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps, and 800 Gbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), optical switch, optical packet platforms, data center interconnect (metro and long haul), and disaggregated WDM. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit https://www.delloro.com
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
|
|||
 |
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
About the Transport Hardware Report
About Cignal AI
|
Huawei and Cambridge Wireless plan private 5G testbed in Cambridge, UK
Huawei and Cambridge Wireless have partnered to deploy and build a private 5G testbed at the Cambridge Science Park. This marks the start of a 3-year partnership which will include digital training, joint events and business support.
This will be the UK city’s first 5G mobile private network, and will support companies with the R&D and application of new digital technologies in areas such as remote surgery, autonomous vehicles and clean energy. The 5G testbed will go live in January 2021. Owned by Cambridge University, the Cambridge Science Park currently has over 120 technology companies and scale-ups.
“We are constantly working to provide value to CW members,” said Simon Mead, CEO of Cambridge Wireless. “As home to one of the world’s most advanced R&D ecosystems, Cambridge is perfectly positioned for the rollout of next-generation wireless technology and we’re delighted to be driving this initiative with our partners.
“We hope to bring something unique to the Science Park to accelerate use cases and development of this technology. We invite ambitious businesses to get involved, and through this exciting 3-year partnership with Huawei, we will support their 5G innovation journey.”
Victor Zhang, vice-president at Huawei, commented: “Huawei’s success is built on a relentless drive for innovation and we are able to keep pushing the boundaries of technology when we partner with those who share this ambition.
“The Cambridge eco-system is recognised as a global leader in technology, and we are excited to work with the talent and vision in this eco-system. We hope to enable Cambridge Wireless members to reach new heights by allowing them access to our state-of-the-art equipment and markets, including China and beyond.
“Our commitment to the UK and industry remains as strong as ever and we will continue to offer our expertise and technology to our partners to promote connections and innovation.”

To find out more and how to get involved, please contact:
Abhi Naha CCO CW (Cambridge Wireless)
Tel: +44(0)1223 967 101 | Mob: +44(0)773 886 2501
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About CW (Cambridge Wireless)
CW is the leading international community for companies involved in the research, development and application of wireless and mobile, internet, semiconductor, hardware and software technologies.
With an active community of over 1000 technology companies ranging from major network operators and device manufacturers to innovative start-ups and universities, CW stimulates debate and collaboration, harnesses and shares knowledge, and helps to build connections between academia and industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Huawei
Founded in 1987, Huawei is a leading global provider of information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure and smart devices. We are committed to bringing digital to every person, home and organization for a fully connected, intelligent world. Huawei’s end-to-end portfolio of products, solutions and services are both competitive and secure. Through open collaboration with ecosystem partners, we create lasting value for our customers, working to empower people, enrich home life, and inspire innovation in organizations of all shapes and sizes. At Huawei, innovation puts the customer first. We invest heavily in fundamental research, concentrating on technological breakthroughs that drive the world forward. We have nearly 194,000 employees, and we operate in more than 170 countries and regions, serving more than three billion people around the world. Founded in 1987, Huawei is a private company fully owned by its employees.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.huawei.com/uk/news/uk/2020/cambridge%20wireless%20partnership
T‑Mobile expands Home Internet to over 130 additional cities
T-Mobile US will increase its Home Internet service to more than 130 additional cities and towns across Michigan, Minnesota, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, West Virginia and Wisconsin. The move comes after it massively expanded its home broadband pilot to more than 20 million households in October.
The $50/month Home Internet pilot service will be deployed in underserved rural markets — through LTE-based coverage, with 5G service coming soon. The company says that only 63 percent of adults in rural America currently have access to high-speed internet.
“Home broadband has been broken for far too long, especially for those in rural areas, and it’s time that cable and telco ISPs have some competition,” said Dow Draper, T-Mobile EVP, Emerging Products. “We’ve already brought T-Mobile Home Internet access to millions of customers who have been underserved by the competition. But we’re just getting started. As we’ve seen in our first few months together with Sprint, our combined network will continue to unlock benefits for our customers, laying the groundwork to bring 5G to Home Internet soon.”
T-Mobile Home Internet is just $50/month all-in and features many of the same benefits that have made T-Mobile the fastest growing wireless provider for the past seven years:
- Self-installation. That means there’s no need for installers to come to your home.
- Taxes and fees included.
- No annual service contracts.
- No maddening “introductory” price offers. What you pay at sign-up is what you’ll pay as long as you have service.
- No hardware rental, sign-up fee or installation costs (because set-up is so easy!).
- No data caps.
- Customer support from the team that consistently ranks #1 in customer service satisfaction year after year.

Now that customers have had access to T-Mobile Home Internet since 2019, the reviews are in … and the feedback speaks for itself. Customers give T-Mobile Home Internet an average Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 42, compared to -75 (that’s a negative 75!) for their previous provider. Seventy-three percent report saving money with T-Mobile Home Internet, with 50% saving more than $30 per month (that’s $360 annually!).
The Home Internet pilot provides home broadband on the Un-carrier’s LTE network. With additional capacity unlocked by the merger with Sprint, T-Mobile is preparing to launch 5G Home Internet commercially nationwide, covering more than 50% of U.S. households within six years and providing a badly needed alternative to incumbent cable and telco ISPs.
Home broadband is one of the most uncompetitive and hated industries in America. Rural areas in particular lack options: more than three-quarters have no high-speed broadband service or only one option available. And when there’s no choice, customers suffer. It’s no wonder internet service providers have the second lowest customer satisfaction ratings out of 46 industries, beating cable and satellite TV companies by just one point according to the ACSI (American Customer Satisfaction Index)!
T-Mobile Home Internet service is available on a first-come, first-served basis, where coverage is eligible, based on equipment inventory and local network capacity, which is expanding all the time. For more information on T-Mobile Home Internet or to check availability for your home in these areas, visit t-mobile.com/isp.
Reference:
Netgear Nighthawk 5G Hotspot Pro from AT&T; Netgear’s audio video over IP (AV over IP)
“The combination of AT&T 5G technology and the NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot Pro gives AT&T customers fast speeds, low-latency and improved bandwidth for all of their WiFi needs,” said David Christopher, executive vice president and general manager, AT&T Mobility. “The 5G addition is innovative in a hotspot and much needed during a time when many of our customers continue to work and learn from home.”
“We are delighted to team with AT&T, to release their next generation 5G hotspot. The NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot Pro combines the best of WiFi and mobile technologies – WiFi 6 and 5G, to keep you always connected at home and on the go via the AT&T 5G network,” said Patrick Lo, chairman and chief executive officer for NETGEAR. “This new mobile hotspot with WiFi 6 provides robust WiFi connectivity to the increasing number of mobile devices and computers simultaneously with the best mobile internet speeds available over 5G.”
The introduction of this hotspot also exceeds AT&T’s commitment to offer 15 5G-capable devices to our lineup in 2020. This expansive portfolio gives our customers a wide variety to choose from, with features and price points that best serve their needs. All of these devices tap into our nationwide 5G network, offering fast, reliable and secure connectivity across the U.S. Plus, 5G access is included in all of our current consumer and business unlimited wireless plans at no extra cost to you.3
NETGEAR NIGHTHAWK 5G MOBILE HOTSPOT PRO FEATURES
The NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot Pro is the perfect portable device. Whether you’re constantly on the move or looking for an alternative to in-home broadband, it offers the following features that will provide a steady and reliable connection wherever you are:
- Capacity: Share your connection with up to 32 WiFi devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops for a connection you can count on.
- 5G Compatibility: In addition to AT&T’s nationwide 5G network, this device can also access AT&T 5G+ in parts of 35 cities across the country. Together, these two flavors of 5G create the best mix of speeds and coverage, and will power new experiences coming to life.
- WiFi 6: Tap into the latest WiFi technology that will power fast surfing, downloading, and streaming for the whole family.
- Touch Screen: Set up your device and manage your usage with ease from the NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot Pro’s touchscreen.
- Battery Life: Power through your day and night with the long-lasting, powerful 5,040 mAh rechargeable battery. It also operates without battery when connected via the quick charge power adapter.
FIRST RESPONDERS
The NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Pro Hotspot will also be FirstNet Ready™, which means first responders can use it to tap into the power of FirstNet® – America’s public safety communications network. FirstNet Ready devices are tested and approved to operate with services using the FirstNet LTE network core. This gives public safety access to the critical capabilities that FirstNet enables, like the full power of AT&T’s LTE network, including Band 14 spectrum, which serves as a VIP lane for first responders.4
For more information on AT&T 5G, visit att.com/5G. For the latest on how we’re using this next generation of wireless technology, head to att.com/5GNews.
https://about.att.com/story/2020/netgear_nighthawk_5g_mobile_hotspot_pro.html
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- An entirely new series of switches developed and engineered for the growing audio, video over IP (AV over IP) market. These AV Line switches combine years of networking expertise with best practices from leading experts in the professional AV market.
- The new AV Line incorporates NETGEAR IGMP Plus™ for flawless video over IP (including audio and control). If you are using Dante or AVB in your audio deployment, you can trust that NETGEAR’s new AV Line switches are designed to seamlessly integrate into your solution.
- The new M4250 AV interface presents the common AV controls right up front with user-selectable profiles for common AV platforms making it a snap to ensure the settings are correct for a specific audio or video application.
CenturyLink rebrands as LUMEN for large enterprise customers; adds Quantum Fiber
CenturyLink has taken on a new identity — Lumen — a name it says better highlights the company’s future direction and focus on selling business services to large customers. [Note that there is already a Texas based company named Lumen Technologies Inc so there’s sure to be confusion and a possible trademark lawsuit in the near future.]

Lumen is a measure of the brightness of light, and the company’s competitive advantage this century has come from its massive fiber network, stretching 450,000 route miles. That has helped CenturyLink survive even as consumers cut their home phone lines in favor of wireless providers and switched off DSL in favor of faster alternatives.
But transporting light signals can also be a commodity service. Lumen is now pushing to offer more higher-value applications and enterprise services directly to its customers, reflected in the company’s new motto: “The Platform for Amazing Things.”
Lumen says on its website:
Lumen is an enterprise technology platform that enables companies to capitalize on emerging applications that power the 4th Industrial Revolution. Most IT leaders don’t feel ready to face the nearly century’s worth of data-driven innovation they expect in the next five years.
“Our people are dedicated to furthering human progress through technology. Lumen is all about enabling the amazing potential of our customers, by utilizing our technology platform, our people, and our relationships with customers and
partners,” said Lumen CEO Jeff Storey, in a statement on the name change.
“For the past three years we have been reinventing ourselves and repositioning the company to deliver on a brand-new promise: Furthering human progress through technology,” said Lumen CTO Andrew Dugan, who held the same title at CenturyLink. “We have been considering this change for many months. We are ideally positioned to help resolve the biggest data and application challenges of our time—this is why now is the right time to introduce Lumen.”
The CenturyLink brand will continue to be used for residential and small business customers using traditional copper based networks. “CenturyLink, with its strong heritage, will remain as a trusted brand for residential and small business customers over traditional networks,” the company said.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The number of telecom and cloud service providers that have been acquired by CenturyLink is truly astounding. That list includes: US West (which was acquired by Qwest Communications), Embarq (which included Sprint Local and US Telecom), Savvis, App Frog, Tier 3, and the big one –Level 3 Communications in a deal valued at around $25 billion. Level 3, in turn, had also acquired a boat load of telecom providers such as Global Crossing and TW Telecom and before that: WilTel Communications, Broadwing Corporation, Looking Glass Networks, Progress Telecom, and Telcove (formerly Adelphia Business Solutions) and ICG Communications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These acquisitions, long with internal software innovations, they have given Lumen the ability to provide enterprise customers with a variety of services in a variety of areas. However, the company still does not have presence in the cellular communications business.
“Unfortunately, today’s network, cloud and IT architectures present latency, cost and security challenges that inhibit the performance of distributed applications and real-time data processing. Ultimately, the world needs a new architecture platform that has been designed to support the intensive performance requirements of next-generation applications. And that is exactly what we aim to provide with Lumen,” said Lumen’s chief marketing officer Shaun Andrews, in a video message.
Smart cities, retail and industrial robotics, real-time virtual collaboration and automated factories are some of the applications that Lumen believes it can help customers achieve in what it and others call the 4th Industrial Revolution. Steam power, electricity and then the computer chip all pushed economic progress, and now the melding of the digital and physical worlds that connectivity permits is doing the same, Andrews added.
That is the future direction, where the company sees the greatest potential for growth and new revenues. But Andrews emphasized that residential and small business consumers will still deal with CenturyLink, a brand executives believe still has value two decades into the new century. It is the name that will continue to show up on residential customers’ bills. CenturyLink Field in Seattle will retain its name.
Another new entity, Quantum Fiber, will handle the residential and small business transition to digital as the company rolls out more fiber-optic connections directly to homes and businesses (FTTH and FTTP, respectively). The company added capacity to reach about 300,000 homes and small businesses last year with gigabit service and plans to reach another 400,000 this year, according to Fierce Telecom.
Lumen says the can provide the ability to control latency, bandwidth and security for applications across cloud data centers, the market edge and on-premises, according to a blog by Dugan. Instead of putting critical applications into a centralized cloud, Lumen’s edge compute platform, which includes more than 100 active edge compute nodes across large metro markets in the U.S—puts them closer to the end user for low latency and better security.
“The Lumen brand is focused on supporting our enterprise business customers. It alludes to our network strength and to the incredible capabilities powered by our platform to help transform how businesses operate,” Dugan said.
“Quantum Fiber is an important new brand within Lumen with a focus on superior fiber connectivity and a fully enabled digital customer experience,” Dugan said. “Quantum Fiber serves residential and small business customers, and Lumen focuses on enterprise, government and global businesses.”
In 2019, CenturyLink expanded its fiber network to reach an estimated 300,000 additional homes and small businesses with its gigabit service. CenturyLink’s consumer fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) projects provide symmetrical speeds of up to 940 Mbps. The faster speeds were enabled in parts of Boulder, Colo., Spokane, Wash., and Tucson, Ariz. last year.
CenturyLink previously said it would build out its fiber network to an additional 400,000 homes and small businesses this year, including in Denver, Omaha, Neb., Phoenix, Portland, Ore., Salt Lake City, Spokane, Wash., and Springfield, MO.
MoffetNathanson analysts wrote in a note to clients (emphasis added):
The flagship Lumen brand is targeted toward larger enterprises, the likes of which would be most likely to adopt the company’s most advanced services. The CenturyLink brand is being retained for legacy copper services delivered to residential customers and some SMBs, as well as existing FTTH customers. And the new Quantum Fiber brand is being introduced for SMB services delivered via the automated platform the company has been developing and has indicated it would soon be rolling out to on-net, out-of-region locations (mostly ex-Level 3 buildings), and will include consumer FTTH sold in a similar manner. The services and capabilities Lumen delivers to each of these customer segments varies dramatically, so it’s not at all inappropriate to have separate brands for each. Innumerable examples of this phenomenon exist across other industries – automotive, consumer products, airlines, apparel, media, and so on. Within the world of telecom, carriers often have brands that target different segments or highlight different product types (Verizon with FiOS, AT&T with Cricket, T-Mobile US with MetroPCS, Altice USA with Optimum vs. Lightpath, and so on).
CenturyLink was an amalgamation of many different companies, assets, and capabilities. Management’s decision to rebrand as Lumen, Quantum Fiber, and CenturyLink acknowledges those differences and gives management an opportunity to refresh and communicate its vision for the company to customers, employees, and investors.
Andrews said the name change won’t include a relocation to Denver of the corporate headquarters, which will remain in Monroe, La., home of the original CenturyLink. Of the company’s 40,000 employees globally, 5,800 are based in Colorado, and metro Denver remains an important hub of operations, especially the ones that Lumen will emphasize.
It remains to be seen what will happen with CenturyLink’s wholesale and carriers carrier backbone services, which acquisitions such as Level 3 and Global Crossing mainly focused on, i.e. selling high bandwidth fiber optic long haul links to other carriers.
References:
https://www.lumen.com/en-us/home.html
https://news.lumen.com/CTO-Andrew-Dugan-explains-how-the-Lumen-platform-keeps-data-moving
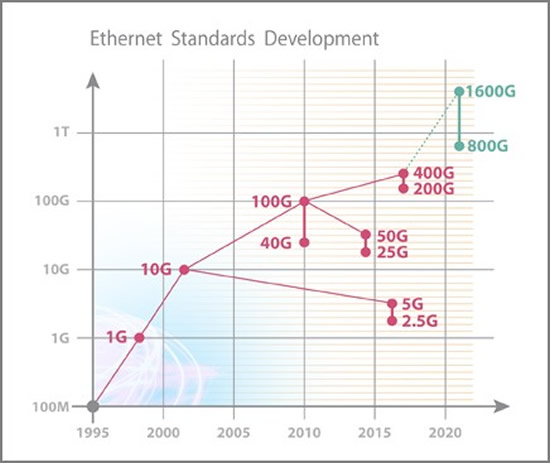
At long last, commercial 400GE is real via Windstream -Evergreen long haul optical circuit
IEEE 802.3‘s “400 Gb/s Ethernet Study Group” started working on the 400 Gbit/s generation standard in March 2013. Results from the study group were published and approved on March 27, 2014. IEEE officially ratified its 802.3bs standard for 200G and 400G over Single Mode Fiber (SMF) and Multi Mode Fiber (MMF) on December 6, 2017.
Below are charts of recent IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standards development and the various option for 400GE over SMF or MMF:
| Name | Medium | Tx Fibers | Lanes | Reach | Encoding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400GBASE-SR16 | MMF | 16 | 16 x 25 Gbps | 70 m (OM3)100 m (OM4) | NRZ |
| 400GBASE-DR4 | SMF | 4 | 4 x 100 Gbps | 500 m | PAM4 |
| 400GBASE-FR8 | SMF | 1 | 8 x 50 Gbps (WDM) | 2 km | PAM4 |
| 400GBASE-LR8 | SMF | 1 | 8 x 50 Gbps (WDM) | 10 km | PAM4 |
| 200GBASE-DR4 | SMF | 4 | 4 x 50 Gbps | 500 m | PAM4 |
| 200GBASE-FR4 | SMF | 1 | 4 x 50 Gbps (WDM) | 2 km | PAM4 |
| 200GBASE-LR4 | SMF | 1 | 4 x 50 Gbps (WDM) | 10 km | PAM4 |
Source: IEEE 802.3
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
There’s been much talk about 400GE since then with continued promised of “deployment this year,” primarily for Data Center Interconnect (DCI), Internet Data Exchange, and wholesale fiber service providers. Now, it’s finally real!
Windstream Wholesale has begun deploying long haul 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400GE) to link the regional teleco’s fiber network with Everstream’s Chicago-to-Cleveland route. For this deployment, Windstream used Infinera’s Groove (GX) Series compact modular platforms and Juniper’s PTX Series transport routers. Windstream provided the 400G Wavelength Service using Infinera’s coherent wavelength technology.
The two primary customer segments for 400GE have been data center operators looking to interconnect two or more data centers, or service providers that want to build metro rings consisting of 400G lines on which they then would lease capacity to data center operators or enterprises through a data center interconnection (DCI) as-a-service offering.
“So this is not just an experiment,” said Buddy Bayer, chief network officer at Windstream. “This is a real world revenue generating circuit for us. We have a lot of peers in this industry that we talk to quite a bit, and there’s a lot of experimentation and lot of discussion going on around about 400 Gig. But this is the first one that we’ve really heard about where it’s a real circuit with real revenue behind it.”

Source: Windstream Wholesale
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Bayer credited the work done in Windstream’s Little Rock lab earlier this year with Infinera for being able to boot up the commercial 400GbE connection with Everstream. In April, Windstream Holdings and Infinera paired 400GE with client-side services with commercially available 400GE-LR8 QSFP-DD compact pluggable interfaces. The trial used Infinera’s commercially available 2x 600G Wavelength muxponder on its Groove (GX) G30 Compact Modular Platform with the CHM-2T sled, which enabled the customer-facing 400GE service to be transmitted using a single-carrier 600G wavelength. Windstream has been aggressive about working with vendors such as Infinera and Ciena in its labs in order to provision 400G services.
“With the LR8, you now you have the optical reach for the long haul. So going from seeing it in the lab environment to now getting it onto our network live with a real customer is pretty exciting. This kind of put us in the driver’s seat from our consumers’ perspective,” Bayer said. “We get to take all their questions and all their needs and put them right inside of those labs and trials and create solutions around them,” he added.
The introduction of Windstream’s 400 GbE Wavelength Service helps Everstream meet the relentless growing bandwidth demands from enterprises and provide the flexibility to support a wide variety of business-class services. The partnership enables Everstream to leverage the national footprint of Windstream’s advanced fiber-optic network and augment its high-demand route between Chicago and Cleveland. Windstream’s Wavelength Service product offering includes routes across its nationwide fiber network from 10GbE to 400GbE.
“Everstream is committed to continually enhancing our business-only network and expanding our partnerships to deliver a customer experience that is unmatched for even the most demanding enterprise requirements,” said Everstream President and CEO Brett Lindsey. “As our customers continue to scale, they need access to high-bandwidth, agile network solutions. This opportunity with Windstream enables us to consistently lead the market in providing the services that businesses demand with the reliability they need.”
“Windstream is committed to tapping into the latest technological innovation, enabling us to offer customers the benefits of ultra-efficient, high-capacity transport solutions across our network,” said Joe Scattareggia, executive vice president, Windstream Wholesale. “By partnering with Windstream Wholesale, regional service providers like Everstream have access to advanced national connectivity solutions to support the increasing bandwidth and capacity demands of their customers.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Cisco and Juniper have produced commercially available 400G for routers, but the optical network transport side has been slower on the uptake, according to Jimmy Yu, vice president and analyst for the optical transport market at Dell’Oro Group.
“So the fact that Everstream is going to be the first announced paying customer really speaks to the fact that they (Windstream) have gone full throttle on getting this not only up, but getting it running and getting a customer,” Yu said. “It does seem like they are kind of hitting the market first among service providers.”
Yu also pointed to Windstream’s work with Ciena for the build-out of Windstream’s new nationwide optical network, which is slated for turn up in the third quarter of this year.
Bayer and Yu expect 400G long-haul deployments will ramp up around the middle of next year after a few smaller launches near the end of this year. Bayer said the cost model for deploying 400G needs to come down for wide-scale adoption.
“I think the typical cost curve hasn’t kicked in yet,” Bayer said. “It’s supply and demand. As soon as there’s a demand on the 400G side, we’re going to see the cost come way down. You’re going to see cost models where it’s cheaper to turn up one 400 Gig as it is for turning up two 100 Gigs. We’re not there yet.
“The router blades are in the same supply and demand curves that the transport optics are in.”
Both Bayer and Yu said ZR pluggable optics, which will be for the longer spans of up to up to 120 kilometers, would start to become more widely available next year. Using ZR and ZR Plus pluggable optics allows service providers to eliminate transponders in the their WDM wavelength-division multiplexing) networks.
“IR8 is absolutely a good technology and it gave us the reach that we needed for 400 Gig, but ZR optics is another level of performance at a lower cost point,” Bayer said. “ZR is a lot lower cost point that’s going to be more appealing. I think that’s when you start to really see 400 Gig take off because now you can take that pluggable and put it in a router or transport gear. I think that’ll really kind of stir the nest for demand for 400G.
Yu said that while ZR is standards-based ZR Plus is not. ZR Plus could span up to 1,000 kilometers but may not fit on a switch or router.
“One of the advantages of ZR is everyone wants to put the pluggable on an Ethernet switch or router instead of on an optical system,” Yu said. “It’s not clear to me if ZR Plus can be put on a router or just go on an optical system but now it’s going to be more pluggable,” Yu added.
400G ZR and the longer-distance 400G ZR Plus will bring interoperability, and with that, potentially lower cost to 400G deployments as companies deploying 400G have more options to mix and match different vendors.
“ZR Plus will probably be generally available mid next year,” Bayer said. “ZR Plus is a lot lower cost point and that’s going to be more appealing. It’s not available to us yet, but as soon as it is we’re right in the labs and environments with it. We’re ready to go.”
References:
Everstream Partners with Windstream to Bring 400GbE Services to Market
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/windstream-powers-up-live-400gbe-service-everstream
Ericsson deploys 25,000 base stations in Russia; 100 5G deployment agreements top Huawei & Nokia
Sebastian Tolstoy, Head of Ericsson in Russia, said:
“Our development enables Tele2’s subscribers the opportunity to use mobile internet services in high quality. As all our network equipment in Russia supports an upgrade to 5G technologies through remote software installation, operators in Russia are able to launch new services as soon as they get the appropriate licenses.
Ericsson’s 5G Innovation Hub in Moscow gives Russian service providers the opportunity to test innovations on live 5G and IoT networks. The Ericsson Academy, our training center co-located at the Innovation Hub, trains more than 1,000 specialists from Russian service providers and students each year.”
The pace of deployment from Ericsson is truly impressive, especially in the context of the ongoing pandemic. If the current pace is maintained, the five-year deal will be completed in two years.
Aleksey Telkov, CTO of Tele2 Russia, comments:
“In the Moscow region, from the very start, we installed 5G-ready base stations. We deployed a pilot 5G network in the center of Russia’s capital, and together with Ericsson, we are carrying out a large-scale network modernization across the country.
This allows us to say that Tele2 is technologically ready for 5G.”

The 5G Zone uses the 28 GHz band in non-Standalone (NSA) mode and the frequency band for anchor LTE band is Band 7 (2600MHz). 5G pocket routers supporting 28 GHz were used as end-user devices for mobile broadband services with ultra-high speeds.
Ericsson and Tele2’s 5G Zone was used to demonstrate the opportunities 5G presents, including immersive VR entertainment, smart buildings, and other consumer and industrial use cases.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ericsson announced it had 100 telco 5G agreements following the announcement of a 5G deal with Telekom Slovenije yesterday. That’s a lot of progress made in a relatively short time. Just under a year ago, Ericsson had publicly announced 24 5G contracts with equipment live in 15 networks. As of today, 58 contracts have been publicly announced and Ericsson’s gear is being used in 56 live 5G networks.
Börje Ekholm, President and CEO, Ericsson, said:
“Our customers’ needs have been central to the development and evolution of Ericsson’s 5G technology across our portfolio from the very beginning. We are proud that this commitment has resulted in 100 unique communications service providers globally selecting our technology to drive their 5G success ambitions.
We continue to put our customers center stage to help them deliver the benefits of 5G to their subscribers, industry, society and countries as a critical national infrastructure.”
Ericsson has been able to capitalize on the uncertainty surrounding Huawei’s future in many Western countries due to security concerns. Even prior to the UK’s decision to ban Huawei’s equipment, many operators in Britain were moving away from the Chinese vendor. India is now moving in that same direction.
In April, Howard Watson, BT’s chief technology and information officer, said:
“Having evaluated different 5G core vendors, we have selected Ericsson as the best option on the basis of both lab performance and future roadmap. We are looking forward to working together as we build out our converged 4G and 5G core network across the UK.”
For comparison, Nokia says it has 85 commercial 5G deals and equipment live in 33 5G networks. In February 2020, Huawei aid it had secured more than 90 commercial 5G contracts worldwide, an increase of nearly 30 from last year despite the relentless pressure from U.S. authorities and being banned in the UK.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Ericsson deploys 25,000 base stations in Russia to support Tele2’s 5G rollout
https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/China-tech/Huawei-claims-over-90-contracts-for-5G-leading-Ericsson
IEEE 802.3cg and IEEE 802.1 Standards play huge role in Operational Technology and Time Sensitive Networks
Introduction:
The Ethernet Alliance and Avnu Alliance have separately released plans to speed up and simplify Ethernet communications networks. Operational Technology (OT) is the target of the IEEE 802.3cg specification from the Ethernet Alliance, while the Avnu Alliance is focusing on IEEE 802.1 time-sensitive networking (TSN) applications.
I. IEEE 802.3 and the Ethernet Alliance:
IEEE 802.3c is titled: IEEE Standard for Ethernet – Amendment 5: Physical Layer Specifications and Management Parameters for 10 Mb/s Operation and Associated Power Delivery over a Single Balanced Pair of Conductors.” It defines the use of Single-Pair Ethernet (SPE) in many circumstances rather than a wide range of fieldbus cables, including RS‑485 twisted-pair, RG‑6 coaxial, and instrumentation cables.
The 802.3c Project Authorization Request (PAR) states:
“Applications such as those used in automotive and automation industries have begun the transition of legacy networks to Ethernet. This has generated an intrasystem control need for a 10 Mb/s solution which will operate over a single balanced pair of conductors. IEEE 802.3 does not currently support 10 Mb/s over a single balanced pair of conductors, and a reduction in the number of pairs of conductors and interface components required for 10 Mb/s Ethernet will provide a basis for an optimized solution in these applications.”
OT networks historically have been siloed from Ethernet-based IT networks and, “these networks, while operating effectively today, use dated, disparate network protocols. They are slow, typically 31.2kb/s, and require translation gateways to convert necessary data to Ethernet. SPE is purpose-built to address the challenges and topologies of OT networks,’ said Peter Jones, chair of the Ethernet Alliance and a distinguished engineer with Cisco.
“As the building- and industrial-automation industries come to rely more on SPE, there is a clear need to bring together the people creating and using the technologies so they can better understand one another,” said Jones.
“We are well positioned as a bridge between the OT experts in building and industrial automation and the IT (Information Technology) expertise that we have traditionally served across the Ethernet ecosystem. This new Ethernet Alliance industry focus will work to align the many disparate stakeholders and, in turn, help the building- and industrial-automation industries get to where they want to go with Ethernet.”
One of the key roles that the Ethernet Alliance plays is supporting the deployment of Ethernet technologies into markets not traditionally served by Ethernet. OT networks, which control manufacturing processes or provide occupant comfort and safety in a building, historically have been siloed from Ethernet-based IT networks.
In the past, application of Ethernet in OT networks required adapting the network to work with normal 10 BASE-T Ethernet. It was effective but created barriers, which limited adoption. SPE tears down those barriers, said Bob Voss, chair of the SPE subcommittee and a senior principal engineer with Panduit.
“SPE allows users to build the facilities served by OT networks in the ways they know work best; SPE is designed to support proven topologies and even uses a similar physical layer. Many SPE experts believe, given good cable health, that it could be possible to reuse physical-layer elements of current OT networks,” said Voss.
“We are excited about the Ethernet Alliance’s launch of an industry focus around building and industrial automation,” said Ron Zimmer, president and chief executive officer, Continental Automated Buildings Association (CABA).
“SPE is a promising technology for our industry, and CABA’s membership of leaders in advancing integrated home systems and building automation worldwide are committed to innovation that empowers connectivity among people, spaces and technology for a better tomorrow.”
Added Brett Lane, chief technical officer, Panduit: “The benefits SPE can bring to building and industrial automation are exciting. SPE is a vital next-generation technology which stands to help industry achieve better business outcomes through the continuation of convergence across the enterprise, and the Ethernet Alliance’s launch of this industry focus around OT networks is well timed.”
The Ethernet Alliance includes a variety of communications vendors, including Broadcom, Cisco, Dell, Juniper, Intel as well as university and industry members. Here’s there 2020 Ethernet Roadmap and Applications:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
II. TSN, IEEE 802.1 and the Avnu Alliance:
TSN is a collection of standards developed by the IEEE 802.1 TSN Working Group, which defines a new set of mechanisms for providing time synchronization and timeliness (deterministic data delivery) for time-sensitive data in a LAN shared with other types of best-effort applications, said Dave Cavalcanti, Avnu Alliance Wireless TSN Workgroup chair and a principal engineer at Intel.
IEEE 802.1 TSN standards define new functions for 802-based LANs such as traffic shaping, frame pre-emption, traffic scheduling, ingress policing, and seamless redundancy. When all parts of a network are running with the same sense of reference time, traffic can be coordinated based on a time-aware schedule, one method that allows for better control of latency for time-critical traffic. These new features provide a whole new layer of control for managing traffic over Ethernet, Cavalcanti said.
The charter of the IEEE 802.1 TSN Task Group is to provide deterministic services through IEEE 802 networks, i.e., guaranteed packet transport with bounded latency, low packet delay variation, and low packet loss. The TSN TG has been evolved from the former IEEE 802.1 Audio Video Bridging (AVB) TG. The TSN TG includes the former IEEE 802.1 Interworking TG. The original work on AVB was done as part of the “Residential Ethernet Study Group” of IEEE 802.3.
Base standards for TSN:
- IEEE Std 802.1Q-2018: Bridges and Bridged Networks
- IEEE Std 802.1AB-2016: Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery (specifies the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP))
- IEEE Std 802.1AS-2020: Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications
- IEEE Std 802.1AX-2020: Link Aggregation
- IEEE Std 802.1BA-2011: Audio Video Bridging (AVB) Systems
- IEEE Std 802.1CB-2017: Frame Replication and Elimination for Reliability
- IEEE Std 802.1CM-2018: Time-Sensitive Networking for Fronthaul
The TSN standards can be applied in many verticals. Some of them are listed in the application of TSN page.
According to Cavalcanti, the IEEE 802.1 TSN standards have seen a lot of growth in the past three to five years, particularly in the industrial market. TSN is a networking layer that leverages under-laying data communication technologies (such as Ethernet, 802.11/Wi-Fi and eventually 5G). As such, TSN can be seen as a unifying layer operating across and potentially integrating heterogeneous connectivity technologies. The role of TSN is to ensure the end-to-end data delivery with determinism, Cavalcanti said. “Each of the individual connectivity technologies may implement its own features to help achieve TSN goals, but TSN has a broader scope than any particular connectivity technology.”
Wireless communications using TSN not only enable mobility, they are flexible and reduce wiring costs. “TSN capabilities over wireless, for instance, can enable manufacturers to easily reconfigure industrial automation and control systems as well as enable optimized routing and utilization of mobile robots and automatic guided vehicles,” Cavalcanti added. Industrial automation system and mobile robots are important use cases because wireless is fundamental for mobility, flexibility and reconfigurability of tasks and routes.
“Electrical power grid systems are another interesting use-case for wireless TSN, as these systems have varied coverage areas which may vary from local (e.g. substation) to wide areas (distribution and transmission). Industrial control systems could also benefit from wireless connectivity, but they will require the highest level of determinism and reliability and rely exclusively on time-aware (IEEE 802.1Qbv) scheduling over wireless links,” Cavalcanti said.
The push for combining wireless and Ethernet TSN comes from the Avnu Alliance which says its members include more than 95% of the Ethernet silicon suppliers as well as automotive industry and audio-visual vendors. Its affiliates include Cisco, Intel, Bose, Bosch, and Extreme. The Avnu Alliance defines requirements for interoperability and is the certification authority – grants certification for interoperable products – for TSN.
The Wireless TSN working group within Avnu Alliance states that “it is important to start early discussions and alignment on topics such as consistent TSN interfaces for wired and wireless technologies, interoperability testing, and certification efforts.”
The Alliance does not do the actual physical testing of products; this is handled by a network of registered test facilities. For example, the University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory is one registered test facility.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://ethernetalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/EA_SPE_PressRelease-FNAL-08AUG20.pdf
Ethernet Alliance to focus on SPE in OT networks for building and industrial automation



