Uncategorized
T-Mobile Earnings Beat + 5G Network Status + 600 MHz and Spectrum Position
T-Mobile US beat analysts’ estimates for quarterly revenue and profit on Thursday, as the wireless carrier added more mobile phone subscribers to its monthly plans, some of which come bundled with a Netflix Inc service.
The third-largest U.S. wireless carrier by subscribers has been awaiting a decision on its proposed merger with Sprint Corp. The two U.S. telcos delivered closing arguments in a federal court last month against a multi-state lawsuit that argues the merger will increase prices for the consumers.
T-Mobile’s fourth-quarter net income rose to $751 million from $640 million, a year earlier. Excluding items, the company earned 87 cents, beating analysts’ average estimate of 83 cents. Revenue rose to $11.88 billion from $11.45 billion, edging past analysts’ average estimate of $11.83 billion, according to IBES data from Refinitiv.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Highlights from the T-Mobile Investor Factbook website:
Strong Customer Growth:
• 1.9 million total net additions in Q4 2019 – 7.0 million in 2019 – 6th year in a row of more than 5 million total net additions
• 1.3 million branded postpaid net additions in Q4 2019, best in industry – 4.5 million in 2019, best in industry
• 1.0 million branded postpaid phone net additions in Q4 2019, best in industry – 3.1 million in 2019, best in industry
• 77,000 branded prepaid net additions in Q4 2019 – 339,000 in 2019
• Branded postpaid phone churn of 1.01% in Q4 2019, up 2 bps YoY – 0.89% in 2019, down 12 bps from 2018
First Nationwide 5G Network:
• Launched the first nationwide 5G network utilizing 600 MHz spectrum, forming the foundational 5G coverage layer for
New T-Mobile; network covers more than 200 million people and more than 5,000 cities and towns
• 4G LTE on 600 MHz now covers 248 million people and 1.5 million square miles
• Currently, more than 33 million 600 MHz compatible devices already on our network
Strong Standalone Outlook for 2020:
• Branded postpaid net additions of 2.6 to 3.6 million
• Net income is not available on a forward-looking basis(2)
• Adjusted EBITDA target of $13.7 to $14.0 billion, which includes leasing revenues of $450 to $550 million
• Cash purchases of property and equipment, including capitalized interest of approximately $400 million, are expected
to be $5.9 to $6.2 billion. Cash purchases of property and equipment, excluding capitalized interest, are expected to
be $5.5 to $5.8 billion
• In Q1 2020, pre-close merger-related costs are expected to be $200 to $300 million before taxes
• Net cash provided by operating activities, excluding payments for merger-related costs and any settlement of interest
rate swaps, is expected to be in the range of $7.9 to $8.5 billion
• Free Cash Flow, excluding payments for merger-related costs and any settlement of interest rate swaps, is expected
to be in the range of $5.4 to $5.8 billion
Total Customers:
• Total net customer additions were 1,863,000 in Q4 2019, compared to 1,747,000 in Q3 2019 and 2,402,000 in Q4 2018. This is the 27th consecutive quarter in which TMobile added more than one million total net customers.
• T-Mobile ended Q4 2019 with 86.0 million total customers, of which 67.9 million were total branded customers.
• For the full-year 2019, total net customer additions were 7,011,000 compared to 7,044,000 in 2018. This was the sixth consecutive year in which total net customer additions exceeded 5 million.
______________________________________________________________
5G NETWORK:
On December 2, 2019, T-Mobile launched America’s first nationwide 5G network, including prepaid 5G with Metro by T-Mobile, covering more than 200 million people and more than 5,000 cities and towns across over 1 million square miles with 5G. In addition, we introduced two new 600 MHz 5G capable superphones, the exclusive OnePlus 7T Pro 5G McLaren and the Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G and anticipate offering an industry-leading smartphone portfolio built to work on nationwide 5G in 2020. This 5G network is our foundational layer of 5G coverage on 600 MHz low-band spectrum.
Should we close our merger with Sprint, we will rapidly deploy 5G on Sprint’s 2.5 GHz spectrum, completing the “layer cake” of spectrum and providing consumers with an unmatched 5G experience. On June 28, 2019, T-Mobile introduced its 5G network using high-band millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum in conjunction with the introduction of our first 5G handset, the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G. The 5G network on mmWave spectrum has been rolled out in parts of seven cities (New York City, Los Angeles, Dallas, Atlanta, Cleveland, Las Vegas and Miami).
600 MHz Spectrum:
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile owned a nationwide average of 31 MHz of 600 MHz low-band spectrum. In total, T-Mobile owns approximately 41 MHz of low-band spectrum (600 MHz and 700 MHz). The spectrum covers 100% of the U.S.
- As of the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile had cleared 275 million POPs and expects to clear the remaining 600 MHz spectrum POPs in 2020.
- T-Mobile continues its deployment of LTE on 600 MHz spectrum using 5G-ready equipment. At the end of Q4 2019, we were live with 4G LTE in nearly 8,900 cities and towns in 49 states and Puerto Rico covering 1.5 million square miles and 248 million POPs.
- Combining 600 and 700 MHz spectrum, we have deployed 4G LTE in low-band spectrum to 316 million POPs.
Currently, more than 33 million devices on T-Mobile’s network are compatible with 600 MHz spectrum.
Spectrum Position:
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile owned an average of 111 MHz of spectrum nationwide, not including mmWave spectrum. The spectrum comprises an average of 31 MHz in the 600 MHz band, 10 MHz in the 700 MHz band, 29 MHz in the 1900 MHz PCS band, and 41 MHz in the AWS band. On June 3, 2019, the FCC announced the results of Auctions 101 (28 GHz spectrum) and 102 (24 GHz spectrum). In the combined auctions, T-Mobile spent $842 million to more than quadruple its nationwide average total mmWave spectrum holdings from 104 MHz to 471 MHz.
- We will evaluate future spectrum purchases in upcoming auctions and in the secondary market to further augment our current spectrum position. We are not aware of any such spectrum purchase options that come close to matching the efficiencies and synergies possible from merging with Sprint.
Network Coverage Growth:
- T-Mobile continues to expand its coverage breadth and covered 327 million people with 4G LTE at the end of Q4 2019.
- At the end of Q4 2019, T-Mobile had equipment deployed on approximately 66,000 macro cell sites and 25,000 small cell/ distributed antenna system sites.
Network Capacity Growth:
- Due to industry spectrum limitations (especially in mid-band), T-Mobile continues to make efforts to expand its capacity and increase the quality of its network through the re-farming of existing spectrum and implementation of new technologies including Voice over LTE (“VoLTE”), Carrier Aggregation, 4×4 multiple-input and multiple-output (“MIMO”), 256 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (“QAM”) and License Assisted Access (“LAA”).
- VoLTE comprised 90% of total voice calls in Q4 2019, flat with 90% in Q3 2019 and up from 87% in Q4 2018. Carrier aggregation is live for T-Mobile customers in 969 markets, up from 956 markets in Q3 2019 and 923 in Q4 2018.
- 4×4 MIMO is currently available in 708 markets, up from 683 markets in Q3 2019 and 564 in Q4 2018.
- T-Mobile customers have 256 QAM available across the Un-carrier’s entire 4G LTE footprint.
Source: Opensignal USA Mobile Network Experience Report January 2020, based on data collection period from 9/16/2019 to 12/14/2019 - T-Mobile is the first carrier globally to have rolled out the combination of carrier aggregation, 4×4 MIMO and 256 QAM. This trifecta of standards has been rolled out to 701 markets, up from 674 markets in Q3 2019 and 549 markets in Q4 2018.
- LAA has been deployed to 30 cities including Atlanta, Austin, Chicago, Denver, Houston, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, Philadelphia, Sacramento, San Diego, Seattle, and Washington, DC.
Network Speed:
- Based on data from Opensignal for Q4 2019, T-Mobile’s average download speed was 25.8 Mbps, AT&T at 27.5 Mbps, Verizon at 25.3 Mbps, and Sprint at 23.9 Mbps.
- Based on data from Opensignal for Q4 2019, T-Mobile’s average upload speed was 8.6 Mbps, compared to Verizon at 7.9 Mbps, AT&T at 6.0 Mbps, and Sprint at 2.7 Mbps.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://investor.t-mobile.com/financial-performance/quarterly-results/default.aspx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CHPuI289U-Q&feature=youtu.be
BICS: 4G roaming traffic doubles for the third consecutive year
4G roaming traffic doubled in 2019 for the third consecutive year, according to a BICS report. Subscriber demand for high-capacity borderless connectivity continues to boom. The findings were from sourced from BICS’ global network, which connects over 700 operators and 500 digital service providers and carries over 50% of global data roaming traffic. The report show an uplift in roaming traffic across all continents, fueled by increased global travel, adoption of roaming tariffs, travel SIMs, and IoT devices.

“The exponential growth in roaming traffic highlights how important international connectivity has become to the subscriber experience,” commented Mikaël Schachne, CMO and VP Mobility & IoT Business at BICS. “Through the provision of seamless, cross-border 5G connectivity, operators will be able to create new revenue streams and support a wide range of new and innovative use cases in areas such as automotive, gaming, telemedicine and logistics. As carriers launch 5G networks, roaming must be at the heart of their offerings to deliver maximum value for subscribers.”
Carrying over a third of all global roaming traffic, BICS is connected to every single mobile network and has a presence in over 180 countries. Through BICS’ IPX platform, service providers can establish roaming and inter-working agreements with over 600 members on the network, enabling them to offer subscribers high-quality data roaming with other mobile and fixed network operators globally. In 2019 BICS consolidated its position at the center of the global connectivity ecosystem, with one in three operators worldwide now utilizing its 4G roaming services.
Last year also saw momentum build for both national and international 5G; approximately 50 national 5G networks are now live, while BICS pioneered several live 5G roaming services, including a 5G intercontinental roaming service between Europe and Asia. In 2020 BICS predicts 5G roaming will gain further traction, as service providers progress 5G deployments and launch 5G roaming to support increasing demand from both subscribers and industries requiring high-speed, ultra-low latency 5G data connectivity.
In July of last year, BICS launched a 5G roaming service between Swiss operator Swisscom and South Korean carrier SK Telecom. The 5G roaming service delivers high-speed, low latency 5G data connectivity between two continents, with operators using BICS’ 5G global IPX network.
Editor’s Caveat:
There won’t be much if any roaming on 5G until the industry agrees on IMT 2020 standards which must include a legitimate 5G Core network (as per 3GPP Release 16).
References:
https://bics.com/news/4g-roaming-traffic-doubles-for-the-third-year-as-industry-gears-up-for-5g/
CES 2020: Lenovo Yoga 5G claims to be the first 5G laptop PC
Lenovo has displayed the world’s first “5G” laptop at CES 2020 in Las Vegas, NV. The Chinese company says the Lenovo Yoga 5G is the first PC to be able to connect to (pre-IMT 2020 standard) 5G mmWave networks. However, neither the spectrum used nor the “5G” networks supported were disclosed. The Yoga 5G also supports Bluetooth 5.0 wireless connectivity, but (astonishingly) WiFi is not listed in the data sheet.
The Lenovo Yoga 5G will go on sale in the first quarter of 2020, starting at $1,499 (around £1,200, AU$2,100), and in North America will be known as the Lenovo Flex 5G.
The Lenovo Yoga 5G was previously known as Project Limitless before its official name was unveiled yesterday at CES 2000. As with other Yoga laptops, this is an ultra-portable 2-in-1 device, with a screen that can be folded backwards to turn it into a tablet.

The Lenovo Yoga 5G is also the first laptop to run on the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8cx platform, which includes built-in support for 5G connections, allowing the Yoga 5G to connect via a service provider and access super-fast mobile internet. According to Lenovo, this will allow the user to download large files easily, with download speeds of around 4Gb/s. The company says its 5G laptop is “up to 10 times faster than 4G through a 5G service provider when on the move and reliable WiFi access at home.” That’s quite impressive!
Lenovo said in a press release “5G technology will change entire industries as we know them, disrupting some while helping to launch others.”
Lenovo NOTES:
- Requires 5G network service and separately purchased cellular data plan that may vary by location. Additional terms, conditions and/or charges apply. Connection speeds will vary due to location, environment, network conditions and other factors.
- “5G” Download speeds vary by region and service provider, e.g. Verizon in U.S. offers up to 4Gbs/second. Network strength also varies by 5G service provider.
References:
Lenovo Breaks Barriers with New Consumer Technology Unveiled at CES 2020
https://news.lenovo.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Lenovo-Yoga-5G_14Inch_Qualcomm.pdf
Samsung #1 in Global 5G smartphone sales with 6.7 Million Galaxy 5G Devices in 2019
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. said that it shipped more than 6.7 million Galaxy 5G smartphones globally in 2019, giving consumers the ability to experience next-generation speed and performance. As of November 2019, Samsung accounted for 53.9% of the global 5G smartphone market and led the industry in offering consumers five Galaxy 5G devices globally, including the Galaxy S10 5G, Note10 5G and Note10+ 5G, as well as the recently launched Galaxy A90 5G and Galaxy Fold 5G.
The 6.7 million in Samsung 5G smartphone sales eclipses the 4 million target the firm set itself, though as its main Android competitor (Huawei) is being stifled by political friction, it is hardly surprising Samsung has stormed into the lead. Note also that Apple has not announced a 5G smartphone and probably will not do so till late 2020. In the absence of main competitors, Samsung is maintaining its leadership position in the 5G segment as well as 4G-LTE.
“Consumers can’t wait to experience 5G and we are proud to offer a diverse portfolio of devices that deliver the best 5G experience possible,” said TM Roh, President and Head of Research and Development at IT & Mobile Communications Division, Samsung Electronics. “For Samsung, 2020 will be the year of Galaxy 5G and we are excited to bring 5G to even more device categories and introduce people to mobile experiences they never thought possible,” he added.
The Galaxy Tab S6 5G, which will be available in Korea in the first quarter of 2020, will be the world’s first 5G tablet bringing ultra-fast speeds together with the power and performance of the Galaxy Tab series. With its premium display, multimedia capabilities and now, 5G, the Galaxy Tab S6 5G offers high-quality video conferencing, as well as a premium experience for watching live and pre-recorded video streams or playing cloud and online games with friends.

“5G smartphones contributed to 1% of global smartphone sales in 2019. However, 2020 will be the breakout year, with 5G smartphones poised to grow 1,687% with contribution rising to 18% of the total global smartphone sales volumes,” said Neil Shah, VP of Research at Counterpoint Research. “Samsung has been one of the leading players catalyzing the 5G market development in 2019 with end-to-end 5G offerings from 3GPP standards contribution, semiconductors, mobile devices to networking equipment. With tremendous 5G growth opportunities on the horizon, Samsung, over the next decade, is in a great position to capitalize by further investing and building on the early lead and momentum, ” Shah added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sidebar: Qualcomm or Samsung 5G silicon in future 5G devices?
It has become widely accepted that the latest Qualcomm chipset features in the majority of flagship smartphone devices throughout the year. Only two smartphone makers – Samsung and Huawei – have said they were making their own 5G chipsets which would be integrated into their 5G smartphones. Will Samsung use both its own silicon as well as Qualcomm’s in future 5G devices?
Over the next few months Qualcomm will begin shipping both the Snapdragon 865 and Snapdragon 765 chipsets. The Snapdragon 865 is more powerful, though 5G is on a separate modem, potentially decreasing the power efficiency of devices. The Snapdragon 765 has 5G connectivity integrated, though is notably less powerful. Whichever chipset OEMs elect for, there will be a trade-off to stomach.
Looking at the rumours spreading through the press, it does appear many of the smartphone manufacturers are electing for the Snapdragon 865 and a paired 5G modem in the device. Samsung’s Galaxy S11, Sony Xperia 2 and the Google Pixel 5 are only some of the launches suggested to feature the Snapdragon 865 as opposed to its 5G integrated sister chipset.
With Mobile World Congress 2020 in Barcelona just two months away, there is amble opportunity for new 5G devices to be launched prior, during and just after the event. It will be interesting to see what 5G silicon is used in them.
Incomplete (or non existent) 5G Standards:
Of critical importance is that there are currently no standards for 5G implementations. The closest is IMT 2020.SPECS which won’t be completed and approved till November 23-24, 2020 ITU-R SG5 meeting or later. That spec will likely not include the 5G packet core (5GC), network slicing, virtualization, automation/orchestration/provisioning, network management, security, etc which will either be proprietary or use 4G LTE infrastructure. It also might not include signaling, ultra low latency or ultra high reliability, depending on completion of those items in 3GPP Release 16 and its disposition to ITU-R WP 5D.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
For nearly a decade, Samsung has worked to bring 5G from the lab to real life by working closely with carrier partners, regulatory groups and government agencies to develop the best 5G experience possible. As a leading contributor to industry groups like 3GPP and O-RAN Alliance, Samsung is committed to an open, collaborative approach to networking, which has helped to accelerate delivery of 5G to consumers and businesses. Over the past year, in addition to launching a robust 5G device portfolio, the company reached several historical milestones including providing network equipment for the world’s first 5G commercial service in Korea as well as working closely with global carrier partners to expand 5G networks and introduce 5G experiences and use cases.
In the year ahead, Samsung says they will continue to lead the market in 5G innovation by introducing new advancements that will improve the speed, performance and security of Galaxy 5G devices even further. In 2020, these advancements will give even more people access to new mobile experiences that change the way they watch and interact with movies, TV and sports, play games and talk with friends and family.
For more information about Samsung Galaxy 5G devices please visit news.samsung.com/us/galaxy-5g/, www.samsungmobilepress.com or www.samsung.com/galaxy.
References:
https://news.samsung.com/us/samsung-galaxy-5g-devices-shipping-more-than-6-million-2019/
https://telecoms.com/501580/samsung-claims-the-5g-lead-after-6-7-million-shipments/
https://www.extremetech.com/mobile/304091-samsung-shipped-over-6-7-million-5g-phones-in-2019
China Internet penetration reached 61.2% in 1st half 2019; 99.1% access Internet via mobile phones!
Internet penetration in China reached 61.2 percent in the first half of the year, with 854 million internet users at end June, according to China government-backed research institute MIC (Market Intelligence & Consulting Institute) and reported by China Internet Watch.
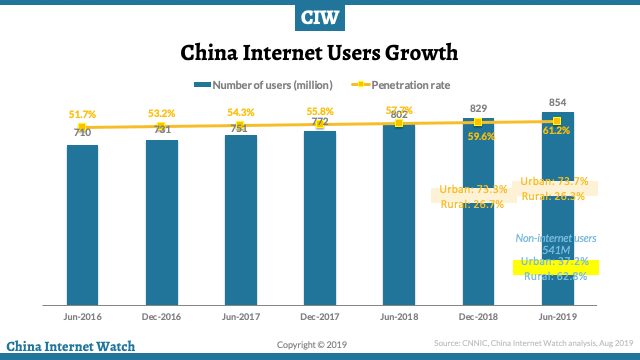
China internet users in urban areas account for 73.7% of total internet users. Among the Chinese population who don’t access the internet (which is 541 million), rural areas account for 62.8%. Internet user growth is mainly relying on mobile terminals, which is also very slow.
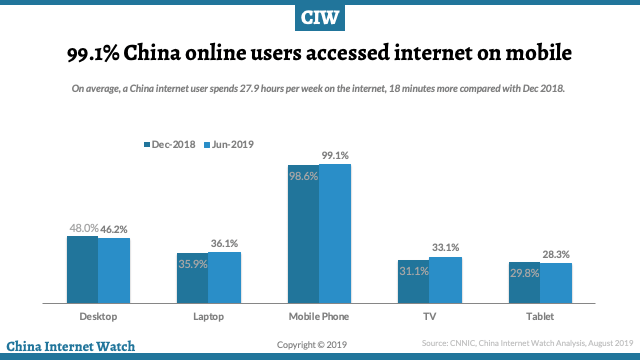
The number of internet users on mobile phones is 847 million, accounting for over 99% of internet users in China. Smartphones have become the top internet access devices in China.
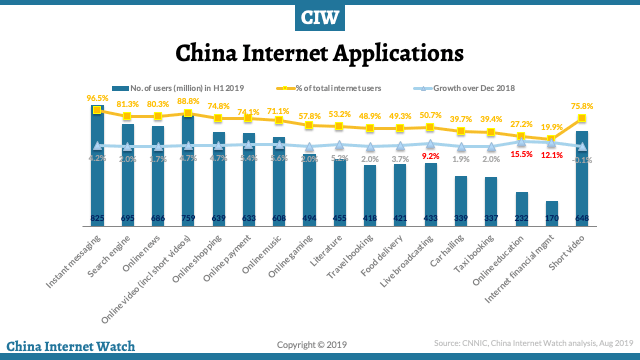
Short video consumers made up 88.8 percent of all internet users, about 760 million, breaking past the 490 million online gamers.
Top online applications by total number of users in the first half of 2019 are instant messaging, search engines, online news, online videos, and online shopping.
About 80.2 percent of internet users on the country’s three major platforms – iQiyi, Tencent, and Youku, watch OTT content. Bilibili, Sohu Video, and Mango TV were also very popular. These platforms are making big investments into exclusive content.
“Content quality has become the key to competitiveness,” MIC said.
References:
https://www.chinainternetwatch.com/statistics/china-internet-users/
https://app.box.com/s/jz9iet7vja58ciqw51j31bxeib986ms1?
ITU Hosted ICT CxO Meeting: achieving ‘self-driving’ IMT-2020/5G networks
Introduction:
Innovation to achieve ‘self-driving’ IMT-2020/5G networks, collaboration in the interests of 5G security and the value of ‘open’ network concepts were among the key topics discussed at an invitation-only meeting of ICT industry executives (‘CxOs’) held last week in Dubai, UAE, in conjunction with the Telecom Review Leaders’ Summit. The CxO meeting’s discussions revolved around industry preparations for IMT-2020/5G.
CxOs shared insights gained from early 5G deployments and trials of 5G–enabled industrial Internet of Things (IoT) applications. They also discussed the importance of building public trust in autonomous driving and the safety-critical radiocommunications supporting Intelligent Transport Systems.
With a view to discussing industry needs and associated standardization priorities, the meeting brought together representatives of companies including du, Etisalat, Facebook, Fujitsu, Korek Telecom, Krypton Security, Nokia, Orange, Roborace, Rohde & Schwarz, SES Networks and TELUS.
The trends discussed at the CxO meeting reflect the evolution of ITU membership, in particular that of ITU’s standardization arm (ITU-T). ITU-T has welcomed 51 new members in 2019, following 45 new members in 2018.
New ITU-T members include companies in energy and utilities, shipping and logistics, mobile payments, over-the-top applications, automotive, IoT connectivity, blockchain and distributed ledger technologies, quantum communications, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The meeting issued a communiqué summarizing ICT trends of growing relevance to ITU standardization.
< Download the CxO meeting communiqué >
The optimization of network management and orchestration – capitalizing on real-time network performance data, machine learning for prediction and self-learning, and the automated build and configuration of virtual network functions – will improve ICT services and introduce new cost efficiencies, said CxOs.
ITU-R WP 5D will produce a draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.C-V2X] on “Application of the Terrestrial Component of IMT for Cellular-V2X.”
3GPP intends to contribute to the draft new Report and plans to submit relevant material at WP 5D meeting #36. 3GPP looks forward to the continuous collaboration with ITU-R WP 5D for the finalization of Report ITU-R M.[IMT.C-V2X].
This optimization is becoming increasingly challenging, and increasingly important, as networks gain in complexity to support the coexistence of a diverse range of ICT services.
CxOs encouraged ITU to study the evolution of network operation and maintenance in view of increasing network complexity and the resulting importance of automation informed by machine learning.
CxOs discussed the progress achieved in responding to the ‘Ottawa Accord’ considered by ITU’s annual Chief Technology Officer (CTO) meeting in Budapest, Hungary, 8 September 2019.
The Ottawa Accord is a set of security priorities developed in June 2019 by network operators, standards bodies and industry associations.
The Budapest CTO meeting endorsed the findings of the Ottawa Accord in relation to three security priorities:
- Global threat exchange: Common understanding of security threats and common terminology to enable the sharing of threat intelligence.
- Best practices for operational security: Best practices for 5G security and widespread commitment to infrastructure protection.
- Security incentives: Measurement schemes based on agreed metrics could bring attention to prevailing levels of security and create incentives for investment in security.
CxOs echoed the sentiment of the Budapest CTO meeting that a holistic approach to 5G security could receive valuable support from a global centre for the development of security solutions and their testing and assurance. Such a ‘living lab’ open to multiple vendors, said CTOs in Budapest, could bring cohesion to 5G security efforts as well as reduce the costs of testing security solutions.
CxOs with experience in the early commercial deployment of 5G reiterated the importance of investment in fibre. Fibre-optic networks form the ‘backbone’ of the ICT ecosystem. Investment in fibre continues to rise, recognizing the importance of this investment to the 5G vision.
Experience with industrial IoT applications as part of the development of 5G-enabled smart sea ports and smart factories, said CxOs, has highlighted the importance of network slicing and shown edge computing to be capable of supporting low latencies. CxOs’ experience with 5G-enabled smart factories, in particular, has shown such factories to be capable of highly efficient production and quality control.
Infrastructure sharing has the potential to assist network operators in reducing time-to-market for new solutions, gaining cost efficiencies and increasing coverage in certain network deployment scenarios.
CxOs illustrated possible scenarios for the sharing of infrastructure such as core networks, central offices, backhaul infrastructure, towers, and RANs.
The meeting considered an example of ‘Multi-Core Operator Networks’, networks said to be capable of reducing an operator’s infrastructure investments through sharing, while improving network performance.
General-purpose ‘white box’ hardware, standardized interfaces and virtualized network elements are the foundations of the ‘open RAN’ concept, said CxOs.
Open RAN could support industry in avoiding the challenges that may result from proprietary RAN interfaces, challenges such as RAN equipment vendor lock-in, limited interoperability between different vendors’ RAN equipment, and limited scope for active RAN sharing.
CxOs offered the view that the standardization of open, interoperable RAN interfaces and RAN functional architecture could support a diverse business ecosystem in deploying and operating RANs with considerable cost efficiency.
ITU has established a new Focus Group on ‘Artificial intelligence for autonomous and assisted driving’ to work towards the establishment of international standards to monitor and assess the performance of the AI ‘Drivers’ in control of automated vehicles.
CxOs discussed the ITU Focus Group’s aim to devise a ‘Driving Test’ for AI ‘Drivers’. The proposed test could become the basis for an International Driving Permit for AI. The right to hold this permit would be assessed continuously, based on the AI Driver’s behavioural performance on the road.
CxOs highlighted their support for the Focus Group’s expected contribution to public trust in automated vehicles as well as the value of ITU collaboration with UNECE in this regard.
Recognizing the importance of new radio technology and applications to Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS), CxOs highlighted the importance of conformance assessment based on harmonized test requirements.
According to the CxOs, compliance, conformance and quality testing will make a key contribution to industry and consumer confidence in safety-critical radiocommunications in the ITS context. Conformance assessment would also support ITS interoperability and cost efficiency, said CxOs.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The participating organizations were:
Arab Information & Communication Technologies Organization (AICTO), du, Etisalat, Facebook,
Fujitsu, Korek Telecom, Krypton Security, Nokia, Orange, Roborace, Rohde and Schwarz, SES
Networks, Telecom Review North America, Telecommunication Industry Association (TIA), TELUS
References:
Intelligence, security and cost efficiency: Industry executives highlight priorities for the 5G era
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/tsbdir/CxO/Documents/Communique%20-%20CxO%20-%20Dubai%202019.pdf
Zayo’s largest capacity wavelengths deal likely for cloud data center interconnection (DCI)
Zayo Group Holdings announced it has signed a deal for the largest amount of capacity sold on any fiber route in the company’s history. The deal with the unnamed customer will provide approximately 5 terabits of capacity that can be used to connect mega scale data centers. While Zayo didn’t disclose the customer, large hyperscale cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Project, and webscale companies such as Facebook, seem to be likely candidates.
Zayo provides a 133,000-mile fiber network in the U.S., Canada and Europe. Earlier this year it agreed to be acquired by affiliates of Digital Colony Partners and the EQT Infrastructure IV fund. That deal is slated to close in the first half of next year.
“Our customers [1] are no longer talking gigabits — they’re talking terabits on multiple diverse routes,” said Julia Robin, senior vice president of Transport at Zayo. “Zayo’s owned infrastructure, scalable capacity on unique routes and ability to turn up services quickly positions us to be the provider of choice for high-capacity infrastructure.”
Note 1. Zayo’s primary customer segments include data centers, wireless carriers, national carriers, ISPs, enterprises and government agencies.

Zayo to extend fiber-optic network in central Florida: The new fiber network infrastructure, comprising more than 2300 route miles, will open Tampa and Orlando as new markets for the fiber-optic network services company.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Zayo’s extensive wavelength network provides dedicated bandwidth to major data centers, carrier hotels, cable landing stations and enterprise locations across our long-haul and metro networks. Zayo continues to invest in the network, adding new routes and optronics to eliminate local stops, reduce the distance between essential markets and minimize regeneration points. Options include express, ultra-low and low-latency routes and private dedicated networks.
Zayo says it “leverages its deep, dense fiber assets in almost all North American and Western European metro markets to deliver a premier metro wavelength offering. Increasingly, enterprises across multiple sectors including finance, retail, pharma and others, are leveraging this network for dedicated connectivity as they seek ways to have more control over their growing bandwidth needs.”
According to a report by market research firm IDC, data created, captured and replicated worldwide will be 175 zettabytes by 2025 and 30% of it will be in real time. A large chunk of that amount will be driven by webscale, content and cloud providers that require diverse, high capacity connections between their data centers. In order to provision high bandwidth amounts, service providers and webscale companies are turning to dedicated wavelength solutions.
Zayo’s wavelength network provides dedicated bandwidth to major data centers, carrier hotels, cable landing stations and enterprise locations across its long-haul and metro networks. Its communications infrastructure offerings include dark fiber, private data networks, wavelengths, Ethernet, dedicated internet access and data center co-location services. Zayo also owns and operates a Tier 1 IP backbone and 51 carrier-neutral data centers.
References:
For more information on Zayo, please visit zayo.com
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/zayo-lands-largest-wavelengths-deal-its-history-at-5-terabits
Nokia and Wipro partner to develop 5G use cases for accelerating technology adoption in India; 5G end-to-end live network trial in Indonesia
At the Indian Mobile Congress (IMC 2019) in New Delhi, Finland headquartered Nokia announced it has partnered with Indian IT services company Wipro to develop 5G use cases for telecom operators and enterprise customers. Nokia said it is testing several 5G use cases at its research and development lab in Bengaluru (previously known as Bangalore) India, while Wipro is expected to provide domain-based solutions required for this new 5G ecosystem.
The collaboration will explore technical and operational feasibility of use cases, such as augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR)-based immersive learning experience, as well as drone-based applications for agriculture, public safety energy, and utilities, using real-time network analytics, life cycle operation management and edge computing. While Nokia will provide a live 5G end-to-end system, including radio, core and devices in its lab, Wipro will integrate its application solutions for 5G use cases that include software solutions and user devices along with key system integration and delivery capabilities. The turnkey solutions are expected to help operators and enterprise customers realize full value from their 5G investments, Nokia said in a press release.
“We are thrilled to be an open-innovation partner to Nokia to work on innovative and creative 5G use cases,” K R Sanjiv, Chief Technology Officer, Wipro, said in a statement. “With Nokia’s expertise and leadership in 5G, we are confident that we will create more useful 5G use cases in the future, which will help the operators in the rapid adoption of the technology and faster realisation of their 5G investment,” Sanjiv added.
As part of the partnership, Nokia will provide a live 5G end-to-end system, while Wipro will integrate its application solutions for 5G use cases that include software solutions and user devices along with key system integration and delivery capabilities. Several enterprise use cases, tested by Wipro in a live 5G network at Nokia’s Bengaluru lab, are being showcased at India Mobile Congress 2019 here.
Nokia and Wipro have already conducted lab tests of two 5G use cases – drone-based transmission line monitoring within the utility domain and in immersive entertainment experiences for large scale events, such as sports championships, aimed at enhancing the user experience. These use cases will be further developed and validated, along with other new use cases that can be rapidly executed for field trials for mass adoption, once the 5G spectrum is available, Nokia said.
“Globally, Nokia is at the forefront of developing the 5G ecosystem. Our state-of-the-art Bengaluru R&D centre is working with several partners to do just this, and we are committed to supporting Indian operators in their 5G journey. Our work with Wipro is a crucial step in this direction. The initiative also supports the Indian government’s plans to fast-track the development of use cases that will be socially beneficial and unique to India” said Randeep Raina, Chief Technology Officer at Nokia India.
Nokia said its network function virtualization infrastructure (NFVI)-based secured edge cloud comes in handy for low-latency use cases whereas its internet of things (IoT) impact platform-based device management to host and manage the lifecycle support 5G use cases in different industry verticals.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The companies have already conducted lab tests of two use cases – drone-based transmission line monitoring within the utilities domain and in immersive entertainment experiences for large scale events such as sports championships, aimed at enhancing the user experience. The companies are looking to further develop and validate other use cases that can be rapidly executed for field trials for mass adoption.
India’s central government is planning to conduct 5G spectrum auctions by the end of this year. Indian Union minister for communications and information technology Ravi Shankar Prasad said earlier this week that reforms are expected in the pricing of the 5G spectrum.
Source: Business Insider Intelligence
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Nokia and Hutchison 3 have completed the first 5G end-to-end live network trial in Indonesia. The trial, which was conducted on a Nokia network on millimeter wave frequencies, demonstrates the 3ID network’s ability to support end-to-end 5G deployment.
Multiple tests were conducted on the 28 GHz spectrum, obtaining the highest data download speeds of up to 1.62 Gbps with 11ms latency while upload speeds of 75.9 Mbps were measured. The trial also included a voice call test, which was initiated on the 5G trial network and realized over VoLTE (voice over existing LTE network) to demonstrate how basic telephony services would be handled in 5G.
The trial, which also involved the Indonesian Ministry of Communication and Information Technology, was conducted at the Sepuluh Nopember Institute of Technology (ITS) in Surabaya, East Java. It focused on education-related use cases, utilizing 5G technology to enable a public lecture conducted in real-time between two major cities, Surabaya and Jakarta. During the trial, ministry officials and academics from the ITS delivered a public lecture, with a representative from the Indonesia 5G Forum joining them via a live stream holographic projection from Jakarta.
The tests were conducted over a Nokia-built network, including radio, core and transport, providing high, unfettered download and upload speeds with low latency. They demonstrated how 5G technology can be used to give students remote access to learning materials that may be difficult to access due to physical distances. The trial also showed how the learning experience can be made more immersive while helping students compete with their academic peers in other locations. It also confirmed the ability of 5G to go well beyond simple connectivity in supporting economic and social development in Indonesia.
KP Goh, Head of Indonesia at Nokia, said: “Completing the first 5G end-to-end trial in Indonesia is an important milestone. 5G is going to change just about everything – every industry, every business, and every experience – including the student experience. With Nokia’s end-to-end 5G technology, Indonesia is ready to support 5G deployment now and Indonesian students are able to reap the benefits of faster connections with lower latency. With 48 commercial 5G contracts and more than 100 customer engagements, we are pleased to see the pace of 5G progress accelerating across the globe – including Indonesia.”
Cliff Woo, Chief Executive Officer at Hutchison 3 Indonesia, said: “This trial, powered by Nokia’s end-to-end capability, showcases how 5G technology can help students across Indonesia to have equal opportunities and compete with their peers in other countries – by connecting them to sources of knowledge from all across the world. Nokia is one of our key technology partners in Indonesia. We are pleased to have completed this important trial with Nokia. It will pave the way for the 5G journey to serve the Indonesian people and industry.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.digianalysys.com/nokia-and-wipro-to-develop-5g-use-cases/
https://nokiapoweruser.com/nokia-and-wipro-joined-hands-to-develop-5g-ecosystem-in-india/
https://www.nokia.com/networks/5g/
IHS Markit: CenturyLink #1 in the 2019 North American SIP Trunking Scorecard
By Diane Myers, senior research director, IHS Markit
Highlights:
- CenturyLink leads the market for session initiation protocol (SIP) trunking with the largest installed base of all North American providers.
- Twilio has been a disruptor in the SIP trunking market and placed second in the scorecard due to solid market momentum.
- Verizon and AT&T were #3 and #4, respectively.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Note:
SIP (Session Initiated Protocol) trunking is a method of sending voice and other unified communications services over the internet. It works with an IP-enabled PBX (private branch exchange). SIP trunking replaces traditional telephone lines or PRIs (Primary Rate Interface).connects both IP and analog devices via the Internet, eliminating the need to maintain separate voice circuits or replace legacy equipment.
Before SIP became a popular and reliable method of transmitting voice signals, telephone calls were carried over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The PSTN is a circuit switched network, which requires a physical connection between two points to complete a call.
SIP trunks are virtual phone lines that enable users to make and receive phone calls over the internet to anyone in the world with a phone number. SIP trunks utilize a packet switch network, in which voice calls are broken down into digital packets and sent across a network to the final destination.

Each SIP trunk supports SIP channels. A SIP channel is equivalent to one incoming or outgoing call. A SIP trunk can hold an unlimited number of channels, so users only need one SIP trunk no matter how many concurrent calls they expect. The number of channels required depends on how many calls the business will make at any one time.
References:
https://www.sip.us/blog/latest-news/sip-trunking-101-the-fundamentals/
https://www.nextiva.com/blog/sip-trunking.html
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IHS Markit analysis:
In its 2019 SIP Trunking North America Scorecard, IHS Markit analyzed and ranked the top SIP trunking providers in North America. For the fourth year in a row, CenturyLink leads the SIP trunking market with solid growth and the largest installed base of trunks. CenturyLink has done extensive work over the past two years bringing together its assets with those of Level 3, a company it acquired in 2017, to build a market-leading service portfolio and customer base.
In this year’s scorecard, Twilio made another jump to the second-ranked position because of its strong financial score and the continued growth of its installed base. Twilio has been a market disruptor with its Elastic SIP Trunking service, which has grown to attain a sizable installed base. The strong growth of Twilio’s Elastic SIP Trunking service reflects the widespread appeal of flexible consumption-based pricing.
Just a few years ago, there was little differentiation in the SIP trunking market. Fast forward to today, and there is a stark difference between traditional trunking services and the new on-demand trunks. Traditional trunking remains grounded in the old world of contracting for voice networking. In contrast, with on-demand trunks, customers simply pay for what they use and never need to worry about capacity planning.
SIP Trunking North America Scorecard:
In the 11th annual SIP Trunking North America Scorecard, IHS Markit analyzes the top-10 North American SIP trunking service providers: CenturyLink, Twilio, Verizon, AT&T, IntelePeer, Fusion, Rogers, Voyant, Windstream and Sprint. The criteria used in this analysis include market share, financial strength, market share momentum, service development and support options.
Huawei to help create China’s first open source software foundation; unveils Honor Vision smart screen with Harmony OS
Huawei Technologies Co. said today that it plans to partner with other companies to set up China’s first open-source software foundation, which is expected to begin to operate in a month or two to expand the nation’s software community.
Wang Chenglu, president of the software department at Huawei’s consumer business group, said software development relies on open-source codes and communities. “If China does not have its own open-source community to maintain, manage and host these open-source codes, the domestic software industry will be vulnerable in the face of uncontrollable factors,” Wang said. The first open-source foundation in China will be nonprofit and open to all companies and software developers. “The plan is going forward very fast. It may officially operate in one or two months,” Wang said. Wang added it is widely agreed that open-source communities are created to be fair and equitable for all, but now have become a means of making a power play between countries.

The first open-source foundation in China will be nonprofit and open to all companies and software developers. [Photo/IC]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last month, Nat Friedman, CEO of GitHub, which is owned by Microsoft, said on Twitter that GitHub is subject to US trade law just like any company that does business in the US. GitHub has enforced restrictions to prevent users in sanctioned countries from accessing private repositories and the GitHub Marketplace and from maintaining private, paid organization accounts, technology news website TechCrunch reported.
Maral Khosroshahi, who identified herself as a deep-learning scientist at Microsoft and founder and chairwoman of Iranian Women in Computing, said in a post on Twitter on July 27th that GitHub suspended all accounts of Iranian developers without any prior notice. “This is a shame, … especially for those who keep saying that sanctions are not supposed to affect ordinary people,” Khosroshahi said in the post, adding that those views are her own.
Xiang Ligang, director-general of the telecom industry association Information Consumption Alliance, said the GitHub incident sent a warning to Chinese professionals that heavy reliance on U.S.-led open source communities may carry risks.
The open source plan also came after Huawei unveiled its in-house operating system Harmony OS on Friday, with the idea of using it in smart TVs, automobiles, wearables and other hardware over the next three years. Lyu Tingjie, a telecom professor at Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, said Huawei decided to build Harmony into an open-source system because it knows that support from a wide range of partners is needed to build a robust ecosystem. “The foundation plan, if well-executed, will help accelerate the development of Huawei and China’s overall software industry,” Lyu said.
For more information contact:
China Daily Multimedia Co. Ltd.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

George Zhao, president of Huawei’s sub-brand Honor, unveils Honor Vision series during the Huawei Developer Conference held in Dongguan, South China’s Guangdong province on Aug 10, 2019. Honor Vision is the world’s first smart screen equipped with HarmonyOS, or Hongmeng in Chinese, Huawei’s open-source operating system. [Photo/Xinhua]
“Huawei will continue to lead a broader effort to build China’s software developer ecosystem and complete industry chain for the electronic information industry, rather than just launch its OS,” Xiang Ligang, director-general of the Beijing-based Information Consumption Alliance, told the Global Times.
The HarmonyOS is an open-source system, but without the support of most application developers, it can’t grow at a rapid pace and neither can the industry, Xiang said. The HarmonyOS was initially seen as an alternative plan to deal with the risks of losing access to Google’s Android software and overseas market share after the US attack. Huawei is confident in keeping its overseas market share and displayed an ambition to make the HarmonyOS successful.
Richard Yu Chengdong, CEO of Huawei’s consumer business, said that the HarmonyOS can make Huawei’s devices functional again overnight, if the Android OS on the devices fails. Huawei has obviously entered a whole new stage of fully developing its OS, developer ecosystem and more terminals equipped with the OS. It will eventually build its Internet of Things based on its leading communication systems, rather than just focusing on mobile phone products, a veteran industry analyst told the Global Times on condition of anonymity.
References:
http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201908/13/WS5d51ed9ea310cf3e35565513.html
http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201908/12/WS5d512715a310cf3e35565454.html
http://www.globaltimes.cn/content/1161064.shtml



