India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for 5G equipment attracts Nokia & Ericsson
Nokia and Ericsson said India’s production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme [1.] for design-led 5G manufacturing will position India as a global manufacturing hub and allow them to deepen their manufacturing capabilities in the country.
Note 1. PLI is the sum of India government incentives that are directly linked to manufacturing performance. The more goods companies manufacture in India the better incentives they will get. The incentives are of diverse types: subsidies, monetary benefits, etc.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Nokia said it is exploring opportunities to manufacture more products in India in a cost-competitive manner to serve both the local and the global market. Nokia’s India spokesperson said the company was on track to fulfil its investment and production commitments under the existing PLI scheme for telecom equipment.
Swedish telecom equipment vendor Ericsson, in a separate statement, said 5G spectrum auction with 100% fiberization (backhaul) with public-private partnership (PPP) model by 2025 will help bridge the digital divide for an inclusive development of the nation in-line with the ‘Digital India’ vision.
“Design-led initiatives for 5G under the PLI scheme and 5% of USOF for R&D purposes will strengthen the ‘Make in India’ initiative, and contribute to making India a global manufacturing hub,” said Nitin Bansal, managing director for India at Ericsson.
Ericsson, along with Nokia, Akashastha Technologies, HFCL, Foxconn, Coral Telecom, VVDN Technologies, Dixon Technologies, Tejas Networks and GS India, were selected for the original PLI scheme. India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT) approved 31 proposals in 2021 entailing investments of INR33.5 billion ($447.3 million) over the next four years.
“The scheme for design-led manufacturing to be launched for the 5G ecosystem as part of PLI will be a boost to the overall telecom and electronic sectors. It will also provide and promote research and development of technology and solutions and will enable affordable broadband and mobile communication,” says Sanjay Gupta, vice president and India managing director, NXP Semiconductors.
Some media reports suggest that it is possible that the funds for this scheme may come from the ongoing PLI scheme for the telecom sector.
The scheme is in keeping with the government’s keenness to position India as a telecom manufacturing destination with a growing emphasis on self-reliance and the domestic manufacturing ecosystem.
Chinese gear makers Huawei and ZTE are yet to receive trusted source approval from the National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC), which means the space is open to Indian manufacturers.
It’s possible that the government may mandate the Indian service providers to procure a certain percentage of their requirement from the Indian vendors only. The PLI scheme is timely, with the announcement that the 5G spectrum auction will be held in 2022.
Service providers are in the midst of conducting 5G trials, and will be investing heavily in 2022 to build networks. 5G capex is likely to increase significantly over the next few years – hopefully helping Indian manufacturers grab some share of the pie.

Orange Espana reveals 700MHz 5G rollout plans
Orange Espana has announced its plans for activation of 5G services on the 700 MHz band, describing the network as the largest 5G-700MHz network in Spain.
The 700 MHz band, already used by some operators for 4G, has the benefit of enabling good penetration inside buildings and good coverage with speeds comparable to those of mono-band 4G.
A few weeks after Vodafone said it would reach 109 localities by the end of the year, Orange responded that it will cover 1,100 towns and cities with the technology by December, including around 140 digital divide localities with less than 1,000 inhabitants.
The rollout will also include 140 towns and cities with more than 50,000 inhabitants and 820 localities with between 1,000 and 50,000 inhabitants across 30 provinces. Benefits of the 700 MHz band frequencies include lower latencies plus significantly better coverage in indoor and larger outdoor areas, said the operator.
Orange activated its first 5G antenna for the 700 MHz band at Valencia’s Polytechnic University last September, having switched on its Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G network in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville and Malaga the previous year.
The launch comes after Orange paid EUR 350 million for a 2×10 MHz block in the government’s July 2021 auction of frequencies in the 700 MHz band. Orange has the largest amount of 5G-compatible spectrum in Spain thanks to its existing 110 MHz concession in the 3.5 GHz band, for which it paid EUR 173 million.
As of 30 September 2021, Orange Espana offered 5G coverage to over 50% of the population and had 620,000 5G subscriptions.
MetroNet’s FTTP buildout in Florida; Merger with Vexus Fiber
Continuing with the massive U.S. fiber to the premises (FTTP) movement, regional fiber carrier MetroNet (headquartered in Evansville, Indiana) said it will bring fiber-optic internet access directly to homes and businesses throughout the Deltona, FL and neighboring communities, including DeBary and Orange City.
Deltona marks the third community in Florida that will have access to MetroNet services through a fully funded $35 million investment in the community. The three-year construction project is set to begin in the summer of 2022, with the first customers able to receive service as early as the fall of 2022.
Once completed, Deltona will join the country’s internet elite as a Gigabit City. Only about 40 percent of households in the U.S. have access to symmetrical upload and download gigabit (1,000 mbps) speeds that only fiber optic networks can provide.
“MetroNet is thrilled for Deltona residents and businesses to have access to our future-proof services that will allow sparkling 4k video streaming, glitch-free gaming, crystal-clear virtual meetings, and internet experiences of the future that we can only begin to imagine,” said John Cinelli, MetroNet’s CEO. “MetroNet is proud to soon be able to add Deltona to our growing list of Gigabit Cities.”
MetroNet plans to hire local market management positions, sales and customer service professionals, and service technicians to support the Deltona area. Those interested in joining the MetroNet team can visit MetroNetInc.com/careers to search available positions and to submit applications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Last week, Metronet announced it has merged with fellow independent fiber based network provider Vexus Fiber. The combined companies will continue to operate under their existing brands and with their existing executive roster. Financial terms of the deal were not disclosed.
Vexus, based in Lubbock, TX, deploys and operates FTTP networks in Texas and Louisiana, with plans for expansion in New Mexico. Markets currently serving those states include Lubbock, Amarillo, Wichita Falls, Abilene and surrounding areas of Texas, as well as Hammond, Covington and Mandeville in Louisiana. New FTTP networks in the Rio Grande Valley are in various stages of deployment (see “Vexus Fiber to Build FTTH Network in Rio Grande Valley Region of Texas”), Tyler, Nacogdoches, and San Angelo, TX; Lake Charles, LA; and Albuquerque and Santa Fe, NM. Investors in the company included Pamlico Capital and Oak Hill Capital.
Metronet is operating or building FTTP networks in more than 120 communities in Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Florida, North Carolina, Virginia, Texas, Wisconsin, and Missouri. It had received cash from KKR last April (see.) “KKR will take stake in Metronet as part of new funding round”) Oak Hill Capital is also an investor. Both companies provide gigabit or faster broadband services to their residential and business customers.
“We are very excited to welcome Vexus Fiber and their partners to Metronet,” said Metronet CEO John Cinelli. “Vexus has rapid growth and a high-customer-service mindset, similar to Metronet, and joining them allows us to expand our service area to even more Americans.”
“At Wexus, our mission is to bring our high-quality service to as many homes and businesses as possible in the Southwest,” said Jim Gleeson, president and CEO of Wexus. “With this merger, we can reach even more people faster.”
About MetroNet:
MetroNet is the nation’s largest independently owned, 100 percent fiber optic company headquartered in Evansville, Indiana. The customer-focused company provides cutting-edge fiber optic communication services, including high-speed Fiber Internet and full-featured Fiber Phone with a wide variety of programming.
MetroNet started in 2005 with one fiber optic network in Greencastle, Indiana, and has since grown to serving and constructing networks in more than 150 communities across Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Florida, North Carolina, Virginia, Texas, Wisconsin, Missouri, and New Mexico. MetroNet is committed to bringing state-of-the-art telecommunication services to communities — services that are comparable or superior to those offered in large metropolitan areas.
MetroNet has been recognized by PC Mag as one of the Top 10 Fastest ISPs in North Central United States in 2020 and Top 10 ISPs with Best Gaming Quality Index in 2021. Broadband Now has recognized MetroNet as the Top 3 Fastest Internet Providers and Fastest Fiber Providers in the Nation in 2020, and #1 Fastest Mid-Sized Internet Provider in two states in 2020. In 2020, MetroNet was awarded the Vectren Energy Safe Digging Partner Award from Vectren. For more information, visit www.MetroNetinc.com.
Media Contact: Katie Custer [email protected] 502.821.6784
References:
Sandvine: Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Apple, Amazon & Netflix generate almost 57% of Internet traffic
Sandvine’s newly released 2022 “Global Internet Phenomena Report” aggregates data from more than 160 Tier 1 and Tier 2 fixed and mobile networks worldwide to reveal unprecedented trends, such as:
• Rapid growth of 1Terabyte per month “heavy app users,” a trend that is expected to accelerate with the transition from 4G to 5G and the explosion of video everywhere across social, gaming, messaging, and immersive experiences;
• First-time “tipping of the scales,” with Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Apple, Amazon, and Netflix generating almost 57% of Internet traffic – more than everyone else, combined;
• QUIC [1.] multiplexed transport, encryption, and privacy protocols like Apple iCloud Private Relay obscuring network visibility for capacity planning and congestion management;
Note 1. QUIC is a Transport layer protocol used by more than half of all connections from the Chrome web browser to Google’s servers. Microsoft Edge and Firefox browsers also support it.
• Mashups of videos, payments, maps, chat, and other features increasing the need for more sophisticated machine learning techniques to measure and deliver optimal app quality of experience (QoE);
• Global rankings of “Top-10 Apps” in Video, Gaming, Social, Messaging, Enterprise Conferencing, with Google’s YouTube retaining the top spot in global app traffic share at 14.67% followed by Netflix at 9.39%, as well as other downstream/upstream and regional trends (Americas, EMEA, and APAC).
Samir Marwaha, Chief Strategy Officer, Sandvine said: “Our latest ‘Global Internet Phenomena Report’ shows that people care more about how their favorite apps perform than the underlying networks. This makes it crucial that 5G and Cloud service providers understand, at a granular level, the application quality of experience they are delivering to customers. That’s going to have the greatest impact on their brands and their ability to generate revenue streams within new business models.”
Gabriel Brown, Principal Analyst, Mobile Networks and 5G, Heavy Reading said:
“The top content producers serving more traffic and accounting for a greater share of network load has a big impact, but at least it is a known quantity. The other part of the story is the increasing diversity of traffic sources – from new streamers, live sports, gaming, and device updates – and the growth of complex apps that combine multiple traffic types and services in a single customer experience. In combination with the rise of QUIC and iCloud Private Relay, this is challenging operators to better understand where and when traffic originates. Insight into these emerging patterns can help operators manage network capacity and meet customer expectations.”
Get the Report and on-demand Webinar to see the hottest trends and insights derived from more than 2.5 billion internet subscribers. Also, check out other resources, such as our 5G Service Innovation and Intelligence Whitepaper, 5G Service Intelligence Engine (NWDAF) Whitepaper, Cloud-Ready Options, and Use Cases eBook.
About Sandvine:
Sandvine’s cloud-based Application and Network Intelligence portfolio helps customers analyze, optimize, and monetize application experiences using contextual machine learning-based insights and real-time actions. Market-leading classification of more than 95% of traffic across mobile and fixed networks by user, application, device, and location significantly enhances interactions between users and applications. For more information about delivering superior quality of experience with uniquely rich, real-time data that can drive performance and revenues, visit http://www.sandvine.com or follow Sandvine on Twitter @Sandvine.
Media Contact:
Susana Schwartz, Sandvine +1 816 680 1447 [email protected]
References:
https://www.sandvine.com/global-internet-phenomena-report-2022?hs_preview=khpPseNo-62343537839
Deutsche Telekom launches 5G private campus network with Ericsson; Sovereign Cloud for Germany with Google in Spring 2022
Overview:
Ericsson and Deutsche Telekom have partnered to deliver a new 5G Standalone (5G SA) private campus network offering, aimed at on-site business communications infrastructure. The new campus network offering is based on a local 5G infrastructure that is exclusively available for the customer’s digital applications. The 5G SA technology works without LTE anchors (as in 5G NSA) and offers all the technical advantages of 5G – even for particularly demanding and safety-critical use cases: fast data transmission rates, maximum network capacity and highly reliable connectivity with low latency.
With the advanced 5G SA technology, Deutsche Telekom and Ericsson support companies from a wide range of industries in developing innovative digital applications and making existing processes more efficient.
The newly offered 5G SA Campus network – powered by the Ericsson Private 5G portfolio – operates completely separated from the public mobile network: all components of the infrastructure from the antennas to the standalone core network to the network server are located on the customer’s premises. This ensures that sensitive data remains exclusively within the local campus network. The local connection of the customer infrastructure also enables particularly simple and fast processing of data via the private network. This standalone 5G architecture of “short distances” is most suitable for supporting business-critical applications that require ultra-short response times in the millisecond range. The 5G SA network operates on frequencies in the 3.7 to 3.8 GHz range that are specifically allocated to the enterprise. Thus, up to 100 MHz bandwidth is available for the exclusive use within the private campus network.
The new 5G private campus network is being launched in Germany under the name “Campus-Netz Private” – and will be offered to business customers in other European countries.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Analysis: It is quite interesting that Deutsche Telekom chose Ericsson as it’s 5G SA Core network vendor, rather than hyper-scalers like Amazon AWS or Microsoft Azure who are building 5G SA core networks for Dish Network and AT&T respectively. Amazon also offers its own private 5G network directly to enterprise customers. So does Microsoft which offers Azure private multi-access edge compute. Earlier this year, Fierce Wireless reported that Google did NOT have a private 5G network offering, but was partnering with other companies to offer one.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Sidebar:
Deutsche Telekom’s T-Systems has partnered with Google Cloud to build and deliver sovereign cloud services to German enterprises, healthcare firms and the public. The two companies say that the goal of this sovereign cloud is to allow customers to host their sensitive workloads while still being able to leverage all the benefits of the public cloud, such as scalability and reliability. The launch of the new Sovereign Cloud for Germany will take place ahead of schedule: Telekom’s business customer arm T-Systems and Google Cloud are launching their new sovereign cloud service in spring 2022. It will be available for all clients, initially out of the Frankfurt Google Cloud Region. Telekom and Google confirmed that they will jointly drive innovation for the cloud, closely aligned with the new German government’s digital plans which aims to build a public administration cloud based on a multi-cloud strategy and open interfaces, as well as meeting strict sovereignty and transparency requirements. To this end, the partners are setting up a Co-Innovation Center in Munich as announced in November 2021. In addition, executive briefing facilities in Munich and one in Berlin will be established for close collaboration with customers.
“Many companies in Germany state that sovereignty matters to them when choosing their Cloud provider. This is particularly important for key sectors such as public, healthcare and automotive,” Höttges said. “That’s why we’re delighted to offer a Sovereign Cloud that addresses additional European compliance requirements.”
In this new joint offering, T-Systems will manage a set of sovereignty controls and measures, including encryption and identity management. In addition, T-Systems will exercise a control function over relevant parts of the German Google Cloud infrastructure. Any physical or virtual access to facilities in Germany (such as routine maintenance and upgrades) will be under the supervision of T-Systems and Google Cloud.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
5G SA Campus Network: Full Control & Flexible Deployment:
Customers can adapt their private 5G SA network flexibly according to their own requirements as well as manage it independently: Whether for real-time communication of robots in factories or for connecting automated vehicles on company premises. Customers can prioritize data traffic within their campus network for specific applications as needed.
The mobile network is administered on site via a cloud-based network management portal by the customer’s IT staff – for example, the administration of users, 5G modules and SIM cards to access the 5G-SA campus network or to the machine control system. The closed system is characterized by its particularly high data security and reliability: Due to the redundant architecture of the local core network, the 5G SA campus network continues to function reliably even in the event of an interruption to the cloud-based management portal.
Managed service by Deutsche Telekom:
If business customers decide to deploy their own 5G SA network, Deutsche Telekom analyzes with them the critical business applications and the requirements for the private mobile network. Due to the simplified local infrastructure, the network can be built from planning to the handover to the customer within just three months. Network equipment supplier Ericsson provides the required modern 5G SA technology, while Telekom takes on the planning, deployment, operation as well as maintenance and optimization. Telekom also provides the set-up and updates so that companies can focus on their core business.
“When it comes to digitalization, industry and SMEs need a reliable partner,” says Hagen Rickmann, Managing Director Business Customers at Telekom Deutschland GmbH. “Together with Ericsson, we help business customers in every industry to increase their productivity and exploit their full potential using 5G standalone technology.”
Arun Bansal, Executive Vice President and Head of Market Area Europe & Latin America at Ericsson says: “Deutsche Telekom and Ericsson share a long-standing partnership in innovation, technology and services. Together, we offer secure, reliable and high-performance network solutions tailored to the specific business needs of our customers.”

Image Credit: Deutsche Telekom
5G Campus Network Private – Available for testing on site:
Deutsche Telekom has already been offering campus network solutions for enterprises since the beginning of 2019 and by now operates more than ten of such local networks based on 5G non-standalone technology or LTE across Germany. With the new fully private 5G SA Campus network solution, the company is expanding its business customer offering with the next development stage of 5G. The new product is being launched in Germany from now on under the name “Campus-Netz Private” – and is also offered to business customers in further European countries. For interested customers, mobile Campus 5G SA test systems are available to test their own use cases on site.
Use Cases and Industry Verticals:
There is currently a huge drive to get private 5G networks onto factory floors for manufacturing. There are some interesting examples of using IoT technology, feeding information back via high speed wireless connections, and analyzing data with machine learning/AI tools to optimize operations and do new things like predictive maintenance. Ericsson touts several industry verticals as candidates for its 5G private network offerings: Airports, Energy Utilities, Airports, Mining, Manufacturing, Ports, Offshore and Processing.
The drive towards business 5G adoptions is reflected In Ericsson’s Q4 2021 financials, in which private networks for enterprise were cited as one of the key drivers of its 41% YoY jump in profit. Evidently, Ericsson and Deutsche Telekom see a lot of potential in private 5G for industrial applications.
References:
https://www.telekom.com/en/media/media-information/archive/new-5g-standalone-campus-networks-645348
https://telecoms.com/513200/dt-and-ericsson-launch-new-5g-sa-campus-offering/
FCC announces $1.2 billion fund for broadband deployment in rural areas
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has announced over $1.2 billion in funding through the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund [1.] to expand broadband service across 32 U.S. states. The FCC calls this “the largest funding round to date,” and notes 23 broadband companies will provide service to more than one million new areas.
Note 1. A total of $20.4 billion to be awarded by the FCC over 10 years. Up to $16 billion will be made available for Phase I of the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund auction, and the remaining Phase I budget, along with $4.4 billion, will be awarded for Phase II of the auction.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In addition, the FCC also introduced the Rural Broadband Accountability Plan, which will double the number of audits and verifications performed this year in comparison to 2021. It will also require the FCC to make the results of verifications, audits as well as speed and latency tests public on the Universal Service Administration Company’s (USAC) website.
The pandemic only amplified the gaps in connectivity affecting rural America, as employees transitioned to working from home and kids attended class virtually. To help remedy the issue, President Joe Biden signed off on a $1 trillion infrastructure package in November that allocates $65 billion to providing broadband to every American household. The FCC also launched a program that provides cheaper internet to low-income households late last year.
In December 2020, the FCC awarded companies a total of $9.2 billion under the Rural Digital Opportunity fund, and that included an $886 million subsidy for SpaceX. The Elon Musk-owned company was supposed to deploy its satellite internet network in rural areas, but last year, the FCC warned SpaceX and other providers to stop misusing these funds to provide service to well-connected areas.
References:
https://www.theverge.com/2022/1/29/22908024/fcc-rural-broadband-deployment-funding
Architecting a Software-Defined Base Station-on-a-Chip for 5G Wireless Infrastructure
by Vinay Ravuri, CEO and Founder of EdgeQ Inc. (edited for clarity by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
EdgeQ emerged from stealth mode in late 2020 as one of the very few semiconductor companies addressing 5G wireless infrastructure with a clean slate design. We wanted to approach 5G as a platform (chip hardware + RAN software) that allows fluidity and scale as customers migrate through new spectrum, new ITU-R standards/ 3GPP specifications, and new endpoints. Our vision is to reconstitute the wireless infrastructure in a manner that is intelligent, agile, and cloud-native.
Removing the Friction Points in 5G:
The success of any silicon design can be premised on three fundamentals: Flexibility, Power, and Cost. 5G is no exception. The industry’s challenge with 5G design can be parsed as follows:
- Flexibility — Very few merchant silicon suppliers can provide a fully production readied L1. With 5G, there is an added complexity where the L1 needs to be adaptive and programmable to the multitude of workloads and use cases.
- Power — At EdgeQ, we are guided by the 50:50 principle. 50% of a base station TCO is related to power. 50% of the power is related to baseband processing. Just changing the power profile of the baseband profoundly impacts the total system.
- Cost – Cost will be a byproduct of the above two. With the anticipated bandwidth and explosion of new end point connections, linear scaling of OpEx and CapEx costs is not sustainable.
Design for Flexibility and Openness: 5G with a Customizable, Deployable PHY:
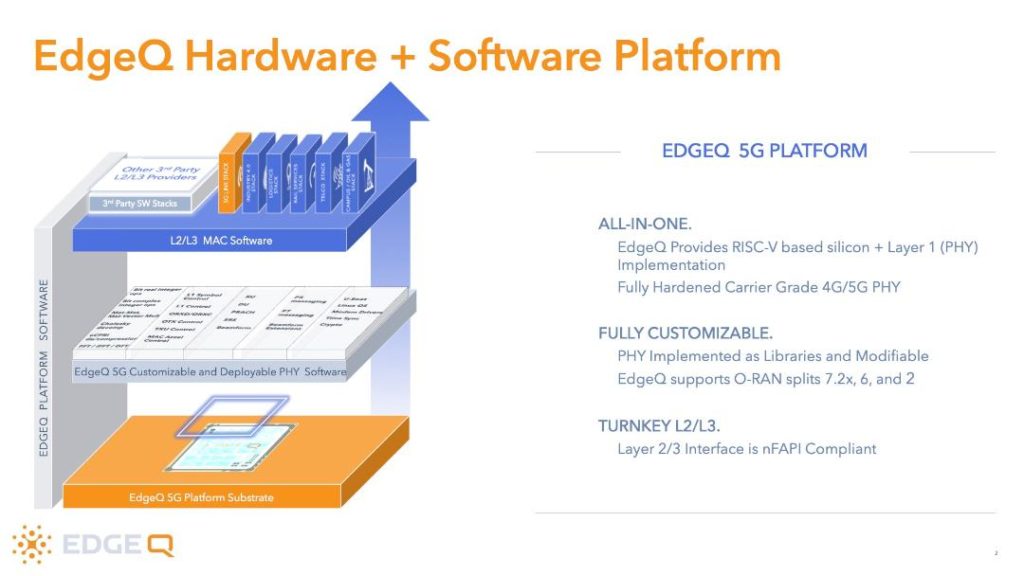
EdgeQ’s approach is to provide a RISC-V based SoC with a production-grade RAN that is fully customizable via C/C++. This would enable the market with the ability to differentiate 5G at the PHY level. This contrasts with traditional solutions which offer a reference stack for 5G RAN algorithms.
Hardening of the PHY layer is both an intensive and extensive process that typically requires 2-3 years of knowledgeable expertise. The level of integration and development is where most companies struggle or fail. EdgeQ offers an open, production-readied PHY out of the box.
By softwardizing the RAN, we can provide a chip that is dynamically programmable to any of the ORAN splits. New 3GPP standards (like REL16, REL 17, REL 18 upgrade) can be rolled out over-the-air. New features (like URLLC or massive MIMO) can be deployed on the fly. Multiple protocols can be simultaneously instantiated and coherently parallelized. Whether it is 4G, 5G, or AI, each network protocol can be turned on-or-off in the field.
EdgeQ’s “5G Base Station-on-a-Chip” is based on an unique hybrid architecture where a RISC-V compute complex is responsible for baseband processing. Our thesis is to enable the ecosystem access to open-source tools to develop on top of our extended RISC-V instruction sets. For the first time in communications history, the market can capitalize on GNU tool chains (compilers, tracers, debuggers, JTAG ….) for wireless communications.
Design for Low Power: Aggressive 5G Power Management for Wireless Infrastructure:
When EdgeQ instrumented its SoC, all the core functionalities of a base station (baseband processor, host CPU, NPU, FEC Acceleration, NIC, Data Converters, Timing Sync, and Machine Learning) are condensed into a single silicon. Depending on the uploaded PHY firmware, the EdgeQ SoC can be function as a small cell (gNB), or a Radio Unit (RU), or Distributed Unit (DU) – please see illustration below.
This highly integrative approach is particularly meaningful for all-in-one access points, where customers may want to converge all the O-RAN splits onto a single chip, and yet run the entire system over Power over Ethernet (PoE). Equally, with such a low power profile, customers can contemplate new macro base station topologies where densely packed PCIe cards within distributed Units (DU) can be dynamically swapped or “spun up” to scale with real-time performance and functional needs.
Design for Cost: Flexibility + Low Power:
One vector to reducing the overall system TCO is by substantially reducing the power envelop. Through integration, advanced power management techniques, and unique design, all L1 baseband processing functions at EdgeQ run in the low teens, thereby significantly reducing a customer’s TCO.
Secondarily, by creating a fully programmable 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip, features and performance points are now all cloud managed and activated over-the-air via a SaaS subscription model. Operators and service providers can now deploy systems at scale and effect wholesale upgrades without ripping and replacing.
As 5G becomes the “lingua franca” of connectivity, edge demands will impact the fluidity and constructs of 5G infrastructure. Foundational to any wireless infrastructure will be a programmable 5G SoC, capable of adapting to infrastructural demands with a production deployable cellular stack that is customizable. The idea is to present a scalable 5G platform in which customers and developers can leverage open-source tools and C/C++ to configure the chip.
About EdgeQ:
EdgeQ is a leading innovator creating the industry’s first 5G Base-Station-on-a-Chip. Led by seasoned executives from Qualcomm, Intel, and Broadcom who have delivered industry-transforming technologies (4G/5G, WiFi, Wimax, Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Servers) for the last few decades, EdgeQ is inventing a new paradigm in 5G wireless infrastructure.
The company’s vision is to reconstitute wireless infrastructure into a fluid, cloud-based form that would extend robust internet access and communications to remote and dense areas, as well as to the next trillion of interconnected devices.
EdgeQ is backed by world-renown investors, as well as luminary advisors Paul Jacobs, Matt Grob, Ajit Pai, and Rene Hass.
About Vinay Ravuri:

Mr. Ravuri obtained a Masters of Engineering (Major: Electrical Engineering Minor: Computer Science) from Georgia Institute of Technology in 1996, and a Bachelors of Engineering from City University of New York in 1994. He also attended Université de Montréal Deep Learning Summer School in 2016.
References:
EdgeQ Samples World’s 1st Software-Defined 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip
SoC start-up EdgeQ comes out of stealth mode with 5G/AI silicon for 5G private networks/IIoT
Picocom PC802 SoC: 1st 5G NR/LTE small cell SoC designed for Open RAN
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
Nokia, China Mobile [1.] and MediaTek have announced a speed record in a test of the world’s first 3 Components (3CC) Carrier Aggregation (CA) technology in Shanghai. The converged 700 MHz/2.6 GHz network reached a peak downlink speed rate of 2.94 Gbps. The trial used Nokia’s AirScale 5G baseband and MediaTek’s Dimensity 9000 5G mobile platform on China Mobile’s 5G SA network. The tests will continue, using China Mobile’s network in Shanghai.
Note 1. China Mobile was banned from the U.S. in 2019.
Nokia said it is the first time the n28 (700MHz band; 30MHz) and n41 (2.6GHz band; 100+60MHz) frequency bands have been successfully combined to reach 190 MHz bandwidth (n28 + n41) with carrier aggregation technology.
CA combines frequency bands for higher data rates and increased coverage, delivering superior network capacity by maximizing the spectral efficiency of 5G networks. The combination of 5G FDD and TDD bands, supplemented by carrier aggregation, can give full play to the advantages of spectrum synergy, greatly reducing the cost of network construction while improving network coverage and user experience. The result is faster data speeds, increased coverage area, and better indoor performance.
The combination of 5G FDD and TDD bands, supplemented by carrier aggregation, augment the advantages of spectrum synergy, cutting the cost of network construction and improving network coverage and service to users.
Nokia has been a partner for over 20 years of China Mobile, which is expanding its network with the convergence of the 700 MHz and 2.6 GHz bands.

JS Pan, General Manager, Wireless Communication Technology at MediaTek, said: “Through this tripartite collaboration we have successfully demonstrated the technical advantages of DL 3CC CA using FDD+TDD. Smartphones powered by the new Dimensity 9000 flagship 5G mobile platform, and forthcoming Dimensity 5G mobile platforms, will be able to take advantage of this cutting-edge 5G connectivity feature, and MediaTek will continue to work closely with industry partners to set new milestones for 5G development.”
Ding Haiyu, Vice President of the Research Institute of China Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.), said: “China Mobile has been fully promoting the evolution and development of 5G technology. CMRI emphasizes that new technology verification provides a technical basis for the improvement of network performance and services, and forms a technical cornerstone for future network planning. China Mobile is also committed to building a 5G multi-frequency collaborative network; This 3CC CA verification can provide users with better throughput and user experience, and provide good technical foundations for new services. China Mobile is willing to work with all vendors to contribute to the 5G evolution.”
Mark Atkinson, SVP, Radio Access Networks PLM at Nokia said: “Nokia has put a strong focus on leading in 5G Carrier Aggregation. This new speed record, using commercially available hardware and software, highlights how Nokia’s pioneering approach continues to drive important innovation in the market. 5G Carrier Aggregation is a critical technology for mobile operators around the world to maximize the impact of their spectrum holdings and deliver enhanced coverage and capacity to subscribers. Nokia will keep pushing the boundaries of 5G to deliver industry-leading performance.”
Resources:
Nokia AirScale
Nokia 5G RAN
Nokia 5G Core
Nokia achieves first 5G carrier aggregation call in standalone architecture with Taiwan Mobile
Spectrum Explained
References:
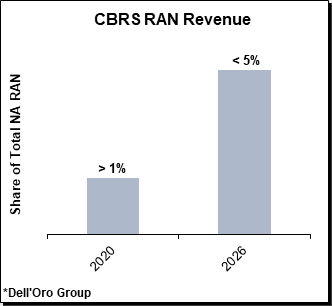
Dell’Oro: CBRS RAN is Behind Schedule: <5% of NA RAN by 2026
With all the air coming out of the next gen cellular hype balloon, Dell’Oro’s report that CBRS RAN is not living up to expectations comes as no surprise. Think about the failed promise of 5G since there is no standard or spec for URLLC in the RAN. Or all the terrific 5G functions and features (including network slicing and security) which are ONLY made possible with a 5G SA core network (very few have been deployed). Or that there is no standard (revision of M.1036) for the mmWave frequencies to be used for 5G.
Dell’Oro says that CBRS adoption continues to increase, but it is significantly below expectations. That’s driven primarily by diverging trends between fixed wireless access (FWA) and non-FWA including public and private LTE/5G NR.
“Adoption gaps across the various CBRS segment remained significant in 2021,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst with Dell’Oro Group. “We have again revised the CBRS RAN projections downward to reflect the lower baseline and slower-than-expected uptake with non-FWA segments. This adjustment does not change the long-term vision—we continue to believe that there is an opportunity to improve spectrum utilization while at the same time stimulating innovation for both public and private networks across various industry segments. So we see this downward revision more as a calibration to reflect the current state of the market and the fact that there is still a significant gap between registered SAS APs and LTE/5G NR base stations,” continued Pongratz.

Source: Counterpoint Research
Other highlights from the CBRS RAN Advanced Research Report:
- LTE is projected to drive the lion share of the investments over the near term while 5G NR based CBRS capex will dominate by 2026.
- CBRS RAN revenues are expected to account for less than 5 percent of North America RAN by 2026.
- Fixed Wireless Access and capacity augmentation for Mobile Broadband (MBB) applications are dominating the CBRS RAN capex mix initially while the enterprise share is expected to improve in the outer part of the forecast period.
Pongratz’s comments were echoed by Norman Fekrat of CBRS vendor Imagine Wireless. In a recent YouTube presentation, Fekrat said that sales of CBRS-based private wireless networking equipment and services to enterprises have been sluggish.
He attributed that in part on the complexities around the technology to use CBRS spectrum. He said the telecom industry in general needs to smooth the sales process for enterprises looking to build their own private wireless networks using CBRS spectrum.
According to Pongratz, there’s a wide range of vendors selling CBRS-capable hardware and software. He said companies like Baicells, BliNQ Networks, Airspan Networks, Telrad Networks and Cambium Networks sell equipment into the FWA market, while companies like Ericsson, Nokia and Samsung have been supplying CBRS equipment into the market for mobile networks.
Verizon was the biggest spender during the FCC’s 3.5GHz CBRS spectrum auction (#105) in 2020, paying almost $1.9 billion for 557 licenses in markets across the U.S. We reported that they planned to test carrier aggregation in the CBRS band, but don’t know if that ever happened. Instead, Verizon’s attention has since shifted following the massive $53 billion it spent in the FCC’s C-band spectrum auction last year. Verizon recently lit up C-band services that covers ~ 95 million people.
Dish Network was another major CBRS spectrum buyer, but they too have not started a major buildout of its CBRS spectrum holdings.
Among the cablecos/MSOs, Comcast, Charter Communications, Cox Communications and others spent millions of dollars on licenses in the auction. However, Charter is the only cable company that has discussed any major efforts to construct a network in the spectrum. Charter may provide additional details on its CBRS efforts during its fourth quarter earnings conference call scheduled for Friday (January 28th).
Financial analysts at New Street Research believe that’s a mistake. “Deployed spectrum has strong long-term strategic benefits. Developing expertise in wireless networking will take years,” they wrote in a note to investors this week. “We think Comcast should be making hard investments in wireless infrastructure now.”
Dell’Oro Group’s Advanced Research: Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) Report offers an overview of the CBRS LTE and 5G NR potential with a 5-year forecast for the CBRS RAN market by technology, location, and market. For more information about the report, please contact us at [email protected].
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/cbrs-isnt-living-up-to-expectations—delloro-group/d/d-id/774899?
FCC CBRS Auction for 5G mid-band spectrum in the 3.5GHz band
FCC permits Verizon to test 5G and carrier aggregation in CBRS spectrum band
Why are 5G SA Core networks taking so long to be commercially deployed?
by Tim Sylvester, Founder and CEO of Integrated Roadways, a smart infrastructure technology provider, with Alan J Weissberger (editor)
5G SA deployments have significantly lagged market expectations for the same reason that 5G NSA has been so rapidly deployed. 5G NSA uses existing 4G LTE signaling , core network, macro-site infrastructure, requiring only updates to its software and hardware at existing tower sites .
On the other hand, 5G SA requires a completely new Distributed Antenna System (DAS) architecture for microcell / nano or small cell deployments that need significant infrastructure with nontraditional requirements.
Unlike macro-cell deployments for 4G LTE, the position of the 5G SA millimeter wave antenna is not very negotiable – with a 5-mile service radius, a 4G LTE antenna can move considerable distances without significant changes to the service area, while a 5G millimeter wave antenna needs to be in exactly the correct spot to deliver service in a significantly smaller radius. The small cell size of 5G SA means that covering the same territory as a macro-site is essentially impossible, restricting deployments of 5G SA to dense urban areas and along highly trafficked interstate and highway routes.
5G SA requires a new core network infrastructure. Prior cell service models were iterations on technologies used in POTS and internet services that were ported to IP networks and only the final link mode changed from wired to wireless, with an emphasis on coverage area and bandwidth. But 5G SA is more than a new, higher-bandwidth link, incorporating new focuses on reliability and ultra-low latency for ehealth, autonomy, M2M services, augmented reality and other real-time or near-real time applications. This requires more than the wireless link improvements as it makes the easy “cloud” data abstraction obsolete, as these applications and databases physical storage location is relevant to maintaining reliability and ultra-low latency.
5G SA also promises network slicing, network function virtualization, cloud-native service management, distributed microservices at the edge, and software defined networking. Delivery of 5G SA has many more moving parts and stakeholders than 5G NSA and requires collaboration of many industries including automotive, tech, and health. It does not permit a monolithic delivery from a handful of parties. At the same time, the business models for ehealth, autonomy, AR, and other key 5G enabled applications are still unproven and in development, meaning that the carriers are expected to take input from many new parties and make investments in markets that are still at-risk.
Aside from the industry risks and complications, the property owners that will permit 5G SA delivery are not aligned to traditional cell service incentives or priorities. Delivering widespread millimeter wave antennas required for 5G SA networks through a DAS requires a utility or municipal license to attach equipment to each required attachment point, or development of countless private owner site leases to install antennas on private property adjacent to the desired service area. The private-owner approach is functional primarily in urban areas. It can’t be relied upon for primary delivery in non-urban interstate and highway routes that lack the necessary power and fiber drops, or in areas that traditionally only have longitudinal transmission or distribution lines, without further increasing costs to implement frequent new utility drops that service a single user. The outcome is existing approaches are very expensive and time consuming.
Regardless of FCC 1TMR requirements, municipalities and utilities are reluctant to give up that number of pole attachments and accept the visual and safety implications of accommodating that amount of visible equipment mounted overhead. These complications have resulted in permitting fees as high as $10K per antenna, as reported by Sprint in San Diego during early 5G trials (before being absorbed by T-Mobile), which makes the costs and complications of deploying infrastructure daunting to the extent of being nearly impossible. Even when tolerated, there’s no guarantee that existing poles are in the correct locations, which is why AT&T has been deploying its own utility poles to ensure they have attachment points where they need them.
There’s also the significant obstacle of locating distributed micro datacenter space proximate to the antenna attachment points as required to deploy the edge services that are natively required by 5G SA.
The hard to swallow reality for 5G deployment is public agencies are the easiest means to deploy the system, as it conceptually allows a single construction and operations contract per municipal area or interstate/highway route, instead of thousands of independently negotiated agreements with individual property owners. However, municipalities have no obligation to issue these permits, and the mandate for public works is to provide roadways and utility easements, with an institutional preference towards preserving aesthetics and limiting safety issues from overhead mounted hardware. Public agencies are responsible for roads, not responsible for delivering cell services, regardless of the desires of the cell companies. Municipal obligations are not aligned to the preferences of the 5G SA delivery industry, and there is no clear or obvious resolution available using the traditional network MSP approaches.
That said, solutions are readily available, despite their non-obvious nature and departure from traditional network MSP approaches. What the cell industry needs to deploy 5G SA widely is:
● An approach that aligns municipal incentives with 5G SA DAS needs by ensuring 5G SA deployments result in improvements to core urban infrastructure that is the obligation and primary concern of public agencies who are required to permit such improvements
● Leveraging delivery of those necessary infrastructure improvement needs alongside 5G SA capabilities in a “dig once” approach to streamline deployment and lower costs
● Incorporating the edge networking and 5G antenna delivery infrastructure into an invisible infrastructure delivery that does not occupy poles or other overhead assets
As with so many technology obstacles, the solution isn’t found within the technology itself, but found with a change in perspective and better understanding the needs of the stakeholders.
If there were a smart infrastructure technology firm that had the capacity to deploy 5G SA infrastructure as a byproduct of improving core urban infrastructure, hiding all of the antennas and edge networking assets, enabling the delivery of a fully virtualized, sliceable, edge-enabled but cloud-native open access network, the obstacles to 5G SA delivery would be resolved in a manner that is agreeable to the network MSPs, municipal authorities, utilities, and citizens.
Now that the needs for a solution have been identified, the only remaining obstacle is to identify a company that is capable of delivering on these requirements and developing partnerships between the network MSPs and the municipalities to begin widespread deployments.
About Tim Sylvester:
Tim is a computer and electrical engineer. He is the Founder, CEO and Chief Technology Officer of Integrated Roadways, a smart infrastructure technology provider. Smart infrastructure is the integration of data, communications, power, and networking systems into core infrastructure like roads, highways, and bridges.
Smart Pavement system from Integrated Roadways
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Feb 8, 2022 Update from Dave Bolan of Dell’Oro Group:
As of December 31, 2021 there were 21 known 5G SA eMBB networks commercially deployed.
|
5G SA eMBB Network Commercial Deployments |
|
|
Rain (South Africa) |
Launched in 2020 |
|
China Mobile |
|
|
China Telecom |
|
|
China Unicom |
|
|
T-Mobile (USA) AIS (Thailand) True (Thailand) |
|
|
China Mobile Hong Kong |
|
|
Vodafone (Germany) |
Launched in 2021 |
|
STC (Kuwait) |
|
|
Telefónica O2 (Germany) |
|
|
SingTel (Singapore) |
|
|
KT (Korea) |
|
|
M1 (Singapore) |
|
|
Vodafone (UK) |
|
|
Smart (Philippines) |
|
|
SoftBank (Japan) |
|
|
Rogers (Canada) |
|
|
Taiwan Mobile |
|
|
Telia (Finland) |
|
|
TPG Telecom (Australia) |
|