CenturyLink rebrands as LUMEN for large enterprise customers; adds Quantum Fiber
CenturyLink has taken on a new identity — Lumen — a name it says better highlights the company’s future direction and focus on selling business services to large customers. [Note that there is already a Texas based company named Lumen Technologies Inc so there’s sure to be confusion and a possible trademark lawsuit in the near future.]

Lumen is a measure of the brightness of light, and the company’s competitive advantage this century has come from its massive fiber network, stretching 450,000 route miles. That has helped CenturyLink survive even as consumers cut their home phone lines in favor of wireless providers and switched off DSL in favor of faster alternatives.
But transporting light signals can also be a commodity service. Lumen is now pushing to offer more higher-value applications and enterprise services directly to its customers, reflected in the company’s new motto: “The Platform for Amazing Things.”
Lumen says on its website:
Lumen is an enterprise technology platform that enables companies to capitalize on emerging applications that power the 4th Industrial Revolution. Most IT leaders don’t feel ready to face the nearly century’s worth of data-driven innovation they expect in the next five years.
“Our people are dedicated to furthering human progress through technology. Lumen is all about enabling the amazing potential of our customers, by utilizing our technology platform, our people, and our relationships with customers and
partners,” said Lumen CEO Jeff Storey, in a statement on the name change.
“For the past three years we have been reinventing ourselves and repositioning the company to deliver on a brand-new promise: Furthering human progress through technology,” said Lumen CTO Andrew Dugan, who held the same title at CenturyLink. “We have been considering this change for many months. We are ideally positioned to help resolve the biggest data and application challenges of our time—this is why now is the right time to introduce Lumen.”
The CenturyLink brand will continue to be used for residential and small business customers using traditional copper based networks. “CenturyLink, with its strong heritage, will remain as a trusted brand for residential and small business customers over traditional networks,” the company said.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The number of telecom and cloud service providers that have been acquired by CenturyLink is truly astounding. That list includes: US West (which was acquired by Qwest Communications), Embarq (which included Sprint Local and US Telecom), Savvis, App Frog, Tier 3, and the big one –Level 3 Communications in a deal valued at around $25 billion. Level 3, in turn, had also acquired a boat load of telecom providers such as Global Crossing and TW Telecom and before that: WilTel Communications, Broadwing Corporation, Looking Glass Networks, Progress Telecom, and Telcove (formerly Adelphia Business Solutions) and ICG Communications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
These acquisitions, long with internal software innovations, they have given Lumen the ability to provide enterprise customers with a variety of services in a variety of areas. However, the company still does not have presence in the cellular communications business.
“Unfortunately, today’s network, cloud and IT architectures present latency, cost and security challenges that inhibit the performance of distributed applications and real-time data processing. Ultimately, the world needs a new architecture platform that has been designed to support the intensive performance requirements of next-generation applications. And that is exactly what we aim to provide with Lumen,” said Lumen’s chief marketing officer Shaun Andrews, in a video message.
Smart cities, retail and industrial robotics, real-time virtual collaboration and automated factories are some of the applications that Lumen believes it can help customers achieve in what it and others call the 4th Industrial Revolution. Steam power, electricity and then the computer chip all pushed economic progress, and now the melding of the digital and physical worlds that connectivity permits is doing the same, Andrews added.
That is the future direction, where the company sees the greatest potential for growth and new revenues. But Andrews emphasized that residential and small business consumers will still deal with CenturyLink, a brand executives believe still has value two decades into the new century. It is the name that will continue to show up on residential customers’ bills. CenturyLink Field in Seattle will retain its name.
Another new entity, Quantum Fiber, will handle the residential and small business transition to digital as the company rolls out more fiber-optic connections directly to homes and businesses (FTTH and FTTP, respectively). The company added capacity to reach about 300,000 homes and small businesses last year with gigabit service and plans to reach another 400,000 this year, according to Fierce Telecom.
Lumen says the can provide the ability to control latency, bandwidth and security for applications across cloud data centers, the market edge and on-premises, according to a blog by Dugan. Instead of putting critical applications into a centralized cloud, Lumen’s edge compute platform, which includes more than 100 active edge compute nodes across large metro markets in the U.S—puts them closer to the end user for low latency and better security.
“The Lumen brand is focused on supporting our enterprise business customers. It alludes to our network strength and to the incredible capabilities powered by our platform to help transform how businesses operate,” Dugan said.
“Quantum Fiber is an important new brand within Lumen with a focus on superior fiber connectivity and a fully enabled digital customer experience,” Dugan said. “Quantum Fiber serves residential and small business customers, and Lumen focuses on enterprise, government and global businesses.”
In 2019, CenturyLink expanded its fiber network to reach an estimated 300,000 additional homes and small businesses with its gigabit service. CenturyLink’s consumer fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) projects provide symmetrical speeds of up to 940 Mbps. The faster speeds were enabled in parts of Boulder, Colo., Spokane, Wash., and Tucson, Ariz. last year.
CenturyLink previously said it would build out its fiber network to an additional 400,000 homes and small businesses this year, including in Denver, Omaha, Neb., Phoenix, Portland, Ore., Salt Lake City, Spokane, Wash., and Springfield, MO.
MoffetNathanson analysts wrote in a note to clients (emphasis added):
The flagship Lumen brand is targeted toward larger enterprises, the likes of which would be most likely to adopt the company’s most advanced services. The CenturyLink brand is being retained for legacy copper services delivered to residential customers and some SMBs, as well as existing FTTH customers. And the new Quantum Fiber brand is being introduced for SMB services delivered via the automated platform the company has been developing and has indicated it would soon be rolling out to on-net, out-of-region locations (mostly ex-Level 3 buildings), and will include consumer FTTH sold in a similar manner. The services and capabilities Lumen delivers to each of these customer segments varies dramatically, so it’s not at all inappropriate to have separate brands for each. Innumerable examples of this phenomenon exist across other industries – automotive, consumer products, airlines, apparel, media, and so on. Within the world of telecom, carriers often have brands that target different segments or highlight different product types (Verizon with FiOS, AT&T with Cricket, T-Mobile US with MetroPCS, Altice USA with Optimum vs. Lightpath, and so on).
CenturyLink was an amalgamation of many different companies, assets, and capabilities. Management’s decision to rebrand as Lumen, Quantum Fiber, and CenturyLink acknowledges those differences and gives management an opportunity to refresh and communicate its vision for the company to customers, employees, and investors.
Andrews said the name change won’t include a relocation to Denver of the corporate headquarters, which will remain in Monroe, La., home of the original CenturyLink. Of the company’s 40,000 employees globally, 5,800 are based in Colorado, and metro Denver remains an important hub of operations, especially the ones that Lumen will emphasize.
It remains to be seen what will happen with CenturyLink’s wholesale and carriers carrier backbone services, which acquisitions such as Level 3 and Global Crossing mainly focused on, i.e. selling high bandwidth fiber optic long haul links to other carriers.
References:
https://www.lumen.com/en-us/home.html
https://news.lumen.com/CTO-Andrew-Dugan-explains-how-the-Lumen-platform-keeps-data-moving
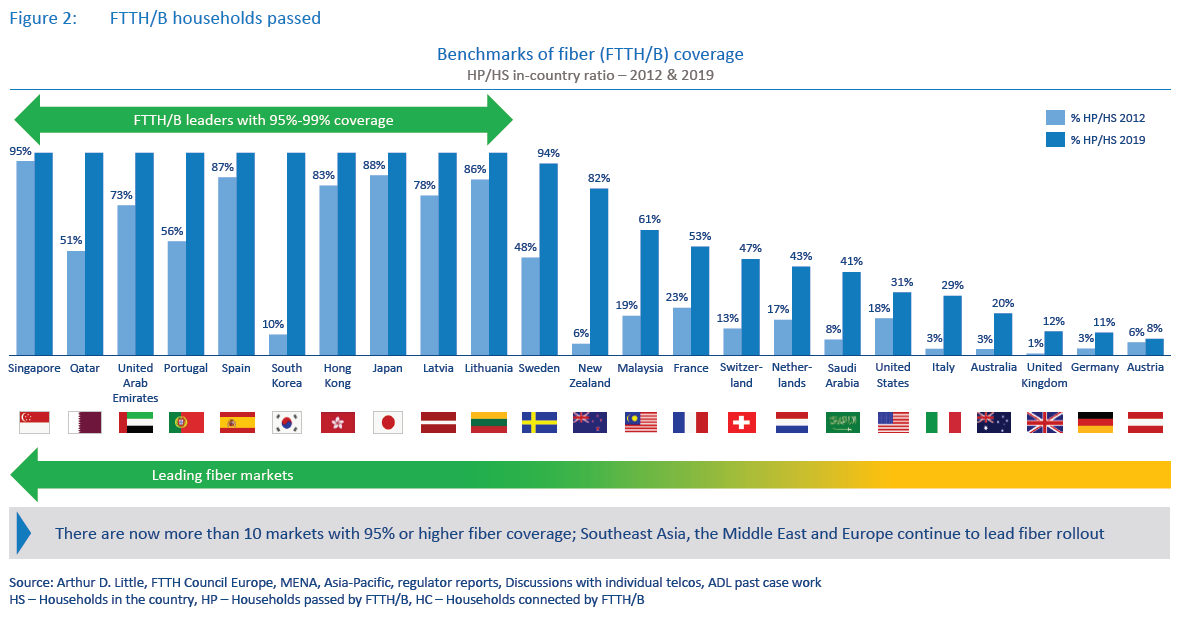
Arthur D Little: 10 countries provide >= 95% FTTH coverage; Gigabit Fiber driving take-up of new apps and services
Gigabit broadband can be delivered using cable DOCSIS, fiber or other 5G-based technologies. This ADL report focuses on the rollout, take-up and services delivered with fiber -based gigabit broadband networks. ADL especially considers the developments made in fiber take-up and gigabit services enabled by fiber. See the previous edition of this study, “Race to gigabit fiber: Telecom incumbents pick up pace”4 for further details on which markets are taking the lead on fiber rollout and the deployment models used for it.
Non-telecom entities such as energy companies, railway operators and local municipalities are also entering the market, with large fiber rollout plans in fiber-lagging countries such as Italy, Germany and Austria, to bridge the gigabit broadband gap.With 5G deployment models crystallizing, operators are also considering 5G-based technologies to complement high-cost,
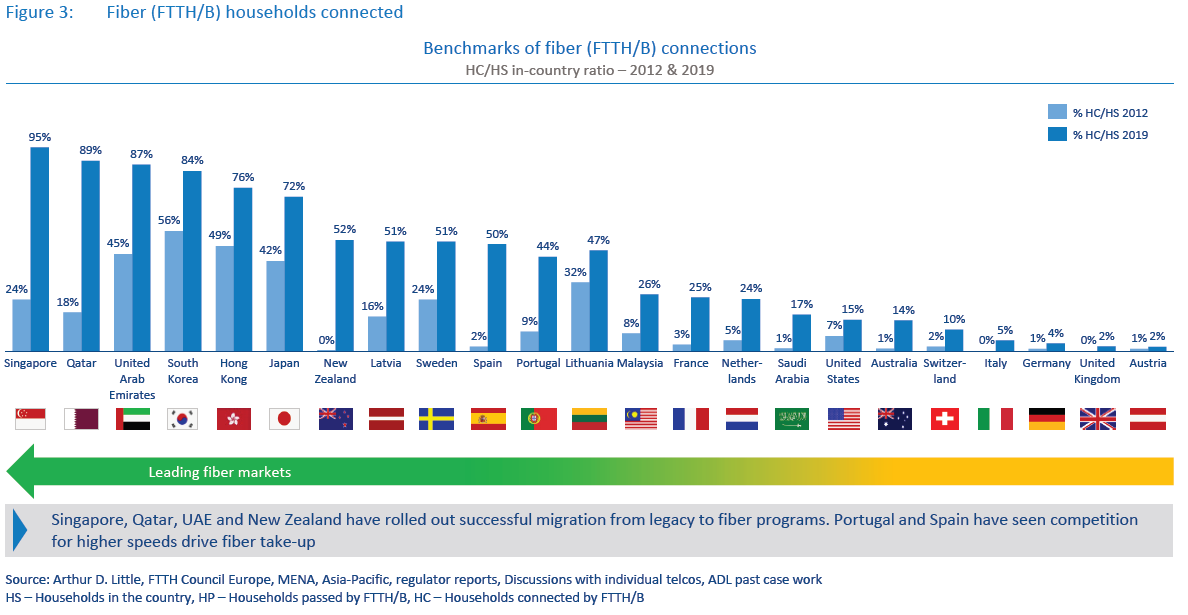
last-mile fiber access, especially in rural areas.While there were big improvements in fiber rollout from 2012 to 2017, take-up was still lagging behind, even though several markets invested large amounts of capex into nationwide fiber. However, we now see take-up rapidly improving, driven by both effective migration of legacy customers to fiber and competition driving demand for higher-speed broadband adoption at home.As the fiber coverage and take-up rates continue to grow, incumbents are increasingly announcing plans to switch off and dismantle their legacy copper networks. Singtel in Singapore turned off its copper network in 2018 and migrated its copper and cable subscribers to fiber, allowing the incumbent Singtel and cable company StarHub to switch off their copper and cable networks. Another example is JT Global in Jersey, which already migrated its entire fixed broadband customer base to fiber and will switch off the copper infrastructure in 2020. Operators in at least three other countries plan to completely migrate their customer base to fiber in the next four to five years (see Figure 4 below).
However, before decommissioning their legacy networks, telcos will need to overcome regulatory and other obstacles, such as providing an alternative to existing regulatory wholesale products and replacing some copper-specific B2B use cases with other technologies. With legacy network switch off, incumbents hope to achieve cost efficiencies especially in network operations. In recent projects, we estimate that fiber networks have up to a 15x lower fault rate and use up to 85 percent less energy compared to legacy copper-based networks.

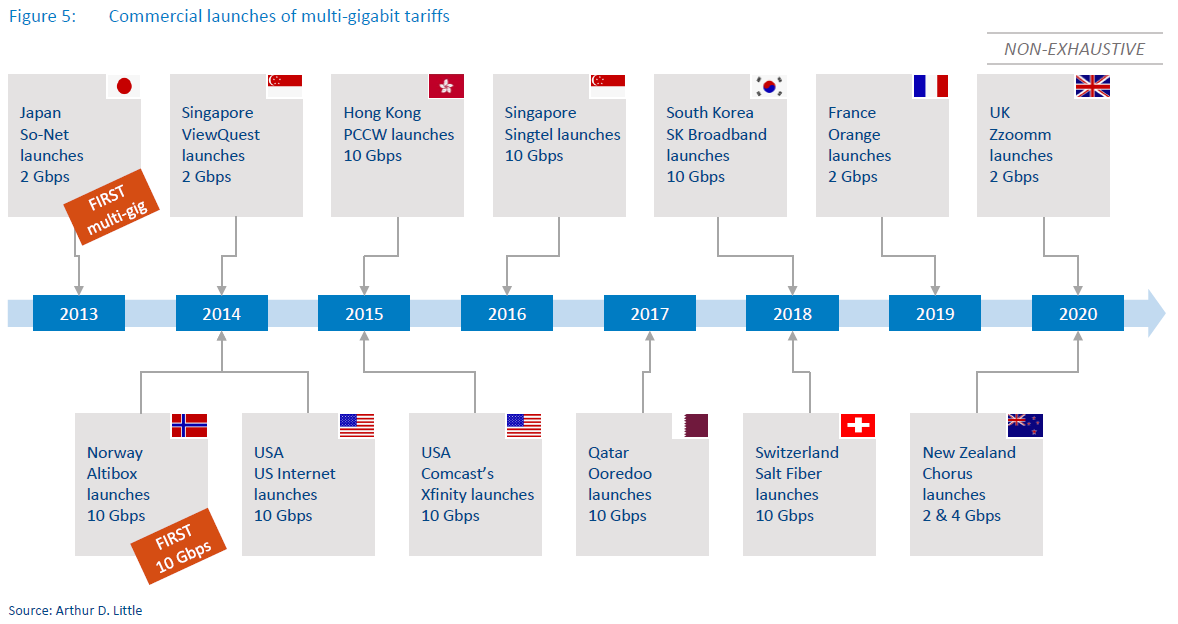
Fiber is undoubtedly an advanced fixed broadband technology that can efficiently deliver multi-gigabit speeds to a large volume of customers in real-life conditions, especially in dense urban areas. Offering 1 Gbps plans has become the norm in the leading Asian fiber markets such as Singapore, Japan, South Korea and Hong Kong, opening the way for multi-gigabit tariffs.
It has been more than five years since the first 10 Gbps plans were initially introduced in the US, Singapore, Hong Kong and Norway (see Figure 5. below). As of September 2020, we are not aware of any faster commercially available plan for the residential segment. Availability of multi-gigabit plans is still limited to a handful of markets and approximately 10-15 ISPs. However, just in the first half of 2020, there have been at least three ISPs that launched multi-gigabit offers: Zzoomm in the UK, Orange in France and Chorus in New Zealand.
Incumbent operator led deployments continue to play the leading role in fiber deployment today. However, we believe the importance of open access fiber providers will gain in significance, especially in important markets such as Italy, Germany, UK and Saudi Arabia, among others. Large-scale investment by non-telco entities such as energy companies and infrastructure funds, among others, will continue to expand fiber coverage in these markets. (For further details on open access fiber developments, please refer to our other report on this topic.)
An increasing number of incumbents acknowledge the inevitability of switching off and dismantling their legacy copper networks as fiber coverage becomes ubiquitous, while the cost economics of maintaining a fiber network are far superior to maintaining a legacy fixed network. Initiatives for legacy network switch off have been announced in multiple markets, and we expect to see results in larger markets such as Spain, France or Sweden soon. We also see regulators opening up to the idea that fiber-based solutions can eventually replace regulated legacy network–based products, giving a further impetus to open access fiber rollout in some regions.
Gigabit tariffs have become commonplace in developed fiber markets (mostly in Asia) and are increasingly being offered to customers worldwide. However, multi-gigabit speeds are still available only in a handful of markets. Salt in Switzerland is an example of a provider that uses its aggressively priced multigigabit offer to differentiate and disrupt the fiber market and not only as a marketing tool. We expect that, with new fiber rollouts and increasing competition on the broadband markets, the number of multi-gigabit offerings will continue to grow.
Note: This report, “The race to gigabit fiber,” is the 2020 update to Arthur D. Little’s Global FTTH study, published in 2010, 2013, 2016 and 2018.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ericsson: Multi-User MIMO with T-Mobile US; 5G with Telefónica; Open RAN Security WARNING
Author’s Note:
This post is actually three separate articles concerning “Ericsson in the news” today. Rather, than read all three parts, simply scroll down to the story that interests you. Let me (and others) know what you think by commenting in the box below the article.
1. Multi-User MIMO demo with T-Mobile US
T-Mobile US and Ericsson demonstrated a 16-layer multi-user multi-input multi-output (MU-MIMO) [1.] on one channel of 2.5 GHz spectrum. The peak cellular data rate was more than 5.6 Gbps.
During the test, engineers connected eight separate smartphones to the same 5G radio and resources using MU-MIMO and beamforming in a specific direction to achieve more than 700 Mbps data rate on each device.
Note 1. Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for wireless communication, in which a set of users or wireless terminals, each with one or more antennas, communicate with each other.
In contrast, single-user MIMO considers a single multi-antenna transmitter communicating with a single multi-antenna receiver. In a similar way that OFDMA adds multiple access (multi-user) capabilities to OFDM, MU-MIMO adds multiple access (multi-user) capabilities to MIMO. MU-MIMO has been investigated since the beginning of research into multi-antenna communication.

…………………………………………………………………………………….
Using MU-MIMO, T-Mobile US could potentially connect many more devices to the same cell infrastructure and still deliver very fast speeds to all of them. Using that set of technologies, wireless telcos might be able to deliver even better 5G performance to more people than was expected.
Using a commercially available massive MIMO radio with 64 antennas from Ericsson and OnePlus 8 5G smartphones T-Mobile sells today, 16 unique data streams were transmitted. Each stream was capable of transmitting/receiving at more than 350 Mbps. With two data streams for each device, that’s 700+ Mbps for each smartphone, all using the same radio resources at the same time.
With 100 MHz of total 5G spectrum used in the demonstration, T-Mobile US was able to achieve a 50+ bps/Hz in spectral efficiency. That is much higher than the single digit efficiency typically experienced today.
“This is what you get when you pair T-Mobile’s unmatched spectrum portfolio with the best damn team in wireless — innovation that changes the game for the entire industry,” said Neville Ray, President of Technology at T-Mobile. “We have a 5G network that’s second to none, and it’s getting better by the day thanks to our amazing engineers and partners. Just wait until you see what they do next for our customers!”
T-Mobile US expects to begin deploying this technology in 2021 as they continue the goal of building America’s best 5G network.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/t-mobile-achieves-mind-blowing-5g-speeds-with-mu-mimo
For more information about T-Mobile’s 5G vision, visit: www.t-mobile.com/5g. To see all the places you’ll get T-Mobile’s current 5G down to a neighborhood level, check out the map at www.t-mobile.com/coverage/5g-coverage-map.
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/t-mobile-us-achieves-5g-speeds-with-mu-mimo–1353491
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. Ericsson partners with Telefónica on Spain 5G launch
Ericsson is providing new 3.5Ghz radio equipment and software upgrades to 5G-ready Ericsson radios in Telefónica’s network. With Ericsson Radio System products already deployed in parts of Telefónica Spain’s network, fast, flexible, and cost-efficient 5G activation is made easier.
Joaquín Mata, CTO, Telefónica Spain, says: “The launch of our 5G network constitutes a leap forward towards the hyper connectivity that will change the future of Spain. We are very pleased with the collaboration with Ericsson to build one of the best 5G networks in Europe.”
Arun Bansal, President of Ericsson Europe and Latin America, says: “With our leading technology, Telefónica will offer its customers 5G faster and support them to reach 75 percent coverage of the population by the end of the year. With our swift 5G roll-out, Spain is ready for the next digital revolution and Ericsson is proud to be powering it together with Telefónica.”
As the industry evolves towards RAN virtualization, with virtual RAN or Open RAN (O-RAN), it is important that a risk-based approach is taken to adequately address security.Virtualization throughout the network and a service-based architecture means that security needs to be handled in a new way.
5G will accelerate innovation and provide transformative use cases across multiple global sectors. However, it will also bring new security challenges for the mobile ecosystem, with broader attack surfaces, more devices and increased traffic loads. We must have networks that are trustworthy, resilient, and secure at every phase of the system lifecycle. These new security challenges are addressed by 3GPP’s SA3 security work group.Expanded threat surface
The introduction of new and additional touch points in O-RAN architecture, along with the decoupling of hardware and software, has the potential to expand the threat and attack surface of the network in numerous ways, including:
- New interfaces increase threat surface – for example, open fronthaul, A1, E2, etc.
- Near-Real-Time (RT) RIC and 3PP xApps introduces new threats that could be exploited
- Decoupling of hardware increases threat to Trust Chain
- Management interfaces may not be secured to industry best practices
- (not exclusive to O-RAN): adherence to Open Source best practices
These and other areas are explored in greater depth in Ericsson’s report, Security considerations of Open RAN. Many of these items are being studied in several O-RAN Alliance working groups, including the Security Task Group, a consensus-based standards group that will ensure that O-RAN implementations meet the levels of security expected by the industry.
Ericsson is committed to providing leadership and guidance in the O-RAN Alliance on these emerging areas of study. In the meantime, let’s take an in-depth look at just one of these new areas of risk:
Weakened Links in the Trust Chain
Virtualization and the use of cloud platforms give the possibility to utilize hardware resources better between different applications, but it will also introduce security risks as isolation between applications are only “logical” in software without physical isolation across hardware resources. Recently discovered vulnerabilities like Meltdown and Spectre reveal that there can be increased security risks when sharing hardware resources.
To establish a secure and trusted communication channel between two endpoints, one needs first to authenticate each side before a secure (confidentiality and integrity-protected) channel can be established. To authenticate each endpoint, a unique identifier and one or more credentials that shall be kept secret are needed. To protect the credentials in a computer environment, hardware security functionality such as Trusted Platform Module (TPM), Hardware Security Module (HSM), and secure enclaves, are used to establish a hardware root of trust.
In the case of virtualization and cloud environments, there are many layers that need to be considered to ensure the trust chain is maintained between applications and the underlying hardware. The authentication process is the base for establishing a secure communication channel, but it must trust the layers underneath to attest that the node, layer or data set has not been compromised. For example, a node could request a valid service, authenticate correctly to the system and be authorized to use that service yet still represent a malicious threat if it is running on compromised firmware.
As there are different layers between the hardware and its security functions and the application, one needs standardized interfaces and APIs to use the hardware security functions and allow those to attest to and validate the layers above. Together with standardized and interoperable APIs, there must also be a transparency to how the different layers use and provide the security functions in the chain, especially as different hardware vendors may have different security functions, capabilities or implementation variances.

Figure 1. O-RAN: Additional functions, interfaces and a modified architecture (Source: Ericsson)
Ericsson will continue its leadership role within the O-RAN Alliance and its Security Task Group to incorporate security best practices, ensuring that new deployments are ready to meet the level of security, resilience and performance expected by service providers and their customers.
The Open RAN Policy Coalition, a U.S. special interest (i.e. lobbying) group looking for U.S. government funding for Open RAN technology, today announced several new members (American Tower, Broadcom, GigaTera Communications, Inseego, Ligado Networks, Nvidia, RIFT, Texas Instruments and Xilinx). Ericsson is not a member, but arch rival Nokia is. Cloud giants AWS, Google and Facebook are members. Obviously, Chinese vendors aren’t welcome to join the Coalition. The complete Coalition membership list is here.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Coalition members believe that by standardizing or “opening” the protocols and interfaces between the various subcomponents (radios, hardware and software) in the RAN, we move to an environment where networks can be deployed with a more modular design without being dependent upon a single vendor. The Coalition will promote policies that:
- Support global development of open and interoperable wireless technologies;
- Signal government support for open and interoperable solutions;
- Use government procurement to support vendor diversity;
- Fund research and development;
- Remove barriers to 5G deployment; and
- Avoid heavy-handed or prescriptive solutions
…………………………………………………………………………………………
The FCC is scheduled to host an open RAN forum on September 14th. FCC Chairman Pai will host experts at the forefront of the development and deployment of open, interoperable, standards-based, virtualized radio access networks to discuss this innovative new approach to 5G network architecture.
Panelists include representatives from Nokia, Parallel Wireless, Mavenir, Altiostar, HP Enterprise, Dell, VM Ware, and other would be Open RAN hardware/software vendors. But Ericsson will not be among them.
SK Telecom, Samsung, HPE and Intel MOU for 5G NFV Technology Evolution; ETSI ISG-NFV?
Who needs the ETSI ISG on NFV? Apparently, no one BUILDING 5G INFRASTRUCTURE! Founded in November 2012 by seven of the world’s leading telecoms network operators, ETSI ISG NFV became the home of the definition and consolidation for Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) technologies. Yet there is very little, if any, commercial deployments based on their specifications. In particular, the greatly promoted ETSI NFV management and orchestration (NFV-MANO).
SK Telecom today announced that it signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Samsung Electronics, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) and Intel for cooperation in the commercialization of an evolved 5G network functions virtualization (NFV) platform.
Under the MOU, the four companies will jointly develop evolved NFV technologies for 5G network infrastructure, establish a standardized process for adoption of NFV, and develop technologies that can harness the capabilities of the virtualized network. Together, the companies will be able to reduce the time required to validate and integrate technologies from various vendors as well as verify them within the network. This will result in a more rapid introduction of new innovative technologies that enhance end user experience.
Mobile operators will be able to benefit from a significantly reduced time-to-market for the latest 5G services such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) through the NFV platform. Previously, they had to install each new hardware equipment or upgrade existing ones to introduce a new service.
The four companies will realize an evolved 5G NFV platform by applying Samsung’s 5G solution based on technologies from Intel and HPE to SK Telecom’s 5G network. To this end, Intel will provide its latest technologies, including Intel Xeon Processors, Ethernet 800 Series Network Adapters and Solid State Drives, and HPE will provide HPE ProLiant Servers to Samsung Electronics for early development and verification purposes. SK Telecom plans to establish a process for 5G network virtualization, which includes interconnecting its 5G core network to Samsung’s virtualized 5G solutions.
“Through this global cooperation, we will secure a solid basis for commercialization of an evolved 5G NFV platform and provide more innovative services to our customers,” said Kang Jong-ryeol, Vice President and Head of ICT Infrastructure Center of SK Telecom. “Going forward, we will continue to develop new technologies for 5G NFV evolution to play a leading role in realizing communication services of the future.”
“Together with SK Telecom, HPE and Intel, Samsung will lay the groundwork for network virtualization to allow SK Telecom to swiftly apply Samsung’s virtualized solutions on partner hardware platforms. As more operators look to virtualized networks, this collaboration will serve as an exemplar of transforming legacy networks to virtual networks,” said Roh Wonil, Senior Vice President and Head of Product Strategy, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “With proven success in 5G commercialization, we will continue to extend our 5G leadership, allowing customers to experience immersive 5G services.”
“Industry collaboration is essential to accelerate the rollout of 5G networks,” said Dan Rodriguez, corporate vice president and general manager of the Intel Network Platforms Group. “The joint work between SK Telecom, Intel, HPE and Samsung will be instrumental in helping SK Telecom implement the latest technologies and new capabilities in a faster and more agile way, ultimately delivering new innovative services to their end users.”
“We are pleased to be providing telco optimized infrastructure for this collaboration with SK Telecom, Samsung and Intel”, said Claus Pedersen, vice president, Telco Infrastructure Solutions, HPE. “HPE believes that the future of 5G lies in open, interoperable software and hardware innovation from different vendors. This is yet another proof point that HPE is the leading open infrastructure provider for 5G, helping telcos to deploy 5G services faster, on secure telco optimized platforms.”
About SK Telecom
SK Telecom is Korea’s leading ICT company, driving innovations in the areas of mobile communications, media, security, commerce and mobility. Armed with cutting-edge ICT including AI and 5G, the company is ushering in a new level of convergence to deliver unprecedented value to customers. As the global 5G pioneer, SK Telecom is committed to realizing the full potential of 5G through ground-breaking services that can improve people’s lives, transform businesses, and lead to a better society.
SK Telecom says they have attained unrivaled leadership in the Korean mobile market with over 30 million subscribers, which account for nearly 50 percent of the market. The company now has 47 ICT subsidiaries and annual revenues approaching KRW 17.8 trillion.
References:
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit our Linkedin page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-
Dell’Oro: Telecom equipment revenues to grow 5% through 2020; Huawei increases market share
Dell’Oro analysts say first half global telecom equipment [1.] revenues were up 4% YoY in 1st half of 2020, as 5G infrastructure investments offset declines due to the impact of the coronavirus pandemic. The market research firm forecasts a 5% advance for the entire year.
Rollouts of 5G wireless, especially in China, were a primary cause of the first half increases, which benefit the entire supply chain, including telecommunications semiconductors. China 5G spending surely helped Huawei increase its market share, despite U.S. sanctions.
Note 1. Dell’Oro includes the following types in the telecom equipment market: Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network, SP Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch
In the first half of 2020, double digit growth in mobile infrastructure offset declining investments in broadband access, microwave and optical transport and service provider routers and ethernet switches, Dell’Oro said. Statista analysts in June said 2020 telecom equipment revenues should nearly reach $50 billion.
Rankings of the biggest telecom equipment providers remained the same in the first half of 2020, with Huawei dominating at 31%, followed by Nokia and Ericsson tied at 14% each, then ZTE at 11% and Cisco at 6%, according to Dell’Oro.

Second quarter results were stronger than expected following a 4% decline in the first quarter. The biggest driver was a strong rebound in China across 5G Radio Access Network, 5G Core and other areas. Supply chain disruptions of the first quarter also stabilized in the second quarter, Dell’Oro said.
Additional key takeaways from the 2Q20 reporting period include:
- Following the 4% Y/Y decline during 1Q20, the overall telecom equipment market returned to growth in the second quarter, with particularly strong growth in mobile infrastructure and slower but positive growth for Optical Transport and SP Routers & CES, which was more than enough to offset weaker demand for Broadband Access and Microwave Transport.
- For the 1H20 period, double-digit growth in mobile infrastructure offset declining investments in Broadband Access, Microwave and Optical Transport, and SP Routers & CES.
- The results in the quarter were stronger than expected, driven by a strong rebound in China across multiple technology segments including 5G RAN, 5G Core, GPON, SP Router & CES, and Optical Transport.
- Also helping to explain the output acceleration in the quarter was the stabilization of various supply chain disruptions that impacted the results for some of the technology segments in the first quarter.
- Shifting usage patterns both in terms of location and time and surging Internet traffic due COVID-19 has resulted in some infrastructure capacity upside, albeit still not proportional to the overall traffic surge, reflecting operators ability to address traffic increases and dimension the network for additional peak hours throughout the day using a variety of tools.
- Even though the pandemic is still inflicting high human and economic losses, the Dell’Oro analyst team believes the more upbeat trends in the second quarter will extend to the second half, propelling the overall telecom equipment market to advance 5% in 2020.
Semiconductor officials are less optimistic for the rest of the year with SIA President John Neuffer recent saying “substantial market uncertainty remains for the rest of the year.” Semiconductor sales were up 5% in July, reaching $35 billion, but dropped in early August, according to reports.
According to the Semiconductor Industry Association, about 33% of all semiconductors made (the largest category) are devoted to communications, including networking equipment and radios in smartphones.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.fierceelectronics.com/electronics/telecom-equipment-revenues-to-grow-5-through-2020
Samsung Electronics wins $6.6B wireless network equipment order from Verizon; Galaxy Book Flex 5G
Samsung Electronics said on Monday it had won a $6.64 billion order to provide wireless communication solutions to Verizon in the United States, a major win for the South Korean firm in the next-generation 5G network market. Samsung’s local unit Samsung Electronics America signed the agreement with Verizon Sourcing, a subsidiary of Verizon Communications, to offer network products for the wireless carrier through the end of 2025. This includes providing, establishing and maintaining the company’s 5G mobile telecom equipment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sidebar: Nokia on the sidelines:
Nokia’s biggest customer is Verizon, JP Morgan research said in a July note to clients. Yet Nokia didn’t win any part of the new Verizon 5G order. That was predicted by Rosenblatt analyst Ryan Koontz, who said in July “Samsung will “leapfrog Nokia to secure one of the largest new supplier telecom contracts in many years.”
Nokia wrote in an email, “We do not comment on our customers’ vendor strategy. Nokia is proud to serve Verizon, and we are committed to continuing to help them build the best, most reliable and highest performing network. Nokia and Verizon have a longstanding strategic partnership in key technologies across their network with our end-to-end solutions portfolio.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Samsung’s global prospects for its network business have improved following U.S. sanctions on its bigger rival Huawei , analysts said. The Trump administration last month unveiled plans to auction off spectrum previously dedicated to military purposes for commercial use starting in mid-2022, to ramp up fifth-generation network coverage in the United States. In July, the UK ordered Huawei equipment to be purged completely from its 5G network by the end of 2027, adding it needs to bring in new suppliers like Samsung Electronics and Japan’s NEC Corporation.
Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg told CNBC in July last year that Verizon does not use any Huawei equipment. Verizon had already been a Samsung customer before the order. Vestberg’s statement about no Huawei gear is not true, as Light Reading and other websites noted on Friday.
The FCC requested information about “the presence or use of Huawei or ZTE equipment and/or services in their networks, or in the networks of their affiliates or subsidiaries.”
The FCC’s goal is to determine how many US companies use equipment from Huawei or ZTE – the equipment has been deemed a threat to national security – and how much it might cost to replace that gear with equipment from “trusted” suppliers.
On Friday, the FCC published a list of companies that reported they have existing Huawei or ZTE equipment and services.
Three of the nation’s five biggest wireline phone providers (Verizon, CenturyLink and Windstream) have admitted to having equipment from Huawei or ZTE, according to Leichtman Research Group.
“Verizon’s networks do not include equipment from any untrusted vendors. In addition, the company is not seeking funds from the FCC to replace equipment,” a Verizon representative wrote in response to questions from Light Reading. “Verizon has a relatively small number of devices, called VoiceLink, which were made by Huawei and are used by some customers to make voice calls. There are no data services associated with these devices. Earlier this year, Verizon started replacing these units. That effort was temporarily halted by the pandemic and is now underway again. We expect to have all Voicelink devices fully retired by the end of the year.”
“Samsung winning the order from Verizon would help the company expand its telecom equipment business abroad, potentially giving leverage to negotiate with other countries,” Park Sung-soon, an analyst at Cape Investment and Securities told Reuters.
The order is for network equipment, a Samsung spokesman said. The company declined to comment on detailed terms the contract such as the portion of 5G-capable equipment included.
Verizon joined with Samsung long before 5G made its debut in smartphones last spring. In early 2018, the two firms teamed up for trial runs of 5G-powered home internet. Verizon officials have previously pledged not to use Huawei for its next-generation rollout. Samsung has supplied some network gear for prior generations including 4G LTE.
To Samsung, the deal represents a major 5G win. The contract, valued at 7.898 trillion South Korean won over five years, compares with the roughly 5 trillion won Samsung’s network business racked up in revenue in all of 2019.
Last year, 5G represented less than half of Samsung’s network business, of which U.S. carriers accounted for 10%, said S.K. Kim, a Seoul-based analyst with Daiwa Securities.
“With this latest long-term strategic contract, we will continue to push the boundaries of 5G innovation to enhance mobile experiences for Verizon’s customers,” Samsung said in a statement.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Sidebar — Telecom Equipment Vendor Market Shares:
Samsung had a 3% market share of the global total telecom equipment market in 2019, behind No. 1 Huawei with 28%, Nokia’s 16%, Ericsson’s 14%, ZTE’s 10% and Cisco’s 7%, according to market research firm Dell’Oro Group.
Among 5G network sales, Samsung ranks No. 4 with about 13% of the total market, according to market research firm Dell’Oro Group. It trails the top three, which include China’s Huawei Technologies Co. and the European firms Ericsson AB and Nokia Corp.
Huawei said early this year that it had signed more than 90 5G contracts, and Ericsson last month touted its 100th 5G “commercial agreement.” Samsung hasn’t divulged how many 5G contracts it has signed. But it has high hopes, having invested more than $30 billion in the U.S. market alone.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Samsung announced the Galaxy Book Flex 5G, an adaptable, 5G-powered addition to its premium laptop line. Galaxy Book Flex 5G is powered by the new 11th Gen Intel® Core™ processor with Intel® Iris® Xe graphics offering intelligent performance and powerful processing for impressive productivity and stunning entertainment, along with Wi-Fi 6 and 5G connectivity for an unparalleled laptop experience.
“Across the world, we’re being asked to adapt and change constantly, and it’s vital we have devices that move with us,” said Mincheol Lee, Corporate VP and Head of New Computing Biz Group at Samsung Electronics. “Thanks to our close collaboration with Intel, Galaxy Book Flex 5G provides users with a powerful performance, next-generation connectivity, effortless productivity and premium entertainment features, all in the form function of their choosing.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Tech Mahindra: “We can build and run an entire 4G and 5G or any enterprise network”
India based IT services provider Tech Mahindra says it has the capability to build and run an entire 4G or 5G network in India. The company’s partnership with Japanese greenfield telco Rakuten Mobile [1.] will help it get more meaningful business in India’s telecom industry, a senior executive said.
Note 1. Rakuten Mobile, together with NEC, is building a 5G Open RAN and cloud native 5G core network based on their own specifications. Open RAN and cloud native 5G core network are two different and independent initiatives.
“We can build and run an entire 4G and 5G or any enterprise network. We have done that already. We bring to the table our ability to design, to plan, to integrate and deploy and then to manage the entire suite of network capabilities, including designing various parts to it in a disaggregated world,” Manish Vyas – President, Communications, Media & Entertainment Business, and the CEO, Network Services, Tech Mahindra, told the Economics Times of India.
In August, the company announced German telecoms company Telefonica Deutschland had selected it for its network and services operations, in addition to further developing 5G, artificial intelligence, and machine learning use cases.
“We are pleased to announce this partnership with Tech Mahindra. We are supported by a globally experienced service provider to consistently drive forward the development of our network and services operations, thus leading to further enhancement of 5G, artificial intelligence and data analysis use cases,” said Mallik Rao, Chief Technology & Information Officer of Telefonica Deutschland.
“This strategic partnership strengthens our long-standing relationship with Telefonica, in which we support the company in realizing its vision of becoming the ‘Mobile Customer and Digital Champion’ by 2022,” said Vikram Nair, President, Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) of Tech Mahindra.
In October 2019, the company launched a 5G enabled Factory of the Future solution. Nilesh Auti, Global Head Manufacturing Industry unit, Tech Mahindra, said:
“Factory equipment holds a great deal of meaningful data which is key to any successful Industry 4.0 project. Tech Mahindra’s solution in partnership with Cisco, will enable us to leverage this data and empower manufacturers to build factories of the future. As part of our TechMNxt charter we are focused on leveraging 5G technologies to address our customer’s evolving and dynamic needs, and enable them to RISETM.”
Tech Mahindra is also looking for strategic investments and acquisition in companies to further bolster its telecom product and services portfolio. The company says the following about their 5G capabilities and experience:
Tech Mahindra provides range of services that enable enterprises to establish private wireless network to span areas of operations & enable a plethora of IoT use cases. Our services remove inefficiencies related to slow, insufficient wireless connectivity & have a strong roadmap to support growing traffic demands for 5G establishment. From media to medicine we believe 5G is “The NXT of Everything.”
Tech Mahindra ccomplishments listed are these:
- 1M+ carrier grade cellular sites designed, delivered and managed
- Enabling 3 of the first 5 carrier 5G introductions in the world
- Strong Telco partnership/reach (80+ Global Tier 1 Telcos)
- 4 smart cities projects launched, Largest WIFI deployments in the world
- 5 connected vehicles engagements, 40+ Connected factories, 12000+ factory Assets
- 600+ Turbines and 100+ aircrafts connected; 2000+ remote healthcare patients supported
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Verizon Trials Quantum Key Distribution for Encryption over Fiber Optic Links
Verizon has begun testing quantum key distribution (QKD) [1.], a new encryption method that uses photon properties to protect subscriber data. The company says they are the first U.S. carrier to do so, although AT&T is also exploring quantum computing applications in partnership with the California Institute of Technology. Verizon said it sent encrypted streaming video from a 5G Lab to two East Coast offices.
Note 1. Unlike number-based encryption methods used today, QKD creates keys based on the quantum properties of photons, making it much harder for even advanced computing systems to crack. QKD could be applied to exchange a key between the two ends of a communication. QKD provides protection against the threat posed by quantum computing to current cryptographic algorithms and provides a high level of security for the exchange of data.
An article by ITU-T SG13 chair Leo Lehmann, PhD, described new ITU-T Recommendations related to IMT 2020 and Quantum Key Distribution. ITU-T SG13 has published two new recommendations for networks to support quantum key distribution (QKD) [1] :
- Y.3800 (Y.QKDN_FR) Overview on networks supporting quantum key distribution
- Y.3801 (Y.QKDN_req) Functional requirements for quantum key distribution networks
Y.3800 describes the basic conceptual structures of QKD networks as the first of a series of emerging ITU standards on network and security aspects of quantum information technologies. SG13 standards for QKD networks – networks of QKD devices and an overlay network – will enable the integration of QKD technology into large-scale ICT networks.
Complementing these activities, ITU-T SG17 standards provide recommendations for the security of these QKD networks.

Image depicting Quantum Cryptography
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Verizon is exploring the physics of the ultra small which could help protect encrypted network connections.
“A QKD network derives cryptographic keys using the quantum properties of photons to prevent against eavesdropping,” Verizon said. It’s also using a quantum random number generator to continuously generate encryption keys.
In the trial, Verizon said it used QKD to encrypt and send a video stream between its 5G Lab and two of its offices in Virginia and Washington DC. Specifically, live video was captured outside of three Verizon locations in the D.C. area, including the Washington DC Executive Briefing Center, the 5G Lab in D.C and Verizon’s Ashburn, Virginia office.
Using a QKD network, quantum keys were created and exchanged over a fiber optic network between Verizon’s locations. Video streams were encrypted and delivered more securely allowing the recipient to see the video in real-time while instantly exposing hackers. A QKD network derives cryptographic keys using the quantum properties of photons to prevent against eavesdropping.
Though the test was conducted over its fiber network, a Verizon representative told Mobile World Live the operator is also aiming to use the technology in their mobile networks.
Verizon also demonstrated that data could be further secured with keys generated using a Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) that, as the name suggests, creates random numbers that can’t be predicted. With QKD, encryption keys are continuously generated and are immune to attacks because any disruption to the channel breaks the quantum state of photons, which signals that eavesdroppers are present.
“The use of quantum mechanics is a great step forward in data security,” said IDC Analyst Christina Richmond, in a statement. “Verizon’s own tests, as well other industry testing, have shown that deriving ‘secret keys’ between two entities via light photons effectively blocks perfect cloning by an eavesdropper if a key intercept is attempted.
“Current technological breakthroughs have proven that both the quantum channel and encrypted data channel can be sent over a single optical fiber. Verizon has demonstrated this streamlined approach brings greater efficiency for practical large-scale implementation allowing keys to be securely shared over wide-ranging networks.”
Verizon chief product development officer Nicola Palmer stated the test was part of an effort to “discover new ways to ensure safe networks and communications” for consumers and enterprises. “Quantum-based technology can strengthen data security today and in the future,” she said.
Verizon outlined additional work focused on 5G security, including tests of a system using AI and machine learning to detect anomalies in the network and analyse cell site performance; network accelerators to mitigate increases in latency caused by security functions; and a credential management system for connected vehicles.
References:
https://www.cnet.com/news/verizon-reveals-quantum-networking-trials/
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/verizon-tunes-up-quantum-technology-trial-to-bolster-security
Quantum Cryptography Demystified: How It Works in Plain Language
New ITU-T SG13 Recommendations related to IMT 2020 and Quantum Key Distribution
Cablecos join telcos in winning FCC auction 105 bids in 3550-3650 MHz band; Buildout
Cable companies (aka MSOs) joined Verizon and Dish Network among the top bidders in the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC’s) latest auction of cellular spectrum licenses, according to FCC data released Wednesday. The FCC auction, which began on July 23 and wrapped up on August 25, offered 70 megahertz of Priority Access Licenses (PALs) in the 3550-3650 MHz band. In total, the FCC auction 105 generated $4,585,663,345 from 228 bidders who won a total of 20,625 licenses.
Verizon, the country’s largest cellphone carrier, topped the list with $1.89 billion in winning bids for licenses in the 3.55 gigahertz band, according to the commission.
- Dish unit Wetterhorn Wireless LLC bid about $913 million.
- Wireless units of Charter Communications Inc., Comcast Corp. and Cox Communications Inc. followed with winning bids of $464 million, $459 million and $213 million, respectively.
- Cellphone carrier T-Mobile US bid less than $6 million in the auction.
- AT&T did not bid.
The FCC said winning bidders have until September 17 to submit a down payment totaling 20 percent of their winning bid(s). Full payment is due by October 1, 2020.

The licenses were considered highly valuable (3.5GHz spectrum) but complicated by a sharing arrangement that allowed some companies to use nearby frequencies without an exclusive license. The military also uses the spectrum band, though radio engineers consider the likelihood of interference from naval radar low in most of the U.S.
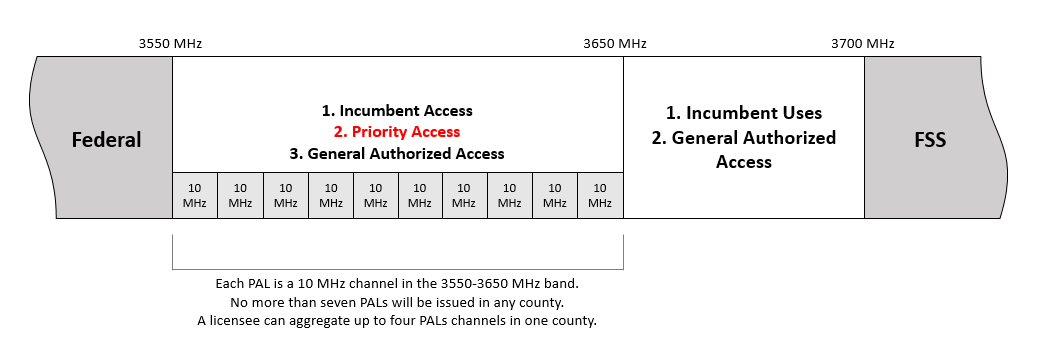
Image Credit: FCC
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
A frequency coordinator called a Spectrum Access System (SAS) will assign the specific channel(s) for a particular licensee on a dynamic basis. Although a Priority Access Licensee may request a particular channel or frequency range from an SAS following the auction, they are not guaranteed a particular assignment, and an SAS may dynamically reassign a PAL to a different channel as needed to accommodate a higher priority Incumbent Access user. To the extent feasible, an SAS will “assign geographically contiguous PALs held by the same Priority Access Licensee to the same channels in each geographic area” and “assign multiple channels held by the same Priority Access Licensee to contiguous frequencies within the same License Area.” An SAS may, however, temporarily reassign individual PALs to non-contiguous channels to the extent necessary to protect incumbent users from harmful interference or if necessary, to perform its required functions.
Technicians installing a cellular base station. Photo credit: GEORGE FREY/REUTERS
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Wireless-industry analysts expected Verizon and Dish to be active participants in the most recent auction, which offered 70 megahertz of “priority access” licenses in a band considered useful for ultrafast fifth-generation, or 5G, transmissions. Rival T-Mobile’s purchase of Sprint Corp. this year gave it a treasure trove of wireless licenses that led Verizon to play catch-up in the race to supply customers with more mobile internet data. Satellite-TV operator Dish has spent the past decade amassing its own spectrum licenses for a brand-new wireless network, though the system hasn’t been built.
The entry of regional cable operators suggests that residential broadband providers are eager to offer more service over the air. Charter and Comcast have added hundreds of thousands of smartphone customers over the past year, but their mobile service runs on Verizon’s network outside the home, limiting the cable companies’ profitability. Charter also has tested fixed home broadband service over 3.5 GHz frequencies to lower the cost of stringing wires to far-flung households.
The cable companies’ wireless bets pale next to their regular investments in landline infrastructure, and the latest bids are no guarantee their strategies will shift. Cable companies have made similar wagers on wireless service before withdrawing and selling their holdings back to established cellphone carriers.
The auction results also set the stage for a more expensive auction of C-Band spectrum, another swath of frequencies useful for 5G service. The commission is expected to kick off an auction for those spectrum bands in December.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-announces-winning-bidders-35-ghz-band-auction
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-366624A1.pdf
https://www.fcc.gov/auction/105/factsheet
https://www.wsj.com/articles/cable-satellite-operators-place-new-bets-on-5g-airwaves-11599063412
https://www.techspot.com/news/86623-fcc-generates-more-than-45-billion-latest-wireless.html
Ciena and TELUS demo 800Gbps fiber optic transmission over 970km link from Toronto to Quebec City; Ciena Earnings & Guidance
Ciena claims to have achieved a worldwide transmission record of 800 Gbps with TELUS, over a record-breaking 971.2km distance. Teams from both organizations worked together and turned up an 800G wavelength from Toronto to Quebec City.

TELUS is one of the early 800 Gbps technology adopters who is in the process of augmenting their network with Ciena’s WaveLogic5 Extreme (WL5e). TELUS will be standardizing WaveLogic 5 Extreme for deployment in the near future. Part of the standardization activities include testing the full capabilities of the product to plan end user service offerings.
TELUS supports 15.3 million customer connections spanning wireless, data, IP, voice, television, entertainment, video and security. The TELUS network extends 6,000 km from Victoria, British Columbia to Halifax, Nova Scotia. Designed with the future in mind, TELUS’s next generation optical network consists of a state-of-the-art, colorless, directionless, contentionless, flexible grid (CDC-F) ROADM architecture with Layer 0 Control Plane, designed to support reliable, fast turn-up and re-route of unpredictable bandwidth demands across the network. Furthermore, it is ready to support new innovations in optical technologies as they become available, including the ability to carry optical channels of any spectrum size across the fiber. This fully flexible, intelligent photonic infrastructure allows for the simple addition of WL5e wavelengths and with that, access to significant cost, footprint, and power benefits.
“TELUS prides itself on having one of the world’s fastest networks and using industry-leading technology to deliver the best experience for our customers across Canada. Our collaboration with Ciena on breaking transmission records is an exciting innovation that speaks to both teams track records of success,” said Ken Nowakowski, Director Planning and Engineering, Transport and IP Infrastructure Development and Operations at TELUS.
Testing continues at TELUS, with planned deployment of WL5e in the coming months. Does this mean 800G will be deployed across long haul links? This is not a yes or no response, but 800G will be deployed where it makes sense in the TELUS network. As has always been the case, the line rate capacity that will be deployed depends on specific link characteristics, number of channels and desired reserved margin by the operator.

Ciena 6500 shelves with WaveLogic 5 Extreme
The real news here is the resulting long-term benefits of the WL5e network upgrade for both TELUS and their end users. TELUS can continue to provide high quality, high speed connectivity to their end users – such as teleworker videoconferencing, multi-player interactive gaming, Internet access for low income families, and even live-streaming the Stanley Cup playoffs – while more efficiently using bandwidth resources and evolving to a greener network.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Ciena announced earnings today. For the fiscal third quarter ended Aug. 1, Ciena (ticker: CIEN) reported revenue of $876.7 million, up 1.7% from a year earlier, and ahead of the Wall Street analyst consensus at $971.8 million. Non-GAAP profit was $1.06 a share, nicely above the Street consensus at 83 cents.
“Operating conditions have complicated and extended the time required to deploy and activate new equipment and services with many of our large and long-standing international customers,” the company said in a presentation prepared for its earnings call with analysts on Thursday. “Conditions have made it more challenging to ramp up and operationalize some of our newer international deals and customer wins on their original timelines.”
Ciena also said “customer uncertainty around broader economic conditions is driving more cautious spending behaviors.” It said “longer term fundamental drivers—increasing network traffic, demand for bandwidth and adoption of cloud architectures—remain strong.” Ciena CEO Gary Smith said Covid-19-related market dynamics were likely to adversely impact revenue “for a few quarters.”
Here are a few data points from the company’s earnings presentation:
- Non-telco represented 43% of total revenue
- Direct web-scale contributed 25% of total revenue
- MSO’s contributed 9% of total revenue
- Americas revenue up 9% YoY
- TTM Adjusted R&D investment was $518M
- 535 100G+ total customers, which includes 37 new wins on WaveLogic Ai and 27 new wins on WaveLogic 5e in Q3-2020
- Shipped WL 5 Extreme to almost 40 customers, and the technology is live and carrying traffic in several networks
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Overview of Ciena’s Technology Portfolio:
PROGRAMMABLE INFRASTRUCTURE:
Converged Packet-Optical Networking: Software-defined platforms, featuring Ciena’s award-winning WaveLogic™ Photonics and agnostic packet/OTN switching, designed to maximize scale, flexibility and openness. Optimizes network performance from the access edge, along the backbone, and across ocean floors.
Packet Networking: Purpose-built platforms hosting a common Service-Aware Operating System that are the building blocks for low-touch, high-velocity Ethernet/MPLS/IP access to metro networks.
SOFTWARE CONTROL AND AUTOMATION:
Open software that includes Blue Planet® multi-domain orchestration, inventory, and route optimization to support the broadest range of closed-loop automation use cases across multi-layer, multi-vendor networks, as well as Ciena’s Manage, Control and Plan (MCP) domain controller for bringing software-defined programmability to next-gen Ciena networks.
ANALYTICS AND INTELLIGENCE:
Blue Planet Unified Assurance and Analytics: An open suite of software products that unifies multilayer, multi-domain assurance with AI-powered analytics to provide unprecedented insights that help transform and simplify business operations for network providers.
INNOVATION AND THE ADAPTIVE NETWORK:
▪ WaveLogic™ roadmap extends beyond 400G and with multiple form factors
▪ Adaptive IP™ capabilities for Packet Networking to address fiber densification (5G & Fiber Deep)
▪ Blue Planet® Intelligent Automation Portfolio and closed-loop automation capability strengthened with recent acquisition of Centina
References: