Ultra Oxymoron: GSMA teams up with O-RAN Alliance without liaison with 3GPP or ITU
The GSMA and O-RAN Alliance are cooperating to accelerate the adoption of Open Radio Access Network (RAN) products and solutions that take advantage of new open virtualized architectures, software and hardware. The organizations will work together to harmonize the open networking ecosystem and agree on an industry roadmap for network solutions, thereby making access networks as open and flexible as possible for new market entrants.
GSMA. made up with established wireless telcos and incumbent network equipment vendors, says that “5G will facilitate the opportunity to create even more agile, purpose-built networks tailored to the different needs of citizens, enterprises and society. For example, 5G is an essential ingredient of the European Commission’s recently launched Industrial Strategy and will help shape its future.”
O-RAN Alliance is a world-wide community of more than 170 mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network (RAN) industry. It’s mission is to re-shape the industry towards more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable mobile networks. The new O-RAN standards will enable a more competitive and vibrant RAN supplier ecosystem with faster innovation to improve user experience. O-RAN-compliant mobile networks will at the same time improve the efficiency of RAN deployments as well as operations by the mobile operators.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Author’s Opinion:
So here we have an upstart consortium (O-RAN Alliance), cooperating with an established mobile ecosystem marketing machine (GSMA) to promote “open and interoperable mobile networks.” Yet the only way for that to be realized is through adherence to “open” standards and cooperating closely with recognized standards bodies. That is the way interoperability is obtained- by defining open interfaces, layers and protocols!
Instead, O-RAN is making their own specifications (e.g. virtual RAN) that are not part of any 5G standard or 3GPP spec! In particular, the O-RAN Alliance has no liaisons with either 3GPP or ITU-R or ITU-T. How is then possible to specify open hardware and software without any inter-change of documents with those standards organizations? One would think that liaisons, spec iterations, close cooperation with feedback would be essential for success, e.g. a closed loop ecosystem between standards bodies and open source consortiums is urgently needed!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In its latest Mobile Economy Report, the GSMA predicts that operators will invest more than a trillion dollars over the next five years globally to serve both consumer and enterprise customers, 80 per cent of which will be on 5G networks.
“When 5G reaches its potential, it will become the first generation of mobile networks to have a bigger impact on enterprises than consumers,” said Alex Sinclair, Chief Technology Officer, GSMA. “In the enterprise sector alone, we forecast $700 billion worth of economic value to be created by the 5G opportunity. The growth of the open networking ecosystem will be essential to meeting enterprise coverage and services needs in the 5G era.”
“As the demand for data and vastly expanded mobile communications grow in the 5G era, a global, cross-border approach is needed to rethink the RAN,” said Andre Fuetsch, Chairman of the O-RAN ALLIANCE, and Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, AT&T. “The GSMA collaboration with the O-RAN ALLIANCE is exactly the sort of global effort that’s needed for everyone, operators and vendors alike, to succeed in this new generation.”
Mobile operators are re-evaluating the way that their networks are deployed. New virtualised architectures with open interfaces can drive cost efficiencies and allow operators to accelerate the deployment of 5G networks. Also, open interfaces can help diversify and reinvigorate the supply chain promoting competition and innovation – for example, by building and operating a RAN based on mix-and-match components from different vendors.
The GSMA and O-RAN ALLIANCE collaboration complements the recently announced inter-working between the GSMA and Telecom Infra Project (TIP), and the O-RAN Alliance and TIP. The goal for these collaborations is to help avoid fragmentation and accelerate the successful evolution of the industry towards a more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable RAN (see Author’s Opinion above) why this is highly unlikely to happen).

Image Credit: O-RAN Alliance
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
June 12, 2020 Update: Press Release from Mavenir and Aliostar:
“Very few companies are participating in the current (OpenRAN) supply chain and mostly offering proprietary radio solutions lacking open interfaces that are not interoperable with other network elements. In addition, the requirement to procure products from trusted vendors in the US market is also causing operators to reconsider supplier options. OpenRAN radios provide new possibilities for operators to implement a secure, cost effective and best of breed solution as networks move to 5G and beyond.”
Mavenir and Altiostar Collaborate to Deliver OpenRAN Radios for US Market
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….About the GSMA
The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide, uniting nearly 750 operators with almost 300 companies in the broader mobile ecosystem, including handset and device makers, software companies, equipment providers and internet companies, as well as organisations in adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces industry-leading events such as Mobile World Congress, Mobile World Congress Shanghai, Mobile World Congress Americas and the Mobile 360 Series of conferences.
For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com. Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA.
About O-RAN ALLIANCE
O-RAN ALLIANCE is a world-wide community of more than 170 mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network (RAN) industry. As the RAN is an essential part of any mobile network, O-RAN ALLIANCE’s mission is to re-shape the industry towards more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable mobile networks. The new O-RAN standards will enable a more competitive and vibrant RAN supplier ecosystem with faster innovation to improve user experience. O-RAN-compliant mobile networks will at the same time improve the efficiency of RAN deployments as well as operations by the mobile operators. To achieve this, O-RAN ALLIANCE publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members in integration and testing of their implementations.
For a short video describing O-RAN’s progress, see www.o-ran.org/videos
For more information please visit www.o-ran.org
Media Contacts:
For the GSMA
Alia Ilyas
+44 (0) 7970 637622
[email protected]
GSMA Press Office
[email protected]
O-RAN ALLIANCE:
Zbynek Dalecky
[email protected]
O-RAN Alliance e.V.
Buschkauler Weg 27
53347 Alfter/Germany
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
GSMA and O-RAN Alliance Collaborate on Opening up 5G Networks
5G breaks from proprietary systems, embraces open source RANs
Qualcomm SoCs for Wi-Fi 6E in 6GHz band and Bluetooth 5.2 with superior performance
Qualcomm has launched a new portfolio of flagship mobile system on a chip (SoC) featuring support for Wi-Fi 6E (aka IEEE 802.11ax), which will soon be operational in the 6 GHz band. The first products to be launched are two SoCs, the Qualcomm FastConnect 6900 and the Qualcomm FastConnect 67000.
The FastConnect 6900 will provide speeds of up to 3.6 Gbps, implementation of 4-stream Dual Band Simultaneous (DBS) with multiband (including 6 GHz) capabilities. The FastConnect 6700 chip will meanwhile deliver speeds approaching 3 Gbps. The Verge noted that one of the chips will be for smartphones and the other for routers.
Both chips will both support Wi-Fi 6, low latency, and Bluetooth audio features for classic and new use cases. They will sport Qualcomm 4K QAM for enhanced gaming and ultra HD streaming and 160 MH channels support in both 5 and 6 GHz bands, expanding throughput while reducing congestion. They will also help save power, by generating less channel congestion. The chips are now sampling and will ship in production during the second half of 2020.

“Wi-Fi 6E delivers an unprecedented improvement in capacity to meet the rapid growth of connected devices and data demand. The introduction of supporting chipsets so soon after the FCC ruling ensures customers will see the benefits quickly and is an indicator of both Qualcomm Technologies’ investment and broad industry collaboration,” said Geoff Blaber, vice president, research, Americas, CCS Insights.
“Wi-Fi Alliance® members have mobilized around 6 GHz in an unprecedented way, and we’re excited to see Wi-Fi 6E solutions rapidly coming to market with the availability of new unlicensed spectrum in the U.S.,” said Kevin Robinson, Senior VP of Marketing, Wi-Fi Alliance. “Solutions like these from Qualcomm will help users fully experience Wi-Fi® in 6 GHz and quickly benefit from faster speeds, higher capacity, and lower latency applications.”
Next-Generation Wi-Fi 6E for Mobile and Computing
New portfolio extends advanced Wi-Fi 6 feature implementations into the 6 GHz band. Key features include:
Unmatched Wi-Fi Speed:
- FastConnect 6900 offers the fastest available Wi-Fi 6 speed, up to 3.6 Gbps, of any mobile Wi-Fi offering in the industry.
- FastConnect 6700 delivers impressive peak speeds approaching 3 Gbps.
Driving this performance for both FastConnect systems are differentiated features such as:
- Qualcomm® 4K QAM (2.4, 5, 6 GHz) – an industry first implementation of this advanced modulation technique can extend the maximum QAM rate, across any supported band, from 1K to 4K for enhanced gaming and ultra HD streaming.
- 160 MHz channels support in both 5 and 6GHz bands, dramatically expanding throughput while reducing congestion.
FastConnect 6900 delivers an extra boost of performance through additional unique feature implementation of 4-stream Dual Band Simultaneous (DBS) with multi-band (including 6 GHz) capabilities.
Essential Improvement of Capacity and Network Efficiency: Delivering reliable performance, even in the most congested home, enterprise and public networks.
- 6 GHz dramatically expands Wi-Fi capacity by adding up to 1200 MHz of additional spectrum, more than doubling the number of pathways currently available for sending and receiving data.
- Dual band 160 MHz supports up to seven additional non-overlapping channels in the 6 GHz band, in addition to 160 MHz channels available in the 5 GHz band.
- Deploys high-performance Uplink / Downlink MU-MIMO and OFDMA mobile technologies across all available bands.
- New Wi-Fi 6 Uplink MU-MIMO capability can increase network capacity by more than 2.5x.
Ultra-Low Latency: A new class of low latency and high speed for emerging mobile applications, providing the foundation for explosive growth in mobile gaming and XR application.
- Feature implementation delivers latency reduction up to 8x in congested environments for dramatically improved mobile gaming experiences.
- Wireless VR-class latency (<3ms) for Head Mounted Displays (HMD) provides a strong foundation for this rapidly growing industry segment.
Advanced Technology and Power Efficiency: Power savings due to less channel congestion and improved scheduling.
- 14nm process node combined with advanced power-management architecture provides up to 50 percent improvement in power efficiency, compared to previous generation solutions.
Bluetooth 5.2 with Advanced Audio
FastConnect 6900 and 6700 integrate Bluetooth 5.2 with the latest audio advancements for greatly improved wireless experiences. Key features include:
Bluetooth 5.2 Above and Beyond
- Leading Bluetooth 5.2 implementation includes a second Bluetooth antenna with intelligent switching capabilities, overcoming common signal shadowing issues for unparalleled Bluetooth reliability and range.
- Engineered to be ready to address emerging LE Audio experiences such as multi-point audio sharing and broadcast audio, enabling multiple audio connections simultaneously.
Superior Bluetooth Audio
- Qualcomm® aptX™ Adaptive supporting wire-equivalent audio (up to 96kHz) and Qualcomm® aptX™ Voice providing super-wideband quality calls.
End-to-End Enhanced Experiences
- When paired with the premium features of Qualcomm® QCC5141, QCC5144, QCC3046 and QCC3040 Audio SoCs, users can expect robust, premium audio quality with low power consumption.
- Innovative transmit power and coexistence algorithms deliver materially improved range and link robustness.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Leveraging decades of focused research and development, our second-generation Wi-Fi 6 platforms set a new performance benchmark for home and enterprise networking applications,” said Nick Kucharewski, vice president and general manager, wireless infrastructure and networking, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. “With Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 and scaling to 16 streams, Qualcomm Networking Pro Series Platforms pair wireless expertise with robust architecture designed to deliver Gigabit speeds, massive capacity, and stable-as-wire reliability our customers depend on.”
“The new 6 GHz band and Wi-Fi 6E standard ushers in a new age in wireless connectivity – a dramatic advance in performance and a new paradigm in wireless networking. Industry-leading Wi-Fi 6E technology – including Qualcomm’s new Wi-Fi 6E platforms – will transform every use case segment, from home to the enterprise, industrial applications, and even fixed wireless access, with new unbelievable applications sure to follow. The Wi-Fi 6E future looks very bright indeed,” said Claus Hetting, CEO & Chairman, Wi-Fi Now.
“Wi-Fi Alliance® members have mobilized around 6 GHz in an unprecedented way, and we’re excited to see Wi-Fi 6E solutions rapidly coming to market with the availability of new unlicensed spectrum in the U.S.,” said Kevin Robinson, Senior VP of Marketing, Wi-Fi Alliance. “Solutions like these from Qualcomm will help users fully experience Wi-Fi® in 6 GHz and quickly benefit from faster speeds, higher capacity, and lower latency applications.”
Qualcomm Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 expands the capabilities of the Qualcomm Networking Pro Series portfolio, whose hallmark is the delivery of consistent high performance in the most densely congested environments:
- Qualcomm® Max User Architecture: Industry-first architecture to manage and maintain connectivity for up to 2,000 clients simultaneously, with network stability and sustained throughput.
- Qualcomm® Multi-User Traffic Management: Provides advanced scheduling algorithms and buffering with universal uplink data support. Advanced multi-user implementations specialized for high user counts include up to 37-user OFDMA support per channel and 8-user MU-MIMO support per channel.
- Qualcomm® 4K QAM technology: Designed to deliver 20% higher throughput compared to standard Wi-Fi 6E, helping achieve device-to-device transfers of up to 2.4 Gbps per link to compatible mobile and compute devices.
- Qualcomm® Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 for Mesh Networks: Qualcomm® Wi-Fi SON has been enhanced to interconnect the Mesh Nodes using the 6 GHz band.
- Qualcomm® Wi-Fi Security Suite: Comprehensive WPA3 implementation coupled with state-of-the-art embedded crypto accelerators designed to provide secure transactions across a full range of Wi-Fi data touchpoints.
“Aruba’s enterprise customers demand high-performance, reliable and secure Wi-Fi connectivity solutions that can be scaled to deliver extreme density and capacity. Through our collaboration with Qualcomm Technologies, we’ve utilized their advanced Wi-Fi technology to continuously evolve the seamless, connected experiences that our customers demand,” said Onno Harms, senior director of Product Management for WLAN Platforms at Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company. “The newly opened 6 GHz spectrum and the advent of Wi-Fi 6E are important industry milestones that promise to usher in a new wave of Wi-Fi innovation that will bring exceptional wireless experiences to life.”
“We see this announcement from Qualcomm Technologies as a positive step forward in what’s possible for networking across the industry,” said David Henry, senior vice president of Connected Home Products and Services for NETGEAR. “We look forward to continuing our collaboration with Qualcomm Technologies as we incorporate the Networking Pro Series to deliver robust and seamless experiences that enable us to expand the ecosystem.”
“Our recent announcement highlighting CommScope’s RUCKUS Wi-Fi 6 Certified access points is a great example of pushing the boundaries of what’s possible for wireless communications. Integrating the Qualcomm Technologies Networking Pro Series platform into the RUCKUS portfolio enables customers to benefit from the latest improvements in security, speed and Wi-Fi connectivity, creating a more powerful and robust product that will strengthen the rich suite of solutions available in the industry,” said Pramod Badjate, senior vice president for CommScope’s RUCKUS portfolio.
Qualcomm Networking Pro Series platforms are shipping now with commercial availability expected this year.
For more information about our Wi-Fi 6E products, visit qualcomm.com/wi-fi-6e
*All peak speeds refer to maximum physical layer (PHY) rate.
About Qualcomm
Qualcomm is the world’s leading wireless technology innovator and the driving force behind the development, launch, and expansion of 5G. When we connected the phone to the internet, the mobile revolution was born. Today, our foundational technologies enable the mobile ecosystem and are found in every 3G, 4G and 5G smartphone. We bring the benefits of mobile to new industries, including automotive, the internet of things, and computing, and are leading the way to a world where everything and everyone can communicate and interact seamlessly.
Qualcomm Incorporated includes our licensing business, QTL, and the vast majority of our patent portfolio. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a subsidiary of Qualcomm Incorporated, operates, along with its subsidiaries, substantially all of our engineering, research and development functions, and substantially all of our products and services businesses, including our QCT semiconductor business.
https://www.qualcomm.com/wi-fi-6e
Grand View Research: Dark Fiber Networks – Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis
Executive Summary
The global dark (unlit) fiber network [1.] market size is estimated to reach $11.22 billion by 2027, according to the new report by Grand View Research, Inc. That market is anticipated to expand at a 12% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period.
Note 1. In fiber-optic communications, fiber optic cables that are not yet put in service by a provider or carrier, are termed as dark or unlit fiber. Network communications and telecom usually use the network. In regular fiber networks, information is sent through the cables in light pulses. Whereas, dark fiber networks are known to be ‘dark’ as no light or data is transmitted from it.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Dark Fiber Market Positioning
The dark fiber market has emerged as a sustainable solution for various organizations that are focusing on enhanced communication and network management. Continuously increasing penetration of internet services, over the period, has paved the way for the high demand for internet bandwidth. This demand is expected to remain rampant over the forecast period. This is the most significant factor driving the market growth. The market is strongly supported by companies with high reliance on internet connectivity. These networks are highly beneficial for organizations with a high volume of data flow in their operation. These benefits include reduced network latency, scalability, reliability, and enhanced security.
Dark fiber networks can be installed and set-up using point-to-multipoint or point-to-point configurations. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is an essential factor for the improvement and development of dark fiber networks. DWDM occurs when many data signals are transmitted using the same optical fiber at the same time. Although these signals are transmitted around the same time, they are transmitted at separate and unique wavelengths to keep these data signals separate. The significant benefits of DWDM include an increase in bandwidth of the optical fiber, high-quality internet performance, lightning-fast internet, and secure and powerful network.
Dark fiber networks are not just used for business purposes but can be installed beneath land and oceans. Some of the interesting uses cases of dark fiber include earthquake research and to monitor permafrost. Some of the disadvantages include high initial cost and loss of time in setting up your infrastructure and high repairing and maintenance costs. Similarly, large dark fiber networks are currently available at metropolitan cities only and yet to at small cities and towns.
Key suggestions from the report:
- The significant benefits of DWDM include an increase in bandwidth of the optical fiber, high-quality internet performance, lightning-fast internet, and secure and powerful network
- Telecommunication is anticipated to present promising growth prospects due to growing adoption of the 5G technology in communication and data transmission services
- Medical and military and aerospace application segments are poised to witness significant growth, attributed to increasing adoption of optic technology devices
- Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth owing to technological advancements and large-scale adoption of the technology in IT and telecommunication and administrative sector
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
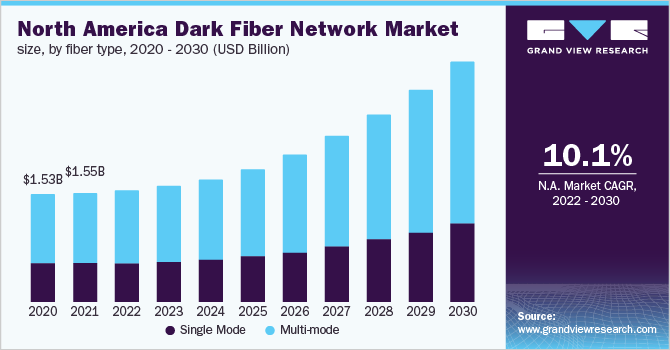
Fiber Type Insights
In 2019, the multimode segment led the market in terms of revenue and held around 60% of the total market share. It is also expected to continue leading the market over the forecast period. This type is best suited for short transmission distances. It is mainly used in video surveillance and Local-area Network (LAN) systems. Single-mode fiber, on the other hand, is best suited for longer transmission distances. It is mainly used in multi-channel television broadcast systems and long-distance telephony. Single mode segment is anticipated to witness considerable growth over the projected period. This product type is used for long distance installations ranging from 2 meters to 10,000 meters. It offers lower power loss in comparison to multimode. However, it is costlier than multimode fibers.
Network Type Insights
Long-haul fiver systems remained the mainstay of the market in 2019, capturing 69.7% revenue share. The segment continues to gather pace due to their capacity to connect over large distances at low signal intensity. Such long-haul terrestrial networks are widely applied in undersea cabling across long oceanic distance, thus attracting the participation of several organizations in terms of investments. For instance, in May 2018, Vodafone Group deployed 200G long-haul network-largest in the world-across 88 cities in India, covering over 43,000 km of network.
Long-haul network is driven by continuously growing investments, development of smart cities, and strong competitive dynamics in the market. However, the broadening availability of metro network fibers at relatively cost-effective price is gradually swinging the momentum towards the segment over the next few years.
Application Insights
In terms of revenue, telecommunication segment dominated the market with a share of 43.3% in 2019 and is anticipated to retain its dominance in terms of market size by 2027. Telecommunication is anticipated to present promising growth prospects due to growing adoption of the 5G technology in communication and data transmission services. Dark fiber enables high-speed data transfer services in both small and long-range communications. Furthermore, increasing cloud-based applications, audio-video services, and Video-on-Demand (VoD) services stimulate the demand.
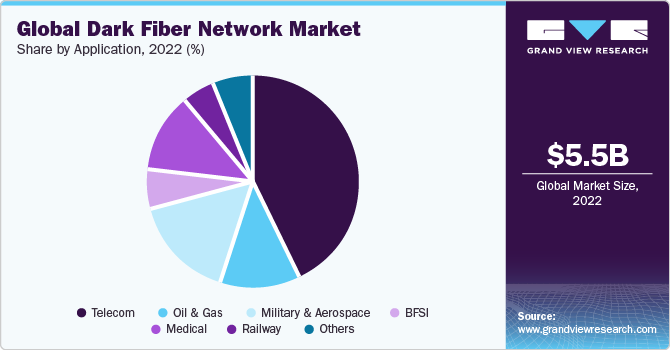
Medical and military and aerospace application segments are poised to witness significant growth, attributed to increasing adoption of optic technology devices. Stringent regulations and standards imposed by the regulatory authorities and medical associations are further fueling the market to flourish in the medical sector, eventually driving the overall growth.
Regional Insights
In 2019, North America led held largest market share in terms of revenue with around 30%. Asia Pacific is spearheading revenue growth owing to technological advancements and large-scale adoption of the technology in IT and telecommunication and administrative sector. High penetration of the technology in manufacturing sector and expanding IT and telecom sector across Asia Pacific are strengthening the regional market hold. Moreover, increasing application of fiber networks in medical sector is catapulting growth across countries, such as China, Japan, and India, thus propelling the overall demand at a significant pace.
Governments of developed countries such as U.S., U.K., Germany, China, and Japan are heavily investing in security infrastructure at country levels. Awareness is growing among the rapidly developing economies that aim to strengthen their hold at the global level. This is eventually necessitating the funding for technologies, majorly across the fiber networks that would enhance the telecommunication sector infrastructure with better security measures.
Dark Fiber Networks Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size value in 2020 | USD 5.09 billion |
| Revenue forecast in 2027 | USD 11.22 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 12.0% from 2020 to 2027 |
| Base year for estimation | 2019 |
| Historical data | 2016 – 2018 |
| Forecast period | 2020 – 2027 |
| Quantitative units | Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2020 to 2027 |
| Report coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments covered | Fiber type, network type, application, region |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; South America; Middle East & Africa |
| Country scope | U.S.; Canada; Mexico; U.K.; Germany; France; Japan; China; India; Australia; Brazil |
| Key companies profiled | AT&T Intellectual Property; Colt Technology Services Group Limited; Comcast; Consolidated Communications; GTT Communications, Inc.; Level 3 Communications, Inc. (CenturyLink, Inc.); NTT Communications Corporation; Verizon Communications, Inc.; Windstream Communications; Zayo Group, LLC |
| Customization scope | Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope |
| Pricing and purchase options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Grand View Research has segmented the global dark fiber network market based on fiber type, network type, application, and region:
- Dark Fiber Network Fiber Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2016 – 2027)
- Single Mode
- Multi-mode
- Dark Fiber Network Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2016 – 2027)
- Metro
- Long-haul
- Dark Fiber Network Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2016 – 2027)
- Telecom
- Oil & Gas
- Military & Aerospace
- BFSI
- Medical
- Railway
- Others
- Dark Fiber Network Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2016 – 2027)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- Germany
- U.K.
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South America
- Brazil
- Middle East & Africa
- North America
- List of Key Players in the Dark Fiber Network Market
- AT&T Intellectual Property
- Colt Technology Services Group Limited
- Comcast, Consolidated Communications
- GTT Communications, Inc.
- Level 3 Communications, Inc. (CenturyLink, Inc.)
- NTT Communications Corporation
- Verizon Communications, Inc.
- Windstream Communications
- Zayo Group, LLC
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/dark-fiber-networks-market
Gartner: 4 “Cool Vendors” for Communications Service Provider Network Operations
-
Cool Vendors for communications service provider (CSP) operational technology (OT)create new value by developing faster and more cost-effective solutions, as well as embedding open and API-driven architecture to accelerate ecosystem creation.
-
These vendors provide network- and vendor-agnostic solutions that CSPs can use to gain network-related insights, modernize their operations and automate to enhance operations efficiency.
-
Cool Vendors tend to be more aligned to CSPs’ transformation objectives as compared with many established vendors, because Cool Vendors are not guided by any legacy business.
Table 1: Cool Vendors in CSP Operational Technology
|
Vendor
|
Approach to Create New Value
|
Solve a Difficult Problem
|
Provide Cost-Efficiency
|
|
Actility
|
Provides tools, platforms and an ecosystem for monetization of IoT beyond just connectivity
|
Enables scaling up of IoT deployments up to national level networks
|
Reduces M2M application development overhead with ThingPark IoT management platform and LoRaWAN IoT support
|
|
DriveNets
|
Provides disaggregated, cloud-native software that runs the routing on white boxes using merchant silicon chipsets
|
Provides economics and flexible scale. Simplifies network operations, and reduces time to market of services.
|
Reduces TCO for router capacity scale
|
|
Federated Wireless
|
Provides novel shared-spectrum ecosystem by harnessing cloud-native software solution
|
Provides reliable connectivity without expertise and resources
|
Reduces spectrum acquisition costs
|
|
Sensat
|
Creates 3D map and digital twin of physical environment for infrastructure planning
|
Applies ML to physical network design to achieve spatial optimization and network efficiency
|
Reduces network design costs
|
|
IoT = Internet of Things; LoRaWAN = long-range wide-area network; M2M = machine-to-machine; ML = machine learning; TCO = total cost of ownership
|
|||
-
Innovation in infrastructure by disaggregation, virtualization and cloud native:
-
Actility, DriveNets and Federated Wireless
-
-
Innovation in operations by resource optimization, platform operations and network automation:
-
Sensat
-

BPI Network: 5G Commercial Deployment Status & Importance of 5G Security?
According to a new global study report, “Toward a More Secure 5G World,” developed by the Business Performance Innovation (BPI) Network, in partnership with A10 Networks. The percentage of mobile service providers who say their companies are “moving rapidly toward commercial deployment” has increased significantly in the past year, climbing from 26 percent in a survey announced in early 2019 to 45 percent in the new survey. Virtually all respondents say improved security [1.] is a critical network requirement and top concern in the 5G era.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note 1. “Improved 5G security” is really an oxymoron, because there are no standards for 5G security. In particular, no substantive work in ITU-T despite SG17 studying 5G security. There are five work items under development by Q.6 in SG17 but nothing has been completed yet.
• X.5Gsec-q, Security guidelines for applying quantum-safe algorithms in 5G systems, started from March 2018
• X.5Gsec-t, Security framework based on trust relationship in 5G ecosystem, started from September 2018
• X.5Gsec-ecs, Security Framework for 5G Edge Computing Services, started from January 2019
• X.5Gsec-guide, Security guideline for 5G communication system based on ITU-T X.805, started from January 2019
• X.5Gsec-netec, Security capabilities of network layer for 5G edge computing, established recently September 2019
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The real 5G Security spec work seems to be taking place in 3GPP. Here is text from 3GPP specification 23.501 (Release 16) on 5G Systems Architecture, related to 5G security (see reference below to download that spec):
5.10 Security aspects:
5.10.1 General
The security features in the 5G System include:
– Authentication of the UE by the network and vice versa (mutual authentication between UE and network).
– Security context generation and distribution.
– User Plane data confidentiality and integrity protection.
– Control Plane signaling confidentiality and integrity protection.
– User identity confidentiality.
– Support of LI requirements as specified in TS 33.126 [35] subject to regional/national regulatory requirements, including protection of LI data (e.g., target list) that may be stored or transferred by an NF.
Detailed security related network functions for 5G are described in TS 33.501.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Early 5G networks are being designed in accordance with the non-standalone (NSA) 5G specification from 3GPP Release 15, However, 30 percent of respondents say they are already proactively planning to add standalone 5G, and another 9 percent say their companies will move directly to standalone. Standalone 5G will require a whole new network core utilizing a cloud-native, virtualized, service-based architecture. Many respondents say they are making significant progress toward network virtualization.
The respondents claim there is steady work toward virtualizing core network functions and a reexamination of the security investments they will need to protect their networks and customers. But once again, there are no standards for that. The only real work here is being done by 3GPP in its “5G core” specification which is part of 3GPP Release 16. Here is the complete list of 5G deliverables in 3GPP Release 16. One of the most important specs is #23.501 Systems Architecture for the 5G System.
“Our latest study indicates that major mobile carriers around the world are on track with their 5G plans, and more expect to begin commercial build-outs in the coming months,” said Dave Murray, director of thought leadership with the BPI Network. “While COVID-19 may result in some short-term delays for operators, the pandemic ultimately demonstrates a global need for higher speed, higher capacity 5G networks and the applications and use case they enable.”
Among key findings of the survey:
- 81% say industry progress toward 5G is moving rapidly, mostly in major markets, or is at least in line with expectations.
- 71% expect to begin 5G network build-outs within 18 months, including one-third who have already begun or will do so in 2020.
- 95% percent say virtualizing network functions is important to their 5G plans, and some three-quarters say their companies are either well on their way or making good progress toward virtualization.
- 99% view deployment of mobile edge clouds as an important aspect of 5G networks, with 65% saying they expect edge clouds on their 5G networks within 18 months.
“Mobile operators globally need to proactively prepare for the demands of a new virtualized and secure 5G world,” said Gunter Reiss, worldwide vice president of A10 Networks, a provider of secure application services for mobile operators worldwide. “That means boosting security at key protection points like the mobile edge, deploying a cloud-native infrastructure, consolidating network functions, leveraging new CI/CD integrations and DevOps automation tools, and moving to an agile and hyperscale service-based architecture as much as possible. All of these improvements will pay dividends immediately with existing networks and move carriers closer to their ultimate goals for broader 5G adoption and the roll-out of new and innovative ultra-reliable low-latency use cases.”

You can download this report at http://bpinetwork.org/thought-leadership/studies/77/download-report-toward-a-more-secure-5g-world
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Challenges—the Security Mandate
The industry’s top 5G challenges:
- Heavy cost of build-outs (59%)
- Security of network (57%)
- Need for new technical skills (55%)
- Lack of 5G enabled devices (42%)
Importance of security to 5G:
- 99% rate security as important to their 5G planning, higher than even network reach and coverage or network capacity and throughput
- 97% say increased traffic, connected devices and mission-critical use case significantly increase security and reliability concerns for 5G
- 93% say their security investments are already being affected (52%) or are under review (41%) due to 5G requirements
Top Use Cases Expected to Power 5G Adoption
Next two years
- Ultra-high-speed connectivity (81%)
- Industrial automation & smart manufacturing (62%)
- Smart cities (54%)
- Connected vehicles
Next 5 to 6 years
- Smart cities (62%)
- Ultra-high-speed connectivity (59%)
- Connected Vehicles (57%)
- Industrial automation & smart manufacturing (42%)
“Mobile operators globally need to be proactively preparing for the demands of a new 5G world,” Reiss said.
About the BPI Network
The Business Performance Innovation (BPI) Network is a peer-driven thought leadership and professional networking organization reaching some 50,000 heads IT transformation, change management, business re-engineering, process improvement, and strategic planning. The BPI Network brings together global executives who are champions of change through ongoing research, authoritative content and peer-to-peer conversations. For more information, visit www.bpinetwork.org.
About A10 Networks:
A10 Networks provides secure application services for on-premises, multi-cloud and edge-cloud environments at hyperscale. Our mission is to enable service providers and enterprises to deliver business-critical applications that are secure, available and efficient for multi-cloud transformation and 5G readiness. We deliver better business outcomes that support investment protection, new business models and help future-proof infrastructures, empowering our customers to provide the most secure and available digital experience. Founded in 2004, A10 Networks is based in San Jose, Calif. and serves customers globally. For more information, visit www.a10networks.com and follow us @A10Networks.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
http://bpinetwork.org/thought-leadership/studies/77/download-report-toward-a-more-secure-5g-world
https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport/SpecList.htm?release=Rel-16&tech=4&ts=1&tr=1
https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3144
Vestaspace Technology joins SpaceX in launching Internet Satellites
Commercial space-tech company Vestaspace Technology will launch 35+ 5G satellites this September for pilot to build 5G speed network connections and IoT functionalities for industries.
Editor’s Note:
Sounds a lot like what Elon Musk’s SpaceX plans to do with its Starlink internet satellites. The satellite constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), working in combination with ground transceivers. Starlink is targeting service in the Northern U.S. and Canada in 2020, rapidly expanding to near global coverage of the populated world by 2021.

Image Credit: SpaceX
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In a statement Tuesday, Vestaspace said it will release beta version of satellite constellations pan-India in September and fully-operational version early next year into Low-Earth-Orbit or Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit.
“The company plans to replace traditional fiber networks with all the satellite constellations and to provide high-speed 5G network connections PAN India with its unmanned Software Data processing,” it said.
The company has tested a live-streamed video of 1080p (Full HD) with less than 34 milliseconds latency with the speed of more than 400 Mbps.
With regards to data privacy and security issues, Vestaspace has put 10 layer firewall that does immediate remediation if any false data is found.
Arun Kumar Sureban, Founder & CEO, Vestaspace Technology said, “To solve the complex system and to provide 5G internet network solutions to the Urban, Rural and unserved regions, we have positioned 8 Ground Stations and 31,000 data receptors all over India. This is made possible with the help of accurate positioning and telemetry related activities.”
The Pune, India-based startup has secured USD 10 million funding from an American investment and advisory firm Next Capital LLC, and has been working with ISRO, NASA and other leading space agencies on various strategic projects.
However, we don’t think these Internet satellites have anything to do with 5G which is defined as a terrestial wireless interface (at least that’s true for IMT 2020).
References:
Sweden Telecom Operators Announce 5G Network Launches and Details
Three major telecom companies in Sweden –Tele 2, Telia, and Tre Sweden– have announced their upcoming 5G network launches and areas covered. Sections of Stockholm, the nation’s capital, already have 5G service, with many more being added to the list as the year goes on, as well as other cities and towns in Sweden.
On May 24th, Tele 2 switched its network to 5G, with availability opening up to customers as of June 24 in Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. The Tele2 network will offer service at more than 1 Gbps through 80 MHz bandwidth on the C-band.
Customers with a Tele2 Unlimited subscription and a compatible handset from Samsung’s Galaxy S20 series will get free access to Tele2’s 5G network from 24 June. Other offers and cooperations with other phone manufacturers will be presented later, and Tele2 will gradually phase in 5G throughout Sweden.
Telia inaugurated its first major 5G commercial network in Stockholm today (May 25th) even though it had already been up and running for a few weeks. It has 15 base stations that are already in place, and 60 more will be built in June hand in hand with Ericsson, who will be powering the network for Telia. Initial services on the 700Mhz band will cover most of central Stockholm by mid-June, including the Norrmalm, Östermalm and Vasastan districts (more below).
Tre Sweden is jumping on the 5G board by bringing its network in the centers of Malmö, Lund, Helsingborg, Vasteras, Uppsala, and western parts of Stockholm in June. Tre said that it would activate 5G in Stockholm city centre after the summer. The earlier start in western Stockholm will include Kungsholmen, Bromma and parts of Solna. This will be an expansion of its already-launched 5G network back in December 2019, when it announced testing.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telia takes center stage to promote 5G:
Telia aims to enhance and supplement its low-band 5G commercial services with additional nationwide 5G coverage, including mid- and high-bands, following the auction of the related spectrum by the Swedish government later this year. For this launch Telia is using its existing 700MHz spectrum, boosted by LTE and New Radio (NR) carrier aggregation.

Fredrik Jejdling Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, Ericsson; Allison Kirkby, CEO, Telia Company; Anders Ygeman, Sweden’s Minister of Energy and Digital Development, at the Telia Company 5G launch in Stockholm.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Having already partnered successfully on 5G in Sweden – including enabling the country’s first live 5G network at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology and partnering with Volvo to operate Sweden’s first industrial 5G network – Telia selected Ericsson as its 5G partner for the launch network. Ericsson President and CEO, Börje Ekholm, said 5G will transform Swedish life, society and business for the better.
Earlier this month Telia’s sister company Telia Norway also launched its first commercial 5G services, with Ericsson as its sole 5G RAN supplier.
Allison Kirkby, CEO of Telia, said in a press release: “Our networks have never been more important to lives and livelihoods, than now. Telia’s 5G launch lays the foundations for the next phase of digital transformation, with innovation, sustainability, and security as three critical pillars, and we are proud to be doing this launch in partnership with Ericsson.”
Kirkby continued “As we roll-out 5G across Sweden, we will open up new user experiences and accelerated innovation in areas such as entertainment, healthcare, manufacturing, and transport, that will collectively strengthen and protect everyone living and working in Sweden, and Swedish competitiveness in the world.”
Telia’s 5G network is due to power most of Stockholm’s city center by June 21, and its private customers that are within range and have a 5G-ready smartphone and Jobbmobil contract will be able to enable the new 5G network. Moreover, its network is run 100% on renewable energy certified by the Swedish Society for Nature Conservation.
5G launches are scheduled for later in the year in other major cities in Sweden including Gothenburg and Malmö.
References:
https://interestingengineering.com/sweden-sets-up-first-5g-network-with-its-major-telecom-companies
https://www.tele2.com/about/who-we-are/tele2-5g
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/tele2-telia-and-3-sweden-announce-5g-networks-launches–1339788
https://www.teliacompany.com/en/news/news-articles/2018/swedens-first-5g-network-goes-live/
COVID-19 has changed how we look at telecom infrastructure, cloud and AI
by John Strand, Strand Consult, Denmark; edited for clarity by Alan J Weissberger
The coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis has proven that telecom infrastructure is critically important. Telecommunications networks delivered service during the lockdown, enabling many to continue to work, learn, shop, and access healthcare.
Policymakers will likely revisit regulation for telecom networks, not only to optimize network investment, but to improve security. Indeed, policymakers will also realize that security which has focused to date on the transport layer of networks is leaving the access and applications layers vulnerable.
While the focus on Huawei is long overdue, the discussion of network security and Huawei’s role are oversimplified. It is insufficient to address only one aspect of conventional components of networks: access, core, and transport.
The bigger issues are how end-user data will be protected while stored in the network/cloud and processed by artificial intelligence (AI) agents? Also, how will connected devices on Internet of Things (IoT) networks and other applications (such as smart city solutions) can be secured?
Historically network connectivity was likened to the dumb pipe, the medium which transmits data. The “smart parts” of the network were the edge and the core, where users access networks and where information processing occurs. These actions have become more complex with third party providers of AI and cloud computing. Naturally, these models don’t fit 5G because intelligence must exist throughout the network. However, telecom regulation has been associated with these three traditional functions.
Now that networks have evolved, it’s time for telecom regulation to evolve. If the goal of security measures is to reduce the risk and vulnerability of exposure to Chinese state-owned and affiliated firms, then policymakers need holistic frameworks that address the multiple aspects of network security at its various layers: application, transport, and access.
Indeed, the singular focus on Huawei in connectivity misses the fact that Huawei sells products for the other layers, and that many other Chinese state-owned firms should be scrutinized. For example, Baidu, WeChat, Alibaba, and Huawei provide AI solutions in the Applications layer; Huawei and ZTE in transport; and Huawei smartphones and laptops by Lenovo (the world’s leading maker of laptops as well as a leader in servers).
Strand Consult has described this in the research note The debate about network security is more complex than Huawei. Look at Lenovo laptops and servers and the many other devices connected to the internet.
The EU’s 5G Toolbox is the first step towards greater security and accountability for a discrete part of 5G network transport, but it does not address all elements of 5G security nor other layers. In performing its security assessment, the United Kingdom looked beyond 5G mobile Radio Access Networks (RAN) and Core to other network layers, types and technology, notably wireline networks. Policymakers need a broader focus than 5G when assessing the security of telecommunications networks in the future. Policymakers need to look at Huawei’s movement into cloud and AI solutions in the application layer as well as the many state-owned Chinese firms in the access layer like Lenovo.
In China, Huawei is vertically integrated and delivers a suite of products and services for all the layers of a network: it transports the data; it provides access through end user devices, and it provides the applications in the form of AI and cloud solutions. While European policymakers debate issues of RAN and core, Huawei is busy selling other solutions for the rest of the network: smartphones, routers, AI, and cloud solutions. As restrictions tighten on Huawei’s network products, the company will naturally push other business lines to compensate for lost revenue. A large operator in Europe works with Huawei on a joint Chinese-German cloud platform, and the reference customer for this solution is the European Organization for Nuclear Research, CERN in Switzerland. It is not logical how Huawei which can be deemed high risk for telecommunications and military networks, but somehow neutral for nuclear research. The agreement for the project is four years old; the question is whether such a project will be acceptable for political and security standards going forward.
Vertical integration was the standard model for traditional state-owned telecommunications. The government built a telephone network (the wires and switches); it delivered a single service – telephony; and it sold the end user device, typically a classic phone. Privatizing networks was about opening up the value chain to different kinds of providers. This worked well in mobile networks; different firms specialized for different parts of the value chain. However, Huawei is driving the decentralized chain back to the state-centered concept, perhaps fitting for its practice in China where it partners with the government to deliver full-service surveillance solutions.
Policymakers, regulators, and competition authorities have long been skeptical of vertical integration in telecommunications, and it was frequently a way to control traditional telecom operators by demanding that the divest certain parts of their business or by prohibiting certain acquisitions.
COVID-19 has proven that telecommunications networks are vital infrastructure at all layers and levels. It’s not just military and public safety networks that need to be secure. Everyone needs to have secure networks if we are live in a digital society. If politicians and telecom operators don’t recognize this, network users do. Change is being driven by companies which themselves are increasingly victims of cyber-attacks. Companies are putting increased pressure on telecom operators and governments to do more to make networks secure.

John Strand of Strand Consult
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Six big issues on the future of telecom regulation:
Strand Consult believes that governments will take a broader view about network security. Here are six categories of issues for policymakers to consider.
- What is critical infrastructure, and how will it be defined in the future? Historically, critical infrastructure had to do with physical and digital network assets which are required for physical and economic security, health, and safety. Indeed, there are many vital network assets deemed “critical” including those for chemicals, communications, manufacturing, dams, defense, emergency services, energy, financials, food/agriculture, government facilities, healthcare, information technology, nuclear reactors, transportations systems, and water/wastewater. Are these networks equally prioritized? What are the security concerns and protocols for each, both on the physical and cyber fronts? Do some have greater security than others? How does this change in the COVID-19 world?
- What are the government’s responsibilities to ensure the security of communications infrastructure?What are the minimum requirements to restrict a vendor? How is this balanced with requirements for fair and open processes for bids and tenders?
- What are the relevant communications networks to secure? Is it enough to focus on 5G mobile RAN and core or should security requirements apply to wireline networks, satellite, Wi-Fi, 3G/4G and so on?
- Is it sufficient only to address the transport element of network security? How will security be ensured for the storage and processing of data, for example on the computers, laptops, and servers provided by Chinese state-owned Lenovo where China’s rules for surveillance and espionage also apply? What about apps like TikTok and Huawei’s AI and cloud solutions?
- Who should perform the security assessment? Telecom operators, military departments, intelligence agencies, private security consultants, law enforcement, or some other actor?
- How will shareholders account for increased security risk in networks? Have shareholder asked relevant questions about operators’ security practices and the associated risk?
Strand Consult believes it is dangerous for telecom operators to make the decision about Huawei themselves without involving the authorities.
There are a lot of arguments for why telecommunications companies should involve the competent and relevant authorities. Telecom operators must understand that If telecommunications companies assume responsibility as those who assess each supplier in relation to national security, they will be held responsible when things go wrong.
When you take on a responsibility, you also take on risk. Thus, shareholders are exposed to increasing risk when using high risk vendors. The historical facts show that telecommunications companies have been wrong in the past when assessing cooperation with partners which have proven to be corrupt. Some partnerships have cost shareholders billions of euros. In practice, operators are limited in their ability to judge whether partners and vendors are trustworthy.
Strand Consult’s research shows that is not only government, intelligence, and security officials who are concerned about companies like Huawei. Nor is it just telecom operators which build and run networks. It is the small, medium, and large enterprises that use networks that fear that their valuable data will be surveyed, sabotaged, or stolen by actors associated with the Chinese government and military. Consequently, it is the clients of telecom operators which push to restrict Chinese made equipment from networks. This is described in this research note, The pressure to restrict Huawei from telecom networks is driven not by governments, but the many companies which have experienced hacking, IP theft, or espionage.
What the future looks like – just ask the banks:
If you want to see the future of the telecom industry, look at what happened with banking. European banks have been required to implement Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and the Counter Terrorist Financing (CFT). About 10% of European banks employees are today working with compliance. Telecom authorities, defense officials, and other policymakers and will likely see cybersecurity is vital for Europe and that telecom infrastructure is critically important. So just as the banks have been put under a heavy regulatory regime to address corruption and financial crimes, the telecom industry will be required to implement deterrence of cyberattacks.
In practical terms, the authorities in the EU and in each nation state will likely make some demands that challenge the network paradigm that telecommunications companies operate today. The rules will likely be so rigid that they will effectively eliminate Huawei and other Chinese companies from being vendors without making explicit bans. However, it won’t be governments alone driving the charge. Corporate customers of telecom networks, companies that have experienced hacking, IP theft, or espionage, will also join the effort. This is described in this research note, The biggest taboo in European telecom industry is the cost of cybersecurity – just ask the banks.
Copyright 2020. All rights reserved
………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Strand Consult:
Strand Consult, an independent company, produces strategic reports, research notes and workshops on the mobile telecom industry.
For 25 years, Strand Consult has held strategic workshops for boards of directors and other leaders in the telecom industry. We offer strategic knowledge on global regulatory trends and the experience of operators worldwide packaged it into a workshop for professionals with responsibility for policy, public affairs, regulation, communications, strategy and related roles.
Learn more about John Strand: www.understandingmobile.com
Learn more about Strand Consult: www.strandreports.com
Strand Consult
Gammel Mønt 14
Copenhagen 1117 K
Denmark
[email protected]
U.S. Government on 5G Integrated and Open Networks + ATIS on U.S. 6G Leadership
In a speech he was scheduled to deliver (but didn’t) Thursday at a Global CTO Roundtable on 5G Integrated and Open Networks (ION), U.S. Attorney General William Barr wrote (bold font added):
The United States and our partners are in an urgent race against the People’s Republic of China (PRC) to develop and build 5G infrastructure around the world. Our national security and the flourishing of our liberal democratic values here and around the world depend on our winning it.
Future 5G networks will be a critical piece of global infrastructure, the central nervous system of the global economy. Unfortunately, the PRC is well on its way to seizing a decisive 5G advantage. If the PRC wins the 5G race, the geopolitical, economic, and national security consequences will be staggering. The PRC knows this, which explains why it is using every lever of power to expand its 5G market share around the globe. The community of free and democratic nations must do the same.
To compete and win against the PRC juggernaut, the United States and its partners must work closely with trusted vendors to pursue practical and realistic strategies that can turn the tide now. Although the ‘Open RAN’ approach is not a solution to our immediate problem, the concept of Integrated and Open Networks (ION), which was the topic of yesterday’s roundtable, holds promise and should be explored. We can win the race, but we must act now.
From Mung Chiang of the U.S. Office of Science and Technology Advisor:
With a broad, inclusive tent of what “open” means, a nuanced appreciation of network deployment reality, and a more solid view on architectural choices, ION becomes one of the areas where the United States and partner countries can lead in 5G innovation. We invite technology leaders in the industry to help make that happen. Speed is the key to winning the 5G race.
While technology should not be mistaken as a solution to the fundamental problem of a distorted market, its exploration is still useful. ION and Edge Computing, for example, are two areas of innovation to realize 5G’s promise of a new level of responsiveness and scale. Such innovation leadership, along with the Clean Networks initiative and supply chain security form three prongs in a global strategy for 5G.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, the Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions (ATIS) has issued a call to action to promote U.S. 6G leadership.
“While innovation can be triggered in reaction to current market needs, technology leadership at a national level requires an early commitment and development that addresses U.S. needs as well as a common vision and set of objectives,” said Susan Miller, President and CEO of ATIS, possibly in acknowledgement of the panic the U.S. has got itself into over 5G and of recent developments in China.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Comment, analysis and assessment:
Mobile standards are global in nature, so talk of regional races seems disingenuous if not counter-productive. It is bad enough that there are six competing IMT 2020 RITs (Radio Interface Technologies) from five different countries/regions being progressed by ITU-R WP5D for IMT 2020.specs with three based on 3GPP 5G NR (Release 15 and 16): China, Korea, India (TSDSI). In addition to 3GPPs RIT/SRIT submissions (from ATIS), there are also the DECT/ETSI IMT 2020 RIT submission based on DECT NR and the Nufront (Chinese company) submission based on their own 5G radio which supposedly supports ultra low latency.
What Attorney General Barr probably means is that he’s worried U.S. 5G networks are going to be second rate compared to the Chinese equivalent from Huawei and ZTE. However, he said that Open RAN is NOT a solution to the U.S.’ current “5G problem.” Barr and Ms Chiang say that ION is a more viable approach (what the *&^%$** is ION?). In particular, “ION becomes one of the areas where the United States and partner countries can lead in 5G innovation.”
Telecoms.com author Scott Bicheno wrote: “Any non-Chinese telecoms company with a few bright ideas would be well advised to stick close to the U.S. government as the public money tap seems to be well and truly open.”
References:
https://www.state.gov/remarks-at-global-chief-technology-officers-roundtable-on-5g-ion/
India telecom revenue to slow through March 2021; 5G spectrum auction delayed yet again
Revenue and profit growth at Indian telecom operators during the financial year ending March 2021 will slow due to lower data growth and weaker economic activity amid the coronavirus pandemic, according to Fitch Ratings.
Mobile service EBITDA will increase by about 15 percent in fiscal 2021 from 25 percent in fiscal 2020, as the industry will realise the full-year benefit of industry-wide tariff hikes of around 30 percent, effective from December 2019.
India telecom operators’ Q4FY2020 EBITDA growth was driven by tariff hikes and 4G data growth, which will decelerate in FY2021, as lockdowns were only implemented from 24 March 2020, Fitch Ratings reported.
Market leader, Reliance Jio, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries Ltd, reported sequential revenue and EBITDA growth of 6% and 11%, respectively, as ARPU growth was less pronounced, at 2%, to INR 131. This was due to the significant proportion of Jio’s customers being on long-tenor plans, on which tariff hikes will be implemented only in 1QFY21. In addition, sale of incremental Jiophones led to slower growth in ARPU. Its monthly data and voice usage per user was at 11.3GB and 771 minutes, respectively. Jio continued to gain market share at the expense of India’s third-largest telco, Vodafone-Idea Limited, as it added 18 million subscribers to reach a customer base of 388 million, the industry’s highest. We expect Jio’s FY21 mobile revenue to increase by at least 20%, led by higher monthly ARPU of INR147 and subscriber additions of 30 million (FY20: 80 million).
Bharti Airtel’s Indian mobile segment’s EBITDA will improve by 15-20 percent, on lower data growth, as smartphone sales are likely to drop significantly in 1HFY21 as feature-phone users are unable to upgrade to 4G smartphones during the lockdowns.
Airtel will be adding around 15 million new subscribers in fiscal 2021 as compared with the earlier prediction of 30 million, as users are unable to port their numbers during the lockdowns.
The pandemic-led economic slowdown will mostly affect lower-revenue users – those who spend INR 50-100 a month – which could prevent further improvements in monthly average revenue per user (ARPU), Fitch Ratings said.
Bharti Airtel management, headed by India CEO Gopal Vittal, is confident that the pandemic will have limited impact on FY21 EBITDA growth, which it forecasts to be at least 25 percent as compared with 25 percent in FY20, supported by ARPU growth to INR 170-175 a month.
Management says that data growth has increased by 20-25 percent in the short-term as users work from home and upgrade to higher-ARPU plans.
Airtel will generate small positive free cash flow in FY21, as Capex / revenue is likely to decline to around 26-27 percent on lower core Capex, interest costs and the government’s two-year moratorium on the payment of existing spectrum dues, which will defer about $840 million in each of FY21 and FY22.
Airtel has almost completed the shutdown of its 3G network across India and has redirected its 900MHz and 2100MHz spectrum for 4G usage. Telecom sector Capex peaked in 2019, as both Airtel and Jio front-laded Capex to expand 4G coverage and capacity and invested in fibre networks and in-building coverage.
Revenue market share is consolidating fast at Jio and Bharti, with Vodafone Idea rapidly losing market share. Vodafone Idea lost about 131 million subscribers in the last six quarters and is struggling to service its debt due to stagnant EBITDA generation, which is insufficient to cover its interest costs. The telco’s subscriber base is shrinking due to its deteriorating network on limited capex. Vodafone Idea has paid only USD 926 million in adjusted gross revenue dues, against the department’s demand of USD 6 billion, and has not yet reported its 4QFY2020 results.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5G Auction to be Delayed:
Fitch Ratings believes a 5G spectrum auction looks increasingly improbable in 2020 in light of incumbent telcos’ limited financial flexibility, a high base price of USD 7 billion for pan-India 5G spectrum in 3.3GHz-3.6GHz bandwidth and a limited business case for 5G, when 4G penetration is only around 50%. Bharti and Vodafone Idea have publicly stated that they will not participate in 5G auctions at such high prices.
A report in The Economic Times of India claims that the government will go ahead with the auction of additional 4G spectrum as planned, later this year but will defer the 5G spectrum sale until 2021.
Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea, who were both hit with multi-billion dollar AGR dues by the country’s Supreme Court last October, have both called for the auction to be delayed, as they battle to rein in expenses.
Sources familiar with the matter told journalists at The Economic Times of India that the country’s Digital Communications Commission had met on Monday to discuss postponing the 5G auction.
“Discussions are on to hold the 5G auctions later as some of the telcos need to buy spectrum but 5G may not be the priority now,” a source told the ET.

Light Reading reports that all the Indian telecom providers (including Reliance Jio, Airtel and Vodafone Idea) have asked the government to lower the high base price for 5G spectrum. Airtel says it will not participate in the auction at the current reserve prices. The Department of Telecommunications has attached a base price of INR4.92 billion ($64.9 million) per MHz to spectrum in the 5G band.
Besides the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, another possible reason for India postponing the sale of 5G spectrum is the deteriorating financial position of the telcos. That makes it unlikely the government would generate decent proceeds from the sale of 5G spectrum at this time. A recent court ruling about fees the telcos owe the government has further harmed their financial health, making it harder for them to participate in the auction.
Equally important is that the 5G ecosystem is far from developed. The lack of “use cases” [1.] for the new technology means telcos are unable to justify the high spectrum costs to investors. This was the main reason Vodafone Idea gave when it pushed for a reduction in fees.
Note 1.: The important 5G use cases of Ultra High Reliability and Ultra Low Latency will not be realized anytime in 2021 as it is only 27% complete at this time in 3GPP Release 16. You can’t implement something which hasn’t been specified yet!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
India to Miss “5G Bus”:
Muntazir Abbas wrote in a May 23rd ETTelecom post:
India is set to miss the ‘5G bus‘ following the lack of preparedness, unavailability of sufficient spectrum, absence of encouraging use cases, and uncertainty around radiowaves sale for the next generation of telecom services.“The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) is yet to form relevant study groups and revise the National Frequency Allocation Plan (NFAP) 2018 to include more bands including mmWave frequencies as a part of 5G roadmap,” an industry executive aware of the developments said.
In the past, Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government maintained that it “won’t afford to miss 5G bus” like in the case of 2G, 3G, and 4G technologies that were deployed in India way later than many countries.
The executive further said that the quantum of spectrum availability in the 3300 – 3600 Mhz range also remains uncertain, while the department has not sought views on 26 GHz from the regulator despite agreeing to its viability for the commercial launch of fifth-generation or 5G networks.
The India government-backed high-level 5G Forum headed by the Stanford University Professor Emeritus AJ Paulraj anticipated the first 5G commercial launch by 2020, while suggesting that most guidelines on regulatory matters be promulgated by March 2019 to facilitate early 5G deployment. That will clearly not happen!
India government authorities have yet to decide whether the 5G market is open to Chinese vendors Huawei and ZTE. Huawei has been banned from several countries, including Australia and the U.S,, over security concerns. Initially, Chinese vendors were not invited to participate in India’s 5G trials, although this was later changed. Now, India’s government is under immense pressure from the US to ban Huawei.
The current backlash against China over coronavirus, which originated in the Chinese city of Wuhan, makes the decision even harder for India’s government. That lack of clarity may have been the main factor in the postponement of the 5G auction, said Gagandeep Kaur, contributing editor to Light Reading
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/india-postpones-5g-spectrum-sale-to-2021/d/d-id/759852?
https://www.telecomlead.com/4g-lte/india-telecom-revenue-will-face-slow-growth-fitch-ratings-95298


