Year: 2020
NeoPhotonics demonstrates 90 km 400ZR transmission in 75 GHz DWDM channels enabling 25.6 Tbps per fiber
NeoPhotonics completed experimental verification of the transmission of 400Gbps data over data center interconnect (DCI) link in a 75 GHz spaced Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) channel.
NeoPhotonics achieved two milestones using its interoperable pluggable 400ZR [1.] coherent modules and its specially designed athermal arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) multiplexers (MUX) and de-multiplexers (DMUX).
Note 1. ZR stands for Extended Reach which can transmit 10G data rate and 80km distance over single mode fiber and use 1550nm lasers.
- Data rate per channel increases from today’s non-interoperable 100Gbps direct-detect transceivers to 400Gbps interoperable coherent 400ZR modules.
- The current DWDM infrastructure can be increased from 32 channels of 100 GHz-spaced DWDM signals to 64 channels of 75 GHz-spaced DWDM signals.
- The total DCI fiber capacity can thus be increased from 3.2 Tbps (100Gbps/ch. x 40 ch.) to 25.6 Tbps (400Gbps/ch. x 64 ch.), which is a total capacity increase of 800 percent.
NeoPhotonics said its technology overcomes multiple challenges in transporting 400ZR signals within 75 GHz-spaced DWDM channels.
The filters used in NeoPhotonics MUX and DMUX units are designed to limit ACI [2.] while at the same time having a stable center frequency against extreme temperatures and aging.
Note 2. ACI stands for Adjacent Channel Interface; it also can refer to Application Centric Infrastructure.

NeoPhotonics has demonstrated 90km DCI links using three in-house 400ZR pluggable transceivers with their tunable laser frequencies tuned to 75GHz spaced channels, and a pair of passive 75GHz-spaced DWDM MUX and DMUX modules designed specifically for this application. The optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) penalty due to the presence of the MUX and DMUX and the worst-case frequency drifts of the lasers, as well as the MUX and DMUX filters, is less than 1dB. The worst-case component frequency drifts were applied to emulate the operating conditions for aging and extreme temperatures, the company said in a press release.
“The combination of compact 400ZR silicon photonics-based pluggable coherent transceiver modules with specially designed 75 GHz channel spaced multiplexers and de-multiplexers can greatly increase the bandwidth capacity of optical fibers in a DCI application and consequently greatly decrease the cost per bit,” said Tim Jenks, Chairman and CEO of NeoPhotonics. “These 400ZR coherent techniques pack 400Gbps of data into a 75 GHz wide spectral channel, placing stringent requirements on the multiplexers and de-multiplexers. We are uniquely able to meet these requirements because we do both design and fabrication of planar lightwave circuits and we have 20 years of experience addressing the most challenging MUX/DMUX applications,” concluded Mr. Jenks.
About NeoPhotonics
NeoPhotonics is a leading developer and manufacturer of lasers and optoelectronic solutions that transmit, receive and switch high-speed digital optical signals for Cloud and hyper-scale data center internet content provider and telecom networks. The Company’s products enable cost-effective, high-speed over distance data transmission and efficient allocation of bandwidth in optical networks. NeoPhotonics maintains headquarters in San Jose, California and ISO 9001:2015 certified engineering and manufacturing facilities in Silicon Valley (USA), Japan and China. For additional information visit www.neophotonics.com.
References:
U.S. Commerce Dept NO-OP rule allows U.S. companies to work with Huawei on 5G & other standards
by Karen Freifeld (Reuters) with Opinion by Alan J Weissberger (does not reflect any IEEE position)
The U.S. Department of Commerce on Tuesday posted a new rule that allows U.S. companies to work with China’s Huawei to develop standards for 5G and other cutting-edge technologies, despite restrictions on doing business with the world’s top telecommunications equipment maker.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Personal Opinion:
This new rule accomplishes NOTHING and may even backfire according to some analysts. First and foremost, the U.S. government has no authority to dictate whether or not U.S. companies are permitted to attend and contribute to international standards committee meetings that are attended by non-U.S. companies deemed to be a threat. It is up to each individual standards body to grant or deny membership to a company. Once that company becomes a member of the committee then NO GOVERNMENT ENTITY can block other companies from working with it on various standards.
Today (June 16th), a joint ITU-R WP5D contribution from Nokia Corporation, Telefon AB – LM Ericsson, Qualcomm, Inc., Samsung Electronics contribution asks WP5D to delete China and Korea IMT 2020 RIT submissions as they are technically identical to 3GPP’s IMT 2020 RIT submission.
Did the Korea government prevent Samsung (#1 company in Korea by far) from co-authoring that contribution, even though it is NOT in the best interest of Korea to have their national 5G (IMT 2020 RIT) standard withdrawn/deleted? Of course not, because they don’t have the authority to do that!
Separately, the U.S. government is dogmatic in destroying Huawei to end that company’s dominance of global telecom equipment, especially 5G where the U.S. wants to encourage (now non-existent) 5G equipment companies. The only U.S. 5G technology company we know of is Qualcomm. The others just do software for so called “Open RAN” (which can’t really be open if two companies have to spec out the radio and radio interface to the digital baseband unit).
“The United States will not cede leadership in global innovation,” said Wilbur Ross, the U.S. Secretary of Commerce, in his statement about the decision. “The Department is committed to protecting U.S. national security and foreign policy interests by encouraging US industry to fully engage and advocate for U.S. technologies to become international standards.”
Light Reading also take a negative view of the U.S. announcement. Iain Morris wrote in a blog post today (Bold font added for emphasis):
If the US is to remain a part of the global standards community, as it inevitably decided it would this week, the only way it can become less dependent on Chinese knowhow is to make the Chinese firms less influential in the standards groups. That could mean imitating China’s strategy of trying to shape the international standard and essentially crowd out the other players.
How successful that strategy has been is up for debate. Huawei undoubtedly plays a more prominent role in the 5G standard than it ever did in 3G or 4G. Yet critics believe the company’s influence has been overstated in the media. Its vast array of patents, they say, includes relatively few that are genuinely “standard-essential,” despite the findings of several studies that tout Huawei’s significance.
Richard Windsor, an analyst with Radio Free Mobile, thinks US semiconductor giant Qualcomm has “a much stronger position in 5G” than one high-profile study gives it credit for. The 3GPP, for its part, remains tight-lipped on this entire subject. Revelations could be awkward.
Whatever transpires in the world of standards, no one should seriously expect a rapprochement between the US and Huawei after all that has already happened. Meng Wanzhou, the Chinese firm’s chief financial officer (and daughter of its founder), remains under house arrest in Canada, awaiting possible extradition to the US to face charges of fraud. Countries including the UK are still under US pressure to ban Huawei from their 5G networks. And trade sanctions have not been eased.
Quite the opposite, in fact. A recent tightening-up of Commerce Department rules will stop Huawei from buying any components made with US technology. Previous restrictions covered only US components made on US soil, inflicting limited damage on Huawei and disappointing its US antagonists. Unable to procure equipment from important suppliers like Taiwan’s TSMC, Huawei could be finished within a year as a result of the latest measures, according to some analysts. If that happens, any concern about US firms working alongside their Chinese counterparts in standards groups would be largely academic.
People walk past a Huawei shop, amid an outbreak of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), in Beijing, China, May 18, 2020. Photo Credit: REUTERS/Thomas Peter …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Reuters reported on Monday that the rule had been approved and sent to the Federal Register, the official U.S. publication for rules. It was posted for public inspection on the Federal Register’s website on Tuesday and is scheduled to be formally published on Thursday.
The rule amends the Huawei “entity listing,” which restricts sales of U.S. goods and technology to the company. The United States placed Huawei on the list in May 2019, citing national security concerns.
The amendment authorizes the release of certain technology to Huawei and its affiliates if it contributes “to the revision or development of a ‘standard’ in a ‘standards organization.’”
Industry and government officials have said the entity listing backfired in standards settings. With U.S. companies uncertain what technology they could share, some U.S. engineers did not engage, and Huawei gained a stronger voice, they said.
Huawei and 114 of its foreign affiliates on the Entity List “continue to participate in many important international standards organizations in which U.S. companies also participate,” the new rule says.
“As international standards serve as the building blocks for product development and help ensure functionality, interoperability and safety of the products, it is important to U.S. technological leadership that U.S. companies be able to work in these bodies in order to ensure that U.S. standards proposals are fully considered.”
Naomi Wilson of the Information Technology Industry Council, which represents tech companies, said the rule was a “long-awaited step to clarify that U.S. companies can participate in international standards bodies – even where certain listed entities are present.”
Boston lawyer Andy Updegrove, who has represented over 150 standards organizations, said he found one catch: Not all standards consortiums may meet the requirements in the rule.
To do so, he said, some may change the way they work, but other foreign ones may not. “Overall, it’s a big improvement, but it’s not going to help U.S. companies in every case,” Updegrove said.
Huawei said in a statement it wants to continue standards discussions with counterparts, including those in the United States, and that “inclusiveness and productive dialogue will better promote” their formulation and encourage development.
References:
ADDENDUM: The Dispatcher- Sept 2020:
After the U.S. Commerce Department last year put HUAWEI on a list of companies that it considered unsuitable for U.S companies and government—and the companies and governments of all its allies—to do business with, engineers in most U.S. technology companies stopped engaging with HUAWEI to develop standards. Since the standards train was going to go down the tracks with or without the U.S. on board, and Europe’s, Japan’s and the rest of the world’s companies were continuing to occupy their seats, the absence of U.S. engineers put the U.S. at a severe disadvantage, said QUALCOMM, Intel, AMAZON and many others. 10 HUAWEI had a louder voice at the table with the U.S. sitting outside.
“Confusion stemming from the May 2019 entity list had inadvertently sidelined U.S. companies from some technical standards conversations, putting them at a strategic disadvantage,” said a representative for the Information Technology Industry Council, a Washington, DC-based trade association that represents the companies making the complaint. After a year, the Commerce Department drafted a new rule which states that if HUAWEI is sitting at any standards table (not just 5G), the U.S. needs to be there. On June 15th, the rule was approved. In confirming the rule’s passing,
U.S. Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross said:
“The United States will not cede leadership in global innovation. The department is committed to protecting U.S. national security and foreign policy interests by encouraging U.S. industry to fully engage and advocate for U.S. technologies to become international standards.”
Nokia and Broadcom collaborate on new 5G ReefShark SoC’s
Nokia and Broadcom said today that they are cooperating to develop advanced system-on-chip (SoC) processors, for integration with Nokia’s 5G Powered by ReefShark portfolio. The new SoC products use Nokia wireless technology and Broadcom expertise in application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) technologies.
The added performance brought by custom silicon solutions is crucial in realizing the capabilities and benefits of 5G and delivering on its requirements. This new alliance extends the range of Nokia ReefShark chipsets available for 5G networks and improves the performance and energy footprint of 5G networks. While collaborating with Broadcom, Nokia continues to expand its silicon capabilities and improve the penetration of Reef Shark products in its AirScale radio access network (RAN) portfolio.

ReefShark is based on 3GPP (Release 15) 5G New Radio specifications, which help offset deployment costs and TCO, while fulfilling architecture-driven network requirements.
ReefShark reduces size, cost and energy consumption at each cell site, while simultaneously boosting the intelligence and performance of massive MIMO antennas.
ReefShark boosts baseband compute capacity through plug-in units fitted into the commercially available Nokia AirScale system module. AirScale is software upgradeable to full 5G functionality, and these plug-in units triple throughput from Nokia’s already market-leading 28 Gbps today, to up to 85 Gbps per module.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new chipsets are designed for deployment in several building blocks of Nokia’s AirScale radio access system. Reef Shark-based items enable operators to benefit from a smaller size and power consumption but a boost in capacity and overall performance, with a lower total cost of ownership.
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks, Nokia:
“This important collaboration highlights our continued commitment to developing our “5G Powered by ReefShark” chipset portfolio and ensures that our 5G solutions deliver a best-in-class performance to our customers.”
Frank Ostojic, SVP and GM, ASIC Products Division, Broadcom:
“Nokia and Broadcom’s collaboration accelerates silicon innovation and enables operators and end users to realize the unprecedented benefits of 5G.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Broadcom
Broadcom Inc. (NASDAQ: AVGO) is a global technology leader that designs, develops and supplies a broad range of semiconductor and infrastructure software solutions. Broadcom’s category-leading product portfolio serves critical markets including data center, networking, enterprise software, broadband, wireless, storage and industrial. Our solutions include data center networking and storage, enterprise, mainframe and cyber security software focused on automation, monitoring and security, smartphone components, telecoms and factory automation. For more information, go to www.broadcom.com
About Nokia
We create the technology to connect the world. Only Nokia offers a comprehensive portfolio of network equipment, software, services and licensing opportunities across the globe. With our commitment to innovation, driven by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs, we are a leader in the development and deployment of 5G networks.
Our communications service provider customers support more than 6.4 billion subscriptions with our radio networks, and our enterprise customers have deployed over 1,300 industrial networks worldwide. Adhering to the highest ethical standards, we transform how people live, work and communicate. For our latest updates, please visit us online www.nokia.com and follow us on Twitter @nokia.
Media Inquiries:
Nokia
Communications
Phone: +358 10 448 4900
Email: [email protected]
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/technologies/reefshark/
Mavenir and Altiostar Collaborate to Deliver OpenRAN Radios for U.S. Market; Parallel Wireless CEO Opinion
Mavenir and Altiostar are among a number of networking software start-ups focusing on delivering Open RAN solutions to wireless network operators . Both companies specialize in cloud telecoms software – so one would expect them to be competing with each other. However, they have decided to collaborate to deliver a wide portfolio of radios based on OpenRAN principles for the US market.
Both companies will be supporting the development of radios through third party OEM’s that will be based on O-RAN open interfaces and will address the frequencies of Tier-1 and Regional/Rural operators in the US.
Analysis:
The two companies will NOT design or build the radios themselves, which is not within the scope of networking software startups. In essence, they will be using O-RAN compliant radios built by (mostly Asian) OEMs/ODMs- many of which are members of the O-RAN Alliance. One has to wonder, however, why such an agreement is necessary? Why aren’t O-RAN compliant interface specifications complete and well enough accepted to ensure multi-vendor interoperability?
The joint press release answers those questions:
“Very few companies are participating in the current (OpenRAN) supply chain and mostly offering proprietary radio solutions lacking open interfaces that are not interoperable with other network elements. In addition, the requirement to procure products from trusted vendors in the US market is also causing operators to reconsider supplier options. OpenRAN radios provide new possibilities for operators to implement a secure, cost effective and best of breed solution as networks move to 5G and beyond.”
Parallel Wireless CEO Steve Papa commented to Light Reading that Open RAN (aka O-RAN) “will only be as good as the radios that are available,” he said. “If Ericsson and Nokia are struggling to be competitive with Huawei’s radios, we should not expect O-RAN to magically solve this problem by using the same semiconductors available to Ericsson and Nokia at present.”
Papa blames a lack of U.S. semiconductor innovation for Huawei’s lead in radios. He has repeatedly urged U.S. authorities to pump an extra $1 billion into radio semiconductor research. He has even suggested using the $1 billion the US recently fined Ericsson for corruption, a remark that is unlikely to win him many friends in Stockholm.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
As part of this effort, it is also planned to have these radios available to support the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act that was signed into law on March 12, 2020.
Public Law No: 116-124 (03/12/2020)
Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act of 2019
This bill establishes (1) a mechanism to prevent communications equipment or services that pose a national security risk from entering U.S. networks, and (2) a program to remove any such equipment or services currently used in U.S. networks.
Specifically, the bill prohibits the use of certain federal funds to obtain communications equipment or services from a company that poses a national security risk to U.S. communications networks. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) must publish and maintain a list of such equipment or services.
Each communications provider must submit an annual report to the FCC regarding whether it has purchased, rented, leased, or otherwise obtained any prohibited equipment and, if so, provide a detailed justification for such action.
The bill also establishes the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program to supply small communications providers (i.e., providers with 2 million or fewer customers) with funds to offset the cost of removing prohibited equipment or services from their networks and replacing it with more secure communications equipment or services.
In addition, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration must establish a program to share information regarding supply chain security risks with trusted communications providers and suppliers.
For a short video describing O-RAN’s progress, see www.o-ran.org/videos
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Altiostar has been at the forefront of the OpenRAN movement that is now being embraced by mobile operators around the world,” said Ashraf Dahod, CEO of Altiostar Networks. “Our collaboration with Mavenir on OpenRAN radios will ensure operators in the US have a truly open end-to-end infrastructure that will be cost effective and allows them to grow their business.”
“We are collaborating with Altiostar to realize the full promise of OpenRAN. Our Radios will have O-RAN compliant interfaces and will interwork with other vendors’ solutions,” said Pardeep Kohli, President and CEO of Mavenir. “I encourage other companies in the OpenRAN Policy Coalition to open their radios and ensure a broad supply of radios with open interfaces that are interoperable with third party equipment.”
Mavenir and Altiostar have committed to work together to develop a full set of FCC banded radios to be available starting June 2020, with a complete set of radios in the market by Q1 2021. The parties are also committed to making these OpenRAN radios available to be sourced by all OpenRAN vendors and system integrators, widening the OpenRAN supply chain in the US market to meet the frequency band needs of Tier-1 and Regional/Rural operators.
Mavenir and Altiostar have been pioneers of OpenRAN, including founding board members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition, as well as part of the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) and O-RAN Alliance.
Members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition include Airspan, Altiostar, AT&T, AWS, Cisco, CommScope, Dell, DISH Network, Facebook, Fujitsu, Google, IBM, Intel, Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Microsoft, NEC Corporation, NewEdge Signal Solutions, Nokia, NTT, Oracle, Parallel Wireless, Qualcomm, Rakuten Mobile, Samsung Electronics America, Telefónica, US Cellular, US Ignite, Verizon, VMWare, Vodafone, World Wide Technology, and XCOM-Labs.
Other software start-ups that are pursuing Open RAN include Parallel Wireless, Robin io., WiSig Networks, and several others. This author has talked with principals of Robin.io and WiSig who have been invited to write guest articles about their work for the IEEE Techblog.
Below is the O-RAN reference architecture model:
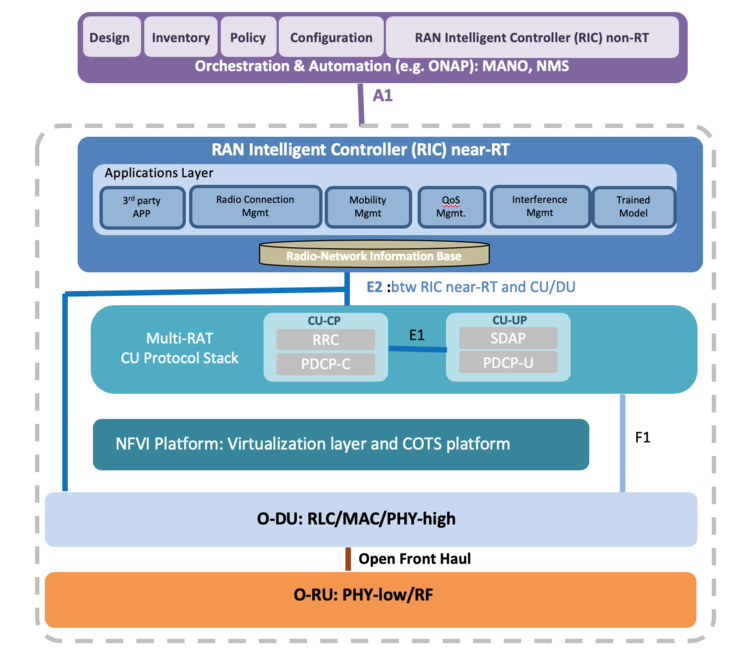
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Mavenir:
Mavenir is the industry’s only end-to-end, cloud-native Network Software and Solutions/Systems Integration Provider for 4G and 5G, focused on accelerating software network transformation for Communications Service Providers (CSPs). Mavenir offers a comprehensive end-to-end product portfolio across every layer of the network infrastructure stack. From 5G application/service layers to packet core and RAN, Mavenir leads the way in evolved, cloud-native networking solutions enabling innovative and secure experiences for end users. Leveraging innovations in IMS (VoLTE, VoWiFi, Advanced Messaging (RCS)), Private Networks as well as vEPC, 5G Core and OpenRAN vRAN, Mavenir accelerates network transformation for more than 250+ CSP customers in over 140 countries, which serve over 50% of the world’s subscribers.
Mavenir embraces disruptive, innovative technology architectures and business models that drive service agility, flexibility, and velocity. With solutions that propel NFV evolution to achieve web-scale economics, Mavenir offers solutions to help CSPs with cost reduction, revenue generation, and revenue protection. www.mavenir.com
About Altiostar:
Altiostar provides a 4G and 5G open virtualized RAN software solution that supports open interfaces and disaggregates the hardware from the software to build a multi-vendor web-scale network. This solution supports indoor and outdoor massive MIMO, as well as macro and small cells, enabling interference management, carrier aggregation and dual connectivity to improve the efficiency of the network. It also enhances the Quality of Experience for the end user, while providing broadband speeds. Operators can add intelligence, quickly adapt the software for different services and automate operations to rapidly scale the network and reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). The Altiostar open vRAN solution has been deployed globally, including the world’s first cloud native-mobile network with Rakuten in Japan. www.altiostar.com
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Ultra Oxymoron: GSMA teams up with O-RAN Alliance without liaison with 3GPP or ITU
Bell Canada Announces Largest 5G Network in Canada
Bell Canada has announced the launch of what it says is Canada’s largest 5G mobile network. Bell’s 5G services have launched in Montreal, the Greater Toronto area, Calgary, Edmonton and Vancouver and will expand to more cities in the future.
Bell Canada is selling a number of compatible 5G devices, including the Samsung Galaxy S20 5G series, the LG V60 ThinQ 5G Dual Screen and the Motorola Edge+, all from CAD 0 upfront with Bell SmartPay. 5G access is CAD 10 a month on any Bell Mobility postpaid plan and will be free as a bonus until the end of March 2021.
“Bell has built the country’s best networks since 1880 with a goal to advance how Canadians connect with each other and the world, and we’re proud to take the next step forward with the country’s largest 5G network,” said Mirko Bibic, President and CEO of BCE and Bell Canada. “As the world rapidly embraces the Fifth Generation of wireless, Bell is ready to ensure Canada remains at the forefront of 5G innovation and accessibility. The COVID-19 crisis has clearly underscored the critical importance of high-quality networks to keeping consumers, businesses and governments connected and informed, and Bell remains committed to building the best as we take wireless into the next generation.”
“With 5G coverage that is 6 times greater than the next largest network, the biggest selection of 5G-capable devices available and faster data speeds than even our award-winning Advanced LTE network, Bell Mobility has once again raised the bar in Canadian wireless,” said Claire Gillies, President of Bell Mobility. “As the scale, speed and capabilities of our next-generation network continue to grow, Bell Mobility will champion the 5G customer experience in every part of our business.”
The first company to trial mobile 5G technology in Canada, Bell is working with a range of leading global and domestic 5G partners, including Ericsson and Nokia, to accelerate Canada’s 5G innovation ecosystem. This includes continued funding of R&D at Canadian institutions, such as the partnership announced today between Western University and Bell to create a new academic centre for research into 5G applications across health, agriculture, transportation, manufacturing and other sectors. On the international stage, Bell is a leader in the setting of global 5G standards with our participation in the Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGMN) consortium and Third Generation Partnership Program (3GPP).
…………………..………………………………………………………………………………
Bell also announced a partnership with Western University, to create an advanced 5G research centre, including the deployment of a campus-wide 5G network. The Canadian carrier will invest CAD 2.7 million into the centre but also help fund research and development initiatives with the university, including training opportunities and tech innovations.
Specifically, the centre will study 5G applications, including virtual and augmented reality use, smart vehicle and city applications, autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT applications, multi-access edge computing, batter and small cell research, machine learning, artificial intelligence and other system for use in fields such as medicine, agriculture, transportation and communications.
…………………..…………………………………………………………………………..
Bell Canada is the largest communications company in Canada. With more than 22 million consumer and business connections, Bell provides advanced broadband wireless, TV, Internet and business communication services throughout the country.
Bell Media is Canada’s premier multimedia company with leading assets in television, radio, out of home and digital media.
References:
Nokia study of consumer & enterprise users: FWA and Video are top 5G services
In a study of wireless consumer users conducted with Parks Associates, Nokia found that fixed wireless access (FWA) services as the top-ranked use case by global consumers (76% of all respondents), although with the caveat that mobile network operators must prove that 5G can perform as well as fixed broadband.
We find that quite interesting, as FWA is NOT a use case for IMT 2020– the global 5G standard (yet to be completed).
The study of enterprise users found that businesses identify video as the most attractive 5G WAN and LAN applications, with 83% finding it appealing and 48% citing 5G-enhanced video monitoring as a near-term opportunity. 90 percent of consumers said that uninterrupted video calls will be a “very valuable” part of 5G connectivity. 83 percent of businesses said that video calls are a “compelling” use case for 5G.
Two-thirds of the enterprises surveyed in the study (65%) said they are familiar with 5G, and one-third (34%) report they are already using 5G and are highly satisfied with the service. The report also noted that while nearly half (47%) of IT decision-makers say their organizations have already started planning for 5G, others are waiting for more widespread 5G availability (54%), and nearly one-third (30%) reported they would also like to better understand the value of 5G before developing a strategy to use it in their organization.
Nokia noted that the research was carried out before the COVID-19 pandemic, but claimed the results were still valid, “perhaps more so in this new environment,” said Josh Aroner, vice president of communication service provider marketing at Nokia. “While current networks are performing well, consumers are newly appreciating the value of quality networking.”
The consumer study surveyed 3,000 people in the UK, US and South Korea, while the enterprise study surveyed over 1,000 IT decision-makers in segments including energy, manufacturing, government/ public safety and automotive/transportation.
Josh Aroner, Vice President of Communication Service Provider Marketing, commented: “Nokia commissioned this research prior to the current global coronavirus pandemic but its insights are still valid and applicable, perhaps moreso in this new environment. While current networks are performing well, consumers are newly appreciating the value of quality networking.
“Video has been a bedrock of social interaction and 5G can greatly improve this capability, while social isolation and remote work likely increase appeal for immersive experience applications. FWA is an attractive early use case for 5G, especially with remote install, but operators must make an informed decision about how to invest in it and in which geographic location.”
Additional report findings:
- Nearly half of those who work remotely indicate a strong willingness to switch providers for 5G service and more likely to intend to purchase a 5G phone. Greatly expanded remote work experience may drive plan and phone upgrades.
- Nearly two-thirds of early 5G users are highly satisfied with the speeds they experience on 5G networks, compared with less than half of 4G users.
- 45 percent of all consumers find connected car concepts appealing with navigation and safety capabilities seen as most valuable, but this jumps to 73 percent amongst vehicle owners. 53 percent of vehicle owners said they would be interested in bundling car connectivity with a 5G data plan.
- Two-thirds of consumers find 5G-enabled Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality services appealing and 56 percent were drawn to cloud gaming. Mandatory physical distancing may be the inflection point for these use cases.
- 77 percent of companies using connected equipment find 5G-enabled remote control machinery appealing. 82 percent of respondents with existing cloud robotics deployments find the idea of 5G-enabled cloud robotics “highly appealing”
Network operators will no doubt be pleased to learn that there is demand among consumers for 5G, although they should note that customers would be prepared to switch operator if their current provider is slow to launch 5G services.
Methodology:
This survey fielded 3,000 smartphone owners across the US, UK, and Korea. Demographic quotas set for age, gender, and household income ensure the sample is representative of the population of each market surveyed. Respondent Characteristics: Adults, ages 18 and older; Smartphone owners; Broadband internet users; Primary decision makers.
Resources:
- To download the research, please go here: The value of 5G services: Consumer perceptions and the opportunity for CSPs
- To download images please go to the Media Library
- Infographic: 5G opportunities for consumers
- Webpage: Extraordinary opportunities for 5G
- Webpage: Nokia FWA
- Webpage: Nokia 5G
About Nokia
We create the technology to connect the world. Only Nokia offers a comprehensive portfolio of network equipment, software, services and licensing opportunities across the globe. With our commitment to innovation, driven by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs, we are a leader in the development and deployment of 5G networks.
Our communications service provider customers support more than 6.4 billion subscriptions with our radio networks, and our enterprise customers have deployed over 1,300 industrial networks worldwide. Adhering to the highest ethical standards, we transform how people live, work and communicate. For our latest updates, please visit us online www.nokia.com and follow us on Twitter @nokia.
Media Inquiries:
Nokia
Communications
Phone: +358 10 448 4900
Email: [email protected]
References:
Nokia: Video is still the 5G ‘killer app’ for both consumers and enterprises
Dell’Oro: Broadband Access Equipment Revenue -15% YoY; Radical Change Coming
A new report by the Dell’Oro Group found that total global revenue for wireline Broadband Access equipment (=Cable, DSL, and PON equipment) dropped to $2.5 B, down 15 percent year-over-year (YoY) from 1Q 2019. The first quarter activity, which is seasonally slow to begin with, was hurt by supply chain disruptions throughout Asia-Pacific as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The first half of 2020 will give way to a sustained rebound in broadband equipment spending in the second half of the year,” said Jeff Heynen, Senior Research Director, Broadband Access and Home Networking. “The need to expand residential broadband speeds and availability will ultimately win out over the current macroeconomic slowdown,” explained Heynen.
Following are additional highlights from the 1Q 2020 Broadband Access Quarterly Report:
- Total cable access concentrator revenue decreased 22 percent YoY to $211 M, driven by a slowdown in CCAP license purchases in North America.
- Total DOCSIS 3.1 CPE shipments remained strong and increased to 5.8 M, representing 67 percent of total Cable CPE shipments. It’s forecast to reach 70 percent of shipments by the end of 2020.
- Total PON ONT (passive optical network/optical network terminal) unit shipments decreased 15 percent YoY, as new installations were limited by the pandemic.
Heynen also expects cable access revenues to rebound a bit in the second quarter as cable operators boost upstream capacity by purchasing additional channel capacity on traditional CCAPs and move ahead with mid-split and high-split projects that expand the amount of spectrum dedicated for the cable network upstream.
Cable remote PHY deployments remain slow today but could pick up as operators begin to touch amplifiers and other parts of the network for future expansions of the cable network upstream. In those cases, “you’re almost required to upgrade to remote PHY at some point,” explains Heynen.
Q1 didn’t produce a major swing in cable access market share among CommScope/Arris, Casa Systems and Cisco Systems. Harmonic, meanwhile, has already warned that some cable network virtualization projects have been pushed out a bit as cable operators reassessed their near-term network-facing priorities during the pandemic.
Regarding the fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) market, Dell’Oro found that total PON ONT (optical network terminal) unit shipments dropped 15% year-over-year as new installations were hindered by the pandemic. However, OLT (optical line terminal) ports were relatively flat over that period, indicating that there is sustained investment being placed in FTTP infrastructure in regions such as Europe, says Heynen.
Heynen expects that activity centered on the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) could provide some lift to the FTTP sector in the US next year.
The Dell’Oro Group Broadband Access and Home Networking Quarterly Report provides a complete overview of the Broadband Access market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and port/unit shipments for Cable, DSL, and PON equipment. Covered equipment includes Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP) and Distributed Access Architectures (DAA); Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexers ([DSLAMs] by technology ADSL/ADSL2+, G.SHDSL, VDSL, VDSL Profile 35b, and G.FAST); PON Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Cable, DSL, and PON CPE (Customer Premises Equipment); and SOHO WLAN Equipment, including Mesh Routers. For more information about the report, please contact [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Source: S&P Global
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum: Cable network undergoing a ‘radical transformation’
Belal Hamzeh, CTO and SVP at CableLabs, told a Light Reading virtual audience that the evolution of the network and a rethinking of HFC are necessary to prepare the cable industry to support a wave of new requirements for a broader set of high-capacity, low-latency applications. These next-gen applications will span everything from augmented and virtual reality and remote healthcare to mobile backhaul and edge computing and others that are still being thought of.
“The requirements of the network are becoming quite diverse,” he said. “For us to efficiently and effectively handle that, we have to look at entirely new perspectives … Rather than looking at the platform as a connectivity platform, we need to start looking at the platform as a connectivity and compute platform.”
Virtualization, Hamzeh added, is a “huge enabler for this transformation.” To address that critical piece, CableLabs has teamed with partners, including Altran, on an open source project nicknamed “Adrenaline” that aims to provide a centrally managed distributed and heterogeneous computing platform that supports the deployment of workloads across the operator’s infrastructure.
“It’s a cable-first initiative, but this is also a general purpose platform,” said Shamik Mishra, VP of research and innovation at Altran, a company that’s primarily focused on engineering and R&D services for multiple industries, including the telecom sector.
“We’re not trying to constrain what use cases there are [for Adrenaline],” added Randy Levensalor, principal architect with CableLabs’s future infrastructure group in the office of the CTO.
Telcos need to fill in gaps to be Edge Computing (5G, IIoT) leaders
The rapidly expanding edge computing space represents a $17 billion opportunity for telecom service providers over the next three years, but those companies are being overlooked by enterprises when it comes to deployments, according to a recent study by World Wide Technology done in conjuction with Analysys Mason.
“The Edge Disconnect” report found that service providers’ deep connectivity expertise and investments in 5G infrastructure are advantages, but that they need to fill gaps in their offerings to become a one-stop shop for enterprises looking to expand to the edge with connectivity, infrastructure, and applications.
“Service providers are under immense pressure to monetize 5G infrastructure investments and create cost-reducing efficiencies,” said Dan Graham, global product leader for edge computing at WWT. “Edge computing provides services as close to the end user or device as possible and is essential to the value proposition of 5G. Next-gen applications, including self-driving vehicles, remote surgery, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), will all hinge on the edge.”
The report found that IT companies and tech companies, rather than telecoms service providers, are invariably seen as the “edge experts.” In particular, the report authors wrote:
“Connectivity is the cornerstone of an enterprise edge strategy, yet enterprises don’t see connectivity providers as the partner they need to make their strategy a success.”
How can carriers better show off their edge muscles in front of enterprises? WWT makes a number of suggestions based on the research, which, it insisted, “reflected the market’s view and was in no way influenced by WWT’s own perspective on edge.”
By developing a “pre-packaged edge solution” composed of connectivity and system integration capabilities, as well as an application platform (which WWT thinks will generate nearly 60% of the resulting revenue) “telecoms service providers can cement their place in the new era of enterprise data management.”
“Cloud service providers and systems integrators may talk up to their ability to satisfy customers’ connectivity needs, but telecoms service providers have been delivering these services for decades,” reassured the authors. “They have an innate understanding of the intricacies involved, and how these can be optimized.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Industries covered by the research include transport, public sector, manufacturing, retail, financial services and healthcare. In each of these sectors, distributing computing through Edge implementations presents an opportunity to transform data management in line with the realities of an increasingly connected digital economy, as well as introducing new cost efficiencies and improvements to data security and compliance.
The report also identifies the 30 industry-specific Edge use cases likely to deliver the greatest revenue potential, all of which benefit from Edge’s suitability for transformative, data-intensive applications.
Key findings in the report:
- Options: Only 6% of enterprise decision-makers would choose service providers for their edge implementations. Instead, 41% would primarily opt for a technology company, while 31% would go with a public cloud provider.
- Demand: 59% of the $17 billion opportunity is at the level of user-facing application and service platforms, far more than connectivity-focused roles telecom service providers play. Telecom service providers need to expand what they offer beyond connectivity to capture more of the opportunity.
- Edge drivers: Across multiple industries, the top reasons organizers are embracing the edge are newer or enhanced customer experiences, data security and privacy, and cost efficiencies.
- Data management: Enterprises see the edge as a way of reducing data management costs by up to 20%.
The edge continues to be a promising opportunity for telecom service providers, cloud service providers, and channel partners. The report says that service providers’ deep understanding of connectivity is a key advantage. With the assistance of a partner who can bridge any gaps in their knowledge of vertical-specific use cases, they can develop pre-packaged solutions covering all three of the above requirements. Achieve this, and service providers will be on the road to changing enterprise perceptions, increasingly cementing themselves as the de facto partners for enterprise Edge deployments.
Grand View Research analysts predict that the global market for edge computing will grow 37.4% a year through 2027, when it will grow to $43.4 billion. A key catalyst for that growth will be 5G technology, which promises significantly faster speeds and more bandwidth and capacity than current 4G LTE networks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://channelnomics.com/2020/06/09/ingram-micro-cloud-simplifies-complex-aws-world/
https://www.lightreading.com/the-edge/telcos-need-to-up-their-edge-game—report/d/d-id/761562?
Broadband Forum and LAN Laboratory Expand Certification Program to include XGS-PON
As demand for fiber networks continues to grow, the Broadband Forum has expanded its BBF.247 Optical Network Unit (ONU) Certification Program to include XGS-PON.
This latest update extends the program to a variety of key features needed by operators deploying XGS-PON networks. The certification is just one piece of Broadband Forum’s vision to provide network operators with the tools, open specifications, and open source references necessary to bring new services and technologies to their customers more rapidly. Certified ONU products can be deployed quickly, with improved interoperability to existing Optical Line Terminal (OLT) equipment already deployed. Similarly, certified ONU products will also work directly with newer Broadband Forum specifications, including the forthcoming virtual OMCI specifications and software defined access networks.
The XGS-PON extensions add to the BBF.247 G-PON initiative – which has now certified nearly 100 products since its launch in 2011. The new test plan will see ONUs undergo rigorous testing at Broadband Forum’s official certification program test laboratory Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN Laboratory), using MT2’s ONU testing solution. The work will confirm conformance to the latest PON ITU-T standards, providing network operators with assurance that they can deliver efficient networks and a high-quality customer experience. New additions to the technology are also now tested, including extended OMCI messages format, Enhanced Unicast & Multicast Operations, and Capacity Tests & Performance Monitoring. This increases the number of certification test cases by more than 50% compared to the previous version.
Eight products, including single or multi-user port ONUs/L2 and Residential Gateways from Altice Labs, CommScope, Huawei, Humax, KAONMEDIA, Sagemcom, Sercomm and ZTE have already been certified under the new BBF.247 certification program.
“The introduction of XGS-PON certification by Broadband Forum is a significant and positive step for the PON ecosystem as interoperability will encourage growth,” said Jaeseok Kim, Head of Infra Planning at SK Broadband. “This will become increasingly important as more operators look to upgrade existing network to meet consumer demand for Gigabit + speeds.”
Claudio Mathys, Product Manager Wireline Access Networks at Swisscom (Schweiz) AG, added: “Establishing interoperability and testing requirements are key elements in a liberated market. The introduction of XGS-PON from Swisscom as a technology leader – in conjunction with the certification and testing program from Broadband Forum – will significantly enhance the confidence from our competitors for CPE certification as based on industry standards and independent references. Achieving Broadband Forum certification is the entry ticket for connectivity to our network. We will definitely avoid the painful experience made with xDSL interoperability/complexity – right from the beginning.”
Hugues Le Bras, Network Engineer in Fixed Access Networks at Orange, said: “The role of interoperability and standards has only become more important as broadband grows in popularity and operators upgrade their networks to meet consumer demand. Orange already requests BBF.247 certification for each ONU deployed on the field. However, this expansion of Broadband Forum’s certification program will give us confidence when deploying next-generation technology that will enable the future era of connectivity. The latest additions to the certification also bring new features, such as flexibility and monitoring, which are essential for Orange throughout the ONU life.”
A future XGS-PON interoperability test event will take place at LAN Laboratory, in Tauxigny, France, from October 5 to 9, 2020, allowing vendors worldwide to exercise their OLT or Optical Network Terminal (ONT) solutions against each other. The event will give all equipment vendors the opportunity to improve the interoperability of their products by testing them against the other solutions presented at the event.
“Our existing G-PON certification has made a significant impact on ensuring products meet standards, and this latest expansion of the program will give operators the confidence to roll out mass XGS-PON deployments,” said Robin Mersh, CEO at Broadband Forum. “We now want to instill this same assurance in the industry for upcoming ITU PON technology, including XGS-PON and NG-PON2. XGS-PON is a major step in network evolution, supporting the expansion of 5G and through BBF.247 certification, we can ensure network interoperability.”
Thierry Doligez, Director of LAN Laboratory, said: “Both operators and vendors increasingly recognize the importance of certification in order to speed up deployment and we are proud to partner with Broadband Forum on this extension of its G-PON certification program. As operators move to upgrade their networks to meet increasing consumer demand, the new testing will make sure they are investing in trusted products which will guarantee a certain level of service. ONU manufacturers will also benefit from this substantial program update as it will give them the chance to prove their conformance against enhanced features.”
For more information or to actively get involved with Broadband Forum’s work on higher speed PON technologies, visit: www.broadband-forum.org.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
BBF.247 certification program is open to all GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON ONU products with Ethernet Interfaces and is based on the Broadband Forum’s TP-247/IR-247 test plan. It tests conformance to TR-156 and TR-280 using OMCI as defined in the ITU G.988, which are the most critical standards to interoperable implementations.
The Broadband Forum has reviewed and authorized the following independent testing agency to administer the approved BBF.247 tests and assess eligibility of products for the Broadband Forum Certification. For more information or to schedule testing, please contact the laboratory directly:
- LAN www.lanpark.eu
-
- Since 2009, the BBF has collaborated with FSAN (Full Service Access Network) on interoperability testing plugfests on the physical, TC and upper layers for GPON, with FSAN leading on the first two and BBF on the last.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Broadband Forum
Broadband Forum is the communications industry’s leading organization focused on accelerating broadband innovation, standards, and ecosystem development. Our members’ passion – delivering on the promise of broadband by enabling smarter and faster broadband networks and a thriving broadband ecosystem.
A non-profit industry organization composed of the industry’s leading broadband operators, vendors, and thought leaders, our work to date has been the foundation for broadband’s global proliferation and innovation. For example, the Forum’s flagship TR-069 CPE WAN Management Protocol has nearly 1 billion installations worldwide.
Broadband Forum working groups collaborate to define best practices for global networks, enable new revenue-generating service and content delivery, establish technology migration strategies, and engineer critical device, service & development management tools in the home and business IP networking infrastructure. We develop multi-service broadband packet networking specifications addressing architecture, device and service management, software data models, interoperability and certification in the broadband market.
Our free technical reports and white papers can be found at https://www.broadband-forum.org/
About Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN Laboratory)
The Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques (LAN) is a unique independent laboratory specialized in conformance, interoperability and coexistence tests of devices deployed by telecom operators in the access and home networks (DSL, G-PON, Broadband-PLC, …), by DSOs in Smartgrids networks using powerline communications (G3-PLC), and by the industry in video security networks (E&PoC). LAN also offers on-demand test services dedicated to PON network operators, addressing their needs in terms of pre-deployment qualification tests for each specific network they operate. LAN is one of the Broadband Forum’s Approved Test Laboratory (ATL), the unique one accredited by the Broadband Forum to conduct the worldwide recognized BBF.247 certification tests for G-PON, XG-PON and XGS-PON terminals.
For more information on Laboratoire des Applications Numeriques, please go to www.lanpark.eu, follow @Laboratoire_LAN on Twitter, or send an Email to [email protected].
About MT2
MT2 leads the industry in FTTH G-PON and XGS-PON network test, offering troubleshoot, monitoring deep analysis of products, and ‘single-click’ automated test suite solutions. MT2’s analyzers and OLT emulators have the unique powerful features to allow the user to simply ‘software-select’, and switch between GPON, XG-PON, XGS-PON or NG-PON2, all within the same single system. MT2 ensures the complicated protocols and subscriber internet access traffic complies with every spec, automatically, using a powerful and intuitive user interface, high precision and innovative design. MT2 actively contributes to the Broadband Forum activity, as a test-tool vendor, and developed its FTTH automated test suites for functionality and performance testing, covering BBF.247, TR-309 and TR-255, critical to ensure system quality and full validation of any operator’s FFTH network.
For more information on MT2, please go to www.mt2.fr, follow MT2ftth on LinkedIn, or send an Email to [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Dell’Oro: Telecom Equipment Market declined 4% YoY; Statista: $49.3B revenues in 2020
Preliminary estimates suggest 1Q20 revenue shares relative to 2019 revenue shares for the top five suppliers – the latter indicated herein parenthesis – show that Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, and Cisco comprised 28% (29%), 15% (16%), 14% (14%), 11% (10%), 6% (7%), respectively.
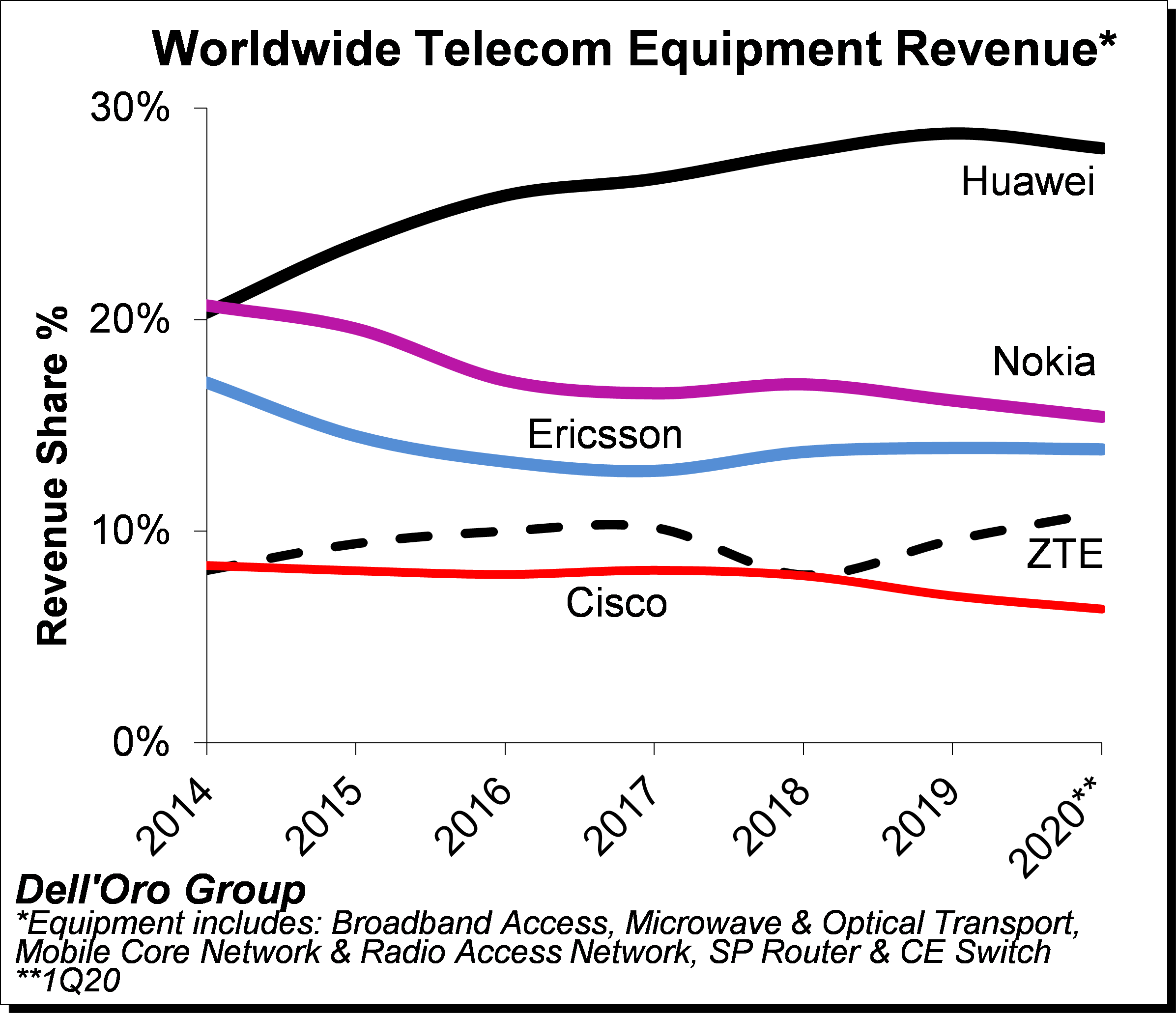
Table 1: Telecom equipment market shares
| Vendor | 2019 market share | Q1 2020 market share |
| Huawei | 29% | 28% |
| Nokia | 16% | 15% |
| Ericsson | 14% | 14% |
| ZTE | 10% | 11% |
| Cisco | 7% | 6% |
| Source: Dell’Oro Group | ||
Additional key takeaways from the 1Q2020 reporting period include:
- Following two years of consecutive growth in 2018 and 2019, the overall telecom equipment market started the year on a weaker note, reflecting mixed market conditions as the positive market sentiment with mobile-related segments, including RAN and Core, was not enough to offset reduced demand for Broadband Access, Routers and CE Switch, and Optical/Microwave Transport.
- While healthy end-user fundamentals and positive 5G momentum outweighed downward risks associated with the COVID-19 pandemic for both RAN and Core investments, the pandemic had a more material impact on some of the non-wireless related segments, driven partly by supply chain disruptions and weakened demand as a result of increased macroeconomic uncertainty.
- Within the technology segments, Mobile RAN and Core revenues together advanced at a single-digit rate, accounting for nearly half of the overall telecom equipment market during 1Q20. At the same time, the combined revenues for Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, and Routers and CE Switch declined at a double-digit pace Y/Y, accounting for about a third of the overall market.
- In contrast to previous recessions, the COVID-19 slowdown is shifting and transforming the way we use the network. But a shift in how users are consuming data doesn’t necessarily result in a corresponding increase in spending on new infrastructure to support that traffic growth. Some suppliers and service providers indicated that network capacity upgrades were required to accommodate data traffic growth, however, traffic surges did not lead to significant demand for network capacity upgrades across all the telecom equipment segments.
- Even though the pandemic is still inflicting high human and economic losses, the Dell’Oro analyst team collectively expect market conditions and supply chain risks to be more favorable in the second half of 2020, propelling the overall telecom equipment market to advance 1% in 2020, reflecting a downward revision from the previous 2% growth outlook.
Dell’Oro Group telecommunication infrastructure research programs consist of: Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Mobile Core Networks, Mobile Radio Access Network, Optical Transport, and Service Provider (SP) Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Statista reports that telecom equipment spending is projected to increase from 44.8 billion U.S. dollars in 2015 to around 49.3 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. In 2019, the estimated revenue of the entire global telecommunications industry was US $610.4 billion.
Ericsson, Cisco Systems, Fujitsu, Nokia, NEC Corporation and Qualcomm are the leading telecom equipment companies worldwide. Cisco Systems is the leading Ethernet switch vendor, with more than 50 percent of the market share. Ethernet switches are an important and profitable part of the industry, as they are an integral part of IT infrastructure. They are used to receive, process and transmit data between two devices connected by a physical layer. Together, the top 5 vendors of Ethernet switches generated more than 25 billion U.S. dollars in revenue in 2017. Cisco is also the main vendor of enterprise WLAN, accounting for 45 percent of the global market share. HPE/Aruba, Arris/Ruckus, Ubiquiti and Huawei are also important vendors of enterprise WLAN worldwide.
Ethernet switch, WLAN and telecom towers are only a few examples of telecom equipment. This industry is vast, and includes other important markets such as smartphones. More than 1.5 billion smartphones were sold worldwide in 2017. Samsung, the global mobile market leader since 2012, sold about 20 percent of this total. Apple and Huawei are Samsung’s closest competitors in the market, with around 14 percent and 10 percent of the global smartphone market share respectively.
References:


