Month: May 2022
Viettel Group and Qualcomm collaborate on 5G Radio Unit with massive MIMO
Vietnam’s Viettel Group and Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. announced plans to collaborate and develop a next-generation 5G Radio Unit (RU) with massive MIMO capabilities and distributed units (DUs). This focuses on helping to expedite the development and roll-out of 5G network infrastructure and services in Vietnam and globally.
Using the Qualcomm® X100 5G RAN Accelerator Card and Massive MIMO Qualcomm® QRU100 5G RAN Platform combined with its own advanced hardware and software systems, Viettel expects to accelerate the development and commercialization of high-performance Open RAN massive MIMO solutions, which simplify network deployment and lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
Viettel is one of four global partners trusted and selected by Qualcomm to participate in the development and application of this new 5G chipset of Qualcomm. According to Qualcomm, the partnership will help advance the cellular ecosystem and accelerate the innovation cycle.
Present in 11 countries and territories, the digital services provided by Viettel serves a customer base of more than 270 million people worldwide from Asia, Africa and the Americas. Viettel has successfully tested 5G in 15 provinces and cities across Vietnam.

“Viettel has been a pioneer in adopting new telecommunications technologies including 5G. We are delighted to have Qualcomm Technologies as a key technology provider in our 5G gNodeB project,” said Nguyen Vu Ha, general director, Viettel High Technology. “This collaboration between Qualcomm Technologies and Viettel Group will be the cornerstone of Vietnam’s national strategy for Made in Vietnam 5G infrastructure.”
“Qualcomm Technologies, as a global technology leader in 5G, is looking forward to collaborating with Viettel for the development of Open RAN solutions that will establish the foundation for Vietnam’s next-generation of wireless networks,” said Durga Malladi, senior vice president and general manager, Cellular Modems and Infrastructure, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
About Viettel:
Viettel has built a large 4G telecommunications infrastructure covering 97% of Vietnam population and has become a pioneer in 5G adoption in Vietnam. Viettel’s 5G services are available in 16 cities and provinces in Vietnam to date. Viettel develops full network elements including Devices, Radio Access Network (RAN), Transmission Network, and Core Network which are forming a strong foundation for digital society.
About Qualcomm:
Qualcomm is the world’s leading wireless technology innovator and the driving force behind the development, launch, and expansion of 5G. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a subsidiary of Qualcomm Incorporated, operates, along with its subsidiaries, substantially all of our engineering, research and development functions, and substantially all of our products and services businesses, including our QCT semiconductor business.
References:
https://viettel-com-vn.translate.goog/vi/?_x_tr_sl=vi&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=sc
CELLSMART: 5G upload speeds are insufficient for industrial/enterprise applications
Research conducted by CELLSMART, a division of French managed services provider SmartCIC, has found that 5G upload speeds are in many cases insufficient to support data transfer for enterprise applications. The Global Cellular Performance Survey was based on independent field tests conducted by 2,536 telecoms network engineers in 51 countries to capture network performance data and then analyzed by the CELLSMART team.
The CELLSMART Global Cellular Performance Survey collects data from telecoms network engineers working in the field to provide an up-to-date snap shot of actual performance across cellular technologies. It is using the data it collects in its planning, network selection and service development and monitoring for fixed wireless enterprise customers.
Top 5 Metro Markets – 5G Average Download Speed
• Cannes (France)
• Munich (Germany)
• Nashville (US)
• Oslo (Norway)
• Singapore
“The research shows how MNOs have prioritized 5G download speeds in their initial rollouts and now there’s an opportunity to focus on enterprise demand for rapid upstream data transfer. 5G networks are showing upload speeds that are 13% of their download speeds while 4G has a balanced download/upload symmetry with 36%. Based on the research sample, we saw 5G delivering higher latency than 4G in some cases. This may be due to a number of the 5G tests being run on low-band networks. Where results have been taken in areas with mmWave, there are dramatically different results including downloads in excess of 800mbps, uploads in excess of 250mbps and latencies of sub 10ms,” said Toby Forman, CEO at SmartCIC.

For capturing network performance data, speed tests were run by 2,536 telecoms network engineers across 51 countries in 331 unique locations globally. Each engineer conducted the tests independently in the field and submitted result anonymously between March 25, 2022 and May 6, 2022. Data samples were collected from Africa, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Europe. The CELLSMART team did the data analysis.
Top 5 Mobile Network Operators – Maximum Download Speeds (All Technologies)
• du (UAE)
• Telia (Sweden)
• Deutsche Telekom (Germany)
• EE (UK)
• Singtel (Singapore)
However, upload speeds were on average only 31.27 Mbps – just 55% better than the 4G global average.
“We went out to our global network of 25,000 engineers and asked them to log network performance wherever they were operating. Over time, as we see more results added to our database and we’ll be able to provide an accurate and evolving snapshot of how cellular technologies are performing in the field. This initial cut of data is just the start of the process. As we begin to see greater density of results globally we will those into insights for our customers and the broader market,” said Forman. “We did this because this information simply didn’t exist on a global scale and we believe the market needs intelligent cellular solutions,” he added.
References:
Orange Poland explores 5G drone management while Verizon shuts down its drone subsidiary
Orange Poland is researching the possibilities for using 5G technology for the management of drones. These activities are being done by its R&D unit – the 5G Lab. Almost 200,000 drone users are currently registered in the country. Latvian operator LMT is also doing research on the same topic. However, Verizon has notified customers that it is closing down Skyward – its drone software company.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..

Separately, Polish telecommunications regulator UKE issued 119 decisions clearing testing of 5G technology on the 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 3.5 GHz and 26 GHz bands in 2021, reports Telko.in.
Orange Poland and P4 (Play) tested 5G the most. The tests were mainly carried out on the 3.5 GHz band in major cities, such as Warsaw and Lodz, and Play also tested 5G on the 26 GHz band in Torun.
Polkomtel, trading under the Plus brand, was the only among major Polish mobile operators which didn’t apply for 5G testing in 2021.
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/orange-poland-researches-use-of-5g-for-drone-management–1424164
https://www.totaltele.com/513296/Drone-company-Skyward-crash-lands-as-Verizon-pulls-plug
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/poland-approves-119-5g-tests-in-2021–1423392
Summary of EU report: cybersecurity of Open RAN
The EU has published a report on the cybersecurity of Open RAN, a 4G/5G (maybe even 2G?) network architecture the European Commission says will provide an alternative way of deploying the radio access part of 5G networks over the coming years, based on open interfaces. The EU noted that while Open RAN architectures create new opportunities in the marketplace, they also raise important security challenges, especially in the short term.
“It will be important for all participants to dedicate sufficient time and attention to mitigate such challenges, so that the promises of Open RAN can be realized,” the report said.
The report found that Open RAN could bring potential security opportunities, provided certain conditions are met. Namely, through greater interoperability among RAN components from different suppliers, Open RAN could allow greater diversification of suppliers within networks in the same geographic area. This could contribute to achieving the EU 5G Toolbox recommendation that each operator should have an appropriate multi-vendor strategy to avoid or limit any major dependency on a single supplier.
Open RAN could also help increase visibility of the network thanks to the use of open interfaces and standards, reduce human errors through greater automation, and increase flexibility through the use of virtualisation and cloud-based systems.
However, the Open RAN concept still lacks maturity, which means cybersecurity remains a significant challenge. Especially in the short term, by increasing the complexity of networks, Open RAN could exacerbate certain types of security risks, providing a larger attack surface and more entry points for malicious actors, giving rise to an increased risk of misconfiguration of networks and potential impacts on other network functions due to resource sharing.
The report added that technical specifications, such as those developed by the O-RAN Alliance, are not yet sufficiently secure by design. This means that Open RAN could lead to new or increased critical dependencies, for example in the area of components and cloud.
The EU recommended the use of regulatory powers to monitor large-scale Open RAN deployment plans from mobile operators and if needed, restrict, prohibit or impose specific requirements or conditions for the supply, large-scale deployment and operation of the Open RAN network equipment.
Technical controls such as authentication and authorization could be reinforced and a risk profile assessed for Open RAN providers, external service providers related to Open RAN, cloud service/infrastructure providers and system integrators. The EU added that including Open RAN components into the future 5G cybersecurity certification scheme, currently under development, should happen at the earliest possible stage.
Following up on the coordinated work already done at EU level to strengthen the security of 5G networks with the EU Toolbox on 5G Cybersecurity, Member States have analysed the security implications of Open RAN.
Margrethe Vestager, Executive Vice-President for a Europe Fit for the Digital Age, said: “Our common priority and responsibility is to ensure the timely deployment of 5G networks in Europe, while ensuring they are secure. Open RAN architectures create new opportunities in the marketplace, but this report shows they also raise important security challenges, especially in the short term. It will be important for all participants to dedicate sufficient time and attention to mitigate such challenges, so that the promises of Open RAN can be realised.”
Thierry Breton, Commissioner for the Internal Market, added: “With 5G network rollout across the EU, and our economies’ growing reliance on digital infrastructures, it is more important than ever to ensure a high level of security of our communication networks. That is what we did with the 5G cybersecurity toolbox. And that is what – together with the Member States – we do now on Open RAN with this new report. It is not up to public authorities to choose a technology. But it is our responsibility to assess the risks associated to individual technologies. This report shows that there are a number of opportunities with Open RAN but also significant security challenges that remain unaddressed and cannot be underestimated. Under no circumstances should the potential deployment in Europe’s 5G networks of Open RAN lead to new vulnerabilities.”
Guillaume Poupard, Director General of France’s National Cyber Security Agency (ANSSI), said: “After the EU Toolbox on 5G Cybersecurity, this report is another milestone in the NIS Cooperation Group’s effort to coordinate and mitigate the security risks of our 5G networks. This in-depth security analysis of Open RAN contributes to ensuring that our common approach keeps pace with new trends and related security challenges. We will continue our work to jointly address those challenges.”
Finally, a technology-neutral regulation to foster competition should be maintained., with EU and national funding for 5G and 6G research and innovation, so that EU players can compete on a level playing field.
References:
https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_22_2881
https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/cybersecurity-open-radio-access-networks
New developments from satellite internet companies challenging SpaceX and Amazon Kuiper
Satellite internet companies making news in recent days include Telesat, Globalstar, Intelsat, EchoStar, and Gogo:
- Telesat reduced the size of its planned low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation for global Internet services. The company still plans to spend a total of $5 billion on its Lightspeed effort, but now plans to operate a total of 188 satellites instead of 298.
- Globalstar signed a term sheet with a “large, global customer” to start deploying some of its spectrum for terrestrial use in the U.S. and elsewhere. “We continue to believe Apple is the most probable wholesale satellite capacity customer but await further clues, with iPhone 14 release later this year a potential catalyst,” the financial analysts at B. Riley Securities wrote in a note to investors.
- Intelsat, having recently emerged from bankruptcy, installed a number of new executives from defense contractor Raytheon, including CEO David Wajsgras. The company remains locked in a contentious legal battle with SES over proceeds from the FCC’s massive C-band auction for 5G spectrum.
- EchoStar announced that the launch of its planned Jupiter 3 satellite will be delayed until next year. A number of other satellite companies have reported similar problems amid a tightening supply of satellite launch providers. EchoStar also has a relatively new CEO in Hamid Akhavan. Further, Anders Johnson, who was leading the integration of EchoStar’s operations with 5G, is leaving the company. However, the financial analysts at Raymond James believe that Johnson’s departure doesn’t necessarily signal a step back from EchoStar’s broader plans to integrate its satellites into terrestrial networks. “We think hybrid solutions will play a major role in EchoStar’s future, including geostationary (GEO), LEO and terrestrial 5G connections, and we think S-band [spectrum] will also play a role,” they wrote. Finally, Gogo announced it’s still on track to deploy a terrestrial 5G network in the US by the end of this year. The network will beam Internet connections to airplanes.
- Gogo executives reiterated their interest in adding LEO capabilities to the company’s overall networking offerings, though they stopped short of making any firm announcements.
These developments help show that a wide range of companies – beyond big-name satellite internet companies like SpaceX and Amazon Kuiper – are heavily investing in space communications. It’s worth noting that an array of big name telecom companies have been inking agreements with satellite operators.
For example, AT&T has an agreement with LEO operator OneWeb; Verizon has a similar deal with LEO hopeful Amazon; and Vodafone is working with upstart AST SpaceMobile to connect regular, existing smartphones to satellites.
References:
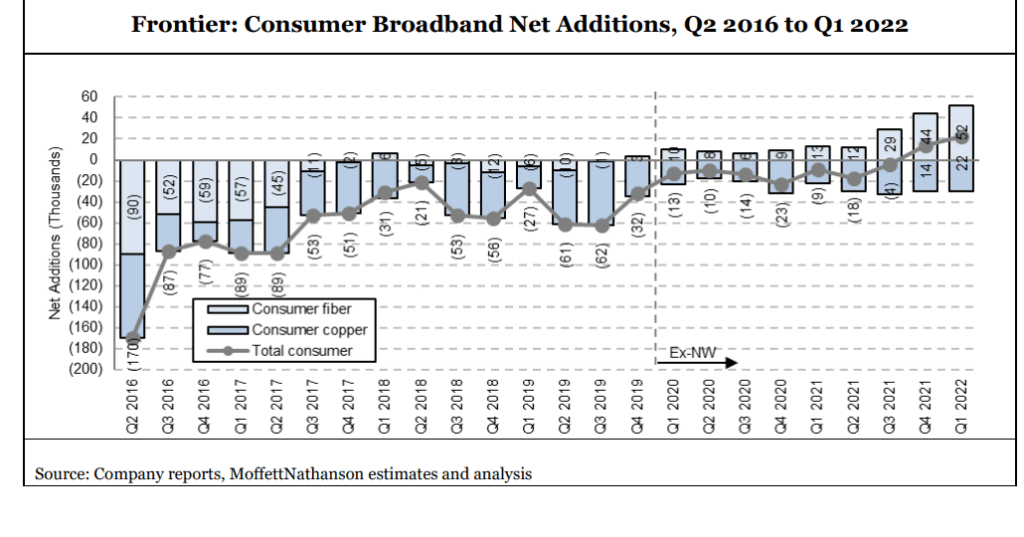
“Fiber is the future” at Frontier, which added a record 54K fiber broadband customers in 1Q-2022
Frontier Communications added a record 54,000 fiber broadband customers in the first quarter of 2022, a 20% gain over the previous record set in Q4 2021 and somewhat higher than expectations coming in to the quarter. These fiber customer adds are coming from both new and existing fiber markets. Frontier’s data continues to track nicely: 22% penetration at the 12-month mark for its 2020 cohort and 18% for its larger 2021 cohort, and 44% at the 24-month mark for its (admittedly small and probably not broadly representative) 2020 cohort. Base market penetration was up 50 basis points in the quarter and 90 basis points over the past two quarters.
Frontier’s aggressive fiber network buildout and a record low churn of 1.19%, enabled the telco to offset copper losses and add 20,000 net broadband subs for Q1 2021. That’s a record nearly two times higher than that set in the prior quarter. Frontier ended the quarter with 1.38 million residential fiber broadband subs, up 11% YoY.
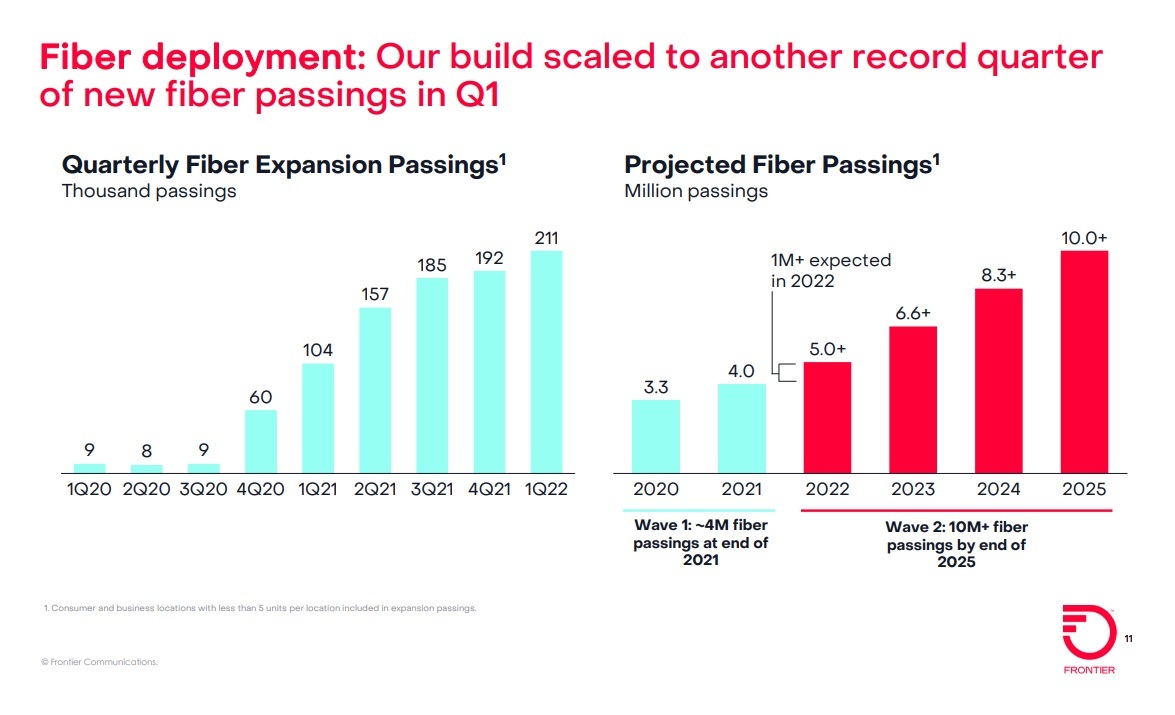
Frontier plans to expand its fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) footprint to 10 million locations by 2025 – a figure that includes the company’s “Wave 1” and “Wave 2” builds. Frontier built fiber out to another 211,000 locations in the first quarter of 2022, and says it’s on track to add more than 1 million FTTP locations for all of 2022, and another 1.6 million in 2023.
Frontier passed another 211K locations with fiber in the quarter, up from the ~190K level of the prior two quarters, a nice accomplishment in light of the disruptions associated with Omicron early in the quarter (100K of the 211K passings were achieved in March alone). Management continues to expect to add at least 1M fiber locations in 2022, and it seems on track to meet or exceed that target.
“Positive net adds is the new normal,” Nick Jeffery, Frontier’s president and CEO, declared on Friday’s earnings call. The CEO continued:
“We gained momentum in business and wholesale, reaching a key inflection point in SMB and we made progress improving our employee engagement. And last week, we unveiled our new Frontier brand. A year ago, we said we will take a long and hard look at our brand and its future and after a thorough data-driven evaluation I am delighted with the results. Our new brand is modern, more relevant, more tech-oriented, and reflects our commitment to relentlessly being better in our business and for our customers. We also gained customers in our mature fiber market, what we refer to as our base fiber footprint. In our base fiber footprint, penetration increased 50 basis points sequentially to 42.4%. And our base fiber footprint serves as a target for where we expect to drive penetration in our expansion fiber footprint and we expect to steadily grow penetration to at least 45% over time.
In our expansion fiber footprint, we are also making excellent progress. At the 12-month mark, our 2021 build cohort reached penetration of 18%, consistent with our target range of 15% to 20%. And at the 24-month mark, our 2020 build cohort reached penetration of 44%, significantly outperforming our target range of 25% to 30%. As larger builds are pulled into our 2020 cohort throughout the year, we continue to expect penetration of 25% to 30% at the 24-month mark.”
Indeed, Frontier’s operations and service levels have improved dramatically over the past two years. Our colleague Nick Del Deo at MoffettNathanson wrote in a research note to clients:
By some measures, Frontier is now operating at as high a level as key competitor Charter in the California market. And this is having an effect on its customer perceptions and market traction. Its American Consumer Satisfaction Index scores are slowly moving up, while its net promoter score has surged, especially where it has rolled out FTTH. Churn has fallen, as have customer care call volumes.
Frontier’s post-emergence management team has taken a data-driven approach to running the business and making key decisions. Put simply, the choice to refresh the company’s font and logo rather than totally rebrand is further evidence that changes to the business are working.”
To reiterate, 1Q-2022 fiber penetration rates rose to 42.45% in the company’s base fiber footprint. Frontier expects to reach penetration rates of at least 45% over time.
In the expansion areas, Frontier realized a penetration rate of 12% at the 12-month mark in its 2021 fiber build cohort – within its target range of 15%-20%. In the 2020 FTTP build cohort, Frontier is seeing a 44% penetration rate at the 24-month mark, outperforming its target range of 25%-30%.
Source: Frontier Communications Q1 2022 earnings presentation
CEO Jeffery said Frontier’s fiber-powered services are taking share from incumbent cable operators, but didn’t elaborate on how much damage Frontier is inflicting. He also acknowledged that fixed wireless access (FWA) could present an attractive option in rural areas where fiber isn’t present. Jeffery also believes fiber represents “a fundamentally different proposition” over FWA, given current data usage trends. In March, the average Frontier fiber subscriber consumed about 900 gigabytes of data, up 30% from pre-pandemic levels, with a portion consistently consuming more than 1 terabyte per month.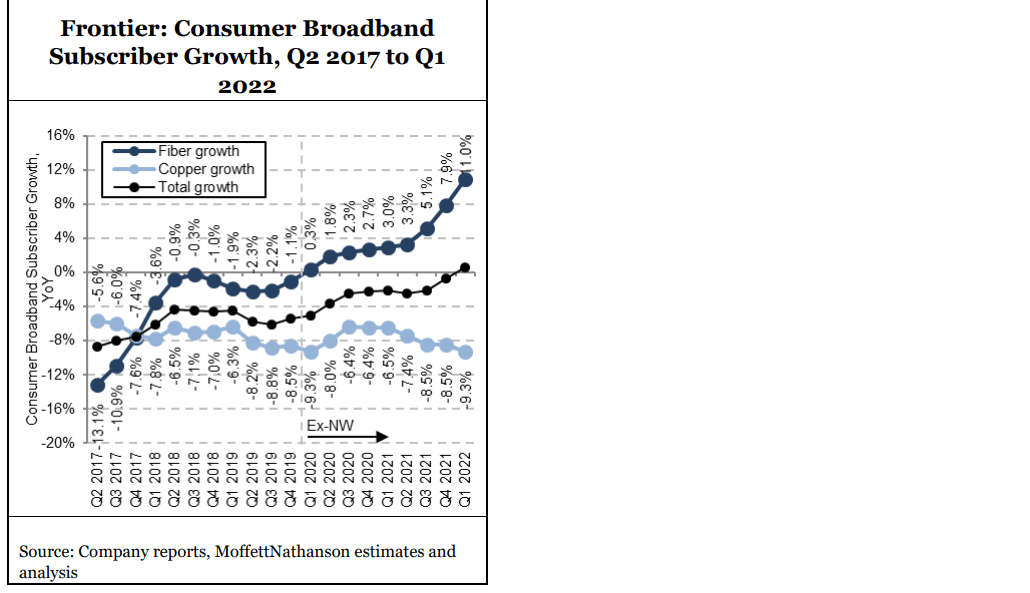
Significantly, Frontier gained new customers in areas where fiber is being built out. “This is critical because we know our future is fiber and fiber customers are the ones that will drive our growth in the years to come,” said Jeffery, a former Vodafone UK exec who took the helm of Frontier in March 2021.
For the full 2022 year, Frontier is targeting adjusted EBIDTA of $2 billion to $2.15 billion, and capital expenditures in the range of $2.4 billion to $2.5 billion, the same as guidance issued last quarter. This implies $2,003M for the remainder of the year at the midpoint. Management continues to target FTTH builds in 2022 of at least 1,000K vs. 638K built in 2021.
References:
https://s1.q4cdn.com/144417568/files/doc_financials/2022/q1/Frontier-First-Quarter-2022-Results.pdf
Viavi’s State of 5G report finds 1,947 5G cities (635 new) -mostly NSA- at end of 2021
As of end-December, the number of cities worldwide with 5G networks was 1,947 , with 635 new cities added in 2021, according to the latest Viavi Solutions report ‘The State of 5G.’
By the end of January 2022, 72 countries had 5G networks, with Argentina, Bhutan, Kenya, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Malta and Mauritius coming online in the second half of 2021.
Europe, Middle East & Africa (EMEA) passed Asia Pacific including Greater China (APAC), to become the region with the most 5G cities, at 839. APAC has 689 5G cities and the Americas has 419.
China has the most 5G cities (356), ahead of the US (296) and the Philippines (98). However, more than half of China’s so called 5G subscribers are on 4G networks. Robert Clark of Light Reading wrote: “China has tried to kick-start 5G with low prices, with the result that it has a huge population of 5G subscribers on 4G networks. Less than half of China Mobile’s 467 million 5G subs are actually using 5G – a ratio that has remained constant for the past year.”
Most 5G networks deployed are Non-Standalone (NSA) networks. There are only 24 5G Standalone (SA) networks. It is widely considered that many of the next-generation use cases and monetization models associated with 5G, beyond enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) will only be possible when Standalone 5G networks built on new 5G core networks are in place.
![]()
The State of 5G also highlights the growing Open RAN ecosystem, combining mobile operators as well as software and infrastructure vendors, seeking to develop an open, virtualized Radio Access Network (RAN) with embedded Artificial Intelligence (AI) control. As of March 2022, 64 operators have publicly announced their participation in the development of Open RAN networks. This breaks down to 23 live deployments of Open RAN networks, 34 in the trial phase with a further seven operators that have publicly announced they are in the pre-trial phase.
As of March 2022, 64 operators publicly announced their participation in the development of Open RAN networks, of which 23 were live deployments, 34 in the trial phase and another 7 operators in the pre-trial phase.
“5G continued to expand, despite the headwinds of a global pandemic,” said Sameh Yamany, CTO, VIAVI Solutions. “What comes next in 5G is the reinforcement of networks. This will take a couple of forms. Firstly, we expect to see more Standalone 5G networks, which will deliver on much of the promise of 5G, both for the operator and for the wider ecosystem of users. And secondly, we expect to see Open RAN continue its rapid development and start to become a de facto standard. VIAVI will continue to play a central role in testing those new networks as they are built and expanded.”
References:
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/literature/state-5g-may-2022-posters-en.pdf
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/consumers-still-seeking-reason-to-buy-5g/d/d-id/777250?
FCC Grants Experimental License to AST SpaceMobile for BlueWalker 3 Satellite using Spectrum from AT&T
The FCC will permit AST SpaceMobile to test transmissions from smartphones directly to its new satellite. Apparently, AST SpaceMobile’s testing in the U.S. will use spectrum licenses owned by AT&T.
AST SpaceMobile said it will conduct the testing “using 3GPP low-band cellular frequencies and Q/V-band frequencies,” though it did not provide details. However, the company’s FCC application, approved Monday, lists three spectrum licenses that are owned by AT&T.
Brian Goemmer, founder of spectrum-tracking company AllNet Insights & Analytics, said AST SpaceMobile will use AT&T’s 846.5-849MHz license in Midland, Texas; its 845-846.5MHz license in Honolulu; and its 788-798MHz license in Pine Springs, Texas. The last one is notable because it’s connected to FirstNet, a government agency working with AT&T to build a nationwide broadband network for public safety users.
Light Reading first reported of a connection between AST SpaceMobile and AT&T in 2020. However, the companies have remained relatively quiet about their work together. Officials from AST SpaceMobile and AT&T did not immediately respond to questions from Light Reading about the planned testing.

According to FierceWireless, AST SpaceMobile will also test its service in Japan with Rakuten Mobile. AST SpaceMobile has also announced deals with the likes of Vodafone, Smart Communications, Africell and UT Mobile.
AST SpaceMobile said it expects to begin testing its offering after it launches its new BlueWalker 3 sometime this summer. The company had hoped to launch the satellite sometime in March or April, but that effort was delayed.
Broadly, both Lynk and AST SpaceMobile promise to connect existing, unmodified cell phones to their low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites by conducting transmissions in the licensed spectrum bands of their mobile network operator partners. Lynk has promised to launch commercial services by next year, while AST SpaceMobile has promised a 2023 commercial launch.
The authorization comes as the company prepares for the planned summer 2022 launch of BlueWalker 3, its test satellite with an aperture of 693 square feet that is designed to communicate directly with cell phones via 3GPP standard frequencies.
“We appreciate the diligent support of the FCC in providing the experimental license for our upcoming satellite launch,” said AST SpaceMobile Founder, Chairman and CEO Abel Avellan. “Together with other testing around the world, this license will enable us to conduct some of our most important testing here, at home, in the United States.”
AST SpaceMobile continues to pursue additional authorizations with the FCC related to its planned constellation of BlueBird satellites.
AST SpaceMobile’s mission is to eliminate the connectivity gaps faced by today’s five billion mobile subscribers moving in and out of coverage zones, and bring cellular broadband to approximately half of the world’s population who remain unconnected. Partners in this effort are leading global wireless infrastructure companies, including Rakuten Mobile, Vodafone and American Tower.
The company’s announcement this week caps a few busy months for AST SpaceMobile. Cogent Communications’ CFO, Sean Wallace, recently signed on as AST SpaceMobile’s new CFO. And the company signed a new Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Globe Telecom in the Philippines.
About AST SpaceMobile:
AST SpaceMobile is building the first and only global cellular broadband network in space to operate directly with standard, unmodified mobile devices based on our extensive IP and patent portfolio. Our engineers and space scientists are on a mission to eliminate the connectivity gaps faced by today’s five billion mobile subscribers and finally bring broadband to the billions who remain unconnected. For more information, follow AST SpaceMobile on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and YouTube. Watch this video for an overview of the SpaceMobile mission.
References:
NTT’s IoT Services for Sustainability supported by new LoRaWAN low power network
Japan’s NTT has launched IoT Services for Sustainability, a new stack of products designed to help businesses advance progress against global sustainability initiatives and make data-driven decisions to reduce their carbon footprint through the intelligent use of IoT connectivity. These products include OCR Meter Reading, Water Leak Management, Predictive Maintenance and Environmental Monitoring.
- OCR Meter Reading is an on optical-based meter reader to provide near real-time data from any type of meter including water, electricity, and gas. The meter can also be used to read any type of gauge including pressure and temperature.
- The Water Leak Management technology provides real-time, IoT-enabled protection against water damage for smart spaces projects.
- The Predictive Maintenance platform collects data from sensors to create models that predict when events of interest might occur, including potential downtime, accidents or when something might need to be replaced.
- The Environmental Monitoring technology uses sensors to identify the presence of pollutants in the air and water as well as tracking temperature and humidity.
NTT’s IoT Services for Sustainability stack incorporates an IT/OT integration and support. This helps organizations to quickly see the benefits of the technology across the entire business following deployment. Benefits include energy cost savings, faster reduction in emissions, advanced operational excellence, and better work enablement across the organization. The stack of products is also supported by NTT’s new LoRaWAN network, and its catalog of sensors to measure, monitor and collect data to drive sustainability objectives.

“IoT technologies are an essential tool in the global fight against climate change,” said Jeff Merritt, Head of Urban Transformation at the World Economic Forum. “We know what actions are needed to build a more sustainable future and have a robust suite of technologies available to help deliver this impact. As the world looks to accelerate the implementation of these solutions, organizations like NTT will have a critical role to play in helping companies and governments capitalize on this opportunity,” he added.
This announcement follows the appointment of two industry veterans to drive growth and momentum across NTT’s IoT and sustainability initiatives. Wireless industry leader Devin Yaung has been appointed as SVP of Group Enterprise IoT Products and Services, NTT, bringing over 25 years of technology experience focused on business transformation. Vicky Bullivant has also been appointed as SVP, Group Sustainability, NTT, Bullivant has 25 years of creating and delivering successful sustainability, social, climate and ESG strategies that underpin commercial objectives in fast-paced and evolving business environments.
“Almost two-thirds (61.4%) of CEOs say they’re aligning business strategies to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. Yet only 2 out of 5 businesses have the solutions needed to meet the organization’s immediate objectives,” said Devin Yaung, SVP of Group Enterprise IoT Products and Services.
“Therefore, it is more critical than ever to prioritize and deliver sustainability solutions for our enterprise customers. Our new stack of solutions will help organizations reach their sustainability goals and improve operations across their business, whether it is reducing waste from manufacturing defects or understanding the carbon footprint of their supply chain. The use of IoT will empower businesses to make decisions in real-time, streamlining processes and transforming the overall sustainability of their business. We’re proud to be announcing this offering at such a critical time, and we look forward to driving change alongside our clients to create a more sustainable future.”
About NTT Ltd.
NTT Ltd. is a leading, global technology services company. To help our clients achieve their digital transformation goals, we use our global capabilities, expertise, and full-stack technology services delivered through our integrated services platform. As their long-term strategic partner, we help them enhance customer and employee experience, transform their cloud strategy, modernize their networks and strengthen their cybersecurity. And across their transformation priorities, we automate their business processes and IT, drawing insights and analytics from their core business data. As a global ICT provider, we employ more than 50,000 people across 57 countries, trading in 73 countries and delivering services in over 200 countries and regions. Together we enable the connected future.
Visit us at services.global.ntt
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/ntt-launches-iot-services-for-sustainability-projects–1422921
IEEE/SCU SoE Virtual Event: May 26, 2022- Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G), IoT, and Cloud Resident Data Centers
This virtual event on ZOOM will be from 10am-12pm PDT on May 26, 2022.
Session Abstract:
IEEE ComSoc and SCU School of Engineering (SoE) are thrilled to have three world class experts discuss the cybersecurity threats, mitigation methods and lessons learned from a data center attack. One speaker will also propose a new IT Security Architecture where control flips from the network core to the edge.
Each participant will provide a 15 to 20 minute talk which will be followed by a lively panel session with both pre-planned and ad hoc/ extemporaneous questions. Audience members are encouraged to submit their questions in the chat and also to send them in advance to [email protected].
Below are descriptions of each talk along with the speaker’s bio:
Cybersecurity for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G NSA and SA) and the IoT
Jimmy Jones, ZARIOT
Abstract:
Everyone agrees there is an urgent need for improved security in today’s cellular networks (3G/4G, 5G) and the Internet of Things (IoT). Jimmy will discuss the legacy problems of 3G/4G, migration to 5G and issues in roaming between cellular carriers as well as the impact of networks transitioning to support IoT.
Note: It’s important to know that 5G security, as specified by 3GPP (there are no ITU recommendations on 5G security), requires a 5G Stand Alone (SA) core network, very few of which have been deployed. 5G Non Stand Alone (NSA) networks are the norm, but they depend on a 4G-LTE infrastructure, including 4G security.
Cellular network security naturally leads into IoT security, since cellular networks (e.g. NB IoT, LTE-M, 5G) are often used for IoT connectivity.
It is estimated that by 2025 we will interact with an IoT device every 18 seconds, meaning our online experiences and physical lives will become indistinguishable. With this in mind it is as critical to improve IoT security as fastening a child’s seatbelt.
The real cost of a security breach or loss of service for a critical IoT device could be disastrous for a business of any size, yet it’s a cost seldom accurately calculated or forecasted by most enterprises at any stage of IoT deployment. Gartner predicts Operational Technologies might be weaponized to cause physical harm or even kill within three years.
Jimmy will stress the importance of secure connectivity, but also explain the need to protect the full DNA of IoT (Device, Network and Applications) to truly secure the entire system.
Connectivity providers are a core component of IoT and have a responsibility to become part of the solution. A secure connectivity solution is essential, with strong cellular network standards/specifications and licensed spectrum the obvious starting point.
With cellular LPWANs (Low Power Wide Area Networks) outpacing unlicensed spectrum options (e.g. LoRa WAN, Sigfox) for the first time, Jimmy will stress the importance of secure connectivity and active collaboration across the entire IoT ecosystem. The premise is that the enterprise must know and protect its IoT DNA (Device, Network & Application) to truly be secure.
Questions from the audience:
I am open to try and answer anything you are interested in. Your questions will surely push me, so if you can let me know in advance (via email to Alan) that would be great! It’s nice to be challenged a bit and have to think about something new.
One item of interest might be new specific IoT legislation that could protect devices and data in Europe, Asia, and the US ?
End Quote:
“For IoT to realize its potential it must secure and reliable making connectivity and secure by design policies the foundation of and successful project. Success in digital transformation (especially where mission and business critical devices are concerned) requires not only optimal connectivity and maximal uptime, but also a secure channel and protection against all manner of cybersecurity threats. I’m excited to be part of the team bringing these two crucial pillars of IoT to enterprise. I hope we can demonstrate that security is an opportunity for business – not a burden.”
Biography:
Jimmy Jones is a telecoms cybersecurity expert and Head of Security at ZARIOT. His experience in telecoms spans over twenty years, during which time he has built a thorough understanding of the industry working in diverse roles but all building from early engineering positions within major operators, such as WorldCom (now Verizon), and vendors including Nortel, Genband & Positive Technologies.
In 2005 Jimmy started to focus on telecom security, eventually transitioning completely in 2017 to work for a specialist cyber security vendor. He regularly presents at global telecom and IoT events, is often quoted by the tech media, and now brings all his industry experience to deliver agile and secure digital transformation with ZARIOT.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Title: Flip the Security Control of the Internet
Colin Constable, The @ Company
The PROBLEM:
With the explosion of Internet connected devices and services carrying user data, do current IT architectures remain secure as they scale? The simple and scary answer is absolutely no, we need to rethink the whole stack. Data breaches are not acceptable and those who experience them pay a steep price.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data sent over the Internet to ensure that eavesdroppers and hackers are unable to see the actual data being transmitted. However, the Router needs meta data (the IP and Port) to make it work. What meta data does the Data level Router have access to?
We need to discuss how to approach the problem and selectively discard, but learn from previous IT architectures so that we can build a more solid, secure IT infrastructure for the future.
Proposition:
I will provide a glimpse of a future security focused IT architecture.
- We need to move most security control functionality to the edge of the network.
- Cloud data center storage should be positioned as an encrypted cache with encryption keys at the edge.
- No one set of keys or system admin can open all the encrypted data.
When data is shared edge to edge we need to be able to specify and authenticate the person, entity or thing that is sharing the data. No one in the middle should be able to see data in the clear.
Issues with Encryption Keys:
- IT and Data security increasingly rely on encryption; encryption relies on keys; who has them?
- Is there really any point to VPN’s Firewalls and Network segmentation if data is encrypted?
- We use keys for so many things TLS, SSH, IM, Email, but we never tend to think about the keys.
- Do you own your keys? If not someone else can see your data!
- What do we need to flip the way IT is architected?
Recommendations for Keys:
- Keys should be cut at the edge and never go anywhere else.
- You should be able to securely share keys along with the data being transmitted/received.
- There needs to be a new way to think about identity on the Internet.
The above description should stimulate many questions from attendees during the panel discussion.
Biography:
Colin Constable’s passion is networking and security. He was one of the founding members of the Jericho Forum in the 2000s. In 2007 at Credit Suisse, he published “Network Vision 2020,” which was seen by some as somewhat crazy at the time, but most of it is very relevant now. While at Juniper, Colin worked on network virtualization and modeling that blurred the boundaries between network and compute. Colin is now the CTO of The @ Company, which has invented a new Internet protocol and built a platform that they believe will change not just networking and security, but society itself for the better.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The Anatomy of a Cloud Data Center Attack
Thomas Foerster, Nokia
Abstract:
Critical infrastructure (like a telecommunications network) is becoming more complex and reliant on networks of inter-connected devices. With the advent of 5G mobile networks, security threat vectors will expand. In particular, the exposure of new connected industries (Industry 4.0) and critical services (connected vehicular, smart cities etc.) widens the cybersecurity attack surface.
The telecommunication network is one of the targets of cyber-attacks against critical infrastructure, but it is not the only one. Transport, public sector services, energy sector and critical manufacturing industries are also vulnerable.
Cloud data centers provide the required computing resources, thus forming the backbone of a telecommunications network and becoming more important than ever. We will discuss the anatomy of a recent cybersecurity attack at a cloud data center, review what happened and the lessons learned.
Questions:
- What are possible mitigation’s against social engineering cyber- attacks?
-Multifactor authentication (MFA)
-Education, awareness and training campaigns
- How to build trust using Operational Technology (OT) in a cloud data center?
Examples:
- Access monitoring
- Audits to international standards and benchmarks
- Security monitoring
- Playbooks with mitigation and response actions
- Business continuity planning and testing
Recommendations to prevent or mitigate DC attacks:
- Privileged Access Management across DC entities
- Individual credentials for all user / device entities
- MFA: One-Time Password (OTP) via text message or phone call considered being not secure 2-Factor Authentication anymore
- Network and configuration audits considering NIST/ CIS/ GSMA NESAS
- Regular vulnerability scans and keep network entities up to date
- Tested playbooks to mitigate security emergencies
- Business continuity planning and establish tested procedures
Biography:
Thomas Foerster is a senior product manager for Cybersecurity at Nokia. He has more than 25 years experiences in the telecommunications industry, has held various management positions within engineering and loves driving innovations. Thomas has dedicated his professional work for many years in product security and cybersecurity solutions.
Thomas holds a Master of Telecommunications Engineering from Beuth University of Applied Sciences, Berlin/ Germany.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Video recording of this event: Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks, IoT, and Cloud-Resident Data Centers – YouTube
Previous IEEE ComSoc/SCU SoE March 22, 2022 event: OpenRAN and Private 5G – New Opportunities and Challenges
Video recording: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i7QUyhjxpzE