Author: Alan Weissberger
Ciena demo’s 45 wavelengths @400G; Joins Google’s Cloud’s 5G/Edge ISV Program
During OFC 2021 last week, Ciena and Lumenisity Ltd. said that they had partnered to demonstrate transmission of 45 wavelengths, each at 400G, over 1,000 km of hollowcore fiber cable.
The demonstration paired Lumenisity’s CoreSmart hollowcore cable with Ciena’s WaveLogic 5 Extreme and Nano coherent optical engines, with the transmission occurring in a recirculating loop. The companies say their work indicates that hollowcore fiber cable can be used for high-bandwidth, long-reach applications such as data center interconnect (DCI) in addition to edge and 5G xHaul applications Lumenisity had previously cited (see “Lumenisity, BT drive 400ZR DWDM transmission over hollowcore fiber“ and “BT testing hollowcore fiber for 5G support”).
Lumenisty said that it has been working over the past six months with ecosystem partners to test the CoreSmart low-latency hollowcore cable in its System Lab in Romsey, UK (see “Startup Lumenisity unveils hollowcore fiber cables for DWDM applications, new funding” for more on Lumenisity’s fiber). Ciena participated in at least some of those exercises, including a second trial in which the two companies achieved a capacity of 38.4 Tbps with 48x800G channels over greater than 20 km without in line amplification using the current generation of CoreSmart. Lumenisity says the next generation of CoreSmart will be able to extend reach in such an application to between 50-100 km with no inline amplification when paired with the WaveLogic 5 Extreme.
“The results obtained both internally and with Ciena commercial WaveLogic 5 systems show further evidence that we are bringing our world-class hollowcore fiber cable technology to market at an accelerating rate for multiple high-capacity applications, that solve real world latency issues for our customers,” commented Tony Pearson, business development director at Lumenisity.
“System characterization results of WaveLogic 5 Extreme programmable 800G and WaveLogic 5 Nano 400ZR coherent pluggables running over CoreSmart show promising results with hollowcore fiber now proven to preserve high-capacity while materially reducing latency,” added Steve Alexander, senior vice president and CTO of Ciena. “We are proud to be at the forefront of this breakthrough technological achievement where we can enable a 50% increase in reach for latency-sensitive data center interconnects.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, CTO Alexander wrote a blog titled, “Ciena has joined Google Cloud’s 5G/Edge ISV Program to help enterprises accelerate migration of their IT resources to the cloud“
Here’s an excerpt:
To facilitate the migration of enterprise IT workloads to the cloud, there is a requirement for higher speed connections from the enterprise edge to cloud provider that are scalable with enhanced security to best protect critical business data. Shared IP network connections to the cloud are acceptable for lower speed (10Gb/s) connections and below. However, when secure, higher speed connections are required to the cloud, connectivity via the IP network can become overly complex, expensive, and inefficient when compared to the optical network (Optical Fast Lane) that can provide a more efficient, cost-effective, and secure option for enterprises needing to reduce their workload migration times to support their evolving business objectives.
For the multi-cloud market to succeed, it must reduce the friction for enterprises to migrate their workloads to a cloud provider, as well as between cloud providers – on demand. This is analogous to the days when you had a mobile plan with one carrier, and to switch to another carrier, you had to switch mobile numbers, which was too complex for most customers, so they stuck with their existing carrier. Only when consumers could keep their phone number when they switched carriers (through Local Number Portability), did it make the mobile market truly competitive leading to improved choice, pricing, and innovation. This is what we’re trying to achieve in the multi-cloud market.
Google Cloud is one of the leading cloud providers in the market that embraces an architecture that enables their enterprise customers to gracefully migrate their workloads to Google Cloud via an Optical Fast Lane that enables Enterprise to develop and leverage the Google Cloud for new and innovative applications. Ciena is excited to be a key player in this program and in addressing this opportunity in the industry. This builds off Ciena’s long standing relationship with Google and other Cloud Providers serving both private and managed high-capacity optical transport networks – principally dominated by subsea, long-haul, metro and DCI connectivity.
Ciena is also a major supplier to Communication Service Providers (CSPs) and MSOs – serving all segments of the network – including high-speed access connectivity for Enterprises as well as cell-site routing and backhaul. In partnership with CSPs, Google Cloud is helping customers leverage their edge real-estate assets to facilitate low latency connectivity to Google Cloud and reduce the friction required for enterprises to improve their mean time to the cloud for their data and workloads.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Highlights of Ericsson’s Mobility report: 4G still on top, but 5G (mostly NSA) growing rapidly
According to Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report, the 5G market is growing by around 1 million subscriptions per day. China, North America and the Gulf Cooperation Council markets are leading the way on subscriber numbers, while Europe is off to a slow start.
The world added around 70 million 5G subscribers in the first quarter of 2021, putting it on track to reach 580 million by the end of this year, Ericsson announced. The high growth rate confirms that 5G will be the fastest adopted mobile generation in history.
However, 5G deployed to date is almost 100% 5G NSA (Non Stand Alone), requiring an LTE anchor. That makes it like “4G on steroids,” according to Stephane Teral of Light Counting. Stephane says there are only eight 5G SA networks (T-Mobile US has one) deployed to date. Only those 5G SA networks can realize the true features/functions of 5G because they have a 5G Core network with associated functions (However, they’re implemented differently by each 5G SA service provider, although Rakuten Mobile wants to change that with its RCS platform).

5G is expected to surpass a billion subscriptions two years ahead of the 4G LTE timeline for the same milestone. This is due mainly to China’s early commitment to 5G and quicker availability of affordable 5G devices.

Average data usage to reach 35 GB/month in 2026:
In the medium term, Ericsson forecasts 5G to grow to 3.5 billion subscriptions in 2026, when coverage should reach around 60 percent of the world’s population. The expansion of 5G will drive strong growth in mobile data traffic as well, which is expected to grow nearly five-fold, from 49 EB per month at the end of 2020 to 237 EB per month in 2026. Average smartphone usage is expected to rise over the same period from 10 GB per user per month to 35 GB.
The data forecast excludes fixed-wireless access, although this element is proving core to 5G offerings. According to the report, almost nine in ten operators that have launched 5G also have a fixed wireless access offering (4G and/or 5G), even in markets with high fiber penetration. FWA traffic is forecast to grow by a factor of seven to reach 64 EB in 2026.
5G Communications Service Providers at the forefront of Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) adoption:
The COVID-19 pandemic is accelerating digitalization and increasing the importance of – and the need for – reliable, high-speed mobile broadband connectivity. According to the latest report, almost nine out of ten communications service providers (CSPs) that have launched 5G also have a fixed wireless access (FWA) offering (4G and/or 5G), even in markets with high fiber penetration. This is needed to accommodate increasing FWA traffic, which the report forecasts to grow by a factor of seven to reach 64 EB in 2026.

Massive IoT on the rise:
Massive IoT technology (NB-IoT and Cat-M) connections are forecast to increase by almost 80 percent during 2021, reaching almost 330 million connections. In 2026, these technologies are forecast to comprise 46 percent of all cellular IoT connections.
Excerpts from the report:
Despite the uncertainty caused by COVID-19, service providers continue to switch on 5G and more than 160 have launched commercial 5G services.1 5G subscriptions with a 5G-capable device grew by 70 million during the first quarter, to reach around 290 million.
We estimate close to 580 million 5G subscriptions2 by the end of 2021. Currently, North East Asia has the highest 5G subscription penetration, followed by North America, Gulf Cooperation Council countries and Western Europe. In 2026, it is projected that North America will have the highest share of 5G subscriptions of all regions at 84 percent.
5G subscription uptake is expected to be faster than that of 4G following its launch in 2009. 5G subscriptions are estimated to reach 1 billion 2 years earlier than 4G.
Key factors include China’s earlier engagement with 5G compared to 4G, as well as the timely availability of devices from several vendors. By the end of 2026, we forecast 3.5 billion 5G subscriptions globally, accounting for around 40 percent of all mobile subscriptions at that time.
4G will remain the dominant mobile access technology by subscription over the forecast period. During Q1 2021, 4G subscriptions increased by approximately 100 million, exceeding 4.6 billion, equaling 58 percent of all mobile subscriptions. It is projected to peak during the year at 4.8 billion subscriptions before declining to around 3.9 billion subscriptions by the end of 2026 as more subscribers migrate to 5G.
The net addition of mobile subscriptions was quite low during Q1 2021, at 59 million. This is likely due to the pandemic and associated lockdown restrictions. India had the most net additions (+26 million), followed by China (+6 million) and Nigeria (+3 million).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Stephane Teral’s favorite chart:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/mobility-report
Development of “IMT Vision for 2030 and beyond” from ITU-R WP 5D
Introduction:
No organization, standards or spec writing body have detailed anything real related to “6G.” All the 6G claims from telecom equipment vendors and network operators are pure propaganda/hype. There is no consensus of what 6G will be, nor is there any effort to standardize “5G Advanced.” Hence, there is no basis whatsoever to talk about standardized 5G Advanced or 6G anytime soon.
Yes, we know 3GPP is working on Release 18 which will have many new features and functions, but their Release 16 (frozen one year ago) is not complete– at least not for the URLLC 5G NR specification and performance testing. Don’t talk about “5G Advanced” or “6G” if the key use case (URLLC) for 5G is not complete. Nor is the implementation specified for “5G core” or 5G advanced functions, e.g. network slicing, as we’ve stated many, many times.
This article examines what’s real: the important ongoing work by ITU-R (the official standards body for cellular communications and frequencies) on the vision, goals and objectives for what may become 6G. Or maybe not?
ITU-R WP 5D Efforts on IMT Vision for 2030 (which will include “6G”):
ITU-R Working Party 5D (WP 5D) has started to develop a new draft Recommendation “IMT Vision for 2030 and beyond” at their March 2021 meeting. This Recommendation might be helpful to drive the industries and administrations to encourage further development of IMT for 2030 and beyond.
This Recommendation will define the framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond, including the role that IMT could play to better serve the needs of the future society, for both developed and developing countries.
For the development of this draft new Recommendation, WP 5D would like to invite the views of External Organizations on the IMT Vision for 2030 and beyond, including but not limited to, user and application trends, evolution of IMT, usage scenario, capabilities and framework and objectives.
WP 5D will also develop a new draft Report ITU-R M.[IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS] which focuses on the following aspects:
“This Report provides a broad view of future technical aspects of terrestrial IMT systems considering the time frame up to 2030 and beyond. It includes information on technical and operational characteristics of terrestrial IMT systems, including the evolution of IMT through advances in technology and spectrally-efficient techniques, and their deployment.”
For the development of these reports, WP 5D invites the views of External Organizations on future technology trends for terrestrial IMT systems, including but not limited to the motivation on driving factors such as new use cases, applications, capabilities, technology trends and enablers. These technical inputs are intended for the timeframe towards 2030 and beyond and are proposed to be significantly advanced and different from that of IMT-2020.
Related documents: ITU Recommendations, Reports, Documents and Handbook:
Recommendation ITU-R M.1645 – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT‑2000 and systems beyond IMT‑2000
Recommendation ITU-R M.2083 – IMT Vision – “Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond”
Recommendation ITU-R M.1457 – Detailed specifications of the terrestrial radio interfaces of International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000)
Recommendation ITU-R M.2012 – Detailed specifications of the terrestrial radio interfaces of International Mobile Telecommunications Advanced (IMT-Advanced)
Recommendation ITU-R M.2150 – Detailed specifications of the terrestrial radio interfaces of International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020)
Report ITU-R M.2243 – Assessment of the global mobile broadband deployments and forecasts for International Mobile Telecommunications
Report ITU-R M.2320 – Future technology trends of terrestrial IMT systems
Report ITU-R M.2370 – IMT Traffic estimates for the years 2020 to 2030
Report ITU-R M.2376 – Technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 6 GHz
Report ITU-R M.2134 – Requirements related to technical performance for IMT‑Advanced radio interface(s)
Report ITU-R M.2410 – Minimum requirements related to technical performance for IMT-2020 radio interface(s)
Report ITU-R M.2441 – Emerging usage of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT)
Report ITU-R M.[IMT.FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS TOWARDS 2030 AND BEYOND] – Future technology trends of terrestrial IMT systems towards 2030 and beyond
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Key objectives of the Vision towards IMT for 2030 and beyond:
-
Focus on continued need for increased coverage, increased capacity and extremally high user data rates;
-
Focus on continued need for lower latency and both high and low speed of movement of the mobile terminals;
-
Fully support the development of a Ubiquitous Intelligent Mobile Society;
-
Focus on tackling societal challenges identified in UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), in particular to meet the needs of Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure;
-
Consider what the future heterogenous mobile broadband networks can offer to the society and the economy through the applications and services they support;
-
Target the changing global scenario on how we work and how we stay safe during the societal challenges such COVID-19 pandemic and global climate changes;
-
Focus on delivering on digital inclusion and connecting the rural and remote communities.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The 4 key pillars for the vision:
-
Any future technology should help in the development of a Ubiquitous Intelligent Mobile Connected Society (whatever that means is TBD).
-
Any future technology should support technologies that can help bridge the digital divide.
-
Any future technology should support technologies that can Personalize / localize services.
-
Any future technology should support the connectivity / compute technologies that can address issues of real-world data ownership sensitivities.
Brief text for each of the pillars is as below:
1. Development of a Ubiquitous Intelligent Mobile Connected Society:
It is anticipated that Public / Private / Enterprise networks, specialized networks (application / vertical specific), IOT / sensor networks will increase in numbers in the coming years and could be based on multiple radio access technologies. Interoperability is one of the most significant challenges to enable a ubiquitous intelligent, connected / compute environment, where different networks, processes, applications, use cases and organizations are connected. This includes supporting very high bandwidth requirements applications such as holographic communications, digital twins etc to supporting extremely low bandwidth requirement use cases such as sensors.
2. Support technologies that can bridge the digital divide: It is a very important considerations for any future technology development.
Future networks / technologies should support affordability as a key parameter and to that end support technologies such as:
-
-
-
Highly composable networks /architectures to address issues of cost and affordability.
-
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technologies which can lower the cost of initial spectrum purchase.
-
Heterogeneous device types to bring the cost of affordability down without compromising high end usage scenarios.
-
Energy efficiency to enable affordability and sustainability.
-
-
3. Support technologies that can Personalize /localize services.
As home network capabilities, edge device / network capabilities are enhanced, there is an opportunity to personalize services like never before. It’s important that personalization (focused on individuals, homes, apartments small / medium enterprises) services is a key focus area.
4. Support technologies that can mimic real world data ownerships and hierarchies.
Personal data protection is becoming important and as nations are focused on data protection and management it is important that any future network / technology takes into account the intrinsic data hierarchies and management aspects. Data ownership granularity spans from personal data, enterprise or group data, organizational data, data considered as national assets (data that is not allowed to leave the geographic boundaries)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
External Organizations will be invited to contribute to this work item via contributions to future ITU-R WP 5D meetings in 2021 and 2022.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Source: ITU-R WP 5D
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Addendum from Leo Lehmann, Chairman ITU-T SG13:
ITU-T had run Focus Group Network-2030, which was concluded in July 2020. This Focus Group studied the capabilities of networks for the year 2030 and beyond. Those networks are expected to support novel forward-looking scenarios, such as holographic type communications, extremely fast response in critical situations and high-precision communication demands of emerging market verticals.
It has produced a remarkable “White Paper: “Network 2030 – A Blueprint of Technology, Applications and Market Drivers Towards the Year 2030 and Beyond” (May 2019).”
Even though studies are focusing only on “non-radio-related” aspects, the given use cases might be very important for the further discussion how they might be supported by corresponding spectrum requirements (whatever “G”).
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/focusgroups/net2030/Pages/default.aspx
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/focusgroups/net2030/Documents/White_Paper.pdf
2021 Optical Fiber Conference (OFC) Highlights and Links to Videos
The premier event in optical telecom—the 2021 Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibition (OFC) concluded last week. The virtual event drew over 6,500 registrants from 83 countries.
“OFC 2021 saw technology announcements and technical presentations spanning the optical communications ecosystem, including advancements in optoelectronic devices, packaging and digital signal processing that are all rapidly evolving to achieve 800G and beyond, as well as those in architectures and algorithms towards more intelligent optical networking,” said Jun-ichi Kani, OFC General Chair, NTT, Japan. “OFC is the only event where attendees can access the full spectrum of trends shaping the industry and the way we connect across the globe.”
Speakers presented breakthroughs in many areas, including 400/ZR+, 800G, co-packaged optics, embedded optics, next-gen optical access, silicon photonics, space-division multiplexing, data center networks, automation and intelligence in networks and more. Sessions on quantum science and technologies, sensor applications and free space optics appealed to a large audience and enriched the OFC experience. Recorded sessions are available to registrants as on-demand content for 60 days following the close of the event.
“OFC is the go-to event for the optics industry,” said Jimmy Yu, vice president, Dell’Oro Group. “From the thought-provoking panel discussions to the product announcements, OFC has always been the place where I learn about emerging technologies.”

Technology experts from global leaders II-VI, Broadcom, Ciena, Cisco, Corning, Innolight, Intel, Juniper Networks, Lumentum, NeoPhotonics, Nokia and Ribbon discussed developments in hardware and software-based networking solutions in daily briefings with leading analysts, Sterling Perrin, Heavy Reading; Ian Redpath, OMDIA; Andrew Schmitt, Cignal AI; Jimmy Yu, Dell’Oro Group and Vladimir Kozlov, LightCounting. The videos can be viewed here.
The TIP sub-group said multi-vendor integration and services operations “were achieved through open standard models and APIs supported by the Optical SDN Controller, including Transport-API, OpenConfig and Open REST.”
“This proof of concept is an important milestone in the journey to fully open and disaggregated optical networking. It offers new levels of visibility and a way to manage the entire multi-vendor environment,” commented Christoph Glingener, CTO at ADVA.
Technology Showcases from 3M, AIM Photonics, Corning, EFFECT Photonics, Infinera, Jabil, Juniper Networks, Keysight Technologies, Lumentum, Luna Innovations, Murata, Nokia, Pi, Renesas, Ribbon, Samtec, Sicoya, Synopsys, Tektronix, Telescent and Xilinx gave deep dives into their cutting-edge products.
OFC 2021 exhibitor news announcements are posted to the OFC Newsroom.
Innovations in Optics
Leading researchers from around the world presented technical peer-reviewed papers, including:
- Trans-Atlantic Real-Time Field Trial Using Super-Gaussian Constellation-Shaping to Enable 30 Tb/s+ Capacity — A team of researchers from Infinera Corporation, USA and Facebook demonstrated a record-breaking transatlantic transmission across MAREA.
- A Latency-Aware Real-Time Video Surveillance Demo: Network Slicing for Improving Public Safety — Researchers presented a latency-aware optical metro network having sophisticated monitoring and data analytics capabilities and discussed the network architecture and enabling technologies, as well as a video surveillance case of the system.
- Demonstration of 100Gbit/s Real-Time Ultra High Definition Video Transmission Over Free Space Optical Communication Links — A team of researchers discussed how they achieved real-time FSO transmission of an ultrahigh-definition video stream between two buildings in Beijing.
- 224-Gb/s PAM4 Uncooled Operation of Lumped-electrode EA-DFB Lasers with 2-km Transmission for 800GbE Application — Researchers at Lumentum showed how they developed an optical solution that uses four 200 Gbps wavelength lanes to reach 800 GbE.
Post Deadline Papers looked to the future with developments in high-speed individual LEDs, modulated lasers, record low loss in hollow core fibers for applications in power delivery and sensing and other topic areas important to industry.
Analysts also revealed their recent findings around the sector to coincide with the event. For instance, Cignal AI suggested there have been strong gains in switching and routing spending by operators in the first quarter of the year, but these were offset by the slightly weaker deployment of optical transport gear.
Scott Wilkinson, lead analyst for transport hardware at Cignal AI, noted that “Chinese spending on optical hardware has plateaued as major 5G network builds mature and new projects have not been initiated.” He added that the country’s “extraordinary growth during 2015 to 2018 could not continue long term due to the impracticality of expanding upon the enormous amounts that had been spent in the region.”
In general, analysts reported subdued activity by Chinese operators across all product categories after last year’s strong growth, while most other territories showed a rebound this quarter.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
OFC 2022 will be held 06 – 10 March at the San Diego Convention Center, San Diego, CA.
For more information contact: [email protected]
References:
https://www.ofcconference.org/en-us/home/
https://www.eetindia.co.in/ofc-highlights-open-optical-nets/
Dell’Oro Group: Telecom equipment market advances in 1Q-2021; Top 7 vendors control 80% of the market
Preliminary estimates from Dell’Oro Group suggests the overall telecom equipment market – Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network, SP Router & Switch – started the year on a high note, advancing 15% year-over-year (Y/Y) in the 1st quarter of 2021, reflecting positive activity in multiple segments and regions, lighter comparisons, and a weaker US Dollar (USD).
The analysis contained in these reports suggests the collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 1Q2021, with the top seven vendors comprising around ~80% of the total market. Not surprisingly, Huawei maintained its leading position. However, the gap between Nokia and Ericsson, which was around 5 percentage points back in 2015, continued to shrink and was essentially eliminated in the quarter. In addition, Samsung passed Ciena in the quarter to become the #6 supplier.
Excluding North America, we estimate Huawei’s revenue share was about 36% in the quarter, nearly the same as the combined share of Nokia, Ericsson, and ZTE.
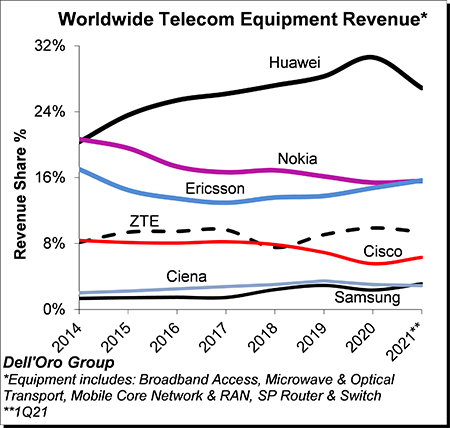
Additional key takeaways from the 1Q2021 reporting period include:
- Following three consecutive years of growth between 2018 and 2020, preliminary readings suggest the positive momentum that characterized the overall telco market in much of 2020 extended into the first quarter, underpinned by double-digit growth on a Y/Y basis in both wireless and wireline technologies including Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, Mobile Core Network, RAN, and SP Router & Switch.
- In addition to easier comparisons due to poor market conditions in 1Q20 as a result of supply chain disruptions impacting some segments, positive developments in the North America and Asia Pacific regions, both of which recorded growth in excess of 15% Y/Y during the first quarter, helped to explain the output acceleration in the first quarter.
- Aggregate gains in the North America region were driven by double-digit expansion in Broadband Access, RAN, and SP Routers & Switch.
- The results in the quarter surprised on the upside by about 2%, underpinned by stronger than expected activity in multiple technology domains including Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, RAN, and SP Routers & Switch.
- The shift from 4G to 5G continued to accelerate at a torrid pace, impacting not just RAN investments but is also spurring operators to upgrade their core and transport networks.
- At a high level, the suppliers did not report any material impact from the ongoing supply chain shortages in the first quarter. At the same time, multiple vendors did indicate that the visibility going into the second half is more limited.
- Overall, the Dell’Oro analyst team is adjusting the aggregate forecast upward and now project the total telecom equipment market to advance 5% to 10% in 2021, up from 3% to 5% with the previous forecast.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Cisco was the top-ranked vendor for market share, followed by Huawei, Nokia, and Juniper.
- The SP Router and Switch market is forecasted to grow at a mid-single-digit rate in 2021.
- The adoption of 400 Gbps technologies is expected to drive double-digit growth for the SP Core Router market in 2021.
Bharti Airtel’s 5G trial network goes live in Gurgaon’s Cyber Hub
Bharti Airtel’s 5G trial network has gone live in Gurgaon’s Cyber Hub [1.] in the Millennium city, sources familiar with the matter said. The site is operating in the 3500 MHz band using Ericsson’s 5G network equipment as per DoT guidelines and is delivering a throughput of over 1 Gbps.
Note 1. Gurgaon is a city located in the northern Indian state of Haryana. It is situated near the Delhi–Haryana border, about 30 kilometers (~19 miles) southwest of the national capital New Delhi and 268 km (167 mi) south of Chandigarh, the state capital. It is one of the major satellite cities of Delhi and is part of the National Capital Region of India.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Airtel is currently working with Oppo, OnePlus, Vivo, Realme and Apple to test its 5G trial network, sources told ETTelecom. A 5G trial network will go live in Mumbai in the coming days.
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) had recently allocated 5G trial spectrum in the 700 Mhz, 3.5 Ghz and 26 Ghz bands to Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea (Vi) to develop India-relevant use cases on the next-gen fast wireless broadband technology.
Airtel has been allotted 5G trial spectrum in 3500 MHz, 28 GHz and 700 MHz in Delhi/NCR, Mumbai, Kolkata and Bengaluru (aka Bangalore). Earlier this year, Airtel became the first telco in India to test 5G over a live network using liberalized spectrum in 1800 MHz band.

Allotment of 5G trial spectrum is particularly crucial for Jio and Airtel, who already have 5G-ready networks and have recently bulked up on crucial airwaves in the recent auction to cater to the surge in data usage amid Covid and also future-proof themselves ahead of 5G rollouts.
Airtel and Vodafone Idea had opted for Finland’s Nokia and Sweden’s Ericsson while BSNL plans to partner state-run Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT). Jio had named Samsung, Nokia and Ericsson besides applying to trial its own technology.
Both Jio and Airtel have already claimed their end-to-end readiness to launch commercial 5G services in the country shortly after the availability of “adequate” spectrum.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In January, Airtel became the first telco to successfully demonstrate live 5G service over a commercial network in Hyderabad in the 1800 MHz band through the NSA (Non-Stand Alone) network technology.
Airtel in the past has noted that 5G will be capable of delivering 10x speeds, 10x latency and 100x concurrency when compared to existing technologies. It noted that in Hyderabad, users were able to download a full-length movie in a matter of seconds on a 5G phone, a demonstration that has underlined the company’s technology capabilities. The full impact of the 5G experience, however, will be available to Airtel’s customers, when an adequate spectrum is available and government approvals are received. Users will not be required to switch SIM cards when the network is available for them.
References:
Samsung & NEC selected by Vodafone for Open RAN deployment
Vodafone has selected its Open RAN vendors: Dell, Samsung, NEC, Wind River, Keysight Technologies and Capgemini Engineering will jointly develop the first Open Radio Access Network commercial deployment in Europe. This is important because Vodafone will now be a “brownfield” telco vs greenfield telcos like Rakuten Mobile and Dish Network that are building 4G/5G Open RANs.
Furthermore, established telecom vendors Samsung and NEC beat competition from Altiostar, Mavenir and Parallel Wireless, the U.S. firms that have been involved in other open RAN deployments.
Wind River is providing the cloud software infrastructure for orchestration, while Keysight and Capgemini – the only European supplier in the mix – look after conformance and interoperability testing to make sure the set-up actually works.
The partnership will initially focus on the 2,500 UK sites that Vodafone committed to Open RAN in autumn 2020. One of the largest Open RAN deployments worldwide, this will be built in partnership with Samsung, NEC, Dell and Wind River. Vodafone will also use new radio equipment through the Evenstar program, with Keysight and Capgemini providing supports for network component interoperability.
Starting in 2021, the vendors and Vodafone will work to increase 4G/5G coverage to more rural areas across the SW of England and most of Wales, before turning to urban areas in a later stage. Vodafone is also working to deploy Open RAN technology in Africa and other markets across Europe. This announcement builds on the group’s new Open RAN lab in Newbury, UK, and planned digital skills hubs in Dresden (Germany) and Malaga (Spain).

Johan Wibergh, Vodafone Chief Technology Officer, said: “Open RAN provides huge advantages for customers. Our network will become highly programmable and automated meaning we can release new features simultaneously across multiple sites, add or direct capacity more quickly, resolve outages instantly and provide businesses with on-demand connectivity.”
“Open RAN is also reinvigorating our industry. It will boost the digital economy by stimulating greater tech innovation from a wider pool of vendors, bringing much needed diversity to the supply chain.”
“Samsung performed well on TIP evaluations they talked about a year and a half ago and so in that sense it is not a surprise,” says Gabriel Brown, a principal analyst with Heavy Reading, a sister company to Light Reading. “Samsung is taking advantage of open RAN to extend its reach.”
“This partnership represents a major breakthrough for Samsung and a strong validation for its 5G RAN portfolio,” said Richard Webb, an analyst with CCS Insight, in emailed comments. “This contract win adds to its credibility and could be a signal for other European operators to consider Samsung as an option.”
Samsung has built its open RAN software on top of Intel’s FlexRAN platform, Light Reading was able to confirm with Vodafone. Asked if that would preclude the use of Arm-based processors in future, the operator insisted open RAN’s flexibility would allow software to evolve as desired.
Heavy Reading’s Brown thinks NEC would have been a natural choice as a supplier of radio units because the Japanese market has already taken advantage of open fronthaul capability. “They have been using radios and baseband from different vendors for a long time and are world leaders in this,” he says. “NEC and Fujitsu have been working in that area for some time.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Vodafone Statement:
Vodafone is working with other operators to lower the entry barriers for smaller vendors and startups. Recently published Open RAN technical requirements by Vodafone and other telecommunications companies will provide a blueprint to help expedite the development of new products and services based on industry specifications from the O-RAN Alliance (of which Vodafone is a member) and eventually (????) ETSI standards (from the European Telecommunications Standards Institute), always compatible with 3GPP (which does not have ANY Open RAN projects at this time).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.vodafone.com/news/press-release/vodafone-europe-first-commercial-open-ran-network
Dell’Oro: Broadband Access equipment spending increased 18% YoY
A newly published Broadband Access and Home Networking 1stQ2021 report by Dell’Oro Group stated that the total global revenue for the Broadband Access equipment market increased to $3.3B in 1st Quarter, up 18 percent year-over-year (YoY). The growth was driven by strong fiber infrastructure investments such as PON (Passive Optical Network) OLT (Optical Line Terminal) ports, particularly 10 Gbps PON technologies.
XGS-PON revenue jumped 500% year-on-year to about $200 million, reflecting several quarters of steady growth as fiber players up their game in anticipation of competition from cable operators deploying DOCSIS 4.0.
- Total broadband access equipment revenue was down 6 percent from the record revenue of 4Q 2020.
- Total cable access concentrator revenue (a category that includes DOCSIS infrastructure elements such as converged cable access platform cores and chassis, virtual CCAP licensing and DAA nodes and modules) increased 15 percent YoY to $243 M.
- Though DOCSIS license purchases were down, new hardware purchases in the form of CCAP chassis, line cards, and DAA nodes and modules helped push revenue higher.
- CommScope led the cable access concentrator market with about 40% of revenues in Q1 2021, followed by Cisco (16%), Harmonic (16%) and Casa Systems (15%).
- 80% of DOCSIS modems shipped in Q1 2021 were of the DOCSIS 3.1 variety.
- Revenue from purchases of remote-PHY and remote MAC-PHY equipment were up 66% from Q4 2020, which can be interpreted as a sign that cable operators are resuming long-term projects that were put on hold during the height of the pandemic last year.
- Total DSL Access Concentrator revenue was down 30 percent YoY, driven by slower port shipments worldwide as more operators shift their spending to fiber.
- Total PON ONT (Optical Network Terminal which is CPE) revenue was down quarter over quarter, but unit shipments remained above 30M globally for the second straight quarter.
The Dell’Oro Group Broadband Access and Home Networking Quarterly Report provides a complete overview of the Broadband Access market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and port/unit shipments for Cable, DSL, and PON equipment. Covered equipment includes Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP) and Distributed Access Architectures (DAA); Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexers ([DSLAMs] by technology ADSL/ADSL2+, G.SHDSL, VDSL, VDSL Profile 35b, and G.FAST); PON Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Cable, DSL, and PON CPE (Customer Premises Equipment); and SOHO WLAN Equipment, including Mesh Routers. For more information about the report, please contact [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Long term, MoffetNathanson analysts forecast cable operators (MSOs) having a 50% broadband share in the markets where they compete with FTTH—significantly less than cable’s 85% market share against VDSL and 95% market share against DSL.
References:
Will Cable Broadband Market Share Decline as Telcos Deploy Fiber?
Google & Subcom to build Firmina cable connecting U.S. and South America
Cable maker/installer SubCom said it has teamed up with Google to build and deploy a new undersea cable connecting North and South America. The cable, named ‘Firmina’ after Brazilian abolitionist and author Maria Firmina dos Reis, will run from the East Coast of the United States to Las Toninas in Argentina, with additional landings in Praia Grande, Brazil and Punta del Este, Uruguay. Designed as a twelve-fiber pair trunk, Firmina will be Google’s second proprietary U.S. to South America cable designed to improve access to the company’s services for users in the region.
SubCom said Firmina will be the world’s longest cable capable of maintaining operations with single-end feed power, in the event of a far-end fault. Manufacture of the cable and equipment will take place at SubCom’s recently-expanded manufacturing campus in Newington during 2021 and early 2022, with main lay installation operations scheduled for summer 2022. The system is expected to be ready for service by the end of 2023.
In a blogpost, Google Cloud’s vice-president of global networking, Bikash Koley, said:
“As people and businesses have come to depend on digital services for many aspects of their lives, Firmina will improve access to Google services for users in South America. With 12 fiber pairs, the cable will carry traffic quickly and securely between North and South America, giving users fast, low-latency access to Google products such as Search, Gmail and YouTube, as well as Google Cloud services.
Connecting North to South America, the cable will be the longest ever to feature single-end power feeding capability. Achieving this record-breaking, highly resilient design is accomplished by supplying the cable with a voltage 20pc higher than with previous systems.”
SubCom’s CEO, David Coughlan, said the partnership with Google will “supply a high-speed, high-capacity undersea cable system that will encompass some of the most advanced transmission technologies in the world.”

Source: Google
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Firmina will join other Google cables in the region, including the 10,500 kilometer Monet system running from Boca Raton in the US to Fortaleza and Praia Grande in Brazil, the Tannat (Brazil-Uruguay) cable and the Junior cable connecting Rio de Janeiro to Santos in Brazil.
Google is also working with fellow tech giant Facebook on two new subsea cables that will connect North America and south-east Asia.
This came after another Google-Facebook subsea cable was blocked. Plans for the Pacific Light Cable Network were cancelled late last year due concerns from the U.S. government about direct communications links between the U.S. and Hong Kong.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About SubCom:
SubCom is the leading global partner for today’s undersea data transport requirements.
SubCom designs, manufactures, deploys, maintains, and operates the industry’s most reliable
fiber optic cable networks. Its flexible solutions include repeaterless to ultra-long-haul, offshore
oil and gas, scientific applications, and marine services. SubCom brings end-to-end network
knowledge and global experience to support on-time delivery and meet the needs of customers
worldwide. To date, the company has deployed over 200 networks – enough undersea cable to
circle Earth more than 17 times at the equator.
Mobile Optical Pluggables (MOPA) Technical Whitepaper
Nokia, Ericsson, II-VI, Lumentum and Sumitomo Electric published a joint technical paper making the case for reducing the wide choice of Mobile Optical Pluggables (MOPA) used to connect cell sites to fiber optic networks. The co-authors of the paper have recommended predefined optical blueprints that help operators speed up time to market using a common list of optical pluggable modules in a market worth $500 million per year.
Optical pluggables are defined as front-panel pluggable optical transceivers in popular form factors like SFP+, SFP28, QSFP28, etc. and the Blueprints are intended as global solutions, i.e., as generic as possible to cover a wide range of network scenarios.
The first-time joint industry initiative, published in time for the Optical Networking and Communication Conference & Exhibition, lays out a set of Mobile Optical Blueprints which describe the most optimized optical pluggable modules and passive optical components. Recommendations include optical characteristics such as data rates, reach, power, wavelengths as well as mechanical characteristics such as form factor, heat dissipation and operational temperature.
Ian Redpath, Practice Leader, Transport Networks and Components at Omdia said: “In a 5G world, optical pluggables will be utilized to connect cell sites to the network core. Network operators are currently challenged with assessing many pluggable variations, increasing their qualification work load and slowing time to deploy. MOPA will streamline efforts for the connectivity community, enabling cost reductions and reducing time to deploy.”
Stefaan Vanhastel, CTO Nokia Fixed Networks said: “Fiber is a critical component of 5G rollouts and provides unmatched capacity for 5G transport. A clear overview of available optics strategies makes it easier to design and deploy 5G networks. We are pleased to be joining forces with Ericsson, II-VI, Lumentum and Sumitomo Electric on this vital initiative which will make the choice for fiber even more compelling in the transport domain.”
References:
https://onestore.nokia.com/asset/210585
Mobile Optical Pluggables (MOPA) Technical Paper, June 8, 2021



