Author: Alan Weissberger
Lumen to provide mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense
Lumen Technologies recently won a $223 million contract from the U.S. Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) to provide secure, mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD).
“The U.S. Department of Defense has a far-reaching mission to provide military forces to deter war and ensure our nation’s security. DoD selected Lumen to deliver voice communications services that will help it carry out its important mission using today’s technologies,” said Zain Ahmed, senior vice president, Lumen public sector. “DoD is modernizing its network and leveraging cloud-based technologies like the new voice system enabled by Lumen that securely connects our troops with modern communications tools wherever they are.”
- Lumen will supply DISA with modern hybrid-cloud voice and audio-conferencing services that support the Department of Defense (DoD)’s mission both inside and outside the U.S.
- The new Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system saves the government money by eliminating the need for desk phones and supporting remote users as DoD transitions to a hybrid workforce.
- Lumen is serving as a trusted provider of secure, resilient communications services that enable more than 250,000 concurrent connections to DISA’s voice cloud system.
- Lumen is supplying unified communications services via an integrated phone system that runs over the company’s fiber network.
- Delivering voice and conferencing services from cloud data centers that meet DoD Impact Level 5 security standards provides modern capabilities with scalable infrastructure ready to meet warfighters’ needs on demand.
The new voice services will support DoD’s transition to a next generation 911 (NG911) system at military bases that can better pinpoint and route first responders to a caller’s location. The Lumen NG911 platform improves the delivery of emergency calls and enables residents to contact 911 not only by making a voice call—it also lays the foundation for the delivery of pictures and videos in the future.
- The $223 million task order has a base performance period of one year, with three additional one-year options and a potential six-month extension.
- It was awarded to Lumen under the General Services Administration’s 15-year, $50 billion Enterprise Infrastructure Solutions (EIS) program.
- Tyto Government Solutions, Inc. is a strategic subcontractor to Lumen. The two companies are working to fulfill the order’s technical requirements by delivering phone and conferencing services from highly available, resilient cloud data centers that meet DoD Impact Level 5 (IL5) security standards.
- Lumen is honored to support military and government agencies with innovative adaptive networking, edge cloud, connected security and collaboration services using the company’s platform for advanced application delivery solutions.
- The company provides a platform for IT modernization that delivers the security and reliability military and civilian agencies need to carry out their important missions.

- Learn more about our Defense Information Systems Agency $1.5 billion award to provide network transport to the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command Area of Responsibility: http://news.lumen.com/2022-11-01-Lumen-wins-1-5-billion-Defense-Information-Systems-Network-contract
- Learn more about our U.S. Department of Agriculture $1.2 billion network services award: https://news.lumen.com/2022-01-20-U-S-Department-of-Agriculture-awards-Lumen-1-2-billion-network-services-contract
- Learn more about our U.S. Department of the Interior $1.6 billion network services award: https://news.lumen.com/2020-01-16-U-S-Dept-of-the-Interior-Awards-CenturyLink-1-6-Billion-EIS-Network-Services-Win
- Learn more about how Lumen is supporting the public sector here:
https://www.lumen.com/public-sector.html
Lumen is guided by our belief that humanity is at its best when technology advances the way we live and work. With approximately 400,000 route fiber miles and serving customers in more than 60 countries, we deliver the fastest, most secure platform for applications and data to help businesses, government and communities deliver amazing experiences. Learn more about the Lumen network, edge cloud, security, communication and collaboration solutions and our purpose to further human progress through technology at news.lumen.com, LinkedIn: /lumentechnologies, Twitter: @lumentechco, Facebook: /lumentechnologies, Instagram: @lumentechnologies and YouTube: /lumentechnologies. Learn more about Lumen’s public sector capabilities on Twitter at @lumengov and on LinkedIn at @lumenpublicsector. Lumen and Lumen Technologies are registered trademarks in the United States.
India to set up 100 labs for developing 5G apps, business models and use-cases
Even as India’s long delayed 5G network roll-out continues at a rapid pace, the government has outlined plans for expanding 5G’s use beyond consumers and enterprises. In her Budget speech, Union Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman called for the development of new applications and business models, which will also create more jobs. There are plans to set up 100 labs in engineering institutions to develop applications and use-cases for 5G services. It should be noted that GE setup India’s first 5G innovation lab in July 2022.
“The labs will cover, among others, applications such as smart classrooms, precision farming, intelligent transport systems, and health care applications,” Sitharaman said in her speech.
“The proposed outlay for 5G labs will further push the development of use-cases and the set-up of private networks in India. The research across universities will push innovations and job opportunities,” said Peeyush Vaish, partner and telecom sector leader, Deloitte India.
The speed at which commercial 5G networks have rolled out, since the official launch in October, has been impressive. India’s 5G auctions, which culminated in the second half of 2022, saw Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vi acquire 5G spectrum for commercial networks, while Adani Data Networks is expected to launch enterprise 5G services with the spectrum it bought. In particular, Reliance Jio confirms it has enabled 5G networks (SA) in 225 cities across India. Airtel doesn’t give a confirmed count of its 5G NSA network service coverage, but continues to add cities every day. Vi is yet to launch 5G services.
“We believe 5G will have country-specific use-cases and India is no different. In fact, India can set an example for the rest of the world,” said Tarun Pathak, research director at Counterpoint Research.
“5G networks and devices without use-cases is akin to highways without places to travel to,” said Muralikrishnan B, president, Xiaomi India.
Test labs for 5G applications provide a sandboxed environment for testing use-case prototypes. Indian telecom equipment company Himachal Futuristic Communications Limited (HFCL) is working closely with tech giant Qualcomm and has a 5G lab which focuses on rural mobile broadband.
GE’s 5G Innovation Lab in India. Top: Jan Makela, president and CEO of imaging at GE Healthcare (center), cuts the ribbon to open the 5G Innovation Lab. Second from left: Girish Raghavan, vice president of engineering for GE Healthcare.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Bipin Sapra, Tax & Regulatory Services, Partner, EY India said that the government had taken a big leap to embrace 5G much more swiftly by setting up these labs. He agreed that they would indeed further boost employment and business opportunities in the country. “Amrit Kaal focuses on being a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with one of the primary visions of growth and job creation. India has made remarkable advancements in the digital realm and various new initiatives have been adopted to improve the lives of people, accelerating the societal benefits of these technologies,’‘ added Mr. Sapra.
“The setting up of 100 labs to develop 5G will better network connectivity in every nook and corner of the country and further help more sectors and communities to access the benefits of 5G networks,” said Sanmeet Singh Kochhar, vice-president – India and MENA at HMD Global.
Piyush N. Singh, Senior Managing Director, Accenture, said setting up new centers of excellence for AI and 5G labs for developing apps would help democratize AI and push for wider adoption of 5G services. “It will be important for the private sector ecosystem to work closely with the government to realize the digital future of India,’‘ Mr. Singh said.
References:
https://www.gehealthcare.com/insights/article/new-5g-innovation-lab-in-india-poised-to-unlock-the-future-of-healthcare
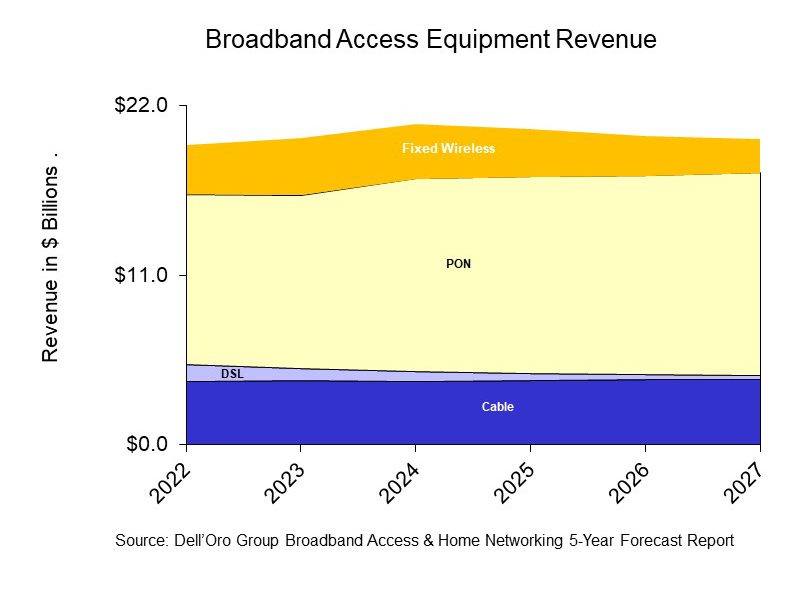
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
A newly published report by Dell’Oro Group predicts that sales of PON (Passive Optical Network) equipment for fiber-to-the-home deployments, cable broadband access equipment, and fixed wireless CPE will all increase from 2022 to 2027, as service providers continue to expand their fiber and DOCSIS 4.0 networks, while expanding the types of services they deliver to residential subscribers.
“Service providers around the world continue to transition their broadband networks to fiber and retire their existing copper and DSL networks,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “With markets expected to become more competitive, broadband providers will have to continue spending in order to differentiate their services not only by increasing advertised speeds, but also improving latency and expanding managed Wi-Fi services,” added Heynen.
Additional highlights from the Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year January 2023 Forecast Report:
- PON equipment revenue is expected to grow from $11.0 B in 2022 to $13.2 B in 2027, driven largely by XGS-PON deployments in North America, EMEA, and CALA.
- Revenue for Cable Distributed Access Equipment (Virtual CCAP, Remote PHY Devices, Remote MACPHY Devices, and Remote OLTs [1.]) is expected to reach $1.5 B by 2027, as operators ramp their DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber deployments.
- Revenue for Fixed Wireless CPE [2.] is expected to reach $2.2 B by 2027, led by shipments of 5G sub-6GHz and 5G Millimeter Wave units.
Note 1. Remote OLTs (Optical Line Terminals) can be deployed in distributed access nodes to support targeted deployments of FTTP. Comcast is already doing that for its next-gen HFC network. But others, such as Charter Communications, are also ramping up their respective efforts and pursuing similar deployment models.
“You’re now talking about a whole new architecture with remote OLTs, virtual CMTSs and remote PHY. It will take longer to operationalize. It’s a slower burn than it used to be in the past,” Heynan said. He expects cable access network spending to continue climbing past 2027 as other cablecos join the mix.
Note 2. Heynen expects FWA CPE spending to stay steady through 2024, but notes that some providers might run into capacity issues that curtail growth and will also be faced with fiercer competition from fiber and newly upgraded HFC networks. “That puts a ceiling on how much growth can happen for fixed wireless,” he said. While T-Mobile and Verizon are now driving FWA growth in the U.S., we wonder how the future will shake out for the WISP (wireless ISP) sector, which is also seeing steady growth at the moment. As WISPs (Wireless Internet Service Providers) seek out government subsidy opportunities, some may need to consider licensed spectrum or transition to fiber across their footprint.
The Dell’Oro Group Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year Forecast Report provides a complete overview of the Broadband Access market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and port/unit shipments for PON, Cable, Fixed Wireless, and DSL equipment. Covered equipment includes Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP), Distributed Access Architectures (DAA), DSL Access Multiplexers (DSLAMs), PON Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Customer Premises Equipment ([CPE] for Cable, DSL, PON, Fixed Wireless), along with Residential WLAN Equipment, including Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 Gateways and Routers. For more information about the report, please contact [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
References:
Broadband network spending set to climb as cable gets its groove back | Light Reading
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
Dell’Oro: PONs boost Broadband Access; Total Telecom & Enterprise Network Equipment Markets
Dell’Oro: PON ONT spending +15% Year over Year
Dell’Oro: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) deployments to be driven by lower cost CPE
Passive Optical Network (PON) technologies moving to 10G and 25G
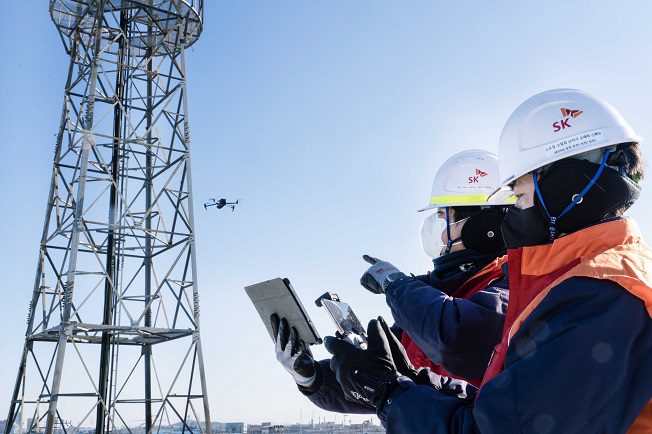
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
SK Telecom, South Korea’s largest wireless carrier, announced on Tuesday that it’s developed a new cell tower safety inspection system using drones and image analysis artificial intelligence (AI). The newly-developed image analysis AI model checks the status of nuts and bolts by analyzing images taken by drones.
Cell towers with antennas for sending and receiving telecommunications signals are installed across the country, with their maximum height estimated at 75 meters. Since cell towers require regular maintenance to prevent accidents that can be caused by deterioration such as corrosion or loosening of nuts and bolts, specialized personnel had to climb them to inspect their condition with their bare eyes.
Engineers from a subsidiary of SK Telecom Co. inspect a cell tower in this photo provided by the wireless carrier on Jan. 31, 2023.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Now with an intelligent safety inspection system in place, not only can SK Telecom prevent accidents due to aging cell towers, but it can also ensure the safety of workers by minimizing the need to go up the cell towers. Moreover, the company can drive up work productivity through the application of an AI model that automatically identifies defects by analyzing images taken by drones.
Previously, safety inspectors had to study around 100 images to complete the inspection of one cell tower by inspecting multiple images taken by drones. With the adoption of the new AI analysis model, SK Telecom has been able to reduce the time required for the process by 95%, while increasing the reliability and consistency of the analysis results.
The company says, going forward, it will enhance the system even further by adding inspection items such as wind pressure safety/inclination. It will also look to improve the AI model and link the application with the safety management system.
In addition to drone-based cell tower inspections, the telecom company is actively applying AI to other areas of its network, including equipment error/anomaly detection, power cost reduction, and work completion inspection.
Park Myung-soon, SKT’s vice president and head of Infra DT Office, said: “By building an intelligent safety inspection system that can complement the existing visual inspection, we have secured greater safety for workers. We will continue to make efforts to achieve AI transformation of our telecommunication networks, while focusing on developing our field workers into experts who can develop and operate AI.”
References:
http://koreabizwire.com/sk-telecom-inspects-cell-towers-using-drones-and-ai/239441
South Korean telecom giant innovates safety inspection with drones
Nordic Semiconductor announces ICs & development kits for low power Wi-Fi 6 IoT applications
Nordic Semiconductor today announced the availability of the nRF7002™ Wi-Fi 6 companion IC and its associated nRF7002 Development Kit (DK). The IC is the first in Nordic’s Wi-Fi product family and is a low power Wi-Fi 6 companion IC providing seamless dual band (2.4 and 5 GHz) connectivity. The nRF7002 IC can be used together with Nordic’s award-winning nRF52® and nRF53® Series multiprotocol Systems-on-Chip (SoCs) and the nRF9160™ cellular IoT (LTE-M/NB-IoT) System-in-Package (SiP), but can equally be used in conjunction with non-Nordic host devices. The DK makes it easy for developers to get started on nRF7002-based IoT projects.
The nRF7002 complements Nordic’s cellular IoT and multiprotocol wireless solutions. By using the new IC, developers can leverage Wi-Fi 6’s higher throughput and ubiquitous domestic and industrial infrastructure when developing IoT applications. Design support through Nordic’s unified software development kit, nRF Connect SDK, and the nRF7002 DK make it easier and quicker to launch new products.
Wi-Fi 6 brings significant benefits to IoT applications—such as smart-home products, industrial sensors, asset trackers, and wearables—including power efficiency gains for battery powered Wi-Fi operation, and management of large IoT networks comprising hundreds of devices.
“The nRF7002 Wi-Fi 6 companion IC is a testament to Nordic Semiconductor’s leadership in low-power wireless technology,” says Svein-Egil Nielsen, CTO/EVP of R&D and Strategy at Nordic. “This highly integrated and flexible solution will empower developers to create new, innovative Wi-Fi 6-enabled products. Supported with the nRF7002 DK and the award-winning nRF Connect SDK, combined with Nordic’s best in class technical support, I believe it has never been easier to develop great Wi-Fi products.”
“The nRF7002 is designed to work alongside Nordic’s nRF52 and nRF53 Series making it a perfect fit for Matter, a smart-home standard backed by Amazon, Apple, Google, Nordic, Samsung, and hundreds of other companies,” says Finn Boetius, Product Marketing Engineer with Nordic. “The introduction of the IC and the nRF7002 DK now makes it easy for developers to get started on Matter and any other Wi-Fi based applications.” Matter uses Thread and Wi-Fi for data transport, and Bluetooth LE for commissioning.
The nRF7002 brings low power and secure Wi-Fi to the IoT. The dual-band IC complies with Station (STA), Soft Access Point (AP), and Wi-Fi Direct operation, and meets the IEEE 802.11b, a, g, n (“Wi-Fi 4”), ac (“5”), and ax (“6”) Wi-Fi standards. The product also offers excellent coexistence with Bluetooth LE, Thread, and Zigbee. The nRF7002 supports Target Wake Time (TWT) a key Wi-Fi 6 power saving feature. Interfacing with a host processor is done via Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) or Quad SPI (QSPI). The IC offers a single spatial stream, 20 MHz channel bandwidth, 64 QAM (MCS7), OFDMA, up to 86 Mbps PHY throughput, and BSS coloring.
In addition to its suitability for general IoT applications and Matter, the nRF7002 is the ideal choice for implementing low power SSID-based Wi-Fi locationing when used together with Nordic’s nRF9160 SiP and the company’s nRF Cloud Location Services. SSID-based Wi-Fi locationing supplements GNSS- or cell-based locationing by providing accurate positioning indoors and in places with a high density of Wi-Fi access points.
nRF7002 DK supports development of low power Wi-Fi applications:
The introduction of the nRF7002 is accompanied by the launch of the nRF7002 DK, a development kit for the Wi-Fi 6 companion IC. The DK includes an nRF7002 IC and features an nRF5340 multiprotocol SoC as a host processor for the nRF7002. The nRF5340 embeds a 128 MHz Arm Cortex-M33 application processor and a 64 MHz high efficiency network processor. The DK supports the development of low-power Wi-Fi applications and enables Wi-Fi 6 features like OFDMA, Beamforming, and TWT. The DK includes: Arduino connectors; two programmable buttons; a Wi-Fi dual-band antenna and a Bluetooth LE antenna, and current measurement pins.
nRF7002 DK – Development Kit for nRF7002 Wi-Fi 6 IC:
.png?h=754&iar=0&mw=350&w=350&hash=1DF0EC6A97E1329DCCD435B7FDBF0B90)
Source Nordic Semiconductor
Together with the DK, developing nRF7002-based designs is made simpler by the support for the IC in the nRF Connect SDK, Nordic’s scalable and unified software development kit for building products based on the company’s wireless devices. With the nRF7002 IC, nRF7002 DK, and nRF Connect SDK, developers can quickly and easily add Wi-Fi connectivity to their products, allowing them to connect to the Internet and communicate with other devices over a Wi-Fi network. Example applications for the nRF7002 DK are included with nRF Connect SDK.
The nRF7002 companion IC and nRF7002 DK are available now from Nordic’s distribution partners.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/nRF7002
https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nRF7002-DK
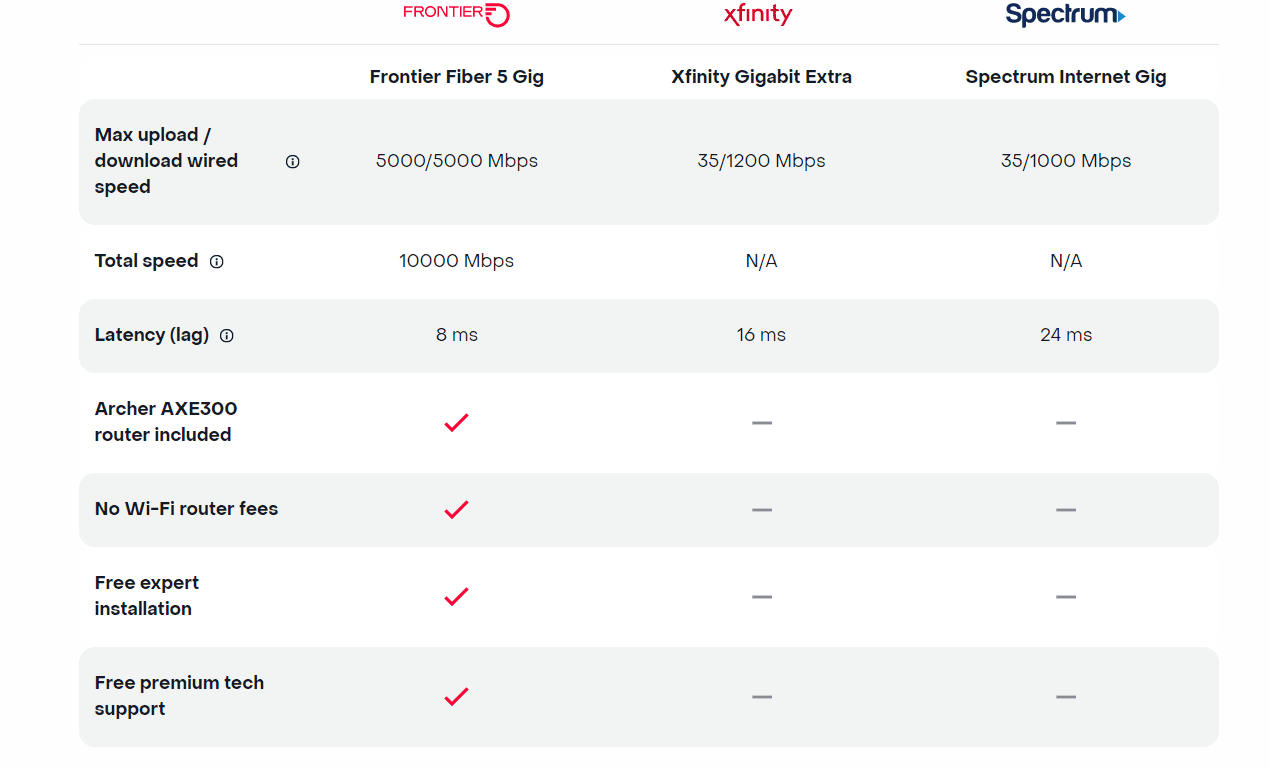
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Today, Frontier Communications launched the nation’s only network-wide 5 Gig fiber internet service. With the launch of 5 Gig, Frontier will provide customers across its 25 state fiber network – not just select markets – the opportunity to sign up for the new premium service with blazing-fast speeds. The company says that 5 Gig internet has 125x faster upload speeds, 5x faster download speeds and 2.5x less latency than cablecos [1.], but they don’t specify the cable network speeds or latency.
Note 1. Comcast currently offers 1 and 2 Gig Internet. The company announced a successful trial of the world’s first live, multigigabit symmetrical Internet connection powered by 10 Gbps and Full Duplex DOCSIS 4.0 last December. Charter Communications is also planning a DOCSIS 4.0 upgrade to deliver download speeds of 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps over the coming years, but isn’t currently planning to bring symmetrical service offerings to market.
Frontier’s 5 Gig fiber internet service enables customers to run multiple connected devices at their fastest possible speeds. This means:
- Symmetrical download and upload speeds at up to 5 gigabits per second
- 125x faster upload speed than cable
- 1.6 seconds to download Adobe Photoshop on PC (1GB)
- <36 seconds to download a House of Dragons episode in 4K (22 GB)
- <2 minutes to download a 100-minute 8K movie (67 GB)
- 99.9% network reliability
The 5 Gig internet offer starts at $154.99 a month with autopay and includes uncapped data + Wi-Fi router + free installation + premium tech support. There are no additional Wi-Fi or router fees, no data caps or overage charges. The inclusion of a Archer AXE300 Wi-Fi 6E router is a major advantage, because most installed WiFi routers are WiFi 5= IEEE 802.11ac which won’t support giga bit speeds.
Frontier also dropped the price of its 2-gig internet service, which debuted in February 2022 at a cost of $149.99 per month. That service is now priced at $109.99 per month.
New Street Research stated that Frontier’s 5-gig rollout will “help establish Frontier as a leader in network capabilities and drive the message that this is a new Frontier.” The analysts added, “It also helps drive the message that they are delivering a product that Cable can’t.” Furthermore, New Street noted the move could contribute to growth in average revenue per user (ARPU) given the price drop for the 2-gig plan could “drive some incremental demand for that too.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On Frontier’s Q3 2022 earnings call, CEO Nick Jeffrey noted 45% to 50% of new customers were taking its 1 Gbps and 2 Gbps plans. Among its installed base, uptake of 1-gig or faster speeds stood at 15% to 20%. That was up sequentially from 10% to 15% in Q2, Jeffrey said at the time.
Frontier is set to report Q4 2022 earnings on February 24th. In a 4Q 2022 earnings preview, the ISP disclosed it added 75,000 new fiber customers and 8,000 total broadband subscribers in the quarter. That was 17% more fiber broadband customers than it had at the end of 2021. For the fifth consecutive quarter, fiber broadband customer additions outpaced copper broadband customer losses, resulting in 8,000 total broadband customer net additions in the fourth quarter of 2022.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other Competition:
AT&T, Altice USA, Lumen Technologies and Ziply Fiber all already provide symmetrical speeds of 5 Gbps or faster. And Google Fiber has announced plans to debut 5-gig and 8-gig plans early this year. But Frontier claimed it is the only operator thus far to roll out such speeds networkwide.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Frontier Communications:
Frontier is a leading communications provider offering gigabit speeds to empower and connect millions of consumers and businesses in 25 states. It is building critical digital infrastructure across the country with its fiber-optic network and cloud-based solutions, enabling connections today and future proofing for tomorrow. Rallied around a single purpose, Building Gigabit America™, the company is focused on supporting a digital society, closing the digital divide, and working toward a more sustainable environment. Frontier is preparing today for a better tomorrow. Visit frontier.com.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Media Contact:
Chrissy Murray, VP, Corporate Communications
+1 504-952-4225 [email protected]
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://frontier.com/shop/internet/fiber-internet/5-gig
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Frontier Communications sets another fiber buildout record; raises FTTP buildout target for 2022
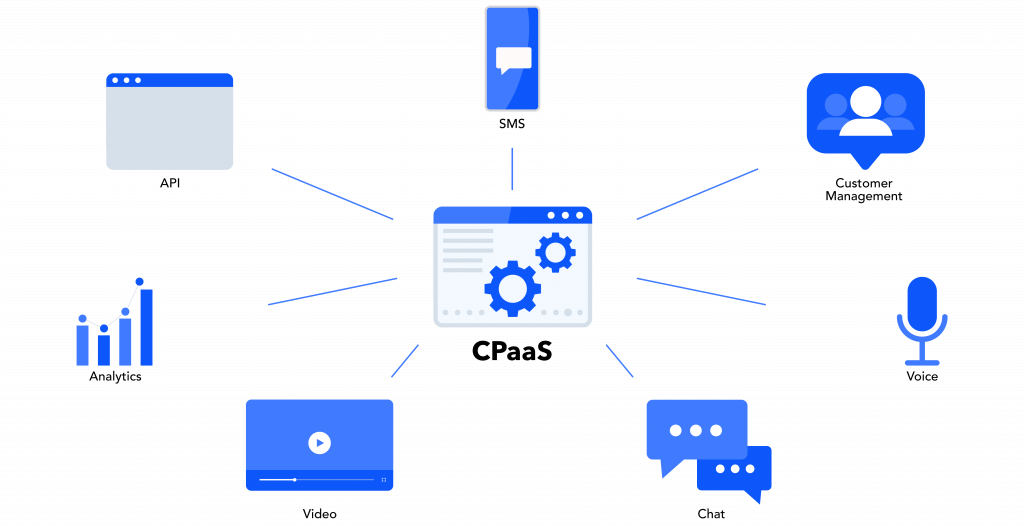
Juniper Research: CPaaS Gobal Market to Reach $29 Billion by 2025
A new study from Juniper Research has found the value of the CPaaS (Communications Platform-as-a-Service) [1.] market will reach $29 billion globally by 2025; rising from $16 billion in 2022. To capitalise on this substantial growth of 80% over the next three years, the report, CPaaS: Market Outlook, Emerging Opportunities & Forecasts 2023-2027, urges CPaaS vendors to focus on the development of managed services over their platforms. These services must enable the creation and management of rich media content over channels such as OTT business messaging, email and social media.
Note 1. Communications Platform as a Service is a cloud-based delivery model that allows organizations to add real-time communications capabilities, such as voice, video and messaging, to business applications by deploying application program interfaces (APIs).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
As markets become increasingly saturated with CPaaS service provision, CPaaS vendors must expand deeper into the SME (Small-to-Medium Enterprise) sector. In addition, the report predicts CPaaS vendors will further focus on the provision of value-added features that enable platform users to fully maximise the benefits of rich media channels though the inclusion of tools, including workflow builders and AI-based chatbot solutions.
Research author Sam Barker commented: “CPaaS vendors now compete on the capabilities of managed services to attract SMEs. As many of these smaller enterprises lack in-house development facilities, they will choose the CPaaS platform that provides the most comprehensive managed services for rich media channels.”
Emerging Channels to Disrupt CPaaS in 2023
SMS has historically been the cornerstone of CPaaS revenue. The report predicts SMS traffic revenue will still account for over 50% of all CPaaS revenue by 2025; owing to its established reliability in termination for traffic such as MFA (Multi-factor Authentication).
However, the report forecasts that rich media channels, such as email and social media, will continue to expand, and account for over $10 billion of revenue by 2025; representing over 40% of the CPaaS market value. As a result, platforms that fail to include managed services for rich media services in their three-year plans risk missing out on the substantial growth predicted for the CPaaS market.
Resources:
View the CPaaS market research: https://www.juniperresearch.com/researchstore/operators-providers/cpaas-research-report
Download the whitepaper: https://www.juniperresearch.com/whitepapers/how-cpaas-will-evolve-in-2023
Juniper Research provides research and analytical services to the global hi-tech communications sector; providing consultancy, analyst reports and industry commentary.
Cybersecurity threats in telecoms require protection of network infrastructure and availability
Telecommunications companies have become an attractive target for attackers, as their networks can be used as a back door to other organizations, thereby making it attractive for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access. These telecoms networks are also used to build, control and operate other critical infrastructure sectors, including energy, information technology, and transportation systems. Given the interconnected nature of telecom networks between critical infrastructure sectors, organizations need to focus on safeguarding network infrastructure and enabling network availability for critical infrastructure communication.
Telecoms face mounting threats due to various factors, such as the absence of technical knowledge, use of legacy systems, presence of sensitive information, inadequate password security, and increasing threat landscape. Operators are also transforming themselves from network infrastructure companies to cloud service companies to improve efficiencies in business operations, roll out new services and applications, and store and distribute content. As telcos are often a gateway into multiple businesses, threats can either target a specific telecom company, its third-party providers, or the subscribers of a telecom service. These attacks can come in various forms.

Trend Micro disclosed that telecoms have a larger cyber-attack surface than most enterprises, often stretching from their base station infrastructure to call centers and home workers’ laptops. The surface area provides ample opportunity for threat actors looking for customer or organizational data, trying to hijack customer accounts, or seeking to disrupt services via DDoS (distributed denial of service) and ransomware. Furthermore, supply chain providers, cloud services, IoT systems and new infrastructure needed to support 5G and network slicing create additional risk.
Industrial Cyber reached out to experts in the telecoms sector to examine the key factors that make the communications sector vulnerable to cyber attacks. They also weigh in on the unique challenges that the communications sector faces when it comes to securing and safeguarding its OT/ICS environments.
Teresa Cottam, the chief analyst at Omnisperience, told Industrial Cyber that in the past, where security was considered in telecoms the focus tended to be how it affected performance – such as minimizing DDoS traffic and attacks. “More recently, as everything has become more interconnected and the threat landscape has evolved, cyberattacks specifically against telecoms firms have increased,” she added.
Cottam pointed out that ultimately four challenges stand out – complexity, exposure, volume and variety, and cost.
On complexity, Cottam said that each individual ‘network’ actually comprises several generations of technology with some of it being decades old, and it might include fixed, mobile, and even satellite infrastructure. “Moving data from one side of the world to another requires multiple networks, each owned by a different company with a different risk profile. The move from 4G to 5G introduces even more complexity. In the 5G era, cloud, data, and IoT are combined – increasing security risks. Breaches now have a company-wide impact from production through supply chains and logistics to corporate systems,” she added.
Cottam also added that “when you consider how much equipment is in public places it’s actually surprising it’s not attacked more often. Malign actors don’t even need to mount a cyberattack, they can simply vandalise equipment to target specific regions or industries.”
Elaborating on volume and variety, Cottam said that the sheer volume of endpoints is staggering and continually increasing. “IoT has already massively increased the number of endpoints and will continue to do so. Many of these so-called smart objects aren’t very smart and are highly vulnerable. Many of the most vulnerable devices are in the home, but wherever they are, each device has the potential to inject malign traffic into the network,” she added.
On cost, Cottam said that the cost of securing a network end-to-end is significant and the reality is that telecoms firms and their customers are having to continually juggle risk versus security.
Turning the question around, Grant Lenahan, partner and principal analyst at Appledore Research, said that one of the huge transitions underway is from fundamentally private data centers and networks to outsourced or managed, secure networks that interconnect distributed enterprise to their digital partners, remote employees, public cloud, and SaaS facilities. Therefore, there is a blurring of public and private targets.
“We certainly can look at those who attack public networks because of the private data and traffic. We can also look at those who attack not an underlying enterprise target per se, but the network infrastructure itself,” Lenahan told Industrial Cyber. “These attacks, rather than going after specific data, or intended either to disrupt, for example, terrorism or to gain control that can later be used to target intellectual property the transit to the network. The very fact that public networks are public, complicates securing them.”
On the other hand, Lenahan added that there is scale and scope, allowing for concentrations of security expertise and automated protections, that might not be possible or affordable by individual enterprises. “We have spent hundreds of pages covering this seismic shift in our security research stream. Some readers might be interested in consulting it,” it added.
Andrei Elefant, CEO of EdgeHawk Security told Industrial Cyber that the key factors that make the communication sector vulnerable to cyber attacks are that the CSPs (communication service providers) face multiple and large attack surfaces. They also have a limited security budget and have to prioritize the security measures they take compared to the cost and priorities.
He also added that security expertise in CSPs is limited. “The various types of attack scenarios, attack methods, the type of data and systems that need to be protected are huge. CSPs cannot build expertise in all the required security domains and have to prioritize focus areas. The CSPs are defined as critical infrastructure and are frequently a target of Nation State Actors, which means higher expertise and more budget on the attackers’ side.”
Elefant added that these challenges are even more noticeable when it comes to protecting the OT/ICS environment. “Attack surfaces grow exponentially with the growth in the number and variety of the endpoints. Many of the OT endpoints have limited inherent protection capabilities (due to resources limitation, legacy devices, etc.,), which means they can be a perfect attack surface to harm CSPs or penetrate their networks. In many cases, these devices are being exploited for DDoS attacks, as they are available in masses with limited protection.”
Addressing the essential components that make cybersecurity in telecoms a vital and fundamental part of protecting the telecommunications landscape, as it also serves much of/all the other critical infrastructure sectors, Cottam said that not having complete visibility of the complexity of the telecoms landscape is one of the biggest challenges. “For example, there could be vulnerabilities in equipment and devices – which is often the focus of analyst reports – but equally there can be vulnerabilities in core processes which were put in place decades ago and haven’t been updated,” she added.
Cottam identified that a typical attack occurs by a criminal convincing the telecoms firm they are the customer and want to move to a new provider. “The telecoms firm – often with only minimal checking – provides the ‘customer’ with the means to do so. In the UK the system is designed to make it as easy as possible for the customer to do this, which also makes it easy for criminals. Such an attack against employees is bad; now consider it targeted at IoT devices. This is a great example of how cybersecurity often focuses on securing equipment (endpoints) but ignores vulnerable processes,” she added.
“Many countries have acted to secure number portability and in this respect, the UK is particularly vulnerable as its current system is so old-fashioned and inefficient,” according to Cottam. “Another problem this causes for IIOT is that the UK system also struggles to port large volumes of numbers such as would need to happen with a large corporate or IoT customer. This has the potential of decreasing competition in the connectivity part of the market since it’s a blocker to switching operators.”
Lenahan said that he doesn’t “believe we need to emphasize how important telecom infrastructure is. Not only is it critical infrastructure and it’s all right, but it is often the control plane for other infrastructure such as water, gas, electricity, emergency services, and many other essential components of both private public, and industrial life. It is, what’s on call, a target rich environment. That said, let’s look at what success looks like,” he added.
Elefant said that the CSPs are becoming a part of the critical infrastructures in any state. “National defense strongly relies on communication availability on the state level, in addition to the fact that these networks provide essential communication infrastructure to many other critical infrastructure facilities,” he added.
The essential components needed to keep CSPs networks available and reliable focus on two main aspects, according to Elefant. “Protecting the network infrastructure from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This includes implementing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other security measures to prevent unauthorized access.”
He also pointed to protecting network availability for critical infrastructure communication by identifying and blocking attempts to saturate the network and accessibility to specific applications/devices using DDoS attacks.
The telecoms industry has had to reconsider its cybersecurity protocols in light of the digitization and incorporation of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies. The executives looked into the main threats posed by increased connectivity techniques and how this shift affects the cybersecurity posture of these communication companies.
Cottam said that often today’s IIoT devices use the same networks as other systems, which presents a double-edged risk. “If a criminal can compromise an IIoT device they could use this as an access point to corporate systems; if they compromise corporate systems or user devices they can hijack IIoT devices. Again, this speaks to the interconnectedness of networks and often the poor understanding of how criminals can utilise connections and access points to compromise industrial customers.”
“The main concerns from customers include exposure of their data, compromised network equipment, attacks on devices and network signaling, as well as creating a gateway for further attacks. Network segmentation is a useful technique to limit the scope of such attacks,” according to Cottam. “Reliable security frameworks are built into 3GPP standards to ensure 4G and 5G cellular connections are secure. But as we move to 5G a range of new exciting techniques are also delivered.”
Another technique is to utilize private networks – effectively campus networks within a factory or industrial complex with limited connections to the public network but complex connections within the private network, Cottam said. “Connectivity is only provided to authorised devices (more secure than WiFi, as it can be based on SIM authentication) and data is processed on-site,” she added.
“The simplest way to look at this is that complexity is increasing dramatically in enterprise networks. There will be an order of magnitude more endpoints; applications and data will reside in various clouds; and dynamically changing ecosystems of digital trading partners will continuously evolve,” Lenahan said. “This implies a complex network that crosses ownership boundaries, and is constantly changing.”
Lenahan noted that the only apparent constant throughout this ‘web’ is the telecom CSP that undertakes end-to-end connectivity, orchestration, and in our view, security. “This is a huge opportunity for our industry. However, it also means we need to think completely differently about security. It cannot be a separate island; it must be integrated into network automation. Furthermore, it must be automated, something tacos in security professionals have long been uncomfortable with,” he added.
Elefant identified some of the threats brought by these increased connectivity techniques, including increased attack surface, unsecured devices, protocol vulnerabilities, and DDoS attacks. With “the exponential increase in the number of connected devices, the attack surface of the network has increased, creating more opportunities for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to the network. Many IoT devices are not designed with security in mind, and may have weak passwords, unpatched vulnerabilities, or lack encryption, making them easy targets for attackers.”
He also pointed out that IoT devices often use proprietary protocols, which may have vulnerabilities that are not well understood and are difficult to patch. IoT devices can be easily compromised and used to launch DDoS attacks, overwhelming the network with traffic and causing availability issues.
Elefant highlighted that the new threats have led to a shift in the cybersecurity posture of CSPs. “Implementing more strict network segmentation, both on their infrastructure and also as a service to their customers. Specifically for the IIoT environment, access control services, delivered by the CSPs, are being applied on a larger scale. Protecting the network from DDoS attacks on the edge and access points became a mandatory consideration. Additionally, there is a need to continuously monitor and assess the security of the network edge and access as more attacks may come from exploited devices connected to the network.”
Like other critical infrastructure sectors, the communications sector has also faced mounting cybersecurity rules and regulations in recent times. The executives address how the communication sector responded to the increase in cybersecurity regulations for critical infrastructure owners and operators, as well as analyze the impact these initiatives have had in enhancing reporting procedures and improving the cybersecurity posture of the telecoms sector.
Cottam said that one of the biggest challenges stems from the ‘democratisation’ of IoT. “As it becomes the norm in manufacturing supply chains, smaller and newer industrial firms are drawn in or adopt IoT to increase their efficiency. These firms often don’t fully understand the importance or complexity of securing their IoT devices and lack the budget and expertise in-house,” she added.
Another challenge is that many enterprises deploy and secure IoT from an IT perspective, according to Cottam. “Traditional IT security largely focuses on end-point and perimeter security. But with hundreds of thousands of IoT endpoints and more permeable boundaries, the emphasis has to shift to securing and managing the network rather than trying to put security into every device – not all of which are designed to be secured,” she added.
“Likewise, while cellular IoT is reasonably secure – and that based on 5G even more so – it is not unhackable. IoT network security isn’t just about securing the network either, it’s about network-based security that can monitor all the connected objects, processes, and applications,” Cottam said. “Neither is it just about hackers anymore. Nation states, protestors, and terrorists are just as likely to want to attack critical infrastructure and their objectives are different and their budgets and expertise are huge. While there has been much talk of bringing together IT/OT/IoT into a single process to make it more manageable and auditable, the risk is that the complexity and volume become overwhelming.”
Lenahan said that details on how telcos are handling critical infrastructure security are hard to get, and in my opinion, rightly so. “That said, we can see many trends in the industry to prepare telecoms to not only be more secure on its own but to be in a good position to secure infrastructure for others. Some things are as simple as the collaborative work in the MEF, on secure transport services — or the transport service in security or considered as one. Similarly, the managed services, with security at their core, that many leading telcos are offering to their enterprise clients, can be applied to protecting public and shared infrastructure as well,” he added.
“One thing we believe they must change is that these ‘managed’ services, which, by definition, are semi-custom, must become more standardized products,” according to Lenahan. “We say this because that is the only way telcos can afford to invest in the level of automation that will truly illuminate errors and omissions and stay ahead of the bad actors. It’s simply a matter of operating a process at scale and concentrating one’s fire, so to speak.”
The CSPs responded in various methods to address the increase in cybersecurity regulations for critical infrastructure, Elefant said. “Increase in network segmentation to protect critical infrastructure, the CSPs designed their networks in a way they can segment their network based on the type of service they need to deliver. Applying more protection capabilities at the edge of the network to protect the network from threats that may come from the access side, in addition to more traditional protection methods they apply on the network core,” he added.
Elefant also suggested adding more secure communication channels, like segmentation and encryption for critical elements, such as the control plane, and adding more monitoring tools to identify security risks in real time. “These initiatives help CSPs to identify security threats in real-time and apply faster response and mitigation, leveraging the new control points, mainly at the edge of the network,” he concluded.
References:
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_se/research/22/b/the-telecoms-cyber-threat-landscape-in-2021.html
Cybersecurity to be a top priority for telcos in 2023
IEEE/SCU SoE Virtual Event: May 26, 2022- Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G), IoT, and Cloud Resident Data Centers
IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond
This ITU-R recommendation in progress will be the main focus of next week’s ITU-R WP5D meeting #43 in Geneva. It defines the framework and overall objectives for the development of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) for 2030 and beyond. There are contributions related to this recommendation from: Apple, Nokia, Ericsson, Wireless World Research Forum, Motorola Mobility, Orange, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Finland, Germany, GSOA, China, Qualcomm, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Brazil, Samsung, ZTE, Huawei, InterDigital, Intel and India, with several being multi-company contributions.
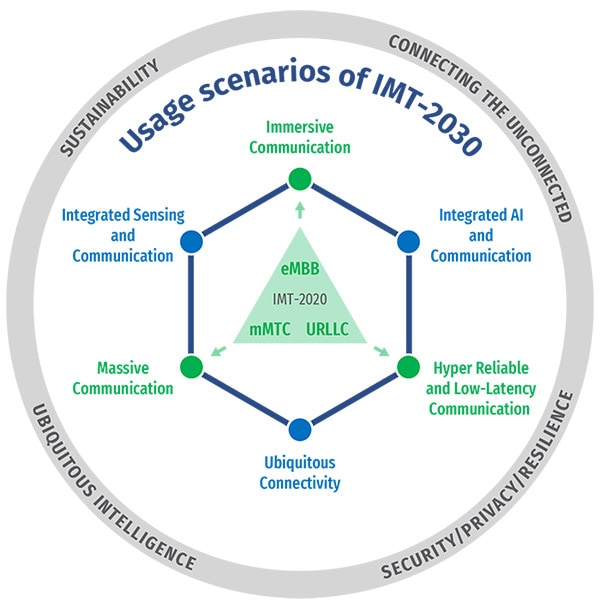
The objective is to reach a consensus on the global vision for IMT-2030 (aka 6G), including identifying the potential user application trends and emerging technology trends, defining enhanced and brand-new usage scenarios and corresponding capabilities, as well as understanding the new spectrum needs.
IMT will continue to better serve the needs of the networked society, for both developed and developing countries in the future and this Recommendation outlines how that will be accomplished. This Recommendation also intends to drive the industries and administrations for encouraging further development of IMT for 2030 and beyond.
The framework of the development of IMT for 2030 and beyond, including a broad variety of capabilities associated with envisaged usage scenarios, is described in detail in this Recommendation.
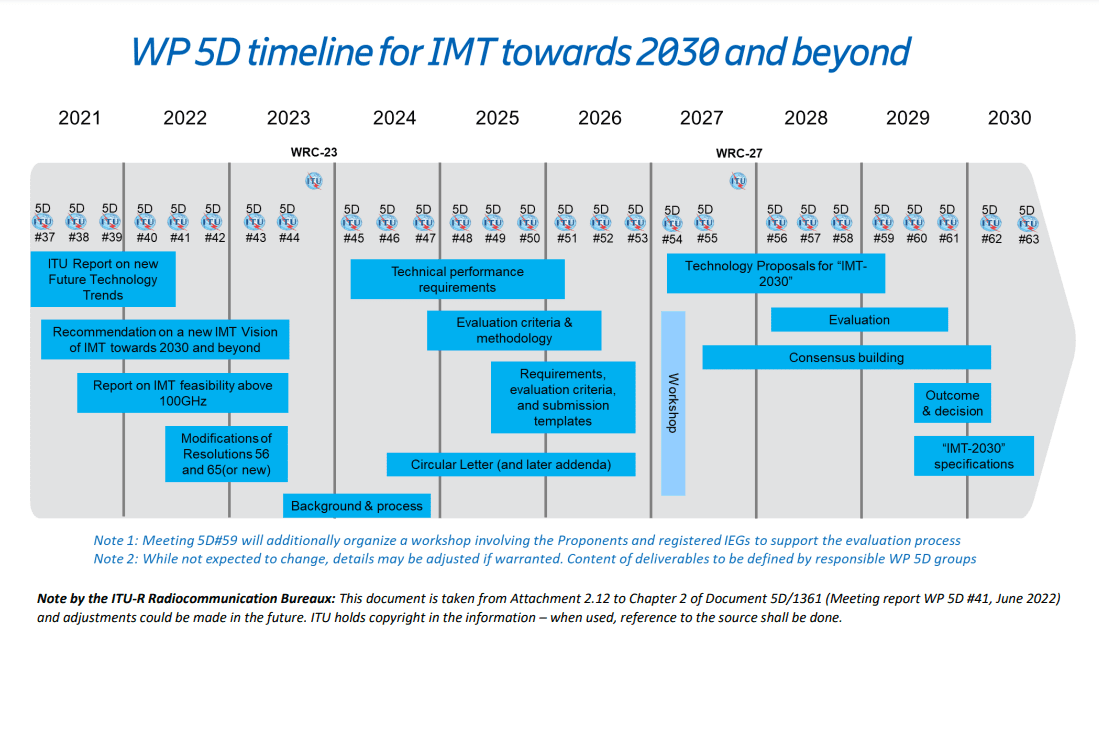
In June 2022, ITU-R decided on the overall timeline for 6G with three major stages:
- Stage 1 – vision definition to be completed in June 2023 before the World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 (WRC-23),
- Stage 2 – requirements and evaluation methodology to be completed in 2026, and
- Stage 3 – specifications to be completed in 2030. The 3-stage timeline and the tasks for each stage are summarized in Figure below.
This draft Recommendation defines a [potential] framework and overall objectives for the development of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) for 2030 and beyond. IMT will continue to better serve the needs of the [networked] society, for both developed and developing countries in the future and this [Recommendation/document] outlines how [possibly] that could be accomplished. This [Recommendation/document] also intends to encourage further development of IMT-2030. In this [Recommendation/document], the [potential] framework of the development of IMT-2030, including a broad variety of capabilities associated with [some possible] envisaged usage scenarios[, and those yet to be developed and] described in detail. Furthermore, this [Recommendation/document] addresses the objectives for the development of IMT-2030, which includes further enhancement and evolution of existing IMT and the development of IMT-2030.
It should be noted that this Recommendation is defined considering the development of IMT to date based on Recommendation ITU-R M.2083 (approved in September 2015).
Technology Trends:
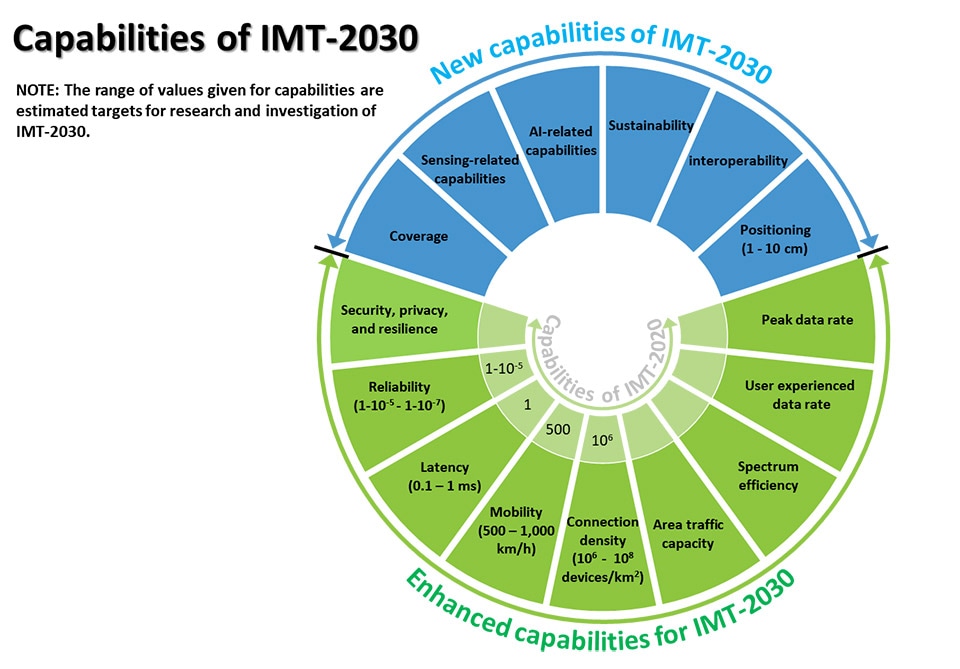
Report ITU-R M.2516 provides a broad view of future technical aspects of terrestrial IMT systems considering the timeframe up to 2030 and beyond, characterized with respect to key emerging services, applications trends, and relevant driving factors. It comprises a toolbox of technological enablers for terrestrial IMT systems, including the evolution of IMT through advances in technology, and their deployment. In the following sections a brief overview of emerging technology trends, technologies to enhance the radio interface, and technologies to enhance the radio network are presented.
An important breakthrough in 3GPP Rel-17, Technical Specifications for Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) were established & defined for satellite direct access to device for both 5G and IoT services. This development reflects a trend that satellite & space technologies can offer many benefits for development & operation of future IMT-2030 networks, to enable 5G & 6G available everywhere, accessible to enterprises and citizens across the globe.
IMT-2030 will consider an AI-native new air interface that refers to the use of AI to enhance radio interface performance such as symbol detection/decoding, channel estimation etc. An AI-native radio network will enable automated and intelligent networking services such as intelligent data perception, supply of on-demand capability etc. Radio network to support AI services is the design of IMT technologies to serve various AI applications, and the proposed directions include on-demand uplink/sidelink-centric, deep edge and distributed machine learning. The integration of sensing and communication functions in future wireless systems will provide beyond-communication capabilities by utilizing wireless communication systems more effectively resulting in mutual benefit to both functions. Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems will also enable innovative services and applications such as intelligent transportation, gesture and sign language recognition, automatic security, healthcare, air quality monitoring, and solutions with higher degree of accuracy. Combined with technologies such as AI, network cooperation and multi-nodes cooperative sensing, the ISAC system will lead to benefits in enhanced mutual performance, overall cost, size and power consumption of the whole system.
Computing services and data services are expected to become an integral component of the future IMT system. Emerging technology trends include processing data at the network edge close to the data source for real-time response, low data transport costs, energy efficiency and privacy protection, as well as scaling out device computing capability for advanced application computing workloads.
Device-to-device (D2D) wireless communication with extremely high throughput, ultra-accuracy positioning and low latency will be an important communication paradigm for the future IMT. Technologies such as THz technology, ultra-accuracy sidelink positioning and enhance terminal power reduction technology can be considered to satisfy requirements of new applications.
Energy efficiency and low power consumption comprises both the user device and the network’s perspectives. The promising technologies include energy harvesting, backscattering communications, on-demand access technologies, etc.
To achieve real-time communications with extremely low latency communications, two essential technology components are considered: accurate time and frequency information shared in the network and fine-grained and proactive just-in-time radio access.
There is a need to ensure security, privacy, and resilient solutions allowing for the legitimate exchange of sensitive information through network entities. Potential technologies to enhance trustworthiness include those for RAN privacy, such as distributed ledger technologies, differential privacy and federated learning, quantum technology with respect to the RAN and physical-layer security technologies.
UPDATE: https://techblog.comsoc.org/2023/07/09/draft-new-itu-r-recommendation-not-yet-approved-m-imt-framework-for-2030-and-beyond/
References:
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/Pages/wsp-imt-vision-2030-and-beyond.aspx
Excerpts of ITU-R preliminary draft new Report: FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS OF TERRESTRIAL IMT SYSTEMS TOWARDS 2030 AND BEYOND
Development of “IMT Vision for 2030 and beyond” from ITU-R WP 5D
ITU-R: Future Technology Trends for the evolution of IMT towards 2030 and beyond (including 6G)
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
ITU-R WP5D: Studies on technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz
https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-M.2083 (Sept 2015)
Canalys: Cloud marketplace sales to be > $45 billion by 2025
Canalys now expects that by 2025, cloud marketplaces will grow to more than $45 billion, representing an 84% CAGR. That was one of the market research firm’s predictions for 2023 and beyond (see chart below).
Cloud marketplaces [1.] are accelerating as a route to market for technology, led by hyperscale cloud vendors such as Alibaba, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Google and Salesforce, which are pouring billions of development dollars into the sector.
Note 1. A cloud marketplace is an online storefront operated by a cloud service provider. A cloud marketplace provides customers with access to software applications and services that are built on, integrate with or complement the cloud service provider’s offerings. A marketplace typically provides customers with native cloud applications and approved apps created by third-party developers. Applications from third-party developers not only help the cloud provider fill niche gaps in its portfolio and meet the needs of more customers, but they also provide the customer with peace of mind by knowing that all purchases from the vendor’s marketplace will integrate with each other smoothly.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“The marketplace route to market is on fire and cannot be ignored by any channel leader,” said Canalys Chief Analyst, Jay McBain. “Marketplaces grew more in the first three months of the pandemic than in the previous decade and have just kept growing,” he added.
“We under-called it,” explained Steven Kiernan, vice president at Canalys. “Cloud marketplaces are accelerating at such a dizzying speed that we’ve doubled our pre-pandemic forecast.
Some software vendors that are active on marketplaces, in particular cybersecurity vendors, are publicly reporting as much as 600% year-on-year growth via this channel, according to McBain.
In addition, the hyperscalers are now reporting growing numbers of billion-dollar customer commitments through enterprise cloud consumption credits, which cover more than just software.
The large cloud marketplaces have lowered fees from upwards of 20% down to 3%, enabling vendors to fund multi-partner offers inside the transaction.
Private equity is funding billions more into marketplace development firms such as AppDirect, Mirakl, Vendasta and CloudBlue to enable hundreds of niche marketplaces across different buyers, industries, geographies, customer segments, product areas and business models.

Canalys Chief Analyst, Alastair Edwards:
“The rise of this route to market represents a threat to both resellers and two-tier distribution. But as more complex technologies are consumed via marketplaces, end customers are also turning to trusted partners to help them discover, procure and manage marketplace purchases. The hyperscalers are increasingly recognizing the value of channel partners, allowing them to create customized vendor offers for end-customers, and supporting the flow of channel margins through their marketplaces. Hyperscalers’ cloud marketplaces are becoming a growing force in global IT distribution as a result.”
By 2025, Canalys conservatively forecasts that almost a third of marketplace procurement will be done via channel partners on behalf of their end customers.
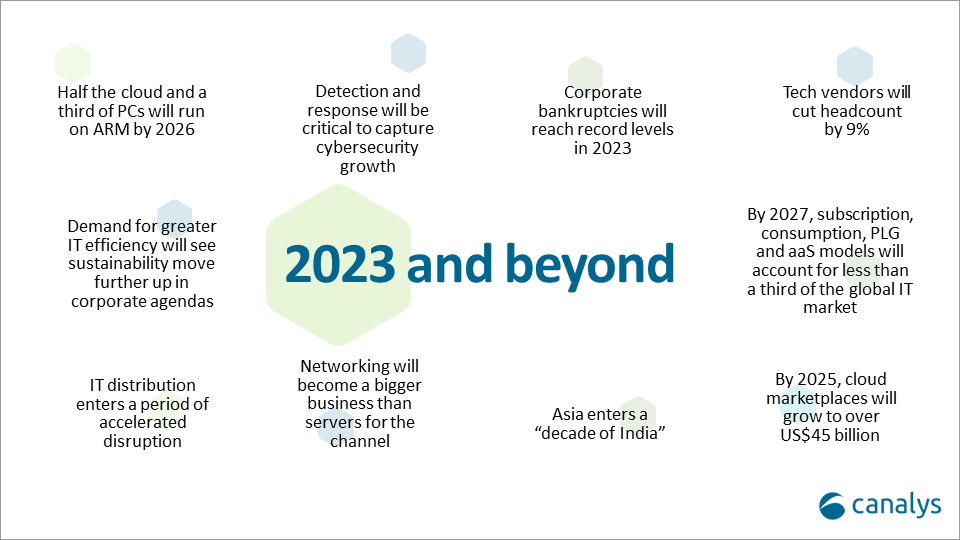
Canalys key predictions for 2023 and beyond:
About Canalys:
Canalys is an independent analyst company that strives to guide clients on the future of the technology industry and to think beyond the business models of the past. We deliver smart market insights to IT, channel and service provider professionals around the world. We stake our reputation on the quality of our data, our innovative use of technology and our high level of customer service.
References:
https://canalys.com/newsroom/cloud-marketplace-forecast-2023
https://www.canalys.com/resources/Canalys-outlook-2023-predictions-for-the-technology-industry
https://www.techtarget.com/searchitchannel/definition/cloud-marketplace
Canalys: Global cloud services spending +33% in Q2 2022 to $62.3B
AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud account for 62% – 66% of cloud spending in 1Q-2022
IDC: Cloud Infrastructure Spending +13.5% YoY in 4Q-2021 to $21.1 billion; Forecast CAGR of 12.6% from 2021-2026