5G Use Cases
Highlights of Nokia’s Smart Factory in Oulu, Finland for 5G and 6G innovation
Nokia has opened a Smart Factory in Oulu, Finland, for 5G/6G design, manufacturing, and testing, integrating AI technologies and Industry 4.0 applications. It brings ~3,000 staff under one roof and is positioned as Europe’s flagship site for radio access (RAN) innovation.
The Oulu campus will initially focus on 5G, including: Standardization, System-on Chips as well as 5G radio hardware and software and patents. Oulu Factory, part of the new campus, will target New Production Introduction for Nokia’s 5G radio and baseband products. The new campus strengthens Oulu’s ecosystem as a global testbed for resilient and secure networks for both civilian and defense applications.
At Oulu “Home of Radio” campus, Nokia’s research and innovation underpins high quality, tested world class products readymade for customers across markets. Nokia’s experts will continue to foster innovation, from Massive MIMO radios like Osprey and Habrok to next-generation 6G solutions, creating secure, high-performance, future-proof connectivity.
Sustainability is integral to the facility. Renewable energy is used throughout the site, with additional energy used to heat 20,000 households in Oulu. The on-site energy station is one of the world’s largest CO2-based district heating and cooling plants.
Active 6G proof-of-concept trials will be tested using ~7 GHz and challenging propagation scenarios.
“Our teams in Oulu are shaping the future of 5G and 6G developing our most advanced radio networks. Oulu has a unique ecosystem that integrates Nokia’s R&D and smart manufacturing with an ecosystem of partners – including universities, start-ups and NATO’s DIANA test center. Oulu embodies our culture of innovation and the new campus will be essential to advancing connectivity necessary to power the AI supercycle,” said Justin Hotard, President and CEO of Nokia

Nokia Oulu Facts:
- Around 3,000 employees and 40 nationalities working on the campus.
- Oulu campus covers the entire product lifecycle of a product, from R&D to manufacturing and testing of the products.
- Footprint of the building is overall 55,000 square metres, including manufacturing, R&D and office space.
- Green campus with all energy purchased green and all surplus energy generated fed back into the district heating system and used to heat 20,000 local households.
- The campus boasts 100% waste utilization rate and 99% avoidance in CO2 emissions.
- Construction started in the second half of 2022, with the first employees moving into the facility in the first half of this year.
- YIT constructed the site and Arkkitehtitoimisto ALA were the architects.
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/analysis/behind-the-scenes-at-nokias-new-home-of-radio/
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Nokia’s Bell Labs to use adapted 4G and 5G access technologies for Indian space missions
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison and Nokia use AI to reduce energy demand and emissions
Verizon partners with Nokia to deploy large private 5G network in the UK
Nokia selects Intel’s Justin Hotard as new CEO to increase growth in IP networking and data center connections
Nokia sees new types of 6G connected devices facilitated by a “3 layer technology stack”
Nokia and Eolo deploy 5G SA mmWave “Cloud RAN” network
Ericsson on 5G use cases: remote surgery, augmented and virtual reality with AI agent all depend on 3GPP URLLC specs
5G for Remote Surgery:
This year, surgeons in Florida working with Ericsson, were able to operate on remote patients in Dubai and Shanghai, using 5G technology, according to Mischa Dohler, Ericsson vice president-emerging technologies.
A hospital in China used a 5G-enabled robot to perform spinal surgery on patients, and doctors used VR headsets to livestream the operation. The robot implanted over 62 pedicle screws in the patients’ spinal cord. Here’s a pic of that:
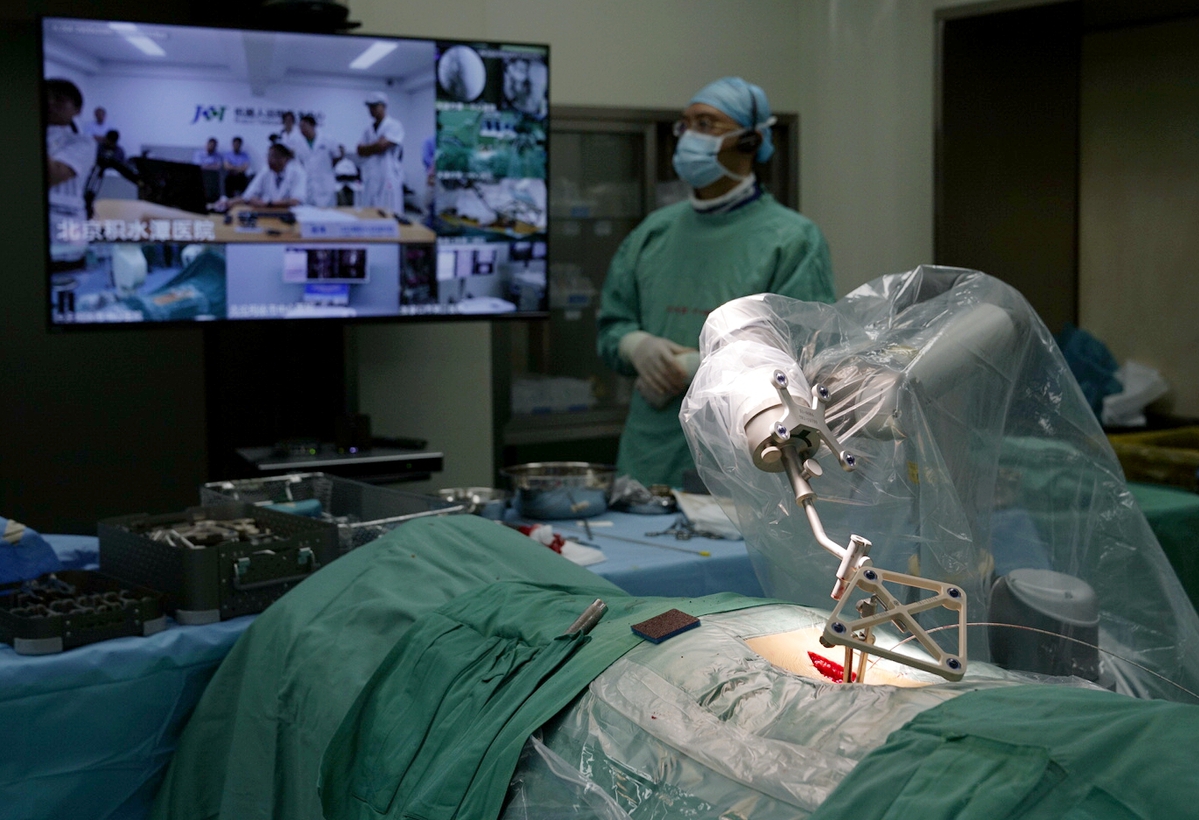
Photo by Wang Fei/For China Daily
Dohler said he’s working with the White House, FCC, NTIA, Food and Drug Administration and others to make remote surgery “a reality.” More widespread use of the technology won’t happen unless smaller carriers also get involved. We will have not only humans using your networks, but also machines more and more,” Dohler added.
Gartner’s market research underscores the importance of 5G SA, predicting that by 2025, it will be the foundation for the majority of applications demanding sub-10 millisecond latency. This transition is not merely a technical upgrade but a strategic enabler for industries poised to benefit from real-time data processing and decision-making. However, the ultra low latency depends on two 3GPP Release 16 specs – 1.] 5GNR enhancements for URLLC in the RAN and 2.]URLLC in the 5G SA core network– being completed, performance tested and implemented. That has not happened yet and without it there can’t be any 5G URLLC use cases like remote surgery!
Real-time remote surgeries, once a concept of futuristic medicine, are becoming a reality. The ability to perform surgical procedures from thousands of miles away, with real-time response and precision, could revolutionize healthcare accessibility and outcomes. For example, a pilot project involving 5G SA-enabled remote surgery successfully demonstrated how surgeons could operate with millisecond-level precision, mitigating geographical barriers to specialized medical care.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Ericsson’s Dohler predicted growing use of augmented and virtual reality and AI “agents,” computer programs capable of performing tasks autonomously, which people will use as part of their daily lives. New technology will require networks that can handle increased traffic, he said. New data traffic patterns “will hit you at some point this decade,” he said. “You will need to do some bold moves.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2024/3/cutting-the-cord-lifesaving-telesurgery-in-the-age-of-5g
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201908/29/WS5d670e17a310cf3e355686fa.html
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/dawn-new-era-navigating-shift-from-5g-nsa-sa-tayroni-fkvre/
IBM: 5G use cases that are transforming the world (really ?)
For many years, this author has been very skeptical about the commercial success of highly touted 5G use cases. That’s mainly because the 3GPP 5G specs and ITU-R M.2150 5G RIT/SRIT standard did not (and still do not) meet the ITU-R M.2410 minimum performance requirements for the URLLC use case for either ultra high reliability or ultra low latency.
Another reason for our skepticism is that “real 5G,” which provides 3GPP specified 5G features (like network slicing, edge computing/MEC, and 5G Security), requires a 5G SA core network, which relatively few wireless network operators have deployed.
Nonetheless, IBM has published an article citing 5G use cases that are transforming the world. Here they are:
Autonomous vehicles
From taxi cabs to drones and beyond, 5G technology underpins most of the next-generation capabilities in autonomous vehicles. Until the 5G cellular standard came along, fully autonomous vehicles were a bit of a pipe dream due to the data transmission limitations of 3G and 4G technology. Now, 5G’s lightning-fast connection speeds have made transport systems for cars, trains and more much faster than previous generations, transforming the way systems and devices connect, communicate and collaborate.
Smart factories
5G, along with AI and ML, is poised to help factories become not only smarter but more automated, efficient and resilient. Today, many mundane but necessary tasks associated with equipment repair and optimization are being turned over to machines thanks to 5G connectivity paired with AI and ML capabilities. This is one area where 5G is expected to be highly disruptive, impacting everything from fuel economy to the design of equipment lifecycles and how goods arrive at our homes.
For example, on a busy factory floor, drones and cameras connected to smart devices utilizing the IoT can help locate and transport something more efficiently than in the past and prevent theft. Not only is this better for the environment and consumers, but it also frees up employees to dedicate their time and energy to tasks that are more suited to their skill sets.
Smart cities
The idea of a hyper-connected urban environment that uses 5G network speeds to spur innovation in areas like law enforcement, waste disposal and disaster mitigation is fast becoming a reality. Some cities already use 5G-enabled sensors to track traffic patterns in real time and adjust signals, helping guide the flow of traffic, minimize congestion and improve air quality.
In another example, 5G power grids monitor supply and demand across heavily populated areas and deploy AI and ML applications to “learn” what times energy is in high or low demand. This process has been shown to significantly impact energy conservation and waste, potentially reducing carbon emissions and helping cities reach sustainability goals.
Smart healthcare
Hospitals, doctors and the healthcare industry as a whole already benefit from the speed and reliability of 5G networks every day. One example is the area of remote surgery that uses robotics and a high-definition live stream connected to the internet via a 5G network. Another is the field of mobile health, where 5G gives medical workers in the field quick access to patient data and medical history, enabling them to make smarter decisions, faster, and potentially save lives.
Lastly, as we saw during the pandemic, contact tracing and the mapping of outbreaks are critical to keeping populations safe. 5G’s ability to deliver of volumes of data swiftly and securely allows experts to make more informed decisions that have ramifications for everyone.
Better employee experiences
5G paired with new technological capabilities won’t just result in the automation of employee tasks, it will dramatically improve them and the overall employee experience. Take virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), for example. VR (digital environments that shut out the real world) and AR (digital content that augments the real world) are already used by stockroom employees, transportation drivers and many others. These employees rely on wearables connected to a 5G network capable of high-speed data transfer rates that improve several key capabilities, including the following:
- Live views: 5G connectivity provides live, real-time views of equipment, events and even people. One way in which this feature is being used in professional sports is to allow broadcasters to remotely call a sporting event from outside the stadium where the event is taking place.
- Digital overlays: IoT applications in a warehouse or industrial setting allow workers equipped with smart glasses (or even just a smartphone) to obtain real-time insights from an application, including repair instructions or the name and location of a spare part.
- Drone inspections: Right now, one of the leading causes of employee injury is inspection of equipment or project sites in remote and potentially dangerous areas. Drones, connected via 5G networks, can safely monitor equipment and project sites and even take readings from hard-to-reach gauges.
Edge computing
Edge computing, a computing framework that allows computations to be done closer to data sources, is fast becoming the standard for enterprises. According to this Gartner white paper (link resides outside ibm.com), by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed at the edge (compared to only 10% today). This shift saves businesses time and money and enables better control over large volumes of data. It would be impossible without the new speed standards generated by 5G technology.
Ultra-reliable edge computing and 5G enable the enterprise to achieve faster transmission speeds, increased control and greater security over massive volumes of data. Together, these twin technologies will help reduce latency while increasing speed, reliability and bandwidth, resulting in faster, more comprehensive data analysis and insights for businesses everywhere.
5G solutions with IBM Cloud Satellite
5G presents big opportunities for the enterprise, but first, you need a platform that can handle its speed. IBM Cloud Satellite lets you deploy and run apps consistently across on-premises, edge computing and public cloud environments on a 5G network. And it’s all enabled by secure and auditable communications within the IBM Cloud. The IBM Cloud Satellite-managed distributed cloud solution delivers cloud services, APIs, access policies, security controls and compliance.
References:
https://www.ibm.com/products/satellite
Big 5 Event: wireless connectivity use cases for healthcare, network slicing, security and private networks
Qualcomm Introduces the World’s First “5G NR-Light” Modem-RF System for new 5G use cases and apps
MoffettNathanson: 5G use cases and revenue streams have not yet materialized
CELLSMART: 5G upload speeds are insufficient for industrial/enterprise applications
BofA on 5G Use Cases and Industry Vertical Applications
Big 5 Event: wireless connectivity use cases for healthcare, network slicing, security and private networks
Emerging use cases for wireless telecommunications technology was discussed at the Big 5G event in Austin, TX last week in a panel session titled, “Future connectivity use cases and the Holy Grail: Private networks, metaverse, 6G and beyond.” The questions addressed included:
- Who is monetizing private networks and what are we learning from their experiences?
- Should telcos move past targeting only large enterprise customers for 5G services?
- When will the metaverse take off?
- How are telcos gearing up for 6G and what are the expectations?
Jodi Baxter, vice president for 5G and IoT connectivity at Telus, described the numerous emerging applications of 5G in healthcare. One example is a connected ambulance project carried out with Alberta Health Services, where, thanks to 5G, doctors can remotely issue authorizations necessary for stroke medication, which needs to be administered within a narrow time window.
Some of the applications developed for the healthcare sector can also be included in telcos’ offerings to corporate customers. Baxter said Telus has included remote doctor and nurse consultations in 5G bundles for small businesses, which can help their staff retention rates. Healthcare companies are also looking at more specific applications, with Baxter citing the example of a healthcare company that would wish to track hip and knee replacements with 5G.
While sustainability is often seen as an unprofitable endeavor, Baxter argued technology can help customers see a return on investment. One of Telus’s projects in this area uses drones and 5G for reforestation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Omdia’s research has shown that about a fifth of midsized to large enterprises “want to invest in 5G network slicing in the next two years, but most people cannot find a commercial offer,” said Camille Mendler, chief analyst of enterprise services at Omdia. “[It’s] not there yet, which is a problem, right?” she added. Note that 5G network slicing requires a 5G SA core network, which most 5G service providers have yet to deploy.
Baxter noted that network slicing will be a game changer for security and transportation of critical data. The panel pointed to autonomous vehicles as another potential application that will require its own slice. She also said slicing will be important for ensuring applications from private 5G networks also have a macro capability.
Lori Thomas, senior vice president for strategic engagement and transformation at MetTel, pointed out that a lot of government agencies are currently looking to bring specific functionalities from the private network onto the public network, and make them accessible in edge devices such as laptops and tablets.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
William Britton, vice president for information technology and CIO at California Polytechnic State University, said it is not always easy to figure out how products offered by telecom companies apply to specific use cases. The university has been told to “go elsewhere” by providers when it has approached them about possible 5G applications, as the solutions on offer did not meet requirements, he said.
Speaking about the particular needs of his university, he highlighted the significant demand for bandwidth during limited events, such as course registration, as well as ad hoc scenarios like high data throughput during online gaming events.
A big concern for universities in general is cybersecurity. Britton points out that the education sector has become a massive target for cyberattacks, such as malware and ransomware. Indeed, research suggests that attacks on educational organizations grew by 44% in 2022, while data from endpoint protection firm Emsisoft suggests that the number of individual schools impacted by ransomware attacks also grew.
Security is a major priority for organizations everywhere, not just in the education sector. Thomas points to IoT, where vast amounts of data travel at high speeds, which is particularly attractive for bad actors. Once 5G can be coupled with blockchain, she noted, data security will improve.
One way to look at specific use cases is through innovation labs, with Thomas saying in the short term these can accelerate the time to revenue. She pointed to MetTel’s partnership with SpaceX and VMware, which saw the latter company’s software-defined wide area network deployed over Starlink to bring high-bandwidth communications to remote areas.
Thomas also said demand for more bandwidth was one of the key trends in the public sector. Customers are, according to her, looking at technologies including 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and satellites to secure it.
A lot of innovation has focused on private networks, but the “real money” lies outside of them, said Mendler. No further details were provided.
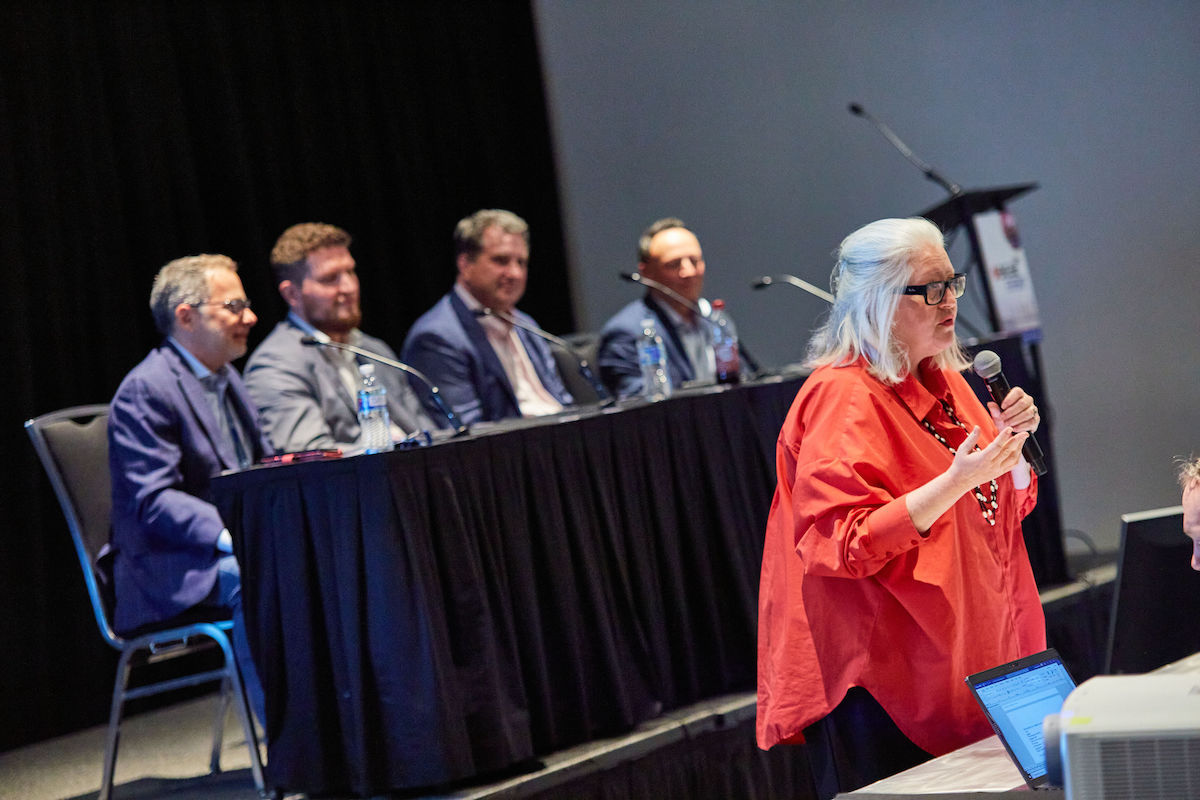

Omdia’s Camille Mendler says companies cannot find commercial network slicing.
Source: JLeitner Photography
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
MoffettNathanson: 5G use cases and revenue streams have not yet materialized
Status of 5G Use Cases:
- Multi-access Edge Compute (MEC) remains relatively intangible, and is likely to be fiercely competitive (hyper-scalers/cloud services, and even tower operators, likely better positioned).
- IoT similarly has not demonstrated material revenue upside potential for carriers.
- Private 5G networks may not include carriers at all; and when they do, it is unclear that carriers will achieve attractive revenue splits with the (many) other participants in the value chain (systems integrators, software providers, hardware providers, security providers, hyperscalers).
- Fixed wireless access has emerged as a “consolation prize,” with incremental revenue but at very low revenue/bit, potentially significantly taxing network resources in a way other 5G applications do not.
Editor’s Notes:
The URLLC use case envisioned by the ITU does not exist because the 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN spec has still n not been completed and the ITU-R M.2150 recommendation uses 3GPP Release 15 URLLC which does not meet the ITU-R M.2410 performance requirements.
Also, the true 5G features, such as network slicing, automation/virtualization and security, can only be realized via a 5G SA core network for which there are relatively few.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telco incumbents always believe the answer is to “move up the (protocol) stack”… but they face much better-equipped competitors in the cloud service providers (Amazon, Microsoft, Google etc.).
Summary and Conclusions:
In our view, the broadband slowdown appears to owe more to a broad market deceleration than to significant shifts in market share…
• Cable broadband churn is at all-time lows
• TelCo broadband gains have not accelerated
• A significant portion of FWA appears to be market expansion
…so pricing and capital intensity do not appear to be at significant risk.
Footprint expansion initiatives are likely sufficient to keep broadband net add growth at least narrowly positive.
Wireless is now Cable’s Act III
Reference:
Moffett Nathanson Oct 2022 Slide Deck (subscribers only)
CELLSMART: 5G upload speeds are insufficient for industrial/enterprise applications
Research conducted by CELLSMART, a division of French managed services provider SmartCIC, has found that 5G upload speeds are in many cases insufficient to support data transfer for enterprise applications. The Global Cellular Performance Survey was based on independent field tests conducted by 2,536 telecoms network engineers in 51 countries to capture network performance data and then analyzed by the CELLSMART team.
The CELLSMART Global Cellular Performance Survey collects data from telecoms network engineers working in the field to provide an up-to-date snap shot of actual performance across cellular technologies. It is using the data it collects in its planning, network selection and service development and monitoring for fixed wireless enterprise customers.
Top 5 Metro Markets – 5G Average Download Speed
• Cannes (France)
• Munich (Germany)
• Nashville (US)
• Oslo (Norway)
• Singapore
“The research shows how MNOs have prioritized 5G download speeds in their initial rollouts and now there’s an opportunity to focus on enterprise demand for rapid upstream data transfer. 5G networks are showing upload speeds that are 13% of their download speeds while 4G has a balanced download/upload symmetry with 36%. Based on the research sample, we saw 5G delivering higher latency than 4G in some cases. This may be due to a number of the 5G tests being run on low-band networks. Where results have been taken in areas with mmWave, there are dramatically different results including downloads in excess of 800mbps, uploads in excess of 250mbps and latencies of sub 10ms,” said Toby Forman, CEO at SmartCIC.

For capturing network performance data, speed tests were run by 2,536 telecoms network engineers across 51 countries in 331 unique locations globally. Each engineer conducted the tests independently in the field and submitted result anonymously between March 25, 2022 and May 6, 2022. Data samples were collected from Africa, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Europe. The CELLSMART team did the data analysis.
Top 5 Mobile Network Operators – Maximum Download Speeds (All Technologies)
• du (UAE)
• Telia (Sweden)
• Deutsche Telekom (Germany)
• EE (UK)
• Singtel (Singapore)
However, upload speeds were on average only 31.27 Mbps – just 55% better than the 4G global average.
“We went out to our global network of 25,000 engineers and asked them to log network performance wherever they were operating. Over time, as we see more results added to our database and we’ll be able to provide an accurate and evolving snapshot of how cellular technologies are performing in the field. This initial cut of data is just the start of the process. As we begin to see greater density of results globally we will those into insights for our customers and the broader market,” said Forman. “We did this because this information simply didn’t exist on a global scale and we believe the market needs intelligent cellular solutions,” he added.
References:
Qualcomm unveils 5G and AI-Enabled Drone Platform
Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. is showing off what is says is the world’s first drone platform and reference design to offer both 5G and AI-capabilities, the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform.
The company says the drone reference design helps accelerate development for commercial, enterprise, and industrial drones, and unleashes innovative possibilities for industries looking to adopt drone solutions and realize the benefits of the intelligent edge. 5G connectivity — including mmWave and sub-6 GHz bands — and WiFi 6. The chip-maker says the networking tech can help support drone-to-drone communications and drone swarms. Both use cases are being explored across industries, from delivering and transporting goods to aerial light displays to military warfare.
The drone model below is includes an embedded Qualcomm® QRB5165 processor and a Qualcomm Spectra 480 Image Signal Processor that can capture 200 megapixel photos and 8K video at 30 FPS. In addition, the drone can record in 4K at 120 FPS with support for HDR.

Image Credit: Qualcomm
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The company says that the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform brings cutting-edge capabilities to the drone industry by condensing multiple complex technologies into one tightly integrated drone system to support evolving applications and new use cases in sectors including film and entertainment, security and emergency response, delivery, defense, inspection, and mapping.
At its core, the Flight RB5 5G platform uses the QRB5165 processor and Kryo 585 CPU and Adreno 650 GPU, based on the Snapdragon 865 CPU. The AI enhancements come by way of the Hexagon Tensor Accelerator in the Hexagon 698 DSP. Third-parties that use the platform will also get access to a trio of software development kits for neural processing, computer vision and multimedia applications.
The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform’s high-performance and heterogeneous computing at ultra-low power consumption provides power efficient inferencing at the edge for AI and Machine Learning (ML) enabling fully autonomous drones. Breakthrough camera capabilities deliver premium image capabilities and performance. With 5G and Wi-Fi 6 connectivity, this platform enhances critical flying abilities beyond visual line-of-sight (BVLOS) to support safer, more reliable flight. In addition, safety controls alone can no longer assure industrial and commercial drone safety, especially when scaling to Beyond Visual Line of Sight operations. The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform is equipped with a Qualcomm® Secure Processing Unit to support modern drone demands for cybersecurity protections as a key enabler of data-protection and safety requirements.
Qualcomm Technologies is working with Verizon to complete network testing of the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform for the Verizon 5G network, and expects the platform, which is 5G mmWave capable, will be offered via the Verizon Thingspace Marketplace.
The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G drone reference design is available for pre-sale now through ModalAI. The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G development kit is expected to be available in Q4 of 2021. For more information on the platform, including technical features, please visit the product details page here.
Backgrounder:
Qualcomm first got involved in drones in 2015, then ventured into robotics in 2019. Last year it combined the two technologies in its RB5 platform. Chad Sweet’s ModalAI, which in 2018 spun out of Qualcomm, will manufacture and distribute the drone platform, and says the first development kits will ship in the last three months of this year.
Qualcomm, which already commands a huge lead in the 4G/5G smartphone industry, is hoping its Snapdragon chipsets can be the silicon that pushes 5G into a wider range of other devices. The company has made a series of drone platforms since its first, Qualcomm Flight, in 2018.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Global carriers and IoT ecosystem leaders showcase validation and support for Qualcomm Technologies latest drone solution:
Asia Pacific Telecom
“As the leader in innovative telecom services in Taiwan, Asia Pacific Telecom Co., Ltd (APT) is excited to work with one of our most important strategic collaborators, Qualcomm Technologies on the support of 5G and AI-enabled drones. APT provides 5G and application integration services to advance the performance of robots and drones in different perspectives. We truly believe that 5G capabilities built into the platform will enable new autonomous drone experiences,” said Mr. Shang-Chen Kao, chief technology officer, network and technology center, Asia Pacific Telecom.
AT&T
“Many of the anticipated benefits of drones will be further accelerated and strengthened with 5G, including delivery, inspections, and search and rescue, which will require a highly secure and reliable connection. We are excited to see Qualcomm Technologies continue to innovate with their latest announcement on a platform for 5G drones,” said Kevin Hetrick, vice-president, access construction and engineering, AT&T.
China Unicom
“The 5G-enabled digital era has brought wider boundaries for every industry and China Unicom is committed to pushing the boundaries of the traditional communications ecosystem and working together with the industrial chain to realize mutual complementarity. As one of our important collaborators, Qualcomm Technologies has been working with China Unicom to drive integration of 5G and IoT into vertical use cases and provide products such as 5G modules and 5G industrial gateways for automation and robotics use cases, with focused areas including industrial equipment, iron and steel manufacturing, transportation and port, mining and energy, and healthcare,” said Li Kai, chief product officer, IoT division, China Unicom Digital Technology Company Limited. “We believe the announcement of the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform will benefit more use cases. China Unicom is looking forward to deepening collaborations with Qualcomm Technologies in IoT and jointly creating a new blueprint for 5G in the future.”
Everguard.ai
“Use of drones to capture imagery for construction site topographic mapping, construction progress tracking, security surveillance and equipment tracking in combination with IoT sensors that are deployed on construction sites are revolutionizing how construction projects are delivered! 5G enabled data from drones can be leveraged to unleash the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms yielding massive improvements in the safety, efficiency and productivity of construction projects,” said Sandeep Pandya, chief executive officer, Everguard.ai.
FlightOps
“By working with Qualcomm Technologies, we have seamlessly installed the FlightOps onboard software on the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform, allowing for unparalleled performance, compute power, low energy footprint, high quality video processing and high speed 5G connectivity to achieve high levels of autonomy and mission scalability,” said Shay Levy, chief executive officer, FlightOps.
Juganu
“Qualcomm Technologies has been a leader of breakthrough technologies for years and their announcement of the world’s first 5G, AI-enabled drone platform – the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform – is the latest example of their continued innovation. We at Juganu are excited to work with Qualcomm Technologies as they continue to push the boundaries of technology and look forward to using these technologies to innovate across our own smart technology quickly, safely and securely,” said chief strategy officer, Eran Efrati, Juganu.
KT Corporation
“KT is excited to see Qualcomm Technologies bringing cutting-edge 5G drone technology based on the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform. We’re leveraging our deep expertise in translating diverse services and use cases into reality across vertical industries,” said Byungkyun Kim, head of device business unit, KT. “We expect Qualcomm Technologies will expand the 5G–based drone industry and pave a way to the development of the drones based on the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform.”
LG Uplus
“Qualcomm Technologies’ launch of the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform has great significance to the drone ecosystem as the integration of drones with 5G communication and AI technology can maximize drone usability and convenience,” said Youngseo Jeon, B2B service development director, LG Uplus. “We are expecting U+ smart drone service which contains telecommunication, control, and video will combine with the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform and play a key role across diverse drone industry fields.”
MITRE
“The reliability, availability, and low latency of 5G enable previously unavailable command and control of UAS, solving critical UAS safety considerations and enabling operation beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS). With this connectivity and the added benefit of moving intelligence to the edge, we are now beginning to realize real solutions with significant impact on business and our everyday lives,” said Rakesh Kushwaha, managing director, MITRE Engenuity Open Generation. “The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform brings advanced intelligence to autonomous decisions, enabling detect and avoid (DAA) even beyond network connectivity. It is a game changer. We are looking forward to having Qualcomm Technologies participate in the MITRE Engenuity Open Generation.”
ModalAI
“ModalAI accelerates autonomy by providing innovators with robot and drone perception and communications systems. Since our founding, we have committed to enabling aerial and ground robot manufacturers with capabilities that can excel a broad set of industries. We are thrilled to collaborate with Qualcomm Technologies to bring the first purpose-built 5G drone that opens cutting-edge computing to a broad set of integrators who can build their applications that take advantage of the coming aerial 5G wave,” said Chad Sweet, chief executive officer, co-founder, ModalAI.
Taiwan Mobile
“We are glad to see Qualcomm Technologies innovate on the 5G drone application continuously, including enterprise-related solutions. Taiwan Mobile offers “real 5G” services with safer and faster advantages to support creative development, and get together with Open Possible,” said Mr. C. H. Wu, vice president, chief enterprise business officer, Taiwan Mobile.
TDK
“TDK is extremely excited to join with Qualcomm Technologies on such a state-of-the-art drone platform,” said Peter Hartwell, chief technology officer, InvenSense, a TDK Group Company. “TDK has a multi-technology focus on Robotics across a robust product portfolio – much of which can be found on the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform and TDK Mezzanine platforms. Our decision to collaborate with Qualcomm Technologies to utilize breakthrough sensor technology alongside the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform, which I believe to be most innovative drone reference design in the world.”
Veea
“Many of the anticipated benefits of drones will be further accelerated and strengthened with 5G, including monitoring critical infrastructure, crowd management, and emergency response which includes detection, containment and extinguishing of wildfires, reporting on crop health, monitoring of livestock and irrigation systems at large acreage farms, and much more. The large majority of these use cases require a highly secure and reliable connection that can be more readily supported with 5G connections. We are excited to see Qualcomm Technologies continuing to push the boundaries of innovation with their latest announcement on the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform and we at Veea are looking forward to using these technologies to innovate across our deployments of hybrid edge-cloud solutions such as at large farms, wildlife parks, stadiums, smart cities, large construction sites and similar projects,” said Allen Salmasi, chief executive officer, Veea.
Verizon Skyward
“The Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform provides a robust hardware platform that can be certified for the Verizon 5G network, offering the ecosystem of drone developers a simple path to get connected. That means drones built with the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform can leverage the massive capacity of Verizon 5G Ultra-Wideband to navigate the National Airspace System in safer and more productive ways than ever before,” said Eric T. Ringer, co-founder, chief of staff, Skyward, a Verizon company.
Zyter
“Many of the anticipated benefits of drones will be further accelerated and strengthened with 5G, which provides a high bandwidth connection that is secure and reliable,” said Sanjay Govil, founder and chief executive officer, Zyter, Inc. “We are excited to begin leveraging and integrating the Qualcomm Flight RB5 5G Platform for 5G drones into our own SmartSpaces™ IoT solutions for smart campuses and cities, smart construction, and other applications.”
About Qualcomm (from the company):
Qualcomm is the world’s leading wireless technology innovator and the driving force behind the development, launch, and expansion of 5G. When we connected the phone to the internet, the mobile revolution was born. Today, our foundational technologies enable the mobile ecosystem and are found in every 3G, 4G and 5G smartphone. We bring the benefits of mobile to new industries, including automotive, the internet of things, and computing, and are leading the way to a world where everything and everyone can communicate and interact seamlessly.
Qualcomm Incorporated includes the company’s intellectual property licensing business, QTL, and the vast majority of their patent portfolio. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a subsidiary of Qualcomm Incorporated, operates, along with its subsidiaries, substantially all of our engineering, research and development functions, and substantially all of our products and services businesses, including the QCT semiconductor business.
…………………………………………………………………………………
References:
BofA on 5G Use Cases and Industry Vertical Applications
Introduction:
The 5G journey is only just beginning and the shape of its implications are barely visible, but the anticipation among industry participants is palpable. Bank of America (BofA) telecom analyst David Barden examines 5G use cases across different industry verticals. Examples span across Healthcare, Industrials, Energy and Consumer just to name a few.
While there is not a “killer app” for 5G yet, BofA expects the app economy to develop the right applications over time as 5G networking deployment and phone adoption is stimulated by the generational tech war between U.S. and China.
Long-term possibilities include doctors performing remote surgeries, flying cars, haptic bodysuits that fully immerse you in the game world, machines proactively monitoring and warning of breakdowns and predictive maintenance, automated loading at warehouses and smart grids for utility providers. Other examples are included in this excerpt from BofA’s global research report.
5G in the wild:
Over the last year, the 5G conversation has evolved from ‘What is 5G?‘ to ‘Why do we want it?‘ to ‘What do you do with 1Gbps speed?‘ What you do with that kind of speed, latency and connectivity capability is push massive amounts of information across a vast number of devices very fast. One example relevant to the drone and auto industries is the notion of ‘beyond the line of sight‘. Take an example where metro traffic cameras can collect and process sensor information from an entire city and feed it directly into your car so your car already knows there is a stopped vehicle in the middle of the road one mile ahead of you on your planned route and adjusts accordingly.
Examples are endless, and are as big as one can dream – think remote surgeries performed by doctors thousands of miles away due to the power of robotics while using 5G powered medical devices and a lightning fast network, 5G-empowered flying vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) cars, connected diapers, haptic bodysuits that fully immerse you in your game world, beyond just ‘looking‘ but also now ‘feeling‘.
While it is still tough to conceive of the killer 5G app that will drive adoption, there is no shortage of people thinking about it. Based on a recent McKinsey study (‘The 5G Era‘), companies are willing to adopt to 5G in order to enable ‘new standard‘ use cases or to comply with future connectivity standards. And these ‘new standard‘ use cases are expected to drive 5G IoT unit sales over the next decade. Below, we survey different industry verticals (from healthcare to industrials, energy to consumer) and specific use cases that may utilize this next generation of connectivity most heavily today and how they may evolve.
Sizing the IoT opportunity:
In the next few exhibits, we will look at the potential market size and economics of 5G-powered IoT technology. By comparing the IoT addressable market in various industry verticals side-by-side we found that while the Consumer IoT market would grow to be the largest IoT market vertical at about $142b in 2026, it would be growing at the slowest rate of 17%. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Market closely trails Consumer IoT as the second largest market opportunity, with a market size that is expected to reach around $123b in 2026 but growing at a faster rate of 27.2%. The industrials IoT market would be growing by far the fastest with a CAGR of 79.1%, but off of a relatively small base of just $500m in 2020.
We note that the consumer IoT market is currently the largest as the term ‘IoT‘ broadly covers a wide array of devices that range from smartphones and fitness wearables, to end-use applications such as in-car entertainment, traffic management, connected cars, home automation and more. It is the vertical that is furthest along the adoption curve in the ‘IoT space‘, thereby explaining the slower-than-peers projected growth rate. Because consumer use cases have been most widely covered in our previous reports, we focus on commercial 5G and IoT use cases in this report.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revolutionizing healthcare with 5G:
5G will play a pivotal role in shaping tomorrow‘s healthcare infrastructure. The common use cases for 5G in healthcare can be broadly bucketed into two key areas 1) providing connectivity everywhere to enable the omnipresence of telemedicine and 2) powering the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
Enabling the omnipresence of telemedicine:
The adoption of telemedicine has been accelerating due in part to the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on a market report by ReportLinker in April 2020, the telehealth market is expected to grow at a 29%+ CAGR from 2019 to 2025. Following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has transformed from a “nice-to-have“ to a necessity as traditional healthcare providers encourage patients with mild to moderate illnesses to be treated virtually rather than via in-person visits. The latest McKinsey study titled “Telehealth: A quarter-trillion-dollar post-COVID-19 reality?“ estimates that up to $250b of current US healthcare spend could be virtualized.
Based on data from FAIR Health from December of 2020, a nonprofit manages the nation‘s largest database of privately billed healthcare insurance claims, telehealth claims increased 2,980% nationally from September 2019 to September 2020, albeit from a small base (0.16% in ‘19 of total claims to 5.07% in ‘20). According to Center of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data, during the beginning stages of the pandemic last March, telehealth visits increased 154% compared to same period in 2019. CDC used data collected from the major participants in the space such as Teladoc (Ticker: TDOC), Amwell (Ticker: AMWL), MDLive and Doctor On Demand.
With accelerating adoption, a fast and reliable network that can support near real-time, HD video without congestion has become pertinent. Today‘s broadband speeds and coverage are sufficient to address the majority of the use cases within the population. Remote areas and physicians, however, will need access to reliable connections sooner rather than later. As applications and technical requirements in telemedicine grow more robust, 5G will play a critical role in enabling the need for speed and applications at the edge.
Carrier efforts:
In addition to providing the connectivity part of telemedicine carriers have introduced solution suites to make the experience more seamless for end users.
Verizon announced BlueJeans Telehealth in April 2021. The platform offers a holistic suite of telehealth solutions that will address two key concerns which are 1) ease of use, and 2) security (i.e. HIPPA compliance and more). The platform offers a one-click, download-free telehealth platform that powers the patient experience from onboarding to education.
AT&T’s Business segment has announced a partnership with VitalTech, a virtual care and remote patient monitoring company. The partnership offers 60 days of free telehealth services through VitalCare to AT&T business customers, such as hospitals, to support physicians and patients.
Empowering the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT):
What is the Internet of Medical Things? It is a blanket term for all medical devices and applications that can be connected to healthcare IT. The adoption of connected medical devices is becoming embedded in healthcare providers‘ buying decisions at the margin. One trend in the healthcare space is the blossoming of outcome-based contracts (OBC). According to an industry survey done by Avalere Health, 59% of payers executed an OBC in 2019 vs. 24% in 2017. In this type of contract, med-tech buying agreements will be tied to whether specific clinical or economic outcomes are met, with provisions for “profit sharing“. In some cases, the agreement may be priced on the value provided for the patient (i.e. treatment outcome vs. cost of delivering the respective outcome).
|
|
|
Source: Grand View Research Report from January 2021 BofA GLOBAL RESEARCH |
Beyond patient monitoring, an increasing number of connected medical devices are enabling the ability to generate, collect, analyze and transmit health care data and images to healthcare providers. PTC, a major player in the IoT space, sells ThingWorx, an IoT platform that can be embedded into virtually any medical device. The possibilities are endless. As an example, Sysmex, a manufacturer of hematology analyzers, wanted to create a smaller, faster and more agile blood analyzer.
Leveraging PTC‘s ThingWorx, Sysmex created Sysmex XW-100, a smart, connected blood analyzer that not only is smaller and more easily deployable, it also enables blood test results to be delivered for same day diagnosis and rapid response.
The broad adoption of IoMT would lead to more accurate diagnoses, fewer mistakes and a lower cost-of-care in the long term. 5G and edge computing are essential for accommodating the volume of data generated by IoMT devices as the number sensors and endpoints increases alongside adoption among care providers and patients alike.
Other use cases for 5G in healthcare:
The examples shared above are the most concrete and immediately monetizable market opportunities in 5G-powered healthcare solutions thus far. There are additional emerging opportunities that will require the capacity and low-latency that 5G can provide including the following.
Healthcare AR/VR: 5G will enable VR/AR clinician training and patient care. As an example, AT&T is collaborating with VITAS Healthcare to study the effect of 5G-enabled AR/VR on hospice patients. By using calming content via 5G-enabled VR/AR, the study tested whether certain patients were able to experience lower pain and anxiety.
Transferring and processing of ultra-high resolution medical imagery: PET scans can generate up to 1GB of information per patient per study. 5G networks will enable instantaneous transmission of large data sets generated from MRIs and PET scans.
Robotic surgery (?): There are many benefits to robotic surgeries, especially in the case of minimally invasive procedures. Robotic surgery is done with more precision, smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, less pain, and quicker healing time. The global robotic surgery market is expected grow at 14.79% CAGR from 2020 to reach $6.5b by 2024, with a focus on developing low-cost robotic surgical systems. At the scale it operates today, it is still relatively costly compared to traditional methods. 5G‘s ultra-low latency is crucial (with zero margin for error), however, in enabling robotic surgeries as they will require massive data transmission, image processing and analysis across large distances at very low latency.
5G transforming industrials
Enterprise 5G applications can provide proactive asset management to directly create value for manufacturers. 5G may be used to connect low-power sensors to machinery and machinery parts, enabling factories, airlines, automakers, and other industrial operators to proactively monitor and manage equipment repairs and replacements. Data collected from the sensors is transmitted via the 5G network to processors with machine learning algorithms to predict the future behavior of the equipment. For example, if a tractor‘s engine begins overheating, sensors would sense the rising temperature and relay the message to the monitoring processors, which would then alert the operator of a potential breakdown before any serious damage occurs. Proactive management of assets can reduce total capex spending in the long run by extending the life of assets.
Why not WiFi? A McKinsey study found that within factories and plants generally speaking, currently available connectivity option have several major shortfalls, making 5G necessary in order to implement the next generation of technology and Fourth Industrial Revolution (4th IR) use cases. Wi-Fi networks often experience interference, especially when sensors and agents grow in mass quantities. Wired connections, while reliable, are not as agile.
A recent survey conducted by Nokia where it interviewed a thousand key stakeholders in IT across the US and UK found that in terms of 5G functionality, video-related use cases are the most common across various business to business (B2B) and business to consumer (B2C) verticals. For example, 75% of businesses surveyed are currently using video for monitoring purposes. With 5G, each end point could be empowered and connected with video and analytics functions. Simple as that sounds, video married to analytics can function as a sensor to detect defects in a factory or monitor any industrial operation via real-time detection of objects, risks, and incidents. As the number of endpoints grow, 5G will be the critical backbone due to the need for uninterrupted connectivity that can handle massive amounts of data traffic.
The manufacturing vertical currently has one of the highest awareness level of 5G and has ventured into advance uses cases such as remote machine control and robotics, a trend that has been accelerated due to the COVID-19 pandemic. In Exhibit 8 below, we see how 5G enables the fourth industrial revolution across a range of applications within industrials by satisfying the application‘s technical requirements across reliability, security, speed, latency, data volume, and density.
5G, AI, and IoT will transform factory floors with predictive maintenance
Minimizing downtime is a huge part of cost control for manufacturers. Furthermore, unplanned downtime can cost up to 9x more than planned downtime. Imagine a scenario where a machine in a high speed assembly line breaks down, the entire production line will halt until the machine is fixed. Studies shows that the cost of machine failing in such a scenario can be more than $10,000 per minute.
The historical way of preventing unplanned downtime was to schedule routine maintenance which also incurs spending in the form of maintenance costs rather than repair costs. This is where advanced predictive maintenance powered by 5G would solve both problems.
By equipping the factory floor with sensors and agents at each endpoint, machine conditions may be monitored in real time and advanced diagnostics may be run to both avoid break-fix events but also unnecessary preventative maintenance spending. 5G is critical to power these sensors because advance analytics will run along dozens of parameters when monitoring assets such as temperature, vibration, humidity, pressure, and many more. The data needs to be holistic and complete in order for connected devices to accomplish what‘s promised making the size of the data a challenge to transmit and process in real time, necessitating the promise of 5G.
Ericsson is one of the most advanced 5G users in manufacturing. In 2018, Ericsson partnered with Audi to roll out and run field tests for various industrial applications in the Audi‘s manufacturing headquarters in Ingolstadt, Germany in a smart factory named the ‘Audi Production Lab‘. In Ericsson‘s factory in Nanjing, the company has approximately 1,000 high-precision screwdrivers that require routine calibration and lubrication based on utilization. This has been a high-touch manual process historically which required manual documentation. By fitting these tools with real time motion sensors that analyze collected data, the factory was able to replace manual tracking with an automated solution to cut the manual workload by 50% and is planning on phasing out manual tracking entirely in the future.
5G can enable precision manufacturing like never before
The availability of advanced, predictive analytics in machinery extends an asset‘s life and lowers the cost for factories, but the real lever for increasing productivity is precision monitoring and control enabled by 5G. With this technology, the entire production process is monitored in real time. 5G connectivity will allow machines to feed real time data back to applications that have machine learning and AI functionality to analyze an item currently in production and compare it to the planned model for any discrepancies. By recognizing when a machine is not working optimally and re-calibrating accordingly to maintain cycle speeds, based on research done by a survey done by STL Partners with manufacturers in August of 2019, manufacturers believe machine productivity could improve by 15% on average.
The concept of precision monitoring is easy to grasp and can transform the way factories run quality control. In order for this model to work properly, ultra-low latency is required (sub 10 milliseconds) due to the need for constant data collection and comparison to the digitally planned model at each sensor endpoint.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This BofA research report continues, but we will end here in deference to BofA clients.
For more information on BofA Global Research:
https://www.bofaml.com/en-us/content/global-research-about.html
For another analyst firm point of view: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/advanced%20electronics/our%20insights/the%205g%20era%20new%20horizons%20for%20advanced%20electronics%20and%20industrial%20companies/the-5g-era-new-horizons-for-advanced-electronics-and-industrial-companies.pdf