AI/ML
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Network operators are bracing themselves for a wave of AI traffic, partially based on a RtBrick survey, as well as forecasts by Cisco and Nokia, but that hasn’t happened yet. The heavy AI traffic today is East to West (or vice-versa) within cloud resident AI data centers and for AI data center interconnects.
1. Cisco believes that AI Inference agents will soon engage “continuously” with end-users, keeping traffic levels consistently high. has stated that AI will greatly increase network traffic, citing a shift toward new, more demanding traffic patterns driven by “agentic AI” and other applications. This perspective is a core part of Cisco’s business strategy, which is focused on selling the modernized infrastructure needed to handle the coming surge. Cisco identified three stages of AI-driven traffic growth, each with different network demands:
- Today’s generative AI models produce “spikey” traffic which spikes up when a user submits a query, but then returns to a low baseline. Current networks are largely handling this traffic without issues.
- Persistent “agentic” AI traffic: The next phase will involve AI agents that constantly interact with end-users and other agents. Cisco CEO Chuck Robbins has stated that this will drive traffic “beyond the peaks of current chatbot interaction” and keep network levels “consistently high”.
- Edge-based AI: A third wave of “physical AI” will require more computing and networking at the edge of the network to accommodate specialized use cases like industrial IoT.
“As we move towards agentic AI and the demand for inferencing expands to the enterprise and end user networking environments, traffic on the network will reach unprecedented levels,” Cisco CEO Chuck Robbins said on the company’s recent earnings call. “Network traffic will not only increase beyond the peaks of current chatbot interaction, but will remain consistently high with agents in constant interaction.”
2. Nokia recently predicted that both direct and indirect AI traffic on mobile networks will grow at a faster pace than regular, non-AI traffic.
- Direct AI traffic: This is generated by users or systems directly interacting with AI services and applications. Consumer examples: Using generative AI tools, interacting with AI-powered gaming, or experiencing extended reality (XR) environments. Enterprise examples: Employing predictive maintenance, autonomous operations, video and image analytics, or enhanced customer interactions.
- Indirect AI traffic: This occurs when AI algorithms are used to influence user engagement with existing services, thereby increasing overall traffic. Examples: AI-driven personalized recommendations for video content on social media, streaming platforms, and online marketplaces, which can lead to longer user sessions and higher bandwidth consumption.
The Finland based network equipment vendor warned that the AI wave could bring “a potential surge in uplink data traffic that could overwhelm our current network infrastructure if we’re not prepared,” noting that the rise of hybrid on-device and cloud tools will require much more than the 5-15 Mbps uplink available on today’s networks. Nokia’s Global Network Traffic 2030 report forecasts that overall traffic could grow by 5 to 9 times current levels by 2033. All told, Nokia said AI traffic is expected to hit 1088 exabytes (EB) per month by 2033. That means overall traffic will grow 5x in a best case scenario and 9x in a worse case.
To manage this anticipated traffic surge, Nokia advocates for radical changes to existing network infrastructure.
- Cognitive networks: The company states that networks must become “cognitive,” leveraging AI and machine learning (ML) to handle the growing data demand.
- Network-as-Code: As part of its Technology Strategy 2030, Nokia promotes a framework for more flexible and scalable networks that leverage AI and APIs.
- 6G preparation: Nokia Bell Labs is already conducting research and field tests to prepare for 6G networks around 2030, with a focus on delivering the capacity needed for AI and other emerging technologies.
- Optimizing the broadband edge: The company also highlights the need to empower the broadband network edge to handle the demands of AI applications, which require low latency and high reliability.
Nokia’s Global Network Traffic 2030 report didn’t mention agentic AI, which are artificial intelligence systems designed to autonomously perceive, reason, and act in their environment to achieve complex goals with less human oversight. Unlike generative AI, which focuses on creating content, agentic AI specializes in workflow automation and independent problem-solving by making decisions, adapting plans, and executing tasks over extended periods to meet long-term objectives.
3. Ericsson did point to traffic increases stemming from the use of AI-based assistants in its 2024 Mobility Report. In particular, it predicted the majority of traffic would be related to the use of consumer video AI assistants, rather than text-based applications and – outside the consumer realm – forecast increased traffic from “AI agents interacting with drones and droids. Accelerated consumer uptake of GenAI will cause a steady increase of traffic in addition to the baseline increase,” Ericsson said of its traffic growth scenario.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Dissenting Views:
1. UK Disruptive Analysis Founder Dean Bubley isn’t a proponent of huge AI traffic growth. “Many in the telecom industry and vendor community are trying to talk up AI as driving future access network traffic and therefore demand for investment, spectrum etc., but there is no evidence of this at present,” he told Fierce Network.
Bubley argues that AI agents won’t really create much traffic on access networks to homes or businesses. Instead, he said, they will drive traffic “inside corporate networks, and inside and between data centers on backbone networks and inside the cloud. “There might be a bit more uplink traffic if video/images are sent to the cloud for AI purposes, but again that’s hypothetical,” he said.
2. In a LinkedIn post, Ookla analyst Mike Dano said he was a bit suspicious about “Cisco predicting a big jump in network traffic due to AI agents constantly wandering around the Internet and doing things.” While almost all of the comments agreed with Dano, it still is an open question whether the AI traffic Armageddon will actually materialize.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
RtBrick survey: Telco leaders warn AI and streaming traffic to “crack networks” by 2030
https://www.fierce-network.com/cloud/will-ai-agents-really-raise-network-traffic-baseline
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Both telecom and enterprise networks are being reshaped by AI bandwidth and latency demands of AI. Network operators that fail to modernize architectures risk falling behind. Why? AI workloads are network killers — they demand massive east-west traffic, ultra-low latency, and predictable throughput.
- Real-time observability is becoming non-negotiable, as enterprises need to detect and fix issues before they impact AI model training or inference.
- Self-driving networks are moving from concept to reality, with AI not just monitoring but actively remediating problems.
- The competitive race is now about who can integrate AI into networking most seamlessly — and HPE/Juniper’s Mist AI, Cisco’s assurance stack, and Nvidia’s AI fabrics are three different but converging approaches.
Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are designing AI-optimized networking equipment, with a focus on real-time observability, lower latency and increased data center performance for AI workloads. Here’s a capsule summary:
Cisco: AI-Ready Infrastructure:
- Cisco is embedding AI telemetry and analytics into its Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, and Catalyst campus gear.
- The focus is on real-time observability via its ThousandEyes platform and AI-driven assurance in DNA Center, aiming to optimize both enterprise and AI/ML workloads.
- Cisco is also pushing AI-native data center fabrics to handle GPU-heavy clusters for training and inference.
- Cisco claims “exceptional momentum” and leadership in AI: >$800M in AI infrastructure orders taken from web-scale customers in Q4, bringing the FY25 total to over $2B.
- Cisco Nexus switches now fully and seamlessly integrated with NVIDIA’s Spectrum-X architecture to deliver high speed networking for AI clusters
HPE + Juniper: AI-Native Networking Push:
- Following its $13.4B acquisition of Juniper Networks, HPE has merged Juniper’s Mist AI platform with its own Aruba portfolio to create AI-native, “self-driving” networks.
- Key upgrades include:
-Agentic AI troubleshooting that uses generative AI workflows to pinpoint and fix issues across wired, wireless, WAN, and data center domains.
-Marvis AI Assistant with enhanced conversational capabilities — IT teams can now ask open-ended questions like “Why is the Orlando site slow?” and get contextual, actionable answers.
-Large Experience Model (LEM) with Marvis Minis — digital twins that simulate user experiences to predict and prevent performance issues before they occur.
-Apstra integration for data center automation, enabling autonomous service provisioning and cross-domain observability
Nvidia: AI Networking at Compute Scale
- Nvidia’s Spectrum-X Ethernet platform and Quantum-2 InfiniBand (both from Mellanox acquisition) are designed for AI supercomputing fabrics, delivering ultra-low latency and congestion control for GPU clusters.
- In partnership with HPE, Nvidia is integrating NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Blackwell architecture GPUs into HPE Private Cloud AI, enabling enterprises to deploy AI workloads with optimized networking and compute together.
- Nvidia’s BlueField DPUs offload networking, storage, and security tasks from CPUs, freeing resources for AI processing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of how Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are approaching AI‑optimized enterprise networking — so you can see where they align and where they differentiate:
| Feature / Focus Area | Cisco | HPE / Juniper | Nvidia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core AI Networking Vision | AI‑ready infrastructure with embedded analytics and assurance for enterprise + AI workloads | AI‑native, “self‑driving” networks across campus, WAN, and data center | High‑performance fabrics purpose‑built for AI supercomputing |
| Key Platforms | Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, Catalyst campus gear, ThousandEyes, DNA Center | Mist AI platform, Marvis AI Assistant, Marvis Minis, Apstra automation | Spectrum‑X Ethernet, Quantum‑2 InfiniBand, BlueField DPUs |
| AI Integration | AI‑driven assurance, predictive analytics, real‑time telemetry | Generative AI for troubleshooting, conversational AI for IT ops, digital twin simulations | AI‑optimized networking stack tightly coupled with GPU compute |
| Observability | End‑to‑end visibility via ThousandEyes + DNA Center | Cross‑domain observability (wired, wireless, WAN, DC) with proactive issue detection | Telemetry and congestion control for GPU clusters |
| Automation | Policy‑driven automation in campus and data center fabrics | Autonomous provisioning, AI‑driven remediation, intent‑based networking | Offloading networking/storage/security tasks to DPUs for automation |
| Target Workloads | Enterprise IT, hybrid cloud, AI/ML inference & training | Enterprise IT, edge, hybrid cloud, AI/ML workloads | AI training & inference at hyperscale, HPC, large‑scale data centers |
| Differentiator | Strong enterprise install base + integrated assurance stack | Deep AI‑native operations with user experience simulation | Ultra‑low latency, high‑throughput fabrics for GPU‑dense environments |
Key Takeaways:
- Cisco is strongest in enterprise observability and broad infrastructure integration.
- HPE/Juniper is leaning into AI‑native operations with a heavy focus on automation and user experience simulation.
- Nvidia is laser‑focused on AI supercomputing performance, building the networking layer to match its GPU dominance.
- Cisco leverages its market leadership, customer base and strategic partnerships to integrate AI with existing enterprise networks.
- HPE/Juniper challenges rivals with an AI-native, experience-first network management platform.
- Nvidia aims to dominate the full-stack AI infrastructure, including networking.
SoftBank’s Transformer AI model boosts 5G AI-RAN uplink throughput by 30%, compared to a baseline model without AI
Softbank has developed its own Transformer-based AI model that can be used for wireless signal processing. SoftBank used its Transformer model to improve uplink channel interpolation which is a signal processing technique where the network essentially makes an educated guess as to the characteristics and current state of a signal’s channel. Enabling this type of intelligence in a network contributes to faster, more stable communication, according to SoftBank. The Japanese wireless network operator successfully increased uplink throughput by approximately 20% compared to a conventional signal processing method (the baseline method). In the latest demonstration, the new Transformer-based architecture was run on GPUs and tested in a live Over-the-Air (OTA) wireless environment. In addition to confirming real-time operation, the results showed further throughput gains and achieved ultra-low latency.
Editor’s note: A Transformer model is a type of neural network architecture that emerged in 2017. It excels at interpreting streams of sequential data associated with large language models (LLMs). Transformer models have also achieved elite performance in other fields of artificial intelligence (AI), including computer vision, speech recognition and time series forecasting. Transformer models are lightweight, efficient, and versatile – capable of natural language processing (NLP), image recognition and wireless signal processing as per this Softbank demo.
Significant throughput improvement:
- Uplink channel interpolation using the new architecture improved uplink throughput by approximately 8% compared to the conventional CNN model. Compared to the baseline method without AI, this represents an approximately 30% increase in throughput, proving that the continuous evolution of AI models leads to enhanced communication quality in real-world environments.
Higher AI performance with ultra-low latency:
- While real-time 5G communication requires processing in under 1 millisecond, this demonstration with the Transformer achieved an average processing time of approximately 338 microseconds, an ultra-low latency that is about 26% faster than the convolution neural network (CNN) [1.] based approach. Generally, AI model processing speeds decrease as performance increases. This achievement overcomes the technically difficult challenge of simultaneously achieving higher AI performance and lower latency. Editor’s note: Perhaps this can overcome the performance limitations in ITU-R M.2150 for URRLC in the RAN, which is based on an uncompleted 3GPP Release 16 specification.
Note 1. CNN-based approaches to achieving low latency focus on optimizing model architecture, computation, and hardware to accelerate inference, especially in real-time applications. Rather than relying on a single technique, the best results are often achieved through a combination of methods.

Using the new architecture, SoftBank conducted a simulation of “Sounding Reference Signal (SRS) prediction,” a process required for base stations to assign optimal radio waves (beams) to terminals. Previous research using a simpler Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) AI model for SRS prediction confirmed a maximum downlink throughput improvement of about 13% for a terminal moving at 80 km/h.*2
In the new simulation with the Transformer-based architecture, the downlink throughput for a terminal moving at 80 km/h improved by up to approximately 29%, and by up to approximately 31% for a terminal moving at 40 km/h. This confirms that enhancing the AI model more than doubled the throughput improvement rate (see Figure 1). This is a crucial achievement that will lead to a dramatic improvement in communication speeds, directly impacting the user experience.
The most significant technical challenge for the practical application of “AI for RAN” is to further improve communication quality using high-performance AI models while operating under the real-time processing constraint of less than one millisecond. SoftBank addressed this by developing a lightweight and highly efficient Transformer-based architecture that focuses only on essential processes, achieving both low latency and maximum AI performance. The important features are:
(1) Grasps overall wireless signal correlations
By leveraging the “Self-Attention” mechanism, a key feature of Transformers, the architecture can grasp wide-ranging correlations in wireless signals across frequency and time (e.g., complex signal patterns caused by radio wave reflection and interference). This allows it to maintain high AI performance while remaining lightweight. Convolution focuses on a part of the input, while Self-Attention captures the relationships of the entire input (see Figure 2).
(2) Preserves physical information of wireless signals
While it is common to normalize input data to stabilize learning in AI models, the architecture features a proprietary design that uses the raw amplitude of wireless signals without normalization. This ensures that crucial physical information indicating communication quality is not lost, significantly improving the performance of tasks like channel estimation.
(3) Versatility for various tasks
The architecture has a versatile, unified design. By making only minor changes to its output layer, it can be adapted to handle a variety of different tasks, including channel interpolation/estimation, SRS prediction, and signal demodulation. This reduces the time and cost associated with developing separate AI models for each task.
The demonstration results show that high-performance AI models like Transformer and the GPUs that run them are indispensable for achieving the high communication performance required in the 5G-Advanced and 6G eras. Furthermore, an AI-RAN that controls the RAN on GPUs allows for continuous performance upgrades through software updates as more advanced AI models emerge, even after the hardware has been deployed. This will enable telecommunication carriers to improve the efficiency of their capital expenditures and maximize value.
Moving forward, SoftBank will accelerate the commercialization of the technologies validated in this demonstration. By further improving communication quality and advancing networks with AI-RAN, SoftBank will contribute to innovation in future communication infrastructure. The Japan based conglomerate strongly endorsed AI RAN at MWC 2025.
References:
https://www.softbank.jp/en/corp/news/press/sbkk/2025/20250821_02/
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/softbank-claims-its-ai-ran-tech-boosts-throughput-by-30-
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/softbank-makes-mwc-25-all-about-ai-ran
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/transformer-model
https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-M.2150/en
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
Dell’Oro Group: RAN Market Grows Outside of China in 2Q 2025
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
Dell’Oro: RAN revenue growth in 1Q2025; AI RAN is a conundrum
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
OpenAI announces new open weight, open source GPT models which Orange will deploy
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent
RtBrick survey: Telco leaders warn AI and streaming traffic to “crack networks” by 2030
Respondents to a RtBrick survey of 200 senior telecom decision makers in the U.S., UK, and Australia finds that network operator leaders are failing to make key decisions and lack the motivation to change. The report exposes urgent warnings from telco engineers that their networks are on a five-year collision course with AI and streaming traffic. It finds that 93% of respondents report a lack of support from leadership to deploy disaggregated network equipment. Key findings:
- Risk-averse leadership and a lack of skills are the top factors that are choking progress.
- Majority are stuck in early planning, while AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, and Comcast lead large-scale disaggregation rollouts.
- Operators anticipate higher broadband prices but fear customer backlash if service quality can’t match the price.
- Organizations require more support from leadership to deploy disaggregation (93%).
- Complexity around operational transformation (42%), such as redesigning architectures and workflows.
- Critical shortage of specialist skills/staff (38%) to manage disaggregated systems.
The survey finds that almost nine in ten operators (87%) expect customers to demand higher broadband speeds by 2030, while roughly the same (79%) state their customers expect costs to increase, suggesting they will pay more for it. Yet half of all leaders (49%) admit they lack complete confidence in delivering services at a viable cost. Eighty-four percent say customer expectations for faster, cheaper broadband are already outpacing their networks, while 81% concede their current architectures are not well-suited to handling the future increases in bandwidth demand, suggesting they may struggle with the next wave of AI and streaming traffic.
“Senior leaders, engineers, and support staff inside operators have made their feelings clear: the bottleneck isn’t capacity, it’s decision-making,” said Pravin S Bhandarkar, CEO and Founder of RtBrick. “Disaggregated networks are no longer an experiment. They’re the foundation for the agility, scalability, and transparency operators need to thrive in an AI-driven, streaming-heavy future,” he added noting the intent to deploy disaggregation as per this figure:

However, execution continues to trail ambition. Only one in twenty leaders has confirmed they’re “in deployment” today, while 49% remain stuck in early-stage “exploration”, and 38% are still “in planning”. Meanwhile, big-name operators such as AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, and Comcast are charging ahead and already actively deploying disaggregation at scale, demonstrating faster rollouts, greater operational control, and true vendor flexibility. Here’s a snapshot of those activities:
- AT&T has deployed an open, disaggregated routing network in their core, powered by DriveNets Network Cloud software on white-box bare metal switches and routers from Taiwanese ODMs, according to Israel based DriveNets. DriveNets utilizes a Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) architecture, where a cluster of bare metal switches act as a single routing entity. That architecture has enabled AT&T to accelerate 5G and fiber rollouts and improve network scalability and performance. It has made 1.6Tb/s transport a reality on AT&T’s live network.
- Deutsche Telekom has deployed a disaggregated broadband network using routing software from RtBrick running on bare-metal switch hardware to provide high-speed internet connectivity. They’re also actively promoting Open BNG solutions as part of this initiative.
- Comcast uses network cloud software from DriveNets and white-box hardware to disaggregate their core network, aiming to increase efficiency and enable new services through a self-healing and consumable network. This also includes the use of disaggregated, pluggable optics from multiple vendors.
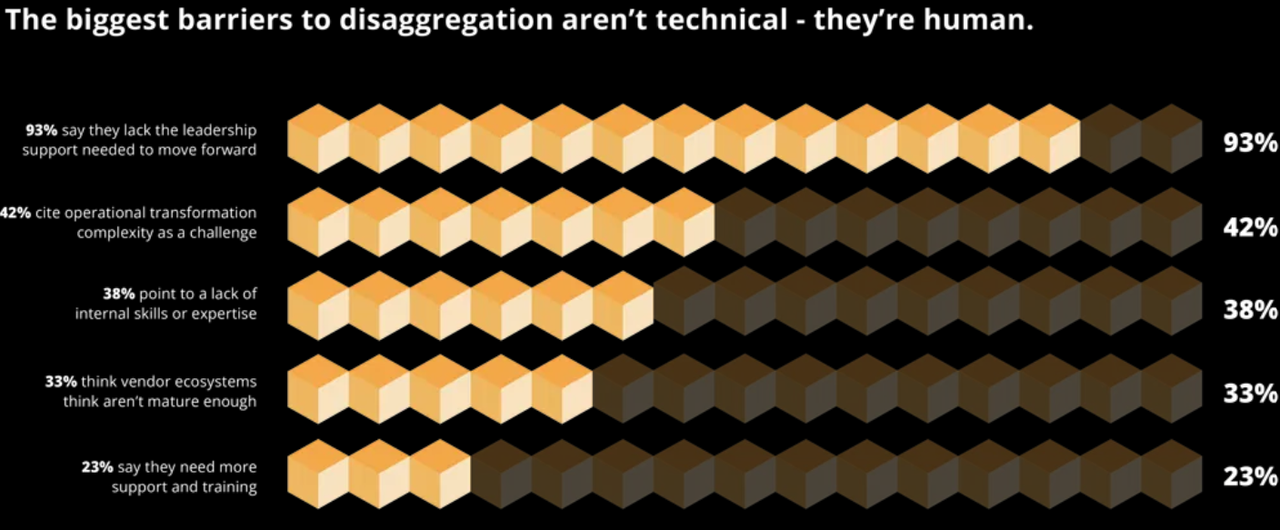
Nearly every leader surveyed also claims their organization is “using” or “planning to use” AI in network operations, including for planning, optimization, and fault resolution. However, nine in ten (93%) say they cannot unlock AI’s full value without richer, real-time network data. This requires more open, modular, software-driven architecture, enabled by network disaggregation.
“Telco leaders see AI as a powerful asset that can enhance network performance,” said Zara Squarey, Research Manager at Vanson Bourne. “However, the data shows that without support from leadership, specialized expertise, and modern architectures that open up real-time data, disaggregation deployments may risk further delays.”
When asked what benefits they expect disaggregation to deliver, operators focused on outcomes that could deliver the following benefits:
- 54% increased operational automation
- 54% enhanced supply chain resilience
- 51% improved energy efficiency
- 48% lower purchase and operational costs
- 33% reduced vendor lock-in
Transformation priorities align with those goals, with automation and agility (57%) ranked first, followed by vendor flexibility (55%), supply chain security (51%), cost efficiency (46%) and energy usage and sustainability (47%).

About the research:
The ‘State of Disaggregation’ research was independently conducted by Vanson Bourne in June 2025 and commissioned by RtBrick to identify the primary drivers and barriers to disaggregated network rollouts. The findings are based on responses from 200 telecom decision makers across the U.S., UK, and Australia, representing operations, engineering, and design/Research and Development at organizations with 100 to 5,000 or more employees.
References:
https://www.rtbrick.com/state-of-disaggregation-report-2
https://drivenets.com/blog/disaggregation-is-driving-the-future-of-atts-ip-transport-today/
Disaggregation of network equipment – advantages and issues to consider
NTT Data and Google Cloud partner to offer industry-specific cloud and AI solutions
NTT Data and Google Cloud plan to combine their expertise in AI and the cloud to offer customized solutions to accelerate enterprise transformation across sectors including banking, insurance, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, life sciences and the public sector.. The partnership will include agentic AI solutions, security, sovereign cloud and developer tools. This collaboration combines NTT DATA’s deep industry expertise in AI, cloud-native modernization and data engineering with Google Cloud’s advanced analytics, AI and cloud technologies to deliver tailored, scalable enterprise solutions.
With a focus on co-innovation, the partnership will drive industry-specific cloud and AI solutions, leveraging NTT DATA’s proven frameworks and best practices along with Google Cloud’s capabilities to deliver customized solutions backed by deep implementation expertise. Significant joint go-to-market investments will support seamless adoption across key markets.
According to Gartner®, worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to reach $723 billion in 2025, up from $595.7 billion in 2024.1 The use of AI deployments in IT and business operations is accelerating the reliance on modern cloud infrastructure, highlighting the critical importance of this strategic global partnership.
“This collaboration with Google Cloud represents a significant milestone in our mission to drive innovation and digital transformation across industries,” said Marv Mouchawar, Head of Global Innovation, NTT DATA. “By combining NTT DATA’s deep expertise in AI, cloud-native modernization and enterprise solutions with Google Cloud’s advanced technologies, we are helping businesses accelerate their AI-powered cloud adoption globally and unlock new opportunities for growth.”
“Our partnership with NTT DATA will help enterprises use agentic AI to enhance business processes and solve complex industry challenges,” said Kevin Ichhpurani, President, Global Partner Ecosystem at Google Cloud. “By combining Google Cloud’s AI with NTT DATA’s implementation expertise, we will enable customers to deploy intelligent agents that modernize operations and deliver significant value for their organizations.”

Photo Credit: Phil Harvey/Alamy Stock Photo
In financial services, this collaboration will support regulatory compliance and reporting through NTT DATA solutions like Regla, which leverage Google Cloud’s scalable AI infrastructure. In hospitality, NTT DATA’s Virtual Travel Concierge enhances customer experience and drives sales with 24×7 multilingual support, real-time itinerary planning and intelligent travel recommendations. It uses the capabilities of Google’s Gemini models to drive personalization across more than 3 million monthly conversations.
Key focus areas include:
- Industry-specific agentic AI solutions: NTT DATA will build new industry solutions that transform analytics, decision-making and client experiences using Google Agentspace, Google’s Gemini models, secure data clean rooms and modernized data platforms.
- AI-driven cloud modernization: Accelerating enterprise modernization with Google Distributed Cloud for secure, scalable modernization built and managed on NTT DATA’s global infrastructure, from data centers to edge to cloud.
- Next-generation application and security modernization: Strengthening enterprise agility and resilience through mainframe modernization, DevOps, observability, API management, cybersecurity frameworks and SAP on Google Cloud.
- Sovereign cloud innovation: Delivering secure, compliant solutions through Google Distributed Cloud in both air-gapped and connected deployments. Air-gapped environments operate offline for maximum data isolation. Connected deployments enable secure integration with cloud services. These scenarios meet data sovereignty and regulatory demands in sectors such as finance, government and healthcare without compromising innovation.
- Google Distributed Cloud sandbox environment: Google Distributed Cloud sandbox environment is a digital playground where developers can build, test and deploy industry-specific and sovereign cloud deployments. This sandbox will help teams upskill through hands-on training and accelerate time to market with Google Distributed Cloud technologies through preconfigured, ready-to-deploy templates.
NTT DATA will support these innovations through a full-stack suite of services including advisory, building, implementation and ongoing hosting and managed services.
By combining NTT DATA’s proven blueprints and delivery expertise with Google Cloud’s technology, the partnership will accelerate the development of repeatable, scalable solutions for enterprise transformation. At the heart of this innovation strategy is Takumi, NTT DATA’s GenAI framework that guides clients from ideation to enterprise-wide deployment. Takumi integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud’s AI stack, enabling rapid prototyping and operationalization of GenAI use cases.
This initiative expands NTT DATA’s Smart AI Agent Ecosystem, which unites strategic technology partnerships, specialized assets and an AI-ready talent engine to help clients deploy and manage responsible, business-driven AI at scale.
Accelerating global delivery with a dedicated Google Cloud Business Group:
To achieve excellence, NTT DATA has established a dedicated global Google Cloud Business Group comprising thousands of engineers, architects and advisory consultants. This global team at NTT DATA will work in close collaboration with Google Cloud teams to help clients adopt and scale AI-powered cloud technologies.
NTT DATA is also investing in advanced training and certification programs ensuring teams across sales, pre-sales and delivery are equipped to sell, secure, migrate and implement AI-powered cloud solutions. The company aims to certify 5,000 engineers in Google Cloud technology, further reinforcing its role as a leader in cloud transformation on a global scale.
Additionally, both companies are co-investing in global sales and go-to-market campaigns to accelerate client adoption across priority industries. By aligning technical, sales and marketing expertise, the companies aim to scale transformative solutions efficiently across global markets.
This global partnership builds on NTT DATA and Google Cloud’s 2024 co-innovation agreement in APAC. In addition it further strengthens NTT DATA’s acquisition of Niveus Solutions, a leading Google Cloud specialist recognized with three 2025 Google Cloud Awards – “Google Cloud Country Partner of the Year – India”, “Google Cloud Databases Partner of the Year – APAC” and “Google Cloud Country Partner of the Year – Chile,” further validating NTT DATA’s commitment to cloud excellence and innovation.
“We’re excited to see the strengthened partnership between NTT DATA and Google Cloud, which continues to deliver measurable impact. Their combined expertise has been instrumental in migrating more than 380 workloads to Google Cloud to align with our cloud-first strategy,” said José Luis González Santana, Head of IT Infrastructure, Carrefour. “By running SAP HANA on Google Cloud, we have consolidated 100 legacy applications to create a powerful, modernized e-commerce platform across 200 hypermarkets. This transformation has given us the agility we need during peak times like Black Friday and enabled us to launch new services faster than ever. Together, NTT DATA and Google Cloud are helping us deliver more connected, seamless experiences for our customers,”
About NTT DATA:
NTT DATA is a $30+ billion trusted global innovator of business and technology services. We serve 75% of the Fortune Global 100 and are committed to helping clients innovate, optimize and transform for long-term success. As a Global Top Employer, we have experts in more than 50 countries and a robust partner ecosystem of established and start-up companies. Our services include business and technology consulting, data and artificial intelligence, industry solutions, as well as the development, implementation and management of applications, infrastructure and connectivity. We are also one of the leading providers of digital and AI infrastructure in the world. NTT DATA is part of NTT Group, which invests over $3.6 billion each year in R&D to help organizations and society move confidently and sustainably into the digital future.
Resources:
https://www.nttdata.com/global/en/news/press-release/2025/august/081300
Google Cloud targets telco network functions, while AWS and Azure are in holding patterns
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent
Ericsson and Google Cloud expand partnership with Cloud RAN solution
NTT & Yomiuri: ‘Social Order Could Collapse’ in AI Era
Nvidia’s networking solutions give it an edge over competitive AI chip makers
Nvidia’s networking equipment and module sales accounted for $12.9 billion of its $115.1 billion in data center revenue in its prior fiscal year. Composed of its NVLink, InfiniBand, and Ethernet solutions, Nvidia’s networking products (from its Mellanox acquisition) are what allow its GPU chips to communicate with each other, let servers talk to each other inside massive data centers, and ultimately ensure end users can connect to it all to run AI applications.
“The most important part in building a supercomputer is the infrastructure. The most important part is how you connect those computing engines together to form that larger unit of computing,” explained Gilad Shainer, senior vice president of networking at Nvidia.
In Q1-2025, networking made up $4.9 billion of Nvidia’s $39.1 billion in data center revenue. And it’ll continue to grow as customers continue to build out their AI capacity, whether that’s at research universities or massive data centers.
“It is the most underappreciated part of Nvidia’s business, by orders of magnitude,” Deepwater Asset Management managing partner Gene Munster told Yahoo Finance. “Basically, networking doesn’t get the attention because it’s 11% of revenue. But it’s growing like a rocket ship. “[Nvidia is a] very different business without networking,” Munster explained. “The output that the people who are buying all the Nvidia chips [are] desiring wouldn’t happen if it wasn’t for their networking.”
Nvidia senior vice president of networking Kevin Deierling says the company has to work across three different types of networks:
- NVLink technology connects GPUs to each other within a server or multiple servers inside of a tall, cabinet-like server rack, allowing them to communicate and boost overall performance.
- InfiniBand connects multiple server nodes across data centers to form what is essentially a massive AI computer.
- Ethernet connectivity for front-end network for storage and system management.
Note: Industry groups also have their own competing networking technologies including UALink, which is meant to go head-to-head with NVLink, explained Forrester analyst Alvin Nguyen.
“Those three networks are all required to build a giant AI-scale, or even a moderately sized enterprise-scale, AI computer,” Deierling explained. Low latency is key as longer transit times for data going to/from GPUs slows the entire operation, delaying other processes and impacting the overall efficiency of an entire data center.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang presents a Grace Blackwell NVLink72 as he delivers a keynote address at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas, Nevada on January 6, 2025. Photo by PATRICK T. FALLON/AFP via Getty Images
As companies continue to develop larger AI models and autonomous and semi-autonomous agentic AI capabilities that can perform tasks for users, making sure those GPUs work in lockstep with each other becomes increasingly important.
The AI industry is in the midst of a broad reordering around the idea of inferencing, which requires more powerful data center systems to run AI models. “I think there’s still a misperception that inferencing is trivial and easy,” Deierling said.
“It turns out that it’s starting to look more and more like training as we get to [an] agentic workflow. So all of these networks are important. Having them together, tightly coupled to the CPU, the GPU, and the DPU [data processing unit], all of that is vitally important to make inferencing a good experience.”
Competitor AI chip makers, like AMD are looking to grab more market share from Nvidia, and cloud giants like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft continue to design and develop their own AI chips. However, none of them have the low latency, high speed connectivity solutions provided by Nvidia (again, think Mellanox).
References:
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/
Networking chips and modules for AI data centers: Infiniband, Ultra Ethernet, Optical Connections
Nvidia enters Data Center Ethernet market with its Spectrum-X networking platform
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Does AI change the business case for cloud networking?
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
Telecom sessions at Nvidia’s 2025 AI developers GTC: March 17–21 in San Jose, CA
Open AI raises $8.3B and is valued at $300B; AI speculative mania rivals Dot-com bubble
According to the Financial Times (FT), OpenAI (the inventor of Chat GPT) has raised another $8.3 billion in a massively over-subscribed funding round, including $2.8 billion from Dragoneer Investment Group, a San Francisco-based technology-focused fund. Leading VCs that also participated in the funding round included Founders Fund, Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, Coatue Management, Altimeter Capital, D1 Capital Partners, Tiger Global and Thrive Capital, according to the people with knowledge of the deal.
The oversubscribed funding round came months ahead of schedule. OpenAI initially raised $2.5 billion from VC firms in March when it announced its intention to raise $40 billion in a round spearheaded by SoftBank. The Chat GPT maker is now valued at $300 billion.
OpenAI’s annual recurring revenue has surged to $12bn, according to a person with knowledge of OpenAI’s finances, and the group is set to release its latest model, GPT-5, this month.
OpenAI is in the midst of complex negotiations with Microsoft that will determine its corporate structure. Rewriting the terms of the pair’s current contract, which runs until 2030, is seen as a prerequisite to OpenAI simplifying its structure and eventually going public. The two companies have yet to agree on key issues such as how long Microsoft will have access to OpenAI’s intellectual property. Another sticking point is the future of an “AGI clause”, which allows OpenAI’s board to declare that the company has achieved a breakthrough in capability called “artificial general intelligence,” which would then end Microsoft’s access to new models.
An additional risk is the increasing competition from rivals such as Anthropic — which is itself in talks for a multibillion-dollar fundraising — and is also in a continuing legal battle with Elon Musk. The FT also reported that Amazon is set to increase its already massive investment in Anthropic.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman. The funding forms part of a round announced in March that values the ChatGPT maker at $300bn © Yuichi Yamazaki/AFP via Getty Images
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
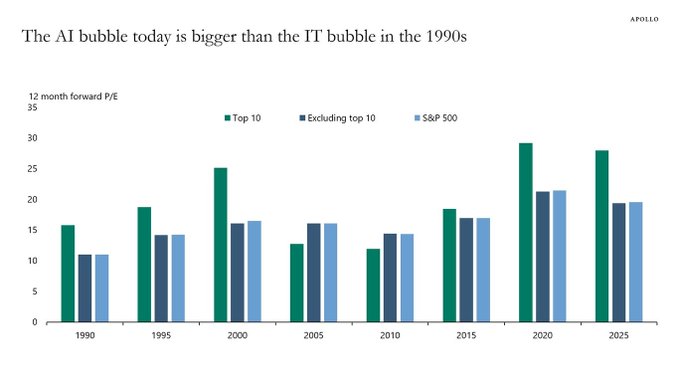
While AI is the transformative technology of this generation, comparisons are increasingly being made with the Dot-com bubble. 1999 saw such a speculative frenzy for anything with a ‘.com’ at the end that valuations and stock markets reached unrealistic and clearly unsustainable levels. When that speculative bubble burst, the global economy fell into an extended recession in 2001-2002. As a result, analysts are now questioning the wisdom of the current AI speculative bubble and fearing dire consequences when it eventually bursts. Just as with the Dot-com bubble, AI revenues are nowhere near justifying AI company valuations, especially for private AI companies that are losing tons of money (see Open AI losses detailed below).
Torsten Slok, Partner and Chief Economist at Apollo Global Management via ZERO HEDGE on X: “The difference between the IT bubble in the 1990s and the AI bubble today is that the top 10 companies in the S&P 500 today (including Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and Meta) are more overvalued than the IT companies were in the 1990s.”
AI private companies may take a lot longer to reach the lofty profit projections institutional investors have assumed. Their reliance on projected future profits over current fundamentals is a dire warning sign to this author. OpenAI, for example, faces significant losses and aggressive revenue targets to become profitable. OpenAI reported an estimated loss of $5 billion in 2024, despite generating $3.7 billion in revenue. The company is projected to lose $14 billion in 2026 while total projected losses from 2023 to 2028 are expected to reach $44 billion.
Other AI bubble data points (publicly traded stocks):
- The proportion of the S&P 500 represented by the 10 largest companies is significantly higher now (almost 40%) compared to 25% in 1999. This indicates a more concentrated market driven by a few large technology companies deeply involved in AI development and adoption.
- Investment in AI infrastructure has reportedly exceeded the spending on telecom and internet infrastructure during the dot-com boom and continues to grow, suggesting a potentially larger scale of investment in AI relative to the prior period.
- Some indices tracking AI stocks have demonstrated exceptionally high gains in a short period, potentially surpassing the rates of the dot-com era, suggesting a faster build-up in valuations.
- The leading hyperscalers, such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Meta, are investing vast sums in AI infrastructure to capitalize on the burgeoning AI market. Forecasts suggest these companies will collectively spend $381 billion in 2025 on AI-ready infrastructure, a significant increase from an estimated $270 billion in 2024.
Check out this YouTube video: “How AI Became the New Dot-Com Bubble”
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/76dd6aed-f60e-487b-be1b-e3ec92168c11
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/openai-funding-frenzy-inflates-the-ai-bubble-even-further
https://x.com/zerohedge/status/1945450061334216905
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Canalys & Gartner: AI investments drive growth in cloud infrastructure spending
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
Introduction:
According to the Wall Street Journal, the U.S. maintains its early lead in AI technology with Silicon Valley home to the most popular AI models and the most powerful AI chips (from Santa Clara based Nvidia and AMD). However, China has shown a willingness to spend whatever it takes to take the lead in AI models and silicon.
The rising popularity of DeepSeek, the Chinese AI startup, has buoyed Beijing’s hopes that it can become more self-sufficient. Huawei has published several papers this year detailing how its researchers used its homegrown AI chips to build large language models without relying on American technology.
“China is obviously making progress in hardening its AI and computing ecosystem,” said Michael Frank, founder of think tank Seldon Strategies.
AI Silicon:
Morgan Stanley analysts forecast that China will have 82% of AI chips from domestic makers by 2027, up from 34% in 2024. China’s government has played an important role, funding new chip initiatives and other projects. In July, the local government in Shenzhen, where Huawei is based, said it was raising around $700 million to invest in strengthening an “independent and controllable” semiconductor supply chain.
During a meeting with President Xi Jinping in February, Huawei Chief Executive Officer Ren Zhengfei told Xi about “Project Spare Tire,” an effort by Huawei and 2,000 other enterprises to help China’s semiconductor sector achieve a self-sufficiency rate of 70% by 2028, according to people familiar with the meeting.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
AI Models:
Prodded by Beijing, Chinese financial institutions, state-owned companies and government agencies have rushed to deploy Chinese-made AI models, including DeepSeek [1.] and Alibaba’s Qwen. That has fueled demand for homegrown AI technologies and fostered domestic supply chains.
Note 1. DeepSeek’s V3 large language model matched many performance benchmarks of rival AI programs developed in the U.S. at a fraction of the cost. DeepSeek’s open-weight models have been integrated into many hospitals in China for various medical applications.
In recent weeks, a flurry of Chinese companies have flooded the market with open-source AI models, many of which are claiming to surpass DeepSeek’s performance in certain use cases. Open source models are freely accessible for modification and deployment.
The Chinese government is actively supporting AI development through funding and policy initiatives, including promoting the use of Chinese-made AI models in various sectors.
Meanwhile, OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman said his company had pushed back the release of its open-source AI model indefinitely for further safety testing.
AI Research:
China has taken a commanding lead in the exploding field of artificial intelligence (AI) research, despite U.S. restrictions on exporting key computing chips to its rival, finds a new report.
The analysis of the proprietary Dimensions database, released yesterday, finds that the number of AI-related research papers has grown from less than 8500 published in 2000 to more than 57,000 in 2024. In 2000, China-based scholars produced just 671 AI papers, but in 2024 their 23,695 AI-related publications topped the combined output of the United States (6378), the United Kingdom (2747), and the European Union (10,055).
“U.S. influence in AI research is declining, with China now dominating,” Daniel Hook, CEO of Digital Science, which owns the Dimensions database, writes in the report DeepSeek and the New Geopolitics of AI: China’s ascent to research pre-eminence in AI.
In 2024, China’s researchers filed 35,423 AI-related patent applications, more than 13 times the 2678 patents filed in total by the U.S., the U.K., Canada, Japan, and South Korea.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/how-china-is-girding-for-an-ai-battle-with-the-u-s-5b23af51
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Big Tech and VCs invest hundreds of billions in AI while salaries of AI experts reach the stratosphere
ZTE’s AI infrastructure and AI-powered terminals revealed at MWC Shanghai
Deloitte and TM Forum : How AI could revitalize the ailing telecom industry?
Huawei launches CloudMatrix 384 AI System to rival Nvidia’s most advanced AI system
On Saturday, Huawei Technologies displayed an advanced AI computing system in China, as the Chinese technology giant seeks to capture market share in the country’s growing artificial intelligence sector. Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 system made its first public debut at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC), a three-day event in Shanghai where companies showcase their latest AI innovations, drawing a large crowd to the company’s booth.
The Huawei CloudMatrix 384 is a high-density AI computing system featuring 384 Huawei Ascend 910C chips, designed to rival Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72 (more below). The AI system employs a “supernode” architecture with high-speed internal chip interconnects. The system is built with optical links for low-latency, high-bandwidth communication. Huawei has also integrated the CloudMatrix 384 into its cloud platform. The system has drawn close attention from the global AI community since Huawei first announced it in April.
The CloudMatrix 384 resides on the super-node Ascend platform and uses high-speed bus interconnection capability, resulting in low latency linkage between 384 Ascend NPUs. Huawei says that “compared to traditional AI clusters that often stack servers, storage, network technology, and other resources, Huawei CloudMatrix has a super-organized setup. As a result, it also reduces the chance of facing failures at times of large-scale training.

Huawei staff at its WAIC booth declined to comment when asked to introduce the CloudMatrix 384 system. A spokesperson for Huawei did not respond to questions. However, Huawei says that “early reports revealed that the CloudMatrix 384 can offer 300 PFLOPs of dense BF16 computing. That’s double of Nvidia GB200 NVL72 AI tech system. It also excels in terms of memory capacity (3.6x) and bandwidth (2.1x).” Indeed, industry analysts view the CloudMatrix 384 as a direct competitor to Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72, the U.S. GPU chipmaker’s most advanced system-level product currently available in the market.
One industry expert has said the CloudMatrix 384 system rivals Nvidia’s most advanced offerings. Dylan Patel, founder of semiconductor research group SemiAnalysis, said in an April article that Huawei now had AI system capabilities that could beat Nvidia’s AI system. The CloudMatrix 384 incorporates 384 of Huawei’s latest 910C chips and outperforms Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72 on some metrics, which uses 72 B200 chips, according to SemiAnalysis. The performance stems from Huawei’s system design capabilities, which compensate for weaker individual chip performance through the use of more chips and system-level innovations, SemiAnalysis said.
Huawei has become widely regarded as China’s most promising domestic supplier of chips essential for AI development, even though the company faces U.S. export restrictions. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang told Bloomberg in May that Huawei had been “moving quite fast” and named the CloudMatrix as an example.
Huawei says the system uses “supernode” architecture that allows the chips to interconnect at super-high speeds and in June, Huawei Cloud CEO Zhang Pingan said the CloudMatrix 384 system was operational on Huawei’s cloud platform.
According to Huawei, the Ascend AI chip-based CloudMatrix 384 with three important benefits:
- Ultra-large bandwidth
- Ultra-Low Latency
- Ultra-Strong Performance
These three perks can help enterprises achieve better AI training as well as stable reasoning performance for models. They could further retain long-term reliability.
References:
https://www.huaweicentral.com/huawei-launches-cloudmatrix-384-ai-chip-cluster-against-nvidia-nvl72/
https://semianalysis.com/2025/04/16/huawei-ai-cloudmatrix-384-chinas-answer-to-nvidia-gb200-nvl72/
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Huawei’s “FOUR NEW strategy” for carriers to be successful in AI era
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Two alarming research studies this year have drawn attention to the damage that Gen AI agents like ChatGPT are doing to our brains:
The first study, published in February, by Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon University, surveyed 319 knowledge workers and concluded that “while GenAI can improve worker efficiency, it can inhibit critical engagement with work and can potentially lead to long-term overreliance on the tool and diminished skills for independent problem-solving.”
An MIT study divided participants into three essay-writing groups. One group had access to Gen AI and another to Internet search engines while the third group had access to neither. This “brain” group, as MIT’s researchers called it, outperformed the others on measures of cognitive ability. By contrast, participants in the group using a Gen AI large language model (LLM) did the worst. “Brain connectivity systematically scaled down with the amount of external support,” said the report’s authors.
Across the 20 companies regularly tracked by Light Reading, headcount fell by 51,700 last year. Since 2015, it has dropped by more than 476,600, more than a quarter of the previous total.
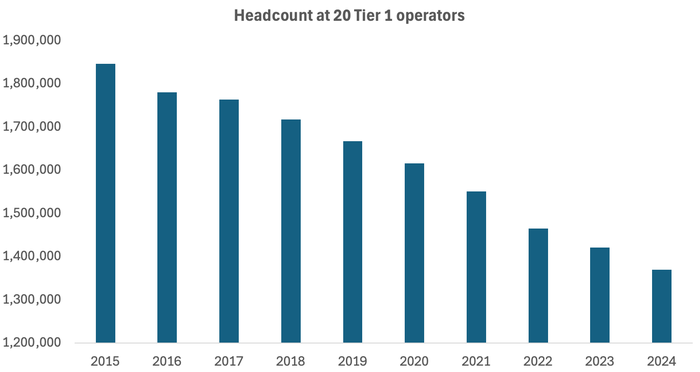
Source: Light Reading
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Doing More with Less:
- In 2015, Verizon generated sales of $131.6 billion with a workforce of 177,700 employees. Last year, it made $134.8 billion with fewer than 100,000. Revenues per employee, accordingly, have risen from about $741,000 to more than $1.35 million over this period.
- AT&T made nearly $868,000 per employee last year, compared with less than $522,000 in 2015.
- Deutsche Telekom, buoyed by its T-Mobile US business, has grown its revenue per employee from about $356,000 to more than $677,000 over the same time period.
- Orange’s revenue per employee has risen from $298,000 to $368,000.
Significant workforce reductions have happened at all those companies, especially AT&T which finished last year with 141,000 employees – about half the number it had in 2015!
Not to be outdone, headcount at network equipment companies are also shrinking. Ericsson, Europe’s biggest 5G vendor, cut 6,000 jobs or 6% of its workforce last year and has slashed 13,000 jobs since 2023. Nokia’s headcount fell from 86,700 in 2023 to 75,600 at the end of last year. The latest message from Börje Ekholm, Ericsson’s CEO, is that AI will help the company operate with an even smaller workforce in future. “We also see and expect big benefits from the use of AI, and that is one reason why we expect restructuring costs to remain elevated during the year,” he said on this week’s earnings call with analysts.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Other Voices:
Light Reading’s Iain Morris wrote, “An erosion of brainpower and ceding of tasks to AI would entail a loss of control as people are taken out of the mix. If AI can substitute for a junior coder, as experts say it can, the entry-level job for programming will vanish with inevitable consequences for the entire profession. And as AI assumes responsibility for the jobs once done by humans, a shrinking pool of individuals will understand how networks function.
“If you can’t understand how the AI is making that decision, and why it is making that decision, we could end up with scenarios where when something goes wrong, we simply just can’t understand it,” said Nik Willetts, the CEO of a standards group called the TM Forum, during a recent conversation with Light Reading. “It is a bit of an extreme to just assume no one understands how it works,” he added. “It is a risk, though.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References: