SKT
SK Group and AWS to build Korea’s largest AI data center in Ulsan
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is partnering with the SK Group to build South Korea’s largest AI data center. The two companies are expected to launch the project later this month and will hold a groundbreaking ceremony for the 100MW facility in August, according to state news service Yonhap.
Scheduled to begin operations in 2027, the AI Zone will empower organizations in Korea to develop innovative AI applications locally while leveraging world-class AWS services like Amazon SageMaker, Bedrock, and Q. SK Group expects to bolster Korea’s AI competitiveness and establish the region as a key hub for hyperscale infrastructure in Asia-Pacific through AI initiatives.
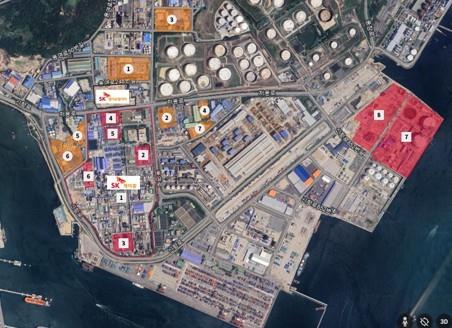
AWS provides on-demand cloud computing platforms and application programming interfaces (APIs) to individuals, businesses and governments on a pay-per-use basis.The data center will be built on a 36,000-square-meter site in an industrial park in Ulsan, 305 km southeast of Seoul. It will be powered by 60,000 GPUs, making it the country’s first large-scale AI data center.
The facility will be located in the Mipo industrial complex in Ulsan, 305 kilometers southeast of Seoul. It will house 60,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and have a power capacity of 100 megawatts, making it the country’s first AI infrastructure of such scale, the sources said.
Ryu Young-sang, chief executive officer (CEO) of SK Telecom Co., had announced the company’s plan to build a hyperscale AI data center equipped with 60,000 GPUs in collaboration with a global tech partner, during the Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025 held in Spain in March.
SK Telecom plans to invest 3.4 trillion won (US$2.49 billion) in AI infrastructure by 2028, with a significant portion expected to be allocated to the data center project. SK Telecom- South Korea’s biggest mobile operator and 31% owned by the SK Group – will manage the project. “They have been working on the project, but the exact timeline and other details have yet to be finalized,” an SK Group spokesperson said.
The AI data center will be developed in two phases, with the initial 40MW phase to be completed by November 2027 and the full 100MW capacity to be operational by February 2029, the Korea Herald reported Monday. Once completed, the facility, powered by 60,000 graphics processing units, will have a power capacity of 103 megawatts, making it the country’s largest AI infrastructure, sources said.
SK Group appears to have chosen Ulsan as the site, considering its proximity to SK Gas’ liquefied natural gas combined heat and power plant, ensuring a stable supply of large-scale electricity essential for data center operations. The facility is also capable of utilizing LNG cold energy for data center cooling.
SKT last month released its revised AI pyramid strategy, targeting AI infrastructure including data centers, GPUaaS and customized data centers. It is also developing personal agents A. and Aster for consumers and AIX services for enterprise customers.
Globally, it has found partners through the Global Telecom Alliance, which it co-founded, and is collaborating with US firms Anthropic and Lambda.
SKT’s AI business unit is still small, however, recording just KRW156 billion ($115 million) in revenue in Q1, two-thirds of it from data center infrastructure. Its parent SK Group, which also includes memory chip giant SK Hynix and energy firm SK Innovation, reported $88 billion in revenue last year.
AWS, the world’s largest cloud services provider, has been expanding its footprint in Korea. It currently runs a data center in Seoul and began constructing its second facility in Incheon’s Seo District in late 2023. The company has pledged to invest 7.85 trillion won in Korea’s cloud computing infrastructure by 2027.
“When SK Group’s exceptional technical capabilities combine with AWS’s comprehensive AI cloud services, we’ll empower customers of all sizes, and across all industries here in Korea to build and innovate with safe, secure AI technologies,” said Prasad Kalyanaraman, VP of Infrastructure Services at AWS. “This partnership represents our commitment to Korea’s AI future, and I couldn’t be more excited about what we’ll achieve together.”
Earlier this month AWS launched its Taiwan cloud region – its 15th in Asia-Pacific – with plans to invest $5 billion on local cloud and AI infrastructure.
References:
https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20250616004500320?section=k-biz/corporate
https://www.koreaherald.com/article/10510141
https://www.lightreading.com/data-centers/aws-sk-group-to-build-korea-s-largest-ai-data-center
SK Telecom unveils plans for AI Infrastructure at SK AI Summit 2024
Introduction:
During the two-day SK AI Summit 2024 [1.], SK Telecom CEO Ryu Young-sang unveiled the company’s comprehensive strategy which revolves around three core components: AI data centers (AIDCs), a cloud-based GPU service (GPU-as-a-Service, GPUaaS), and Edge AI. SK Telecom is planning to construct hyperscale data centers in key regions across South Korea, with the goal of becoming the AIDC hub in the Asia Pacific region. Additionally, the company will launch a cloud-based GPU service to address the domestic GPU shortage and introducing ‘Edge AI’ to bridge the gap between AIDC and on-device AI. This innovative approach aims to connect national AI infrastructure and expand globally, in collaboration with partners both in South Korea and abroad.
Note 1. The SK AI Summit is an annual event held by the SK Group, where global experts in various AI fields gather to discuss coexistence in the era of artificial general intelligence (AGI) and seek ways to strengthen the ecosystem.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Constructing AI Data Centers in South Korea’s key regions:
SK Telecom plans to start with hyperscale AIDCs that require more than 100 megawatts (MW) in local regions, with future plans to expand its scale to gigawatts (GW) or more, to leap forward as the AIDC hub in the Asia Pacific region.
By extending the AIDC to national bases, centers can secure a stable power supply through the utilization of new renewable energy sources such as hydrogen, solar and wind power, and easily expand to global markets through submarine cables. SK Telecom anticipates building AIDC cost-effectively when the data center combines SK Group’s capabilities in high-efficiency next-generation semiconductors, immersion cooling, and other energy solutions, along with its AI cluster operation.
Prior to this, SK Telecom plans to open an AIDC testbed in Pangyo, Korea, in December, which combines the capabilities of the SK Group and various solutions owned by partner companies. This facility, where all three types of next-generation liquid cooling solutions—direct liquid cooling, immersion cooling, and precision liquid cooling—are deployed, will be the first and only testbed in Korea. It will also feature advanced AI semiconductors like SK hynix’s HBM, as well as GPU virtualization solutions and AI energy optimization technology. This testbed will provide opportunities to observe and experience the cutting-edge technologies of a future AIDC.
Supplying GPU via cloud to metropolitan areas:
SK Telecom plans to launch a cloud-based GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) by converting the Gasan data center, located in the metropolitan area, into an AIDC to quickly resolve the domestic GPU shortage.
Starting in December, SK Telecom plans to launch a GPUaaS with NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU through a partnership with U.S.-based Lambda. In March 2025, SK Telecom plans to introduce NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPU in Korea, gradually expanding to meet customer demand.
Through the AI cloud services (GPUaaS), SKT aims to enable companies to develop AI services easily and at a lower cost, without needing to purchase their own GPUs, ultimately supporting the vitalization of Korea’s AI ecosystem.
Introducing ‘Edge AI’ to open a new opportunity in telco infrastructure:
SK Telecom plans to introduce ‘Edge AI,’ which can narrow the gap between AIDC and on-device AI, using the nationwide communication infrastructure.
Edge AI is an infrastructure that combines mobile communication networks and AI computing, offering advantages in reduced latency, enhanced security, and improved privacy compared to large-scale AIDCs. Additionally, it enables large-scale AI computing, complementing the existing AI infrastructure, compared to on-device AI.
SKT is currently conducting research on advanced technologies and collaborating with global partners to build AIDC-utilizing communication infrastructure and develop customized servers. The company is also carrying out various proof of concept (PoC) projects across six areas, including healthcare, AI robots, and AI CCTV, to discover specialized Edge AI services.
“So far, the competition in telecommunications infrastructure has been all about connectivity, namely speed and capacity, but now the paradigm of network evolution should be changed,” said Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SK Telecom. “The upcoming 6G will evolve into a next-generation AI infrastructure where communication and AI are integrated.”
Developing a comprehensive AIDC solution to enter global market:
SK Telecom plans to develop a comprehensive AIDC solution that combines AI semiconductors, data centers, and energy solutions through collaboration with AI companies in Korea and abroad, with the aim of entering the global market.SK Telecom aims to lead the global standardization of Edge AI and collaborate on advanced technology research, while working towards the transition to 6G AI infrastructure.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company with a strong global presence. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of AI Infrastructure, AI Transformation (AIX) and AI Service to deliver greater value for industry, society, and life.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit our LinkedIn page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-telecom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SKT-Samsung Electronics to Optimize 5G Base Station Performance using AI
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
SKT-Samsung Electronics to Optimize 5G Base Station Performance using AI
SK Telecom (SKT) has partnered with Samsung Electronics to use AI to improve the performance of its 5G base stations in order to upgrade its wireless network. Specifically, they will use AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology (AI-RAN Parameter Recommender) to commercial 5G networks.
The two companies have been working throughout the year to learn from past mobile network operation experiences using AI and deep learning, and recently completed the development of technology that automatically recommends optimal parameters for each base station environment. When applied to SKT’s commercial network, the new technology was able to bring out the potential performance of 5G base stations and improve the customer experience.
Mobile base stations are affected by different wireless environments depending on their geographical location and surrounding facilities. For the same reason, there can be significant differences in the quality of 5G mobile communication services in different areas using the same standard equipment.
Accordingly, SKT utilized deep learning, which analyzes and learns the correlation between statistical data accumulated in existing wireless networks and AI operating parameters, to predict various wireless environments and service characteristics and successfully automatically derive optimal parameters for improving perceived quality.
Samsung Electronics’ ‘Network Parameter Optimization AI Model’ used in this demonstration improves the efficiency of resources invested in optimizing the wireless network environment and performance, and enables optimal management of mobile communication networks extensively organized in cluster units.
The two companies are conducting additional learning and verification by diversifying the parameters applied to the optimized AI model and expanding the application to subways where traffic patterns change frequently.
SKT is pursuing advancements in the method of improving quality by automatically adjusting the output of base station radio waves or resetting the range of radio retransmission allowance when radio signals are weak or data transmission errors occur due to interference.
In addition, we plan to continuously improve the perfection of the technology by expanding the scope of targets that can be optimized with AI, such as parameters related to future beamforming*, and developing real-time application functions.
* Beamforming: A technology that focuses the signal received through the antenna toward a specific receiving device to transmit and receive the signal strongly.
SKT is expanding the application of AI technology to various areas of the telecommunications network, including ‘Telco Edge AI’, network power saving, spam blocking, and operation automation, including this base station quality improvement. In particular, AI-based network power saving technology was recently selected as an excellent technology at the world-renowned ‘Network X Award 2024’.
Ryu Tak-ki, head of SK Telecom’s infrastructure technology division, said, “This is a meaningful achievement that has confirmed that the potential performance of individual base stations can be maximized by incorporating AI,” and emphasized, “We will accelerate the evolution into an AI-Native Network that provides differentiated customer experiences through the convergence of telecommunications and AI technologies.”
“AI is a key technology for innovation in various industrial fields, and it is also playing a decisive role in the evolution to next-generation networks,” said Choi Sung-hyun, head of the advanced development team at Samsung Electronics’ network business division. “Samsung Electronics will continue to take the lead in developing intelligent and automated technologies for AI-based next-generation networks.”
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SKT said it is expanding the use of AI to various areas of its communications network, such as “Telco Edge AI,” network power reduction, spam blocking and operation automation, including basestation quality improvement.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
South Korea has 30 million 5G users, but did not meet expectations; KT and SKT AI initiatives
SKT Develops Technology for Integration of Heterogeneous Quantum Cryptography Communication Networks
India Mobile Congress 2024 dominated by AI with over 750 use cases
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia have agreed to work on artificial intelligence (AI) assisted “fiber sensing,” a wired network technology that employs AI to monitor the environment around optical cables. The two companies signed a memorandum of understanding (see photo below) last Wednesday, with a plan to “accumulate empirical data based on machine learning” from SKT’s commercial network. SKT, South Korea’s largest mobile network carrier, said on Monday that it will utilize Nokia’s product to detect earthquakes, climate changes and other unexpected situations that might arise from nearby construction areas in order to stabilize network conditions. The objective is nationwide deployment in South Korea by the end of this year.
In a joint statement, the companies explained when data runs through an optical cable, the phase of the light can change due to various factors like temperature fluctuations or physical strain on the cable. The changes can be detected and analyzed to provide precise measurements of the environmental conditions affecting the fiber. Using AI-based technology, SKT and Nokia aim to stabilize fiber optic networks in advance by tracking the impact of weather conditions and construction on optical cables. The statement added “fiber sensing” has no distance limitations, unlike some existing wired network monitoring technologies, making it possible to quickly apply the new technology to major backbone networks.
SKT-Nokia monitors wired network status with AI:
– Tracking the impact of weather, earthquakes, construction, etc. on optical cables with ‘fiber sensing’ technology
– Immediately applicable to existing networks and no distance restrictions, making it easy to apply to backbone networks
– Both companies’ capabilities will be combined to quickly internalize new AI-based wired network technology
A signing ceremony for the memorandum of understanding took place at SK Telecom’s headquarters Wednesday in central Seoul. SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, attended the event.

SK Telecom’s Ryu Jung-hwan, head of infrastructure strategy and technology, right, and John Harrington, Nokia’s senior vice president and head of network infrastructure sales for the Asia-Pacific region, pose for a photo after a signing ceremony at SK Telecom’s headquarters in central Seoul on Wednesday, August 7th. Photo Credit: SK TELECOM
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In July, SKT and Singtel announced that they have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to collaborate on building next-generation telecommunications networks that will drive innovation, improve network performance and security and deliver enhanced customer experiences over the next two years. The partners will explore the use of artificial intelligence (AI), orchestration tools, and deepen the domain knowledge of network virtualization and other technologies – central to laying the necessary building blocks for progressing to 6G.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7228552138988134402/
SK Telecom and Singtel partner to develop next-generation telco technologies using AI
SK Telecom (South Korea) and Singtel (Singapore) have initiated a two-year project to develop advanced telecommunication networks. This collaboration aims to drive innovation, improve network performance and security, and enhance customer experiences through the use of artificial intelligence (AI), orchestration tools, and network virtualization.
The project will focus on creating innovative solutions like Edge-AI Infrastructure to enhance connectivity and provide unique AI service offerings. A white paper will describe advancements to assist other global telcos to harnessing the capabilities of 5G and preparing for 6G.
This MOU initiative is expected to not only enhance connectivity but also provide customers with unique AI service offerings and enable the operators to restore services faster, thus improving the customer experience.
Additionally, SKT and Singtel will be putting together a white paper on their advancements in areas such as virtualization, slicing and network evolution that can help other telcos globally to capitalize on the capabilities of 5G and to prepare for 6G in 2030.

SK Telecom (SKT) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Singtel, Singapore’s leading telecommunications provider, to collaborate on the application of AI technology in communication networks, the development of use cases for 5G network slicing technology, and preparation for 6G technology, aimed at fostering advancements in 5G and next-generation communication technologies. Photo Courtesy of SKT
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Kang Jong-ryeol, SKT’s Head of ICT Infra(CSPO) stated, “The collaboration between SKT and Singtel marks a significant first step in shaping the future of the global telecommunications industry.” He further emphasized, “By combining the strengths of both companies, we aim to achieve efficient high-performance network construction, enhance network stability, and discover new network-based services. Additionally, we will strive to make significant advancements in next-generation communication technologies, including AI-powered wired and wireless infrastructure.”
Tay Yeow Lian, Singtel’s Managing Director, Networks, said, “As a global leader in 5G technology, we’re keen to capitalize on the myriad of capabilities this technology has to offer, especially in the areas of network slicing and with the inclusion of AI. With SKT, we’re looking to not only enhance the experience of our customers but to also drive industry innovation and help us prepare for the evolution to 6G.”
ANNEX: Singtel’s 5G advancements
· Developed Paragon, the industry’s first all-in-one aggregation and business orchestration platform, which allows enterprises to interact with and manage networks, clouds and multi-access edge computing (MEC) infrastructure and applications
· Developed Singtel CUBΣ, a Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) that makes it easier for enterprises to subscribe and manage desired services and multiple vendors as well as gain insights on network utilisation, workload performance and sustainability metrics via a single sign-on digital portal. CUBΣ leverages and integrates AI into its network management systems to deliver enhanced services such as proactive user experience monitoring, incident automation and predictive analytics to anticipate, detect and address incidents faster. This results in improved network performance, optimised resource allocation, enhanced security protocols, elevated the overall user experience, and the development of a network that learns, evolves and self-improves over time – all of which enable faster digital transformation for greater economic growth and innovation.
Major 5G developments from Singtel:
2022
· Launched first public multi-access edge compute for enterprises in Asia with Microsoft
· Launched iSHIP to provide critical satellite-enabled connectivity and digital services for the maritime industry
2023
· Singapore’s first 5G-enabled smart retail showcase
· Achieved 5G upload speed of more than 1.6Gbps in an enterprise deployment
· Completed more than 30 5G trials at Sentosa
· Successfully trialed RedCap technology for better energy savings for IoT devices
2024
· Addition of Starlink satellites for maritime connectivity
· Offered the 5G Express Pass service to concertgoers for Coldplay and Taylor Swift
· Pioneered app-based network slicing, aka User Equipment Route Selection Policy
· Singtel Paragon integrated into Telkomsel’s enterprise product portfolio
· Launch of Paragon-S to spur digital transformation for satellite operators
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company with a strong global presence. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of AI Infrastructure, AI Transformation (AIX) and AI Service to deliver greater value for industry, society, and life.
References:
https://www.koreaittimes.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=132974
SK Telecom, DOCOMO, NTT and Nokia develop 6G AI-native air interface
SK Telecom, Intel develop low-latency technology for 6G core network
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
SK Telecom, Intel develop low-latency technology for 6G core network
In collaboration with Intel, SK Telecom (SKT) has successfully developed technology to reduce communication delays necessary for the evolution of 6G Core Network Architecture. The Core network is the gateway through which all voice and data traffic generated from a customer’s mobile device passes through to access the Internet network. It is a mobile communication service system that is responsible for security and service quality through the inter-connection of various systems.
Editor’s NOTE: Of course, 6G is currently undefined with only the features and functions being defined by ITU-R WP 5D which is meeting this week in Geneva. The 6G core network specifications will be done by 3GPP and NOT ITU-T as was the case for 5G core.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The 6G Core Architecture is required to have higher flexibility and safety than previous generations of wireless communications, and to provide stable AI service quality and technologies to customers by embedding intelligent and automation technologies.
As Core network technology continues to develop, the various systems that make up the network and the detailed functions that provide various services are also explosively increasing. As network complexity continues to increase, the process of sending and receiving messages is frequently recreated. Therefore, communication delays will increase compared to before. It is difficult to address these limitations with communication standard technologies (service communication proxies) for interconnection between unit functions within the existing Core network.
Inline Service Mesh, a low latency technology the two companies developed utilizing Intel Xeon processors with built in AI, is capable of increasing the communication speed within the Core network by reducing latency between unit function without Proxy.
Through this technology development, AI, which requires a large amount of computation, can be applied to the Core network in a wider variety of models. SKT has already commercialized a technology that reduces wireless resources by 40% and improves connectivity by analyzing movement patterns of real users in real time. Through this cooperation, the two companies will be able to reduce communication delays by 70% and increase service efficiency by 33% in the Core network through the application of the 6G Core Architecture.
SKT aims to apply the results of this study to commercial equipment next year. A technical white paper has been published by Intel that describes the technology, development process and benefits.
SKT and Intel have been continuing to cooperate for research on the development of key wired/wireless mobile communication technologies for the past 10 years. Based on the results of this study, the two companies plan to continue research and development for traffic processing improvement technologies incorporating AI technology in various areas of the Core network.
“We have made another technical achievement through continuous technology development cooperation with Intel to secure leadership in 6G,” said Yu Takki, Vice President and Head of Infra Tech at SKT. “We will continue our research and make efforts to commercialize AI-based 6G Core Architecture.”
“Our research and development efforts with SK Telecom continue to deliver innovations that have been deployed by Communications Service Providers worldwide”, said Dan Rodriguez, Corporate Vice President of Intel Network & Edge Solutions Group. “By leveraging the latest Intel Xeon processors with built in AI features, our companies are able to drive both performance and efficiency improvements that will be vital to the future Core networks.
Last March, SKT and NTT DOCOMO released a white paper addressing the requirements for future 6G networks.
The South Korean carrier said the new white paper contains its views on 6G key requirements and 6G evolution methodology, along with its opinions on the latest trends in frequency standardization. The 6G white paper also provides analysis, development directions and methodologies pertaining to promising 6G use cases, technology trends as well as and candidate frequencies.
The 6G White Paper reviews the following:
- Performance requirements and implementation scenarios for each frequency band, taking into account the characteristics of each frequency
- Issues concerning coverage and devices in high-frequency bands
- Standardization for migration to 6G architecture and application of cloud-native / open architecture

References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1597¤tPage=1&type=&keyword=
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
https://www.docomo.ne.jp/english/corporate/technology/rd/docomo6g/whitepaper_dcmskt.html#title02
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
Korean telco SK Telecom and digital security firm Thales have tested quantum-resistant cryptography based on a 5G standalone (5G SA) network. The trial is focused on encrypting and decrypting identity data on a 5G network to protect user privacy from future quantum threats. It was performed using Thales 5G Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) SIM cards and a trial 5G standalone network environment from SKT. The test involved cryptographic algorithms designed to resist attacks from quantum computers, as well as ‘classical’ computers.
The end user identity on the 5G SA network is concealed and secured on the device side via the 5G SIM card. The security mechanisms involve cryptographic algorithms designed to resist attacks from future quantum computers, providing a level of security that is considered robust in the post-quantum era.

Photo Credit: rawpixel
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been leading an initiative to standardize post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, and SKT and Thales have used the Crystals-Kyber one for this successful real condition trial. These post-quantum secure algorithms are being developed to withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers.
“This collaboration between SKT and Thales highlights our commitment to staying ahead of the curve in terms of cybersecurity and ensuring the safety of our customers’ data. PQC provides enhanced security through the use of cryptographic algorithms that are thought to be secure against quantum computer attacks. Going forward, we will combine PQC SIM with our additional Quantum expertise to achieve end-to-end quantum-safe communications,” said Yu Takki, Vice President and Head of Infra Technology Office of SKT.
“As quantum computers have the potential to break certain existing cryptographic algorithms, there is an emerging need to transition to cryptographic algorithms believed to be secure against quantum attacks. For 5G networks, Thales started to invest on cryptographic algorithms that are quantum-resistant to enhance continued communications security and privacy for users,” said Eva Rudin, SVP Mobile Connectivity & Solutions at Thales.
As quantum computing gets more reliable and presumably starts getting used more widely in the future, this type of security is going to become increasingly important. Nokia recently announced it had completed a proof of concept trial alongside Greek research consortium HellasQCI, demonstrating what it calls quantum-safe connectivity infrastructure.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, SK Broadband, an internet and paid TV service affiliate of SK Telecom, launched additional personalized internet protocol television (IPTV) services utilizing AI technology to enhance its competitiveness in the country’s paid TV market, the company said Wednesday.
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of telecommunications, media, AI, metaverse, cloud and connected intelligence to deliver greater value for both individuals and enterprises.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit SKT’s LinkedIn page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-telecom.
About Thales:
Thales (Euronext Paris: HO) is a global leader in advanced technologies within three domains: Defence & Security, Aeronautics & Space, and Digital Identity & Security. It develops products and solutions that help make the world safer, greener and more inclusive.
References:
https://www.newswire.co.kr/newsRead.php?no=981374
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/sk-telecom-and-thales-trial-quantum-resistant-cryptography-for-5g-sa
https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/tech/2023/12/133_365470.html
SKT Develops Technology for Integration of Heterogeneous Quantum Cryptography Communication Networks
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom announced that they signed a Letter of Intent (LOI) to jointly develop a telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs) that will enable global telecommunication companies (telcos) to develop generative AI models easily and quickly. The LOI signing ceremony took place at SK Seorin Building located in Seoul with the attendance of key executives from both companies including Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SKT, Chung Suk-geun, Chief AI Global Officer of SKT, Tim Höttges, CEO of Deutsche Telekom, Claudia Nemat, Board Member Technology and Innovation of Deutsche Telekome, and Jonathan Abrahamson, Chief Product and Digital Officer of Deutsche Telekom.

SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific LLM
This marks the first fruition of discussions held by the Global Telco AI Alliance, which was launched by SKT, Deutsche Telekom, E&, and Singtel, in July 2023, and lays the foundation to enter the global market. SKT and Deutsche Telekom plan to collaborate with AI companies such as Anthropic (Claude 2) and Meta (Llama2) to co-develop a multilingual – i.e, German, English, Korean, etc. – large language model (LLM) tailored to the needs of telcos. They plan to unveil the first version of the telco-specific LLM in the first quarter of 2024.
The telco-specific LLM will have a higher understanding of telecommunication service-related areas and customer’s intentions than general LLMs, making it suitable for customer services like AI contact center. The goal is to support telcos across the world, including Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, to develop generative AI services such as AI agents flexibly according to their respective environment. That will enable telcos to save both time and cost for developing large platforms, and secure new business opportunities and growth engines through AI innovation that shifts the paradigm in the traditional telecommunications industry. To this end, SKT and Deutsche Telekom plan to jointly develop AI platform technologies that telcos can use to create generative AI services to reduce both development time and cost.
For instance, when a telco tries to build an AI contact center based on generative AI, it itself will be able to build one that suits their environment more quickly and flexibly. In addition, AI can be applied to other areas such as network monitoring and on-site operations to increase efficiency, resulting in cost savings in the mid- to long-term.
Through this collaboration, the two companies will proactively respond to the recent surge in AI demand from telcos, while also promoting the expansion of the global AI ecosystem through the successful introduction of generative AI optimized for specific industries or domains.
“AI shows impressive potential to significantly enhance human problem-solving capabilities. To maximize its use especially in customer service, we need to adapt existing large language models and train them with our unique data. This will elevate our generative AI tools,” says Claudia Nemat, Member of the Board of Management for Technology and Innovation at Deutsche Telekom.
“Through our partnership with Deutsche Telekom, we have secured a strong opportunity and momentum to gain global AI leadership and drive new growth,” said Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SKT. “By combining the strengths and capabilities of the two companies in AI technology, platform and infrastructure, we expect to empower enterprises in many different industries to deliver new and higher value to their customers.”
References:
Global Telco AI Alliance to progress generative AI for telcos
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
Bain & Co, McKinsey & Co, AWS suggest how telcos can use and adapt Generative AI
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
Google Cloud infrastructure enhancements: AI accelerator, cross-cloud network and distributed cloud
Cloud infrastructure services market grows; AI will be a major driver of future cloud service provider investments
TPG, Ericsson launch AI-powered analytics, troubleshooting service for 4G/5G Mobile, FWA, and IoT subscribers
South Korea government fines mobile carriers $25M for exaggerating 5G speeds; KT says 5G vision not met
South Korea’s antitrust regulator said it had imposed a total of 33.6 billion won ($25.06 million) in fines on three domestic mobile carriers for exaggerating their 5G network speeds. The Korea Fair Trade Commission (KFTC) said the three South Korean firms – SK Telecom Co Ltd, KT Corp, and LG Uplus Corp – had also unfairly advertised that they were the fastest relative to their competitors.
“The three telecom companies advertised that consumers could use target 5G network speeds, which cannot be achieved in real-life environment … companies advertised that their 5G network speed was faster than competitors without evidence,” the KFTC said in a statement.
In support of ongoing civil lawsuits filed by consumers, the advertisements released by the three mobile carriers have been presented by the regulator to a local court.
SK Telecom and KT Corp declined to comment. A spokesperson at LG Uplus said the company is reviewing the sanctions.
The KFTC imposed a fine of 16.8 billion won on SK Telecom, 13.9 billion won on KT and 2.8 billion won on LG Uplus.
There were 30.76 million 5G network users in South Korea in June, accounting for about 38% of the total 80.23 million mobile subscriptions in the country, according to data from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Source: Reuters
In a paper issued last week, SK Telecom states correctly the industry is far from achieving its 5G goals even four years after commercialization. There were “misunderstandings” about network performance and problems such as device form factors and lack of market demand, it said. “A variety of visionary services were expected, but there was no killer service,” the paper stated. “We should have taken a more objective perspective,” it added. In particular:
A variety of visionary services were expected, but there was no killer service Even at the time when preparing for 5G, services such as autonomous driving, UAM, XR, hologram, and digital twin had appeared and expected, but most of them did not live up to expectations. We should have taken a more objective perspective. For example, whether 5G technology alone could change the future, or whether the overall environment constituting the service was prepared together. If so, the gap between the public’s expectations for 5G and the reality would not have been large. 3D video, UHD streaming, AR/VR, autonomous driving, remote surgery, etc. are representative services that are not still successful presented by the 5G Vision Recommendation. Most of them are the result of a combination of factors such as form factor constraints, immaturity of device and service technology, low or absent
market demand, and policy/regulation issues, rather than a single factor of the lack of 5G performance.
The authors concluded that instead of expecting that the new technology alone could create successful services, it would have been more effective to have collaborated with partners to build a broader 5G ecosystem.
Gap between 5G Vision Recommendations and customer expectations:
Although the usage scenarios and capability goals presented in the 5G Vision Recommendation are future goals to be achieved in the long term, misunderstandings have been created that can lead to excessive expectations of 5G performance and innovative services based on it from the beginning of commercialization. To prevent this misunderstanding from recurring in 6G, it is necessary to consider various usage scenarios of 6G, set achievable goals, and communicate accurately with the public. In particular, there were issues raised about the maximum transmission speed of 20Gbps, which was considered an icon of 5G key performance indicators. As 3G evolved into LTE, the radio access technology also evolved from WCDMA to OFDMA, and with the introduction of CA and multi-antenna technology, it became possible to use a much wider bandwidth than 3G. This can be seen as a ‘revolutionary’ improvement. On the other hand, 5G is considered as an ‘evolutionary’ improvement that supplements the performance of LTE based on the same radio access technology, CA, and multi-antenna system technology. Due to this, it was difficult to implement the increase in transmission speed shown in LTE in 5G at once. Moreover, the difference in technology perception was further revealed in the initial stage of 5G commercialization. Early commercialization was promoted for 5G, however, 5G required more base station compared to LTE to build a nationwide network due to frequency characteristics, requiring more efforts in terms of cost and time.
SK Telecom has made significant efforts to expedite 5G nationwide rollout, but customers wanted the same level of coverage as LTE in a brief period.
References:
https://newsroom-prd-data.s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/SKT6G-White-PaperEng_v1.0_web.pdf
SKT Develops Technology for Integration of Heterogeneous Quantum Cryptography Communication Networks
SK Telecom (SKT) today announced that for the first time in the world, it developed a technology that allows for integrated control and operation of quantum cryptography networks by integrating networks composed of equipment from different manufacturers via software-defined networking (SDN) and distributing quantum keys in an automated manner.
So far it was impossible to connect and operate quantum cryptography communication networks of different companies and countries. However, with SKT‘s new technology, quantum cryptography communication networks of diverse manufacturers, mobile operators and nations can be interconnected and co-operated.
The company said that it completed verification of the technology on the Korea Advanced Research Network (KOREN), a non-profit testbed network infrastructure operated by the National Information Society Agency (NIA) to facilitate research, test and verification of future network leading technologies and related equipment.
Based on the results of development and verification of the technology, SKT has been actively promoting standardization by sharing the case with global telcos.
To set international standards for the integration of quantum cryptography communication networks, SKT proposed two standardization tasks – i.e. ‘Control Interface of Software Defined Networks’ and ‘Orchestration Interface of Software Defined Networks for Interoperable Key Management System’ – to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), and they were chosen as work items by the ETSI industry specification group for QKD (ISG-QKD) in March 2023.
If approved as international standards, they will provide a technical basis for creating a large-scale network by interconnecting quantum cryptography communication networks built by many different operators. SKT plans to continue developing additional technologies for interworking of services between different operators/countries, as well as management of service quality.
Through these efforts, the company expects to strengthen the competitiveness of domestic companies and boost the quantum cryptography ecosystem both home and abroad.
Meanwhile, at this year’s IOWN Global Forum Workshop, SKT presented ‘Quantum Secure Interconnection for Critical Infrastructure,’ covering use cases for next-generation transmission encryption technology and proposal for a proof-of-concept (PoC) of quantum cryptography in All-Photonics Network (APN). The company also showcased its quantum cryptography communication technologies at 2023 MWC Barcelona.
“The two standardization tasks approved as work items by ETSI will boost the expansion of quantum cryptography communication in the global market,” said Ha Min-yong, Chief Development Officer of SKT. “We will work with diverse global players in many different areas to create new business opportunities in the global market.”

Disclaimer:
SK Telecom Co. Ltd. published this content on 05 April 2023 and is solely responsible for the information contained therein. https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1563¤tPage=1&type=&keyword=
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
From SDxCentral:
Quantum cryptography communication transmits each bit of information as a single photon of light, which encrypts that information against eavesdropping or decryption. Telecom operators and vendors have been working for several years on integrating that level of encryption into networks.
For instance, Toshiba and the Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization at Tohoku University used quantum technology in 2018 to hit one-month-average key distribution speeds exceeding 10 Mb/s over installed optical fiber lines. They also used the technology to monitor the performance of installed optical fiber lines in different environments.
Toshiba later partnered with U.K.-based operator BT on using QKD across to secure a network transmission.
SK Telecom also has a long quantum history, including work with Swiss-based strategic partner ID Quantique, which focuses on quantum cryptography communication technology.
Industry trade group GSMA last year announced its Post-Quantum Telco Network Taskforce focused on supporting the industry’s creation of a roadmap to secure networks, devices and systems across the entire supply chain.” That work was initiated with IBM and Vodafone, and has since gained more than 45 members.
Lory Thorpe, GSMA Post-Quantum Telco Networks chairperson and head of IBM Consulting’s Telco Transformation Offerings, told SDxCentral last month that the core objective of the taskforce is to ensure the implementation of the right requirements and standards in a timely manner to avoid being “late to the party.” Thorpe explained the initial problem statement was “around how do we support the telco ecosystem to navigate the path to quantum safe.”
“When you look at where cryptography is used in telco systems, it impacts basically all of the different systems. But it also then impacts all of the standards that underpin these systems as well,” she said. “We’re advocating that people start planning, not panicking, but at least planning because … this isn’t something that just happens overnight.”


