AI/ML
HPE-Juniper combo + Cisco restructuring create enterprise network uncertainty
Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s (HPE) pending acquisition of Juniper Networks and Cisco’s recent corporate restructuring (which de-emphasizes legacy networking products like access/core routers and Ethernet switches) is putting enterprise networking customers in a holding pattern. They are pausing investments in network equipment as they wait out the uncertainty.
“I’ve had customers put things on hold right now, and not just the Juniper side but both sides,” Andre Kindness, principal analyst at Forrester Research, said in an interview with SDxCentral about how Juniper and HPE customers are reacting to uncertainty around the deal. “Typically, if customers are strong enough to look outside of Cisco and they’re not a Cisco shop, then HPE, Aruba, Juniper are the primary ones that they’re looking at. I’ve had customers put some of that on hold at this point.”
That holding pattern is tied to uncertainty over what systems and platforms will emerge from a combined HPE-Juniper. Mr. Kindness noted in a blog post when the deal was announced that “the journey ahead will be rife with obstacles for Juniper and HPE/Aruba customers alike.” Kindness explained that one important move for HPE would be to “rationalize/optimize the portfolio, the products and the solutions.”
“HPE will try to reassure you that nothing will change; it doesn’t make sense to keep everything, especially the multiple AP [access point] product lines (Instant On, Mist, and Aruba Aps), all the routing and switching operating systems (Juno, AOS-CX, and ArubaOS) and both management systems (Central and Mist),” Kindness wrote.
“Though not immediately, products will need to go and the hardware that stays will need to be changed to accommodate cloud-based management, monitoring, and AI.” HPE CEO Antonio Neri and his management team has attempted to temper these concerns by stating there is virtually no overlap between HPE and Juniper’s product lines, which Kindness said, “just boggles my mind,” he added.
Juniper’s AI product, called Marvis (part of the Mist acquisition in 2019), is by far the most advanced AI solution in the networking market. That’s not a profound statement; no vendor has anything close to it. The quick history: Juniper’s acquisition of Mist brought the company a cloud-based Wi-Fi solution with a leading AI capability, Marvis. Juniper quickly started integrating its switching and routing portfolio into Marvis. Walmart, Amazon, and others took notice. Fast-forward to today: This gives HPE Aruba a two-year lead against its competitors by bringing Juniper into the fold.
“I think [Neri’s] got to worry about the financial analyst out there in the stock market or the shareholders to pacify them, and then at the same time you don’t want to scare the bejesus out of your customer base, or Juniper customer base, so you’re going to say that there’s going to be either no overlap or no changes, everything will coexist,” Kindness said.
While overlap and other concerns could alter what a potential Juniper HPE combo looks like, Kindness said he expects the result to lean heavily on Juniper’s telecom and networking assets. That includes HPE products like Aruba networking gear being replaced by Juniper’s artificial intelligence (AI)-focused Mist and Marvis platforms.
“Mist has been really a game changer for the company and just really opened a lot of doors,” Kindness explained. “[Juniper] really did a 180 degree turn when they bought [Mist], and just the revenue that’s brought in and the expansion of the product line itself, and the capabilities of Mist and actually Marvis in the background would be hard for [HPE] to replicate at this point. My perception was HPE looked at it and said, Marvis and Mist is just something that would take too long to get to.” Kindness added that he does not expect significant platform thinning to happen for a couple of years after a potential closing of the deal, but the interim could be filled with challenges tied to channel partners and go-to-market strategies that could chip away at market opportunities similar to what is happening at VMware following the Broadcom acquisition. “Broadcom is ruthless, right or wrong, it’s its business model,” Kindness said. “HPE is not quite that dynamic.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Cisco CFO Scott Herren told the audience at a recent investor conference that HPE’s pending Juniper acquisition is causing “uncertainty” in the enterprise WLAN market that could be benefit Cisco. “I think for sure that’s created just a degree of uncertainty and a question of, hey, should I consider if I was previously a vendor or a customer of either of those, now is the time to kind of open up and look at other opportunities,” Herren said. “And we’ve seen our wireless business, our orders greater than $1 million grew more than 20% in the fourth quarter.”
Cisco is also working through its own networking drama as part of the vendor’s recently announced restructuring process. Those moves will see Cisco focus more on high-growth areas like AI, security, and cloud at the expense of its legacy operations, including the pairing down of its networking product lines.
“It looks like Cisco’s realizing that all the complexity of customer choice and all these variations and offering a zillion features is probably not the way to go. I think Chuck realized it,” Kindness said of Cisco’s efforts. “If you look at the ACI [Application Centric Infrastructure] and Cloud Dashboard for Nexus starting to consolidate, and then the Catalyst line and the Aironet line and the Meraki line are consolidating, it’s just the right move. The market has told them that for the last 10 years, it just took them a while to recognize it.”
References:
https://www.juniper.net/us/en.html
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
FT: New benchmarks for Gen AI models; Neocloud groups leverage Nvidia chips to borrow >$11B
The Financial Times reports that technology companies are rushing to redesign how they test and evaluate their Gen AI models, as current AI benchmarks appear to be inadequate. AI benchmarks are used to assess how well an AI model can generate content that is coherent, relevant, and creative. This can include generating text, images, music, or any other form of content.
OpenAI, Microsoft, Meta and Anthropic have all recently announced plans to build AI agents that can execute tasks for humans autonomously on their behalf. To do this effectively, the AI systems must be able to perform increasingly complex actions, using reasoning and planning.
Current public AI benchmarks — Hellaswag and MMLU — use multiple-choice questions to assess common sense and knowledge across various topics. However, researchers argue this method is now becoming redundant and models need more complex problems.
“We are getting to the era where a lot of the human-written tests are no longer sufficient as a good barometer for how capable the models are,” said Mark Chen, senior vice-president of research at OpenAI. “That creates a new challenge for us as a research world.”
The SWE Verified benchmark was updated in August to better evaluate autonomous systems based on feedback from companies, including OpenAI. It uses real-world software problems sourced from the developer platform GitHub and involves supplying the AI agent with a code repository and an engineering issue, asking them to fix it. The tasks require reasoning to complete.
“It is a lot more challenging [with agentic systems] because you need to connect those systems to lots of extra tools,” said Jared Kaplan, chief science officer at Anthropic.
“You have to basically create a whole sandbox environment for them to play in. It is not as simple as just providing a prompt, seeing what the completion is and then evaluating that.”
Another important factor when conducting more advanced tests is to make sure the benchmark questions are kept out of the public domain, in order to ensure the models do not effectively “cheat” by generating the answers from training data, rather than solving the problem.
The need for new benchmarks has also led to efforts by external organizations. In September, the start-up Scale AI announced a project called “Humanity’s Last Exam”, which crowdsourced complex questions from experts across different disciplines that required abstract reasoning to complete.
Meanwhile, the Financial Times recently reported that Wall Street’s largest financial institutions had loaned more than $11bn to “neocloud” groups, backed by their possession of Nvidia’s AI GPU chips. These companies include names such as CoreWeave, Crusoe and Lambda, and provide cloud computing services to tech businesses building AI products. They have acquired tens of thousands of Nvidia’s graphics processing units (GPUs) through partnerships with the chipmaker. With capital expenditure on data centres surging, in the rush to develop AI models, the Nvidia’s AI GPU chips have become a precious commodity.
Nvidia’s chips have become a precious commodity in the ongoing race to develop AI models © Marlena Sloss/Bloomberg
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The $3tn tech group’s allocation of chips to neocloud groups has given confidence to Wall Street lenders to lend billions of dollars to the companies that are then used to buy more Nvidia chips. Nvidia is itself an investor in neocloud companies that in turn are among its largest customers. Critics have questioned the ongoing value of the collateralised chips as new advanced versions come to market — or if the current high spending on AI begins to retract. “The lenders all coming in push the story that you can borrow against these chips and add to the frenzy that you need to get in now,” said Nate Koppikar, a short seller at hedge fund Orso Partners. “But chips are a depreciating, not appreciating, asset.”
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/866ad6e9-f8fe-451f-9b00-cb9f638c7c59
https://www.ft.com/content/fb996508-c4df-4fc8-b3c0-2a638bb96c19
https://www.ft.com/content/41bfacb8-4d1e-4f25-bc60-75bf557f1f21
Tata Consultancy Services: Critical role of Gen AI in 5G; 5G private networks and enterprise use cases
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
AI winner Nvidia faces competition with new super chip delayed
SK Telecom unveils plans for AI Infrastructure at SK AI Summit 2024
Introduction:
During the two-day SK AI Summit 2024 [1.], SK Telecom CEO Ryu Young-sang unveiled the company’s comprehensive strategy which revolves around three core components: AI data centers (AIDCs), a cloud-based GPU service (GPU-as-a-Service, GPUaaS), and Edge AI. SK Telecom is planning to construct hyperscale data centers in key regions across South Korea, with the goal of becoming the AIDC hub in the Asia Pacific region. Additionally, the company will launch a cloud-based GPU service to address the domestic GPU shortage and introducing ‘Edge AI’ to bridge the gap between AIDC and on-device AI. This innovative approach aims to connect national AI infrastructure and expand globally, in collaboration with partners both in South Korea and abroad.
Note 1. The SK AI Summit is an annual event held by the SK Group, where global experts in various AI fields gather to discuss coexistence in the era of artificial general intelligence (AGI) and seek ways to strengthen the ecosystem.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Constructing AI Data Centers in South Korea’s key regions:
SK Telecom plans to start with hyperscale AIDCs that require more than 100 megawatts (MW) in local regions, with future plans to expand its scale to gigawatts (GW) or more, to leap forward as the AIDC hub in the Asia Pacific region.
By extending the AIDC to national bases, centers can secure a stable power supply through the utilization of new renewable energy sources such as hydrogen, solar and wind power, and easily expand to global markets through submarine cables. SK Telecom anticipates building AIDC cost-effectively when the data center combines SK Group’s capabilities in high-efficiency next-generation semiconductors, immersion cooling, and other energy solutions, along with its AI cluster operation.
Prior to this, SK Telecom plans to open an AIDC testbed in Pangyo, Korea, in December, which combines the capabilities of the SK Group and various solutions owned by partner companies. This facility, where all three types of next-generation liquid cooling solutions—direct liquid cooling, immersion cooling, and precision liquid cooling—are deployed, will be the first and only testbed in Korea. It will also feature advanced AI semiconductors like SK hynix’s HBM, as well as GPU virtualization solutions and AI energy optimization technology. This testbed will provide opportunities to observe and experience the cutting-edge technologies of a future AIDC.
Supplying GPU via cloud to metropolitan areas:
SK Telecom plans to launch a cloud-based GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) by converting the Gasan data center, located in the metropolitan area, into an AIDC to quickly resolve the domestic GPU shortage.
Starting in December, SK Telecom plans to launch a GPUaaS with NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU through a partnership with U.S.-based Lambda. In March 2025, SK Telecom plans to introduce NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPU in Korea, gradually expanding to meet customer demand.
Through the AI cloud services (GPUaaS), SKT aims to enable companies to develop AI services easily and at a lower cost, without needing to purchase their own GPUs, ultimately supporting the vitalization of Korea’s AI ecosystem.
Introducing ‘Edge AI’ to open a new opportunity in telco infrastructure:
SK Telecom plans to introduce ‘Edge AI,’ which can narrow the gap between AIDC and on-device AI, using the nationwide communication infrastructure.
Edge AI is an infrastructure that combines mobile communication networks and AI computing, offering advantages in reduced latency, enhanced security, and improved privacy compared to large-scale AIDCs. Additionally, it enables large-scale AI computing, complementing the existing AI infrastructure, compared to on-device AI.
SKT is currently conducting research on advanced technologies and collaborating with global partners to build AIDC-utilizing communication infrastructure and develop customized servers. The company is also carrying out various proof of concept (PoC) projects across six areas, including healthcare, AI robots, and AI CCTV, to discover specialized Edge AI services.
“So far, the competition in telecommunications infrastructure has been all about connectivity, namely speed and capacity, but now the paradigm of network evolution should be changed,” said Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SK Telecom. “The upcoming 6G will evolve into a next-generation AI infrastructure where communication and AI are integrated.”
Developing a comprehensive AIDC solution to enter global market:
SK Telecom plans to develop a comprehensive AIDC solution that combines AI semiconductors, data centers, and energy solutions through collaboration with AI companies in Korea and abroad, with the aim of entering the global market.SK Telecom aims to lead the global standardization of Edge AI and collaborate on advanced technology research, while working towards the transition to 6G AI infrastructure.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company with a strong global presence. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of AI Infrastructure, AI Transformation (AIX) and AI Service to deliver greater value for industry, society, and life.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or visit our LinkedIn page www.linkedin.com/company/sk-telecom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SKT-Samsung Electronics to Optimize 5G Base Station Performance using AI
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
Huawei’s “FOUR NEW strategy” for carriers to be successful in AI era
At the 10th Ultra-Broadband Forum (UBBF 2024) in Istanbul, Turkey, James Chen, President of Huawei’s Carrier Business, delivered a speech entitled “Network+AI, Unleashing More Business Value.”
“To explore the potential of AI, the ‘FOUR NEW’ strategy — new hub, new services, new experience, and new operation is crucial. It helps carriers to expand market boundaries, foster innovative services, and enhance market competitiveness, while also optimize network O&M and achieve business success. Huawei is committed to working with global carriers and partners to unleash more business value and forge a win-win digital and intelligent future through the “FOUR NEW” strategy.”

James Chen, President of Huawei’s Carrier Business, delivering a keynote speech
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Huawei believes that its “FOUR NEW” strategy is key to unleashing more business value through the combination of networking and AI.
- New Hub: The new Hub is the AI Hub for home services. The core of the AI Hub is the development of AI agents. AI agents need to connect people, things, and applications, understand and respond to the requirements of family members, control smart devices to meet family requirements, and connect AI applications to expand the boundaries of home services. The new hub helps carriers achieve business breakthroughs in the home market.
- New Services: Carriers enable new services and aggregate high-quality contents with AI to gradually build a home AI application ecosystem. AI not only can upgrade traditional services, such as interactive fitness and motion-sensing games, but also innovate home services, such as home service robots, health care, and education, etc. It improves quality of life and gradually builds a home AI ecosystem.
- New Experience: New services such as cloud gaming, live commerce, AI searches for photos and videos, are emerging one after another. These services have high requirements on network quality, including latency, uplink and downlink bandwidth, and jitter. This brings new network monetization opportunities to carriers. Carriers can seize monetization opportunities through new business models, such as latency-based charging, upstream bandwidth-based charging, and AI-function based charging. High-quality service experience requires high-quality networks. Carriers build “Premium vertical and premium horizontal” high-quality networks to support high-quality service experience and business monetization. The key to building a “Premium vertical and premium horizontal” network is to build 1 ms connections between data centers and 1 ms access to a data center.
- New Operation: As carriers’ network scale is getting larger, autonomous driving network is becoming more important. AI supports high-level network autonomous driving and improves network operation efficiency. Huawei’s L4 autonomous driving network based on the Telecom Foundation Model helps operators reduce customer complaints, shorten the complaint closure time, improve service provisioning efficiency, reduce the number of site visits, and accelerate fault rectification.
In the wave of digital intelligence transformation, the “FOUR NEW” strategy is not only the embodiment of network technology innovation, but also the important driving force for continuously releasing network business value. New Hub, New Services, New Experience, and New Operation support each other and together form a complete road to digital intelligence business success.
In the future, Huawei will continue to remain customer-centric, work with global carriers and partners to explore the digital intelligence era, accelerate the release of the business value of network + AI, and embrace a prosperous intelligent world.
References:
Huawei’s First-Half Net Profit Rose on Strong Smartphone Sales, Car Business
China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Despite U.S. sanctions, Huawei has come “roaring back,” due to massive China government support and policies
Huawei to revolutionize network operations and maintenance
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
Bloomberg reports that OpenAI, the fast-growing company behind ChatGPT, is working with Broadcom Inc. to develop a new artificial intelligence chip specifically focused on running AI models after they’ve been trained, according to two people familiar with the matter. The two companies are also consulting with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company(TSMC) the world’s largest chip contract manufacturer. OpenAI has been planning a custom chip and working on its uses for the technology for around a year, the people said, but the discussions are still at an early stage. The company has assembled a chip design team of about 20 people, led by top engineers who have previously built Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) at Google, including Thomas Norrie and Richard Ho (head of hardware engineering).
Reuters reported on OpenAI’s ongoing talks with Broadcom and TSMC on Tuesday. It has been working for months with Broadcom to build its first AI chip focusing on inference (responds to user requests), according to sources. Demand right now is greater for training chips, but analysts have predicted the need for inference chips could surpass them as more AI applications are deployed.
OpenAI has examined a range of options to diversify chip supply and reduce costs. OpenAI considered building everything in-house and raising capital for an expensive plan to build a network of chip manufacturing factories known as “foundries.”

REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights
OpenAI may continue to research setting up its own network of foundries, or chip factories, one of the people said, but the startup has realized that working with partners on custom chips is a quicker, attainable path for now. Reuters earlier reported that OpenAI was pulling back from the effort of establishing its own chip manufacturing capacity. The company has dropped the ambitious foundry plans for now due to the costs and time needed to build a network, and plans instead to focus on in-house chip design efforts, according to sources.
OpenAI, which helped commercialize generative AI that produces human-like responses to queries, relies on substantial computing power to train and run its systems. As one of the largest purchasers of Nvidia’s graphics processing units (GPUs), OpenAI uses AI chips both to train models where the AI learns from data and for inference, applying AI to make predictions or decisions based on new information. Reuters previously reported on OpenAI’s chip design endeavors. The Information reported on talks with Broadcom and others.
The Information reported in June that Broadcom had discussed making an AI chip for OpenAI. As one of the largest buyers of chips, OpenAI’s decision to source from a diverse array of chipmakers while developing its customized chip could have broader tech sector implications.
Broadcom is the largest designer of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) — chips designed to fit a single purpose specified by the customer. The company’s biggest customer in this area is Alphabet Inc.’s Google. Broadcom also works with Meta Platforms Inc. and TikTok owner ByteDance Ltd.
When asked last month whether he has new customers for the business, given the huge demand for AI training, Broadcom Chief Executive Officer Hock Tan said that he will only add to his short list of customers when projects hit volume shipments. “It’s not an easy product to deploy for any customer, and so we do not consider proof of concepts as production volume,” he said during an earnings conference call.
OpenAI’s services require massive amounts of computing power to develop and run — with much of that coming from Nvidia chips. To meet the demand, the industry has been scrambling to find alternatives to Nvidia. That’s included embracing processors from Advanced Micro Devices Inc. and developing in-house versions.
OpenAI is also actively planning investments and partnerships in data centers, the eventual home for such AI chips. The startup’s leadership has pitched the U.S. government on the need for more massive data centers and CEO Sam Altman has sounded out global investors, including some in the Middle East, to finance the effort.
“It’s definitely a stretch,” OpenAI Chief Financial Officer Sarah Friar told Bloomberg Television on Monday. “Stretch from a capital perspective but also my own learning. Frankly we are all learning in this space: Infrastructure is destiny.”
Currently, Nvidia’s GPUs hold over 80% AI market share. But shortages and rising costs have led major customers like Microsoft, Meta, and now OpenAI, to explore in-house or external alternatives.
References:
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
AI Frenzy Backgrounder; Review of AI Products and Services from Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Google and Meta; Conclusions
AI sparks huge increase in U.S. energy consumption and is straining the power grid; transmission/distribution as a major problem
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
SKT-Samsung Electronics to Optimize 5G Base Station Performance using AI
SK Telecom (SKT) has partnered with Samsung Electronics to use AI to improve the performance of its 5G base stations in order to upgrade its wireless network. Specifically, they will use AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology (AI-RAN Parameter Recommender) to commercial 5G networks.
The two companies have been working throughout the year to learn from past mobile network operation experiences using AI and deep learning, and recently completed the development of technology that automatically recommends optimal parameters for each base station environment. When applied to SKT’s commercial network, the new technology was able to bring out the potential performance of 5G base stations and improve the customer experience.
Mobile base stations are affected by different wireless environments depending on their geographical location and surrounding facilities. For the same reason, there can be significant differences in the quality of 5G mobile communication services in different areas using the same standard equipment.
Accordingly, SKT utilized deep learning, which analyzes and learns the correlation between statistical data accumulated in existing wireless networks and AI operating parameters, to predict various wireless environments and service characteristics and successfully automatically derive optimal parameters for improving perceived quality.
Samsung Electronics’ ‘Network Parameter Optimization AI Model’ used in this demonstration improves the efficiency of resources invested in optimizing the wireless network environment and performance, and enables optimal management of mobile communication networks extensively organized in cluster units.
The two companies are conducting additional learning and verification by diversifying the parameters applied to the optimized AI model and expanding the application to subways where traffic patterns change frequently.
SKT is pursuing advancements in the method of improving quality by automatically adjusting the output of base station radio waves or resetting the range of radio retransmission allowance when radio signals are weak or data transmission errors occur due to interference.
In addition, we plan to continuously improve the perfection of the technology by expanding the scope of targets that can be optimized with AI, such as parameters related to future beamforming*, and developing real-time application functions.
* Beamforming: A technology that focuses the signal received through the antenna toward a specific receiving device to transmit and receive the signal strongly.
SKT is expanding the application of AI technology to various areas of the telecommunications network, including ‘Telco Edge AI’, network power saving, spam blocking, and operation automation, including this base station quality improvement. In particular, AI-based network power saving technology was recently selected as an excellent technology at the world-renowned ‘Network X Award 2024’.
Ryu Tak-ki, head of SK Telecom’s infrastructure technology division, said, “This is a meaningful achievement that has confirmed that the potential performance of individual base stations can be maximized by incorporating AI,” and emphasized, “We will accelerate the evolution into an AI-Native Network that provides differentiated customer experiences through the convergence of telecommunications and AI technologies.”
“AI is a key technology for innovation in various industrial fields, and it is also playing a decisive role in the evolution to next-generation networks,” said Choi Sung-hyun, head of the advanced development team at Samsung Electronics’ network business division. “Samsung Electronics will continue to take the lead in developing intelligent and automated technologies for AI-based next-generation networks.”
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SKT said it is expanding the use of AI to various areas of its communications network, such as “Telco Edge AI,” network power reduction, spam blocking and operation automation, including basestation quality improvement.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
South Korea has 30 million 5G users, but did not meet expectations; KT and SKT AI initiatives
SKT Develops Technology for Integration of Heterogeneous Quantum Cryptography Communication Networks
India Mobile Congress 2024 dominated by AI with over 750 use cases
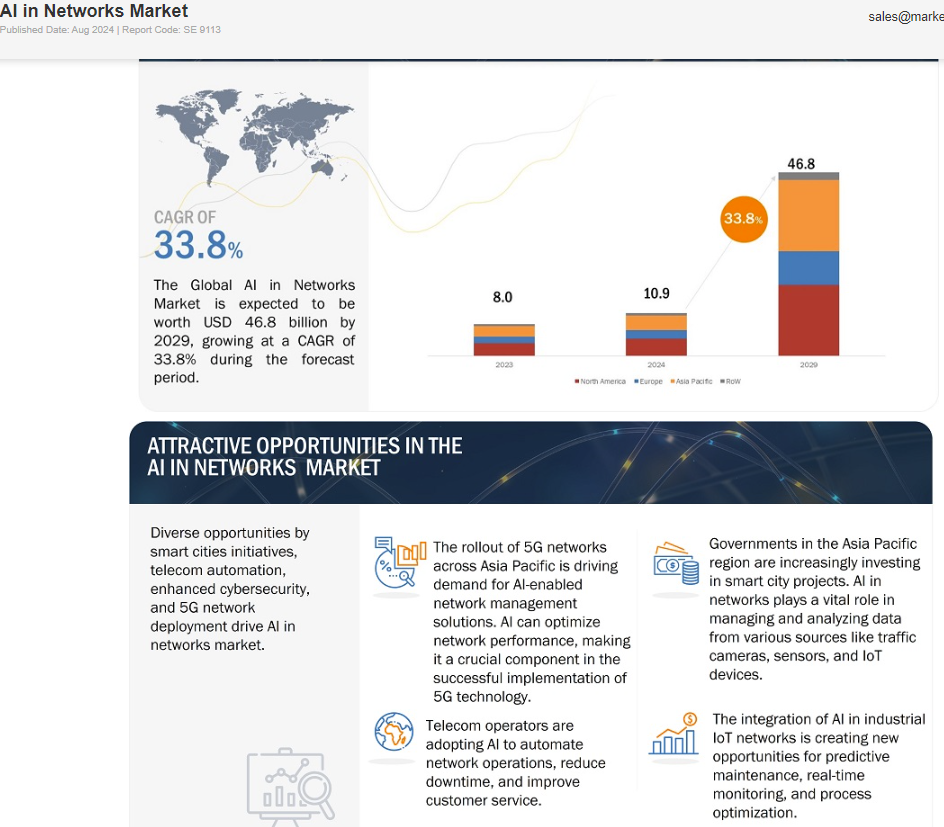
Markets and Markets: Global AI in Networks market worth $10.9 billion in 2024; projected to reach $46.8 billion by 2029
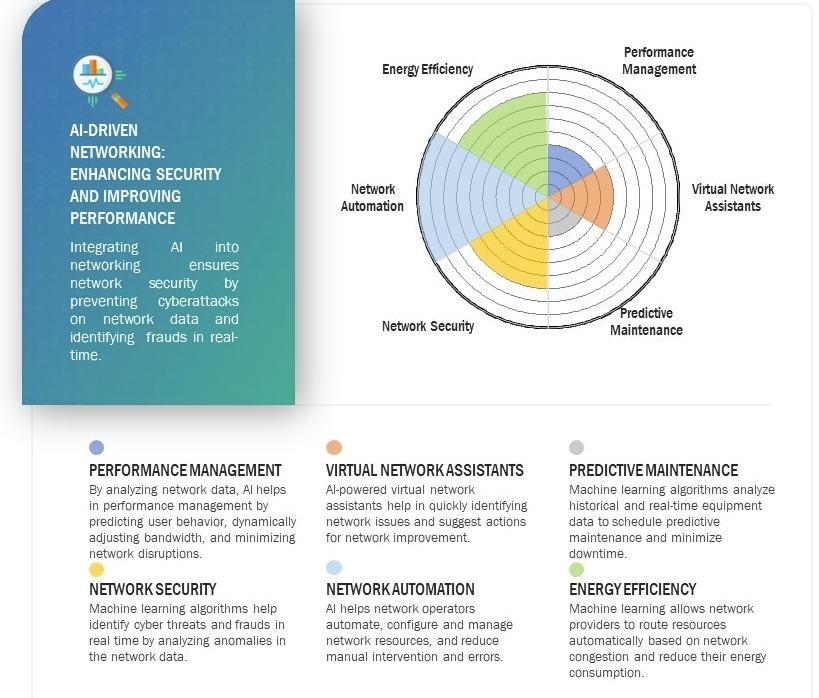
According to research firm Markets and Markets, the global AI in Networks market is expected to be valued at USD 10.9 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 46.8 billion by 2029 and grow at a CAGR of 33.8% from 2024 to 2029. AI in networks market is experiencing high growth driven by increasing adoption of 5G technology, edge computing, IoT connected devices, and expansion of smart cities. Increasing deployment of 5G networks has led to the vast amount of network data, generated by high bandwidth application such as video streaming and online gaming, driving network operators to integrate AI driven solutions to manage network data and allocate resources to reduce network congestion. Network operators are also integrating AI driven solutions to automate network operations and predictive maintenance, to reduce human dependency and errors, leading to efficient network management.
Network operators invest heavily in developing AI-driven solutions to manage and optimize network traffic. AI in networks allows operators to efficiently perform network management tasks such as traffic routing, resource allocation, and network security. As the 5G technology advances, the demand for cybersecurity solutions will also rise, driving the AI in networks market.
Constraint: Data privacy and security concerns in AI in networks
Integration of artificial intelligence technology in the networking leads to various risks affiliated with collecting, storing, and transmitting network traffic data. AI driven network collect users and network operations data information, creating a high risk environment of privacy breaches, due to the rising cyberthreats. These cyberattacks may lead to unauthorized access to network and user data, disrupting network operations. Additionally, data generated by connected and Iot devices such as smartphones, smart home systems, surveillance system is collected by network, leads to concerns regarding unauthorized surveillance and cyberattacks.
Opportunity: Increasing prevalence of smart city initiatives
Rapid urbanization has led to the exapsnion of smart cities globally. Countries around the world are investing heavily towards smart infrastructure by integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI). For instance, smart city ecosystem consist of various sensors and connected and IoT devices, and to ensure efficient transmission and processing of data generated by these sensor and devices. AI driven network solutions play a vital role in collecting and processing of data, identifying anomalies and equipment failure based on present and historical data, helping network operator to schedule maintenance in advance and reduce downtime.
Challenge: Rapid change in the technology landscape
As the technology landscape evolves rapidly, AI presents a major challenge in the network market. As new technologies appear and current technology evolves, companies in the ecosystem must continuously invest in the research and development of changing market demand and advancements. Additionally, intense competition in the market and pressure to offer innovative solutions further restrict companies from maintaining market leadership. Companies’ negligence in identifying the technological shift can result in a decline in market share and revenue.
AI in networks market in North America will hold the highest market share during the forecast period.
The AI in networks market for North America is expected to hold the highest market share during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the presence of leading AI and network technology companies in the region. These companies are investing heavily towards the advancement of technologies such as AI, 5G, edge computing, due to the high internet penetration rate in the region. The demand for high bandwidth network application such as video streaming and online gaming also on the rise, driving the investments and innovations towards AI driven solutions in network management.
******************************
References:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/ai-in-networks-market-131514910.html
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
Nvidia enters Data Center Ethernet market with its Spectrum-X networking platform
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
The case for and against AI in telecommunications; record quarter for AI venture funding and M&A deals
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
InfiniBand, which has been used extensively for HPC interconnect, currently dominates AI networking accounting for about 90% of deployments. That is largely due to its very low latency and architecture that reduces packet loss, which is beneficial for AI training workloads. Packet loss slows AI training workloads, and they’re already expensive and time-consuming. This is probably why Microsoft chose to run InfiniBand when building out its data centers to support machine learning workloads. However, InfiniBand tends to lag Ethernet in terms of top speeds. Nvidia’s very latest Quantum InfiniBand switch tops out at 51.2 Tb/s with 400 Gb/s ports. By comparison, Ethernet switching hit 51.2 Tb/s nearly two years ago and can support 800 Gb/s port speeds.

While InfiniBand currently has the edge, several factors point to increased Ethernet adoption for AI clusters in the future. Recent innovations are addressing Ethernet’s shortcomings compared to InfiniBand:
- Lossless Ethernet technologies
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
- Ultra Ethernet Consortium’s AI-focused specifications
Some real-world tests have shown Ethernet offering up to 10% improvement in job completion performance across all packet sizes compared to InfiniBand in complex AI training tasks. By 2028, it’s estimated that: 1] 45% of generative AI workloads will run on Ethernet (up from <20% now) and 2] 30% will run on InfiniBand (up from <20% now).
In a lively session at VM Ware-Broadcom’s Explore event, panelists were asked how to best network together the GPUs, and other data center infrastructure, needed to deliver AI. Broadcom’s Ram Velaga, SVP and GM of the Core Switching Group, was unequivocal: “Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen.” Velaga opening remarks asked the audience, “Think about…what is machine learning and how is that different from cloud computing?” Cloud computing, he said, is about driving utilization of CPUs; with ML, it’s the opposite.
“No one…machine learning workload can run on a single GPU…No single GPU can run an entire machine learning workload. You have to connect many GPUs together…so machine learning is a distributed computing problem. It’s actually the opposite of a cloud computing problem,” Velaga added.
Nvidia (which acquired Israel interconnect fabless chip maker Mellanox [1.] in 2019) says, “Infiniband provides dramatic leaps in performance to achieve faster time to discovery with less cost and complexity.” Velaga disagrees saying “InfiniBand is expensive, fragile and predicated on the faulty assumption that the physical infrastructure is lossless.”
Note 1. Mellanox specialized in switched fabrics for enterprise data centers and high performance computing, when high data rates and low latency are required such as in a computer cluster.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ethernet, on the other hand, has been the subject of ongoing innovation and advancement since, he cited the following selling points:
- Pervasive deployment
- Open and standards-based
- Highest Remote Direct Access Memory (RDMA) performance for AI fabrics
- Lowest cost compared to proprietary tech
- Consistent across front-end, back-end, storage and management networks
- High availability, reliability and ease of use
- Broad silicon, hardware, software, automation, monitoring and debugging solutions from a large ecosystem
To that last point, Velaga said, “We steadfastly have been innovating in this world of Ethernet. When there’s so much competition, you have no choice but to innovate.” InfiniBand, he said, is “a road to nowhere.” It should be noted that Broadcom (which now owns VMWare) is the largest supplier of Ethernet switching chips for every part of a service provider network (see diagram below). Broadcom’s Jericho3-AI silicon, which can connect up to 32,000 GPU chips together, competes head-on with InfiniBand!
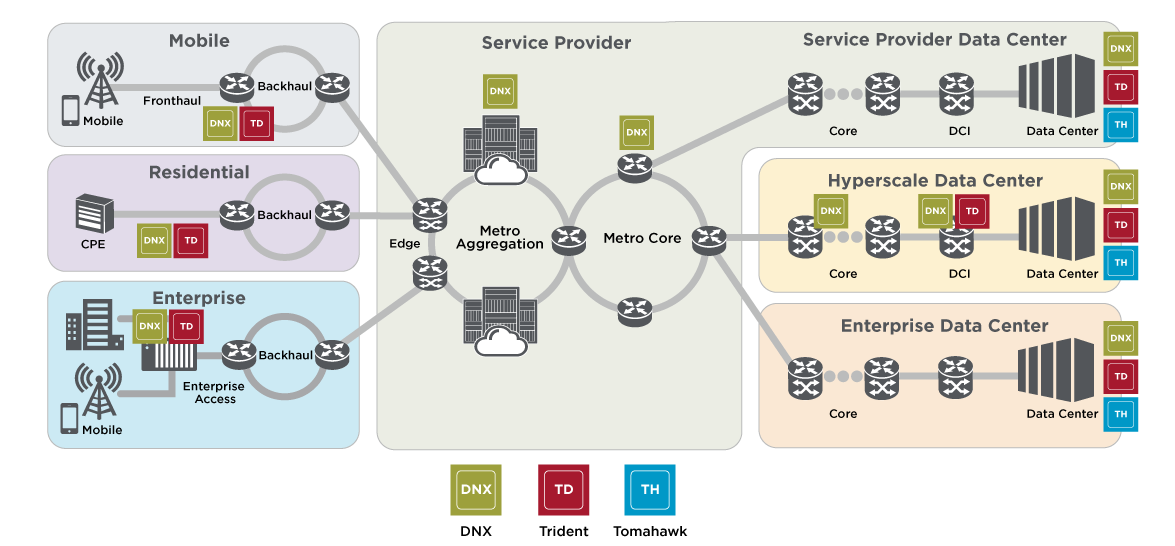
Image Courtesy of Broadcom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
While InfiniBand currently dominates AI networking, Ethernet is rapidly evolving to meet AI workload demands. The future will likely see a mix of both technologies, with Ethernet gaining significant ground due to its improvements, cost-effectiveness, and widespread compatibility. Organizations will need to evaluate their specific needs, considering factors like performance requirements, existing infrastructure, and long-term scalability when choosing between InfiniBand and Ethernet for AI clusters.
–>Well, it turns out that Nvidia’s Mellanox division in Israel makes BOTH Infiniband AND Ethernet chips so they win either way!
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.perplexity.ai/search/will-ai-clusters-run-on-infini-uCYEbRjeR9iKAYH75gz8ZA
https://www.theregister.com/2024/01/24/ai_networks_infiniband_vs_ethernet/
Broadcom on AI infrastructure networking—’Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen’
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/infiniband/h
ttps://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/ethernet/
Part1: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part II
Part-2: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML
AI RAN Alliance selects Alex Choi as Chairman
Backgrounder:
The AI RAN Alliance, formed earlier this year, is a groundbreaking collaboration aimed at revolutionizing the RAN industry. Partnering with tech giants, the goal is to transform traditional Radio Access Networks (RANs) into intelligent, self-optimizing systems using advanced AI technologies. Their website states:
Bringing together the technology industry leaders and academic institutions, the AI-RAN Alliance is dedicated to driving the enhancement of RAN performance and capability with AI. Moreover, we aim to optimize RAN asset utilization, and unlock new revenue streams. By pioneering AI-based innovations in RAN, we aspire to profitably propel the telecom industry towards 6G.
The alliance’s founding members include Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), Arm, DeepSig Inc. (DeepSig), Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (Ericsson), Microsoft Corporation (Microsoft), Nokia, Northeastern University, NVIDIA, Samsung Electronics, SoftBank Corp. (SoftBank) and T-Mobile USA, Inc. (T-Mobile).
The group’s mission is to enhance mobile network efficiency, reduce power consumption, and retrofit existing infrastructure, setting the stage for unlocking new economic opportunities for telecom companies with AI, facilitated by 5G and 6G.

Image Courtesy of the AI RAN Alliance.
Purpose:
The AI RAN Alliance is dedicated to eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional RAN systems by embedding AI directly into network infrastructures. This shift will enable, for example, dynamic resource allocation, predictive maintenance, and proactive network management.
Industry Benefits:
Enhanced Network Efficiency: Real-time optimized bandwidth allocation and improved user experiences.
Economic Advantages: Cost savings from AI-driven automation and reduced energy consumption.
Innovative Revenue Opportunities: New services such as real-time AI Assistants on your mobile devices.
Key Focus Areas:
- AI for RAN
- AI on RAN (RAN for AI)
- AI and RAN
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
New AI RAN Alliance Chairman:
On August 15, 2024, the AI RAN Alliance appointed Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi, Principal Fellow of SoftBank Corp.’s Research Institute of Advanced Technology as Chairman.
“The AI-RAN Alliance is set to transform telecommunications through AI-RAN advancements, increased efficiency, and new economic opportunities,” said Choi. “As Chair, I’m excited to lead this AI-RAN initiative, working with industry leaders to enhance mobile networks, reduce power consumption, and modernize infrastructure with 5G and 6G with AI/ML. Our goal is to drive societal progress through AI-RAN, transitioning from traditional to next-generation communications infrastructure.”
Satadal Bhattacharjee, Sr. Director of Marketing, Infrastructure BU, ARM, said, “We’re excited to collaborate with Choi, the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. Like Choi, we believe that AI will fundamentally change the way wireless services are deployed, fostering broad innovation and enhancing operational efficiency. We look forward to working with key industry leaders from silicon to software to fulfill the promise of ubiquitous AI and 6G.”
Jim Shea, Co-founder and CEO of DeepSig, said, “As a pioneer in AI-native communications together with his prior experience growing the O-RAN ALLIANCE, Choi will lead this important initiative that is shaping the future of intelligent radio access networks. DeepSig’s extensive AI/ML wireless expertise will play a key role in this exciting collaboration to leverage advanced technologies to help the industry unlock unprecedented network efficiency and accelerate innovation.”
Mathias Riback, VP & Head of Advanced Technology U.S., Ericsson, said, “I’m thrilled to welcome Dr. Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. As a non-standardization organization, the Alliance can uniquely complement the work of existing SDOs by focusing on shaping innovative use cases that integrate AI with RAN. In addition to realizing benefits from AI in RAN implementations, it will be important to advance ‘AI on RAN’ use cases, where mobile networks play a critical role in enabling AI applications. Ericsson is fully committed to fostering a collaborative environment that unites all players in the evolving AI ecosystem to shape the future of telecom together.”
Shawn Hakl, VP of 5G Strategy, Microsoft, said, “At Microsoft, we recognize artificial intelligence (AI) as a pivotal technology of our era. We are excited to be a part of the AI-RAN Alliance and are particularly pleased to see Choi step into the role of Chair. Choi’s leadership will be key as we collaborate to leverage AI in optimizing RAN infrastructure investments and expanding the capabilities of RAN to introduce new AI-driven services for modern mobile applications.”
Ari Kynäslahti, Head of Strategy and Technology, Mobile Networks at Nokia commented, “Nokia is proud to be part of the AI-RAN Alliance and contribute towards integrating AI into radio access networks. The potential of AI to optimize networks, predict and resolve issues, and enhance performance and service quality is significant. As we embark on this transformative journey, collaboration is essential to harness our collective expertise. We are pleased to see Dr. Alex Choi appointed to this role, and look forward to him guiding our efforts to achieve these goals.”
Tommaso Melodia, William L. Smith Professor, Northeastern University, said, “We are pleased to have Choi as the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance, leading our efforts to transform the industry. Choi has been a strong advocate for the evolution towards a more open, software-driven, and AI-integrated future. Under Choi’s leadership, the AI-RAN Alliance is set to fast-track the development of new services and use cases by leveraging openness, softwarization, and AI integration to enhance network performance, energy efficiency, spectrum sharing, and security, ultimately redefining the landscape of global communications.”
Soma Velayutham, GM, AI and Telecoms, NVIDIA, said, “The AI-RAN Alliance is a critical initiative for advancing the convergence of AI and 5G/6G technologies to drive innovation in mobile networks. The consortium’s new leadership will bring a fresh perspective and focus on delivering the next generation of connectivity.”
Dr. Ardavan Tehrani, Samsung Research, AI-RAN Alliance Board of Directors Vice Chair, said, “We are excited to have Dr. Alex Choi leading the AI-RAN Alliance as the Chair of the Board. The Alliance will play a pivotal role in fostering collaboration, driving innovation, and transforming future 6G networks utilizing AI. Under Dr. Choi’s leadership, the Alliance will strive to deliver substantial value to end users and operators through pioneering AI-based use cases and innovations.”
Ryuji Wakikawa, VP and Head of Research Institute of Advanced Technology, SoftBank Corp., said, “SoftBank is committed to realizing an AI-powered network infrastructure, and we strongly believe that Choi’s extensive background and expertise will be a great force in advancing AI-RAN technology and driving significant progress for the mobile industry in this AI era with lightning speed.”
John Saw, EVP and CTO, T-Mobile, said, “We are thrilled to have Alex Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. AI is advancing at an unprecedented rate and with our 5G network advantage we have a unique opportunity to harness this momentum. By developing solutions that make the most of both RAN and AI on GPUs — and working alongside Choi and the top industry leaders within the Alliance — we believe there is potential for change that will revolutionize the industry.”
Dr. Akihiro Nakao, Professor, The University of Tokyo, said, “Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi’s appointment as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance represents a pivotal step in advancing AI within the telecommunications sector. His leadership is expected to unite academic and industry efforts, nurturing the next wave of innovators who will drive the future of AI and telecommunications. This initiative will not only fast-track the adoption of AI across diverse applications but also foster international collaboration and set new standards for efficiency, energy management, resilience, and the development of AI-driven services that will reshape the telecommunications industry and benefit society worldwide.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://ai-ran.org/news/industry-leaders-in-ai-and-wireless-form-ai-ran-alliance/
AI sparks huge increase in U.S. energy consumption and is straining the power grid; transmission/distribution as a major problem
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
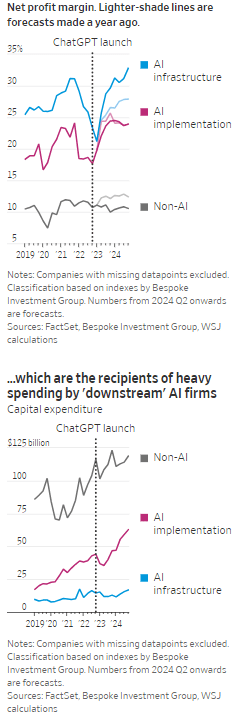
According to the Wall Street Journal, the AI industry has become an “Echo Chamber,” where huge capital spending by the AI infrastructure and application providers have fueled revenue and profit growth for everyone else. Market research firm Bespoke Investment Group has recently created baskets for “downstream” and “upstream” AI companies.
- The Downstream group involves “AI implementation,” which consist of firms that sell AI development tools, such as the large language models (LLMs) popularized by OpenAI’s ChatGPT since the end of 2022, or run products that can incorporate them. This includes Google/Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta Platforms (FB), along with IBM, Adobe and Salesforce.
- Higher up the supply chain (Upstream group), are the “AI infrastructure” providers, which sell AI chips, applications, data centers and training software. The undisputed leader is Nvidia, which has seen its sales triple in a year, but it also includes other semiconductor companies, database developer Oracle and owners of data centers Equinix and Digital Realty.
The Upstream group of companies have posted profit margins that are far above what analysts expected a year ago. In the second quarter, and pending Nvidia’s results on Aug. 28th , Upstream AI members of the S&P 500 are set to have delivered a 50% annual increase in earnings. For the remainder of 2024, they will be increasingly responsible for the profit growth that Wall Street expects from the stock market—even accounting for Intel’s huge problems and restructuring.
It should be noted that the lines between the two groups can be blurry, particularly when it comes to giants such as Amazon, Microsoft and Alphabet, which provide both AI implementation (e.g. LLMs) and infrastructure: Their cloud-computing businesses are responsible for turning these companies into the early winners of the AI craze last year and reported breakneck growth during this latest earnings season. A crucial point is that it is their role as ultimate developers of AI applications that have led them to make super huge capital expenditures, which are responsible for the profit surge in the rest of the ecosystem. So there is a definite trickle down effect where the big tech players AI directed CAPEX is boosting revenue and profits for the companies down the supply chain.
As the path for monetizing this technology gets longer and harder, the benefits seem to be increasingly accruing to companies higher up in the supply chain. Meta Platforms Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg recently said the company’s coming Llama 4 language model will require 10 times as much computing power to train as its predecessor. Were it not for AI, revenues for semiconductor firms would probably have fallen during the second quarter, rather than rise 18%, according to S&P Global.
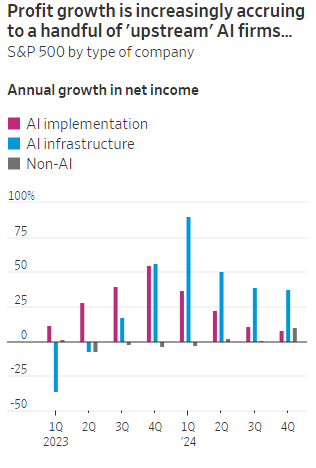 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
A paper written by researchers from the likes of Cambridge and Oxford uncovered that the large language models (LLMs) behind some of today’s most exciting AI apps may have been trained on “synthetic data” or data generated by other AI. This revelation raises ethical and quality concerns. If an AI model is trained primarily or even partially on synthetic data, it might produce outputs lacking human-generated content’s richness and reliability. It could be a case of the blind leading the blind, with AI models reinforcing the limitations or biases inherent in the synthetic data they were trained on.
In this paper, the team coined the phrase “model collapse,” claiming that training models this way will answer user prompts with low-quality outputs. The idea of “model collapse” suggests a sort of unraveling of the machine’s learning capabilities, where it fails to produce outputs with the informative or nuanced characteristics we expect. This poses a serious question for the future of AI development. If AI is increasingly trained on synthetic data, we risk creating echo chambers of misinformation or low-quality responses, leading to less helpful and potentially even misleading systems.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a recent working paper, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) economist Daron Acemoglu argued that AI’s knack for easy tasks has led to exaggerated predictions of its power to enhance productivity in hard jobs. Also, some of the new tasks created by AI may have negative social value (such as design of algorithms for online manipulation). Indeed, data from the Census Bureau show that only a small percentage of U.S. companies outside of the information and knowledge sectors are looking to make use of AI.
References:
https://deepgram.com/learn/the-ai-echo-chamber-model-collapse-synthetic-data-risks
https://economics.mit.edu/sites/default/files/2024-04/The%20Simple%20Macroeconomics%20of%20AI.pdf