China
Analysis & Economic Implications of AI adoption in China
Executive Summary:
Visible signs of artificial intelligence adoption in China are everywhere. Consumers interact seamlessly with chatbots, livestream hosts promote algorithmically selected products, and recommendation engines exhibit an almost anticipatory understanding of user preferences. Yet, beyond these consumer-facing applications, a deeper and potentially more consequential transformation is unfolding. Across China’s retail and services sectors, AI is shifting from demand generation to cost optimization. Enterprises are deploying machine learning in logistics, inventory management, customer service, and fulfillment operations to reduce inefficiencies as revenue growth slows and pricing power tightens.
Highlights:
-
Chinese companies are increasingly using AI to control operational costs and improve efficiency in a low-growth economic environment.
-
AI is being deployed in logistics, inventory management, and customer service to reduce expenses rather than primarily drive demand.
-
This shift towards AI for cost reduction is leading to steadier cash flow and improved operating margins for consumer companies.

China’s Consumer Sector: AI Powers Efficiency Over Growth:
As China’s economy adjusts to structural deceleration—marked by subdued household confidence, persistent real-estate overhang, and maturing market saturation—consumer companies face an unfamiliar imperative: prioritize resilience over expansion. With pricing power eroded and cost inflation persistent, traditional growth levers have lost potency. Leading platforms are responding by reorienting AI investments toward operational efficiency, transforming algorithms from engagement engines into margin-defense mechanisms. For investors, this evolution signals a new phase of earnings potential—one where incremental productivity gains could prove more durable than cyclical demand recovery.
“In a low-growth environment, incremental efficiency gains matter more than top-line expansion,” notes Zhao Ming, senior analyst for China internet companies at Hongyuan Capital. “AI has become a strategic lever for margin preservation.”
China’s consumer sector entered 2026 navigating familiar structural headwinds: cautious household sentiment, a fading property-wealth effect, and fierce price competition. Unlike in previous cycles, companies are finding it increasingly difficult to pass rising costs on to consumers. The result has been a strategic realignment. Where past growth phases emphasized volume and engagement, today’s market is rewarding operational discipline. That shift has sharpened the appeal of AI—not as a marketing showcase, but as a core instrument of productivity and cost control.
“In a slower-growth environment, leading Chinese consumer companies are using AI primarily to improve productivity and reduce operating costs rather than to drive incremental demand,” McKinsey said in a recent analysis of AI adoption across China’s retail and services sectors.
From Growth Catalyst to Cost Lever:
The center of gravity for AI investment has shifted from customer-facing innovation to operational optimization. E-commerce platforms and logistics operators have been among the earliest to integrate AI into mission-critical workflows. Demand-forecasting models are helping warehouses fine-tune inventory levels and reduce exposure to slow-moving goods. Routing algorithms are compressing last-mile delivery times and cutting fuel consumption. Automated customer-service systems are deflecting an ever-larger share of inquiries typically handled by human agents.
On their own, each of these applications may appear incremental. Taken together, they represent a meaningful improvement in margin resilience at a time when top-line expansion remains constrained. In an environment where minor percentage-point gains in efficiency can significantly affect earnings quality, AI is emerging as a quiet but potent differentiator.
Logistics as a Testbed for Scalable Efficiency:
The operational impact of AI is most visible in the logistics ecosystem, a sector that remains one of the largest cost centers in China’s consumer economy. Machine-learning systems are now proficient at forecasting order density by neighborhood and time of day, enabling fulfillment centers to position inventory closer to anticipated demand. In dense urban markets, adaptive algorithms continually adjust delivery routes in response to evolving conditions—from traffic and weather to cancellations and reorders—reducing both transit times and redundancy.
For investors, the value proposition is compelling: logistics efficiency scales. Once AI models are trained and stress-tested, they can be deployed across regions at low incremental cost, generating operating leverage even in periods of stagnant demand. Crucially, incumbents benefit from data scale. Years of transaction and delivery records translate into more accurate predictive models, reinforcing competitive moats and raising barriers to entry. This dynamic is reshaping industry structure even as consumer-facing platform features converge toward commoditization.
AI Extends Gains to Physical Retail:
Beyond e-commerce, brick-and-mortar retail—long considered a laggard in China’s digital transformation—is also seeing measurable efficiency dividends. Smart shelving, computer-vision inventory systems, and automated stock monitoring are cutting labor intensity while increasing inventory turnover. Grocery and convenience chains now rely on AI to optimize product assortments at the store level, calibrating selections to localized consumption patterns instead of applying national averages. The effect is twofold: reduced waste and fewer markdowns, both of which have historically weighed on profitability. The outcomes may not register as eye-catching innovation, but they align closely with investor priorities—stabler cash flows and predictable margins.
Labor Efficiency as a Strategic Imperative:
AI-enhanced customer service represents another underappreciated margin driver. Major consumer platforms report that routine customer interactions—order tracking, returns, product troubleshooting—are now predominantly handled through automated systems. This transition is particularly relevant in a labor market where wage growth continues to outpace consumption. Limiting headcount growth while maintaining response times and service quality has become a key operational goal.
“AI doesn’t replace customer service,” says Li Wenyuan, chief technology officer at retail software firm Qimeng Tech. “It filters it, so humans deal only with the expensive problems.” That filtering function is transforming customer operations from cost centers into scalable service platforms, balancing efficiency with user satisfaction.
Economic Implications:
For investors, the impact of China’s second-wave AI adoption will likely manifest less in headline growth metrics and more in incremental financial performance indicators. Key areas to watch include:
-
Operating margin expansion driven by process automation
-
Reduced fulfillment and logistics costs as a share of revenue
-
Improved capital-expenditure efficiency through data-driven asset utilization
The first chapter of China’s AI consumer story was about differentiation—using algorithms to personalize experiences, boost engagement, and drive sales. The next chapter is about discipline. As growth normalizes, companies are deploying AI to do more with less: compress costs, stabilize earnings, and build leaner, more adaptive operating models. In a market where scale alone no longer guarantees profitability, AI has become not just a tool for innovation—but a mechanism for survival.
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/china-ai-boom-commerce-warehouses-b1ad55f1
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
China’s telecom industry rapid growth in 2025 eludes Nokia and Ericsson as sales collapse
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Bloomberg: China Lures Billionaires Into Race to Catch U.S. in AI
China’s telecom industry rapid growth in 2025 eludes Nokia and Ericsson as sales collapse
According to a Chinese government update, “Telecommunications business volume and revenue grew steadily, mobile internet access traffic maintained rapid growth, and the construction of network infrastructure such as 5G, gigabit optical networks, and the Internet of Things was further promoted.”
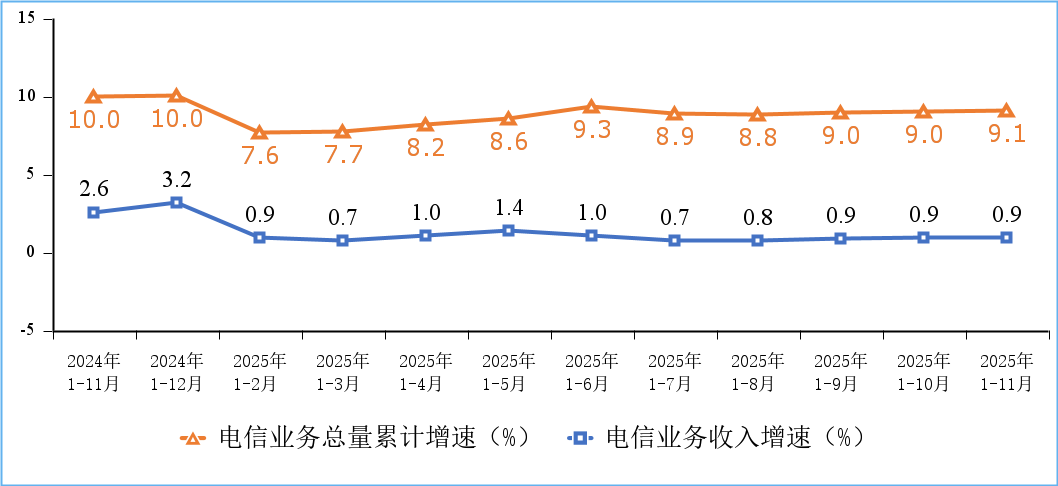
Figure 1. Cumulative growth rate of telecommunications service revenue and total telecommunications service volume
There were 4.83 million 5G base stations in service in China at the end of November 2025, an increase of 579,000 since late 2024 and 37.4% of the total number of mobile base stations in China. In one year, China claims to have added more 5G base stations than Europe has installed since the 5G technology was first put into service.
The total number of mobile phone users of the top four Chinese telcos (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, China Broadcasting Network) reached 1.828 billion, a net increase of 38.54 million from the end of last year. Among them, 5G mobile phone users reached 1.193 billion, a net increase of 179 million from the end of last year, accounting for 65.3% of all mobile phone users.
Meanwhile, the total number of fixed broadband internet access users of the three state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom) reached 697 million, a net increase of 27.12 million from the end of last year. Among them, fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 100Mbps and above reached 664 million, accounting for 95.2% of the total users; fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 1000Mbps and above reached 239 million, a net increase of 32.52 million from the end of last year, accounting for 34.3% of the total users, an increase of 3.4 percentage points from the end of last year.
The construction of gigabit fiber optic broadband networks continues to advance. As of the end of November, the number of broadband internet access ports nationwide reached 1.25 billion, a net increase of 48.11 million compared to the end of last year. Among them, fiber optic access (FTTH/O) ports reached 1.21 billion, a net increase of 49.42 million compared to the end of last year, accounting for 96.8% of all broadband internet access ports. As of the end of November, the number of 10G PON ports with gigabit network service capabilities reached 31.34 million, a net increase of 3.133 million compared to the end of last year.
The penetration rate of gigabit and 5G users continued to increase across all regions. As of the end of November, the penetration rates of fixed broadband access users with speeds of 1000Mbps and above in the eastern, central, western, and northeastern regions were 34.6%, 33.8%, 35.8%, and 28.5%, respectively, representing increases of 3.4, 2.6, 4.1, and 4.9 percentage points compared to the end of last year; the penetration rates of 5G mobile phone users were 64.9%, 65.9%, 65.1%, and 65.9%, respectively, representing increases of 8.2, 8.7, 8.8, and 9.6 percentage points compared to the end of last year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Light Reading reports that Ericsson and Nokia sales of networking equipment to China have collapsed.
Ericsson recently published earnings release for the final quarter of 2025 puts China revenues at just 3% of total sales last year. This would equate to revenues of 7.1 billion Swedish kronor (US$798 million). Based on a rounding range of 2.5% to 3.4%, it works out to be between SEK5.92 billion ($665 million) and SEK8.05 billion ($905 million) – down sharply compared with the SEK10.2 billion ($1.15 billion) Ericsson made in 2024, according to that year’s Ericsson annual report.
Nokia does not break out details of revenues from mainland China, instead lumping them together with the sales it generates in neighboring Hong Kong and Taiwan. But this “Greater China” business is in decline. Total annual revenues – which include Nokia’s sales of fixed, Internet Protocol and optical network products, as well as 5G – slumped from almost €2.2 billion ($2.6 billion) in 2019 to around €1.5 billion ($1.8 billion) in 2020, before creeping back up to nearly €1.6 billion ($1.9 billion) by 2022. Two years later, they had fallen to about €1.1 billion ($1.3 billion).
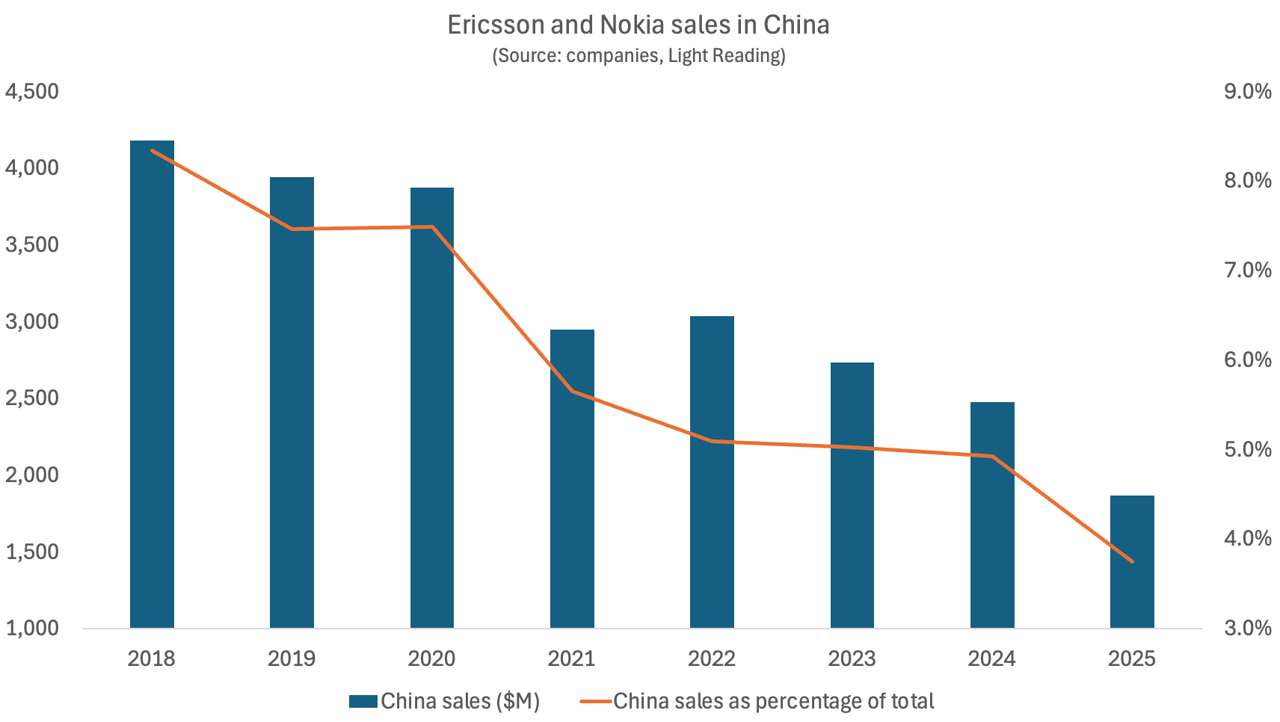
Bar Chart Credit: Light Reading
Nokia has recently indicated the complete disappearance of its China business. “Western suppliers, which is only us and Ericsson, have 3% market share now in China and it’s been coming down, and we are going to be excluded from China for national security reasons,” said Tommi Uitto, the former president of Nokia’s mobile networks business group, at a September press conference in Finland also attended by Justin Hotard, Nokia’s CEO. It implies China’s government is now treating the Nordic vendors in the same way Europe and the U.S. are banning Huawei and ZTE networking equipment.
Nokia revealed in its latest earnings update that Greater China revenues for 2025 had fallen by another 19%, to €913 million ($1.08 billion) – just 42% of what Nokia earned in the region seven years earlier. In the last few years, moreover, Nokia has cut more jobs in Greater China than in any other single region. While figures are not yet available for 2025, the Greater China headcount numbered 8,700 employees in 2024, down from 15,700 in 2019.
Ericsson has significantly reduced its China operations following greatly reduced 5G market share. In September 2021, the company consolidated three operator-specific customer units into a unified structure, impacting several hundred sales and delivery roles within its ~10,000-person local workforce. This followed the divestment of a Nanjing-based R&D center (approx. 650 employees), aligning with strategic pivots away from legacy 2G-4G technologies. The company’s total workforce in Northeast Asia plummeted from about 14,000 in mid-2021 to roughly 9,500 at the end of last year, according to Ericsson’s financial statements.
Exclusion from China would leave Ericsson and Nokia on the outside of the world’s most promising 6G market in 2030. That would intensify concern about a bifurcation of 6G into Western and Chinese variants of IMT 20230 RIT/SRIT standard and the 3GPP specified 6G core network.
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2025/art_7514154ec01c42ecbcb76057464652e4.html
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-see-their-sales-in-china-fall-off-a-cliff
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
- Purpose: The planned systems are intended to provide global broadband connectivity, data relay, and positioning services, directly competing with U.S. efforts like SpaceX’s Starlink network.
- Filing Entities: The primary filings were submitted by the state-backed Institute of Radio Spectrum Utilization and Technological Innovation, along with other commercial and state-owned companies like China Mobile and Shanghai Spacecom.
- Status: These filings are an initial step in a long international regulatory process and serve as a claim to limited spectrum and orbital slots. They do not guarantee all satellites will ultimately be built or launched. The actual deployment will be a gradual process over many years.
- Context: The move is part of an escalating “space race” to dominate the LEO environment. Early filings are crucial for securing priority access to orbital resources and avoiding signal interference. The sheer scale of the Chinese proposal would, if realized, dwarf most other planned constellations.
- Regulations: Under ITU rules, operators must deploy a certain percentage of the satellites within seven years of the initial filing to retain their rights.
- Shanghai Yuanxin (Qianfan), currently China’s most advanced LEO satellite operator, has submitted a regulatory request for an additional 1,296 satellites.
- Telecommunications giant China Mobile is planning two separate constellations totaling 2,664 satellites.
- ChinaSat, the established state-owned satellite provider, is focusing on a 24-satellite medium-Earth orbit (MEO) system.
- GalaxySpace, a private satellite manufacturer based in Beijing, has applied for 187 satellites, and China Telecom has applied for 12.

Image Credit: Klaus Ohlenschlaeger/Alamy Stock Photo
“This gives SpaceX what they need for the next couple of years of operation. They’re launching a bit over 3,000 satellites a year, so 7,500 satellites being authorized is potentially enough for SpaceX to do what they want to do until late 2027,” said Tim Farrar, satellite analyst and president at TMF Associates.
SpaceX has plans for a larger D2D satellite constellation that would use the AWS-4 and H-block spectrum it is acquiring from EchoStar. It is awaiting FCC approval for the US$17 billion deal, but the spectrum is not expected to be transferred until the end of November 2027.
The FCC noted that the changes will allow the Starlink system to serve more customers and deliver “gigabit speed service.” Along with permission for another tranche of satellites, the FCC has set new parameters for frequency use and lower orbit altitudes. The modified authorizations will also apply to new satellites to be launched.
Starlink’s LEO satellite network competitors are Amazon Leo, OneWeb and AST Space Mobile.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
Huge significance of EchoStar’s AWS-4 spectrum sale to SpaceX
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
SpaceX has majority of all satellites in orbit; Starlink achieves cash-flow breakeven
Amazon Leo (formerly Project Kuiper) unveils satellite broadband for enterprises; Competitive analysis with Starlink
NBN selects Amazon Project Kuiper over Starlink for LEO satellite internet service in Australia
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
Amazon launches first Project Kuiper satellites in direct competition with SpaceX/Starlink
Vodafone and Amazon’s Project Kuiper to extend 4G/5G in Africa and Europe
China’s state owned telcos slash CAPEX to the lowest in decades!
China’s big three state-owned telecom operators are drastically slashing capital expenditures (CAPEX) before the next wave of heavy spending on 6G mobile network infrastructure beginning in 2030. Over a year ago, the IEEE Techblog reported the planned CAPEX reductions in this post.
- China Telecom expects its capital expenditure to decline by 11% to 83.6 billion yuan in 2025, returning to pre-5G expansion levels.
- China Mobile also plans to cut its capital expenditure by 8% in 2025, bringing spending close to 2012 levels.
- China Unicom, the smallest of the three, recorded the sharpest drop in spending.
Reasons for the Cuts:
- The 5G network infrastructure buildout has largely reached its peak, with China already having 3.5 million 5G base stations.
- The companies are preparing for the next major investment cycle, which is expected to focus on 6G and AI infrastructure.
- The CAPEX cuts are also being driven by government directives to improve market value and increase shareholder dividends.
- The companies are prioritizing investments in AI infrastructure and computational infrastructure.
- China Mobile’s Chairman Yang Jie stated that the next major investment cycle is expected to focus on 6G and is unlikely to begin before 2028.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1. China Mobile, the largest wireless carrier in China with over 1 billion subscribers, slashed its annual capital expenditure by over 9% to 164 billion yuan in 2024. The company plans to cut another 8% this year to 151.2 billion yuan. That amount is approaching the 2012 level of 127.4 billion yuan, and is set to decline further in the years to come.
“The overall investment size in the next two to three years will continue to steadily fall,” Yang Jie, China Mobile’s chairman, told reporters in Hong Kong last Thursday. Asked what would trigger the next capital spending spree, Yang said: “From what I see now, the next investment peak will be on 6G” — but he expects that to kick off around 2028. Until then, the industry veteran expects “the proportion of investment to expand in the areas of computation and AI.”

China Mobile Chairman Yang Jie told reporters in Hong Kong on March 20 that the next telecom investment peak would be for 6G mobile network building. (Photo by Kenji Kawase)
Jefferies telecom analyst Edison Lee, said China Mobile’s capex figures were “lower than expected.” The ratio versus its revenue was 18% last year, marking the first dip below 20%, and he expects this proportion to further sink to 16% this year. “This is negative for equipment vendors such as ZTE,” Lee said, although it provides more room for returns to shareholders.
2. China Telecom (#2 in China) announced on Tuesday that its CAPEX for 2024 came to 93.51 billion yuan ($12.9 billion), 5% lower than the previous year. The forecast for this year is even lower, at 83.6 billion yuan, down 11% and lowering the amount to the level before the peak 5G network investment years of around 2020 to 2023. However, with soaring demand for AI computing, it plans a further hike in digital infrastructure spending. It will boost investment in cloud computing and data centers by 22% to RMB45.5 billion ($6.3 billion), making it the biggest single capex item, accounting for 38% of the total.
The company said it’s focused on four technology directions: network, cloud and cloud-network integration, AI and quantum security. It revealed it had deployed 70,000 5G-A base stations in 121 cities, with 5G RedCap coverage in more than 200 cities, and said it had signed up 2.4 million subs to its pioneering D2D mobile satellite service.
Chairman Ke Ruiwen told Nikkei Asia that “the general trend is heading downward.” He added that “before building the new large-scale network (apparently referring to 6G), the investment trend is going continue falling.” He said the company would continue to pursue its strategy focused on cloud and digital transformation.

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
3. China Unicom, the smallest of the three state owned telcos, also slashed its capital spending by 17% to 61.37 billion yuan in 2024, while planning a further reduction to 55 billion yuan this year. “Our investment emphasis has already shifted away from mobile broadband to computing network capabilities for internet data centers and cloud,” said Tang Yongbo, Unicom’s vice president. He also mentioned the impending heavy investment period when the 6G era arrives.
China Telecom and China Unicom have a “co-build, co-share” partnership for 5G investment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
All three Chinese network operators’ actual capital expenditure in 2024 were lower than the previous guidance they had provided, by an average of 5%. The sum of annual capital expenditure for the three Chinese telcos was 319 billion yuan for 2024, and the combined estimate for 2025 is 289.8 billion yuan. Including China Tower — a tower builder established in 2014 through a merger of the three telecom companies’ related businesses, and publicly listed in 2018 — the total capex last year was 351 billion yuan. This year’s projected amount of 322 billion yuan would be one of the lowest in decades.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/china-telecom-boosts-profit-cuts-capex
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
According to a new research report from Goldman Sachs-China, the three major, state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) are quietly becoming the core beneficiaries of China’s AI boom. One reason is that, thanks to their deployment of China’s most extensive cloud infrastructure, they can serve other cloud companies as well as provide their own cloud services to their end user customers. They also enjoy the cost and scale advantages of owning their own data centers and bandwidth. For some IaaS companies, data center and connectivity together account for as much as 60% of total expense, according to Goldman-China.
Goldman analysts believe that telecom operators’ cloud businesses have obvious cost advantages compared to other cloud companies. Those are the following:
- The big 3 Chinese network operators have built their own Data Centers (DCs) and so do not rely on external DC service providers. They even provide DC services to other cloud companies such as Alibaba, which makes the IDC expenses of their cloud business lower.
- The bandwidth cost of operator cloud business is significantly lower than that of other cloud companies because operators use their own network infrastructure, while other cloud companies need to pay operators for bandwidth and private network fees connecting different data centers.
- For the IaaS cloud business, if external DC and bandwidth are used, data center costs (DC services and bandwidth) will account for a considerable proportion of the total cost of the cloud company. Goldman cites QingCloud Technology as an example, its data center costs (including cabinets, bandwidth, etc.) account for 50%-60% of its total costs.
Looking ahead, the telcos are strongly placed to take advantage of the DeepSeek AI boom, thanks to their early embrace of DeepSeek and the government’s push to promote AI among the state-owned enterprises that account for about 30% of operator revenue, Goldman argues. The report states, “the state-owned enterprise background makes the deployment of AI/Deepseek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises more beneficial to telecom operators.”
In the past two weeks, China’s three major operators have begun to help important customers deploy DeepSeek models. China Mobile supports PetroChina in deploying a full-stack Deepseek model; China Telecom provides the same service to Sinopec; and China Unicom cooperates with the Foshan Municipal Bureau of Industry and Information Technology. More importantly, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC) launched the “AI+” action plan on February 21 to encourage Chinese state-owned enterprises to accelerate the development and commercial application of AI. According to Goldman Sachs research, government-related customers account for about 30% of telecom operators’ cloud revenue. Therefore, the deployment of AI/DeepSeek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises will clearly benefit telecom operators.
Separately, China Mobile announced at Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona that it is leveraging artificial intelligence to transform telecommunications networks and drive unprecedented data growth while positioning itself at the forefront of AI-Native network innovation. China Mobile Executive Vice President Li Huidi outlined the company’s ambitious “AI+NETWORK” strategy in a keynote address titled “AI+NETWORK, Pioneering the Digital-Intelligent Future” during the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit on Sunday.
.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Li Huidi, executive vice president of China Mobile, speaks at the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain, March 2, 2025. (Photo/China Mobile)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://wallstreetcn.com/articles/3741901 (Chinese)
https://www.telecoms.com/partner-content/china-mobile-unveils-ai-network-strategy-at-mwc
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/china-telcos-rush-to-embrace-deepseek
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China adds 20M “5G package” subscribers in July; 1H-2024 earnings gains outpace revenues for all 3 major China telcos
The number of 5G subscribers in China increased by a sizeable 20 million last month, according to new data from the country’s big three state owned network providers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom). Of the three, China Mobile is still the only one to report actual customers using its 5G network; China Telecom and China Unicom are sticking to their 5G package subscribers metric, which essentially means customers signed up to a 5G plan, regardless of whether they use 5G network services (most continue to use 4G).
- China Mobile’s July net adds came in at 13.7 million, pushing its 5G customer base up to a colossal 528 million. China Mobile disclosed that it has 129 million customers using its 5G New Calling over high-definition video service reached 129 million, of which, smart application subscribers numbered 11.82 million.
- China Telecom added 3.1 million 5G package customers for a total of 340 million. They did not talk about 5G in their earnings report (more below).
- China Unicom added 2.9 million 5G package customers for a total of 279 million. China Unicom shared details of its 5G network build-out, pointing out that its 5G mid-band base stations numbered in excess of 1.31 million as of mid-year, while low-band sites reached 780,000.
For each of them, cloud and digital transformation (rather than 5G subs) drove topline growth, profit rose more than revenue and shareholder returns increased.
- China Mobile said net profit had improved 5.3% to RMB80.2 billion ($11.2 billion), outpacing revenue, which rose 3% to RMB546.7 billion ($76.6 billion).
- China Telecom, reported net earnings of 21.8 billion Chinese yuan (US3.1 billion), an 8.2% gain over last year, with revenue up 2.8% and service revenue 4.3% higher.
- China Unicom reported 11.3% higher net income of 13.8 billion ($1.93) on the back of a 2.9% lift in sales to RMB197.3 billion ($27.6 billion).
China Mobile says its digital transformation business grew 11% to RMB147.1 billion ($20.6 billion), accounting for 26% of all revenue. China Telecom reported digital industry sales of RMB73.7 billion ($10.3 billion), a 7% increase, and China Unicom said revenue grew 7% to RMB43.5 billion ($6.1 billion).

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo)
All three state owned telcos experienced double-digit growth in cloud services. China Telecom’s Tianyi Cloud grew revenue by 20% to RMB55 billion ($7.7 billion), while China Mobile Cloud hiked sales by 19% to RMB50 billion ($7 billion) and China Unicom grew 24% to RMB32 billion ($4.5 billion).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Silence is Golden?
There was a distinct lack of 5G commentary in China Telecom’s half year report; it is the last of the three to post numbers and did so alongside the publication of the market’s operational statistics for July. The telco shared its 5G package figures – it added almost 18 million in the first six months of 2024, incidentally – but made no other reference to the technology in a fairly wordy statement about its year-to-date performance. Instead, the operator focused on the progress of its digital transformation strategy, leaning heavily on the promise of artificial intelligence. Specifically, China Telecom is talking up what it terms AI+ – there’s always one – and the Xingchen large language model it launched at the back end of last year.
“The Company strengthened the integration and mutual promotion of capabilities in various fields, continuously enriched the Xingchen large model series product portfolio, empowered the intelligent transformation for thousands of industries, and supported enterprises to achieve costs reduction and efficiency enhancement,” it said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-added-20-million-5g-subs-last-month
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/cloud-digital-transformation-drive-chinese-telcos-h1-growth
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
China’s ZTE reported a 2.9% rise in total revenue to RMB62.5 billion ($8.76 billion), with net profit attributable to holders of ordinary shares of the Hong Kong listed company at RMB 5.73 billion, up 4.8% year-over-year (YoY). The biggest growth surge was in the corporate and government unit, which boosted revenue by 56% to RMB9.2 billion yuan ($1.29 billion), mainly through stronger server and storage sales. However, that was offset by a 68% hike in costs, depressing the gross margin by 5.7 points – a result of “changes in revenue mix,” the company said.
The company’s core carrier network equipment business declined 8.6% in the first half of 2024, holding back underlying earnings to 4.96 billion Chinese yuan (US$700 million) – a gain of just 1.1% over last year. The carrier unit, which accounted for 60% of the company’s total revenue, brought in RMB37 billion ($5.18 billion) in sales in H1, the company revealed in its stock exchange filing.
ZTE said demand from Chinese telecom operators had been constrained by “overall investment sentiments,” but it pointed to improved sales of indoor distribution, high-speed rail and metro networking equipment. ZTE’s consumer business, which includes mostly handsets and home routers, grew 14% to RMB16 billion ($2.24 billion). R&D spending remained flat at RMB12.7 billion ($1.78 billion).
_International_Software_Products.jpeg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
China’s domestic market accounted for 69% of total sales, roughly the same as last year. The biggest offshore growth region was Asia (excluding China), which grew 23%. ZTE said it is positioning itself as a “path-builder for the digital economy” and aimed to further expand its legacy connectivity business while growing its computing business. Its AI portfolio includes full-stack intelligent solutions, backed by key technologies such as high-speed networking, network computing and data processing.
ZTE is developing their own custom silicon. In the first half of 2024, the company continued to increase investment in advanced semiconductor process technologies, advanced architecture and seal packaging design, core intellectual properties and digitalized efficient development platform on the back of close to 30 years’ R&D build-up. We are an industry leader in terms of the ability to design the whole process of chip. On top of a solid foundation in the R&D of base-level technology for DICT chip, the Group has also constructed an ultra-efficient, green and intelligent full-stack computing network base pivoting on “data, computing and network” in line with developments in computing-network integration. The creation of a product regime meeting the core requirements of the diversified scenarios of “cloud, edge, terminal” has supported our ongoing leading position in terms of competitiveness.
ZTE has used its expertise in communication software and hardware development, engineering capabilities and industrialization to intensify its investment in computing power products and solutions. The company has launched a comprehensive suite of full-stack, full-scenario intelligent computing solutions, covering computing, networks, capabilities, intelligence and applications. These solutions include a full range of general computing servers, high-performance AI training servers, inference servers, liquid-cooled servers, distributed storage systems, high-end multi-control magnetic arrays, integrated training-inference machines and high-speed lossless switches.
In the terminal sector, ZTE has introduced the concept of “AI for All”, focusing on five core consumer scenarios: sports and health, audio and video entertainment, business and travel, home and education, and smart driving. The company has launched a full range of AI-driven terminal products, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and mobile internet devices, as part of its Full-Scenario Intelligent Ecosystem 3.0. This ecosystem promotes the integration of AI technology across mobile terminal devices, smart home devices, cloud computing and automotive electronics.
Moving forward, ZTE is dedicated to advancing its core technological innovations and accelerating its expansion into the “connectivity + computing + capability + intelligence” domain. The company will focus on strengthening its digital and intelligent infrastructure. By fostering open collaboration and pursuing diverse, mutually beneficial partnerships, ZTE aims to build a highly efficient and intelligent digital future with industry partners. The company said it expects: gradual adoption of 5G-Advanced, further rollout of 400G optical and construction of intelligent computing centers to drive the China’s telecom carrier market in the second half. Offshore, it will continue to focus on large national markets and big telcos for its wirelines and wireless product lines.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-s-carrier-sales-slump-9-in-h1
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0816/2024081601602.pdf
ZTE reports H1 2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
China’s mobile data consumption slumps; Apple’s market share shrinks-no longer among top 5 vendors
Mobile data demand is in a steep decline in China, the world’s largest 5G market by subscribers. China’s MIIT numbers released this week show per user data consumption (DOU) grew just 8.1% in the first half of the year. That compares to a 68% increase in 2019, the year that 5G licenses were issued. That fell to 13% in 2022 and 11% at end- 2023. Since then, there’s been a decrease in growth of nearly three percentage points in six months.
| Indicator name | unit | Cumulative from January to June | Year-on-year
Growth ( %) |
| Total volume of telecommunication business (at constant prices of the previous year) | 100 million yuan | 8992 | 11.1 |
| Operating income | 100 million yuan | 10712 | 2.8 |
| Including: Telecommunication business income | 100 million yuan | 8941 | 3.0 |
| Total call duration of fixed-line outgoing calls | 100 million minutes | 380 | -3.4 |
| Total mobile phone call duration | 100 million minutes | 10688 | -4.6 |
| Mobile SMS traffic | 100 million | 9407 | 0.5 |
| Mobile Internet access traffic | 100 million GB | 1604 | 12.6 |
| Average mobile Internet access traffic per household in the month (DOU) | GB/household · month | 18.15 | 8.1 |
| Note: 1. The duration of fixed-line outgoing calls and mobile phone calls includes the corresponding IP phone call duration.
2. Starting from February 2024, the 5G mobile Internet access traffic and the number of 5G mobile Internet users of China Radio and Television Network Group Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as China Radio and Television) will be included in the industry summary data, and the data for the same period last year will be adjusted synchronously. |
|||
“While China has rapidly rolled out 5G and continues to perform well vs other markets, there is a limit to the number of people in the market that will engage in advanced data services; the slowdown in traffic growth is an indication that we could be reaching that limit,” according to GSMA.
Commercial 5G standalone (SA) networks, now present in seven APAC countries (Australia, India, Japan, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, and Thailand), will help fuel this growth, alongside 5G Advanced, RedCap and AI, creating opportunities to launch new 5G applications and kick start a fresh round in 5G investments for enterprises and consumers.
The authors of the report, GSMA Intelligence, expect 5G to add almost $130 billion to the Asia Pacific economy in 2030, with the manufacturing industry forecast to benefit the most, driven by new 5G-enabed applications including smart factories, smart-grids, and IoT-enabled products. Financial services and public administration are also expected to be big beneficiaries, as they turn to 5G to digitally transform services and operations. To help support this growth the GSMA today launched the GSMA APAC Fintech Forum, a new community programme to unite the connected fintech and commerce sectors with Asia Pacific’s mobile network operators through new technologies.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Meanwhile, Apple’s smartphone market share in China shrank by two percentage points in the second quarter of 2024 and the company is no longer one of the top vendors, according to data from market research firm Canalys. The decline underscores the difficulties the U.S. tech giant faces in its third-largest market.
Huawei’s smartphone shipments surged 41 per cent year on year in the the quarter, bolstered by the launch of its new Pura 70 series in April. Chinese smartphone vendors held the top five spots in the second quarter.
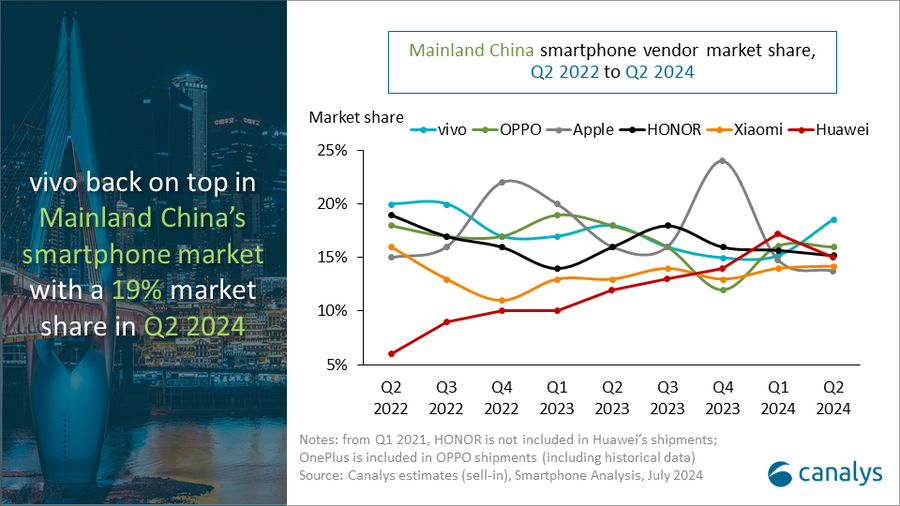
“It is the first quarter in history that domestic vendors dominate all the top five positions,” said Canalys Research Analyst Lucas Zhong. “Chinese vendors’ strategies for high-end products and their deep collaboration with local supply chains are starting to pay off in hardware and software features. HONOR’s latest Magic V3, which leverages GenAI, has significantly enhanced the user experience of foldable devices. Conversely, Apple is facing a bottleneck in mainland China. The vendor’s current channel strategy maintains a healthy inventory level and aims to stabilize retail prices and protect margins of channel partners. In the long term, the Chinese high-end market is ripe with opportunity. Local brands such as Huawei, HONOR, OPPO, and vivo are leading the way by incorporating technologies such as GenAI into products and services. Additionally, the localization of Apple’s Intelligence services in mainland China will be crucial in the next 12 months.”

People’s Republic of China (Mainland) smartphone shipments and annual growth
Canalys Smartphone Market Pulse: Q2 2024
|
Vendor |
Q2 2024 |
Q2 2024 |
Q2 2023 |
Q2 2023 |
Annual |
|
vivo |
13.1 |
19% |
11.4 |
18% |
15% |
|
OPPO |
11.3 |
16% |
11.4 |
18% |
-1% |
|
HONOR |
10.7 |
15% |
10.3 |
16% |
4% |
|
Huawei |
10.6 |
15% |
7.5 |
12% |
41% |
|
Xiaomi |
10.0 |
14% |
8.6 |
13% |
17% |
|
Others |
14.8 |
21% |
15.1 |
24% |
-2% |
|
Total |
70.5 |
100% |
64.3 |
100% |
10% |
|
Notes: from Q1 2021, HONOR is not included in Huawei’s shipments; OnePlus is included in OPPO shipments. |
|||||
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2024/art_e2f06366bb134479a40cf4cf86445b1e.html
https://canalys.com/newsroom/china-smartphone-market-Q2-2024
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/slowing-mobile-numbers-cast-doubt-on-gsma-s-buoyant-forecasts
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
Chinese engineers field test a “6G” network with semantic communications on 4G infrastructure
According to the Xinhua news agency, Chinese telecom engineers have established the world’s first field test network for 6G communication and intelligent integration. That’s before 6G is even defined let alone specified by ITU-R WP5D or 3GPP Release 21. The experimental network has demonstrated that semantic communication [1.] can reach the transmission capabilities of 6G on existing 4G infrastructure.
Note 1. Semantic communication aims at the successful transmission of information conveyed by the source rather than the accurate reception of each single symbol or bit regardless of its meaning.
The network has achieved a remarkable tenfold improvement in key communication metrics, including capacity, coverage and efficiency, according to a team from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications who unveiled their work at a seminar on July 10th. The network serves as a platform which facilitates the efforts of research institutions in conducting theoretical research and initial verification of 6G pivotal technologies. It can effectively lower the entry threshold for 6G research, making it more accessible for innovation, according to the team.
“The integration of the two will accelerate the formation of new business forms of the digital economy,” Professor Zhang Ping, who heads the university’s research team, reportedly said at the conference where the 6G field test network was unveiled. “AI will improve the perception and semantic understanding of communication, while the ubiquitous communication of 6G will in turn extend the reach of artificial intelligence to all corners of all fields,” Zhang was quoted as saying.

Existing 4G and 5G infrastructure has potential to ramp up to 6G, according to the results of a test network. Photo: Shutterstock
China is working to commercialize 6G, the next-generation wireless technology after 5G, by around 2030, the same time at which 6G standards are expected to be completed. The ITU-R says 6G could promote the growth of a range of advances, allowing communication to be immersive and connectivity universal. But with existing communication technology reaching its theoretical bandwidth limit, there are a series of big problems that have to be overcome. These include the difficulty of increasing capacity, the high cost of coverage, and high energy consumption.
The 6G technology market is also expected to enable major improvements in imaging, presence technology and location awareness. In conjunction with AI, the 6G computing infrastructure should be able to determine the best location for computing, including decisions about data storage, processing and sharing.
References:
https://english.news.cn/20240711/5dd430b4f66141d6a75a7fc505597fb3/c.html
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/china-builds-world-s-first-6g-field-test-network
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
IMT-2030 Technical Performance Requirements (TPR) from ITU-R WP5D
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
6th Digital China Summit: China to expand its 5G network; 6G R&D via the IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China’s ZTE reported 3.7% higher Q1-2024 earnings of 2.7 billion Chinese yuan (US$380 million), with sales up 5% to RMB30.6 billion ($4.2 billion).
With decreased CAPEX from China’s network operators, ZTE accelerated its transition from full connectivity to “connectivity + computing power” ino order to expand its addressable market.
Internationally, ZTE said it “continued to achieve continuous breakthroughs with major telecom operators in key countries, sustaining its growth trend. Simultaneously, in terms of government-enterprise business and consumer business, the company intensified its expansion in these two sectors, with both segments returning to rapid growth paths.”
That’s in sharp contrast to its European network equipment rivals, who have been exposed by the worldwide 5G wind-down. Nokia lost a fifth of its revenue in Q1; Ericsson reported a 14% slide, with network sales off by 19%.
ZTE didn’t break out its segment figures for Q1, but its 2023 full-year filing showed it remains heavily reliant on its home market, which contributed just under 70% of total revenue. Both ZTE and Huawei derive at least 80% of network spending by China’s state-owned telco giants (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom).
ZTE, leveraging its long-term accumulation of ICT full-stack full-domain capabilities, is pursuing strategic opportunities in digitization, intelligence, and decarbonization. Keeping pace with the wave of AI development, the company deepens its business layout of “connectivity + computing power,” providing global customers in high-speed networks, computing infrastructure, and industrial digital transformation with an open and innovative intelligent network foundation.
ZTE says it’s committed to deeply integrating AI technology with terminals to drive product innovation and intelligent upgrades, thus constructing a smart ecosystem. For terminals, ZTE has proposed the concept of “AI for All,” launched an AI-driven all-scenario intelligent ecosystem 3.0, and released a variety of innovative products and technologies.
In the first quarter of 2024, the company’s research and development expenses were RMB 6.38 billion, accounting for 20.9% of operating revenue. That provided sustained strong impetus for business innovation and product enhancement/competitiveness.
Moving forward, ZTE says it is committed to actively embracing the digital construction wave, accelerating its transition towards “connectivity + computing power,” thereby driving the company’s high-quality development. The company will continue collaborating with industry partners to establish highly efficient, green, and intelligent digital infrastructure, aiming to advance the development of the global ICT industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, ZTE was honored with 2023 Climate Leadership Award (A list) at “Embracing International Disclosure Standards and Amplify the Voice of Chinese Companies – CDP China 2023 Annual Report Release and Award Ceremony.” This recognition comes as ZTE’s case study, “Target-Driven, Layered Decoding: Pathways and Actions to Achieve Climate Goals” was featured in 2023 CDP China Corporates Disclosure Report. The event further acknowledged ZTE’s outstanding contributions to climate change mitigation and sustainable development.
Summer Chen, Vice President and General Manager of Branding & PR Strategies at ZTE, shared the company’s actions and leadership in promoting green innovations during her speech titled “Shaping Digital Innovation for a Shared Sustainable Future.” She stated, “Green and sustainable development is a global consensus, with digital intelligence playing a pivotal role. In line with this trend, ZTE has dedicated itself to green and low-carbon innovations, and received an A rating for its leading climate action in CDP Climate Change 2023 Questionnaire, an honor achieved by only 2% of global participants.”

Ms. Chen emphasized ZTE’s commitment to green development, leveraging technological innovation to shape an eco-friendly ecosystem. This commitment is underpinned by four dimensions: green operations, green supply chain, green digital infrastructure and green empowerment, contributing to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals. ZTE focuses on energy conservation and carbon reduction within its business operations, while empowering industries to foster new quality productive forces, aiming to set a global benchmark as a green, sustainable, and low-carbon tech company.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/content/dam/zte-site/investorrelations/en_quarter_report/20240425.pdf
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/zte-scoops-2023-climate-leadership-award-a-list.html
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-defies-capex-slump-with-higher-q1-earnings-revenue
https://www.zte.com.cn/content/dam/zte-site/investorrelations/en_annual_report/20240326.pdf


