ZTE
ZTE’s AI infrastructure and AI-powered terminals revealed at MWC Shanghai
ZTE Corporation unveiled a full range of AI initiatives under the theme “Catalyzing Intelligent Innovation” at MWC Shanghai 2025. Those innovations include AI + networks, AI applications, and AI-powered terminals. During several demonstrations, ZTE showcased its key advancements in AI phones and smart homes. Leveraging its underlying capabilities, the company is committed to providing full-stack solutions—from infrastructure to application ecosystems—for operators, enterprises, and consumers, co-creating an era of AI for all.
ZTE’s Chief Development Officer Cui Li outlined the vendor’s roadmap for building intelligent infrastructure and accelerating artificial intelligence (AI) adoption across industries during a keynote session at MWC Shanghai 2025. During her speech, Cui highlighted the growing influence of large AI models and the critical role of foundational infrastructure. “No matter how AI technology evolves in the future, the focus will remain on efficient infrastructure, optimized algorithms and practical applications,” she said. The Chinese vendor is deploying modular, prefabricated data center units and AI-based power management, which she said reduce energy use and cooling loads by more than 10%. These developments are aimed at delivering flexible, sustainable capacity to meet growing AI demands, the ZTE executive said.
ZTE is also advancing “AI-native” networks that shift from traditional architectures to heterogeneous computing platforms, with embedded AI capabilities. This, Cui said, marks a shift from AI as a support tool to autonomous agents shaping operations. Ms. Cui emphasized the role of high-quality, secure data and efficient algorithms in building more capable AI. “Data is like fertile ‘soil’. Its volume, purity and security decide how well AI as a plant can grow,” she said. “Every digital application — including AI — depends on efficient and green infrastructure,” she said.
ZTE is heavily investing in AI-native network architecture and high-efficiency computing:
- AI-native networks – ZTE is redesigning telecom infrastructure with embedded intelligence, modular data centers and AI-driven energy systems to meet escalating AI compute demands.
- Smarter models, better data – With advanced training methods and tools, ZTE is pushing the boundaries of model accuracy and real-world performance.
- Edge-to-core deployment – ZTE is integrating AI across consumer, home and industry use cases, delivering over 100 applied solutions across 18 verticals under its “AI for All” strategy.
ZTE has rolled out a full range of innovative solutions for network intelligence upgrades.
-
AIR RAN solution: deeply integrating AI to fully improve energy efficiency, maintenance efficiency, and user experience, driving the transition towards value creation of 5G
-
AIR Net solution: a high-level autonomous network solution that encompasses three engines to advance network operations towards “Agentic Operations”
-
AI-optical campus solution: addressing network pain points in various scenarios for higher operational efficiency in cities
-
HI-NET solution: a high-performance and highly intelligent transport network solution enabling “terminal-edge-network-computing” synergy with multiple groundbreaking innovations, including the industry’s first integrated sensing-communication-computing CPE, full-band OTNs, highest-density 800G intelligent switches, and the world’s leading AI-native routers
Through technological innovations in wireless and wired networks, ZTE is building an energy-efficient, wide-coverage, and intelligent network infrastructure that meets current business needs and lays the groundwork for future AI-driven applications, positioning operators as first movers in digital transformation.
In the home terminal market, ZTE AI Home establishes a family-centric vDC and employs MoE-based AI agents to deliver personalized services for each household member. Supported by an AI network, home-based computing power, AI screens, and AI companion robots, ZTE AI Home ensures a seamless and engaging experience—providing 24/7 all-around, warm-hearted care for every family member. The product highlights include:
-
AI FTTR: Serving as a thoughtful life assistant, it is equipped with a household knowledge base to proactively understand and optimize daily routines for every family member.
-
AI Wi-Fi 7: Featuring the industry’s first omnidirectional antenna and smart roaming solution, it ensures high-speed and stable connectivity.
-
Smart display: It acts like an exclusive personal trainer, leveraging precise semantic parsing technology to tailor personalized services for users.
-
AI flexible screen & cloud PC: Multi-screen interactions cater to diverse needs for home entertainment and mobile office, creating a new paradigm for smart homes.
-
AI companion robot: Backed by smart emotion recognition and bionic interaction systems, the robot safeguards children’s healthy growth with emotionally intelligent connections.
ZTE will anchor its product strategy on “Connectivity + Computing.” Collaborating with industry partners, the company is committed to driving industrial transformation, and achieving computing and AI for all, thereby contributing to a smarter, more connected world.
References:
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
Malaysia’s U Mobile signs MoU’s with Huawei and ZTE for 5G network rollout
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Dell’Oro: RAN revenue growth in 1Q2025; AI RAN is a conundrum
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
Dell’Oro: Global RAN Market to Drop 21% between 2021 and 2029
Malaysia’s U Mobile signs MoU’s with Huawei and ZTE for 5G network rollout
Malaysia’s second 5G network operator, U Mobile Sdn Bhd has signed separate memorandum of understandings (MoU’s) with Chinese technology leaders Huawei Technologies Co Ltd and ZTE Corporation to facilitate the implementation of Malaysia’s second 5G network. U Mobile has invested over RM8 billion in its network and technological infrastructure, with over 10,000 network sites. DNB, the country’s first wholesale 5G network, selected Ericsson as its network equipment provider.
U Mobile chairman Tan Sri Vincent Tan said Huawei will be responsible for deploying the 5G network in Peninsular Malaysia, while ZTE will manage the rollout in Sabah and Sarawak. “We are pleased to formalize our vendor agreements with Huawei and ZTE, two of the world’s leading 5G technology providers. The vendor selection process was conducted in a transparent manner to ensure we chose the most suitable technology partners to support our ambitious goals,” Tan said in his speech at the signing ceremony in Putrajaya. “Huawei and ZTE are no strangers to U Mobile. Having been our long-term infrastructure partners, they have a proven global deployment track record, hence, we are looking forward to pivoting our business together,” Tan added.
U Mobile chief technology officer Woon Ooi Yuen said the selection process began last year with invitations to tender issued to network equipment and software providers from various regions. “Ultimately, only two Chinese companies responded to our 5G tender and we are delighted to work with Huawei and ZTE on this significant endeavor. Apart from their global technology track record, they have also shared vision for an efficient and rapid rollout,” Woon said.
_theedgemalaysia.jpg&w=1080&q=75https://assets.nst.com.my/images/articles/HQ2411038834.jpg_1744701671.jpg)
From left: Huawei M’sia CEO Simon Sun, Huawei president of Apac Terry He, U Mobile CEO Wong Heang Tuck and chairman Tan Sri Vincent Tan, Communications Ministry Deputy SecGen (Telecommunications Infrastructure) Mano Verabathran, Communications Minister Datuk Fahmi Fadzil, China’s Industry & IT Ministry Party Secretary Li Lecheng, Chinese Ambassador to M’sia Ouyang Yujing, U Mobile deputy CEO Kenneth Chang, ZTE vice president of marketing & solutions for Asia & CIS region Bai Yang, and ZTE Malaysia Managing Director Steven Ge.

NSTP/ASWADI ALIAS
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U Mobile chief executive officer Wong Heang Tuck said the company is targeting to achieve 80% 5G network penetration within 12 months of its rollout, which is scheduled to begin in the second half of this year (2H25). He said the goal is expected to be achievable through the appointment of Huawei and ZTE as strategic technology partners for the implementation of next-generation 5G networks in the country.
“Huawei and ZTE will play a key role in helping U Mobile meet its network expansion targets. We aim to achieve 80% coverage in populated areas within the first 12 months of rollout and subsequently reach 90% coverage in the following 12 months,” he said during the press conference.
Wong said this move aligns with U Mobile’s overall strategy to accelerate the adoption of 5G and 5G-A technologies in Malaysia, with a strong emphasis on supporting the enterprise sector. The signing with Huawei today was witnessed by Communications Minister Datuk Fahmi Fadzil, Tan, party secretary of China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Li Lecheng and Huawei Asia Pacific president Terry He. U Mobile reaffirmed that it remains committed to going for a public listing, though it cautioned that timing would depend on global market conditions which are in an “upheaval state today,” Wong said.
The separate MOU with ZTE was approved by U Mobile’s Fahmi, Li Lecheng, Tan and Bai Yang, ZTE’s vice president of marketing and solutions for the Asia and CIS Region. Separately, the ZTE Privacy Protection White Paper (2025) was released today. The White Paper offers a systematic and comprehensive overview of the company’s achievements in privacy compliance, spanning privacy protection policy, framework, co-building, and practical implementation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Backgrounder:
The Malaysian government announced its dual 5G network model in May 2023 to ensure competition, better quality of service and wider coverage, especially in underserved and remote areas. It committed to allowing the construction of a second wholesale network once the DNB network reached 80% coverage. U Mobile was appointed by the government to deploy the second 5G network in November 2024, winning out over larger and more established telco rivals such as CelcomDigi and Maxis. Industry observers considered this a controversial choice. U Mobile is the smallest operator in Malaysia, raising questions about its ability to build a 5G network to rival DNB’s.
The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) issued the official letter of award to U Mobile more than two weeks ago, paving the way for the construction of the country’s second 5G network.
The choice of the Chinese vendors was somewhat controversial in light of Western sanctions against them. In September 2023, Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim sparked controversy when he said that the decision to allow a second wholesale 5G network would allow for “more effective participation by Huawei.” Ibrahim argued the construction of a second 5G network was made so that Malaysia could benefit from different technologies. “We in Malaysia, and I believe rightly, decided that while we get the best from the West, we also should benefit the best from the East,” he said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U Mobile’s other MoU:
Last week, U Mobile announced that it has signed a memorandum of understanding with EdgePoint Infrastructure to become one of its preferred partners for 5G in-building communications (IBC) infrastructure. U Mobile will leverage EdgePoint’s expertise for its 5G IBC infrastructure rollout, with plans to collaborate on 5G IBC innovations Both parties will also seek to achieve the most cost-effective rapid rollout through a competitive commercial offer.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
U Mobile picks Chinese giants Huawei, ZTE for 5G network rollout
U Mobile to roll out 5G network with Huawei, ZTE; sees ‘similar’ rates to DNB
U Mobile collaborates with Huawei, ZTE for 5G infrastructure rollout
U Mobile picks Huawei and ZTE to deploy Malaysia’s second 5G network
U Mobile Names EdgePoint as a Preferred 5G IBC Infrastructure Partner for Its Upcoming 5G Rollout
Malaysia’s Maxis agreement with DNB to provide nationwide 5G services
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Malaysia’s DNB to offer free 5G services to telcos during initial rollout
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
China’s ZTE reported a 2.9% rise in total revenue to RMB62.5 billion ($8.76 billion), with net profit attributable to holders of ordinary shares of the Hong Kong listed company at RMB 5.73 billion, up 4.8% year-over-year (YoY). The biggest growth surge was in the corporate and government unit, which boosted revenue by 56% to RMB9.2 billion yuan ($1.29 billion), mainly through stronger server and storage sales. However, that was offset by a 68% hike in costs, depressing the gross margin by 5.7 points – a result of “changes in revenue mix,” the company said.
The company’s core carrier network equipment business declined 8.6% in the first half of 2024, holding back underlying earnings to 4.96 billion Chinese yuan (US$700 million) – a gain of just 1.1% over last year. The carrier unit, which accounted for 60% of the company’s total revenue, brought in RMB37 billion ($5.18 billion) in sales in H1, the company revealed in its stock exchange filing.
ZTE said demand from Chinese telecom operators had been constrained by “overall investment sentiments,” but it pointed to improved sales of indoor distribution, high-speed rail and metro networking equipment. ZTE’s consumer business, which includes mostly handsets and home routers, grew 14% to RMB16 billion ($2.24 billion). R&D spending remained flat at RMB12.7 billion ($1.78 billion).
_International_Software_Products.jpeg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
China’s domestic market accounted for 69% of total sales, roughly the same as last year. The biggest offshore growth region was Asia (excluding China), which grew 23%. ZTE said it is positioning itself as a “path-builder for the digital economy” and aimed to further expand its legacy connectivity business while growing its computing business. Its AI portfolio includes full-stack intelligent solutions, backed by key technologies such as high-speed networking, network computing and data processing.
ZTE is developing their own custom silicon. In the first half of 2024, the company continued to increase investment in advanced semiconductor process technologies, advanced architecture and seal packaging design, core intellectual properties and digitalized efficient development platform on the back of close to 30 years’ R&D build-up. We are an industry leader in terms of the ability to design the whole process of chip. On top of a solid foundation in the R&D of base-level technology for DICT chip, the Group has also constructed an ultra-efficient, green and intelligent full-stack computing network base pivoting on “data, computing and network” in line with developments in computing-network integration. The creation of a product regime meeting the core requirements of the diversified scenarios of “cloud, edge, terminal” has supported our ongoing leading position in terms of competitiveness.
ZTE has used its expertise in communication software and hardware development, engineering capabilities and industrialization to intensify its investment in computing power products and solutions. The company has launched a comprehensive suite of full-stack, full-scenario intelligent computing solutions, covering computing, networks, capabilities, intelligence and applications. These solutions include a full range of general computing servers, high-performance AI training servers, inference servers, liquid-cooled servers, distributed storage systems, high-end multi-control magnetic arrays, integrated training-inference machines and high-speed lossless switches.
In the terminal sector, ZTE has introduced the concept of “AI for All”, focusing on five core consumer scenarios: sports and health, audio and video entertainment, business and travel, home and education, and smart driving. The company has launched a full range of AI-driven terminal products, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and mobile internet devices, as part of its Full-Scenario Intelligent Ecosystem 3.0. This ecosystem promotes the integration of AI technology across mobile terminal devices, smart home devices, cloud computing and automotive electronics.
Moving forward, ZTE is dedicated to advancing its core technological innovations and accelerating its expansion into the “connectivity + computing + capability + intelligence” domain. The company will focus on strengthening its digital and intelligent infrastructure. By fostering open collaboration and pursuing diverse, mutually beneficial partnerships, ZTE aims to build a highly efficient and intelligent digital future with industry partners. The company said it expects: gradual adoption of 5G-Advanced, further rollout of 400G optical and construction of intelligent computing centers to drive the China’s telecom carrier market in the second half. Offshore, it will continue to focus on large national markets and big telcos for its wirelines and wireless product lines.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-s-carrier-sales-slump-9-in-h1
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0816/2024081601602.pdf
ZTE reports H1 2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Telecom, along with its partners [1.], says it has launched the world’s first live single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber optics transmission system with unidirectional capacity over 100T bps.
Note 1. ZTE, Yangtze Optical Fibre, Cable Joint Stock Limited Company and Huaxin Design Institute were also involved in the project, which was deployed over a transmission distance of 20km in the live network of the All-Optical Network Technology and Application in the Intelligent Computing Era seminar of the CCSA TC618/NGOF.
ZTE optical transport equipment was used for project, alongside some improvements in spectral efficiency, baud rate optimization, and amplification optimization technologies. The system extends 41 C-band 1.2T bps and 64 L-band 800G bps wavelengths, and archives unidirectional transmission capacity of over 100T bps and a transmission distance of 20km in the field network.
This demonstration completed the hollow-core fiber deployment and large-capacity transmission between China Telecom’s Hangzhou Intelligent Computing Center and Yiqiao IDC. As a key node of China Telecom’s intelligent computing power layout “2+3+7+M”, the Hangzhou Intelligent Computing Center has been deployed with the 1k GPUs computing power of the China Telecom Cloud. It also hails ‘breakthroughs in hollow-core fiber fusion splicing technologies,’ such as low-power discharge and mode field matching related to the demonstration.

To meet the requirements for distributed computing power with large bandwidth and low latency of optical networks, ZTE used its advanced high-speed optical transport equipment. Combined with improvements in spectral efficiency, baud rate optimization, and amplification optimization technologies, the system extends 41 C-band 1.2Tbit/s wavelengths and 64 L-band 800Gbit/s wavelengths. It achieves a unidirectional transmission capacity of over 100Tbit/s and a transmission distance of 20km in the field network.
The hollow-core fiber cable, independently developed by YOFC, is deployed in the field network with multiple waterproofing solutions. For instance, water-blocking glue and double-layer plastic caps are used at the cable ends to isolate the atmosphere, a pulling unit with a swivel is employed for cable deployment to minimize wear on the end caps, and a horizontal waterproof cable closure is utilized at the fusion splice point. Additionally, breakthroughs in hollow-core fiber fusion splicing technologies, such as low-power discharge and mode field matching, have achieved 0.05dB fusion splice loss between hollow-core fibers and 0.25dB fusion splice loss with 54dB return loss between hollow-core fibers and standard solid-core single-mode fibers.
China Telecom’s Zhejiang branch said: “We have always maintained the leading position in the field of basic transmission networks. By undertaking the national key R&D project, we have demonstrated and verified the hollow-core fiber and 1.2Tbit/s transport system in the field network, and can offer detailed engineering data and demonstration applications. In the future, we will further cooperate with the industry to conduct research on a larger scope, and provide practical scenarios for the interconnection of distributed intelligent computing centers.”
China Telecom says they will continue to expand the hollow-core optical cable environment and build a platform for testing and verifying new technologies and applications oriented towards intelligent computing scenarios. This effort aims to continuously promote technological innovation and application expansion in the telecommunications industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, China Telecom received four awards at the “Asia’s Best Managed Companies Poll 2024” by FinanceAsia, a reputable financial magazine in Asia:
⚫ “Best Investor Relations in China” – Gold Award
⚫ “Best Managed Company in China” – Silver Award
⚫ “Best Telecommunication Services Company” – Silver Award
⚫ “Best Large-Cap Company in China” – Bronze Award
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/china-telecoms-claims-a-world-s-first-hollow-core-fibre-demonstration
https://www.chinatelecom-h.com/en/media/news/p240730.pdf
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
China Telecom, ZTE jointly build spatiotemporal cognitive network for digital transformation
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China’s ZTE reported 3.7% higher Q1-2024 earnings of 2.7 billion Chinese yuan (US$380 million), with sales up 5% to RMB30.6 billion ($4.2 billion).
With decreased CAPEX from China’s network operators, ZTE accelerated its transition from full connectivity to “connectivity + computing power” ino order to expand its addressable market.
Internationally, ZTE said it “continued to achieve continuous breakthroughs with major telecom operators in key countries, sustaining its growth trend. Simultaneously, in terms of government-enterprise business and consumer business, the company intensified its expansion in these two sectors, with both segments returning to rapid growth paths.”
That’s in sharp contrast to its European network equipment rivals, who have been exposed by the worldwide 5G wind-down. Nokia lost a fifth of its revenue in Q1; Ericsson reported a 14% slide, with network sales off by 19%.
ZTE didn’t break out its segment figures for Q1, but its 2023 full-year filing showed it remains heavily reliant on its home market, which contributed just under 70% of total revenue. Both ZTE and Huawei derive at least 80% of network spending by China’s state-owned telco giants (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom).
ZTE, leveraging its long-term accumulation of ICT full-stack full-domain capabilities, is pursuing strategic opportunities in digitization, intelligence, and decarbonization. Keeping pace with the wave of AI development, the company deepens its business layout of “connectivity + computing power,” providing global customers in high-speed networks, computing infrastructure, and industrial digital transformation with an open and innovative intelligent network foundation.
ZTE says it’s committed to deeply integrating AI technology with terminals to drive product innovation and intelligent upgrades, thus constructing a smart ecosystem. For terminals, ZTE has proposed the concept of “AI for All,” launched an AI-driven all-scenario intelligent ecosystem 3.0, and released a variety of innovative products and technologies.
In the first quarter of 2024, the company’s research and development expenses were RMB 6.38 billion, accounting for 20.9% of operating revenue. That provided sustained strong impetus for business innovation and product enhancement/competitiveness.
Moving forward, ZTE says it is committed to actively embracing the digital construction wave, accelerating its transition towards “connectivity + computing power,” thereby driving the company’s high-quality development. The company will continue collaborating with industry partners to establish highly efficient, green, and intelligent digital infrastructure, aiming to advance the development of the global ICT industry.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, ZTE was honored with 2023 Climate Leadership Award (A list) at “Embracing International Disclosure Standards and Amplify the Voice of Chinese Companies – CDP China 2023 Annual Report Release and Award Ceremony.” This recognition comes as ZTE’s case study, “Target-Driven, Layered Decoding: Pathways and Actions to Achieve Climate Goals” was featured in 2023 CDP China Corporates Disclosure Report. The event further acknowledged ZTE’s outstanding contributions to climate change mitigation and sustainable development.
Summer Chen, Vice President and General Manager of Branding & PR Strategies at ZTE, shared the company’s actions and leadership in promoting green innovations during her speech titled “Shaping Digital Innovation for a Shared Sustainable Future.” She stated, “Green and sustainable development is a global consensus, with digital intelligence playing a pivotal role. In line with this trend, ZTE has dedicated itself to green and low-carbon innovations, and received an A rating for its leading climate action in CDP Climate Change 2023 Questionnaire, an honor achieved by only 2% of global participants.”
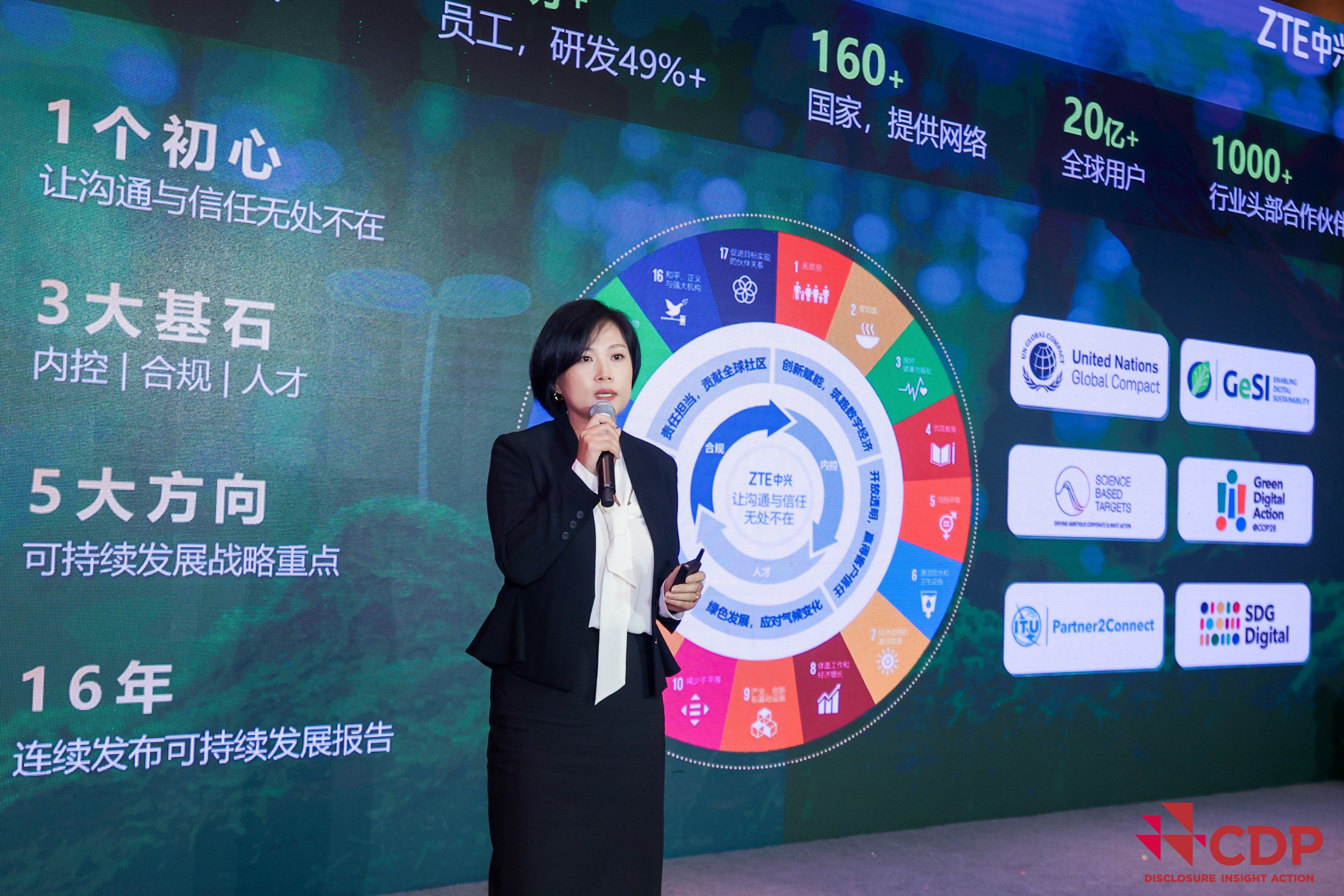

Ms. Chen emphasized ZTE’s commitment to green development, leveraging technological innovation to shape an eco-friendly ecosystem. This commitment is underpinned by four dimensions: green operations, green supply chain, green digital infrastructure and green empowerment, contributing to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals. ZTE focuses on energy conservation and carbon reduction within its business operations, while empowering industries to foster new quality productive forces, aiming to set a global benchmark as a green, sustainable, and low-carbon tech company.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/content/dam/zte-site/investorrelations/en_quarter_report/20240425.pdf
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/zte-scoops-2023-climate-leadership-award-a-list.html
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-defies-capex-slump-with-higher-q1-earnings-revenue
https://www.zte.com.cn/content/dam/zte-site/investorrelations/en_annual_report/20240326.pdf
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
Vodafone Idea (Vi) to launch 5G services “soon;” Awards optical network equipment contract to ZTE
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
Türk Telekom and ZTE have carried out a 50G PON trial in Turkey. The two firms announced that their trial delivered speeds in excess of 50 Gbps in the downstream over a single fiber and did so in a way that was compatible with existing PON generations already deployed in Türk Telekom’s network. The PON technologies used were GPON and XGS-PON – the latter offering 10 Gbps symmetrical speeds – technologies alongside 50G PON.
“This interoperability significantly expands the OLT’s potential applications, paving the way for future services such as ultra-high bandwidth access, mobile xHaul, and deterministic campus networks in both home and enterprise environments,” ZTE said.

Yong Jie, CEO of ZTE Türkiye, said: “At the MWC 2022, ZTE unveiled the world’s first precise 50G PON prototype. In 2022, the 50G PON standard was finalized and received wide attention in the industry. It is expected that by 2025, the 50G PON industry chain will be ready for commercialization. As a frontrunner in the transformative journey to 50G PON, ZTE is pleased to empower Türk Telekom to accelerate the realization of their vision to provide unparalleled connectivity solutions to customers across Türkiye.”
In February, ZTE introduced the industry’s first symmetric 50G PON ONU, ZXEN G300-N9, featuring a 50G Ethernet optical port and seamless integration with the symmetric 50G PON Combo line card to meet high-speed access needs for government and enterprise campuses.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Mehmet Beytur, Support Services and Procurement Management Assistant General Manager of Türk Telekom, said:
“As Türk Telekom, we are at the forefront of our country’s digital transformation, constantly spearheading innovative projects. Our successful collaboration with ZTE on the 3-in-1 50G PON Combo trial exemplifies this commitment. We will continue to take pioneering steps in innovative solutions.”
…………………………………………………………………………………….
However, 50G PON commercial deployment is not imminent as 25G PON is what’s being rolled out now by fiber facilities based telcos. Network operators have repeatedly indicated that they do not want to disrupt their optical distribution networks (ODNs) by moving to a new technology too quickly.
There are a number of technological barriers to 50G PON, one of which is alluded to in the ZTE announcement: while 50G PON can offer 50 Gbps-plus downstream speeds, it is not yet symmetrical, uplink speeds being half that or less.
Nonetheless, the trial is an important step in the ongoing development of 50G PON, even if future deployments are perhaps further away than the vendor community might like.
Dell’Oro pointed out that the coexistence of 50G PON with previous PON generations, and the implementation of combo PON, will be critical to the successful rollout of the technology. The analyst firm noted that “much more significant growth is expected after 2027, as operators begin to evolve their 10Gbps PON networks to next-generation technologies.”
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/t-rk-telekom-and-zte-trial-50g-pon
Nokia’s launches symmetrical 25G PON modem
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
Omdia: Cable network operators deploy PONs
Omdia Surveys: PON will be a key part of network operator energy reduction strategies
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
According to a senior executive, ZTE Corp has seen “tremendous” opportunities due to the increased demand for high-speed internet and smart home solutions globally following the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s despite a slower-than-expected development of 5G outside of China.
“Deployment of 5G technology in overseas markets has been slower than what we previously thought and investments in the field have also lagged behind,” said Chen Zhiping, vice-president of ZTE Corp.
“However, we have seen rapid growth of two sectors in our business – fixed broadband and home network solutions – internationally, especially in the Latin American market.”

The COVID-19 pandemic has pushed up demand for these two types of businesses, as people who were confined to their homes became more reliant on high-speed internet connections and home automation, she said.
“We are actively promoting these two areas of business in Latin America. Besides, the Asia-Pacific region is also where we put great focus on, such as Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand, as the region has a huge demand for network convergence, network modernization and digitalization,” Chen said.
The Asia-Pacific region is a market from which the company generates most of its overseas revenue, she added.
ZTE posted 60.7 billion yuan ($8.36 billion) in operating revenue in the first half of the year, up 1.5 percent from the year-ago period, according to its interim results announced on Aug 18. Of the total, 17.6 billion yuan, or 29 percent, came from international markets.
Net profit grew 19.9 percent on a yearly basis to 5.47 billion yuan.
“Exploring the domestic market is far from enough for a technology company, whether it is research and development or marketing. We have been committed to the international markets and promoting the globalization of research and development, supply chain and collaboration all along,” she said.
Chen acknowledged that factors such as geopolitical tensions, economic slowdown and a deteriorating business environment in some countries have posed serious challenges to ZTE‘s operations in overseas markets. She stressed that the company had established a sound system of management as well as risk identification and control to deal with potential risks.
On November 225, 2022, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) voted unanimously to ban U.S. sales of new Chinese telecommunications equipment and devices produced by Huawei and ZTE—as well as to restrict the use of other Chinese-made video surveillance equipment—over national security concerns. The Chinese companies have denied the allegations.
According to a report by German market intelligence platform Statista, the global ICT market is expected to reach $6 trillion in 2023, up from $5.5 trillion last year. China would rank third in global market share with over 11%, following the United States and European Union (EU).
References:
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202309/02/WS64f26e23a310d2dce4bb384f.html
Vodafone Idea (Vi) to launch 5G services “soon;” Awards optical network equipment contract to ZTE
FCC bans Huawei, ZTE, China based connected camera and 2-way radio makers
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Telekom Malaysia Berhad (TM) and ZTE have entered into a new strategic partnership to build out a hybrid cloud 5G core network in Malaysia which is designed for future technologies and will lead the way for next-generation networks. It’s a three year strategic partnership and the hybrid cloud aspect is part of a plan to ‘foster innovation and advancement of state-of-the-art technologies’ for TM’s 5G Core project, which includes bare metal containers, SDN-based architecture, hardware acceleration, CUPS, and 3-layer decoupling.
As well as generally improving network bandwidth and speed in Malaysia, it’s also pitched as a means to which TM can provide new connectivity services to healthcare, finance, transportation, and education, develop smart city and IoT applications, and it is ‘anticipated to revolutionize Malaysia’s telecommunications industry.
The integration of this converged network will strengthen TM’s capabilities to provide seamless connectivity and exceptional network performance, serving a diverse range of industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and education. Additionally, the hybrid cloud 5G core network will aid in the growth of smart cities, Internet of Things (IoT), and other next-generation technologies that necessitate rapid, low-latency connectivity.
This collaboration marks a significant achievement in the advancement of 5G technology in Malaysia, with the novel hybrid cloud 5G core network anticipated to revolutionize Malaysia’s telecommunications industry. With the deployment of these sophisticated technologies, customers will gain unparalleled user experience, while also improving the network’s dependability, safety, and efficiency.
Source: Jordi Boixareu/Alamy Live News
“TM is pleased to partner ZTE in building a hybrid cloud 5G core network that is designed to meet the rising needs for future technologies,” said Jasmine Lee Sze Inn, TM’s Executive Vice President for Mobile. “This strategic partnership will transform 5G-enabled networks to deliver innovative solutions and services through our state-of-the-art network and infrastructure, and enable seamless connectivity and exceptional network performance.”
Steven Ge, ZTE Malaysia’s Chief Executive Officer added: “We’re excited to strengthen our partnership with TM through the development of a hybrid cloud 5G core network. This will accelerate the launch of 5G network across Malaysia, which will bring forth new innovation into the market. As a global leading provider of information and communication technology solutions, we are confident that the advancement of our hybrid cloud 5G core network will be the model for future networks. ZTE is committed in this collaboration that will put Malaysia as one of the leading countries in the region to roll-out its 5G network.”
It’s broadly the same pitch as was delivered in places where the 5G rollout is more advanced, such as the US and Western Europe. While we don’t appear to be much closer to the utopian vision of smart cities over here, there has been some progress in private 5G networks in enterprise and industry settings – though much the emphasis now is on things like 5G SA and mmWave to bring the initial promises over the line.
East Asian contracts may be increasingly important for ZTE following U.S. led bans on Chinese vendor (Huawei and ZTE) equipment and phones. As a result of sanctions, ZTE has become more reliant on its home market. It increased domestic sales 9.2% last year compared to 3.4% offshore, with the China market now accounting for 69% of the total, up from 64% three years ago.
Chairman Li Zixue said 2022 was the start of ZTE’s “strategic expansion phase.” He said the company had achieved good growth from innovative products including server and storage, 5G industry applications, auto electronics, digital energy and smart home. “We firmly grasped the opportunities presented by the global trend of digitalization and low-carbon green principles,” he said.
The company further ramped up R&D spending. Research outlays rose 14.9%, mostly on 5G-related products, chip, server and storage businesses. R&D spending accounts for 17.6% of revenue, up from 13.8% three years ago, with the research division now totaling 49% of total headcount.
Li added that ZTE would seek opportunities for industrial transformation presented by new energy and digitalized industries. While the external environment would likely become more unpredictable, “the digital economy has grown into an irreversible trend.” He also said ZTE would “persist in an approach of precision and pragmatism in 2023,” targeting domestic opportunities in the digital economy and seeking breakthroughs in large telco customers offshore.
“We will strengthen our corporate resilience and control operating risks to achieve prudent growth,” Li concluded.
References:
https://telecoms.com/520567/tm-and-zte-team-up-on-hybrid-cloud-5g-core-network-in-malaysia/
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/zte-hikes-full-year-earnings-by-19-/d/d-id/783787?
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ZTE, in partnership with China Telecom, has released a 5G-Advanced solution, named Cluster DFS at Mobile World Congress 2023 in Barcelona, Spain. According to ZTE, the new offering will facilitate the development of specific B2B and B2C services using a single 5G network.
China Telecom claims to have deployed the world’s largest 5G SA network with more than 1 million 5G base stations based on a RAN-sharing strategy. The Chinese carrier noted it continues to focus in the B2B segment, with the number of private 5G networks hitting over 3,000, and commercial projects in this segment totaling 9,000 by the end of 2022.

Image Credit: ZTE
ZTE explained that that the new solution will be key as the service-level agreements (SLAs) requirements for the provision of 5G for industrial verticals such as smart manufacturing or smart grid are different from the requirements for the provision of 5G services for consumers. ZTE further explained that it launched the new solution given to the increasing complexity of 5G networks and to enable a coordinated development of B2B and B2C services on a single network and deliver differentiated service experiences.
To adapt to vertical application traffic dynamics on uplink and downlink, China Telecom and ZTE have introduced the innovative Cluster DFS, by which, base stations with same heavy uplink characteristics are intelligently formed as “cluster” to implement accurate adaptation between frame structure and services requirements. Consequently, a 5G network can synergize B2B and B2C services with optimal user experiences.
Li Peng, Director of Network Development and Sharing Department of China Telecom, said, “5G has become an important driving force of digital economy development. China Telecom is continuously exploring and promoting innovative technologies and solutions that combine the development of 5G high-quality networks and industrial applications.”
“Based on previous successful experience of Cluster DSS, China Telecom further extends ‘cluster-level’ radio resource management mechanism from ‘frequency domain’ to ‘time domain’, which provides more flexible radio resource strategy and promotes the development of fully-connected factories. The commercial trial of Lierda shows that Cluster DFS has increased the uplink throughput of B2B applications by 60~80% while ensuring stable B2C experiences, significantly improving network performance and efficiency, ” added Huang Lilian.
Tang Xue, VP of RAN Products, said, “B2B and B2C coordinated development on one network requires more flexible and more intelligent resource management strategy, therefore, RAN intelligence is of great importance. ZTE uses RAN native-AI to enable adaptive radio resource adjustment, including spectrum, frame structure, power and beams. With four key features, specifically, intelligent traffic prediction, cluster self-generating, intra-cluster traffic shaping and inter-cluster coordination, the potential of commercial 5G networks can be fully unlocked to offer optimal experiences for both industrial applications and consumer users.”
Cluster DFS provides precise and on-demand user experiences for both consumers and enterprises based on AI capability, enabling network policy shift from “one-size-fit-all” to “context-aware” and coordinating the development of B2B and B2C on 5G commercial networks.
Moving forward, ZTE and China Telecom will continue working together to carry out innovative practices and facilitate the development of 5G-Advanced applications for a digital, intelligent and green future.
ZTE said Cluster DFS provides precise on-demand user experiences for consumers and enterprises based on its AI capability to coordinate the development of B2B and B2C on 5G commercial networks.
China Telecom and rival network operator China Unicom had previously signed an agreement to co-build and co-share their 5G networks. According to the latest available statistics, China Telecom added a total of 5 million 5G subscribers during the first months of the year to take its total 5G subscribers base to 273 million. During 2022, the telco added a total of 80.16 million 5G subscribers.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/china-telecom-and-zte-release-cluster-dfs-at-mwc-2023.html
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/20220526e2.html
FCC bans Huawei, ZTE, China based connected camera and 2-way radio makers
On Friday, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) banned Huawei Technologies Co. and ZTE Corp. from selling electronics in the U.S. by regulators who say they pose a security risk, continuing a years-long effort to limit the reach of Chinese telecommunications companies into U.S. telecommunications networks.
The FCC also named connected-camera makers Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co. and Dahua Technology Co., as well as two-way radio manufacturer Hytera Communications Corp.
“The FCC is committed to protecting our national security by ensuring that untrustworthy communications equipment is not authorized for use within our borders, and we are continuing that work here,” Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in a news release. “These new rules are an important part of our ongoing actions to protect the American people from national security threats involving telecommunications.”
“On March 12, 2021, we published the first-ever list of communications and services that pose an unacceptable risk to national security as required under the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act. This initial Covered List included equipment from the Chinese companies Huawei, ZTE, Hytera, Hikvision, and Dahua. Since then, we’ve added equipment and services from five additional entities. Last year I also proposed stricter data breach reporting rules and worked with the Department of State to improve how we coordinate national security issues related to submarine cable licenses.”
In the 4-0 vote, the FCC concluded the products pose a risk to data security. Past efforts to curb Chinese access include export controls to cut off key, sophisticated equipment and software. Recently US officials have weighed restrictions on TikTok over fears Chinese authorities could access US user data via the video sharing app.
“This is a culminating action,” said Klon Kitchen, a senior fellow at the Washington-based American Enterprise Institute, a public-policy think tank. “Things that began under Trump are now being carried out. The Biden administration is continuing to turn the screws on these companies because the threat isn’t changing.”
Hikvision said its video security products “present no security threat to the United States and there is no technical or legal justification for the Federal Communications Commission’s decision.” The company said the ruling will “make it more harmful and more expensive for US small businesses, local authorities, school districts, and individual consumers to protect themselves, their homes, businesses and property.”
Huawei declined to comment, while Dahua, Hytera and ZTE didn’t respond to emails sent outside normal business hours in China.
The looming FCC move didn’t come up in the bilateral meeting between US President Joe Biden and Chinese President Xi Jinping in Indonesia last week, a US official said, speaking on condition of anonymity. Biden did discuss technology issues more broadly with Xi and was clear that the US will continue to take action to protect its national security, the official said.
“This is the death knell for all of them for their US operations,” said Conor Healy, director of government research for the Bethlehem, Pennsylvania-based surveillance research group IPVM. “They won’t be able to introduce any new products into the US.”
Dahua and Hikvision stand to be affected most since their cameras are widely used, often by government agencies with many facilities to monitor, Healy said. Agencies including police also use handheld Hytera radios, he said.
In its order, the FCC also asked for comment on whether to revoke existing equipment authorization, Rosenworcel said in an online statement.
According to Healy, merchants could be stuck with gear that’s illegal to sell.
In 2018, Congress voted to stop federal agencies from buying gear from the five companies named by the FCC. The agency said earlier that the companies aren’t eligible to receive federal subsidies, and also has barred Chinese phone companies from doing business in the U.S.
The order released Friday was required under the Secure Equipment Act – a bill President Biden signed into law on November 2021.
The big picture: Huawei and ZTE are two of the world’s biggest suppliers of telecom equipment.
- Countries including Canada, Britain and Australia have ramped up restrictions against the use of 5G technologies from Huawei and ZTE in recent years.
- Huawei executives have previously said the company does not give data to the Chinese government and that its equipment is not compromised.
- The company’s chief security officer Andy Purdy has also argued that a ban would hurt American jobs because it spends over $11 billion a year from American suppliers.
References:
https://www.axios.com/2022/11/25/fcc-bans-huawei-zte-equipment-national-security


