Telecom in China
China to introduce early 6G applications by 2025- way in advance of 3GPP specs & ITU-R standards
Liu said early 6G “application scenarios” will be introduced by 2025 in China, home to the world’s largest internet user population and biggest smartphone market, which has been conducting research and development on the technology since 2019. He said the commercial launch of 6G in China is expected to start from 2030, according to a report by local media National Business Daily.
At the same event, China’s Minister of Industry and Information Technology Jin Zhuanglong said in his speech that China was leading the pace of 6G research and development worldwide. He said the country is already ahead in rolling out 5G mobile networks and applications.

The statements made at the CDF about China’s 6G efforts have come after the Global 6G Conference, held from March 22 to 24 in Nanjing, where telecommunications industry experts reached a consensus that 6G mobile services in the country will start to roll out by early 2030.
The country’s three telecoms network operators – China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom – have all been reported to be involved in early 6G research and development, as they also expedited the roll-out of 5G infrastructure and services across the country.
Tensions between Beijing and Washington, however, have led to major telecoms equipment suppliers Huawei Technologies Co and ZTE Corp being handicapped by various US sanctions, including access to advanced IC’s used in smartphones and networking gear.
In spite of the disruptions caused by US pressure and the coronavirus pandemic, China has already built the world’s largest 5G mobile network, with more than 2.31 million 5G base stations deployed at the end of last year, according to MIIT data.
This year will mark the beginning of a long journey for 6G, as new studies are initiated by more countries and organisations around the world, according to a report last month by the non-profit telecoms industry body the GSMA.
The ITU-R World Radiocommunication Conference in November (WRC 23) is expected to set the spectrum foundations for 6G, the GSMA report said. Spectrum refers to the radio frequencies allocated to the mobile industry and other sectors for communications over the airwaves.
References:
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
India unveils Bharat 6G vision document, launches 6G research and development testbed
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China’s government has selected 6G as one of its priority projects for 2023. At a national conference on industry and information technology, the Ministry for Industry and IT (MIIT) Jin Zhuanglong, said China intends to push forward in “comprehensive” development of 6G this year. In 2023, China will introduce policies and measures to promote coordinated development of new information infrastructure construction and accelerate the construction of 5G and gigabit optical networks, Jin said. MIIT will also improve policies on telecom market development, and strengthen the protection of personal information and users’ rights and interests.
Editor’s Note: Work on 6G has not yet started in either 3GPP or ITU-R WP 5D. The latter SDO is progressing draft reports on the vision of IMT for 2030 and Beyond, but no 6G requirements will be identified.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
More than 2.3 million 5G base stations have been put into service, and notable progress has been made in the construction of new data centers, according to the conference.
In recent years, China has intensified efforts to promote the construction of new information infrastructure, deepen the construction of 5G, gigabit optical network and industrial internet, and promote the deep integration of the digital economy and the real economy.

Image Credit: Alan Novelli/Alamy Stock Photo
At the end of last year China Telecom issued a white paper setting out its vision for 6G. Written by the China Telecom Research Institute, the paper proposes a distributed and intelligent programmable RAN (P-RAN) network architecture and what it calls a “three-layer and four-sided” framework. The white paper notes that because of the cost of building out the dense mmWave or terahertz-band networks, it will be essential to provide device-to-device connectivity.
Six months ago, heavyweight China Mobile issued its own 6G vision, calling for “three bodies, four layers and five sides.”
China’s other 6G news is a call for proposals on potential key technologies from the national coordinating body, the IMT-2030 6G Promotion Group. According to an English-language statement posted by CAICT, the main objectives are “to inspire university-academy-industry-association entities for technology innovations, gather and form a rich reserve of 6G potential key technologies, and support 6G research, standardization, and industrial R&D.”
Non-Chinese universities and research organizations are welcome to apply ahead of the deadline in November 2023. The proposed solutions should have “application and promotion value for 6G innovation and development,” and the key technical indicators should be capable of being evaluated and verified, the statement said.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/chinese-government-confirms-focus-on-6g-development/d/d-id/782727?
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/the-6g-mess-is-getting-out-of-hand/a/d-id/782245
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
IMT towards 2030 and beyond (“6G”): Technologies for ubiquitous computing and data services
Excerpts of ITU-R preliminary draft new Report: FUTURE TECHNOLOGY TRENDS OF TERRESTRIAL IMT SYSTEMS TOWARDS 2030 AND BEYOND
Development of “IMT Vision for 2030 and beyond” from ITU-R WP 5D
China to launch world’s first 5G cruise ship via China Telecom Corp Ltd Shanghai Branch
China will debut the world’s first cruise ship covered by a 5G network later this year, due to a collaboration between CSSC Carnival Cruise Shipping Ltd’s own cruise brand Adora Cruises and China Telecom Corp Ltd Shanghai Branch. Adora Cruises [1.] has partnered with Shanghai Telecom, a major 5G network service provider in China, to bring 5G connectivity to its first China-built large cruise ship. This partnership marks a major milestone, as it is the first time a 5G network has been installed on a cruise ship in the world and sets a new standard for connectivity and convenience, according to a press release on Thursday.
Note 1. Adora Cruises is part of CSSC Carnival Cruise Shipping Limited, a joint venture between shipbuilder China State Shipbuilding Corp (CSSC) and U.S.-based leisure travel company Carnival Corporation.
“From network layout, satellite communication, to various digital applications, our goal is to deliver seamless multimedia interactions and consistent mobile connectivity for guests and crew, allowing them to stay connected with loved ones and the world while at sea,” said Chen Ranfeng, Managing Director of CSSC Carnival Cruise Shipping Limited. “By seizing a first-mover advantage in the cruise industry’s 5G market, we hope to set a new standard for digital communication in the marine travel sector.”
Adora Cruises is working towards a future where guests can enjoy an enhanced cruise experience with 5G connectivity and access to all-around multimedia and real-time interaction, the company said.

Image Courtesy of CSSC Carnival Cruise Company
“Combining 5G and satellite technology, we will focus on network communication, digital high-definition, AR/VR and other content services to further improve our guest experience and jointly promote high-quality development of the tourism economy,” said Gong Bo, general manager of Shanghai Telecom. “By seizing a first-mover advantage in the cruise industry’s 5G market, we hope to set a new standard for digital communication in the marine travel sector,” said Ranfeng.
The cruise company’s first two China-built large cruise ships are currently under construction at Shanghai Waigaoqiao Shipbuilding Corp, and will be operated under the brand name of Adora in the future.
The first 135,500-gross-ton Adora cruise ship is expected to start its journey by the end of 2023, while the second vessel is currently still being designed and constructed.
References:
http://www.ecns.cn/news/sci-tech/2023-01-13/detail-ihcircrp9799635.shtml
5G hits the open water with Adora Cruises, China Telecom partnership
China Telecom, ZTE jointly build spatiotemporal cognitive network for digital transformation
ZTE Corporation and the Zhejiang Branch of China Telecom have jointly built a self-adaptive spatiotemporal cognitive network based on ZTE’s Radio Composer, improving dynamic user experiences in high-capacity scenarios. Under the collaboration with intelligent user navigation, the network solution matches network resources with traffic distribution more precisely and efficiently through on-demand elastic coverage of two-layer network, adapting to user group flow in space over different time periods.
The spatiotemporal cognitive network intelligently predicts traffic distribution in the first place. According to location change of user groups in different time periods within base station coverage, the network solution, by virtue of LSTM (long short-term memory) algorithms, performs in-depth study and prediction of traffic distribution on physical grid level and analyses the traffic space distribution trend in different periods.
Based on the traffic distribution trend in both time and frequency, the spatiotemporal cognitive network implements the intelligent carrier power scaling function through power sharing, to achieve flexible coverage adjustment. Below is an example of Traffic distribution of different periods in one area over time:

When the traffic loads within coverage of the two carriers are both high, the solution balances the two carriers with the same coverage to guarantee capacity. When the traffic loads within coverage of the two carriers differentiates obviously, the solution adjusts the coverage mode. It adopts high power to cover the high-load area and decreases power in the low-load area, therefore precisely matching radio resources to ensure user experiences.
The spatiotemporal cognitive network focuses on intelligent experience collaboration and establishes AI logic grid knowledge base of base stations, in order to further balance network efficiency and user experiences.
Moving forward, the Zhejiang Branch of China Telecom and ZTE will keep innovating together to provide superb network performance and boost digital transformation.
References:
China’s telecom sector: stable growth in Q1-2022; cloud services revenue soared 138.1% YoY
China’s telecommunications sector posted steady expansion in the first quarter of 2022, with emerging businesses such as big data and cloud computing experiencing rapid growth, official data showed.
The combined industrial revenue rose 9.3 percent year on year to 393.5 billion yuan (about 60.92 billion U.S. dollars), a pace 2.8 percentage points faster than the same period last year, according to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
Emerging businesses, such as big data, cloud computing, internet data centers and the Internet of Things, registered rapid expansion. The emerging business revenue of China’s three telecom giants — state owned China Telecom, China Mobile and China Unicom, surged 36.3 percent year on year to 79.7 billion yuan.

The revenue for cloud computing services soared 138.1 percent year on year, while that for big data and Internet of Things surged 59.1 percent and 23.9 percent, respectively.
Steady progress was also made in the construction of 5G base stations. By the end of March, China’s 5G base stations reached 1.56 million in number, with 134,000 built in the first three months of the year.
References:
China’s telecom sector sees stable growth in Q1 (ecns.cn)
Telecommunications industry in China – Wikipedia
China’s state policy: shape global tech standards to increase influence and enhance global reputation
In line with China President Xi Jinping‘s goal of making the country a ‘major power with pioneering global influence’ by 2049, China has been leveraging its technological prowess and geopolitical heft to shape the global technological environment and standards to serve its commercial and strategic interests, a media report said.
China has adopted a state-directed strategy to influence international standards setting, and use them as a foreign policy tool to enhance its global standing, the Times of Israel reported, adding that, the Xi administration has employed a dual-track approach to set the international technological standards.

On the one hand, it seeks to influence both the multilateral (governmental) and the multi-stakeholder technical Standards Development Organizations (SDOs) by placing Chinese nationals in senior leadership positions (like in 3GPP and ITU-R WP5D) and larger representation of Chinese tech companies (the three China state owned network providers, Huawei, ZTE and smaller players like Nufront with its own 5G RIT spec), and other Chinese companies, with guidance from the Party-State (CCP), are creating standards utilizing the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and Digital Silk Road (DSR).
With respect to 5G radio interface technology (RIT) standards, three China ministries (MIIT, NDRC and MOST) jointly established the “IMT-2020(5G) Promotion Group” in February 2013. The objectives have been met:
– Promote the development of 5G technologies in China.
– Facilitate cooperation with foreign companies and organizations MIIT Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
– Drive China’s contributions to ITU-R WP5D 5G standards (M.2150 and revisions of M.1036) and 3GPP release 15 and 16 specifications (a Chinese national heads up the critical 3GPP “URLLC in the RAN” project).
The Group helped progress the ITU-R M.2150 standard for 5G RAN/RIT/SRITs. Initially China had it’s own 5G RIT spec, but it was later merged with 3GPPs as was South Korea’s.
At the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), the involvement of Chinese commercial entities have increased after the impetus provided by ITU‘s current Secretary-General, Zhao Houlin who has served two terms as Director of ITU’s Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (STB). China is second only to the U.S. in the number of entities registered as ITU members, according to the referenced Times of Israel blog.
In 2021 alone, Chinese entities backed 145 new standards at the ITU, up from 46 in 2015 and six times more than Western entities.
The number of Chinese nationals in secretariat and leadership positions in critical multi-stakeholder SSOs such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electro-technical Commission (IEC) has also surged in the past decade.
Beyond the IEC, ISO, and ITU, Chinese actors are also active in other SDOs including the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) that develops 5G technical specifications, as well as Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the report said, adding that the companies such as Alibaba, Baidu, Huawei, Tencent and ZTE are advanced members of the IEEE Standards Association.
Not only do Chinese firms ‘flood’ committees with a huge volume of standards proposals and contributions, but they also typically vote as a single bloc. Beijing also has a tendency to use its debt and trade leverage to influence the votes of a number of countries in favour of its proposals. This produces a strikingly high rate of success in the number of Chinese submissions at the ITU, the Times of Israel blog noted.
Another emerging facet of China’s approach to technology standards setting is the Digital Silk Road (DSR) initiative, which is one of the primary vehicles delivering Chinese technology to BRI partner states. By signing agreements with BRI partner governments, Beijing is propagating its own technology standards in project host states, creating dependencies that lock these countries into using Chinese vendors and standards.
Beijing’s moves are aimed at setting global standards for the next-generation technologies, the report said, adding, that it wants to gain control over key technologies like the Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, Big Data, 5G and artificial intelligence.
In light of above, it is apparent that Beijing’s moves are aimed at setting global standards for the next-generation technologies. The CCP wants to gain control over key technologies like Internet of Things (IoT), Cloud Computing, Big Data, 5G and artificial intelligence.
International organizations need to be wary of these maneuvers in order to prevent Beijing from dominating global technology standards and thus gaining a monopoly over the world’s future-shaping technologies, the Times of Israel report concluded.
References:
https://blogs.timesofisrael.com/double-standards-chinas-influence-in-international-standards/
https://www.ifri.org/sites/default/files/atoms/files/seaman_china_standardization_2020.pdf
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2018/11/18/with-no-5g-standard-imt-2020-china-is-working-on-6g/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/tag/chinas-imt-2020-promotion-group/
Dell’Oro: PONs boost Broadband Access; Total Telecom & Enterprise Network Equipment Markets
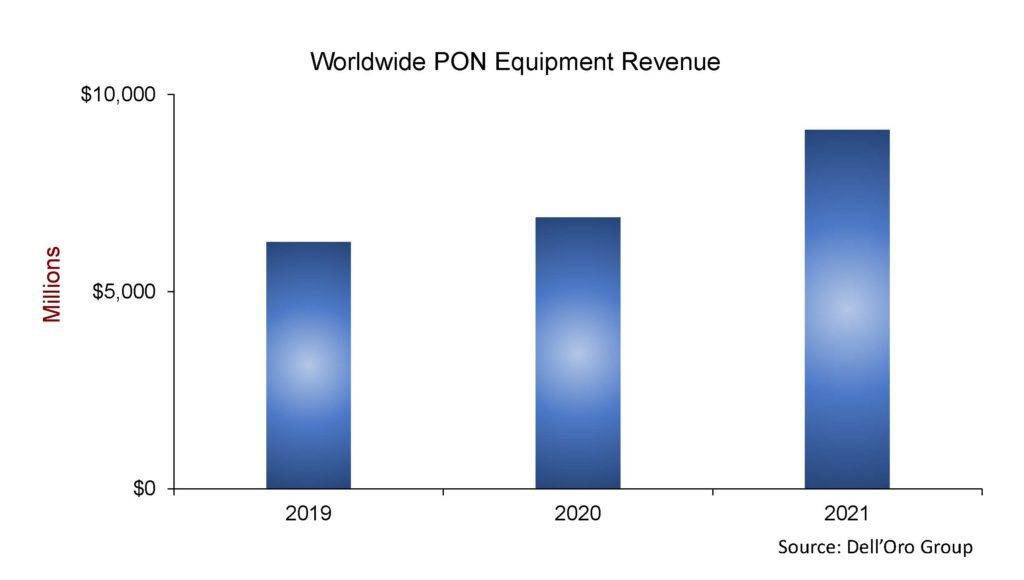
According to a newly published report by Dell’Oro Group, total global revenue for the Broadband Access equipment market increased to $16.3B in 2021, up 12 percent year-over-year (Y/Y). Growth came once again from spending on both PON infrastructure and fixed wireless CPE.
“2021 was a record year for PON (Passive Optical Network) equipment spending, with some of the highest growth coming from the North American market, where expansion projects and fiber overbuilds are picking up considerably,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President, Broadband Access and Home Networking at Dell’Oro Group. “These fiber expansion projects show no signs of slowing heading into 2022.”
Additional highlights from the 4Q 2021 Broadband Access and Home Networking quarterly report:
- Total cable access concentrator revenue increased 4 percent Y/Y to just over $1B. Steady growth in Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) deployments helps offset declines in traditional CCAP licenses.
- Total PON ONT unit shipments reached a record 140 M units for the year, bucking the supply chain constraints that have dogged the cable CPE market.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Dell’Oro just completed the 4Q2021 reports for all the Telecom Infrastructure programs covered, including Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network (MCN), Radio Access Network (RAN), and SP Router & Switch. The data contained in these reports suggests that total year-over-year (Y/Y) revenue growth slowed in the fourth quarter to 2%, however, this was not enough to derail full-year trends.
The market research firm estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market advanced 7% in 2021, recording a fourth consecutive year of growth, underpinned by surging wireless revenues and healthy demand for wireline-related equipment spurred on by double-digit growth both in RAN and Broadband Access. Total worldwide telecom equipment revenues approached $100 B, up more than 20% since 2017.
In addition to challenging comparisons, we attribute the weaker momentum in the fourth quarter to external factors including COVID-19 restrictions and supply chain disruptions.
The analysis contained in these reports suggests the collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 2021, with the top seven vendors comprising around 80% of the total market.
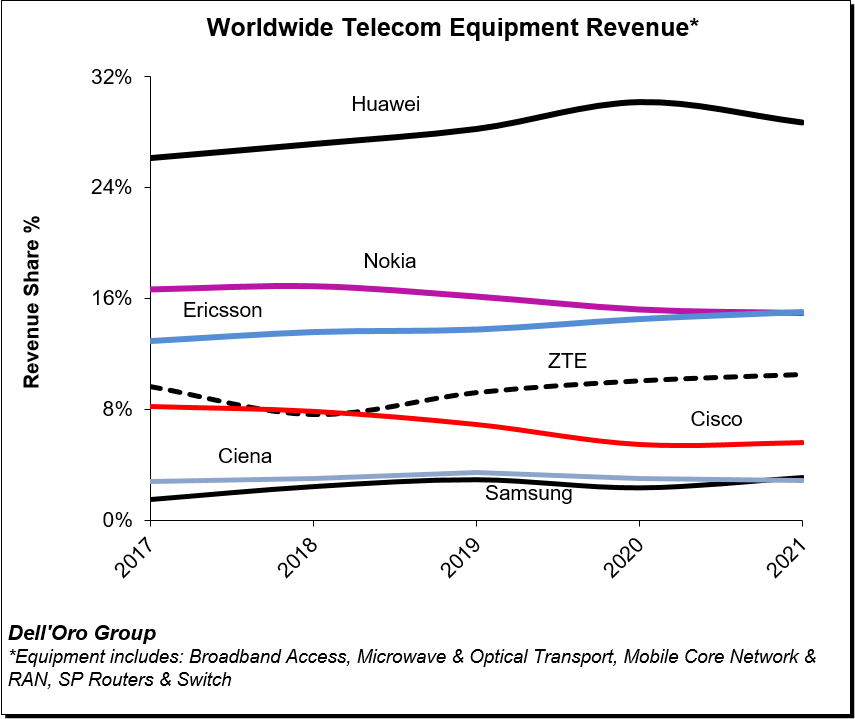
Despite U.S. sanctions, Huawei continued to lead the global market, underscoring its grip on the Chinese market, depth of its telecom portfolio, and resiliency with existing footprints. Initial readings suggest the playing field is more even outside of China, with Ericsson and Nokia essentially tied at 20% and Huawei accounting for around 18% of the market.
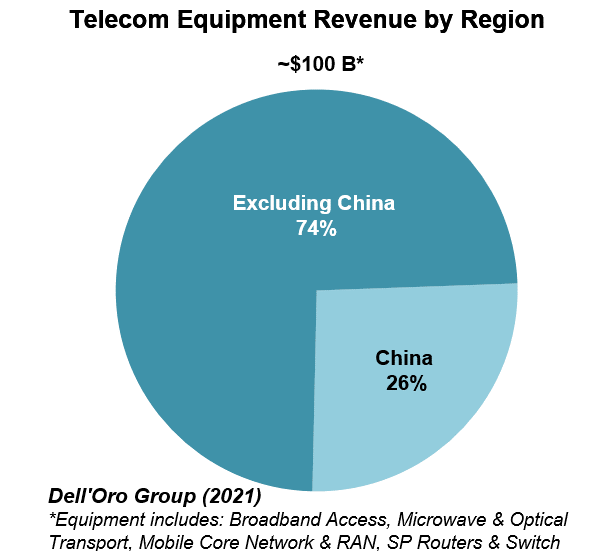
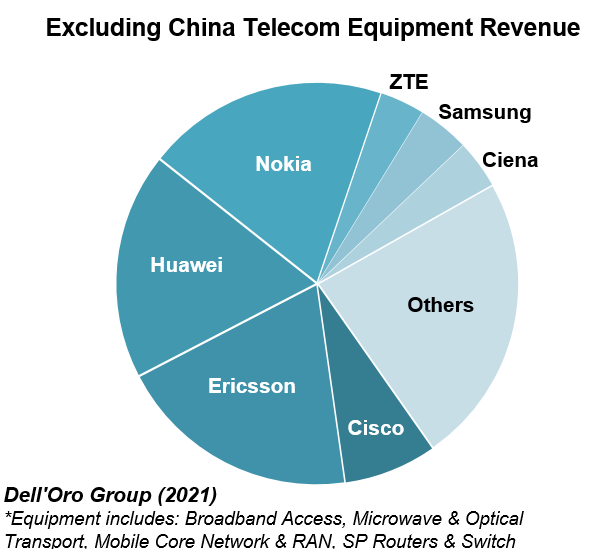
The relative growth rates have been revised upward for 2022 to reflect new supply chain and capex data. Still, global telecom equipment growth is expected to moderate from 7% in 2021 to 4% in 2022.
Risks are broadly balanced. In addition to the direct and indirect impact of the war in Ukraine and the broader implications across Europe and the world, the industry is still contending with COVID-19 restrictions and supply chain disruptions. At the same time, wireless capex is expected to surge in the U.S. this year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Top 10 Enterprise Network Equipment Vendors:
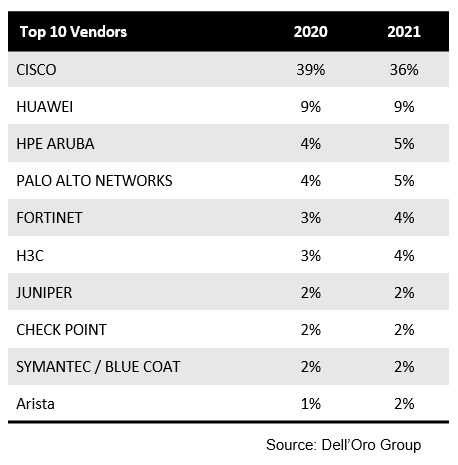
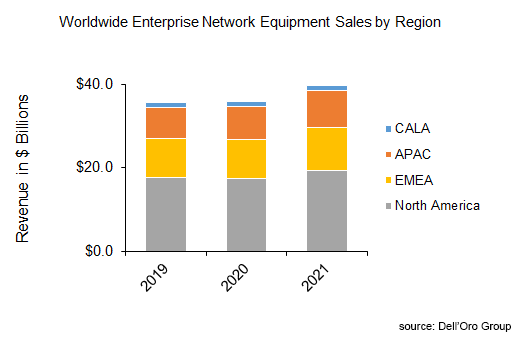
References:
Key Takeaways—2021 Total Enterprise Network Equipment Market
ZTE using TSMC’s 7-nm process to build custom chips for its 5G base stations
ZTE is on a roll! China’s #2 telecom firm said in its annual report that it gained market share in China last year for servers, core networks and storage solutions — the three areas where Huawei is a key player. Revenues grew at a double-digit percentage rate last year, rising inside and outside China and across all three business units – carrier (networks), enterprise (business) and consumer (gadgets).
With TSMC’s business booming, Nikkei Asia believes that ZTE is quietly building a technological edge in the base station market for fifth-generation (5G) cellular connectivity. These base stations are used by telecommunications carriers to meet consumer demands, and the publication believes that ZTE has designed its equipment to be based on the 7-nanometer (nm) process node.
The company [ZTE] has been utilizing some of TSMC’s most advanced chip production technology — the so-called 7-nm tech — to build processors for its 5G base stations. Sources said it also uses the Taiwanese chipmaker’s advanced chip packaging technology, which uses stacking technology to arrange chips with different functions into one package.
Nikkei Asia also said that Huawei’s inability to conduct business with TSMC due to American sanctions has left the field wide open for ZTE. The company is targeting double-digit growth for its server and base station segment, and it is also interested in TSMC’s leading-edge chip node, which is the company’s 5nm process.
However, while ZTE might not be sanctioned to procure the latest chip technologies from TSMC, the company still can not sell its 5G base stations to several Western companies. This has resulted in it focusing its efforts mostly on China, as the U.S. will rely on small cell 5G Open RAN platform developed by Qualcomm Incorporated on the 4nm node.
Source: Jordi Boixareu/Alamy Live News
“ZTE has turned quite aggressive in pursuing its chip capability in the past few years. Although the volume is still small, it is showing impressive progress,” said one unnamed source.
TSMC, as well as ZTE, seems to be on a very solid growth track. On the back of another robust set of quarterly financials Q4 FY21 and a strong balance sheet, the world’s #1 chip making firm announced a massive capex budget hike to increase manufacturing capacity in “advanced process technologies,” including 2nm, 3nm, 5nm and 7nm.
TSMC also sells products built on the 4nm, which is a design extension of the company’s 5nm process families. Different process technologies marketed under the 4nm branding are expected to commence production from the second half of this year to the first half of 2023.
References:
https://wccftech.com/tsmc-reveals-36-revenue-growth-as-chinas-zte-reportedly-using-7nm-for-5g/
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/zte-has-designs-on-chips-with-tsmc/d/d-id/775180?
China’s telecom revenue: +8.1% YoY from Jan-Nov 2021
With the caveat that you can’t trust any economic numbers reported by China’s government………….
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology says that the country’s telecommunications industry registered robust growth in revenue in the first 11 months of this year, according to “official data.”
The combined industrial revenue rose 8.1% year on year (YoY) to over 1.35 trillion yuan (about 212 billion U.S. dollars) in the January-November period.
The growth was down 0.1 percentage points from the figure for the January-October period, the data showed.
By the end of November, China’s three state owned telecom giants — China Telecom, China Mobile and China Unicom — had over 1.64 billion mobile phone users, a net increase of 47.92 million users compared with the end of last year. The number of 5G mobile subscribers reached 497 million, up 298 million from the end of last year, according to the ministry.

A poster of commercial 5G applications shown outside a branch of China Telecom in Beijing. Photo Credit: SHEN BOHAN/XINHUA
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
China’s big three telecom companies also saw a steady increase in the number of fixed broadband internet users by the end of November, with subscribers rising by 51.85 million from the end of last year to stand at 535 million.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
As of 2021, China is the only country known to work towards a single-stack IPv6 network. The country announced plans in 2017 to lead globally in IPV6 adoption by 2025, and achieve full nationwide rollout by 2030. Experts believe that such a plan to widely adopt IPv6 for the country’s internet infrastructure, can help China to increase its leadership in 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) across multiple varying industries.
References:
http://www.china.org.cn/business/2021-12/26/content_77953625.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telecommunications_industry_in_China
China plans to triple the number of 5G base stations by end of 2025
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) plans to more than triple the number of 5G base stations over the next four years, targeting a total of 3.64 million by end-2025, local newspaper China Daily reported.
China aims to have about 3.64 million 5G base stations by the end of 2025. That’s 26 5G base stations for every 10,000 people. In comparison, there were only five 5G base stations for every 10,000 people in China in 2020.
Xie Cun, director of MIIT, said the overall goal proposed in a five-year plan for the information and communication industry is to basically build a high-speed, ubiquitous, smart, green, safe and reliable new digital infrastructure by 2025.
The plan also proposed that the penetration rate of 5G users in China will increase from 15 percent in 2020 to 56 percent in 2021, and by then, 80 percent of China’s administrative villages will have 5G signal accessibility.
Xie said that China so far has already built more than 1.15 million 5G base stations, accounting for more than 70 percent of the global total, and 5G network coverage has been achieved in urban areas of all prefecture-level cities, 97 percent of counties and 40 percent of rural towns across the country.
The 5G mobile subscriber accounts in China, numbering some 450 million, make up over 80 percent of the global total, Xie added.
The five-year plan also forecast that by the end of 2025, the information and communication industry will maintain an annual growth rate of about 10 percent to reach a total revenue of 4.3 trillion yuan ($674.2 billion) in 2025. The plan also forecast that the cumulative investment in telecom infrastructure will increase from 2.5 trillion yuan in 2020 to 3.7 trillion yuan in 2025.
Widening the industrial use of 5G will also be a key focus for China. Xie said 5G has already been used in 22 industries. The application of 5G in industrial manufacturing, mining and ports is relatively mature, where 5G has been expanded from production assistance to core businesses such as equipment control and quality control. Meanwhile, a number of 5G-powered applications have also emerged in industries such as medical care, education and entertainment.
“In the next step, we will work with other parties to focus on promoting 5G applications in 15 industries that target information consumption, real economy and people’s livelihood services,” Xie said.
Wang Zhiqin, deputy head of the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, a government think tank, said China is likely to achieve several breakthroughs in 5G technological evolution, network construction and applications by 2025.
“By the end of the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2021-25), China will have built the world’s largest and most extensive stand-alone 5G network and basically achieve full network coverage in urban and rural areas,” Wang said.
Ding Yun, president of Huawei Technologies carrier business group, said:
“5G is no longer for early adopters. It is improving our daily lives. This year is the first year with large-scale 5G industry applications. Operators will need new capabilities in network planning, deployment, maintenance, optimization and operations, in order to achieve zero to one, and replicate success from one to many.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..

Technicians check a 5G base station in Tongling, Anhui province, China
[Photo by Guo Shining/For China Daily]
Chinese operators recorded a net gain of 43.88 million 5G subscribers in September, according to the carriers’ latest available figures.
China Mobile, the world’s largest operator in terms of subscribers, added a total of 27.08 million 5G subscribers in September. The state owned #1 carrier said it ended last month with 331.22 million 5G subscribers, compared to 113.59 million 5G customers in September 2020. China Mobile has added a total of 166.22 million subscribers in the 5G segment since the beginning of the year.
Rival operator China Unicom said it added a total of 7.88 million 5G subscribers during last month. During the first nine months of the year, the carrier added a total of 66.11 million 5G subscribers. The telco ended September with 136.94 million 5G subscribers. China Unicom started to provide 5G statistics earlier this year.
China Telecom added 8.92 million 5G subscribers in September to take its total 5G subscribers base to 155.54 million. During the January-September period, the telco added a total of 69.04 million 5G subscribers.