Orange
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Optical network equipment maker Infinera announced today that Orange deployed Infinera’s GX Series-based ICE6 “coherent optical engine” on its new AMITIE subsea cable, which is ready for service today from an end-to-end point of view and offers network operators unique and robust transatlantic connectivity with ultra-low latency.

Orange owns two pairs of fiber optic cables as part of the AMITIE subsea cable system, offering capacity up to 23 Tbp/s each.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Orange selected Infinera’s solution based on its industry-leading optical performance to offer up to 400 GbE services to its customers from the U.S. to France, and across its long-haul terrestrial backhaul network from Boston to New York and Le Porge to Bordeaux in France.
The sixth-generation Infinite Capacity Engine (ICE6), from Infinera’s Advanced Coherent Optical Engines and Subsystems, is a 1.6 Tb/s optical engine that delivers two independently programmable wavelengths at up to 800 Gb/s each. Utilizing a 7-nm CMOS process node DSP and advanced PIC technology, ICE6 leverages ultra-high baud rates, high modem SNR, and innovative features to break performance and spectral efficiency barriers, including 800G single-wavelength performance over 1000+ km in a commercial network.

Infinera’s ICE6- 800G Generation Optical Engine Photo credit: Infinera
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Orange powers fully resilient global connectivity capability along the world’s busiest route, using two state-of-the-art subsea mega cables, Dunant and AMITIE, to connect France and the U.S. Deploying Infinera’s innovative ICE6 technology on the GX Series Compact Modular Platform enables Orange to keep pace with future generations of optical transmission technologies while maintaining a high level of performance for the next 20 years. This deployment also significantly reduces Orange’s energy cost per megabit and minimizes its carbon footprint.
“We are pleased to integrate Infinera’s industry-leading technology for the first time on one of our key transatlantic routes and terrestrial backhaul. With this future-proof technology, Orange is well-positioned to continue to be a major player in the global wholesale market, developing our infrastructure to connect continents together and delivering a unique, high-performance, and robust solution to our customers,” said Aurélien Vigano, VP International Transmission Network at Orange.
“Infinera is delighted to partner with Orange to deliver our innovative ICE6 solution across Orange’s critical subsea and terrestrial backhaul routes, offering network operators, wholesale carriers, and enterprise customers resilient and reliable global connectivity capability,” said Nick Walden, Senior Vice President, Worldwide Sales, Infinera.
References:
https://www.infinera.com/innovation/ice6-800g-wavelengths/
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Orange Telco Cloud to use Equinix Bare Metal to deliver virtual services with <10 ms latency
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
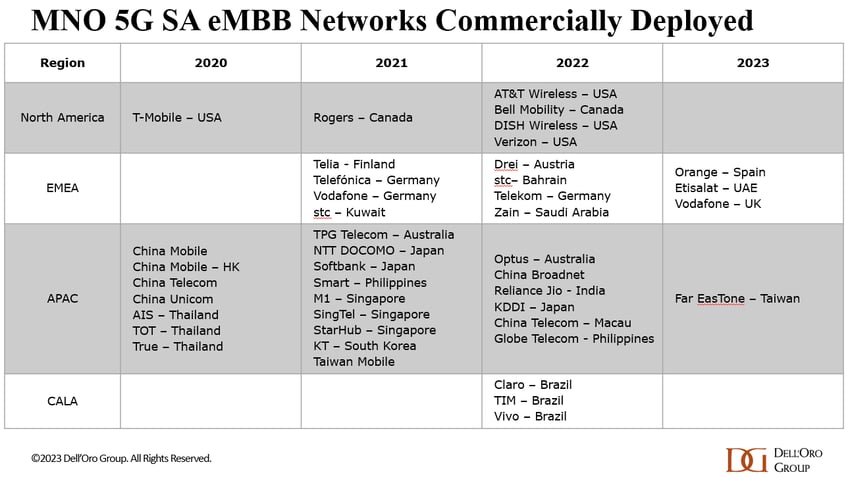
According to a May 2023 report from the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), just 35 network operators in 24 countries and territories “are now understood to have launched or deployed public 5G SA networks.” That’s out of approximately 240 service providers which have now launched commercial 5G services, as per the recent Ericsson Mobility Report.
Dell’Oro’s Dave Bolan said, “Currently we count 43 live 5G SA networks for eMMB [enhanced mobile broadband]. For 2023, four [mobile network operators] have launched 5G SA networks,” he added. It should be noted that Dell’Oro doesn’t factor in fixed wireless access (FWA) or private 5G networks in its SA totals.
In Europe, Vodafone UK and Telefónica Spain join what remains a small set of network operators that have launched 5G SA, including Orange Spain and Vodafone Germany. Spain should provide an interesting study of what happens when two rival operators launch 5G SA service.
There are some glimmers of hope that 5G SA launches will accelerate soon. GSA (aka GSMA) has identified at least 1,063 announced devices with declared support for standalone 5G in sub-6GHz bands, 864 of which are commercially available. Furthermore, it said 116 operators in 53 countries and territories are now investing in 5G SA, including those that have actually deployed a public network. “This equates to 22.1% of the 524 operators known to be investing in 5G licenses, trials or deployments of any type,” the GSA said.
Separately, analysts say that 5G SA branding by network operators is quite confusing (we agree). Vodafone UK’s decision to use 5G Ultra for its 5G SA branding vs Telefonica using 5G+ are examples of that.
Gabriel Brown of Heavy Reading said, “customers don’t really know what it means, other than it denotes some form of technical advance.” He points out that 5G SA “requires a lot of investment and deep engineering expertise; this makes it a useful proxy for network quality. Operators need to take all the technical marketing opportunities they can get.”
“What happens when BT launches? Are they going to call it 5G+ or 5G Super Ultra or something like that? That’s going to make it even more confusing,” said Kester Mann, an analyst with CCS Insight. At the same time, he agrees that 5G standalone is a significant network upgrade and it makes sense that operators would want to gain a marketing edge over rivals that have yet to launch the service.
Notably, neither Vodafone nor Telefónica is charging extra for the more advanced 5G service, and both have focused on the improved speeds and reliability it will bring. They also emphasize eco-friendly aspects, such as lower energy consumption. However, Mann questioned Vodafone’s claim that customers with an eligible 5G Ultra device can expect up to 25% longer battery life. “Twenty-five percent faster than what?” he asked. “It’s a bit unclear.” However, such a claim would certainly be welcome news to consumers. “In a lot of our consumer research, battery life comes out as one of the common bugbears among people using mobile phones,” said Mann.
In the U.S., T-Mobile is the only network operator that’s deployed a 5G SA network. AT&T and Verizon have been talking about it for years, but the time frame for deployment has been pushed back several times.
Deloitte Global said it expects the number of mobile network operators investing in 5G SA networks via trials, planned deployments or rollouts to grow from more than 100 operators in 2022 to at least 200 by the end of this year.
One reason why there are relatively few 5G SA networks deployed is there are no implementation standards. 3GPP 5G Architecture specs, rubber stamped by ETSI, provide several options to realize a 5G cloud-native core network which leads to different implementations. 3GPP decided NOT to liaise their 5G non-radio aspects specs (including 5G Architecture and 5G Security) to ITU-T.
Here are the key 3GPP 5G system specs:
- TS 22.261, “Service requirements for the 5G system”
- TS 23.501, “System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 23.502 “Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)”
- TS 32.240 “Charging management; Charging architecture and principles”
- TS 24.501 “Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3”
The latest 3GPP 5G Architecture spec is System architecture for the 5G System (5GS) (3GPP TS 23.501 version 17.9.0 Release 17), published by ETSI on July 5, 2023.
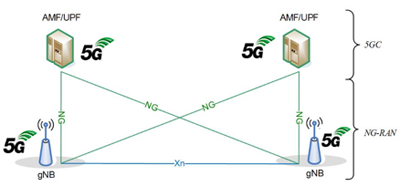
Source: 3GPP
Hence, the ITU JCA on IMT2020 and Beyond is dependent on other organizations for inputs to their roadmap. “The scope of JCA-IMT2020 is coordination of the ITU-T IMT-2020 standardization work with focus on non-radio aspects and beyond IMT2020 within ITU-T and coordination of the communication with standards development organizations, consortia and forums also working on IMT2020 and beyong IMT-2020 related standards.”
References:
https://www.silverliningsinfo.com/5g/5g-sa-springs-action
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
Orange-Spain deploys 5G SA network (“5G+”) in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia and Seville
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
Tech Mahindra and Microsoft partner to bring cloud-native 5G SA core network to global telcos
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
https://urgentcomm.com/2023/01/19/standalone-5g-progress-remains-a-disappointment/
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/jca/imt2020/Pages/ToR.aspx
Orange Telco Cloud to use Equinix Bare Metal to deliver virtual services with <10 ms latency
Orange and Equinix announced today a collaboration to expand the Orange Telco Cloud footprint, using Equinix’s Bare Metal as a Service capability—Equinix Metal®—to speed the deployment of Orange’s New Generation International Network.
This new business model enables Orange to provide business and wholesale customers with powerful on-demand Telco Cloud Points of Presence (PoPs), delivering essential services such as SD-WAN, CDN, 5G roaming and voice services, with an expected latency below ~10 milliseconds.
Three locations will be deployed by the end of this year: Amsterdam, Madrid and Seattle.
The advancement of network-based services, largely driven by evolving customer requirements around speed of deployment and flexibility, is compelling network providers to deploy a new class of connectivity and infrastructure platform. Indeed, the Equinix 2022 Global Tech Trends Survey found 72% of companies surveyed around the world are planning to expand in the next 12 months, despite economic concerns and supply chain challenges—and they’re relying on digital strategies to achieve that.
By integrating with Equinix’s automated dedicated Bare Metal (see image below) as a Service located in proximity to its existing networks at Equinix, Orange can quickly meet customer demand for growth, deploying in weeks from inception (instead of months).

Equinix Metal infrastructure (Image source: Equinix)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Leveraging Equinix Metal, Orange accelerates its next-generation services without the up-front CAPEX or complexities of global supply chains, while retaining full choice and control over IT infrastructure and digital transformation projects. This approach to cleaner energy consumption was also determinant for Orange to choose to partner with Equinix, in line with its 2040 carbon neutral objective, on top of its strategy to avoid energy consumption where there is no customer demand.
“We are delighted to partner with Equinix to deploy Orange Telco Cloud PoPs technology on top of Equinix Metal,” explained Jean-Luc Vuillemin, Executive Vice President, International Networks at Orange. “By embracing an ‘as a service’ infrastructure model and focusing investment in our SDN and VNF capabilities, Orange can provide a fully flexible and elastic solution to customers, speed up the deployment of our planned 100 Telco Cloud PoPs, and quickly adapt capacity to meet demand. This confirms Orange’s position as a trusted infrastructure partner, optimizing application performance with secured and consistent connectivity, regardless of end user location, and supporting cloud management and transformation.”
Through its Telco Cloud Platform, Orange uniquely provides customers with end-to-end optimized levels of performance, security and flexibility. Powered by industry-leading innovation in virtualized network functions and software-defined networks (SDN), Orange already has 40 SDN PoPs around the world and is targeted to reach 100+ “Telco Cloud PoPs” by 2024 as part of its eNGINe (New Generation International Network) transformation program. Each Telco Cloud PoP can host virtualized network service functions such as voice, 5G, CDN, SD-WAN or Security Services, as well as connect customers to key content and cloud service providers. With its Telco Cloud PoP architecture, Orange’s customers can access and manage applications in the cloud with reliable, fast connectivity, and choose from an expanded portfolio with on-demand and adapted services.
“We have a rich 20-year history of collaboration with Orange and are pleased to see them accelerate innovation for their customers by becoming the first provider to combine their extensive global network footprint at Equinix with the new possibilities provided by our investments in automated digital infrastructure capabilities. We’re excited to see them expand this offering into additional markets in 2023,” said Zachary Smith, Global Head of Edge Infrastructure Services at Equinix.
Iiro Stubin, principal product manager for Equinix Metal, told Light Reading that Equinix Metal provides pre-installed storage at Equinix locations that is ready for customers to access when additional network capacity is required. Equinix Metal also integrates with a library of application programming interfaces (APIs) for “an element of automation,” said Stubin. “That’s kind of been in the heart of our service portfolio to build more data center locations into different regions, where our telco customers can then expand and we’ve been working with Orange very closely to let them expand their PoPs globally with us,” Stubin added.
Orange EVP Jean-Louis Le Roux told Light Reading that about 20 of the operator’s existing 40 Telco Cloud points of presence (PoPs) are deployed in collaboration with Equinix but utilize Orange’s hardware. Le Roux said the three new PoPs will rely on Equinix hardware instead of deploying Orange’s own compute and storage hardware. “We keep control because on top of this hardware, we deploy our own SDN [software defined network] stack. So we keep control over our digital transformation. This elasticity is really useful for us; we can easily add or remove a compute server or storage server, really following the customer activity.”
Le Roux added that a “pay-as-you-grow” model provides Orange with the ability to deploy storage for its customers without upfront capital expenses or the worry of navigating a troublesome supply chain.
Orange said the partnership with Equinix will provide the network operator with the ability to “meet customer demand for growth” in weeks versus months.
Courtney Munroe, Vice President for Telecommunications Research at IDC commented:
“This partnership between Orange and Equinix is a smart move enabling Orange to enhance its existing platform and its ability to facilitate reliable, agile digital capabilities for its customers—all while being able to more quickly meet customer demand by using Equinix Metal. IDC research shows that enterprises look to Telcos and digital infrastructure providers as key partners for hybrid IT infrastructure and cloud networking requirements. Furthermore, the enhanced Telco Cloud Platform will improve Orange’s operational efficiency, and flexibility, and most importantly will allow it to offer enhanced low latency performance and on-demand requirements for enterprises around the world.”
About Equinix:
Since its founding in 1998, Equinix has helped the world’s networks connect and deploy services for their customers. Today, digital leaders like Orange are looking to move even faster. This has fueled Equinix’s strategy to help unlock value from their existing network presence in its data centers, with an as a Service model that delivers choice and control of dedicated infrastructure, powered by clean and renewable energy.
Equinix Metal® provides developer-friendly physical compute, storage and networking infrastructure services to help digital leaders move faster and more easily access Equinix’s unique ecosystem of thousands of enterprises, clouds, services and networks.
About Orange:
Orange is one of the world’s leading telecommunications operators with sales of 42.5 billion Euros in 2021 and 137,000 employees worldwide at 30 June 2022, including 76,000 employees in France. The Group has a total customer base of 282 million customers worldwide at 30 June 2022, including 236 million mobile customers and 24 million fixed broadband customers. The Group is present in 26 countries. Orange is also a leading provider of global IT and telecommunication services to multinational companies under the brand Orange Business Services. In December 2019, the Group presented its “Engage 2025” strategic plan, which, guided by social and environmental accountability, aims to reinvent its operator model. While accelerating in growth areas and placing data and AI at the heart of its innovation model, the Group will be an attractive and responsible employer, adapted to emerging professions.
References:
Samsung partners with Orange to deliver 5G vRAN and O-RAN compliant base stations
Samsung Electronics has announced that it is collaborating with the France headquartered telecom operator Orange, to disaggregate the software and hardware elements of traditional RAN. The South Korea based tech giant will provide its virtualized RAN (vRAN), “which has been proven in the field through commercial deployments with global Tier one operators including the U.S.”
As one of the world’s leading telecommunications operators, Orange provides mobile services to 222 million users in 26 countries along with Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Through this partnership, Samsung and Orange aim to deploy O-RAN Alliance-compliant base stations beginning with rural and indoor configurations and then, expanding to new deployments in the future.
“Open RAN is a major evolution of radio access that requires deeper cooperation within the industry. With our European peers, we want to accelerate the development of Open RAN solutions that meet our needs. After the publication of common specifications, Orange’s Open RAN Integration Center will support the development and tuning of solutions from a broad variety of actors,” said Arnaud Vamparys, Senior Vice President of Radio Access Networks and Microwaves at Orange.
Samsung’s vRAN solutions can help ensure more network flexibility, greater scalability and resource efficiency for network operation by replacing dedicated baseband hardware with software elements. Additionally, Samsung’s vRAN supports both low and mid-band spectrums, as well as indoor and outdoor solutions. Samsung is the only major network vendor that has conducted vRAN commercial deployments with Tier one operators in North America, Europe and Asia.
“We are pleased to participate in Orange’s innovative laboratory,” said Woojune Kim, Executive Vice President, Head of Global Sales & Marketing, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Through this collaboration, we look forward to taking networks to new heights in the European market, enabling operators to offer more immersive mobile services to their users.”
By opening its Open RAN Integration Center in Châtillon, near Paris, Orange will enable the testing and deployment of networks capable of operating with innovative technologies, which will serve as the backbone of the operator’s future networks. At the center, Samsung and Orange will conduct trials to verify capabilities and performance of Samsung’s vRAN, radio and Massive MIMO radio.
With a vRAN approach, carriers are able to rapidly shift capacity to address customer needs. For business customers, vRAN can drive more efficient access to private 5G networks through easy deployment of baseband software in Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) facilities.
“We are committed to providing reliable, secure, and flexible network solutions that deliver the power of 5G around the world,” said Magnus Ojert, Vice President, Networks Division, Samsung Electronics America. “We believe vRAN’s next phase of innovation will accelerate what’s possible for society and look forward to collaborating with an industry-leader like Verizon to make 5G a reality for millions in 2021.”

Samsung says they have “pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end infrastructure solutions including chipsets, radios and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from fully virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing network solutions to mobile operators that deliver connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.”
References:
https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-and-orange-collaborate-to-advance-5g-networks-to-a-new-level
https://www.samsung.com/global/business/networks/products/radio-access/virtualized-ran/
Samsung’s 5G vRAN adoption could be a key turning point for the industry
2Africa subsea cable system adds 4 new branches
2Africa, which will be the largest subsea cable project in the world, will deliver faster, more reliable internet service to each country where it lands. Communities that rely on the internet for services from education to healthcare, and business will experience the economic and social benefits that come from this increased connectivity.

Alcatel Submarine Networks (ASN) has been selected to deploy the new branches, which will increase the number of 2Africa landings to 35 in 26 countries, further improving connectivity into and around Africa. As with other 2Africa cable landings, capacity will be available to service providers at carrier-neutral data centers or open-access cable landing stations on a fair and equitable basis, encouraging and supporting the development of a healthy internet ecosystem.
Marine surveys completed for most of the cable and cable manufacturing is underway. Since launching the 2Africa cable in May 2020, the 2Africa consortium has made considerable progress in planning and preparing for the deployment of the cable, which is expected to ‘go live’ late 2023. Most of the subsea route survey activity is now complete. ASN has started manufacturing the cable and building repeater units in its factories in Calais and Greenwich to deploy the first segments in 2022.
Egypt terrestrial crossing already completed
One of 2Africa’s key segments, the Egypt terrestrial crossing that interconnects landing sites on the Red and the Mediterranean Seas via two completely diverse terrestrial routes, has been completed ahead of schedule. A third diverse marine path will complement this segment via the Red Sea.
About MTN GlobalConnect
GlobalConnect is a Pan-African digital wholesale and infrastructure services company, and an operating company in the MTN Group. GlobalConnect manages MTN’s international and national major wholesale activities, in addition to offering reliable wholesale and infrastructure solutions for fixed connectivity and wholesale mobility solutions that include international mobile services, Voice, SMS, signalling, roaming and interconnect. The MTN Group launched in 1994 is a leading emerging market operator with a clear vision to lead the delivery of a bold new digital world and is inspired by the belief that everyone deserves the benefits of a modern connected life. Embracing the Ambition 2025 strategy, MTN is anchored on building the largest and most valuable platform business, with a clear focus on Africa. The MTN Group is listed on the JSE Securities Exchange in South Africa under the share code “MTN”.
For more information, please visit www.globalconnect.solutions – https://www.mtn.com
About stc
With its headquarter in Riyadh, stc group is the largest in the Middle East and North Africa based on market cap. stc’s revenue for 2020 amounted to 58,953million SAR (15,721 million US dollars) and the net profit amounted to 10,995 million SAR (2,932 million US dollars). stc was established in 1998 and currently has customers around the globe. It is ranking among the world’s top 50 digital companies and the first in the Middle East and North Africa according to Forbes. It focuses on providing services to enterprise and consumer customers through a fiber-optic network that spans 217,000 kilometers. stc group was among the first in MENA region to launch 5G networks and was considered one of the fastest globally in deploying 5G network as stc already deployed around 4,000 5G towers as end of 2020. stc group has 14 subsidiaries in the Kingdom, gulf and around the world, and its own 100% of stc Bahrain, 51.8% stake in stc Kuwait and 25% stake in Binariang GSM Holding in Malaysia which owns 62% of Maxis in Malaysia.
In Saudi Arabia (the group’s main operation site) stc operates the largest modern mobile network in the Middle East as it covers more than 99% of the country’s populated areas in addition to providing 4G mobile broadband to about 90% of the population across the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In addition to the above-mentioned, stc is a strong regional player in IoT, managed services, system integration, cloud computing, information security, big data Analytics fintech and artificial intelligence.
For more information, please visit https://www.stc.com.sa; or to follow us on Twitter: @stc , @stc_ksa
About Telecom Egypt
Telecom Egypt is the first total telecom operator in Egypt providing all telecom services to its customers including fixed and mobile voice and data services. Telecom Egypt has a long history serving Egyptian customers for over 160 years maintaining a leadership position in the Egyptian telecom market by offering its enterprise and consumer customers the most advanced technology, reliable infrastructure solutions and the widest network of submarine cables. Aside from its mobile operation “WE”, the company owns a 45% stake in Vodafone Egypt. Telecom Egypt’s shares and GDRs (Ticker: ETEL.CA; TEEG.LN) are traded on The Egyptian Exchange and the London Stock Exchange. Please refer to Telecom Egypt’s full financial disclosure on ir.te.eg
For more information, email: [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.orange.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2021/new-branches-2africa-subsea-cable-system
Telefónica switches on 5G; 75% of Spain to be covered this year
Telefónica has launched commercial 5G services throughout Spain, pledging to reach 75 percent of the Spanish population by the end of the year. In a statement, the company’s executive chairman Jose Maria Alvarez-Pallete described the deployment as the most ambitious in the European Union. “The launch of 5G is a leap forward towards the hyperconnectivity that will change the future of Spain,” he said, noting that “it’s 5G for everyone, without any exceptions, in all the autonomous communities.” [That assumes low enough 5G tariffs, such that poorer working class Spaniards can afford the service]. Telefonica is accelerating “the digitalisation of small and medium companies, public administrations and citizens, ”Alvarez-Pallete added.
“Our network has always been a differential asset. People’s lives pass through it and it has demonstrated unparalleled strength when it’s been most needed”, Álvarez-Pallete continued. He pointed out that Spain already leads Europe’s digital infrastructures with the largest fiber optic network.
Editor’s Note: Telefonica’s 5G announcement follows Vodafone – Spain‘s commercial 5G network deployment in 21 cities in Spain. Initial 5G speeds of up to 1 Gbps for Vodafone subscribers in Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Malaga, Zaragoza, Bilbao, Vitoria, San Sebastian, La Coruna, Vigo, Gijon, Pamplona, Logrono and Santander. Speeds will rise to 2 Gbps by the end of the year, some 10 times the current 4G maximum, with latency reduced to less than 5 milliseconds in ideal conditions.
Orange and Masmovil set to launch their 5G networks in Spain this month. All four of Spain’s MNOs (Mobile Network Operators) are expected to bid for frequencies in the 700 MHz band when the government holds its delayed spectrum auction in the first quarter of 2021.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

Telefonica said 5G technology will give residential customers access to far faster speeds and lower latency, allowing sports fans to enjoy live 360-degree broadcasts and mobile gamers to access a “fibre-like” experience. Businesses will have access to services such as Multi-Access Edge Computing, 5G private networks, mass IoT and critical communications, as well as network virtualisation to facilitate more effective use of the network’s resources.
The Spain based network operator (also active in Latin America) clarified that it will initially launch NSA (non-standalone) 5G combined with DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing) ahead of the “immediate deployment” of 5G SA (standalone) when the technology becomes fully available after standardisation. The company said it will make use of its current sites and infrastructure for the initial rollout, to be complemented by new base stations and small cells according to capacity and coverage needs.
It’s also having to rely on the 3.5 GHz band, together with mid-band (1800-2100 MHz) frequencies, for the initial coverage thanks to equipment that can operate with 4G and 5G at the same time. Telefonica also announced that it intends to shut down its 3G network in 2025, when 100 percent of its copper network will have been replaced by fiber optics.
“With 5G everything happens in a millisecond. A millisecond is what makes remote surgery, autonomous cars, the smart management of energy resources and cities and highly advanced entertainment possible. A millisecond is much more than a new response time. It’s Telefónica’s response to the new times. It’s Telefónica’s commitment to the country’s future”, concluded Álvarez-Pallete.
For residential customers, in addition to the benefits brought by 5G in terms of greater speed and lower latency, which will allow them, for example, to download a film in seconds, 5G will provide the possibility, among other features, of enjoying live sports broadcasts during which users will obtain a 360º experience and be able to view any angle of the match as if they were on the pitch itself. Gaming enthusiasts will obtain a mobility experience similar to that provided by fibre in the home, in other words, without any interruptions or latency. 5G will thus enable them to play on their mobile phones as if they were on their home computer screens or their video consoles.
5G business customers will have access to services like Multi-Access Edge Computing, which offers ultra-low latency services and greater computing capacity “on the network edge”, in addition to services such as 5G private networks, mass IoT and critical communications, as well as network virtualisation to facilitate more effective use of the network’s resources in keeping with the customers’ needs.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

Telefónica operates with the latest radio (base station) generations that allow dual 4G and 5G usage, with the aim of bringing 5G to the largest number of people from the outset. This first phase will witness the launch of the 5G network, thanks to a technology that combines the deployment of NSA (non-standalone) 5G and DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing) and the subsequent immediate deployment of the SA (standalone) 5G network when the technology becomes fully available after standardisation. This initial deployment will also make use of the current sites and infrastructure and, in the mid and long terms, it will be complemented by new base stations and small cells as the capacity and coverage require.
The 3.5 GHz band frequency (the only 5G band frequency already licensed to operators) and the mid-band (1800-2100 MHz) frequencies are being used for this purpose. This is the current location of 4G, capitalising on the possibility of using NR (New Radio) equipment that can operate with both technologies (4G and 5G) at the same time.
The new deployments will take place in tandem with a gradual shut-down of the old second and third-generation networks. 100% of the copper network will have been replaced by fibre by 2025, when the 3G network will also be shut down. This will permit more effective management of investments, as it won’t be necessary to increase them to address the new deployments.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………