Uncategorized
Highlights of ITU Global Connectivity Report 2025 and the Baku Action Plan
The ITU Global Connectivity Report 2025, released at the conclusion of the World Telecommunication Development Conference (WTDC-25) in Baku, Azerbaijan, delivers a comprehensive assessment of how global connectivity has evolved from a scarce asset in 1994 into a foundational layer of the digital economy and everyday life, with close to 6 billion users projected to be online by 2025. Its analytical framework is anchored in the policy objective of achieving universal and meaningful connectivity (UMC), structured across six interdependent dimensions: Quality, Availability, Affordability, Devices, Skills, and Security.
The report underscores the socio‑economic gains associated with large‑scale digital transformation, including enhanced productivity, innovation, and service delivery across sectors. At the same time, it emphasizes that progress is constrained by persistent digital divides along income, gender, age, and geographic lines, as well as by escalating exposure to online harms, misinformation, and non‑trivial environmental externalities from ICT infrastructure and usage.
It suggests the era of easy, organic network expansion is over. While 74% of the world is now online, the curve is flattening, and the remaining deficits are structural rather than merely about access.
With an estimated 2.2 billion people still offline, ITU Member States (194) agreed this week on the Baku Action Plan—a four-year roadmap to 2029 designed to close these persistent divides.
The report provides detailed analysis of structural barriers to universal and meaningful connectivity (UMC), notably high connectivity and device costs, gaps in digital skills, and constrained access to appropriate end‑user devices. It translates this analysis into evidence‑based policy guidance focused on regulatory coherence, targeted affordability interventions, and demand‑side enablers to ensure that connectivity translates into effective and inclusive digital usage.
From a network engineering and infrastructure perspective, the report highlights the critical role of resilient, high‑capacity backbones, including submarine cable systems and satellite constellations, as strategic layers of the global connectivity fabric. It stresses the need for coordinated investment, robust redundancy and security models, and integrated planning across terrestrial, subsea, and space‑based networks to support UMC objectives.
The report identifies high service and device costs, insufficient digital skills, and limited device availability as key barriers, and provides evidence‑based policy guidance on regulatory coherence, affordability, and demand‑side enablers. It emphasizes the importance of resilient infrastructure such as submarine cables and satellites, along with stronger national data ecosystems, to support inclusive connectivity strategies and informed digital policy‑making.
Finally, the report calls for strengthening national data ecosystems—covering data collection, governance, sharing, and analytics—as a prerequisite for effective digital inclusion strategies and evidence‑driven policy‑making. It positions mature data capabilities and coherent digital governance frameworks as key enablers for monitoring progress across the six UMC dimensions and for calibrating telecom and ICT policy in line with evolving market and technology dynamics.
References:
https://www.itu.int/itu-d/reports/statistics/global-connectivity-report-2025/
ITU’s Facts and Figures 2025 report: steady progress in Internet connectivity, but gaps in quality and affordability
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
ITU-R report: Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages
https://www.itu.int/itu-d/reports/statistics/global-connectivity-report-2022/
VC4 Advances OSS Transformation with an Efficient and Reliable AI enabled Network Inventory System
By Juhi Rani assisted by IEEE Techblog editors Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal
Introduction:
This year, 2025, VC4 [a Netherlands Head Office (H/O) based Operational Support System (OSS) software provider] has brought sharp industry focus to a challenge that many experience in telecom. Many operators/carriers still struggle with broken, unreliable, and disconnected inventory systems. While many companies are demoing AI, intent-based orchestration, and autonomous networks, VC4’s newly branded offering, Service2Create (or S2C as it’s known to some), is refreshingly grounded. Also as we have learnt very quickly, bad data into AI is a “no-no”. None of the orchestration and autonomous networks, will work accurately if your OSS is built on flawed data. The age-old saying “Garbage in, Garbage out” comes to mind.
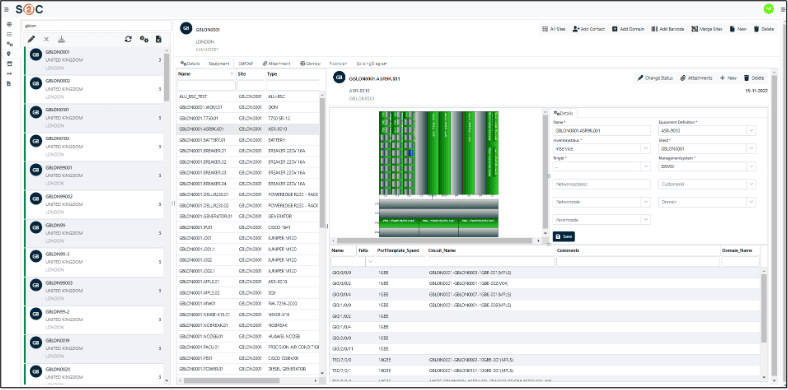
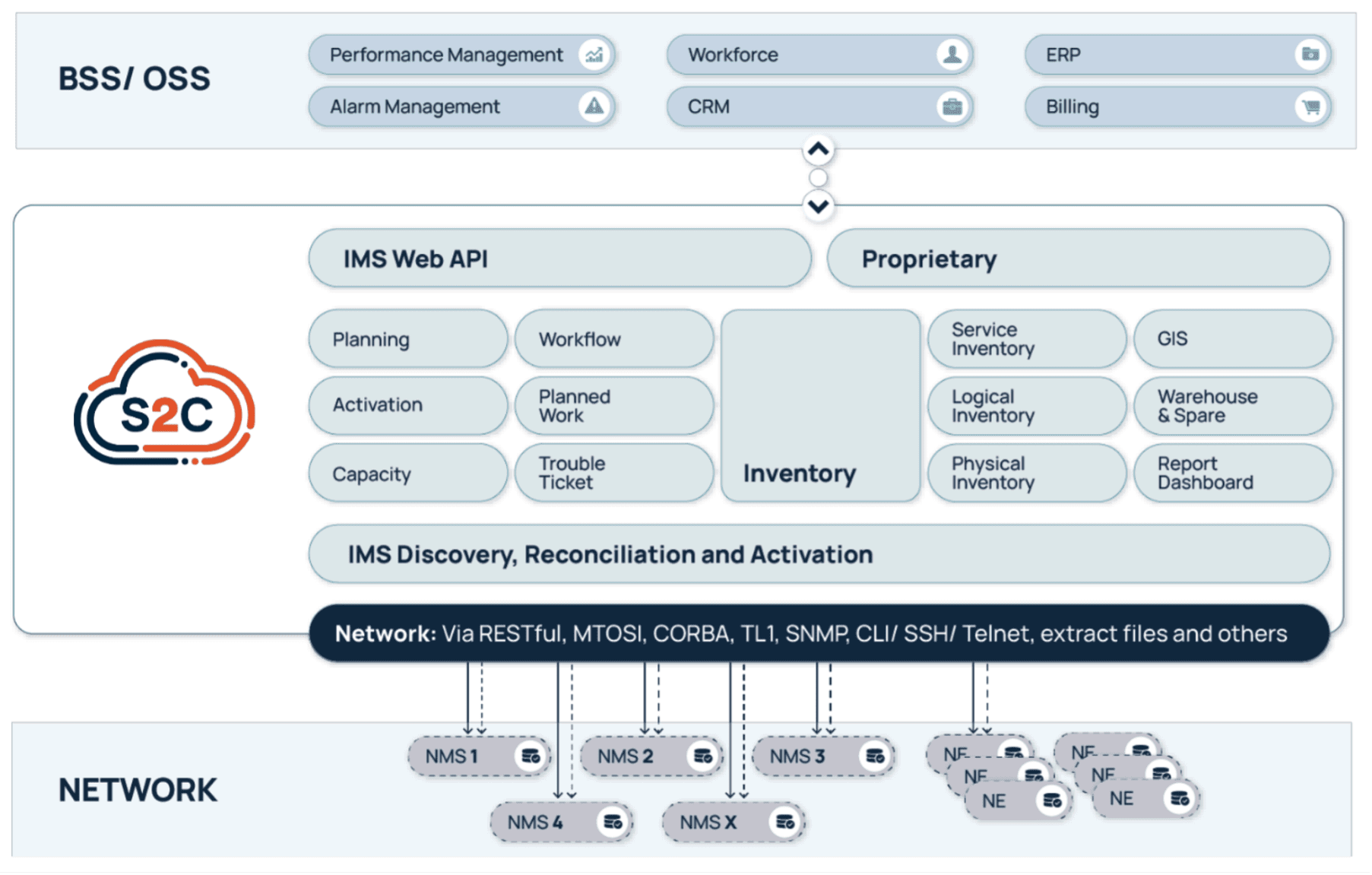
VC4’s platform, Service2Create (S2C), is a next-generation OSS inventory system that supports the evolving needs of telecom operators looking to embrace AI, automate workflows, and run leaner, smarter operations. Service2Create is built from over two decades of experience of inventory management solutions – IMS. By focusing on inventory accuracy and network transparency, S2C gives operators a foundation they can trust.
Inventory: The Most Underestimated Barrier to Transformation
In a post from TM Forum, we observed that operators across the world are making huge investments in digital transformation but many are slowed by a problem closer to the ground: the inability to know what exactly is deployed in the network, where it is, and how it’s interconnected.
VC4 calls this the “silent blocker” to OSS evolution.
Poor mis-aligned inventory undermines everything. It breaks service activations, triggers unnecessary truck rolls, causes billing mismatches, and frustrates assurance teams. Field engineers often discover real-world conditions that don’t match what’s in the system, while planners and support teams struggle to keep up. The problem doesn’t just stop with network data.
In many cases, customer records were also out of date or incomplete… and unknown inventory can also be a factor. Details like line types, distance from the central office, or whether loading coils were present often didn’t match reality. For years, this was one of the biggest issues for operators. Customer databases and network systems rarely aligned, and updates often took weeks or months. Engineers had to double-check every record before activating a service, which slowed delivery and increased errors. It was a widespread problem across the industry and one that many operators have been trying to fix ever since.
Over time, some operators tried to close this gap with data audits and manual reconciliation projects, but those fixes never lasted long. Networks change every day, and by the time a cleanup was finished, the data was already out of sync again.
Modern inventory systems take a different approach by keeping network and customer data connected in real time. They:
- Continuously sync with live network data so records stay accurate.
- Automatically validate what’s in the field against what’s stored in the system.
- Update both customer and network records when new services are provisioned.
In short, we’re talking about network auto-discovery and reconciliation, something that Service2Create does exceptionally well. This also applies for unknown records, duplicate records and records with naming inconsistencies/variances.
It is achieved through continuous network discovery that maps physical and logical assets, correlates them against live service models, and runs automated reconciliation to detect discrepancies such as unknown elements, duplicates, or naming mismatches. Operators can review and validate these findings, ensuring that the inventory always reflects the true, real-time network state. A more detailed explanation can be found in the VC4 Auto Discovery & Reconciliation guide which can be downloaded for free.
Service2Create: Unified, Reconciled, and AI-Ready
Service2Create is designed to reflect the actual, current state of the network across physical, logical, service and virtual layers. Whether operators are managing fiber rollout, mobile backhaul, IP/MPLS cores, or smart grids, S2C creates a common source of truth. It models infrastructure end-to-end, automates data reconciliation using discovery, and integrates with orchestration platforms and ticketing tools.
To make the difference clearer here is the table below shows how Service2Create compares with the older inventory systems still used by many operators. Traditional tools depend on manual updates and disconnected data sources, while Service2Create keeps everything synchronized and validated in real time.
Comparison between legacy inventory tools and Service2Create (S2C)
| Feature | Legacy OSS Tools | VC4 Service2Create (S2C) |
|---|---|---|
| Data reconciliation | Manual or periodic | Automated and continuous |
| Inventory accuracy | Often incomplete or outdated | Real-time and verified |
| Integration effort | Heavy customization needed | Standard API-based integration |
| Update cycle | It takes days or weeks | Completed in hours |
| AI readiness | Low, needs data cleanup | High, with consistent and normalized data |
What makes it AI-ready isn’t just compatibility with new tools, it’s data integrity. VC4 understands that AI and automation only perform well when they’re fed accurate, reliable, and real-time data. Without that, AI is flying blind.
Built-in Geographic Information System (GIS) capabilities help visualize the network in geographic context, while no/low-code workflows and APIs support rapid onboarding and customization. More than software, S2C behaves like a data discipline framework for telecom operations.
Service2Create gives operators a current, trusted view of their network, improving accuracy and reducing the time it takes to keep systems aligned.
AI is Reshaping OSS… But only if the Data is Right
AI is driving the next wave of OSS transformation from automated fault resolution and dynamic provisioning to predictive maintenance and AI-guided assurance. But it’s increasingly clear: AI doesn’t replace the need for accuracy; it demands it.
In 2025, one common thread across operators and developers was this: telcos want AI to reduce costs, shorten response times, and simplify networks. According to a GSMA analysis, many operators continue to struggle as their AI systems depend on fragmented and incomplete datasets, which reduces overall model accuracy.
VC4’s message is cutting through: AI is only as useful as the data that feeds it. Service2Create ensures the inventory is trustworthy, reconciled daily with the live network, and structured in a way AI tools can consume. It’s the difference between automating chaos and enabling meaningful, autonomous decisions.
Service2Create has been adopted with operators across Europe and Asia. In national fiber networks, it’s used to coordinate thousands of kilometers of rollout and maintenance. In mixed fixed-mobile environments, it synchronizes legacy copper, modern fiber, and 5G transport into one unified model.
Designed for Operational Reality
VC4 didn’t build Service2Create for greenfield labs or ideal conditions. The platform is designed for real-world operations: brownfield networks, legacy system integrations, and hybrid IT environments. Its microservices-based architecture and API-first design make it modular and scalable, while its no/low-code capabilities allow operators to adapt it without long customization cycles. See the diagram below.
S2C is deployable in the cloud or on-premises and integrates smoothly with Operational Support System / Business Support System (OSS/BSS) ecosystems including assurance, CRM, and orchestration. The result? Operators don’t have to rip and replace their stack – they can evolve it, anchored on a more reliable inventory core.
What Industry Analysts are Saying
In 2025, telco and IT industry experts are also emphasizing that AI’s failure to deliver consistent ROI in telecom is often due to unreliable base systems. One IDC analyst summed it up: “AI isn’t failing because the models are bad, it’s failing because operators still don’t know what’s in their own networks.”
A senior architect from a Tier 1 European CSP added, “We paused a closed-loop automation rollout because our service model was based on inventory we couldn’t trust. VC4 was the first vendor we saw this year that has addressed this directly and built a product around solving it.”
This year the takeaway is clear: clean inventory isn’t a nice-to-have. It’s step one.
Looking Ahead: AI-Driven Operations Powered by Trusted Inventory
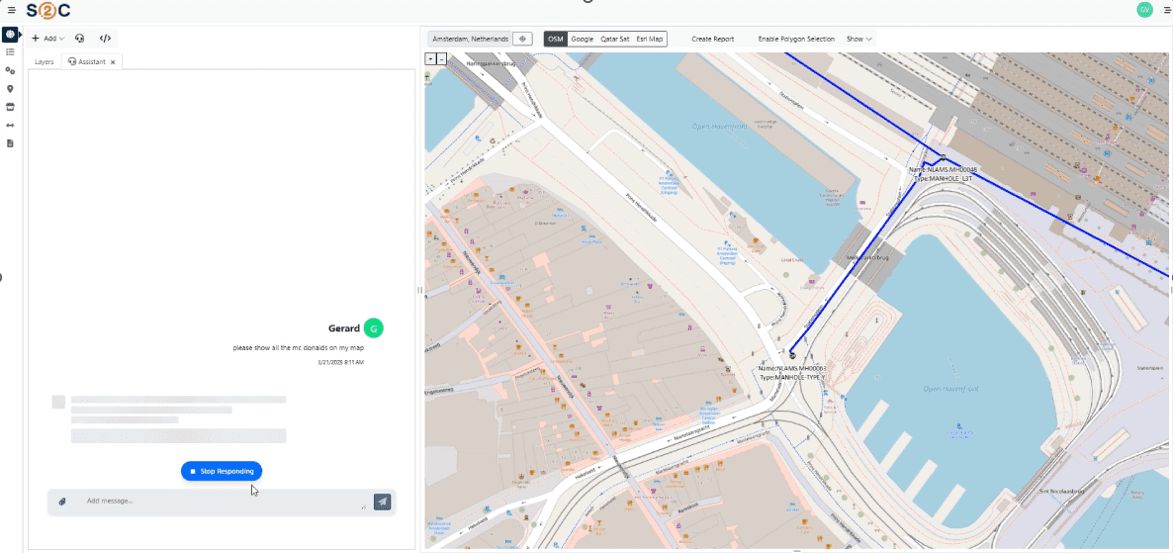
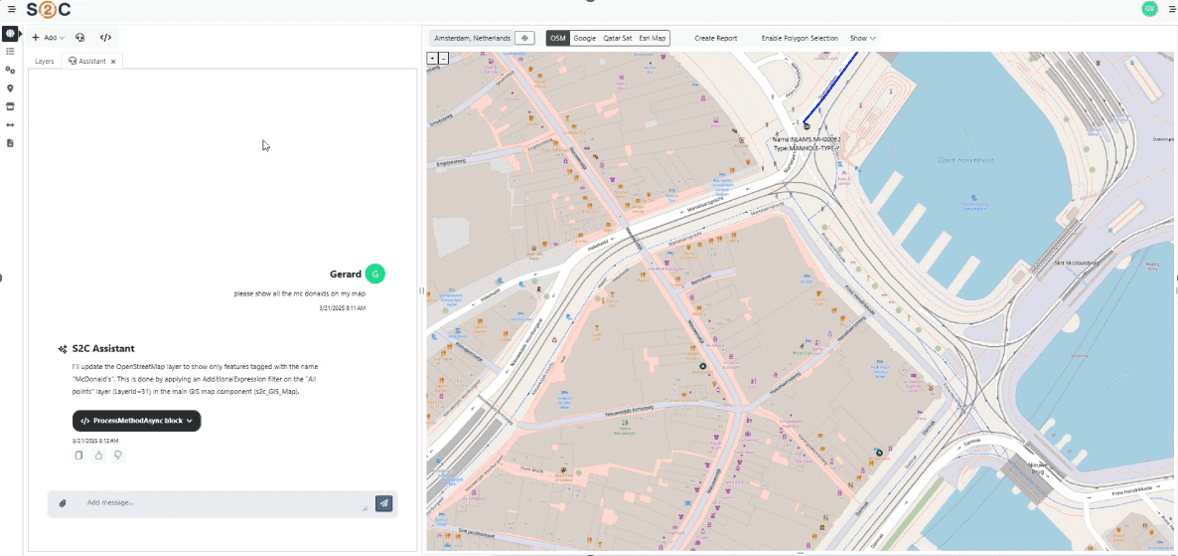
VC4 is continuing to enhance Service2Create with capabilities that support AI-led operations. Currently, S2C is enhanced with AI-powered natural language interfaces through Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. This creates a revolutionary way for users to access their data and makes it also easier for them to do so. Simply ask for what you need, in plain language, and receive instant, accurate results from your systems of record.
The S2C platform now offers multiple synchronized access methods:
- Natural Language Interface
- Ask questions in plain language: “Show me network capacity issues in Amsterdam”
- AI translates requests into precise system queries
- No training required – productive from day one
- Direct API Access via MCP
- Programmatic access using Language Integrated Query (LINQ) expressions
- Perfect for integrations and automated workflows
- Industry-standard authentication (IDP)
- S2C Visual Platform
- Full-featured GUI for power users
- Parameterized deeplinks for instant component access
- Low/no-code configuration capabilities
- Hybrid Workflows
-
- Start with AI chat, graduate to power tools
- AI generates deeplinks to relevant S2C dashboards
Export to Excel/CSV for offline analysis
-
What It All Comes Down To
Digital transformation sounds exciting on a conference stage, but in the trenches of telecom operations, it starts with simpler questions. Do you know what’s on your network? Can you trust the data? Can your systems work together?
That’s what Service2Create is built for. It helps operators take control of their infrastructure, giving them the confidence to automate when ready and the clarity to troubleshoot when needed.
VC4’s approach isn’t flashy. It’s focused. And that’s what makes it so effective – a direction supported by coverage from Subseacables.net, which reported on VC4’s partnership with AFR-IX, to automate and modernize network operations across the Mediterranean.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About the Author:
Juhi Rani is an SEO specialist at VC4 B.V. in the Netherlands. She has successfully directed and supervised teams, evaluated employee skills and knowledge, identified areas of improvement, and provided constructive feedback to increase productivity and maintain quality standards.
Juhi earned a B. Tech degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering from RTU in Jaipur, India in 2015.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ajay Lotan Thakur and Sridhar Talari Rajagopal are esteemed members of the IEEE Techblog Editorial Team. Read more about them here.
Nokia Bell Labs and KDDI Research partner for 6G energy efficiency and network resiliency
Nokia Bell Labs and KDDI Research have partnered to advance 6G technology, focusing on improving network energy efficiency and resilience. The collaboration combines KDDI’s real-world network data and operational insights with Nokia Bell Labs’ expertise in energy consumption models and programmable network architectures. This joint research agreement, signed on November 5, 2025, builds on a long history of cooperation and aims to accelerate the development and deployment of sustainable, intelligent 6G networks.
Under this new agreement, the two companies are conducting research in two key areas of 6G:
- mMIMO energy efficiency: New techniques for reducing base-station energy consumption while enhancing communication, specifically targeted at proposed 6G spectrum.
- Distributed programmable core network services for 6G: New mobile core technologies that will ensure continuous communication during infrastructure failures and natural disasters.
KDDI Research and Nokia Bell Labs will demonstrate their initial work in mMIMO energy efficiency at the Brooklyn 6G Summit Nov 5 – 7.
Peter Vetter, President, Core Research, Nokia Bell Labs:
“Tackling the inherent challenges in a new generation of networking requires close collaboration in the industry. Working side by side, KDDI Research and Nokia Bell Labs can advance the state of the art in networking thanks to different perspectives on the problems and possible solutions. Ultimately, the joint outcomes will make 6G a more resilient, efficient and intelligent technology.”
Satoshi Konishi, President and CEO, KDDI Research:
“Through our strategic and close collaboration with Nokia Bell Labs, we aim to accelerate R&D initiatives and further strengthen the ‘Power to Connect’ toward 6G. We strive to continuously deliver new value to our customers and make meaningful contributions to societal progress.”
References:
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
KDDI Deploys DriveNets Network Cloud: The 1st Disaggregated, Cloud-Native IP Infrastructure Deployed in Japan
AWS Integrated Private Wireless with Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, T-Mobile US, and Telefónica partners
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
Nokia’s Bell Labs to use adapted 4G and 5G access technologies for Indian space missions
Nokia and Rohde & Schwarz collaborate on AI-powered 6G receiver years before IMT 2030 RIT submissions to ITU-R WP5D
Highlights of Nokia’s Smart Factory in Oulu, Finland for 5G and 6G innovation
Will the wave of AI generated user-to/from-network traffic increase spectacularly as Cisco and Nokia predict?
Nokia Bell Labs claims new world record of 800 Gbps for transoceanic optical transmission
Nokia Bell Labs sets world record in fiber optic bit rates
Market research firms Omdia and Dell’Oro: impact of 6G and AI investments on telcos
Market research firm Omdia (owned by Informa) this week forecast that 6G and AI investments are set to drive industry growth in the global communications market. As a result, global communications providers’ revenue is expected to reach $5.6 trillion by 2030, growing at a 6.2% CAGR from 2025. Investment momentum is also expected to shift toward mobile networks from 2028 onward, as tier 1 markets prepare for 6G deployments. Telecoms capex is forecast to reach $395 billion by 2030, with a 3.6% CAGR, while technology capex will surge to $545 billion, reflecting a 9.3% CAGR.
Fixed telecom capex will gradually decline due to market saturation. Meanwhile, AI infrastructure, cloud services, and digital sovereignty policies are driving telecom operators to expand data centers and invest in specialized hardware.
Key market trends:
- CP capex per person will increase from $74 in 2024 to $116 in 2030, with CP capex reaching 2.5% of global GDP investment.
-
Capital intensity in telecom will decline until 2027, then rise due to mobile network upgrades.
-
Regional leaders in revenue and capex include North America, Oceania & Eastern Asia, and Western Europe, with Central & Southern Asia showing the highest growth potential.
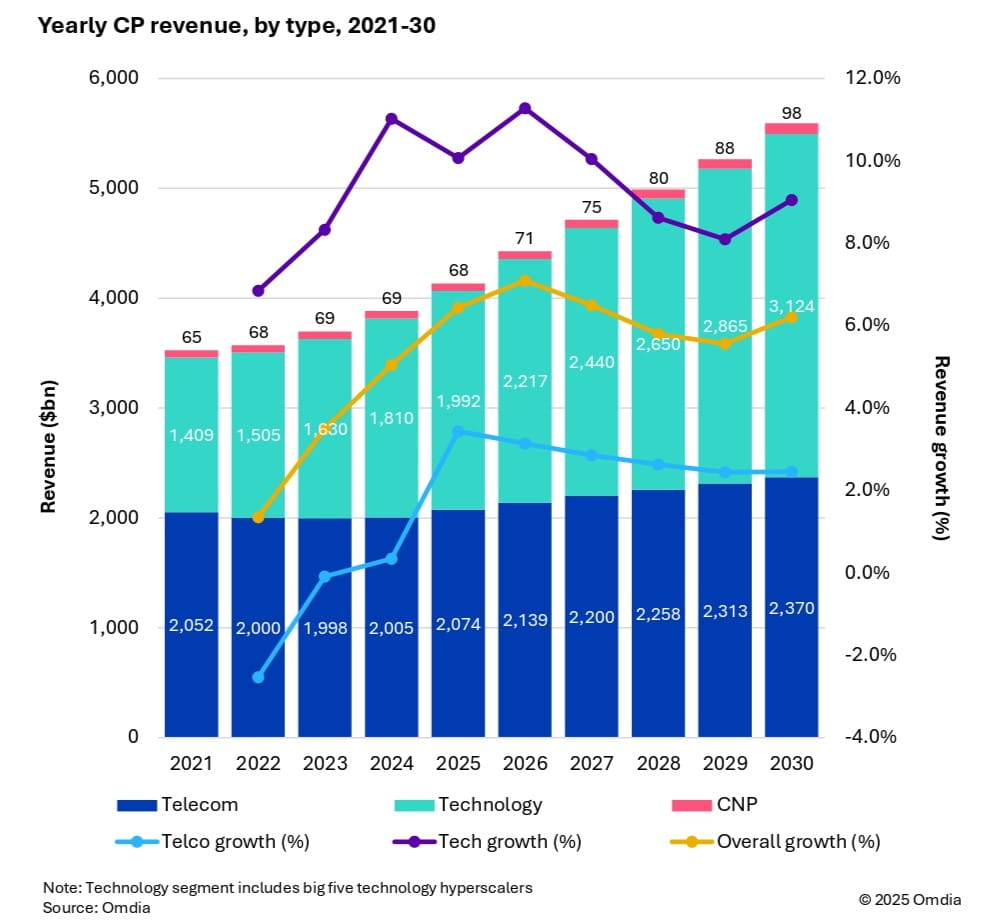 Dario Talmesio, research director at Omdia said, “telecom operators are entering a new phase of strategic investment. With 6G on the horizon and AI infrastructure demands accelerating, the connectivity business is shifting from volume-based pricing to value-driven connectivity.”
Dario Talmesio, research director at Omdia said, “telecom operators are entering a new phase of strategic investment. With 6G on the horizon and AI infrastructure demands accelerating, the connectivity business is shifting from volume-based pricing to value-driven connectivity.”
Omdia’s forecast is based on a comprehensive model incorporating historical data from 67 countries, local market dynamics, regulatory trends, and technology migration patterns.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Dell’Oro Group sees 6G capex ramping around 2030, although it warns that the RAN market remains flat, “raising key questions for the industry’s future.” Cumulative 6G RAN investments over the 2029-2034 period are projected to account for 55% to 60% of the total RAN capex over the same forecast period.
“Our long-term position and characterization of this market have not changed,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President of RAN and Telecom Capex research at Dell’Oro Group. “The RAN network plays a pivotal role in the broader telecom market. There are opportunities to expand the RAN beyond the traditional MBB (mobile broadband) use cases. At the same time, there are serious near-term risks tilted to the downside, particularly when considering the slowdown in data traffic,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from Dell’Oro’s October 2025 6G Advanced Research Report:
- The baseline scenario is for the broader RAN market to stay flat over the next 10 years. This is built on the assumption that the mobile network will run into utilization challenges by the end of the decade, spurring a 6G capex ramp dominated by Massive MIMO systems in the Sub-7GHz/cm Wave spectrum, utilizing the existing macro grid as much as possible.
- The report also outlines more optimistic and pessimistic growth scenarios, depending largely on the mobile data traffic growth trajectory and the impact beyond MBB, including private wireless and FWA (fixed wireless access).
- Cumulative 6G RAN investments over the 2029-2034 period are projected to account for 55 to 60 percent of the total RAN capex over the same forecast period.
Dell’Oro Group’s 6G Advanced Research Report offers an overview of the RAN market by technology, with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue for total RAN over the next 10 years. 6G RAN is analyzed by spectrum (Sub-7 GHz, cmWave, mmWave), by Massive MIMO, and by region (North America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, China, Asia Pacific Excl. China, and CALA). To purchase this report, please contact by email at [email protected].
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/6g-momentum-is-building
6G Capex Ramp to Start Around 2030, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/6g-course-correction-vendors-hear-mno-pleas
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/what-at-t-really-wants-from-6g
AT&T’s convergence strategy is working as per its 3Q 2025 earnings report
AT&T reported a 1.6% increase in third-quarter revenue to $30.7 billion, driven by its convergence strategy which combines wireless and fiber services. This strategy attracted profitable customers, as evidenced by 405,000 postpaid phone net additions and 550,000 new subscribers for AT&T’s advanced broadband services, including Fiber and Internet Air. The growth in these areas offset a decline in business wireline revenue.
“We have the key building blocks in place to give our customers the best connectivity experience in the industry and we’re winning the race to lead in convergence,” said John Stankey, AT&T Chairman and CEO.
“We continue to add highly-profitable customers that are choosing AT&T for all their connectivity needs on the country’s fastest and largest wireless and fiber networks. It’s clear our differentiated investment-led strategy is working, and we remain on track to achieve all of our 2025 consolidated financial guidance.”

Here are a few AT&T 3Q 2025 highlights:
- Postpaid Phone Subscribers: Gained 405,000 net additions.
- AT&T Fiber: Added 288,000 new subscribers.
- AT&T Internet Air: Added 270,000 new subscribers, marking a strong quarter for broadband net additions overall.
- Total Revenue increased 1.6% year-on-year to $30.7 billion.
- Mobility Revenue grew 3.1% year-over-year, supported by higher equipment sales and subscriber additions.
- Latin America Revenues were up 7.1% year on year to USD 1.10 billion amid subscriber and ARPU growth, higher equipment sales and the favourable effects of foreign exchange rates.
- Consumer Wireline Revenue increased 4.1%, led by an 8.2% rise in broadband revenue and strong fiber growth.
- Business Wireline Revenue declined 7.8%, mainly due to reductions in legacy services, though this was partially offset by growth in fiber and advanced connectivity services.
- The strategy is working because customers who bundle fiber and wireless services have lower churn and higher lifetime values, according to AT&T CEO John Stankey.
- More than 41% of AT&T Fiber households also have an AT&T Mobility service, which shows the success of this strategy.
- The company is on track to achieve its consolidated financial guidance for the year.
Stankey on AT&T’s competitive advantage (from Earnings Call transcript):
“We offer fast and reliable connectivity for 5G and fiber at attractive price points. More people are choosing AT&T for both wireless and home internet services. Today, more than 41% of AT&T Fiber households also choose AT&T for wireless. And the pace of this convergence trend within our customer base continues to grow. These customers remain our most valuable, with the lowest churn profile and highest lifetime values.
Our success with convergence also extends to fixed wireless. More than half of our Internet Air subscribers also choose AT&T for their wireless service. Similar to fiber, these customers exhibit lower churn and drive higher lifetime values than customers with stand-alone services.
The EchoStar spectrum we agreed to acquire will improve our 5G wireless performance in a cost-efficient manner, while allowing us to grow Internet Air at a faster pace. We’re already making great progress, delivering on our commitment to deploy this valuable spectrum for the benefit of American consumers and businesses.
We started deploying the 3.45 GHz spectrum that we have agreed to acquire from EchoStar under a short-term spectrum manager lease. Based on our current rate and pace, we expect these mid-band licenses will be deployed in cell sites covering nearly two-thirds of the US population by mid-November.
This should position us to further expand the availability of Internet Air 5G FWA) in our sales channels in 2026. Our ability to move this quickly reflects the great work of our teams and the FCC’s pro-investment and supportive policy environment. We’re also making great progress in preparing to close our transaction with Lumen. Most of the senior leadership team has been identified, and we now expect to close this transaction in the early part of 2026.
As I’ve said before, where we have fiber, we win with both fiber and 5G, and we plan to win even more as our investments in these assets bring advanced connectivity to more Americans. The supportive (FCC) policy environment is also making it easier for us to transition away from outdated legacy infrastructure and invest in the AI-ready connectivity that Americans want and need.
The bottom line is that we now have the right building blocks in place to realize our scaled fiber and fixed wireless ambitions, complete our wireless modernization, and successfully transition away from legacy infrastructure. As we complete our key investments, acquisitions, and transformation initiatives, we expect to increase our fiber and convergence penetration rates and see a majority of incremental revenue growth originate from converged customer relationships.”
Outlook & Financial Guidance:
AT&T reiterated its guidance for the 2025 financial year, with service revenue growth in the low single-digit range and mobility service revenue growth of 3 percent or better. It still foresees consumer fibre broadband revenue growth in the mid-to-high teens. Annual adjusted EBITDA growth should be 3 percent or better. Mobility EBITDA growth will be about 3 percent. Business wireline EBITDA will decline at a low double-digit rate and EBITDA growth for consumer wireline is still forecast in the low to mid-teen range. FY capital investment will be in the USD 22 billion to USD 22.5 billion range. AT&T predicts free cash flow in the low-to-mid USD 16 billion range. It continues to forecast FY adjusted EPS of USD 1.97 to USD 2.07.
AT&T reiterated its long-term financial guidance of service revenue growth in the low-single-digit range annually from 2026-2027, adjusted EBITDA growth of 3 percent or better annually, and adjusted EPS accelerating to double-digit percentage growth in 2027. AT&T foresees capital investment in the range USD 23 billion to USD 24 billion annually from 2026-2027. It predicts free cash flow of USD 18 billion or more in 2026 and USD 19 billion or more in 2027.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/3q-earnings.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/att-says-convergence-boosts-q3-revenue-and-profitability–1551778
AT&T deploys nationwide 5G SA while Verizon lags and T-Mobile leads
AT&T to buy spectrum licenses from EchoStar for $23 billion
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
T-Mobile’s new CEO Srini Gopalan faces fierce competition from AT&T, Verizon and MVNOs
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
Can the debt fueling the new wave of AI infrastructure buildouts ever be repaid?
IEEE Techblog has called attention to the many challenges and risks inherent in the current mega-spending boom for AI infrastructure (building data centers, obtaining power/electricity, cooling, maintenance, fiber optic networking, etc) . In particular, these two recent blog posts:
AI Data Center Boom Carries Huge Default and Demand Risks and
This article focuses on the tremendous debt that Open AI, Oracle and newer AI cloud companies will have to obtain and the huge hurdles they face to pay back the money being spent to build out their AI infrastructures. While the major hyperscalers (Amazon, Microsoft, Google and Meta) are in good financial shape and won’t need to take on much debt, a new wave of heavily leveraged firms is emerging—one that could reshape the current AI boom.
OpenAI, for example, is set to take borrowing and large-scale contracts to an unbelievable new level. OpenAI is planning a vast network of data centers expected to cost at least $1 trillion over the coming years. As part of this effort, the company signed a $300 billion, five-year contract this month under which Oracle “is to set up AI computing infrastructure and lease it to OpenAI.” In other words, OpenAI agreed to pay Oracle $300 billion over five years for the latter company to build out new AI data centers. Where will OpenAI get that money? It will be be burning billions in cash and won’t be profitable till 2029 at the earliest.
To fulfill its side of the deal, Oracle will need to invest heavily in infrastructure before receiving full payment—requiring significant borrowing. According to a recent note from KeyBanc Capital Markets, Oracle may need to borrow $25 billion annually over the next four years. This comes at a time when Oracle is already carrying substantial debt and is highly leveraged. As of the end of August, the company had around $82 billion in long-term debt, with a debt-to-equity ratio of roughly 450%. By comparison, Alphabet—the parent company of Google—reported a ratio of 11.5%, while Microsoft’s stood at about 33%.
Companies like Oracle and other less-capitalized AI players such as CoreWeave have little choice but to take on more debt if they want to compete at the highest level. Nebius Group, another Nasdaq-listed AI cloud provider similar to CoreWeave, struck a $19.4 billion deal in September to provide AI computing services to Microsoft. The company announced it would finance the necessary capital expenditures “through a combination of its cash flow and debt secured against the contract.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Sidebar – Stock market investors seem to love debt and risk:
CoreWeave’s shares have more than tripled since its IPO in March, while Nebius stock jumped nearly 50% after announcing its deal with Microsoft. Not to be outdone, Oracle’s stock surged 40% in a single day after the company disclosed a major boost in projected revenue from OpenAI in its infrastructure deal—even though the initiative will require years of heavy spending by Oracle.
–>What’s so amazing to this author is that OpenAI selected Oracle for the AI infrastructure it will use, even though the latter is NOT a major cloud service provider and is certainly not a hyperscaler. For Q1 2025, it held about 3% market share, placing it #5 among global cloud service providers.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Data Center Compute Server & Storage Room; iStock Photo credit: Andrey Semenov
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Among other new AI Cloud players:
- CyrusOne secured nearly $12 billion in financing (much in debt) for AI / data center expansion. Around $7.9 billion of that is for new data center / AI digital infrastructure projects in the U.S.
- SoftBank / “Stargate” initiative: The Stargate project (OpenAI + Oracle + SoftBank + MGX, etc.) is being structured with major debt. The plan is huge—around $500 billion in AI infrastructure and supercomputers, and financing is expected to be ~70% debt, ~10% equity among the sources.
- xAI (Elon Musk’s AI firm): xAI raised $10 billion in combined debt + equity. Specifically ~$5 billion in secured notes / term loans (debt), with the remainder in equity. The money is intended to build out its AI infrastructure (e.g. GPU facilities / data centers).
There’s growing skepticism about whether these companies can meet their massive contract obligations and repay their debts. Multiple recent studies suggest AI adoption isn’t advancing as quickly as supporters claim. One study found that only 3% of consumers are paying for AI services. Forecasts projecting trillions of dollars in annual spending on AI data centers within a few years appear overly optimistic.
OpenAI’s position, despite the hype, seems very shaky. D.A. Davidson analyst Gil Luria estimates the company would need to generate over $300 billion in annual revenue by 2030 to justify the spending implied in its Oracle deal—a steep climb from its current run rate of about $12 billion. OpenAI has financial backing from SoftBank and Nvidia, with Nvidia pledging up to $100 billion, but even that may not be enough. “A vast majority of Oracle’s data center capacity is now promised to one customer, OpenAI, who itself does not have the capital to afford its many obligations,” Luria said.
Oracle could try to limit risk by pacing its spending with revenue received from OpenAI. Nonetheless, Moody’s flagged “significant” risks in a recent note, citing the huge costs of equipment, land, and electricity. “Whether these will be financed through traditional debt, leases or highly engineered financing vehicles, the overall growth in balance sheet obligations will also be extremely large,” Moody’s warned. In July (two months before the OpenAI deal), it gave Oracle a negative credit outlook.
There’s a real possibility that things go smoothly. Oracle may handle its contracts and debt well, as it has in the past. CoreWeave, Nebius, and others might even pioneer new financial models that help accelerate AI development.
It’s very likely that some of today’s massive AI infrastructure deals will be delayed, renegotiated, or reassigned if AI demand doesn’t grow as fast as AI spending. Legal experts say contracts could be transferred. For example, if OpenAI can’t make the promised, Oracle might lease the infrastructure to a more financially stable company, assuming the terms allow it.
Such a shift wouldn’t necessarily doom Oracle or its debt-heavy peers. But it would be a major test for an emerging financial model for AI—one that’s starting to look increasingly speculative. Yes, even bubbly!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/debt-is-fueling-the-next-wave-of-the-ai-boom-278d0e04
Verizon’s 6G Innovation Forum joins a crowded list of 6G efforts that may conflict with 3GPP and ITU-R IMT-2030 work
Verizon has established a 6G Innovation Forum with a group of companies to drive innovation and enabling the 6G era. Verizon’s future-forward initiative is uniting key players across the technology ecosystem, including leading network vendors Ericsson, Samsung Electronics, and Nokia; and device and chipset innovators Meta, and Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., in the early stages of development to define 6G together by identifying potential new use cases, devices and network technology. The forum aims to establish an open, diversified, and resilient 6G ecosystem and develop foundational 6G technologies while ensuring global alignment.
This effort underscores Verizon’s commitment to drive the collaborative evolution of connectivity and deliver transformative experiences for consumers and enterprises. Verizon’s networks form the backbone of the emerging Artificial Intelligence economy, delivering the infrastructure and expertise essential for businesses to fully harness AI’s potential. For over a decade, Verizon has integrated AI into its operations to optimize network performance and infrastructure, a commitment that will continue with the evolution of 6G. This will accelerate Verizon’s AI Connect strategy and intelligent edge capabilities, enabling businesses to manage real-time AI workloads at scale by leveraging Verizon’s comprehensive suite of solutions with its award-winning network.
The forum will move beyond theoretical discussions and rapidly progress toward tangible 6G advancements and the realization of potential new and innovative use cases. Key areas of focus will include:
- Unlocking the full potential of 6G by testing new spectrum bands and bandwidths.
- Fostering a globally harmonized 6G landscape by actively working with global standards bodies like 3GPP to ensure that the forum’s work aligns with mainstream 6G development and promotes interoperability across the industry.
- Allowing forum partners to test and refine 6G technologies in a real-world environment by establishing dedicated Verizon 6G Labs, starting in Los Angeles, to serve as hubs for collaborative research, prototyping, and early lab and field trials.
“Verizon is consistently at the forefront of network innovation. We were the first in the world to turn up 5G and continue to enhance our best, most reliable and fastest 5G network in ways that open the door to possibilities far beyond what we can imagine today,” said Joe Russo, EVP & President, Global Networks and Technology at Verizon. “5G Advanced lays the foundation for the 6G future – whether that’s new wearables, AI experiences, or entirely new use cases we haven’t even thought of yet, and that’s what excites me the most. With the best team in the industry, we will build the future of these solutions with our partners. We’re already building a network designed for the next era – one that will transform how we live, work and play.”

Yago Tenorio, the chief technology officer of Verizon told Light Reading he wants the Forum to identify and refine 6G use cases before technology details are agreed upon by 3GPP and ITU-R WP5D. Smart glasses combined with artificial intelligence (AI) have arguably emerged as the prime candidate to succeed smartphones as a mass-market 6G consumer gadget. Last week, displayed the sort of smart glasses that could become popular in a future 6G scenario.
“One example of why this forum matters is that if you go to the standards today there is a lot of talk about uplink capacity with eight antennas in the device,” Tenorio said . “I don’t have any problem with that. It’s going to be very useful for FWA [fixed wireless access] and maybe useful for some smartphones, some classes of devices. But can you imagine a wearable with eight antennas? I mean, it’s difficult enough to have two,” he added.
Comment and Analysis:
It seems there are way too many 6G Forums and Consortiums that overlap and potentially can generate conflicting specifications. The two main bodies are ITU-R and 3GPP.
- ITU-R WP5D sets the formal requirements for terrestrial international mobile telecommunications (IMT) and is working on the framework for IMT-2030 (the official designation for 6G). This framework, outlined in the ITU-R’s IMT-2030 vision and Recommendation ITU-R M. 2160, includes key aspects like technology trends, usage scenarios, and performance capabilities for the next generation of mobile networks. 5D also develops the minimum technical performance requirements (TPRs) for IMT-2030 (“6G”) which will be specified in a Report ITU-R M. [IMT-2030.TECH PERF REQ]. In February 2025, WP5D discussed a draft document on these requirements, and the next step is to detail the specific values for key metrics like peak data rate and spectral efficiency, with candidates for the radio interfaces to be submitted by early 2029 and finalized around mid-2030.
- 3GPP creates cellular specifications which are submitted to ITU-R WP5D by ATIS as contributions directed towards Radio Interface Technologies (RITs) and Sets of Radio Interface Technologies (SRITs). 3GPP began its 6G study work in 2024. It is working toward a first-phase 6G specification to be completed in Release 21 by late 2028, which will be submitted for consideration as the IMT 2030 RIT/SRIT standard. Note that ONLY 3GPP defines the 5G and 6G core network specifications. There is no serious work in ITU-T for the non-radio aspects of 5G or 6G.
Summary of 6G Forums:
- Next G Alliance: An initiative within the Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions (ATIS) to advance North American leadership in wireless technology. It includes working groups focused on creating a 6G roadmap, defining applications and use cases, and addressing spectrum issues.
- AI-RAN Alliance: This group brings together technology and telecom leaders to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) directly into radio access network (RAN) technology to improve network performance, efficiency, and resource utilization in the lead-up to 6G.
- Verizon 6G Innovation Forum: Established in September 2025, this consortium unites companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung, Meta, and Qualcomm to develop the 6G ecosystem, identify use cases, and define foundational technologies.
- Brooklyn 6G Summit (B6GS): An annual flagship event hosted by Nokia and NYU, bringing together vendors, academia, and operators to discuss 6G research and innovation.
- 6G Smart Networks and Services Industry Association (6G-IA): A European-based group that represents the private sector and collaborates with the European Commission on 6G research initiatives. It oversees projects like Hexa-X and Hexa-X-II, which have helped define the 6G vision.
- 6G Flagship (Finland): Based at the University of Oulu, this is one of the world’s first 6G research programs. It leads multiple national and international projects, working to develop the components, tools, and test network for a 6G-enabled digital world.
- one6G: This non-profit association works to accelerate the adoption of next-generation wireless technologies by supporting global 6G research and standardization.
- China IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group, established in 2019 by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) to coordinate government, academia, and industry efforts in promoting 6G research, development, and international cooperation. The group focuses on defining technical standards, exploring new applications like integrated sensing and non-terrestrial networks, and aims for 6G commercialization around 2030.
- 6G Forum (Korea): An organization working to lead and promote the evolution of wireless technology beyond 5G and into 6G, encouraging collaboration between industries, government, and academia.
- Bharat 6G Alliance (India): A partnership between Indian companies, academia, and research organizations to accelerate the country’s innovation and collaboration in 6G.
- XG Mobile Promotion Forum (Japan): This group, which has a memorandum of understanding with the Next G Alliance, focuses on advancing the 5G and 6G ecosystem.
- IEEE Future Networks: This IEEE initiative includes a Testbed Working Group that collaborates with existing 5G testbeds to accelerate the development of next-generation networks, including 6G.
- Research initiatives: Numerous specific projects and academic consortia worldwide are also driving focused research on various aspects of 6G, such as integrating AI into networks or developing specific components.
- See References below for more collaborative efforts directed at 6G.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-leads-future-wireless-development-new-industry-6g-forum
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/verizon-cto-worries-whether-6g-will-measure-up-in-the-us
Verizon launches 6G forum; it’s all about the use cases, CTO says
https://www.ericsson.com/en/6g/spectrum
ITU-R WP5D IMT 2030 Submission & Evaluation Guidelines vs 6G specs in 3GPP Release 20 & 21
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
Ericsson and e& (UAE) sign MoU for 6G collaboration vs ITU-R IMT-2030 framework
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
Qualcomm CEO: expect “pre-commercial” 6G devices by 2028
Mulit-vendor Open RAN stalls as Echostar/Dish shuts down it’s 5G network leaving Mavenir in the lurch
Last week’s announcement that Echostar/ Dish Network will sell $23 billion worth of spectrum licenses to AT&T was very bad news for Mavenir. As a result of that deal, Dish Network’s 5G Open RAN network, running partly on Mavenir’s software, is to be decommissioned. Dish Network had been constructing a fourth nationwide U.S. mobile network with new Open RAN suppliers – one of the only true multi-vendor Open RANs worldwide.

Credit: Kristoffer Tripplaar/Alamy Stock Photo
Echostar’s decision to shut down its 5G network marks a very sad end for the world’s largest multivendor open RAN and will have ramifications for the entire industry. “If you look at all the initiatives, what the US government did or in general, they are the only ones who actually spent a good chunk of money to really support open RAN architecture,” said Pardeep Kohli, the CEO of Mavenir, one of the vendors involved in the Dish Network project. “So now the question is where do you go from here?”
As part of its original set of updates on 5G network plans, Dish revealed it would host its 5G core – the part that will survive the spectrum sale – in the public cloud of AWS. And the hyperscaler’s data facilities have also been used for RAN software from Mavenir installed on servers known as central units.
Open RAN enters is in the fronthaul interface between Mavenir’s DU software and radios provided by Japan’s Fujitsu. Its ability to connect its software to another company’s radios validates Mavenir’s claims to be an open RAN vendor, says Kohli. While other suppliers boast compatibility with open RAN specifications, commercial deployments pairing vendors over this interface remain rare.
Mavenir has evidently been frustrated by the continued dominance of Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia, whose combined RAN market share grew from 75.1% in 2023 to 77.5% last year, according to research from Omdia, an Informa company. Dish Network alone would not have made a sufficient difference for Mavenir and other open RAN players, according to Kohli. “It helped us come this far,” he said. “Now it’s up to how far other people want to take it.” A retreat from open RAN would, he thinks, be a “bad outcome for all the western operators,” leaving them dependent on a Nordic duopoly in countries where Chinese vendors are now banned.
“If they (telcos) don’t support it (multi-vendor OpenRAN), and other people are not supporting it, we are back to a Chinese world and a non-Chinese world,” he said. “In the non-Chinese world, you have Ericsson and Nokia, and in the Chinese world, it’s Huawei and ZTE. And that’s going to be a pretty bad outcome if that’s where it ends up.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Open RAN x-U.S.:
Outside the U.S., the situation is no better for OpenRAN. Only Japan’s Rakuten and Germany’s 1&1 have attempted to build a “greenfield” Open RAN from scratch. As well as reporting billions of dollars in losses on network deployment, Rakuten has struggled to attract customers. It owns the RAN software it has deployed but counts only 1&1 as a significant customer. And Rakuten’s original 4G rollout was not based on the industry’s open RAN specifications, according to critics. “They were not pure,” said Mavenir’s Kohli.
Plagued by delays and other problems, 1&1’s rollout has been a further bad advert for Open RAN. For the greenfield operators, the issue is not the maturity of open RAN technology. Rather, it is the investment and effort needed to build any kind of new nationwide telecom network in a country that already has infrastructure options. And the biggest brownfield operators, despite professing support for open RAN, have not backed any of the the new entrants.
RAN Market Concentration:
- Stefan Pongratz, an analyst with Dell’Oro, found that five of six regions he tracks are today classed as “highly concentrated,” with an HHI score of more than 2,500. “This suggests that the supplier diversity element of the open RAN vision is fading,” wrote Pongratz in a recent blog.
- A study from Omdia (owned by Informa), shows the combined RAN market share of Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia grew from 75.1% in 2023 to 77.5% last year. The only significant alternative to the European and Chinese vendors is Samsung, and its market share has shrunk from 6.1% to 4.8% over this period.
Concentration would seem to be especially high in the U.S., where Ericsson now boasts a RAN market share of more than 50% and generates about 44% of its sales (the revenue contribution of India, Ericsson’s second-biggest market, was just 4% for the recent second quarter). That’s partly because smaller regional operators previously ordered to replace Huawei in their networks spent a chunk of the government’s “rip and replace” funds on Ericsson rather than open RAN, says Kohli. Ironically, though, Ericsson owes much of the recent growth in its U.S. market share to what has been sold as an open RAN single vendor deal with AT&T [1.]. Under that contract, it is replacing Nokia at a third of AT&T’s sites, having already been the supplier for the other two thirds.
Note 1. In December 2023, AT&T awarded Ericsson a multi-year, $14 billion Open RAN contract to serve as the foundation for its open network deployment, with a goal of having 70% of its wireless traffic on open platforms by late 2026. That large, single-vendor award for the core infrastructure was criticized for potentially undermining the goal of Open RAN which was to encourage competition among multiple network equipment and software providers. AT&T’s claim of a mulit-vendor network turned out to be just a smokescreen. Fujitsu/1Finity supplied third-party radios used in AT&T’s first Open RAN call with Ericsson.
Indeed, AT&T’s open RAN claims have been difficult to take seriously, especially since it identified Mavenir as a third supplier of radio units, behind Ericsson and Japan’s Fujitsu, just a few months before Mavenir quit the radio unit market. Mavenir stopped manufacturing and distributing Open RAN radios in June 2025 as part of a financial restructuring and a shift to a software-focused business model.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Arguably, Kohli describes Echostar/ Dish Network as the only U.S. player that was spending “a good chunk of money to really support open RAN architecture.”
Ultimately, he thinks the big U.S. telcos may come to regret their heavier reliance on the RAN gear giants. “It may look great for AT&T and Verizon today, but they’ll be funding this whole thing as a proprietary solution going forward because, really, there’s no incentive for anybody else to come in,” he said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/open-ran/echostar-rout-leaves-its-open-ran-vendors-high-and-dry
AT&T to to buy spectrum Licenses from EchoStar for $23 billion
AT&T to deploy Fujitsu and Mavenir radio’s in crowded urban areas
Dell’Oro Group: RAN Market Grows Outside of China in 2Q 2025
Mavenir and NEC deploy Massive MIMO on Orange’s 5G SA network in France
Spark New Zealand completes 5G SA core network trials with AWS and Mavenir software
Mavenir at MWC 2022: Nokia and Ericsson are not serious OpenRAN vendors
Ericsson expresses concerns about O-RAN Alliance and Open RAN performance vs. costs
Nokia and Mavenir to build 4G/5G public and private network for FSG in Australia
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Both telecom and enterprise networks are being reshaped by AI bandwidth and latency demands of AI. Network operators that fail to modernize architectures risk falling behind. Why? AI workloads are network killers — they demand massive east-west traffic, ultra-low latency, and predictable throughput.
- Real-time observability is becoming non-negotiable, as enterprises need to detect and fix issues before they impact AI model training or inference.
- Self-driving networks are moving from concept to reality, with AI not just monitoring but actively remediating problems.
- The competitive race is now about who can integrate AI into networking most seamlessly — and HPE/Juniper’s Mist AI, Cisco’s assurance stack, and Nvidia’s AI fabrics are three different but converging approaches.
Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are designing AI-optimized networking equipment, with a focus on real-time observability, lower latency and increased data center performance for AI workloads. Here’s a capsule summary:
Cisco: AI-Ready Infrastructure:
- Cisco is embedding AI telemetry and analytics into its Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, and Catalyst campus gear.
- The focus is on real-time observability via its ThousandEyes platform and AI-driven assurance in DNA Center, aiming to optimize both enterprise and AI/ML workloads.
- Cisco is also pushing AI-native data center fabrics to handle GPU-heavy clusters for training and inference.
- Cisco claims “exceptional momentum” and leadership in AI: >$800M in AI infrastructure orders taken from web-scale customers in Q4, bringing the FY25 total to over $2B.
- Cisco Nexus switches now fully and seamlessly integrated with NVIDIA’s Spectrum-X architecture to deliver high speed networking for AI clusters
HPE + Juniper: AI-Native Networking Push:
- Following its $13.4B acquisition of Juniper Networks, HPE has merged Juniper’s Mist AI platform with its own Aruba portfolio to create AI-native, “self-driving” networks.
- Key upgrades include:
-Agentic AI troubleshooting that uses generative AI workflows to pinpoint and fix issues across wired, wireless, WAN, and data center domains.
-Marvis AI Assistant with enhanced conversational capabilities — IT teams can now ask open-ended questions like “Why is the Orlando site slow?” and get contextual, actionable answers.
-Large Experience Model (LEM) with Marvis Minis — digital twins that simulate user experiences to predict and prevent performance issues before they occur.
-Apstra integration for data center automation, enabling autonomous service provisioning and cross-domain observability
Nvidia: AI Networking at Compute Scale
- Nvidia’s Spectrum-X Ethernet platform and Quantum-2 InfiniBand (both from Mellanox acquisition) are designed for AI supercomputing fabrics, delivering ultra-low latency and congestion control for GPU clusters.
- In partnership with HPE, Nvidia is integrating NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Blackwell architecture GPUs into HPE Private Cloud AI, enabling enterprises to deploy AI workloads with optimized networking and compute together.
- Nvidia’s BlueField DPUs offload networking, storage, and security tasks from CPUs, freeing resources for AI processing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of how Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia are approaching AI‑optimized enterprise networking — so you can see where they align and where they differentiate:
| Feature / Focus Area | Cisco | HPE / Juniper | Nvidia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core AI Networking Vision | AI‑ready infrastructure with embedded analytics and assurance for enterprise + AI workloads | AI‑native, “self‑driving” networks across campus, WAN, and data center | High‑performance fabrics purpose‑built for AI supercomputing |
| Key Platforms | Silicon One chips, Nexus 9000 switches, Catalyst campus gear, ThousandEyes, DNA Center | Mist AI platform, Marvis AI Assistant, Marvis Minis, Apstra automation | Spectrum‑X Ethernet, Quantum‑2 InfiniBand, BlueField DPUs |
| AI Integration | AI‑driven assurance, predictive analytics, real‑time telemetry | Generative AI for troubleshooting, conversational AI for IT ops, digital twin simulations | AI‑optimized networking stack tightly coupled with GPU compute |
| Observability | End‑to‑end visibility via ThousandEyes + DNA Center | Cross‑domain observability (wired, wireless, WAN, DC) with proactive issue detection | Telemetry and congestion control for GPU clusters |
| Automation | Policy‑driven automation in campus and data center fabrics | Autonomous provisioning, AI‑driven remediation, intent‑based networking | Offloading networking/storage/security tasks to DPUs for automation |
| Target Workloads | Enterprise IT, hybrid cloud, AI/ML inference & training | Enterprise IT, edge, hybrid cloud, AI/ML workloads | AI training & inference at hyperscale, HPC, large‑scale data centers |
| Differentiator | Strong enterprise install base + integrated assurance stack | Deep AI‑native operations with user experience simulation | Ultra‑low latency, high‑throughput fabrics for GPU‑dense environments |
Key Takeaways:
- Cisco is strongest in enterprise observability and broad infrastructure integration.
- HPE/Juniper is leaning into AI‑native operations with a heavy focus on automation and user experience simulation.
- Nvidia is laser‑focused on AI supercomputing performance, building the networking layer to match its GPU dominance.
- Cisco leverages its market leadership, customer base and strategic partnerships to integrate AI with existing enterprise networks.
- HPE/Juniper challenges rivals with an AI-native, experience-first network management platform.
- Nvidia aims to dominate the full-stack AI infrastructure, including networking.
Muon Space in deal with Hubble Network to deploy world’s first satellite-powered Bluetooth network
Muon Space, a provider of end-to-end space systems specializing in mission-optimized satellite constellations, today announced its most capable satellite platform, MuSat XL, a high-performance 500 kg-class spacecraft designed for the most demanding next-generation low Earth orbit (LEO) missions. Muon also announced its first customer for the XL Platform: Hubble Network, a Seattle-based space-tech pioneer building the world’s first satellite-powered Bluetooth network. IEEE Techblog reported Hubble Network’s first Bluetooth to space satellite connection in this post.
The XL Platform delivers a dramatically expanded capability tier to the flight-proven Halo™ stack – delivering more power, agility, and integration flexibility while preserving the speed, scalability and cost-effectiveness needed for constellation deployment. Optimized for Earth observation (EO) and telecommunications missions supporting commercial and national security customers that require multi-payload operations, extreme data throughput, high-performance inter-satellite networking, and cutting-edge attitude control and pointing, the XL Platform sets a new industry benchmark for mission performance and value. “XL is more than a bigger bus – it’s a true enabler for customers pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in orbit, like Hubble,” said Jonny Dyer, CEO of Muon Space. “Their transformative BLE technology represents the future of space-based services and we are ecstatic to enable their mission with the XL Platform and our Halo stack.”

The Muon Space XL platform combines exceptional payload power, precise pointing, and high-bandwidth networking to enable advanced space capabilities across defense, disaster response, and commercial missions.
Enhancing Global BLE Coverage:
In 2024, Hubble became the first company to establish a Bluetooth connection directly to a satellite, fueling global IoT growth. Using MuSat XL, it will deploy a next-generation BLE payload featuring a phased-array antenna and a receiver 20 times more powerful than its CubeSat predecessor, enabling BLE detection at 30 times lower power and direct connectivity for ultra-low-cost, energy-efficient devices worldwide. MuSat XL’s large payload accommodation, multi-kW power system, and cutting-edge networking and communications capabilities are key enablers for advanced services like Hubble’s.
“Muon’s platform gives us the scale and power to build a true Bluetooth layer around the Earth,” said Alex Haro, Co-Founder and CEO of Hubble Network.
The first two MuSat XL satellites will provide a 12-hour global revisit time, with a scalable design for faster coverage. Hubble’s BLE Finding Network supports critical applications in logistics, infrastructure, defense, and consumer technology.
A Next Generation Multi-Mission Satellite Platform:
MuSat XL is built for operators who need real capability – more power, larger apertures, more flexibility, and more agility – and with the speed to orbit and reliability that Muon has already demonstrated with its other platforms in orbit since 2023. Built on the foundation of Muon’s heritage 200 kg MuSat architecture, MuSat XL is a 500 kg-class bus that extends the Halo technology stack’s performance envelope to enable high-impact, real-time missions.
Key capabilities include:
- 1 kW+ orbit average payload power – Supporting advanced sensors, phased arrays, and edge computing applications.
- Seamless, internet-standards based, high bandwidth, low latency communications, and optical crosslink networking – Extremely high volume downlink (>5 TB / day) and near real-time communications for time-sensitive operations critical for defense, disaster response, and dynamic tasking.
- Flexible onboard interface, network, compute – Muon’s PayloadCore architecture enables rapid hardware/software integration of payloads and deployment of cloud-like workflows to onboard network, storage, and compute.
- Precise, stable, and agile pointing – Attitude control architected for the rigorous needs of next-generation EO and RF payloads.
In the competitive small satellite market, MuSat XL offers standout advantages in payload volume, power availability, and integration flexibility – making it a versatile backbone for advanced sensors, communications systems, and compute-intensive applications. The platform is built for scale: modular, manufacturable, and fully integrated with Muon’s vertically developed stack, from custom instrument design to full mission operations via the Halo technology stack.
Muon designed MuSat XL to deliver exceptional performance without added complexity. Early adopters like Hubble signal a broader trend in the industry: embracing platforms that offer operational autonomy, speed, and mission longevity at commercial scale.
About Muon Space:
Founded in 2021, Muon Space is an end-to-end space systems company that designs, builds, and operates mission-optimized satellite constellations to deliver critical data and enable real-time compute and decision-making in space. Its proprietary technology stack, Halo™, integrates advanced spacecraft platforms, robust payload integration and management, and a powerful software-defined orchestration layer to enable high-performance capabilities at unprecedented speed – from concept to orbit. With state-of-the-art production facilities in Silicon Valley and a growing track record of commercial and national security customers, Muon Space is redefining how critical Earth intelligence is delivered from space. Muon Space employs a team of more than 150 engineers and scientists, including industry experts from Skybox, NASA, SpaceX, and others. SOURCE: Muon Space
About Hubble Network:
Founded in 2021, Hubble is creating the world’s first satellite-powered Bluetooth network, enabling global connectivity without reliance on cellular infrastructure. The Hubble platform makes it easy to transmit low-bandwidth data from any Bluetooth-enabled device, with no infrastructure required. Their global BLE network is live and expanding rapidly, delivering real-time visibility across supply chains, fleets, and facilities. Visit www.hubble.com for more information.
References:
Hubble Network Makes Earth-to-Space Bluetooth Satellite Connection; Life360 Global Location Tracking Network
WiFi 7: Backgrounder and CES 2025 Announcements