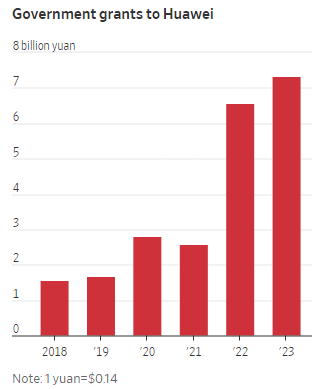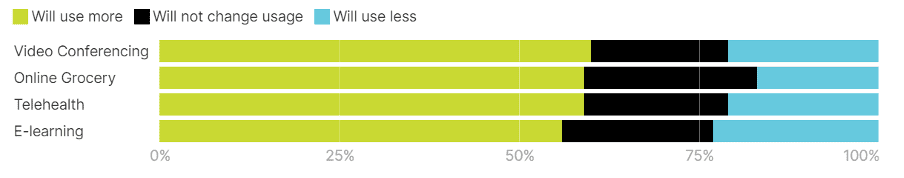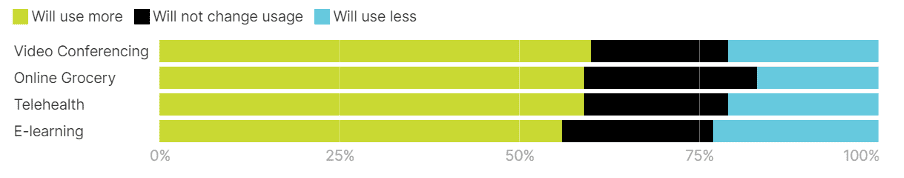Uncategorized
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
China’s ZTE reported a 2.9% rise in total revenue to RMB62.5 billion ($8.76 billion), with net profit attributable to holders of ordinary shares of the Hong Kong listed company at RMB 5.73 billion, up 4.8% year-over-year (YoY). The biggest growth surge was in the corporate and government unit, which boosted revenue by 56% to RMB9.2 billion yuan ($1.29 billion), mainly through stronger server and storage sales. However, that was offset by a 68% hike in costs, depressing the gross margin by 5.7 points – a result of “changes in revenue mix,” the company said.
The company’s core carrier network equipment business declined 8.6% in the first half of 2024, holding back underlying earnings to 4.96 billion Chinese yuan (US$700 million) – a gain of just 1.1% over last year. The carrier unit, which accounted for 60% of the company’s total revenue, brought in RMB37 billion ($5.18 billion) in sales in H1, the company revealed in its stock exchange filing.
ZTE said demand from Chinese telecom operators had been constrained by “overall investment sentiments,” but it pointed to improved sales of indoor distribution, high-speed rail and metro networking equipment. ZTE’s consumer business, which includes mostly handsets and home routers, grew 14% to RMB16 billion ($2.24 billion). R&D spending remained flat at RMB12.7 billion ($1.78 billion).
_International_Software_Products.jpeg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
China’s domestic market accounted for 69% of total sales, roughly the same as last year. The biggest offshore growth region was Asia (excluding China), which grew 23%. ZTE said it is positioning itself as a “path-builder for the digital economy” and aimed to further expand its legacy connectivity business while growing its computing business. Its AI portfolio includes full-stack intelligent solutions, backed by key technologies such as high-speed networking, network computing and data processing.
ZTE is developing their own custom silicon. In the first half of 2024, the company continued to increase investment in advanced semiconductor process technologies, advanced architecture and seal packaging design, core intellectual properties and digitalized efficient development platform on the back of close to 30 years’ R&D build-up. We are an industry leader in terms of the ability to design the whole process of chip. On top of a solid foundation in the R&D of base-level technology for DICT chip, the Group has also constructed an ultra-efficient, green and intelligent full-stack computing network base pivoting on “data, computing and network” in line with developments in computing-network integration. The creation of a product regime meeting the core requirements of the diversified scenarios of “cloud, edge, terminal” has supported our ongoing leading position in terms of competitiveness.
ZTE has used its expertise in communication software and hardware development, engineering capabilities and industrialization to intensify its investment in computing power products and solutions. The company has launched a comprehensive suite of full-stack, full-scenario intelligent computing solutions, covering computing, networks, capabilities, intelligence and applications. These solutions include a full range of general computing servers, high-performance AI training servers, inference servers, liquid-cooled servers, distributed storage systems, high-end multi-control magnetic arrays, integrated training-inference machines and high-speed lossless switches.
In the terminal sector, ZTE has introduced the concept of “AI for All”, focusing on five core consumer scenarios: sports and health, audio and video entertainment, business and travel, home and education, and smart driving. The company has launched a full range of AI-driven terminal products, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and mobile internet devices, as part of its Full-Scenario Intelligent Ecosystem 3.0. This ecosystem promotes the integration of AI technology across mobile terminal devices, smart home devices, cloud computing and automotive electronics.
Moving forward, ZTE is dedicated to advancing its core technological innovations and accelerating its expansion into the “connectivity + computing + capability + intelligence” domain. The company will focus on strengthening its digital and intelligent infrastructure. By fostering open collaboration and pursuing diverse, mutually beneficial partnerships, ZTE aims to build a highly efficient and intelligent digital future with industry partners. The company said it expects: gradual adoption of 5G-Advanced, further rollout of 400G optical and construction of intelligent computing centers to drive the China’s telecom carrier market in the second half. Offshore, it will continue to focus on large national markets and big telcos for its wirelines and wireless product lines.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-s-carrier-sales-slump-9-in-h1
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0816/2024081601602.pdf
ZTE reports H1 2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
Tech layoffs continue unabated: pink slip season in hard-hit SF Bay Area
A combination of strategic pivots toward the red-hot AI sector and corrections after pandemic-era over hiring have pushed companies across the tech sector to lay off massive number of employees, according to outplacement firm Challenger, Grey & Christmas. Tech companies including Cisco Systems, Intel and Dell have cut tens of thousands of jobs in August, the latest in a year that began with layoffs at companies such as Amazon and Google.
On Wednesday, Cisco announced in a notice posted with the Securities and Exchange Commission that it was laying off 5,500 workers (7% of its employees) as part of an effort to invest more in AI. In a short statement, CEO Chuck Robbins used the term “AI” five times, highlighting the company’s efforts to keep up in the ongoing AI race. Earlier this year, Cisco also laid off 4,000 or 5% of its workforce, saying that the company wanted to “realign the organization and enable further investment in key priority areas.” Cisco joins a litany of other companies like Microsoft and Intuit that have used AI as the justification for mass layoffs.
- As of August 17, 2024, 404 tech companies have laid off 132,498 workers this year, according to layoffs.fyi, a website that tracks tech industry job cuts. This includes major tech companies like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Tesla, TikTok, and Snap, as well as smaller startups and apps.
- Crunchbase says that in 2023, more than 191,000 workers in U.S.-based tech companies (or tech companies with a large U.S. workforce) were laid off in mass job cuts. In 2022, more than 93,000 jobs were slashed from public and private tech companies in the U.S.
The SF Bay Area has been particularly hard-hit, with companies such as Twitter, Meta, and Salesforce announcing significant job cuts. The layoffs are sending shockwaves through the region’s economy. The tech industry has long been a major driver of growth and employment in the Bay Area, accounting for a significant portion of tax revenue and supporting numerous ancillary businesses. The sudden loss of jobs has raised concerns about a potential economic downturn. Many of the affected workers are highly skilled in areas such as software engineering, product development, and data science.
Here are the largest Bay Area tech company layoffs in 2024 and 2023:
| March 14, 2023 | Meta/FB |
21,000
|
13% | Menlo Park |
| August 1, 2024 | Intel |
18,720
|
15% | Santa Clara |
| January 20, 2023 | Alphabet |
12,000
|
6% | Mountain View |
| Feb 14 & Aug14, 2024 | Cisco Systems | 9,500 | 13% | San Jose |
The tech layoffs have created a fiercely competitive job market, with many qualified individuals seeking new employment. This has put pressure on salaries and benefits, further exacerbating the economic impact. The tech layoffs have also had a psychological toll on the Bay Area community. Many workers have lost their sense of stability and are worried about their financial future. The uncertainty has created a climate of anxiety and stress, particularly among those who are still employed.
Government officials and economic development agencies are working to mitigate the effects of the layoffs. They are providing support services to displaced workers, such as job retraining and placement assistance. However, the full extent of the economic impact remains to be seen. The surge in tech layoffs underscores the cyclical nature of the industry. While the Bay Area has weathered economic downturns in the past, the unprecedented scale of the current tech job cuts raises questions about the long-term health of the tech sector. As companies adapt to a changing economic landscape, the region’s economy is struggling to evolve to meet the challenges and perceived opportunities (e.g. AI).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/finance/investing/tech-media-telecom-roundup-market-talk-12947dd6
https://futurism.com/the-byte/cisco-layoff-ai-profit
https://news.crunchbase.com/startups/tech-layoffs/
https://www.challengergray.com/tags/job-cut-report/
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Huge Loss & Restructuring:
In its August 1st press release detailing a $1.6 billion 2Q-2024 loss (mainly from it’s foundry business) [1.] Intel announced it was cutting more than 15% of its workforce by 2025 with most of those coming by year end. The company is also suspending its dividend starting in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Note 1. Intel Foundry, which reported a $2.5bn operating loss during the first quarter of 2024, lost an additional $2.8bn in Q2-2024. That business is seen as a U.S. strategic asset in a major move to bring back chip making to the U.S. from Taiwan, China and South Korea.
“Our Q2 financial performance was disappointing, even as we hit key product and process technology milestones. Second-half trends are more challenging than we previously expected, and we are leveraging our new operating model to take decisive actions that will improve operating and capital efficiencies while accelerating our IDM 2.0 transformation,” said Pat Gelsinger, Intel CEO. “These actions, combined with the launch of Intel 18A next year to regain process technology leadership, will strengthen our position in the market, improve our profitability and create shareholder value.”
CEO/CFO Earnings Call prepared remarks:
“We are targeting a headcount reduction of greater than 15% by the end of 2025, with the majority of this action completed by the end of this year. We do not do this lightly, and we have carefully considered the impact this will have on the Intel family. These are hard but necessary decisions. Our actions will reduce OpEx (operating expenses) to approximately $20 billion in 2024, and we see a bigger impact next year, with 2025 OpEx targeted at $17.5 billion, more than 20% below prior estimates. We expect further benefits in 2026, with OpEx to decline in absolute dollars yet again. Even as we lower overall spending, we will continue to fund the investments needed to deliver our strategy.”
The company’s latest filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) stated there were 124,800 employees as of December 2023, down from 131,900 a year before. Therefore, a 15% reduction could translate to the loss of 18,720 employees and we wouldn’t be surprised by total job cuts exceeding 20,000! In addition to layoffs, Intel is pushing older employees to retire.
CEO Pat Gelsinger wrote in a letter to Intel employees:
“Next week, we’ll announce a companywide enhanced retirement offering for eligible employees and broadly offer an application program for voluntary departures. I believe that how we implement these changes is just as important as the changes themselves, and we will adhere to Intel values throughout this process.”
The objective is to greatly reduce various operational costs (research and development plus marketing, general and administrative expenses) to about $20 billion this year and $17.5 billion in 2025, “with further reductions planned in 2026,” said Intel. That $17.5 billion would be about $4.2 billion less than Intel booked for these expenses in 2023, according to its last annual SEC filing, and a reduction of $7 billion compared with the figure for 2022.
Fitch Ratings downgraded Intel’s Long-Term Issuer Default Rating to ‘BBB+’ from “A-,” citing execution risks and potential negative rating actions. Fitch also affirmed Intel’s Short-Term IDR and commercial paper rating at ‘F2’. Fitch believes execution risk remains significant for Intel and that missteps could result in further negative rating actions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Analyst Comments:
Rosenblatt Securities analyst Hans Mosesmann reiterated his sell rating on Intel stock with a price target of 17. “We anticipate that the company (Intel) will continue to lose share to AMD as its manufacturing roadmap is tepid compared to that of the leading-edge player,” Mosesmann said in a client note.
Bernstein analyst Stacy Rasgon was particularly grim about Intel’s prospects.
“The company’s issues are now approaching the existential,” he said in a client note. “In other circumstances we believe we would now be having ‘going concern’ conversations with clients.”
Impact on Intel’s 5G Business:
The company’s website states: “From Cloud to Network to Edge: 5G Is Powered by Intel Intel-powered 5G networks deliver a powerful data-centric future where compute is fluid, intelligent, and pervasive—creating an evolutionary leap in agility and scalability.”

PHOTO Credit: Intel
Intel incorrectly states, “Intel is embedded throughout the 5G value chain, offering flexible performance, Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, custom RAN configurations, accelerators, software, and a common toolchain.” Does anyone really believe that?
Intel wants 5G network equipment vendors to switch from custom ASIC silicon they design to its general-purpose processors (GPPs). But there has been very limited adoption of those processors in the radio access network (RAN) to date. Many telco executives remain unconvinced GPPs, especially based on x86, can measure up. Arguments about using the same platforms for multiple needs look spurious when most RAN compute is at the mast site, where it cannot realistically be shared with anything else.
Of the big three 5G kit vendors, only Ericsson says Intel is a good option for Layer 1 (PHY), the category of most demanding RAN software. Huawei and Nokia remain vehemently opposed to using Intel silicon in this area. As expected, most of Ericsson’s 5G products today are based on its own custom silicon, not Intel’s GPPs.
References:
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/newsroom/news/actions-accelerate-our-progress.html#gs.d2jtpn
https://download.intel.com/newsroom/2024/corporate/Earnings-Call-2Q2024-080124.pdf
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/5g-overview.html
Despite U.S. sanctions, Huawei has come “roaring back,” due to massive China government support and policies
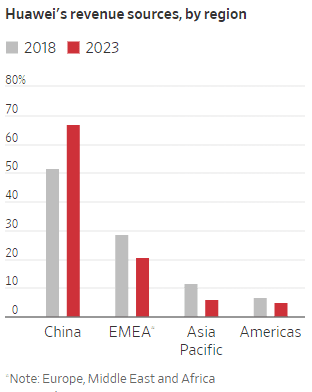
On March 30th we wrote that Huawei Technologies was back, with its net profit more than doubled from the same period last year (2023). Today, a Wall Street Journal (WSJ) news story reaffirmed that with reasons which were really no surprise! Huawei’s profit more than doubled last year, the largest jump in at least two decades. Roughly two-thirds of its revenue comes from domestic (China) clients.
Five years ago, the U.S. sanctioned Huawei, cutting off the Chinese company’s access to advanced U.S. technologies like semiconductors and the Android OS for its smartphones. Initially, the company struggled. In 2021, its revenue dropped almost 30% from the year before. Its core telecom equipment business was suffering. Apple’s iPhone was taking over Huawei market share in smartphones.
Yet in the last year, Huawei has come roaring back, boosted by billions of dollars in China government support. Huawei has expanded into new businesses, boosted its profitability and found fresh ways to curb its dependence on U.S. suppliers. It has held on to its leading position in the global telecom-equipment market, despite American efforts to squeeze Huawei out of its allies’ networks. Also, it’s making a big comeback in high-end smartphones, using sophisticated new chips developed in-house, such that it has captured 15% market share in China (knocking Apple out of the top five smartphone brands).
“The U.S. government’s campaign against Huawei is inadvertently bolstering the company’s resilience, echoing the age-old adage that what doesn’t kill you makes you stronger,” said Sameh Boujelbene, an analyst at research firm Dell’Oro Group.
China state support has paid off big time! After the U.S. imposed restrictions, Huawei and China’s government grew closer. Soon, Huawei leaders declared that every product they made going forward should be able to rely entirely on components developed by Chinese companies. China government contracts and company registration records, as well as WSJ interviews with former and current employees, reveal that billions of dollars flowed from the Chinese government to Huawei through preferential buying contracts and subsidies. State-owned enterprises, government agencies and Communist Party bodies sought Huawei chips, smartphones, cloud services and software, with some procurement contracts calling for Huawei gear by name.
Local governments have bought Huawei businesses, providing cash injections. Once reliant on Google’s Android for its consumer devices, Huawei built its own operating system. It has even made a foray into electric vehicles, a task that Apple gave up on, and developed its own version of Bluetooth. Huawei still faces challenges. Its most advanced semiconductors remain a step behind industry leaders such as Nvidia, whose chips are made by TSMC in Taiwan, which Huawei no longer has access to due to U.S. sanctions. U.S. export restrictions, which effectively barred Huawei from using American technology anywhere along the chipmaking process, meant the Chinese company could no longer source its chips from TSMC. Some analysts believe it will be hard for Huawei to keep innovating without access to more advanced Western technologies, especially chip making equipment and software.
One current U.S. official said Washington is closely tracking Huawei’s efforts to make its own semiconductors, in case more actions are needed to block China from manufacturing artificial-intelligence-focused chips that can give Beijing a military edge.
On May 16, 2019, China’s local government in Shenzhen, where Huawei is based, registered an investment company Shenzhen Major Industry Investment Group (SMII), focused on semiconductors, investing in foundries, manufacturing equipment and materials that would help ensure Huawei was supplied with enough domestically made chips and other technologies. Two companies established by SMII, including a chip foundry, employed former Huawei executives, according to people familiar with the matter. One received around a dozen patented technologies transferred from Huawei. Huawei human-resources managers had asked company researchers if they would work at that entity, promising them they could keep their benefits if they moved, according to people familiar with the matter. Shenzhen’s imports of semiconductor manufacturing equipment surged after SMII’s inception, official data shows. Through various state-backed funds, the Chinese government has invested in more than two dozen chip-related startups, over the past five years, according to corporate database Tianyancha.
That’s in addition to government investments in Huawei’s HiSilicon chip unit (more below), which made the silicon used in the company’s popular Mate 60 Pro smartphone. HiSilicon became an independent, wholly owned Huawei subsidiary in 2004. It was founded in 1991 as Huawei’s ASIC Design Center.
A majority-owned Shenzhen company also bought Huawei’s Honor smartphone business, which was struggling because of the U.S. sanctions. The deal was worth several billions of dollars, a person familiar with the transaction said. The cash allowed Huawei to focus on other businesses, including its higher-end Mate series of phones.
“We’ve been through a lot over the past few years. But through one challenge after another, we’ve managed to grow,” Huawei said in a written statement, adding that the company owed its survival and development to the trust and support of global customers, partners and “all sectors of society.” Sustaining R&D investment will be crucial going forward, the company said.
“We’ve been through a lot over the past few years, but through one challenge after another, we’ve managed to grow,” Huawei said in a written statement, adding that the company owed its survival and development to the trust and support of global customers, partners and “all sectors of society.” Sustaining R&D investment will be crucial going forward, the company said.
Huawei focused on building out more of its own supply chain and expanding into new areas that could generate revenue to help keep the company going, including cloud computing and other services, according to Chris Peirera, a former Huawei senior director in public affairs. “In the past, we chased the ideal of globalization, determined to serve mankind. What are our goals now? It’s to survive. We will make money wherever we can,” Huawei founder Ren Zhengfei later told the company’s staff in an internal letter.
Huawei received over $1 billion in China government grants in 2023, more than quadruple the amount it received in 2019, according to Huawei’s financial reports. In all, Huawei received nearly $3 billion in the past five years, accounting for 3% of its total R&D expenses.
Source: Huawei via WSJ
China’s government directed state agencies to buy more of Huawei’s software, chips and mobile devices, a policy that boosted Huawei while reducing China’s reliance on American companies, including Apple, whose iPhones are no longer allowed in the workplace for many government employees. A Chinese government research unit named Huawei as one of four tech giants spearheading the nation’s push to wean itself off foreign technology, while another government body singled out Huawei as a preferred state supplier of AI chips, servers and other enterprise software.
Though Huawei is still seeking to sell its products abroad in places such as Southeast Asia and Africa, it is more reliant on China’s market than ever, with 67% of revenue last year coming from domestic clients. The company often portrays itself as a national champion that gives priority to serving China.
Source: Huawei via WSJ
A WSJ investigation found more than 300 government procurement contracts worth around $5 billion specifically calling for the purchase of servers and other tech infrastructure powered by Huawei’s Kunpeng central processing units, or CPUs, in 2023. Other contracts listed Huawei CPUs among a handful of preferred local vendors. All of this was a sharp contrast to five years ago, when government agencies specifically requested products from U.S. chip makers Intel or AMD.
China’s buy-local policy is even more pronounced in the telecom-equipment space, Huawei’s largest revenue source. State-owned Chinese wireless carriers have largely stopped buying equipment from Huawei’s foreign rivals, Sweden’s Ericsson and Finland’s Nokia, even when one of them priced their contracts more cheaply than Chinese companies. The shift came while Sweden and other European countries indicated that they would cut Huawei and another Chinese equipment maker, ZTE, from their networks. Ericsson and Nokia held about 15% of China’s cellular network equipment market before 5G began rolling out in 2019. In China’s current 5G cellular-equipment market, Huawei holds about 4% to 5%, according to market research firm Dell’Oro.
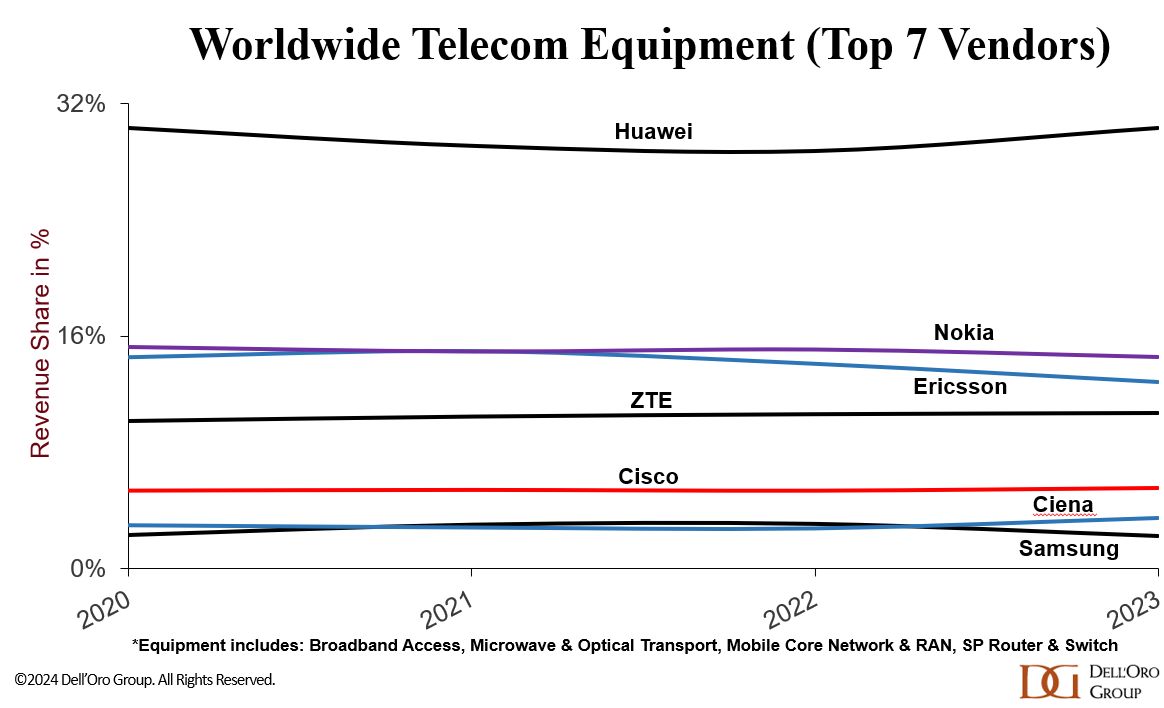
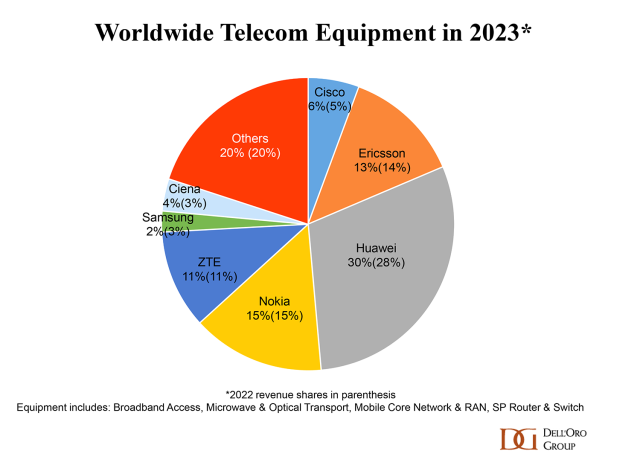
They peg Huawei’s 2023 global telecom market share (#1) at 30% – double that of #2 Nokia as per this pie chart:
With so much government support, Huawei was able to avoid massive job and spending cuts that would have gutted its R&D or led to a talent exodus. Huawei boosted R&D spending to almost 165 billion yuan, or $23 billion, last year, up from 102 billion yuan in 2018. More than half of Huawei’s 207,000 employees are in R&D.
Huawei is now at the vanguard of China’s push to develop cutting-edge chips to wean reliance on Nvidia and Intel, as the Biden administration seeks to curb China’s ability to develop advanced chips and technology that could aid its warfare and surveillance. U.S. chip juggernaut Nvidia singled out Huawei as a top competitor in February.
Huawei is leading a government-funded project to develop memory units for advanced AI chips, people familiar with the matter said, with at least 11 national AI data centers now using Huawei chips. WSJ reports that last summer, a group of Huawei researchers gathered at a barbecue restaurant on the outskirts of Beijing to congratulate engineers who worked on the Mate 60 Pro chip set at Huawei owned HiSilicon.
![]()
“You HiSilicon people kick ass,” one of the Huawei researchers said, according to a person who attended. “Managers tell us daily that our work helps the country fight against foreign oppression,” a HiSilicon engineer who was present responded. “We’re becoming more and more like a state-owned company, aren’t we?” another researcher chimed in.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/telecom/huawei-china-technology-us-sanctions-76462031
Huawei is back – net profits more than doubled in 2023!
Dell’Oro: 2023 global telecom equipment revenues declined 5% YoY; Huawei increases its #1 position
Huawei to revolutionize network operations and maintenance
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
China’s mobile data consumption slumps; Apple’s market share shrinks-no longer among top 5 vendors
Comcast faces competitive intensity; loses 120K broadband subs in 2Q-2024
Comcast today reported adjusted earnings of $1.21 a share for the quarter, beating Wall Street’s call for $1.12, according to FactSet. Revenue of $29.7 billion was slightly below consensus estimates of $30 billion. However, the company reported a loss of 120,000 total domestic broadband customers and 419,000 domestic video subscribers in the 2nd quarter.
“The competitive intensity that we’ve seen for the past several quarters, and which is particularly felt in the market for price-conscious consumers, remains essentially unchanged,” Comcast President Mike Cavanagh said on today’s earnings call.
“One of the most important metrics we monitor is the magnitude of data traffic flowing across our network. And again, we saw a double-digit year-over-year growth this quarter, with broadband-only households consuming over 700 gigabytes of data each month. And our customers continue to take faster speeds, with around 70% of our residential subscribers receiving speeds of 500 megabits per second or higher and one-third getting a gigabit or more. These positive consumer trends play to our strengths and will only accelerate with the shift of live sports to streaming, which together with entertainment on streaming accounts for nearly 70% of our network traffic today.My final thought on broadband is the importance of bundling with mobile, with 90% of Xfinity Mobile smartphone traffic traveling over our WiFi network. These two products work seamlessly together to benefit our customers from both the products’ experience and financial value standpoint.”
Seaport Research analyst David Joyce:
“Due to continued Broadband subscriber losses (where growth is driven by pricing), an elevated competitive environment for the time being, and the mixed Media topline and profitability trajectories, we remain Neutral,” Joyce wrote. Sentiment will improve when there are signs of stabilization in broadband market share, he added.
Comcast is moving ahead with HFC network upgrades, including “mid-splits” that dedicate more capacity to the upstream. Watson said mid-splits have been completed in about 42% of Comcast’s HFC footprint, a figure he expects to reach 50% by the end of the year. Comcast’s mid-splits are occurring alongside a plan to deploy DOCSIS 4.0 upgrades that are initially delivering symmetrical speeds of up to 2 Gbit/s. Comcast has D4.0-based services available in three markets – Philadelphia, Atlanta and Colorado Springs – with Seattle up next.
Broadband average revenue per unit (ARPU), which was up 3.6% in the quarter, remains a bright spot as customers continue to gravitate to higher speed tiers. Comcast CEO Brian Roberts: “Broadband ARPU increased by 3.6% and we delivered 6% revenue growth in our connectivity businesses, while expanding our Adjusted EBITDA margin across Connectivity & Platforms to a record-high 41.9%.”
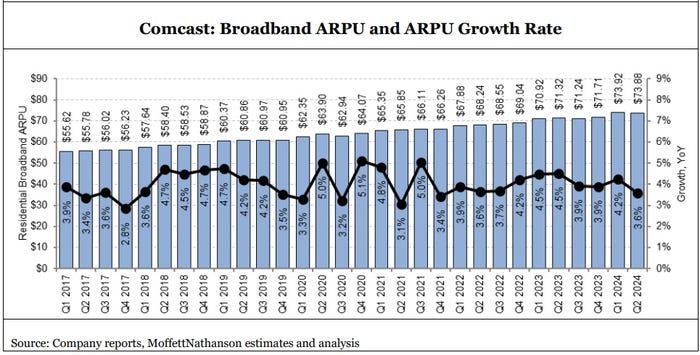
“Faster homes passed growth shouldn’t be expected to turn broadband subscribership back into a growth engine, but it is a critical factor in keeping broadband subscriber results stable,” MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett explained in a research note (payment required) issued today.
Comcast also expects to participate in the $42.45 billion Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program.
Comcast’s pay-TV business continued its downward spiral. The company lost 419,000 video subs in Q2, an improvement from a year-ago loss of 543,000. Analysts were expecting Comcast to shed about 502,000 video subs in Q2.
The Peacock streaming service, which broadcasts live sporting events like the upcoming summer Olympics, reported paid subscribers soared 38% from a year ago to 33 million, while revenue rose 28% in the 2nd quarter to $1 billion.
2nd Quarter 2024 Highlights:
• Adjusted EPS Increased 7.0% to $1.21; Generated Free Cash Flow of $1.3 Billion, Including a Tax
Payment Related to the Previously Announced Hulu Transaction and Other Tax Related Matters
• Return of Capital to Shareholders Totaled $3.4 Billion Through a Combination of $1.2 Billion in
Dividend Payments and $2.2 Billion in Share Repurchases
• Connectivity & Platforms Adjusted EBITDA Increased 1.6% to $8.5 Billion and Adjusted EBITDA
Margin Increased 90 Basis Points to 41.9%, Its Highest on Record
• Continued the Successful Execution of Our Domestic Network Expansion and Upgrade Strategy;
Expanded Deployment of Mid-Split Technology to 42% of Our Footprint; And Added 302,000 New
Homes and Businesses Passed in the Second Quarter
• Domestic Broadband Average Rate Per Customer Increased 3.6%, Driving Domestic Broadband
Revenue Growth of 3.0% to $6.6 Billion.
• Domestic Wireless Customer Lines Increased 20% Compared to the Prior Year Period to 7.2 Million,
Including Net Additions of 322,000 in the Second Quarter.
• Business Services Connectivity Adjusted EBITDA Increased 4.4% to $1.4 Billion and Adjusted
EBITDA Margin Was 57.0%.
• Media Adjusted EBITDA Increased 9.0% to $1.4 Billion, Driven by Improved Performance at Peacock
• Peacock Paid Subscribers Increased 38.0% Compared to the Prior Year Period to 33 Million;
Peacock Revenue Increased 28% to $1.0 Billion; Best Year-Over-Year Improvement in Adjusted
EBITDA for Any Quarter Since Launch in 2020.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.cmcsa.com/static-files/68abe434-80f7-437e-8e7a-fa457e43e63b
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4705822-comcast-corporation-cmcsa-q2-2024-earnings-call-transcript
Nokia cuts sales forecast as mobile sales drop 25%
Yesterday, Nokia cut its full-year sales forecast as the telecom market remains uncertain with network operators continuing to cut spending (CAPEX) in new network equipment, especially for the disappointing 5G (which is actually 4G with a 5GNR for 5G NSA which are by far the majority of 5G network deployments).
Nokia, like its Swedish rival Ericsson, has struggled to replace the strong revenue, high-margin contracts they enjoyed in North America early in the 5G cycle. When work in the region dried up, India became the main revenue generator, but work there attracted much lower margins and sales have now also slowed sharply.
Overall, sales at Nokia’s key mobile networks business fell 25% on year, mainly due to the sharp drop in India, but the company got a EUR150 million boost from a contract resolution with AT&T. 2Q-2024 net sales declined 18% y-o-y in constant currency (-18% reported) primarily due to strong year-ago quarter in India.
Nokia doesn’t provide specific group sales guidance but instead offers sales growth assumptions across its business units, which are all now seen at a weaker level than earlier as the expected net sales recovery is happening later than previously hoped.

The company said Thursday that comparable operating profit guidance of 2.3 billion euros to 2.9 billion euros ($2.52 billion-$3.17 billion) this year remains intact, tracking toward the mid-point or slightly below the mid-point.
“We believe the industry is stabilizing and given the order intake seen in recent quarters we expect a significant acceleration in net sales growth in the second half,” said Chief Executive Pekka Lundmark.
High inflation and rising interest rates have seen network operators spend cautiously over the last couple of years, but orders have slowly ticked higher over the last couple of quarters and the trend is continuing, particularly in network infrastructure, he said.
Late last year the U.S. operator awarded a major network contract to Ericsson for OpenRAN, replacing Nokia equipment. Nokia had contracts with AT&T and the Finnish company said it will still receive the value of those contracts while remaining a significant customer through other deals.
Network infrastructure sales declined 11% on the year, but Nokia said the unit has returned to growth in North America, which is important as it was one of the first markets to experience the 2023 market slowdown.
Nokia is desperately trying to reduce annual costs. Lundmark’s goal is to make cuts of between €800 million ($875 million) and €1.2 billion ($1.3 billion) by 2026, reducing the size of the workforce from about 86,000 employees when the program was first announced to between 72,000 and 77,000. Expect at least 14,000 Nokia employees to be axed in the next 18 months
To date, Nokia has been able to achieve “run-rate” savings of about €400 million ($437 million), it revealed in its earnings report.
“With the challenges of 2023 behind us, and more normalized customer inventory levels, we believe we can now look forward to a stronger second half and a return to growth [in network infrastructure], which we expect to continue into 2025,” Lundmark said.
The company reported an operating margin of 8.7% in its mobile networks unit and it now expects to report a margin of between 4% and 7% in 2024, from 1% to 4% previously. It reported a margin of 6.4% in network infrastructure and still expects a margin of between 11.5% and 14.5% this year.
Group comparable net profit fell 21% to EUR325 million in the second quarter, beating a FactSet estimate of EUR280 million. Sales fell 18% to EUR4.47 billion, missing consensus at EUR4.78 billion.
Improving cash generation means Nokia now intends to accelerate its continuing EUR600 million buyback program with the view to completing it by the end of this year, compared to its previous end-of-2025 target, it said.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/nokia-takes-big-axe-to-mobile-jobs-but-grows-footprint-outside-at-t
Analysts: Telco CAPEX crash looks to continue: mobile core network, RAN, and optical all expected to decline
Nokia (like Ericsson) announces fresh wave of job cuts; Ericsson lays off 240 more in China
Ericsson expects continuing network equipment sales challenges in 2024
Recon Analytics (x-China) survey reveals that Ericsson, Nokia and Samsung are the top RAN vendors
Nokia: 5G Costs Hit Q1 Outlook as Shares Crash and Dividend Suspended
Analysts: Telco CAPEX crash looks to continue: mobile core network, RAN, and optical all expected to decline
Dell’Oro has just cut its outlook for mobile core spending for the fifth consecutive time. Not a single operator has adopted 5G SA this year.
“It bears repeating, this is the fifth consecutive time we have reduced the growth rate of the MCN market as the build-out of 5G SA networks continue to wane compared to 5G Non-standalone networks,” said Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “This is the first 5-year forecast out of the last five where the 5-year CAGR (2023-2028) has fallen into negative territory. The count of 5G SA networks commercially deployed by MNOs remains the same as it was at the end of 2023, about 50 5G SA networks.
“For the same reasons outlined for the MCN market, we reduced the 5-year cumulative revenue forecast for the Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) market, a sub-segment of the MCN market, by 18 percent. In the case of MEC, the adoption rate is slowed much more dramatically than the overall MCN market. The industry is addressing these concerns with several initiatives such as open gateway application programmable interfaces (APIs) to attract the application development community to develop applications for the mobile industry that can easily be leveraged across all MNOs. Release 18 is introducing capabilities for new use cases, and Reduced Capability (RedCap) RAN software to bring more 5G IoT devices to market. However, these will take time to bring solutions to market and more importantly at scale to have an impact on the overall market growth,” Bolan added.
Additional highlights from the Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing 5-Year July 2024 Forecast Report:
- The CAGR is negative for all product segments—Packet Core, Policy, Signaling, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core.
- The CAGR for the market segments is positive for 5G MCN and MEC, and negative for 4G MCN and IMS Core.
- The CAGR by regions is positive for Asia Pacific excl. China, Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA), and Worldwide excluding China. The regions with negative CAGRs are North America, CALA, China, and Worldwide excluding North America.
Dell’Oro has called the RAN market as “a disaster.” “It’s difficult to find a silver lining in the first quarter,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst at the Dell’Oro Group. “We’ve been monitoring the RAN market since the year 2000, and the contraction experienced in the first quarter marked the steepest decline in our entire history of covering this market. In addition to the known coverage related challenges that the market is dealing with when comps in the advanced 5G markets are becoming more challenging, there are now serious concerns about the timing of the capacity upgrades given current network utilization levels and data traffic growth rates,” continued Pongratz.
While the overarching RAN sentiment appears to be mostly aligned over the long term, it is worth noting that internal expectations across the key players vary quite a bit over the short term. In addition to the coupling between coverage capex and the state of the 5G networks (per Ericsson’s Mobility report, 5G POP coverage is lower in CALA/MEA/APAC excl China&India), the dynamics between urban and rural sites also impact growth prospects. The Chinese RAN vendors are generally more optimistic about 2024 than the leading non-Chinese RAN suppliers.
It’s no secret that telecom operators are scaling back their investments in 5G. Preliminary findings show that worldwide telecom capex, the sum of wireless and wireline/other telecom carrier investments, declined for the full year 2023 in nominal USD terms, recording the first contraction since 2017. This deceleration in the broader capex spend is consistent with the aggregate telco equipment slump previously communicated for the six Dell’Oro telecom programs (Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network, Radio Access Network, Service Provider Routers & Switch).
“The fundamental challenges have not changed. Operators have a fixed capital intensity budget and capex is largely constrained by the revenue trajectory,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst with Dell’Oro Group. “What is complicating the situation is that the revenue pie remains fixed. Following some positive developments amidst the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, our analysis shows that operator revenue growth slowed in 2023 and has more or less remained stagnant over the past decade. And based on the guidance, operators, in general, are not overly optimistic that emerging opportunities with generative AI, edge computing, enterprise 5G, FWA, and 5G-Advanced will expand the pie,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from the Dell’Oro March 2024 Telecom Capex report:
- Global carrier revenues are expected to increase at a 1 percent CAGR over the next 3 years.
- Market conditions are expected to remain challenging in 2024. Worldwide telecom capex is now projected to decline at a mid-single-digit rate in 2024 and at a negative 2 to 3 percent CAGR by 2026.
- The mix between wireless and wireline remains largely unchanged, reflecting challenging times still ahead for wireless. Wireless related capex is on track to decline at a double-digit rate in the US in 2024.
- 5G era capital intensity ratios peaked in 2022 and are on track to approach 15 percent by 2026, down from 18 percent in 2022.
The market research firm and also forecasts optical transport spending (which includes 5G backhaul) to decline as well.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
What’s more important is that mobile network traffic growth is slowing. In the latest Ericsson mobility report, the authors cut mobile data traffic figures for the second half of 2023, yet declared that the growth outlook was virtually unchanged.
William Webb, a consultant and senior advisor at Access Partnership, is one who’s called out the authors of the report for this leap in logic. “If lower numbers are being reported for 2023 … then why should the traffic growth rate predicted remain the same?” he posted on LinkedIn. He denounces the forecast as “a mess,” pointing out that the report, without any explanation, has somehow introduced a 10% jump in growth over 2023-24 to bring its new forecast into line with the old.
Separately, a new Analysys Mason paper says the telecom industry is running up against the limits of growth and faces a “crisis of bandwidth overproduction.” It says the telco responses to this looming crisis – volume price discounts and untried business models – replicate every other other industry in the same predicament. “Growth rates are not declining because of supply-side constraints such as spectrum or coverage; access networks have never been emptier,” the author argues. “Rather, the two principal drivers of traffic growth, smartphone usage and broadcast-to-streaming migration on mobile and fixed networks, respectively, have both run up against human limits; limited hours for engagement and the limits of human vision.”
If demand does not revive, then the lower unit costs brought about by over-investment in capacity will result in further deflation of margins and profitability, the paper maintains. It calls on telcos to reduce CAPEX to make available more resources to invest in M&A, into other adjacent infrastructure businesses, or in some key non-connectivity B2B segments.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/the-specter-of-a-capex-drought-looms-over-6g
Analysys Mason’s gloomy CAPEX forecast: “there will not be a cyclical recovery”
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
MTN Consulting: Generative AI hype grips telecom industry; telco CAPEX decreases while vendor revenue plummets
Telecom and AI Status in the EU
By Afnan Khan with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Introduction
In the eerie silence of deserted streets and amidst the anxious hum of masked conversations, the world found itself gripped by the rapid proliferation of COVID-19. Soon labelled a global pandemic due to the havoc wreaked by soaring death tolls, it brought unprecedented disruption and accelerated the inevitable rise of the digital age. The era of digital transformation has swiftly transitioned, spawning a multitude of businesses catering to every human need. Today, our dependence on digital technology remains steadfast, with remote work becoming the norm and IT services spending increasing from $1.071 trillion in 2020 to $1.585 trillion. [1]
The chart below, sourced from Oliver Wyman Forum Analysis,[2] vividly illustrates our increasing dependence on technology. It presents findings from a survey conducted in the latter half of 2020 across eight countries – US, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Singapore, and China. The survey reveals that 60% of respondents favoured increased use of video conferencing, while online grocery shopping and telehealth services each garnered 59% approval, and E-learning showed a strong preference at 56%. This data underscores how swiftly digital solutions integrated into our daily lives during the pandemic.
Source: Olive Wyman Forum Analysis [2]
Advancements in Telecom and AI Applications Across EU
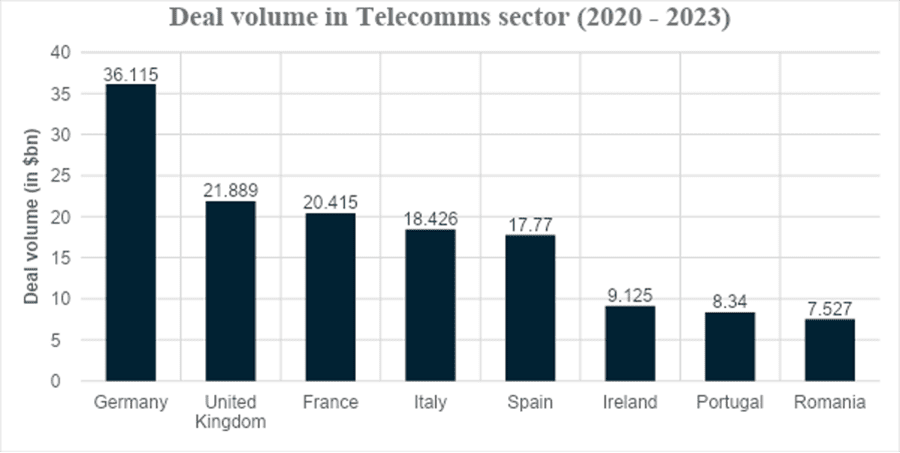
The graph below represents the project and infrastructure finance deal volume in the telecommunications sector from 2020 to 2023. The dominance of Germany is evident, with the deal volume reported to be $36.115 billion, followed by the UK at $21.889 billion. France follows closely in third place with a deal volume of $20.415 billion, representing significant market potential. The only other two countries with substantial figures are Italy and Spain, although there have been some promising deals closing in Ireland, Portugal, and Romania with large new financing deals in the project finance sector.
Source: Proximo Intelligence [5]
Deutsche Telekom, the national provider, has spearheaded advancements with AI-powered network optimisation tools. These tools leverage real-time analytics, resulting in a notable 20% enhancement in network performance and a 15% reduction in customer complaints. [14] While 2022 marked a pivotal year for the industry in Germany, the evolution of German fibre optics infrastructure has continued apace. Germany led Europe’s FTTH (Fibre to the Home) initiative, with significant financings closing throughout the year. According to Proximo Data, 16 European FTTH financings concluded in 2022, amassing nearly $26 billion in deal volume, with German deals accounting for almost $9 billion of that total.
Spain’s Telefónica has deployed an advanced AI-driven fraud detection system that effectively blocks over 95% of fraudulent activities. This initiative not only protects Telefónica from financial losses but also enhances security for its customers. [15] The adoption of AI for cybersecurity underscores a broader trend in the telecom industry towards leveraging advanced technologies to bolster trust and safeguard digital transactions.
Orange has introduced AI-driven chatbots that autonomously handle more than 90% of customer queries in France, resulting in a significant reduction in customer service costs by 40% and a notable increase in customer satisfaction rates by 25%. [16] This innovation represents a paradigm shift in customer service automation within the telecom sector, demonstrating the effectiveness of AI in improving operational efficiency and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Telecom Italia (TIM) has implemented AI-powered network security solutions to proactively detect and mitigate cyber threats in real-time, achieving a remarkable 60% reduction in cybersecurity. [17]
This strategic deployment of AI highlights TIM’s commitment to enhancing network resilience and safeguarding critical infrastructure from evolving cyber threats, setting a precedent for cybersecurity strategies in the telecommunications industry.
Predictive Analysis Enhancing Telecom Resilience
Interference mitigation strategies are essential for smooth digital operations in the post-pandemic world. Picture digital experts rapidly addressing problems from rogue networks and environmental noise, creating a digital shield against disruptions, and ensuring a seamless user experience. These strategies propel telecom companies towards better connectivity and user satisfaction.
These examples highlight the trend of using AI and predictive analytics to boost network performance in cities. As urban areas contend with population growth and increasing digital demands, telecom companies invest in advanced technologies. These reduce network congestion, enhance service reliability, and support sustainable urban development. This trend not only improves customer experience but also positions telecom providers as leaders in developing future smart cities.
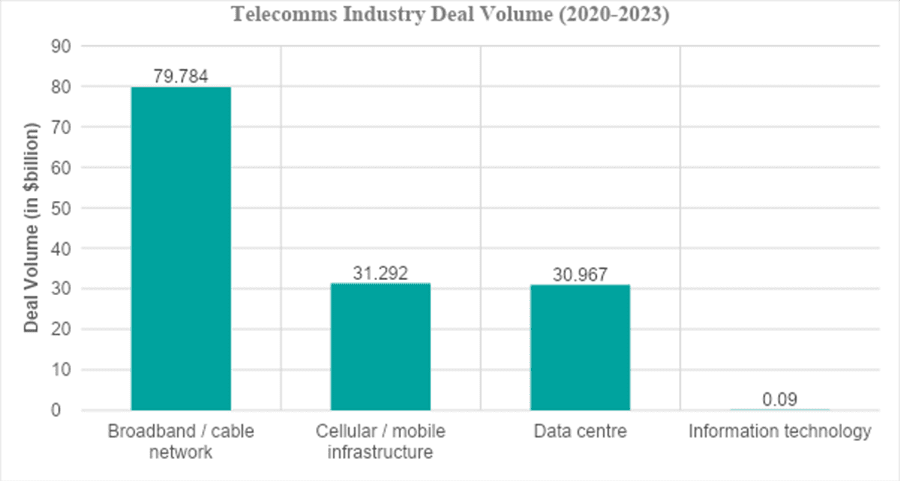
The chart below, from the Proximo Intelligence database, shows European deal volumes over the past three years, categorised by sub-sectors. The broadband and cable network sector leads with a deal volume of $79.784 billion from 86 deals out of a total 137 in project and infrastructure finance. Cellular and mobile infrastructure follows with $31.292 billion across 25 deals. Data centres, a growing trend, also report a deal volume of $30.967 billion across 25 deals.
Source: Proximo Intelligence [5]
In the post-COVID era, the adoption of predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring has accelerated, becoming a critical component of the new normal for businesses. These technologies enable companies to build more resilient infrastructures, proactively mitigate risks, and enhance operational efficiency. As businesses continue adapting to a rapidly changing environment, the integration of predictive maintenance solutions plays a pivotal role in sustaining long-term growth and stability.
Europe has seen profound impacts from these advancements, setting a precedent for global telecom strategies moving forward.
Future Trends and The Way Forward
European telecommunications face challenges shaped by regulatory frameworks, economic conditions, and technological advancements:
- Brexit introduces regulatory uncertainties for UK telecoms. [18]
- Germany’s GDPR compliance challenges demand heavy investment. [19]
- Spain faces economic instability affecting telecom investments. [20]
- France’s 5G deployment is delayed by regulatory barriers. [21]
- Italy’s 5G rollout is hindered by spectrum allocation challenges. [22]
- The Netherlands invests in cybersecurity for evolving threats. [23]
- Sweden focuses on bridging rural connectivity gaps. [24]
- Switzerland navigates complex regulatory landscapes for innovation. [25]
In the wake of COVID-19, with masks now a thing of the past and streets deserted only due to construction, digital technologies are transforming European telecommunications amidst regulatory shifts and economic uncertainties. Investments in infrastructure and AI innovations are pivotal, shaping the industry’s future and its adaptation to rapid change while driving economic recovery across Europe. How will the industry sustain innovation and meet growing digital demands ahead? Only time will tell.
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/203291/global-it-services-spending-forecast/
- https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/perspectives/health/2021/mar/why-4-technologies-that-boomed-during-covid-19-will-keep-people-.html
- https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/news/new-data-shows-small-businesses-received-213-billion-in-covid-19-local-authority-business-support-grants#:~:text=Press%20release-,New%20data%20shows%20small%20businesses%20received%20%C2%A321.3%20billion%20in,and%20arts%2C%20entertainment%20and%20recreation.
- Proximo Intelligence Data: www.proximoinfra.com
- Vodafone Press Release, 2022.
- “McKinsey & Company. “Predictive maintenance: The rise of self-maintaining assets.”
- Deloitte. “Predictive maintenance: Taking proactivity to the next level.”
- Forbes. “Why Virtual Assistants Are Becoming Essential for Businesses.”
- Statista. “Growth in Demand for Virtual Assistants in Europe.”
- TechRadar. “Vodafone’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 25% in London.”
- The Guardian. “BT/EE’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 30% in London.”
- FCC (2023). Spectrum Efficiency Report. Federal Communications Commission. Available at: https://www.fcc.gov/reports-research/reports/fcc-research/spectrum-efficiency.
- Deutsche Telekom’s AI-Powered Network Optimization,” TechInsights
- “Telefónica’s AI-Driven Fraud Detection,” TelecomsToday. Available at: TelecomsToday AI Fraud Detection
- “Orange’s AI-Enabled Customer Support,” AI Insider. Available at: AI Insider AI Customer Support
- “TIM’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity Measures,” CyberTechNews. Available at: CyberTechNews AI Cybersecurity
- TelecomsInsight. “Brexit’s Regulatory Impact on UK Telecoms.”
- DataPrivacyToday. “GDPR Compliance Challenges for German Telcos.”
- BusinessWire. “Spain’s Economic Recovery Challenges.”
- TelecomsObserver. “France’s Regulatory Roadblocks to 5G Deployment.”
- SpectrumInsight. “Italy’s Spectrum Allocation Challenges.”
- CyberDefenseMag. “Netherlands’ Cybersecurity Imperatives.”
- DigitalInclusionHub. “Sweden’s Rural Connectivity Initiatives.”
- RegTechInsights. “Switzerland’s Regulatory Adaptation Challenges.”
Afnan Khan is a Machine Learning Engineer specialising in Marketing Analytics, currently working as a Marketing Analyst at the Exile Group in London. He is involved in various projects, research, and roles related to Machine Learning, Data Science, and AI.
Ajay Lotan Thakur is a Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member, BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s Open-Source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.
Post COVID Telco AI Blueprint for the UK
By Afnan Khan with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Introduction
In the eerie silence of deserted streets and amidst the anxious hum of masked conversations, the world found itself gripped by the rapid proliferation of COVID-19. Soon labelled a global pandemic due to the havoc wreaked by soaring death tolls, it brought unprecedented disruption and accelerated the inevitable rise of the digital age. The era of digital transformation has swiftly transitioned, spawning a multitude of businesses catering to every human need. Today, our dependence on digital technology remains steadfast, with remote work becoming the norm and IT services spending increasing from $1.071 trillion in 2020 to $1.585 trillion. [1]
The chart below, sourced from Oliver Wyman Forum Analysis,[2] vividly illustrates our increasing dependence on technology. It presents findings from a survey conducted in the latter half of 2020 across eight countries – US, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Singapore, and China. The survey reveals that 60% of respondents favoured increased use of video conferencing, while online grocery shopping and telehealth services each garnered 59% approval, and E-learning showed a strong preference at 56%. This data underscores how swiftly digital solutions integrated into our daily lives during the pandemic.
Accelerating Telecom Growth in Britain
Europe was among the hardest-hit regions by the pandemic, with death tolls exceeding 2.1 million. [3] This crisis accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, prompting businesses to invest in smarter, more sustainable operations to increase their longevity and stay relevant in the market.
In the United Kingdom, despite the government’s injection of £21.3 billion into the economy to support small businesses, the emphasis on digital transformation has been paramount. [4] The push towards digital solutions, including enhanced internet connectivity and robust data centres, underscores the long-term strategic shift towards a more resilient and technologically advanced business landscape.
Statistically, the UK telecom industry has experienced significant growth, driven by increased demand and advancements in network equipment. The shift towards digital dependency, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the rise of remote work, is expected to be long-term. This trend has also led to a surge in 5G and data centre deals.
According to Proximo, a leading Project and Infrastructure Finance Journal, projects worth $30.967 billion have closed in Europe between 2020 and 2023, highlighting the critical role of data centres in boosting the telecommunications sector. Of this, the UK accounted for $14.133 billion across seven deals, comprising both refinancing and new financing deals, representing 45.6% of Europe’s total contribution. Notably, one of the recent financing deals to close was for Ark Data Centres, based in London, with the term loan reported to be in the region of £170 million for five years, aimed at supporting a significant data project in the UK – thus establishing the country as one of the market leaders in Europe. [5]
Telecom Landscape in the UK’s New Normal
Imagine having the ability to pinpoint precisely when hardware needs replacement, akin to pre-emptively replacing floorboards. Vodafone’s United Performance Management (UPM) facilitates real-time monitoring and proactive identification of anomalies. [6] Predictive maintenance can reduce unplanned downtime by 30-50%, lower maintenance costs by 10-40%, and extend asset lifespan by 20-40%. [7][8]
Virtual Assistants
The integration of virtual assistants has not only streamlined operations but has also emerged as one of the most sought-after roles, as reported by Forbes. [9] In the telecom industry, where customer service reigns supreme, consider the live example of broadband giant BT/EE. Their adoption of remote customer support in the post-COVID world has propelled them to the forefront as the leading data provider in the UK. Mirroring European trends, the demand for virtual assistant roles has surged by 20%, [10] spurred on by initiatives such as digital nomad visas in Spain and Portugal. This trend not only reflects the changing landscape of customer service but also signals significant injections into the economy.
Traffic congestion
In the hustle and bustle of post-pandemic London, navigating the city’s streets amidst fluctuating traffic patterns and network demands presents a unique challenge. Telecom companies are stepping up to the plate, leveraging cutting-edge AI and ML technologies to tackle these issues head-on. By predicting traffic patterns and dynamically managing network loads, they’re ensuring that Londoners experience optimal connectivity and responsiveness, even during peak hours when congestion is at its peak. Imagine this: congestion hotspots are pinpointed in real-time, and network resources are strategically directed to these areas, reducing disruptions. This means that residents and commuters alike enjoy a smoother, more reliable connection, whether they’re streaming, working remotely, or simply staying connected on the go.
One shining example is Vodafone, which has implemented AI-driven traffic prediction models specifically tailored to London’s intricate traffic patterns. The result? A remarkable 25% reduction in network congestion during peak hours, as reported by TechRadar. [11] This underscores the significance of bespoke solutions in addressing London’s unique challenges post-pandemic, solidifying network performance and reliability for the city’s diverse population and thriving businesses.
Another notable case is BT/EE, which has also deployed AI-driven traffic prediction models in London. This initiative led to a significant 30% reduction in network congestion during peak hours. [12] Such tailored AI solutions not only enhance operational efficiency but also demonstrate the telecom industry’s commitment to leveraging technology to improve urban infrastructure.
Dynamic Spectrum
In the dynamic realm of post-COVID technology, telecom pioneers are revolutionising spectrum management with dynamic spectrum allocation. Imagine a digital symphony where frequencies dance to the beat of demand, seamlessly adapting to surges in digital traffic. This innovative approach ensures uninterrupted connectivity, even in the busiest digital arenas. According to recent studies, dynamic spectrum allocation has shown to increase spectrum efficiency by up to 40%, supporting seamless connectivity for the data-hungry masses. [13] Telecom wizards are thus reshaping the digital landscape, delivering turbo-charged connectivity.
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/203291/global-it-services-spending-forecast/
- https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/perspectives/health/2021/mar/why-4-technologies-that-boomed-during-covid-19-will-keep-people-.html
- https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/news/new-data-shows-small-businesses-received-213-billion-in-covid-19-local-authority-business-support-grants#:~:text=Press%20release-,New%20data%20shows%20small%20businesses%20received%20%C2%A321.3%20billion%20in,and%20arts%2C%20entertainment%20and%20recreation.
- Proximo Intelligence Data: www.proximoinfra.com
- Vodafone Press Release, 2022.
- “McKinsey & Company. “Predictive maintenance: The rise of self-maintaining assets.”
- Deloitte. “Predictive maintenance: Taking proactivity to the next level.”
- Forbes. “Why Virtual Assistants Are Becoming Essential for Businesses.”
- Statista. “Growth in Demand for Virtual Assistants in Europe.”
- TechRadar. “Vodafone’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 25% in London.”
- The Guardian. “BT/EE’s AI traffic prediction cuts network congestion by 30% in London.”
Afnan Khan is a Machine Learning Engineer specialising in Marketing Analytics, currently working as a Marketing Analyst at the Exile Group in London. He is involved in various projects, research, and roles related to Machine Learning, Data Science, and AI.
Ajay Lotan Thakur is a Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member, BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s Open-Source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
ITU-R has commenced the process of developing ITU-R Recommendations for the terrestrial components of the IMT-2030 (6G) radio interface(s). This work is guided by Resolutions ITU-R 56 and ITU-R 65. As you can see from the timeline below, the final IMT-2030 recommendation won’t be completed until 2030.
The ITU Radiocommunication Bureau has established a “Web page for the IMT-2030 submission and evaluation process” to facilitate the development of proposals and the work of the evaluation groups. The IMT-2030 web page will provide details of the process for the submission of proposals, and will include the RIT and SRIT submissions, evaluation group registration and contact information, evaluation reports and other relevant information on the development of IMT‑2030.
Candidate RITs (Radio Interface Technologies) or SRITs (Set of Radio Interface Technologies) will be evaluated by the ITU membership, standards organizations and other independent evaluation groups. Evaluation groups are requested to register with ITU-R1, preferably before [February/the end of 2027].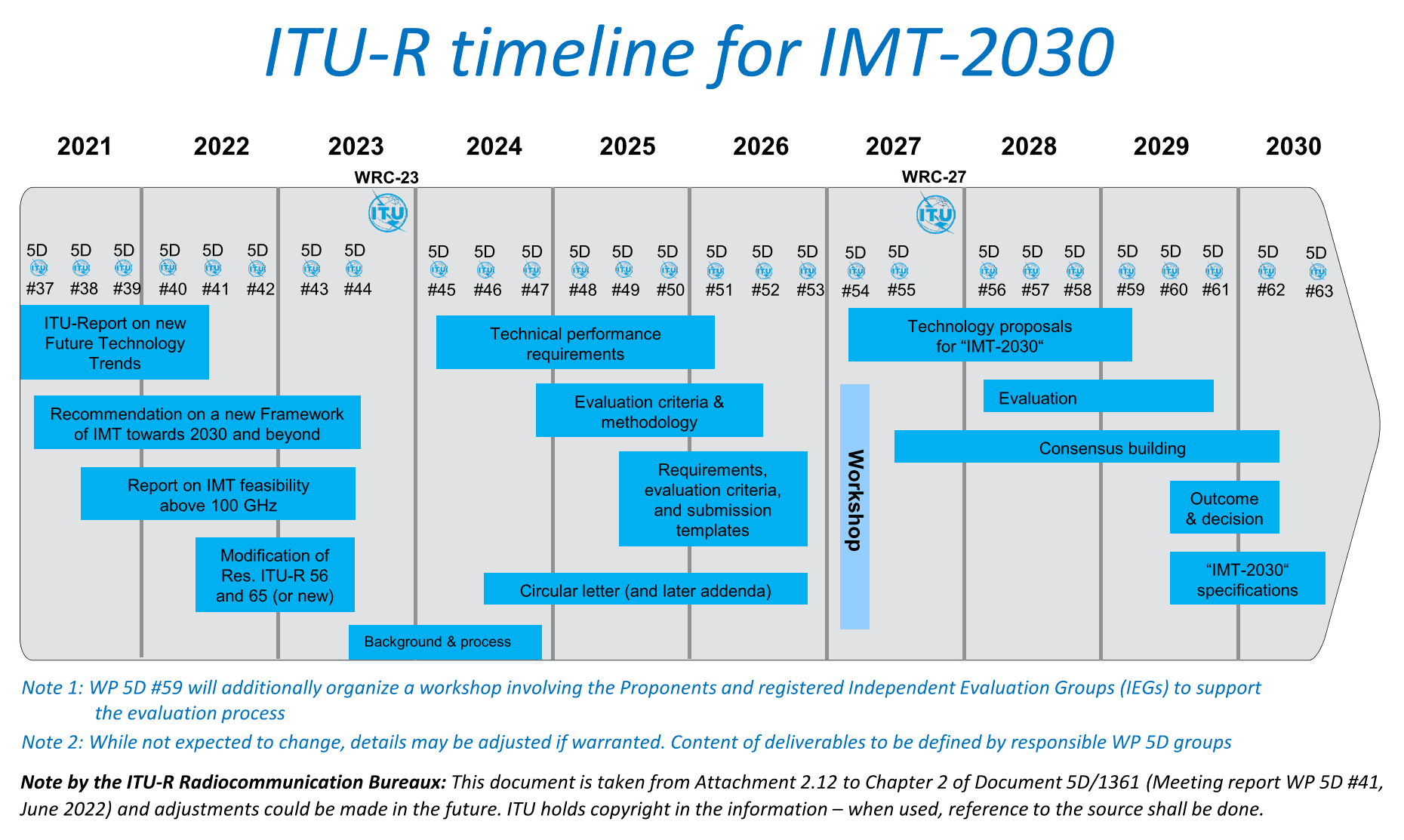
The evaluation groups are kindly requested to submit evaluation reports to the ITU-R in accordance with the evaluation process delineated on the IMT‑2030 web page. The evaluation reports will be considered in the development of the ITU-R Recommendation describing the radio interface specifications.
The evaluation guidelines, including the criteria and methodology, are to be finalized by WP 5D in June 2026. The availability of these guidelines on the IMT-2030 web page will be announced in a forthcoming Addendum to a Circular Letter calling for IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions.
3GPP’s contributions will most likely be presented to ITU-R WP5D by ATIS. It remains to be seen what other entities will submit IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT proposals.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2030/Pages/default.aspx
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/oth/0a/06/R0A060000C80001PDFE.pdf